Submitted:
02 April 2024
Posted:
02 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Result and Discussion
2.1. Characteristics of B@PM & BCEKH
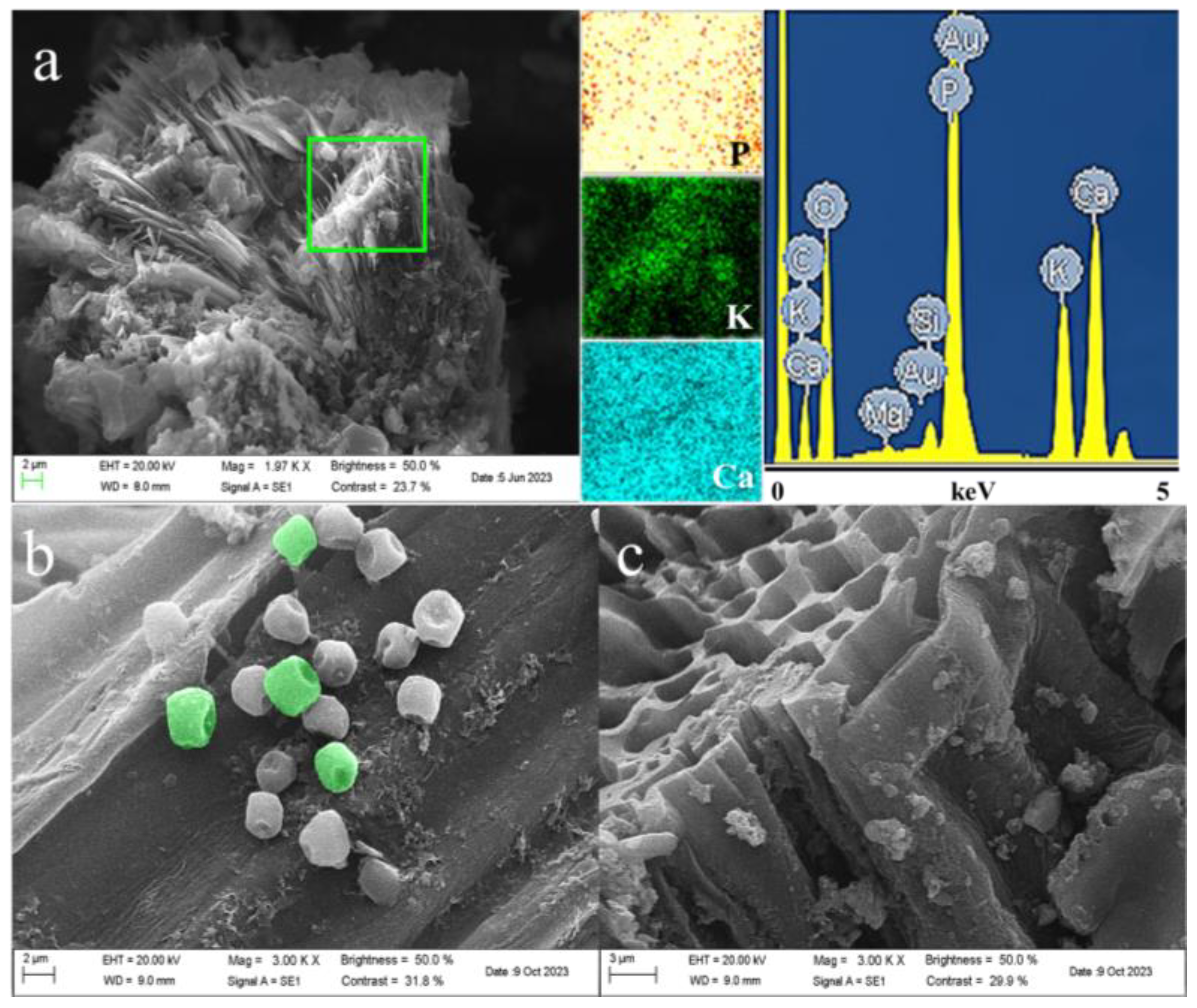
2.1.1. SEM and EDS Analysis of BCEKH& B@PM
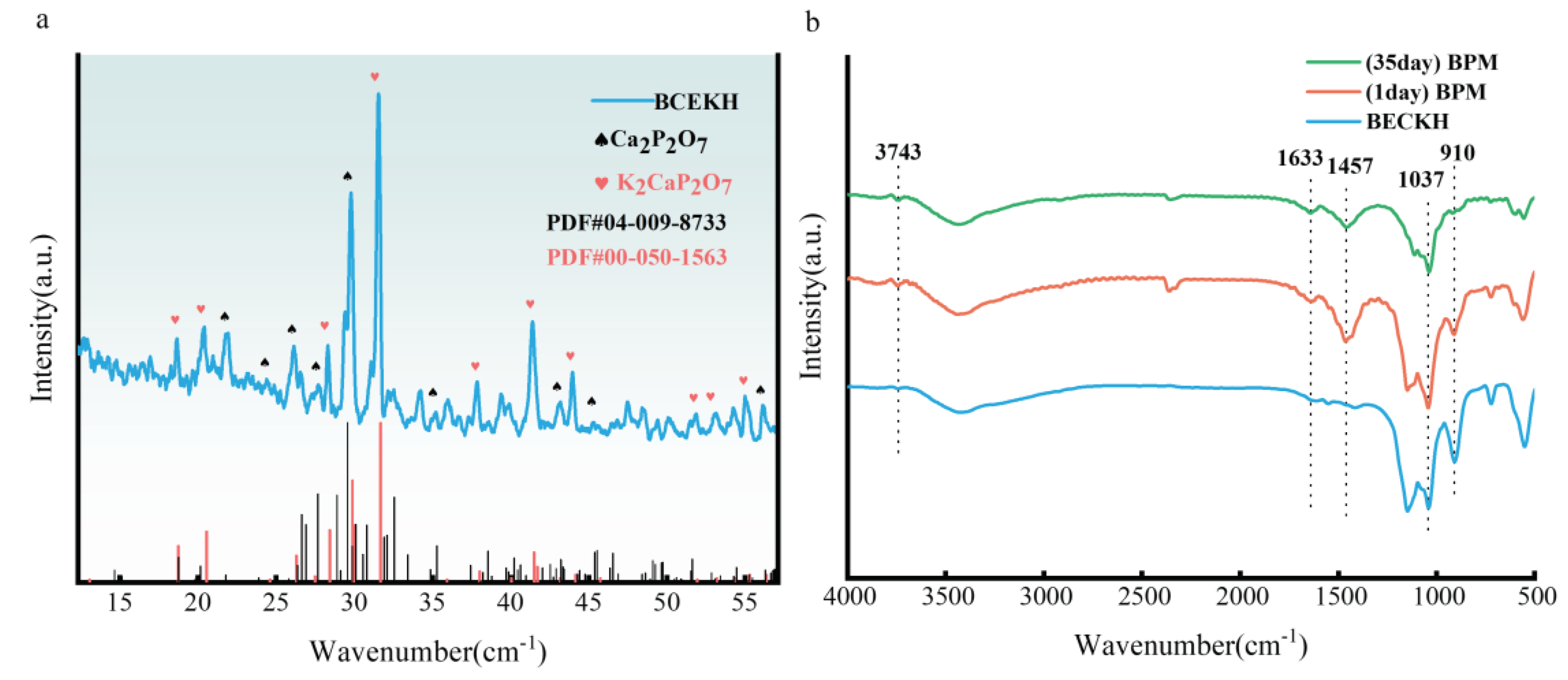
2.1.2. XRD and FTIR Analysis of BCEKH& B@PM
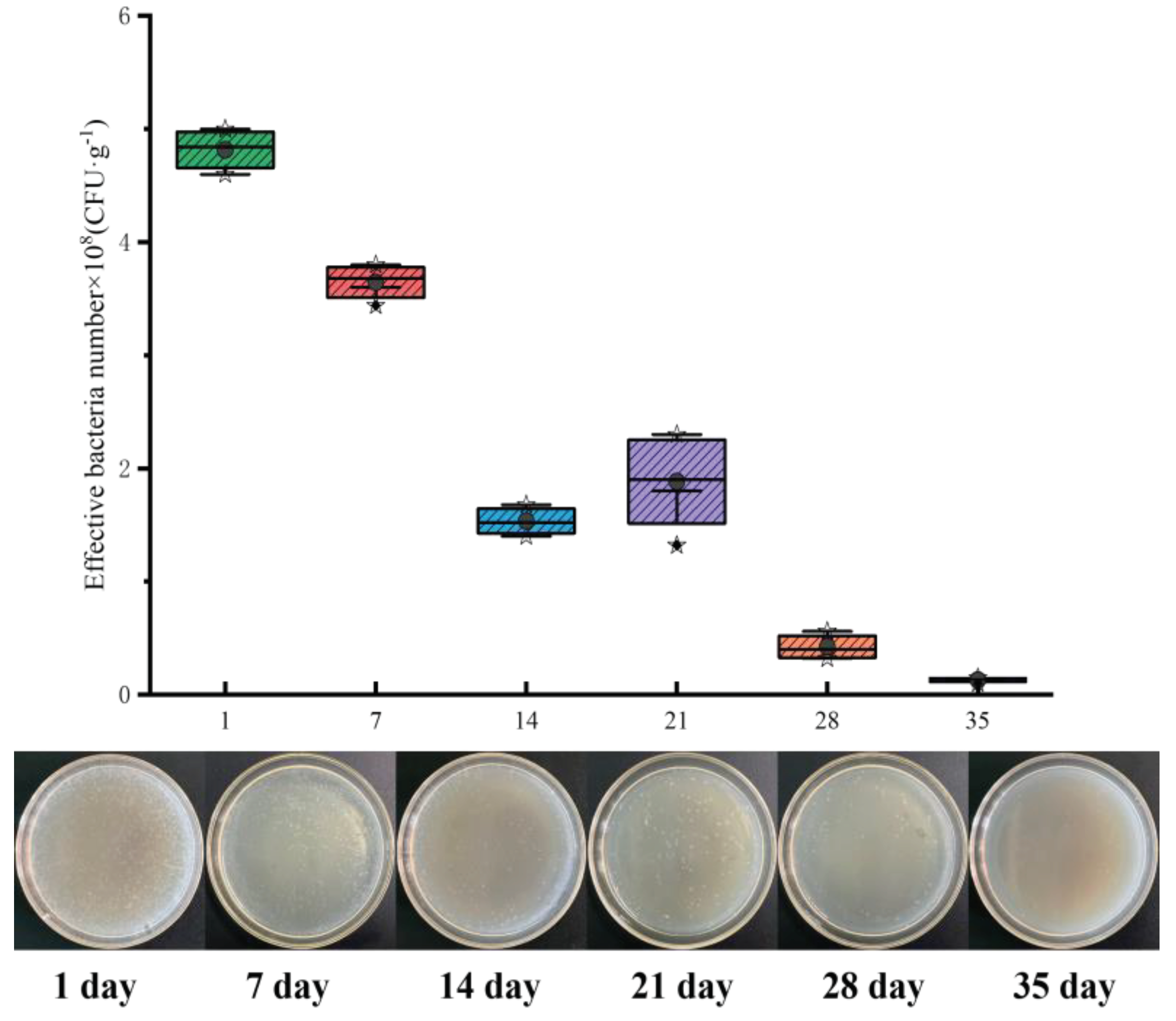
2.2. Effective Number of Live Bacteria Loaded by B@PM
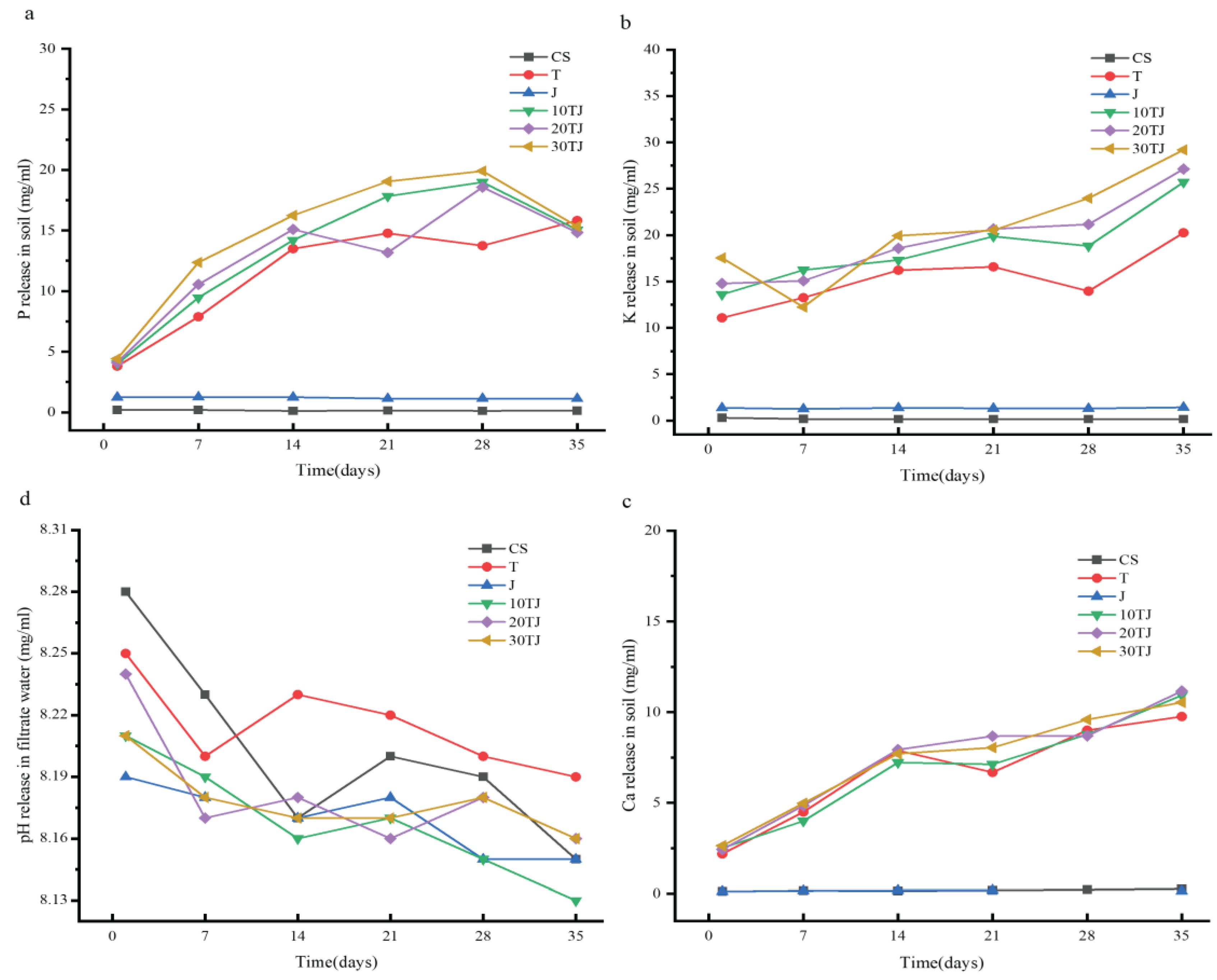
2.3. Slow-Release Behavior of the B@PM
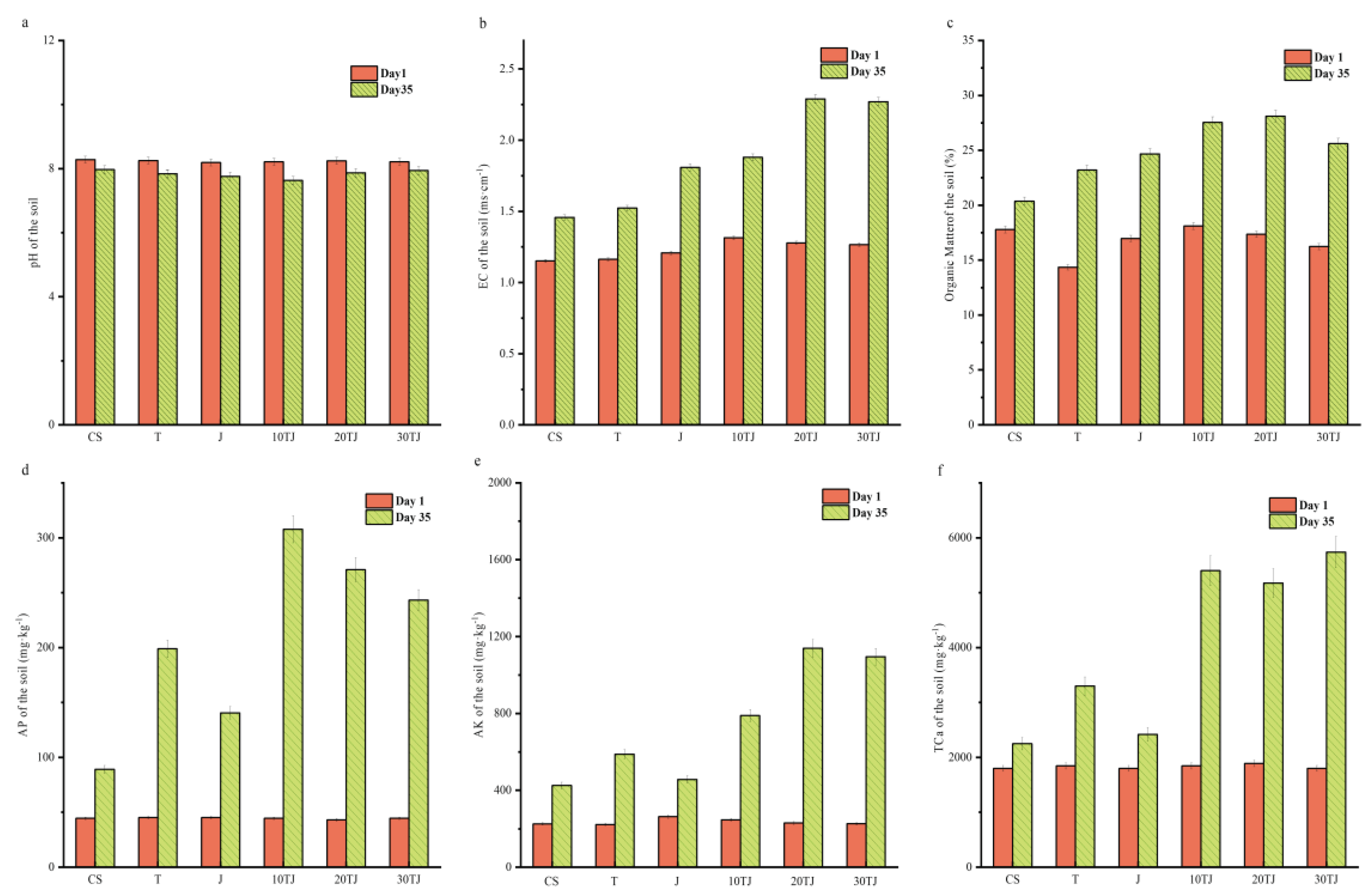
2.4. Effect of B@PM on Soil Physico-Chemical Properties and Enzyme Activities
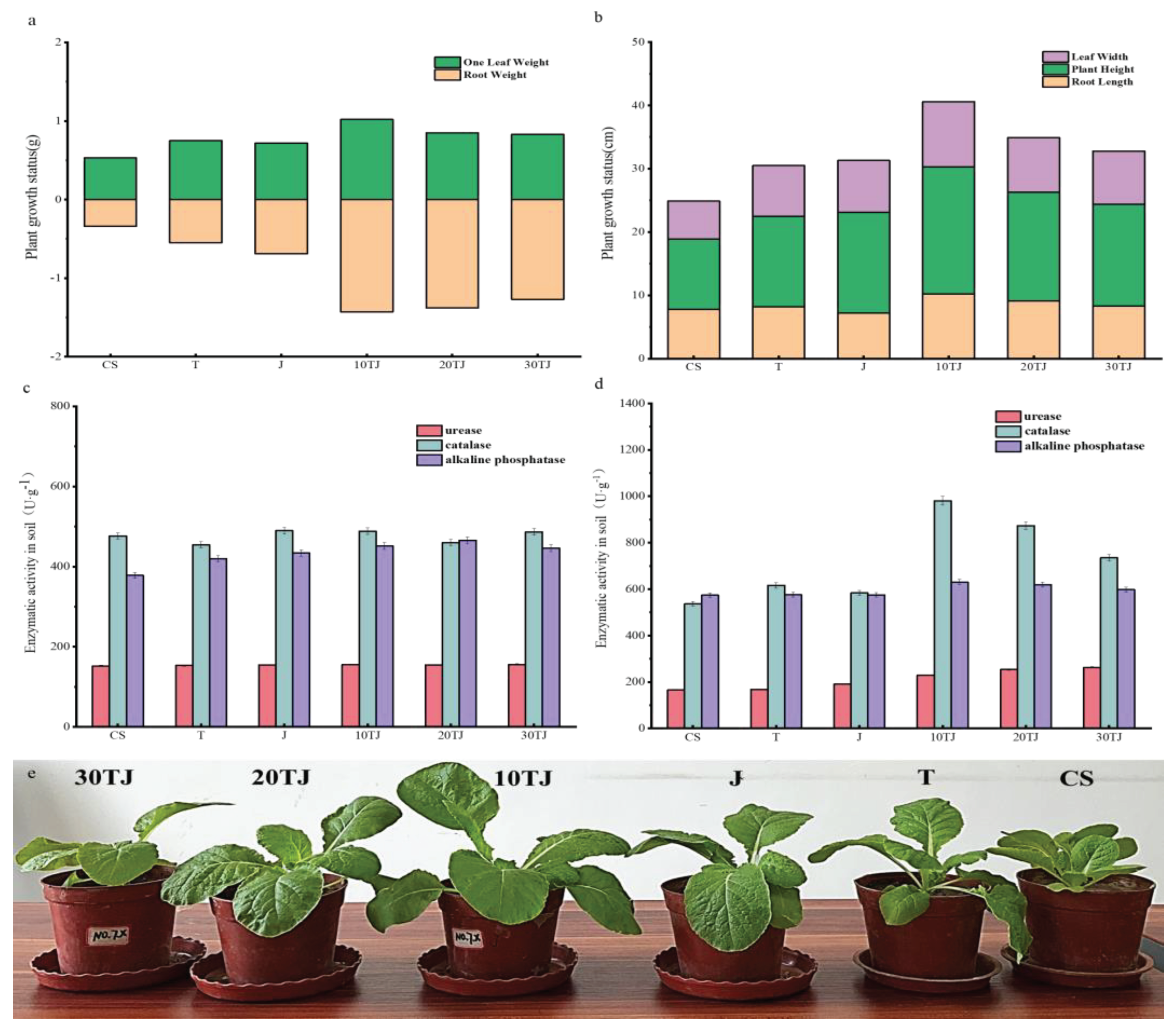
2.5. Effect of B@PM on Plant Growth Conditions
2.6. Effect of B@PM on Microbial Communities in Soil
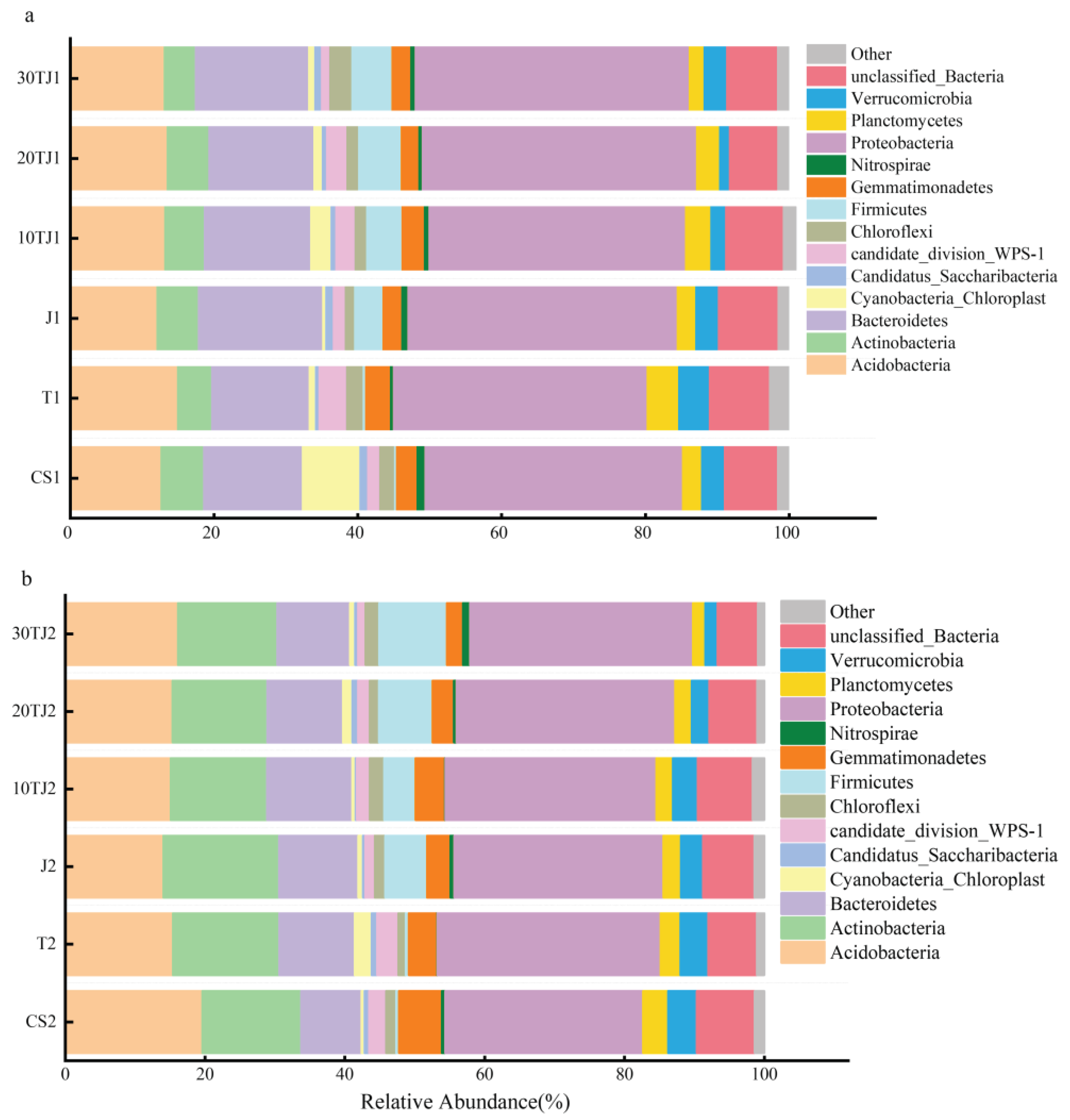
2.6.1. Microbial Community Structure
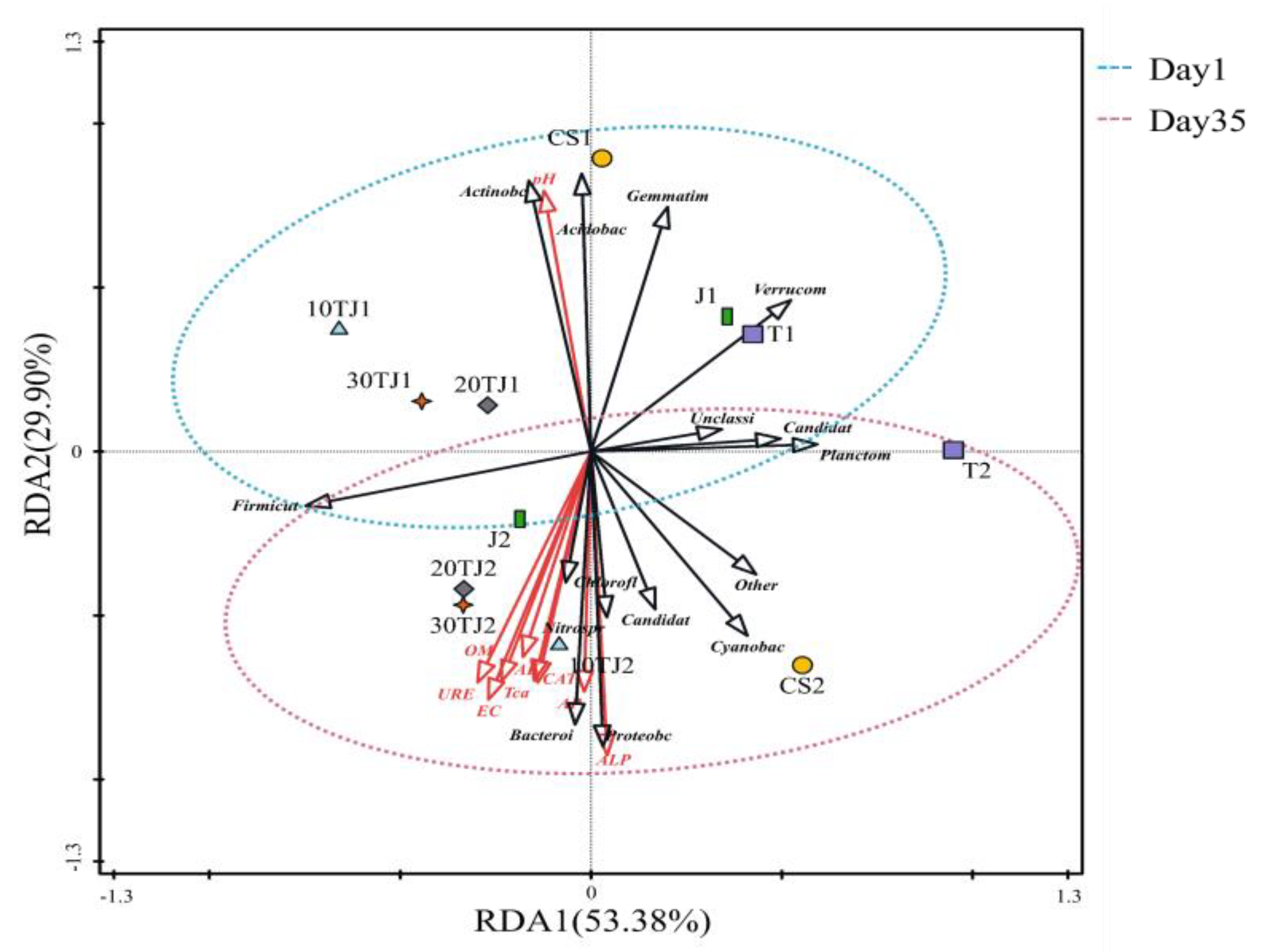
2.6.2. RDA Analyses between Samples and Environmental Factors and Species
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Characterization of Modified Biochar
3.3. Determination of Effective Bacterial Count
3.4. Potting Experiment
3.5. Kinetics of Nutrient Release from Biochar in Soil
3.6. Analysis of Plant Growth
3.7. Analysis of the Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgement
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability Statement
References
- Zhang, Y.; Long, H.; Wang, M.Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Chen, K.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, T. The Hidden Mechanism of Chemical Fertiliser Overuse in Rural China. Habitat Int. 2020, 102, 102210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Cotton, A.; Wei, Z.; Xia, Y.; Daniell, T.; Yan, X. How Does Partial Substitution of Chemical Fertiliser with Organic Forms Increase Sustainability of Agricultural Production? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida-García, F.; Lago-Olveira, S.; Rebolledo-Leiva, R.; González-García, S.; Moreira, M.T.; Ruíz-Nogueiras, B.; Pereira-Lorenzo, S. Growing Triticum Aestivum Landraces in Rotation with Lupinus Albus and Fallow Reduces Soil Depletion and Minimises the Use of Chemical Fertilisers. Agric. 2022, 12, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Li, J.; Ye, H.; Du, D.; Sun, P.; Ma, M.; Zhang, T.C. Bioleaching of Silicon in Electrolytic Manganese Residue (EMR) by Paenibacillus Mucilaginosus: Impact of Silicate Mineral Structures. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, M.; Tan, W. Characteristics of Bio-Desilication and Bio-Flotation of Paenibacillus Mucilaginosus BM-4 on Aluminosilicate Minerals. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 168, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tang, W.; Yang, F.; Meng, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X. Influence of Biochar Application on Potassium-Solubilizing Bacillus Mucilaginosus as Potential Biofertilizer. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 47, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Wei, J.; Guan, F.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Luo, Y. Biochar and Bacteria Inoculated Biochar Enhanced Cd and Cu Immobilization and Enzymatic Activity in a Polluted Soil. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Lv, X.; Sohail, M.A.; Li, M.; Huang, B.; Wang, J. Control Efficiency of Biochar Loaded with Bacillus Subtilis Tpb55 against Tobacco Black Shank. Processes 2022, 10, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Wu, Z.; Wei, M.; Liu, X.; He, Y.; Ye, B.-C. Bacillus Subtilis SL-13 Biochar Formulation Promotes Pepper Plant Growth and Soil Improvement. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamenković, S.; Beškoski, V.; Karabegović, I.; Lazić, M.; Nikolić, N. Microbial Fertilizers: A Comprehensive Review of Current Findings and Future Perspectives. Spanish J. Agric. Res. 2018, 16, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Ma, M.C. Situation and Development Direction for Microbial Fertilizer Industry in the near Future of China. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2020, 26, 2108–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, H.; Yuan, Z.; Feng, J.; Chen, S.; Sun, G.; Wei, Z.; Hu, T. Effects of Microbial Fertilizer and Irrigation Amount on Growth, Physiology and Water Use Efficiency of Tomato in Greenhouse. Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam). 2024, 323, 112553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koryagin, Y.; Kulikova, E.; Efremova, S.; Sukhova, N. The Influence of Microbiological Fertilisers on the Productivity and Quality of Winter Wheat. Plant, Soil Environ. 2020, 66, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xiao, C.; Yang, S.; Yin, H.; Yang, Z.; Chi, R. Life Cycle Assessment and Life Cycle Cost Analysis of Compound Microbial Fertilizer Production in China. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 28, 1622–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Hou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Sun, Q. Regular Biochar and Bacteria-Inoculated Biochar Alter the Composition of the Microbial Community in the Soil of a Chinese Fir Plantation. Forests 2020, 11, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, A.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, D.; Xu, J.; Rensing, C.; Zhang, L.; Xing, S.; Ni, W.; Yang, W. Biochar Loaded with Bacteria Enhanced Cd/Zn Phytoextraction by Facilitating Plant Growth and Shaping Rhizospheric Microbial Community. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Tang, L.; Wang, Z.; Su, M.; Tian, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z. Evaluating the Protection of Bacteria from Extreme Cd (II) Stress by P-Enriched Biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolan, S.; Hou, D.; Wang, L.; Hale, L.; Egamberdieva, D.; Tammeorg, P.; Li, R.; Wang, B.; Xu, J.; Wang, T.; et al. The Potential of Biochar as a Microbial Carrier for Agricultural and Environmental Applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 886, 163968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Piechota, T.; Niewiadomska, A.; Kamiński, A.; Kayzer, D.; Grzyb, A.; Pilarska, A.A. The Effect of Biochar-Based Organic Amendments on the Structure of Soil Bacterial Community and Yield of Maize (Zea Mays L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Hua, M.; Reckling, M.; Wirth, S.; Dorothea, S.; Kimura, B. Potential Effects of Biochar - Based Microbial Inoculants in Agriculture. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 1, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Harindintwali, J.D.; Wang, F.; Redmile-Gordon, M.; Chang, S.X.; Fu, Y.; He, C.; Muhoza, B.; Brahushi, F.; Bolan, N.; et al. Integrating Biochar, Bacteria, and Plants for Sustainable Remediation of Soils Contaminated with Organic Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 16546–16566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fachini, J.; Figueiredo, C.C. de; Vale, A.T. do Assessing Potassium Release in Natural Silica Sand from Novel K-Enriched Sewage Sludge Biochar Fertilizers. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 314, 115080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.; Wu, Z.; Shi, W.; Qi, H.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Yu, B. Biochar for Simultaneously Enhancing the Slow-Release Performance of Fertilizers and Minimizing the Pollution of Pesticides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Wu, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X. Biochar Combined with Bacillus Subtilis SL-44 as an Eco-Friendly Strategy to Improve Soil Fertility, Reduce Fusarium Wilt, and Promote Radish Growth. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 251, 114509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripti; Kumar, A.; Usmani, Z.; Kumar, V. Anshumali Biochar and Flyash Inoculated with Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria Act as Potential Biofertilizer for Luxuriant Growth and Yield of Tomato Plant. J. Environ. Manage. 2017, 190, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azeem, M.; Hassan, T.U.; Tahir, M.I.; Ali, A.; Jeyasundar, P.G.S.A.; Hussain, Q.; Bashir, S.; Mehmood, S.; Zhang, Z. Tea Leaves Biochar as a Carrier of Bacillus Cereus Improves the Soil Function and Crop Productivity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 157, 103732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorzelski, D.; Filho, J.F.L.; Matias, P.C.; Santos, W.O.; Vergutz, L.; Melo, L.C.A. Biochar as Composite of Phosphate Fertilizer: Characterization and Agronomic Effectiveness. Sci Total Env. 2020, 743, 140604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzickova, J.; Koval, S.; Raclavska, H.; Kucbel, M.; Svedova, B.; Raclavsky, K.; Juchelkova, D.; Scala, F. A Comprehensive Assessment of Potential Hazard Caused by Organic Compounds in Biochar for Agricultural Use. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, V.M.; Nguyen, H.T.; Nguyen, A.M.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, T.-L.; Uteau, D.; Nguyen, N.H.; Tran, T.M.; Dultz, S.; Nguyen, M.N. Pelletized Rice-Straw Biochar as a Slow-Release Delivery Medium: Potential Routes for Storing and Serving of Phosphorus and Potassium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, A.; Falk, J.; Borén, E.; Lindgren, R.; Skoglund, N.; Boman, C.; Öhman, M. Ash Transformation during Fixed-Bed Combustion of Agricultural Biomass with a Focus on Potassium and Phosphorus. Energy & Fuels 2022, 36, 3640–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shen, F.; Qi, X. Adsorption Recovery of Phosphate from Aqueous Solution by CaO-Biochar Composites Prepared from Eggshell and Rice Straw. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jetsrisuparb, K.; Jeejaila, T.; Saengthip, C.; Kasemsiri, P.; Ngernyen, Y.; Chindaprasirt, P.; Knijnenburg, J.T.N. Tailoring the Phosphorus Release from Biochar-Based Fertilizers: Role of Magnesium or Calcium Addition during Co-Pyrolysis. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 30539–30548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Wan, J.; Wang, X.; Peng, C.; Wang, G.; Liang, W.; Zhang, W. Mixed Bacteria-Loaded Biochar for the Immobilization of Arsenic, Lead, and Cadmium in a Polluted Soil System: Effects and Mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 152112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Hu, S.; Han, S.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Akindolie, M.S.; Ji, M.; et al. Efficient Removal of Atrazine by Iron-Modified Biochar Loaded Acinetobacter Lwoffii DNS32. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 682, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustosa Filho, J.F.; Penido, E.S.; Castro, P.P.; Silva, C.A.; Melo, L.C.A. Co-Pyrolysis of Poultry Litter and Phosphate and Magnesium Generates Alternative Slow-Release Fertilizer Suitable for Tropical Soils. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9043–9052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, C.L.; Sethupathi, S.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Ahmed, W. Adsorptive Behaviour of Palm Oil Mill Sludge Biochar Pyrolyzed at Low Temperature for Copper and Cadmium Removal. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 237, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathvika, T.; Saraswathi, A.R.K.; Rajesh, V.; Rajesh, N. Confluence of Montmorillonite and Rhizobium towards the Adsorption of Chromium (vi) from Aqueous Medium. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 28478–28489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Zhai, X.; Dai, K.; Lian, J.; Cheng, L.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Yang, C.; Yin, Z.; Li, H.; et al. Synthesis of Acidified Magnetic Sludge-Biochar and Its Role in Ammonium Nitrogen Removal: Perception on Effect and Mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 154780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinhanmi, T.F.; Ofudje, E.A.; Adeogun, A.I.; Aina, P.; Joseph, I.M. Orange Peel as Low-Cost Adsorbent in the Elimination of Cd (II) Ion: Kinetics, Isotherm, Thermodynamic and Optimization Evaluations. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2020, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hou, J.; Zhang, S.; Hu, W.; Yi, G.; Chen, W.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Q. Preparation of a New Biochar-Based Microbial Fertilizer: Nutrient Release Patterns and Synergistic Mechanisms to Improve Soil Fertility. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHEN, Y.; YANG, X.; Zhuang, L.I.; AN, X.; LI, Y.; CHENG, C. Efficiency of Potassium-Solubilizing Paenibacillus Mucilaginosus for the Growth of Apple Seedling. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 2458–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwanree, S.; Knijnenburg, J.T.N.; Kasemsiri, P.; Kraithong, W.; Chindaprasirt, P.; Jetsrisuparb, K. Engineered Biochar from Sugarcane Leaves with Slow Phosphorus Release Kinetics. Biomass and Bioenergy 2022, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piash, M.I.; Iwabuchi, K.; Itoh, T. Synthesizing Biochar-Based Fertilizer with Sustained Phosphorus and Potassium Release: Co-Pyrolysis of Nutrient-Rich Chicken Manure and Ca-Bentonite. Sci Total Env. 2022, 822, 153509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, J.; Ribeiro, I.C.A.; Nardis, B.O.; Barbosa, C.F.; Lustosa Filho, J.F.; Melo, L.C.A. Long-Term Effect of Biochar-Based Fertilizers Application in Tropical Soil: Agronomic Efficiency and Phosphorus Availability. Sci Total Env. 2021, 760, 143955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Yang, C.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Sui, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, R.; Hu, Y. Effects of Organic Acid Root Exudates of Malus Hupehensis Rehd. Derived from Soil and Root Leaching Liquor from Orchards with Apple Replant Disease. Plants 2022, 11, 2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.-P.; Kammann, C.; Niggli, C.; Evangelou, M.W.H.; Mackie, K.A.; Abiven, S. Biochar and Biochar-Compost as Soil Amendments to a Vineyard Soil: Influences on Plant Growth, Nutrient Uptake, Plant Health and Grape Quality. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHEN, Y. hui; YANG, X. zhu; LI, Z.; AN, X. hong; MA, R. peng; LI, Y. qing; CHENG, C. gang Efficiency of Potassium-Solubilizing Paenibacillus Mucilaginosus for the Growth of Apple Seedling. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 2458–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, T.; Mahmoud, A.; Li, J.; Zhu, R.; Jiao, X.; Jing, P. A Quantitative Review of the Effects of Biochar Application on Rice Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Paddy Fields: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Yuan, P.; Ullah, S.; Iqbal, A.; Zhao, Q.; Liang, H.; Khan, A.; Imran; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; et al. Biochar Amendment and Nitrogen Fertilizer Contribute to the Changes in Soil Properties and Microbial Communities in a Paddy Field. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Qi, G.; Ma, G.; Zhao, X. Biochar Amendment Controlled Bacterial Wilt through Changing Soil Chemical Properties and Microbial Community. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 231, 126373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, A.; Kwapinski, W.; Griffiths, B.S.; Schmalenberger, A. The Role of Sulfur- and Phosphorus-Mobilizing Bacteria in Biochar-Induced Growth Promotion of Lolium Perenne. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparecido, A.; Tielle, N.; Rossetto, R.; Antonie, J. Verrucomicrobial Community Structure and Abundance as Indicators for Changes in Chemical Factors Linked to Soil Fertility. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 108, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Sun, A.; Jiao, X.; Ge, A.; Hu, H.; Jin, S.; Liu, X.; Lin, Y.; He, J. Fertilization Has a Greater Effect than Rhizosphere on Community Structures of Comammox Nitrospira in an Alkaline Agricultural Soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 175, 104456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babalola, O.O. Beneficial Bacteria of Agricultural Importance. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; Xue, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, Y. Science of the Total Environment Biochar-Based Fertilizer Amendments Improve the Soil Microbial Community Structure in a Karst Mountainous Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsbrink, J.; Sara, L. Bacteroidetes Bacteria in the Soil: Glycan Acquisition, Enzyme Secretion, and Gliding Motility, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc., 2020; Vol. 110. [Google Scholar]
- Hashmi, I.; Bindschedler, S.; Junier, P. Firmicutes. In Beneficial microbes in agro-ecology; Elsevier, 2020; pp. 363–396. [Google Scholar]
- Kalam, S.; Basu, A.; Ahmad, I.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Finley, S.J. Recent Understanding of Soil Acidobacteria and Their Ecological Significance: A Critical Review. 2020; 11, 580024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, T.; Barrett, J.; Brennan, J.; Moran, N. Use of a Spectrophotometric Bioassay for Determination of Microbial Sensitivity to Manuka Honey. J. Microbiol. Methods 2006, 64, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodge, R.; Ludington, W.B. Fast Colony Forming Unit Counting in 96-Well Plate Format Applied to the Drosophila Microbiome. JoVE (Journal Vis. Exp. 2023; e64298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Wu, Z.; Yu, J.; Ge, L.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Yu, B. High-Efficiency Reclaiming Phosphate from an Aqueous Solution by Bentonite Modified Biochars: A Slow Release Fertilizer with a Precise Rate Regulation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 6090–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X. Bioremediation of Petroleum Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Soil by Petroleum-Degrading Bacteria Immobilized on Biochar. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 35304–35311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndoung, O.C.N.; Figueiredo, C.C. de; Ramos, M.L.G. A Scoping Review on Biochar-Based Fertilizers: Enrichment Techniques and Agro-Environmental Application. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




