Current Understanding of the Effects of AB126 (In Vitro and In Vivo)
Aruna Bio’s proprietary NSC EV is referred to as AB126 and has obtained Investigational New Drug (IND) clearance from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to begin clinical trials. Published SPECT studies indicate substantial blood-brain barrier (BBB) crossing of AB126 and homing to the stroke infarct following IV injection [
1]. Previous studies by other groups have shown that increased infarct homing of IV-infused cell-based therapies is correlated with reduced lesion size and improved functional recovery by having more direct effects on the central nervous system (CNS) microenvironment [
2,
3], which indicates that the innate ability of AB126 to home to the infarct site may correspond to a more robust effect on CNS tissue. This correlation was confirmed in a pig middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) which showed that AB126 reduced lesion size and edema formation, preserved white matter integrity, and promoted functional outcomes [
4].
Cell-based assays and animal stroke models have elucidated several potential direct and indirect pathways by which AB126 functions to improve stroke outcomes [
1,
4,
5]. AB126 possesses ATPase enzymatic function, which is involved in converting ATP to anti-inflammatory adenosine, possibly through the activity of CD73 on the EV membrane [
2]. AB126 treatment leads to a significant, dose-dependent reduction in protein levels of proinflammatory C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2 (CCL2) in activated human microglia cells. CCL2 acts to disrupt the tight junctions of the BBB endothelium allowing for infiltration of T cells and macrophages into the brain, and simultaneously promotes the polarization of these immune cells to an inflammatory phenotype. AB126 also modulates the interconnected RIPK-1 necroptosis and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways, further dampening the inflammatory cascade. AB126 has also been shown to significantly reduce infarct size in multiple animal models, leading to other tissue-level improvements including reduced incidence of hemorrhagic transformation, enhanced white matter integrity, and reduced cerebral atrophy [
1,
4]. These tissue-level improvements correlate with the preserved sensorimotor function of stroked animals. Taken together, these data suggest that the anti-inflammatory effects of AB126 are via receptor-mediated AMPase activation, which mitigates the inflammatory signaling cascade and subsequently inhibits microglial secretions, cell death, and the NLRP3 inflammasome, which in turn reduces the activation and brain infiltration of circulatory immune cells. These cellular-level changes are thought to dampen tissue-level inflammation and reduce cerebral damage. Smaller infarct size, a possible metric of protected brain tissue in the stroke penumbra, leads to preserved sensorimotor function in the stroked animal. These findings suggest a potential mechanism by which AB126 exerts its therapeutic action in acute ischemic stroke (AIS).
In the future, the anti-inflammatory potential of AB126 could be further investigated by collecting the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) from AB126-treated, stroked, and non-stroked controls in the pig MCAO model. Analysis of CSF at multiple time points post-MCAO could help characterize the currently unknown time course of this inflammatory response in this MCAO model. Still, it would also allow for direct interpretation of the cytokine and immune cell expression profiles of AB126-treated animals over time [
6]. In addition to increases in CCL2 and neurofilament light chain (NfL), CSF analysis could further indicate how generalizable this potentially anti-inflammatory effect is; if it is attenuating complement-activated system or more widespread inflammation [
7]. For example, flow cytometry could reveal an alteration in the number of CD11b+ microglia, a subunit of CR3, after AB126 treatment compared to stroked non-treated animals [
7]. This could indicate that AB126 directly affects the complement system cascade. Furthermore, multiplex immunoassay analysis of secreted cytokines could further specify affected pathways of activation. For example, if there was a decrease in IL-6 secretion, but no change in IL-1β in AB126-treated animals, this may indicate attenuation of NF-κB-associated inflammatory responses but not ROS- associated responses [
8]. This enhanced understanding of the timing and specificity of inflammatory pathways affected by AB126 treatment would allow for better-informed AB126 dosing strategies. Since the pathway most affected by AB126 treatment may occur in a specific timeframe during the post-stroke inflammatory cascade, the therapeutic window for AB126 treatment could be established.
The impetus for the mechanism of action (MOA) investigation of AB126 toward anti-inflammatory pathways is supported not only in general EV literature but also specifically regarding AB126. In a previous study assessing AB126 therapeutic efficacy in a rodent embolic model of stroke, flow cytometry revealed a significant increase in peripheral functional M2 macrophages, an increase in immunosuppressive T regulatory cells, and a decrease in pro-inflammatory TH-17 cells [
1]. This suggests that intravenously administered AB126 fosters a reparative immune state in the typically pro-inflammatory post-stroke environment. Most compelling, AB126 was able to significantly invoke this proinflammatory-to-reparative transition more so than mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) EVs, which have previously been highlighted by recent reviews for their widespread anti-inflammatory capacity [
9]. This finding spurred further investigation into the effects of AB126
in vitro on complex mixed- and monoculture systems.
AB126 Attenuates Morphological and Functional Responses of Microglia Following Proinflammatory Stimulation
We have investigated the effects of AB126 in vitro on BV2 microglia (unpublished). In these studies, BV2 microglia were stimulated with LPS and TNF-α. TNF-α, a cytokine known to increase in CSF and blood after ischemic stroke, was included to mimic the in vivo ischemic environment (216). LPS, an endotoxin found in gram-negative bacterial cell walls, was utilized to induce an inflammatory response in recipient microglia, non-characteristically associated with ischemic injury. In both activation strategies, AB126 treatment was able to significantly decrease proliferation, M1-like morphological transitions, and downstream characteristic functional increases in microglia dry mass with inflammatory activation. AB126 treatment was also able to attenuate BV2 microglia to a lower proliferative state than non-stimulated controls, which may indicate an ability to encourage microglia into a momentary quiescent state. With further experiments, if AB126 is shown to effectively attenuate M1-like microglial response for 24, but not 48 hours, 2 doses of AB126 may be necessary to quell post-stroke inflammation throughout the acute and subacute stages effectively. These dosing and timing studies would also allow for the generation of concentration vs. time curves. For example, a higher dose of AB126 may be effective for longer and therefore, depending on degradation kinetics, only one dose may be necessary. While the main target of AB126 treatment is activated microglia in the post-stroke brain, AB126 may also be interacting with other neural cell types, such as neurons and astrocytes. Conducting further experiments with multiple CNS-specific cell types will allow for generation of concentration vs. time and concentration-response curves for other cell types, as well, as allowing for deeper analysis, such as EC50 calculation. Demonstrating a specific relationship between and the effect of AB126 on microglia, one might expect the EC50 for EVs on microglia to be below that of other cell types, indicating increased efficacy in microglia due to this specificity. Knowing this information would allow for precise dosing, both in concentration and time, allowing for effective targeting of activated microglia.
In addition to further experiments to ascertain dosing and timing information for AB126 treatment, downstream flow and multiplexed immunoassay analysis of microglia spent media should be conducted. This may assist in answering the time dependence and residual effects of AB126 treatment on activated microglia. A time course analysis of cytokine responses with various AB1216 doses administered at various times relative to cytokine stimulation should be investigated. While pre-treatment of cultures with AB126 before cytokine stimulation would be expected to have the most significant effect on quelling downstream inflammation, an investigation should be conducted of post-treatment timepoints as well given their increased translational relevance. These experiments would not only help to better define the therapeutic window of AB126 treatment for stroke but through testing of different stimulatory factors, could also help define the therapeutic window for other inflammatory conditions.
AB126 Reverses Pro-Inflammatory Morphological Transitions Following the Ischemic Incident
The promising attenuative effect of AB126 on stimulated microglial responses
in vitro spurred further investigation of their effects on inflammatory cells
in vivo (unpublished). In the pig MCAO model of stroke, the histopathological effects of AB126 on 5 different cell types were assessed. This study revealed that upon ischemic injury, IBA1+ cells (microglia) undergo a morphological transition to more swollen, rounded, amoeboid cells, and GFAP+ cells (astrocytes) transition to more ramified, extended cells in this large animal model, as is seen in rodent models. Interestingly, AB126 treatment was able to prevent these well-characterized pro-inflammatory morphological transitions of IBA1+ and GFAP+ cells in multiple parameters, making them morphologically indistinguishable from microglia and astrocytes, respectively, in non-MCAO animals (unpublished). Most compelling, for some morphological parameters of IBA1+ and GFAP+ cells, AB126 treatment was able to shift the morphological transitions in the complete opposite direction of stroked-non-treated animals with respect to normal non-stroked animals. This unexpected result indicates that AB126 treatment not only attenuates acute ischemia-induced proinflammatory morphological transitions but also may even be able to quell baseline inflammation in animals. This AB126-induced quelling of proinflammatory responses after MCAO may also be responsible for the preservation of other cytoarchitectural cells after stroke, namely NeuN+ neurons. Following activation of astrocytes and microglia in acute ischemic stroke, secreted proinflammatory cytokines induce Fas, TNF-α, and TRAIL pathways, which lead to caspase-initiated apoptosis or MLKL-initiated necroptosis [
10]. In these studies, while there was a significant loss of neurons in stroked animals and a transition to an apoptosis-associated morphology, AB126 treatment significantly preserved the number of NeuN+ cells, as well as prevented this apoptotic transition when compared to stroked, non-treated animals.
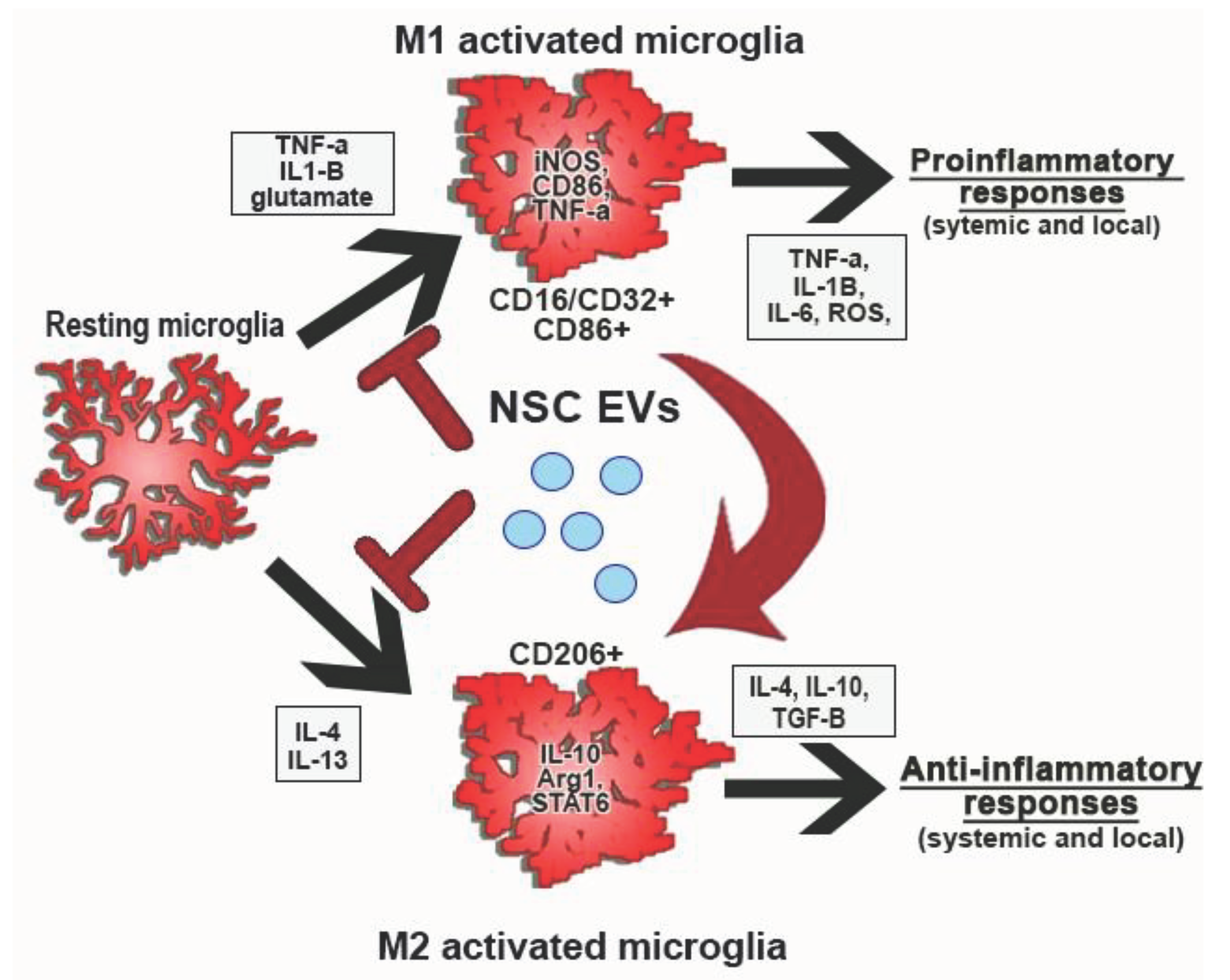
To better understand and further investigate these findings, an analysis of the transcriptional and expression profiles of certain morphological subtypes in each treatment group should be conducted. Transcriptional and cytokine expression for each treatment group can be compared to their morphological transitions to ascribe a certain morphological alteration to a specific M1- or M2-associated activation state. These studies could reveal the overall effect of AB126 on microglial polarization is illustrated in
Figure 1. A potential mechanism of action of AB126 responsible for the improved survival, recovery, and functional outcomes observed in
in vivo porcine MCAO studies.
Imaging the Longitudinal Progress of Stroke Patients after AB126 Treatment
Analysis of the porcine MCAO model of stroke revealed a unique relationship between midline shift (MLS) and chronic functional outcomes previously undescribed in an animal model of stroke. While the relationship between MLS and modified Rankin Scale (mRS) [
11,
12,
13,
14] scores and survival [
15,
16] had been previously established in clinical studies, we have established a relationship between MLS (measured from the same structure and plane as human studies) and gait, behavior, survival, and mRS score in MCAO non-treated pigs. Remarkably, AB126 treatment was able to disrupt the linear correlations between MLS and functional outcomes, revealing improved survival and mRS score at day 6 post-MCAO, even in animals with a high degree of MLS. In clinical stroke, MLS has been used as a measure of overall edema and intracranial pressure (ICP) in the brain in accordance with the Monroe-Kellie doctrine [
17,
18]. Increased ICP after a malignant middle cerebral artery stroke can result in a range of detrimental effects on the brain, including uncal, transtentorial, and tonsillar herniation of the cerebellum through the foramen magnum [
19]. AB126 treatment, however, was able to prevent this herniation event with increased MLS, indicating that AB126 can prevent this detrimental edematous transition [
5]. This finding suggests the therapeutic MOA of AB126 may be associated with quelling inflammation and secondary injury after MCAO.
In this study, the MLS measurement was conducted at 24 hours and 84 days post-stroke [
5]. Ideally, to further probe this potential antiedematous effect of AB126, multiple MRIs or CTs over time should be conducted to track changes in MLS in the acute post-MCAO phase, as is done clinically. Human studies have shown that MLS measurements evolve over the first 48 hours after a middle cerebral artery stroke. For example, while patient MLS measurements may be small at early acute time points, by 40 hours after stroke there is a significant increase in MLS in patients with eventual poor prognosis. In some cases, high mRS-scoring patients may have a 5x increase in MLS compared to their 20-hour timepoint and even low mRS patients [
20].
These edematous changes are often ascribed to infiltrating leukocytes and local increases in ROS and proinflammatory cytokines over the acute and subacute phases of stroke [
21]. For these reasons, rigorous imaging in humans post-MCAO should be conducted. Comparison of MLS at these time points would allow for further assessment of the effects of AB126 on inflammation over time. If AB126 does have a significant anti-inflammatory effect, the MLS of AB126-treated patients should peak in the early acute phases, during the initial injury, but then taper off and eventually stay stable. The MLS of non-treated patients would be expected to rise steadily over the 48-hour interval post-MCAO.
Summary
Here, we presented both published and unpublished data on AB126 effects in preclinical models of stroke. We will strengthen these findings through efforts to understand AB126 pleiotropic mechanisms of action. Future studies will inform the future human clinical trial dose regimen and translational surrogate pharmacological endpoints to quantify AB126 treatment effect.
References
- Webb, R.L.; Kaiser, E.E.; Scoville, S.L.; Thompson, T.A.; Fatima, S.; Pandya, C.; Sriram, K.; Swetenburg, R.L.; Vaibhav, K.; Arbab, A.S.; et al. Human Neural Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles Improve Tissue and Functional Recovery in the Murine Thromboembolic Stroke Model. Transl. Stroke Res. 2017, 9, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Roh, J.; Kim, E.-C.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.U.; Yoon, B.-W. Long-Term Effects of Magnetically Targeted Ferumoxide-Labeled Human Neural Stem Cells in Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Cell Transplant. 2015, 24, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, N.; Yu, S.P.; Gu, X.; Taylor, T.M.; Song, D.; Liu, X.-F.; Wei, L. Delayed Intranasal Delivery of Hypoxic-Preconditioned Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhanced Cell Homing and Therapeutic Benefits after Ischemic Stroke in Mice. Cell Transplant. 2013, 22, 977–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb Robin, L. , et al. , Human Neural Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles Improve Recovery in a Porcine Model of Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2018, 49, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Spellicy, S.E.; Kaiser, E.E.; Bowler, M.M.; Jurgielewicz, B.J.; Webb, R.L.; West, F.D.; Stice, S.L. Neural Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles Disrupt Midline Shift Predictive Outcomes in Porcine Ischemic Stroke Model. Transl. Stroke Res. 2019, 11, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhu, X.; Smerin, D.; Zhong, Y.; Gu, L.; Fang, W.; Xiong, X. The Involvement and Therapy Target of Immune Cells After Ischemic Stroke. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, G.-Y. Significance of Complement System in Ischemic Stroke: A Comprehensive Review. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 429–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carta, S. , et al. , Dysregulated IL-1β Secretion in Autoinflammatory Diseases: A Matter of Stress? Frontiers in Immunology 2017, 8, 345. [Google Scholar]
- Harrell, C.R.; Jovicic, N.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Volarevic, V. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles as New Remedies in the Therapy of Inflammatory Diseases. Cells 2019, 8, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duris, K.; Splichal, Z.; Jurajda, M. The Role of Inflammatory Response in Stroke Associated Programmed Cell Death. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quattrocchi, K.B.; Prasad, P.; Willits, N.H.; Wagner, F.C. Quantification of midline shift as a predictor of poor outcome following head injury. Surg. Neurol. 1991, 35, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiss, W.-D. Malignant MCA Infarction: Pathophysiology and Imaging for Early Diagnosis and Management Decisions. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badih, D. , et al. , Decompressive hemicraniectomy: predictors of functional outcome in patients with ischemic stroke. Journal of Neurosurgery JNS 2016, 124, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar]
- Asuzu, D.; Nyström, K.; Sreekrishnan, A.; Schindler, J.; Wira, C.; Greer, D.; Halliday, J.; Kimberly, W.T.; Sheth, K.N. TURN Score Predicts 24-Hour Cerebral Edema After IV Thrombolysis. Neurocritical Care 2015, 24, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, P.M.P. , et al., Mass effect and death from severe acute stroke.1997.
- Kumar, J.R. , et al. 287). 2015.
- Mokri, B. , The Monro–Kellie hypothesis. Neurology 2001, 56, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-F.; Xiao, F. Brain Midline Shift Measurement and Its Automation: A Review of Techniques and Algorithms. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2018, 2018, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, A.J.; Vink, R.; Helps, S.C.; Knox, S.J.; Blumbergs, P.C.; Turner, R.J. Elevated Intracranial Pressure and Cerebral Edema following Permanent MCA Occlusion in an Ovine Model. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0130512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerriets, T.; Stolz, E.; König, S.; Babacan, S.; Fiss, I.; Jauss, M.; Kaps, M. Sonographic Monitoring of Midline Shift in Space-Occupying Stroke. Stroke 2001, 32, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Yang, G.; Li, G. Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: role of inflammatory cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).