1. Introduction
Recently, polylactide (Polylactic Acid -PLA) has attracted increasing attention of re-searchers, since it is one of the most promising biodegradable thermoplastic polymers [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Polylactide is thermoplastic, aliphatic polyester, the monomer of which is lactic acid.
Polylactide was invented in the 1930s, but its commercial production began only fifty years later. Recently, the use of this material has grown to a huge scale as a packaging material and a starting material - a filament for 3D printing, and in the popularity it has become the number one bioplastics in the world. The versatility of PLA is closely related to one of its main advantages - the ability to biodegrade.
In the form of a filament, PLA is widely used in 3D printing, which is easy to handle, so it is most suitable for novice operators.
PLA has relatively low thermal and mechanical resistance. In addition, it is hygroscopic, which can make a PLA product potentially fragile, and if used incorrectly, it can cause some problems, such as clogging of the extruder nozzle. Nevertheless, when using PLA, the 3D printing process is accelerated due to relatively lower printing temperatures: from 180 to 230°C as compared to other thermoplastics [
3,
4].
In addition, PLA is intensively used in food and industrial packaging [
3] and it can successfully replace traditional petroleum-based plastics such as polystyrene, polyetylene, polypropylene, polyethylene terephthalate in many single-use or short-term applications [
4].
PLA exhibits good mechanical properties such as high strength, high Young's modulus and high biocompatibility [
5].
The PLA polymer is made from organic renewable raw materials – soy protein, corn, and cane, making production inexpensive. By adjusting the lactic acid level during the production of polylactide, it is possible to identify various properties of the polymer, thus expanding the scope of its use [
6].
Natural PLA is an opaque plastic of a cloudy light shade, having a glass transition temperature of 60 °C; resistance to temperatures up to 70 °C; high mechanical strength; flexibility and elasticity. Both lactic acid and polylactide exhibit optical activity, thus they exist in the form of two L- and D-stereoisomers, which are mirror images of each other. By varying the relative content of these forms in polylactide, it is possible to set the properties of the resulting polymer, to obtain various classes of polylactide materials. Polylactide made of 100% L-lactide (L-PLA) has a high degree of stereoregularity, which gives it a crystallinity with a density of 1,290 g/cm
3. Using a mixture of D- and L-forms of lactide during polymerization, an amorphous polylactide (L,D- PLA) with a density of 1.248 g/cm
3 is obtained [
7].
The polylactide of 100% L-lactide (L-PLA) has a high degree of stereoregularity, which provides the crystalline form of an orthorhombic phase α-Poly(L-lactide) with the chemical formula (C
3H
5O
3)
n and unit cell parameters : a=10.61, b=6.05 and c=28.8 Ǻ (PDF-2-2006 card number 00-054-1917, Diffract Plus 2005). Thus, it follows from the literature review [
1] that the α-phase is more stable as compared to another known phase of the β-Poly(L-Lactide) polylactide, also with an orthorhombic unit cell, but with the other unit cell parameters: a= 10.3, b= 18.2, c =9.0 Ǻ.
The most important advantage of using PLA is safety, as it is completely eco-friendly, biocompatible and biodegradable for about six months under the right conditions. There-fore, it is safe for the use in the food industry and medicine, and can also be recycled and reused [
8].
Polylactide for 3D printing is produced by most manufacturers of consumables for personal 3D printers in the form of a Filament PLA in a wide range of colors. At the same time, unpainted PLA has the lowest degree of crystallinity and the highest mechanical strength compared to the painted versions [
9].
However, any 3D printer, even the most entry-level, is capable of working with these materials.
The aim of this work is to study the effect of the 3D printing process on the microstructural and hydrophilic properties of polylactic acid (PLA) samples with various model printing patterns obtained from the black Filament PLA by sequentially applying polymer layers using the FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) method.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
We produced the samples for the study using the most common 3D printing technology, which uses fused filament fabrication (FFF) molten thermoplastic filament as a raw material.
The samples were made from black polylactide filament (Filament PLA) with a diameter of 1.75 mm on a Hercules Original 3D printer by layered FDM polymer layers (Fused Deposition Modeling) [
1,
2,
3,
4]. The temperature of the extruder is 260
oC, the power is 500 W, the nozzle diameter is 0.5 mm, the printing speed is of 40 mm/sec. Five cylindrical samples with a diameter of 20 mm and a thickness of 5 mm were printed. The printed samples were distinguished by 3D printing model patterns.
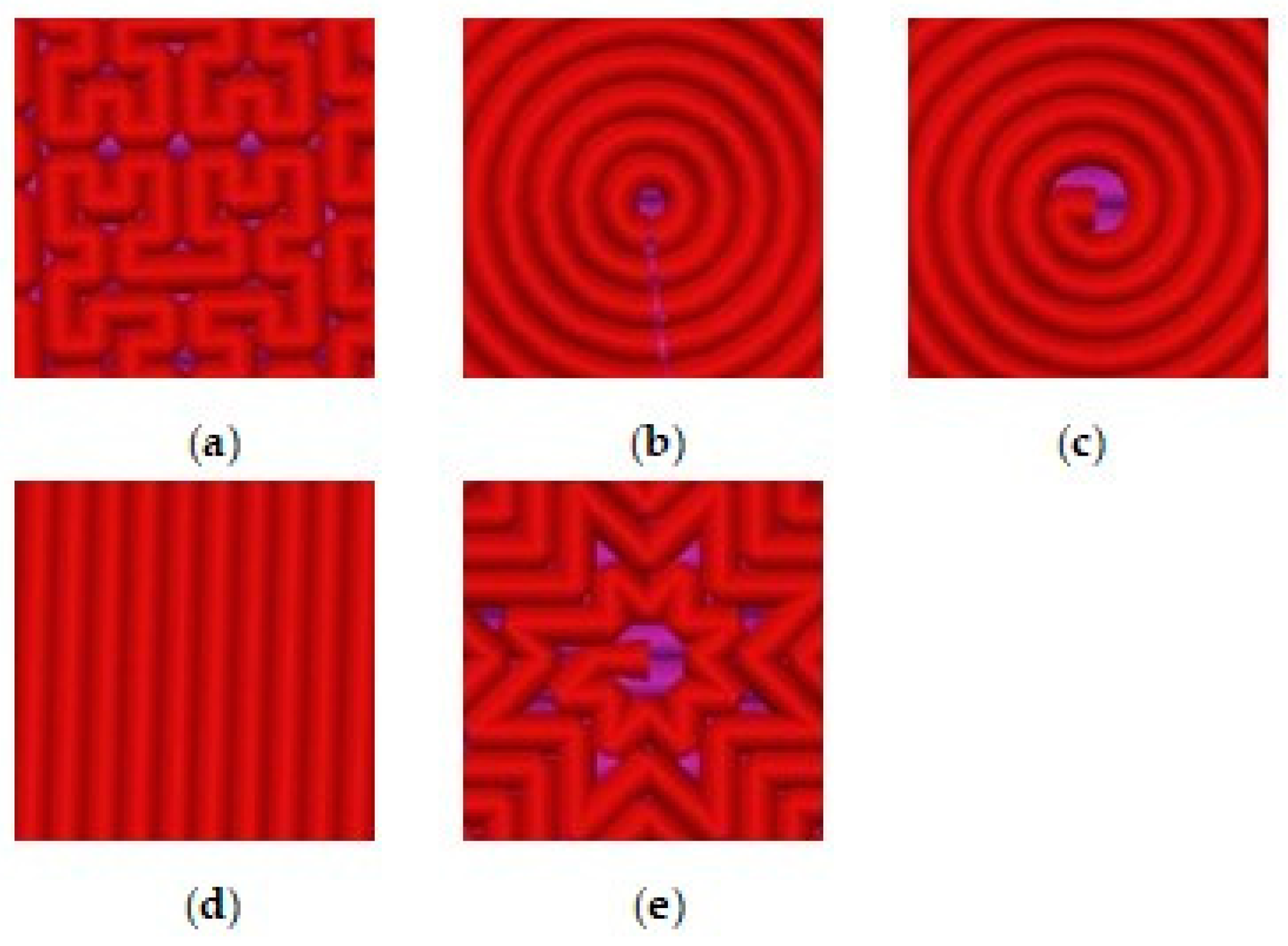
Figure 1 shows five types of the model patterns used in 3-D printing of the samples from PLA Filament.
Along with the printed samples, the initial sample of the Filament PLA was studied, therefore, the results of the study of microstructural properties for six samples will be presented in the next section.
2.2. Methods
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of the surface of five printed samples with different model patterns was performed with a scanning electron microscope JSM 6510LV.
To obtain a better contrast on SEM microphotographs, studies of morphology of the surface of printed samples were carried out for the surfaces of samples coated with the thinnest layer of gold several nanometers thick, with different magnifications х40, x500, x1000.
The phase composition and structure of the printed samples and the initial Filament PLA was analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) method on ARLX'TRA diffractometer with a monochromator operating in parallel beam geometry and in the mode θ−θ within the angle range 2θ =2-40o and Cu Kα1 radiation at high voltage U= 29 kV and the anode current of the X-ray tube I= 25 mA.
IR spectroscopy is a non–destructive optical method used to solve specific problems, including determining the fundamental characteristics of a molecule, quantitative analysis of the known phases in a substance, identification of chemical compounds and elucidation of their structure. This optical method is based on measuring the intensity of infrared radiation absorbed or reflected by a certain material, which is associated with vibrational and rotational vibrations of molecular fragments and manifests itself in the intensity distribution in the absorption bands depending on the wavelength (λ) or its inverse value, which is known as the wave number (v).
Studies of the molecular structure were carried out for five printed samples with different model patterns and the initial Filament PLA by measuring the IR transmission spectra by the attenuated total internal reflection method with the IR Fourier spectrometer Brucker Vertex 70 in the range of 400-4000 cm-1.
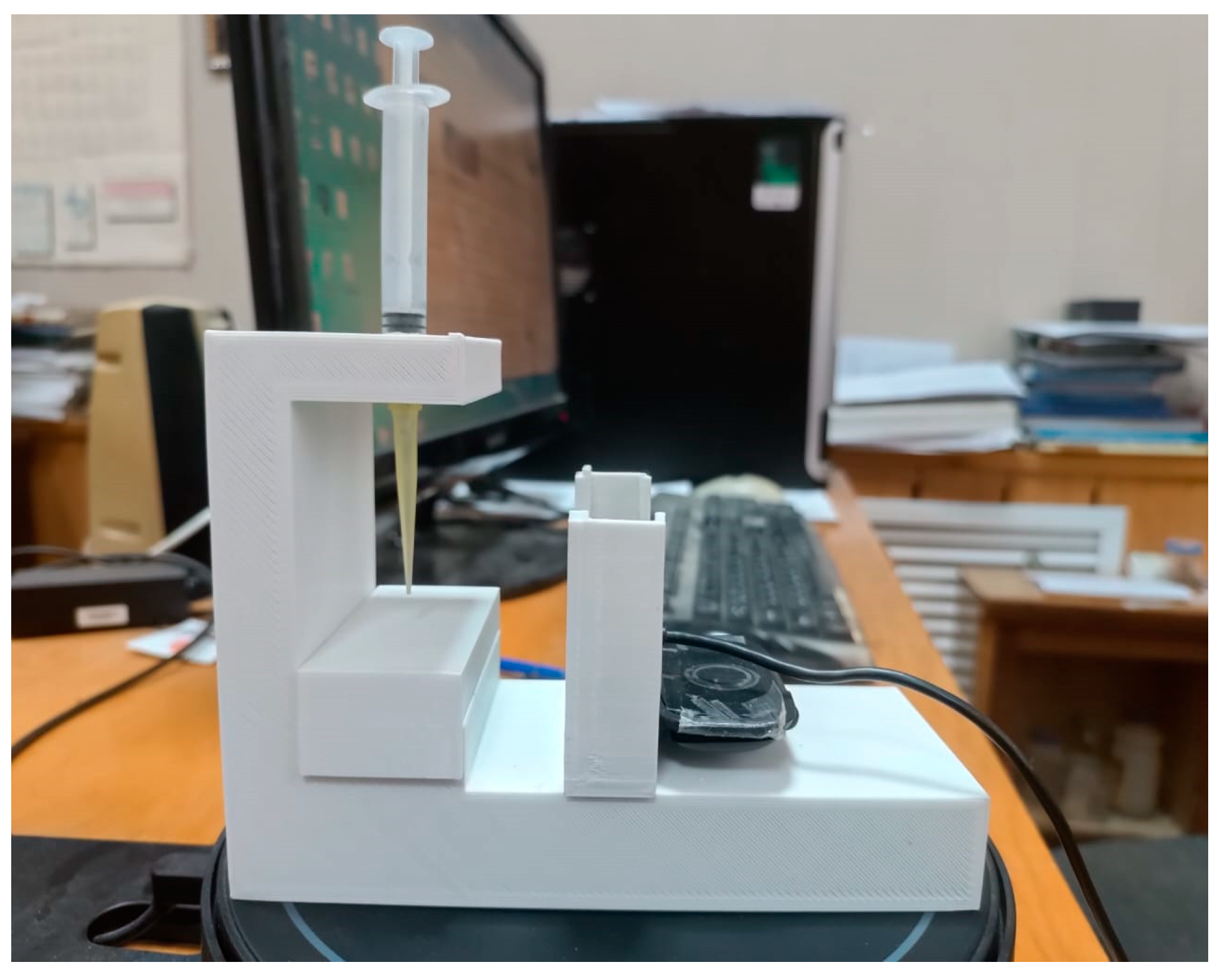
The wettability of the surface of flat printed samples with various 3D printing patterns was studied using the original installation for measuring the edge angles of wetting (
Figure 2), which we manufactured with a 3D printer. The installation is a stand with a sample holder on which a flat sample is placed. A drop gauge is installed on top, which creates droplets on the surface of the sample to measure the wetting edge angle. A webcam is installed opposite the stand with the sample under study, which displays an image of a drop on the screen, and using the Pic-pic graphic editor program, the wetting edge angle φ of the sample is measured.
A drop of liquid on the surface of a solid, depending on the nature of the sample, the liquid and the medium where it is located, can spread completely or partially and to acquire such a form as shown in
Figure 3. The angle φ between the tangent to the surface of the drop and the surface of a solid body, measured towards the surface of the drop, is called the wetting edge angle φ [
9,
10].
If a drop of liquid completely or partially spreads over the surface of the sample and forms an acute angle φ < 90° with it, as shown in
Figure 3, then the liquid moistens this surface. Only those liquids that reduce the surface tension of a given solid at the boundary with air moisten the solid surface. Surfaces of solids wetted with water are called hydrophilic. Surfaces over which the liquid does not spread and the drop forms with it an obtuse edge angle φ > 90° are called hydrophobic.
The accuracy of measuring the wetting edge angles φ in our original installation was about 1 degree.
If a liquid drop completely or partially spreads over the sample surface and forms an acute angle θ < 90° with it, as is shown in
Figure 3, then the liquid wets this surface. Only those liquids can moisten a solid surface that have lower the surface tension than a given solid at the boundary with air. Surfaces of solids wetted by water are called hydrophilic.
Surfaces where water does not spread and forms an obtuse contact angle θ › 90° are called hydrophobic.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
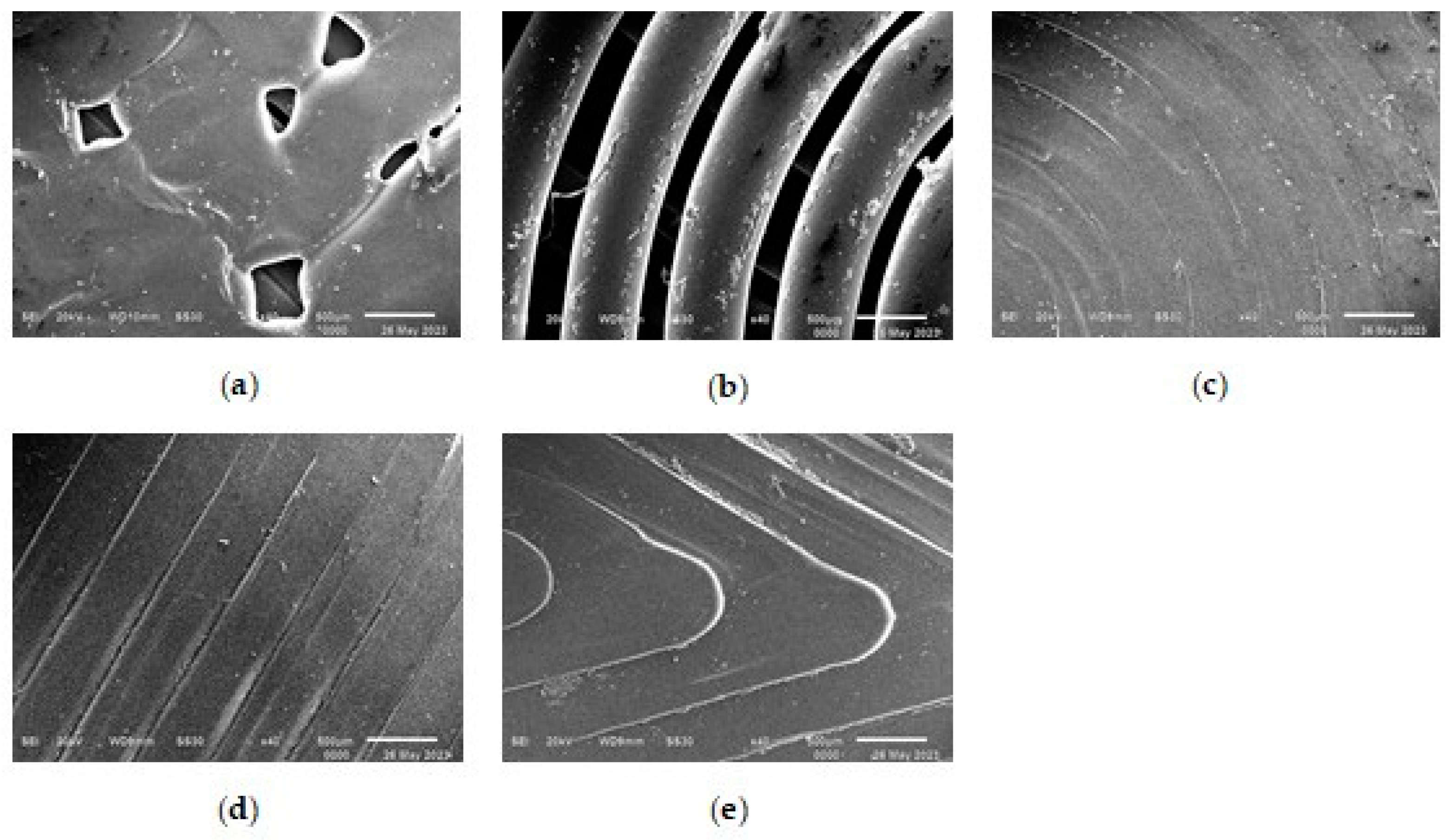
Figure 4 shows SEM micrographs obtained with magnification of x40 for five samples printed from Filament PLA with different model patterns.
The results of the SEM show that the micrograph of the 1_Hilbert sample surface least represents the most complex geometry of its model pattern. At the smeared surface of this sample it shows the large number of microdefects of triangular and rectangular shapes that occur at complex angular turns of the model pattern when scanning the extruder. And the most contrasting is the micrograph of the sample with the 2_Concentric pattern, representing the clear relief of the concentric circles of the PLA with deep dips between them of a smaller width.
The other three micrographs of the surface of the samples 3_Archimedean, 4_Rectilinear, 5_Octagram represent the geometry of their model drawings more or less equally.
Thus, a question arises whether the geometry of the model pattern, manifested in the morphology of the surface, affects the atomic structure of the printed samples and the wettability of their surface. The answer to this question is contained in the following sections of our work.
3.2. XRD Phase and Structure Analysis
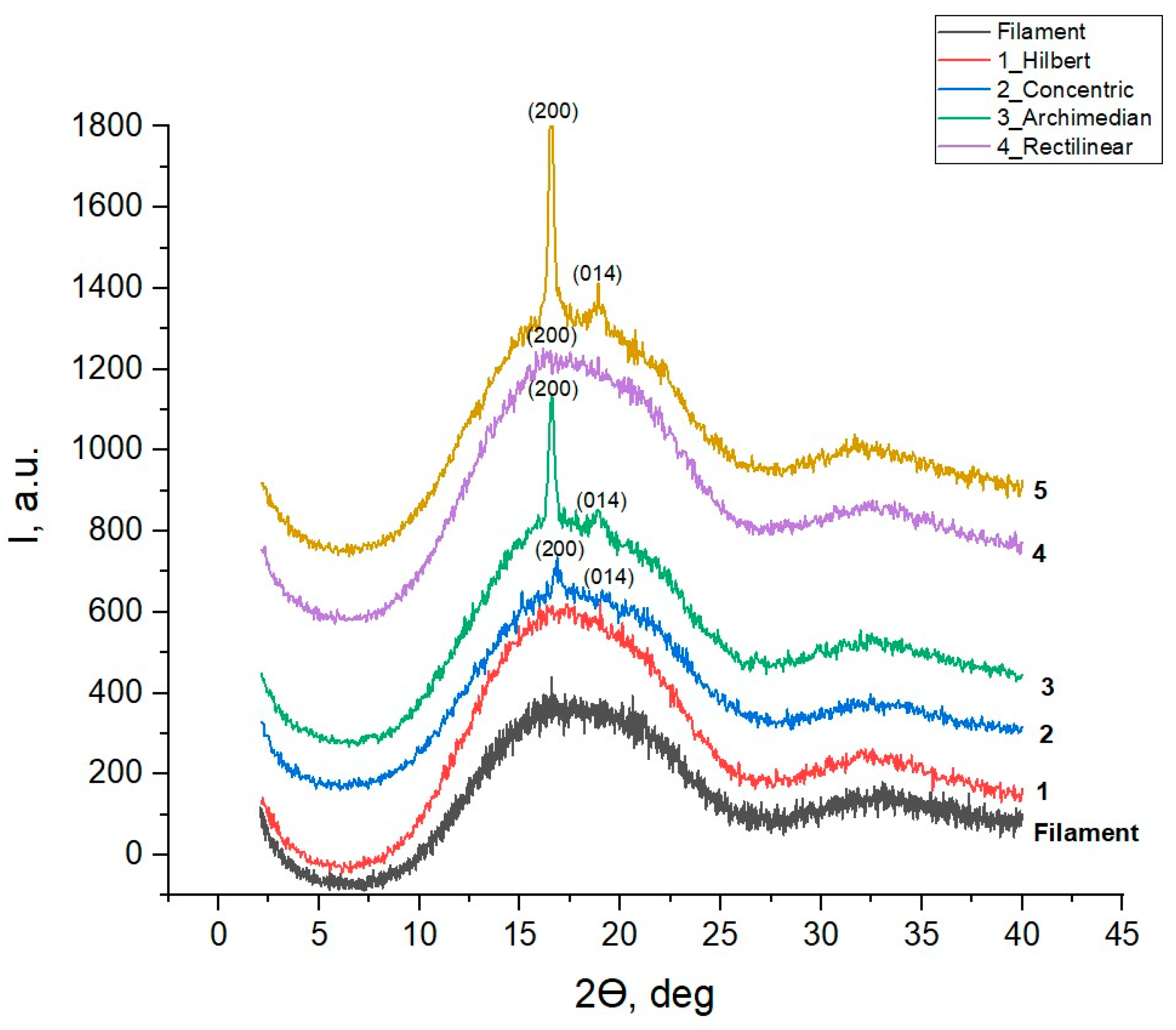
Figure 5 shows the results of a study of the crystal state in the printed samples with five different 3D printing patterns and the initial Filament PLA, obtained by X-ray diffraction (XRD) in the range of Bragg angles 2θ = 2- 40
ο.
The obtained results show that the diffractograms of all printed samples, as well as the original filament PLA, include two wide reflection bands (halos) from amorphous phase of PLA with the most intense band in the range of angles 2θ≈10-25
ο and the second less intense band in the range of 2θ≈30-40
ο (
Figure 5). Against the background of these wide bands, three out of five printed samples have one or two narrow diffraction lines from the crystalline phase of α-Poly(L-lactide) with the chemical formula (C
3H
5O
3)
n and orthorhombic structure (according to ICDD Card: 00-054-1917 [
11] with unit cell parameters : a=10.61, b=6.05 and c=28.8 Ǻ. It follows from the literature review [
1] that this phase is more stable compared to another known phase of β-Poly(D,L-Lactide), also with an orthorhombic unit cell, but with other unit cell parameters: a= 10.3, b= 18.2, c =9.0 Ǻ.
Table 1 shows the values of the Bragg angles 2θ and the interplane distances d (Ǻ) of the two most intense lines of the orthorhombic phase of the α-Poly(L-lactide), which appear in some printed samples. The last column of
Table 1 contains literature data on the interplanar distances and indices of these two lines from the international ICDD Card database [
11].
The results presented in
Table 1 and
Figure 5 show that the sample with the 1_Hilbert pattern and the most blurred surface morphology (
Figure 4) remains amorphous, as does the original Filament PLA. In the sample with the 4_Rectilinear pattern, the most intense diffraction line (200) of the crystalline α-phase with an interplane distance of d=5.30851 Ǻ is barely outlined, and in the sample with the most contrasting 2_Concentric pattern, it becomes the only noticeable line. But the highest relative intensity against the background of an amorphous halo is shown by this line (200) in samples with figures 3_Archimedian and 5_Octagram, along with the appearance of the second intense line (014) of this crystalline α-phase [
11].
Previously in [
12] it was shown that the level of atomic organization in PLA strongly depends on the conditions of sample preparation and processing. Thus, the volumetric PLA used by the authors as a reference involved, along with the amorphous polycrystalline c phase α-Poly(L-lactide), in the diffractogram of which seven diffraction lines with the two most intense lines (200) at 2θ=16.8° and (014) at 2θ =19.2° were registered against the background of an amorphous halo. These two lines with indices (200) and (014) are in good agreement with our data shown in
Table 1 and
Figure 5.
At the same time, the structure of the sample with misoriented nanofibers obtained by electroscission in another work [
12] turned out to be amorphous with typical two wide X-ray bands (halos) in the regions 2θ≈10-25
ο and 2θ≈30-40
ο, coinciding with our halos in
Figure 5, since the rapid hardening of the fibers in the process electroscreening limited the long-term three-dimensional order at the atomic level of the PLA.
However, after annealing the nanofibers below the melting point of PLA, a line (200) appeared on the diffractogram of the annealed sample at 2θ=16.8 ° from the crystalline phase of ᾳ-Poly(L-lactide), which, according to the authors [
12], indicated self-assembly of PLA polymer chains at the atomic level.
Similar differences found by us in the diffractograms of the printed samples from the diffractogram of the original Filament PLA are due to the partial crystallization of the initially misoriented polymer chains of amorphous Filament PLA, which occurs in the extruder under thermal and mechanical effects on the original filamentous sample during 3D printing.
At the same time, the most noticeable ordering under appearance of the orthorhombic phase of ᾳ-Poly(L-lactide) occurs in the printed samples with precisely those drawings 3_Archimedian and 5_Octagram, where the extruder operates continuously within each layer with their layered set of the full thickness of the samples equal to 5mm. This is how the influence of the 3D printing model pattern affects on the atomic structure andthe phase composition of the PLA polylactide, the initial filament of which is amorphous PLA.
Here we should compare the results obtained from the X-ray phase state of PLA samples with different model patterns with the corresponding results for the samples with the same 3D printing patterns printed from a similar polymer polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) with traces of polycrystalline coloring white pigment rutile TiO2, which we obtained in our previous work [
13].
Unlike the results presented in this paper on the varying degree of influence of the 3D printing model pattern on the X-ray phase state of PLA in the printed samples in the form of more or less noticeable crystallization against the background of the main amorphous phase, the effect of the type of model pattern on the amorphous state of PETG was not detected. Thermal and mechanical effects on the original PETG filament during 3D printing of the samples with the same different model patterns as those of PLA samples were manifested in the same way for all five drawings. It consisted in an increase in the relative intensity of the main diffraction maximum (halo) of amorphous PETG by an order of magnitude in the printed samples as compared to the original amorphous filament, which was due to the greater ordering of the polymer chains of amorphous PETG in the printed samples. No traces of crystallization of the samples during 3-d printing from amorphous PETG filament were found [
13].
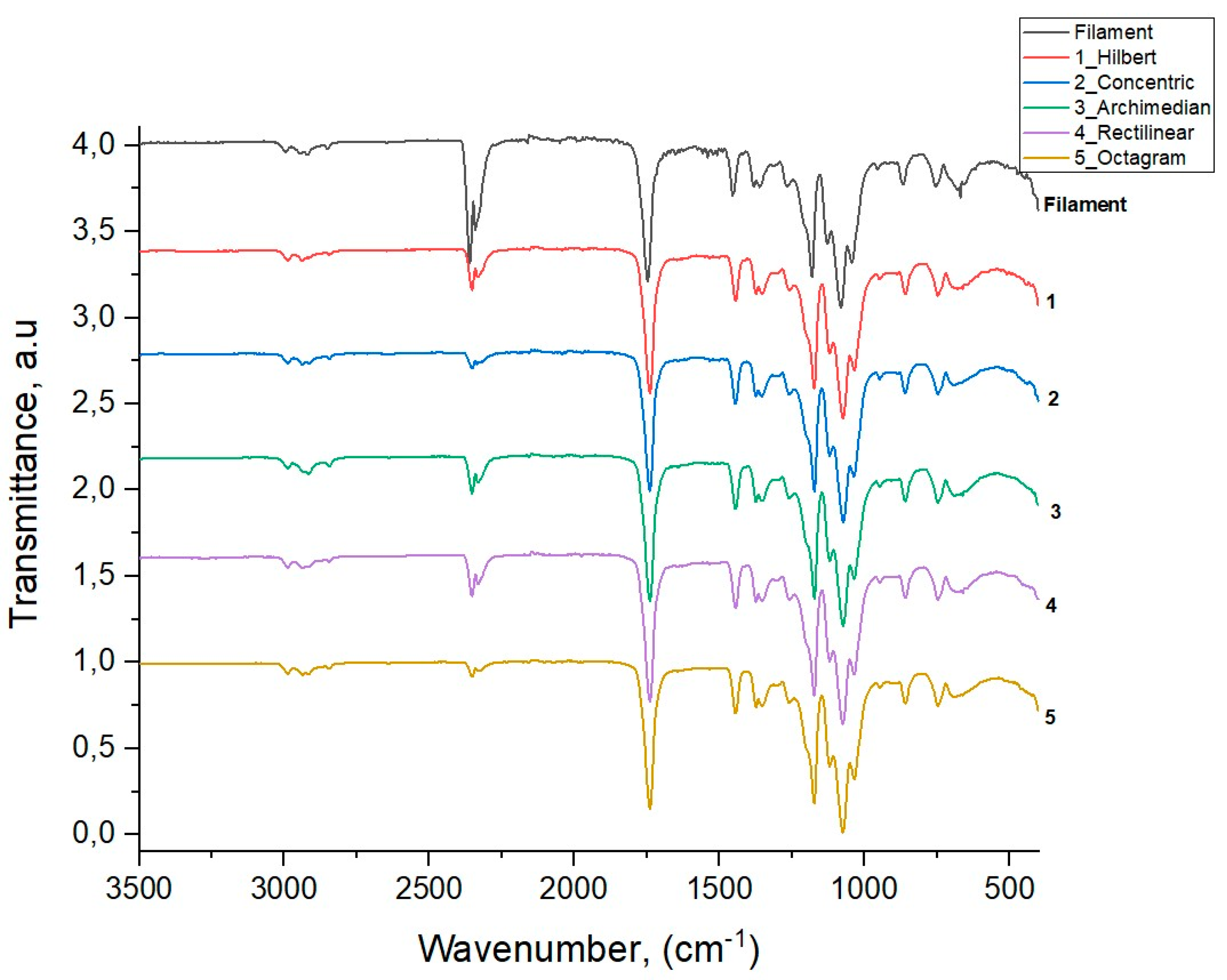
3.3. IR Spectroscopy
IR spectroscopy is a universal method for obtaining information about the molecular structure of substances and allows us to determine the nature of atomic grouping, the nature of chemical bonds and their changes under the influence of external conditions. [
14,
15]. Any molecule has its own individual oscillation spectrum, therefore, by comparing the modes of the obtained experimental spectrum with known literature data, it is possible to identify the substance under study.
Figure 6 shows the IR transmission spectra for the initial Filament PLA and five 3D-printed samples with various model patterns obtained by the method of attenuated total internal reflection [
16,
17] with the IR spectrometer Brucker Vertex 70.
Table 2 shows the results of the assignment for all of vibration modes of the studied samples, along with the literature data for PLA polymer modes from [
18], given in the last column.
The results of IR spectroscopy show that the wave numbers and relative intensities of the vibration modes of all five printed samples with different patterns have similar values and correspond to values of the main modes of the original PLA filament used in 3D printing of samples and the literature data for PLA polymer modes [
18]. This means that the intrastructural chemical bonds of the PLA polymer are not subjected to mechanical and thermal effects during the 3D printing process. These effects affect only the degree of ordering of the polymer chains and manifest themselves in the partial crystallization of the amorphous polymer PLA, more or less noticeable in the printed samples with different model patterns as compared to the original amorphous Filament PLA sample.
3.3. Wettability of the Printed PLA Samples Surface with Various Model Patterns
The wettability of the sample surface is a manifestation of the intermolecular interaction at the interface of three phases: solid, liquid and gas, expressed in the spreading of liquid on the surface of a solid. Since the measurement of the wetting edge angle of the surface is carried out only on flat samples, this section presents the results of a wettability study for only five printed samples.
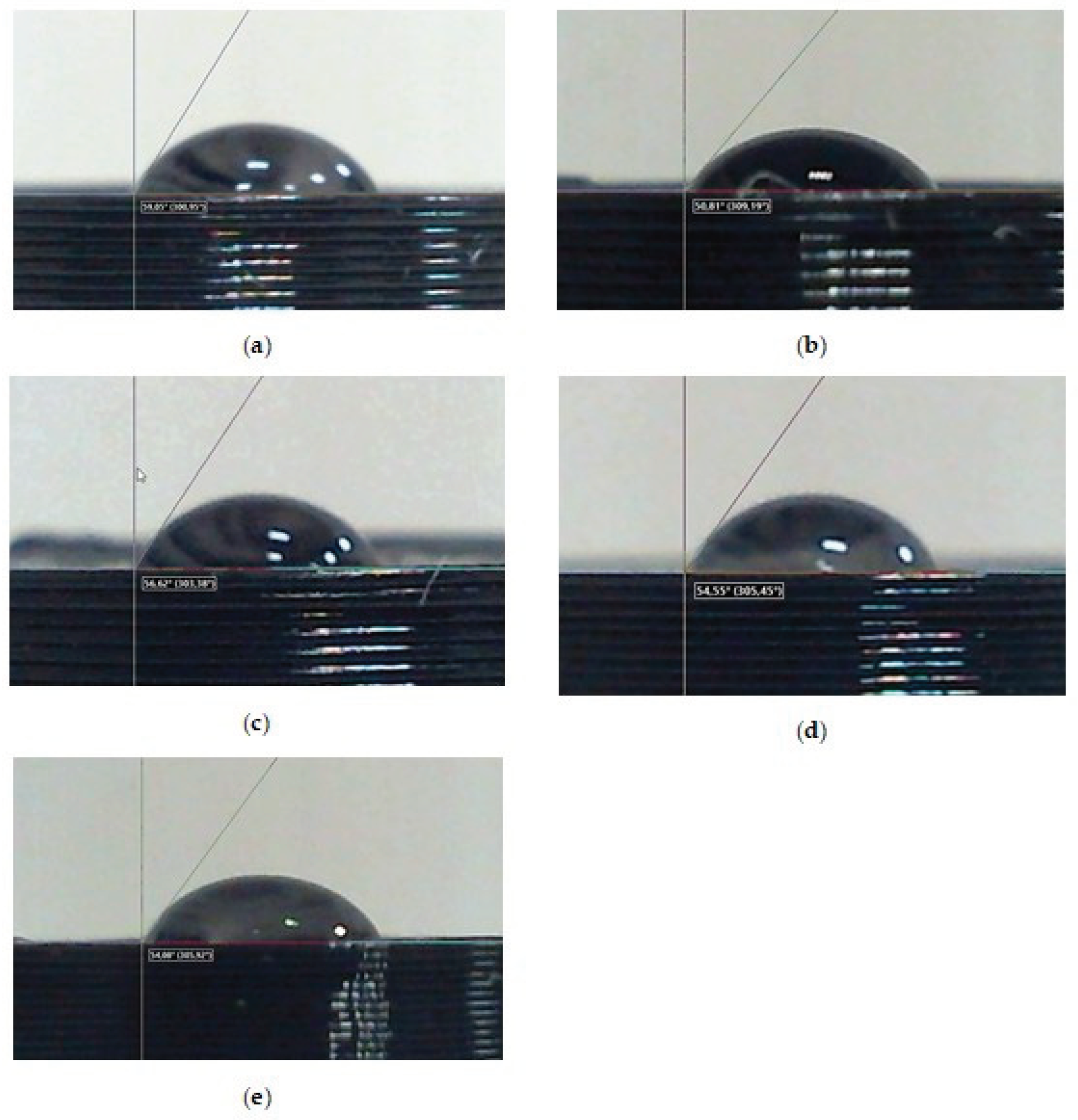
Figure 7 shows images of droplets on the screen of the installation while measuring the wetting edge angle on the surface of five samples with different 3D printing patterns made of PLA polymer.
Measurements of the edge angles of wetting for water droplets on the surface of the samples were carried out at five points of each sample with an accuracy of one degree.
Table 3 shows the average values of these angles φ.
The wettability of the sample surface is a manifestation of the intermolecular interaction at the interface of three phases: solid, liquid and gas, expressed in the spreading of liquid on the surface of a solid. Since the measurement of the wetting edge angle of the surface is carried out only on flat samples, this section presents the results of a wettability study for only five printed samples.
Figure 7 shows images of droplets on the screen of the installation while measuring the wetting edge angle on the surface of five samples with different 3D printing patterns made of PLA polymer.
A comparative analysis of the values of the wetting edge angles for the surface of samples with different model patterns shows that the wetting edge angles of all printed samples vary within φ =50°- 60°. The large deviation of the average wetting angles values for all samples with respect to the right angle of 90 ° shows that the surfaces of all five printed samples with different patterns are wettable, i.e. hydrophilic.
At the same time, three samples with figures 3_Archimedian, 4_ Rectilinear, 5_ Octagram, whose surface micrographs in
Figure 4 represent the geometry of their model drawings more or less adequately, have almost equal values of the wetting edge angles φ≈55ο. The sample with the least pronounced 1_Hilbert pattern on a smoother surface with individual defects shows the highest value of the wetting angle φ = 59
ο, i.e. it is less hydrophilic as compared to the other samples.
While the sample with the most contrasting pattern of concentric circles on the surface, separated by noticeable concentric dips, 2_Concentric, shows the lowest value of the wetting angle φ = 50ο, and in comparison to the samples with other patterns it is most hydrophilic one.
Thus, a positive qualitative answer was obtained to the question of whether the geometry of the model pattern, manifested in the morphology of the sample surface, affects the wettability of its surface. It should be recalled here that in our previous work [
13] we obtained similar but almost identical values of the edge angles of surface wetting for samples with the same model patterns (φ≈50
ο), but did not find a noticeable effect of the geometry of the model pattern on the wettability of the surface of samples printed from PETG polymer.
And since the wettability of the solid surface is a manifestation of intermolecular interactions at the interface of liquid contact with the solid surface, it could be assumed that one of the mechanisms of such interaction may be the participation of hydrogen groups of the more plastic polylactide PLA in the formation of more or less strong hydrogen bonds with water molecules on the surface of all five samples, leading to a significant decrease in the marginal the wetting angles are relative to 90° and the hydrophilicity of the printed samples.
4. Conclusions
The results of the study for the printed samples obtained from the PLA filament by sequentially applying layers of Polylactic Acid polymer with various model patterns using the Fused Deposition Modeling method on a Hercules Original 3D printer at the extruder temperature of 260°C and a power of 500 W, revealed a different degree of influence of the 3D printing model pattern on their microstructural and hydrophilic properties using methods of X-ray diffraction, IR spectroscopy and measurement of the wetting edge angle.
The differences we found between the phase composites of the printed samples and the original Filament PLA are due to the partial crystallization of the initially misoriented polymer chains of amorphous PLA with the appearance of the orthorhombic phase ᾳ-Poly(L-lactide), which occurs in the extruder under thermal and mechanical influences on the original amorphous filament PLA during 3D printing.
The most noticeable crystallization with the appearance of orthorhombic ᾳ-phase of polylactide occurs in the printed samples with those 3_Archimedian and 5_Octagram patterns, which the extruder performs continuously within each layer with a continuous layered set of the full thickness of the samples of 5mm. In this way the influence of the 3D printing model pattern on the atomic structure and phase composition of the initial amorphous filament PLA is manifested.
Regardless of the partial crystallization and corresponding changes in the phase composition of some printed samples, the intrastructural chemical bonds of PLA polylactide are not subjected to noticeable effects of the 3D printing process. Therefore the wave numbers and relative intensities of the IR oscillation modes of all five printed samples with different model patterns have almost identical values and good agreement with the corresponding values of the main modes for the original Filament PLA and the literature data.
The values of the edge angles of wetting water droplets on the surface of all printed samples measured at the original installation are within φ=50ο-60ο, significantly less than the right angle θ= 90ο, which corresponds to the hydrophilic properties of the surface of the printed samples.
With the general hydrophilicity of all printed samples, the influence of different geometry of the model pattern was found to have an effect not only on the morphology of the surface from SEM micrographs, but also on its wettability. Three samples with figures 3_Archimedian, 4_ Rectilinear, 5_Octagram, whose micrographs of the surface represent the geometry of their model drawings more or less adequately, have almost equal values of the wetting edge angles φ≈55ο.
The sample with the least pronounced pattern on the surface 1_Hilbert shows the highest value of the wetting angle φ =59ο, i.e. it is less hydrophilic as compared to others, while the sample with the most contrasting 2_Concentric pattern on the surface shows the lowest value of the wetting angle φ = 50ο, and in relation to samples with other patterns is the most hydrophilic.
One of the mechanisms of intermolecular interaction at the boundary of contact of water droplet with the surface of printed samples may be the participation of PLA hydrogen groups of n the formation of more or less strong hydrogen bonds with water molecules on the surface of samples, leading to a significant decrease in the wetting edge angles relative to 90o and the hydrophilicity of printed samples.
Thus, according to the results of our study, polylactide has claimed itself as a material suitable for 3D printing using a common 3D printer model. In this case, 3D printing causes statistically significant orientation of the polymer chains of polylactide with more or less noticeable partial crystallization, depending on the geometry of the model pattern, resulting from molecular alignment caused by extrusion, without destroying the intrastructural chemical bonds of the polymer.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.P., A.S. and V.E.; methodology, A.S.; E.P. and V.E.; software, S.K..; validation, E.P.; formal analysis, E.P. and A.S.; investigation, V.E. and A.S..; resources, A.S.; data curation, E.P.; writing—original draft preparation, E.P. and V.E.; writing—review and editing, E.P.; A.S. and V.E. visualization, E.P.; A.S. and V.E. supervision, E.P..; project administration, E.P.; funding acquisition, A.S.
Funding
The research was carried out with the support of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation partly within the framework of the state task for universities in the field of scientific activity, project No. FZGU-2023-006, and Agreement No. 075-15-2021-1351 in parts of the XRD research.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be provided on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors express special gratitude to Alexander Stanislavovich Shestakov, Doctor of Chemical Sciences, Head of the Department of High Molecular Compounds and Colloidal Chemistry of Voronezh State University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
The declared contribution of the authors
The authors have made an equivalent contribution to the preparation of the publication.
References
- Garlotta, D. A. Literature review on the field (milk jelly). J. Polym. Environment 2001, Volume 9, pp. 63-84.
- Slomkovsky, S.; Penchek, S.; Duda, A. Polylactides. Polym. Adv. Technology 2014, Volume 25, pp. 436-447.
- Silva, A.L.; Salvador G.M. Castro S.V.F.; Carvalho N.M.F.; Munoz R.A. A 3D printer guide for the development and application of electrochemical cells and devices. Front. Chem. 2021, Volume 9.
- Vidakis N.; Petousis M.; Velidakis E.; Libsher M.; Mechcherin V.; Tsunis L. On the sensitivity to the deformation rate of thermoplastic polymers PLA, ABS, PETG, PA6 and PP for the manufacture of fused filaments (TTT). Polymers 2022, 12.
- Gordeev E.G.; Ananikov V.P. Advanced technologies of chemical engineering, biochemistry and pharmaceuticals: applications, materials, prospects. The successes of chemistry 2020, Volume 89, p. 12.
- Mark J.E. The Polymer Data Handbook. Oxford University Press, 2nd ed. 1999, 1012 p.
- Martino S. P.; Jimenez A.; Rusetskaya R.A.; Averous L. Structure and properties of clay nanobiocomposites based on poly (lactic acid) plasticized polyadipates. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, Volume 22, pp. 2206-2213.
- Maharanaa T.; Mohantyb B.; Negi Y.S. Melt-solid polycondensation of lactic acid and its biodegradability. Progress in Polymer Science 2009, Volume 34, pp. 99—124.
- Kiselev M.G.; Savich V.V.; Pavich T.P. Determination of the wetting edge angle on flat surfaces. Bulletin of the BNTU 2006, Volume 1, p. 38.
- Yelesina V.V. Wetting edge angle. Methodological recommendations. Publishing House of the Altai State Technical University named after I.I. Polzunov 2019, pp. 1-22.
- PDF-2-2006 card number 00-054-1917, Diffract. Plus 2005.
- Gomez-Pachon E.I.; Vera-Graziano R.; Montiel Campos R. Structure of frameworks made of poly (lactic acid) PLA nanofibers, bold research method. In Proceedings of IOP Conf. Series: Mathematics and Engineering 2014, Volume 59.
- Lenshin A.S.; Frolova V.E.; Ivkov S.A.; Domashevskaya E.P. Microstructural and hydrophilic properties of polyethylene terephthalate glycol polymer samples with various patterns in 3D printing. Condensed Media and Interphase Boundaries 2024, Volume 26, pp. 78-87.
- Gremlich H.U. The language of spectra. An introduction to the interpretation of the spectra of organic compounds. LLC "Brooker Optik" 2002, 94 p.
- Тolstoy V.P.; Chernyshova I.V.; Skryshevsky V.A. Infrared spectroscopy In Handbook of Infrared Spectroscopy of Ultrathin Films. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, New Jersey; 2003, 739 р.
- J.M. Hollas. Modern Spectroscopy. John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Fourth Edition. The Atrium, Southern Gate, Chichester, West Sussex, England; 2004, 452 p.
- Pavlov I.N.; Rinkevics B.S.; Tllasolkachev A.V.. Application for familiarization with the privacy policy on the Internet. Laser beam removal. Instruments and Techniques of Experiment 2013, Volume 2, pp.130-135.
- Uniarto K.; Purvanto J.A.; Purvanto S.; et al. Infrared and Raman studies of a mixture on polylactide acid and polyethylene glycol-400 blend. AIP Conference Proceedings 2016 Volume 1725.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).