Submitted:
30 March 2024
Posted:
02 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
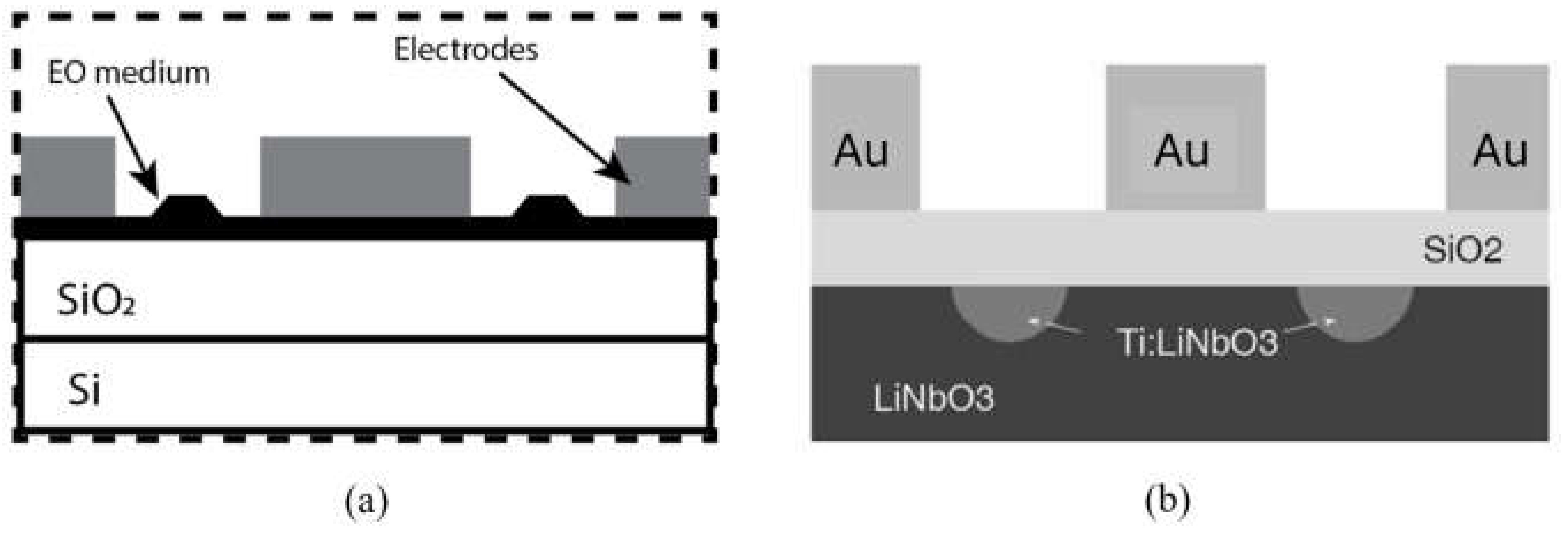
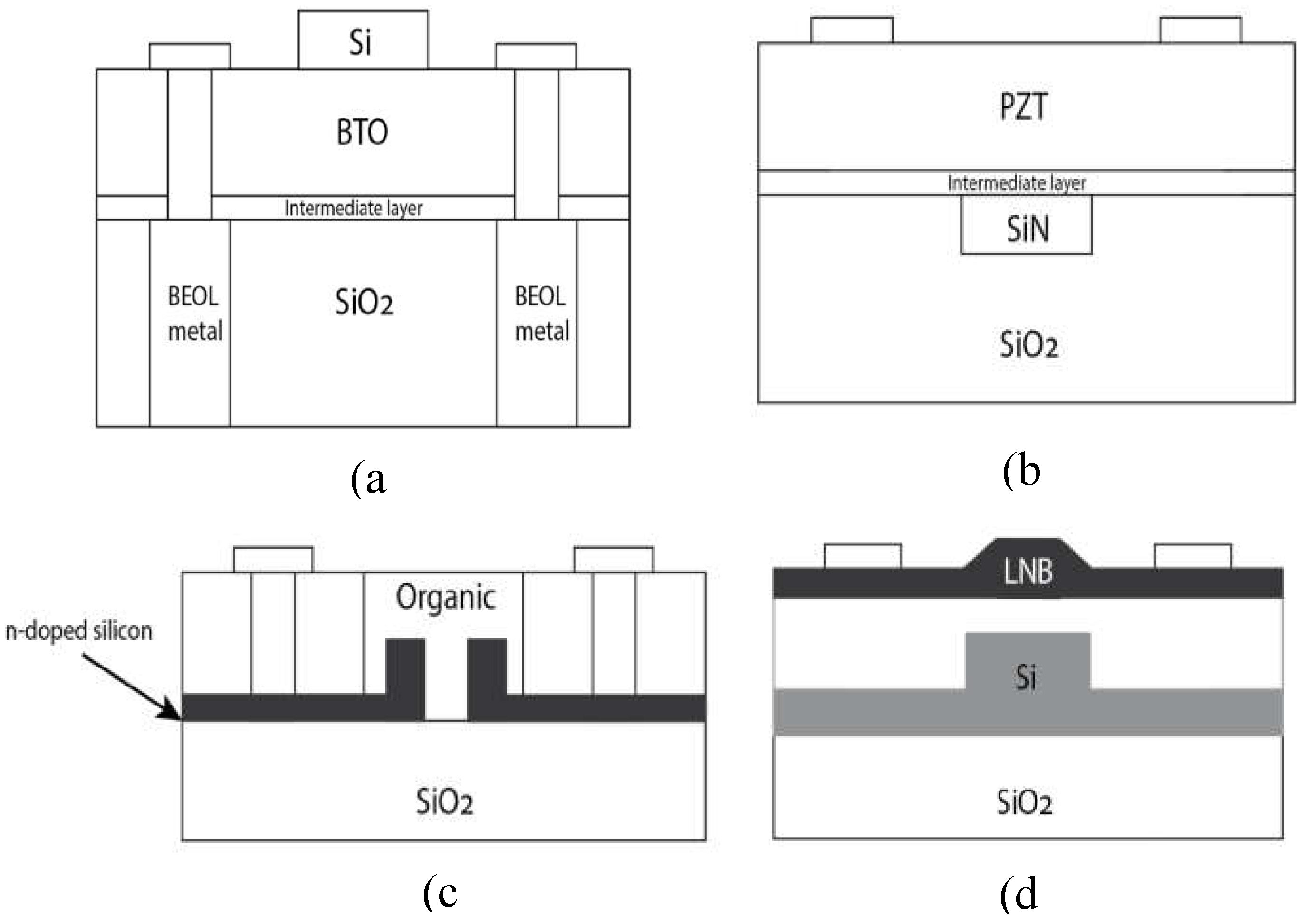
2.1. Selecting the Material and Geometry
- The traditional χ(2) materials which have low non-linearities, such as LNB, KNB, Barium Titanate (BTO), and Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT). This class of EO materials was considered in this study, and some traditional χ(2) materials with their main properties are listed in Table 1.
- The application-specific engineered quantum well-heterostructured materials which exhibit a very high χ(2) in a narrow band (Δλ≈11 nm), like organic EO molecules JRD1 in polymethylmethacrylate. The nonlinearities in this case will be 10 – 100 times higher than the traditional nonlinear materials. This class of EO materials was not considered in this study.
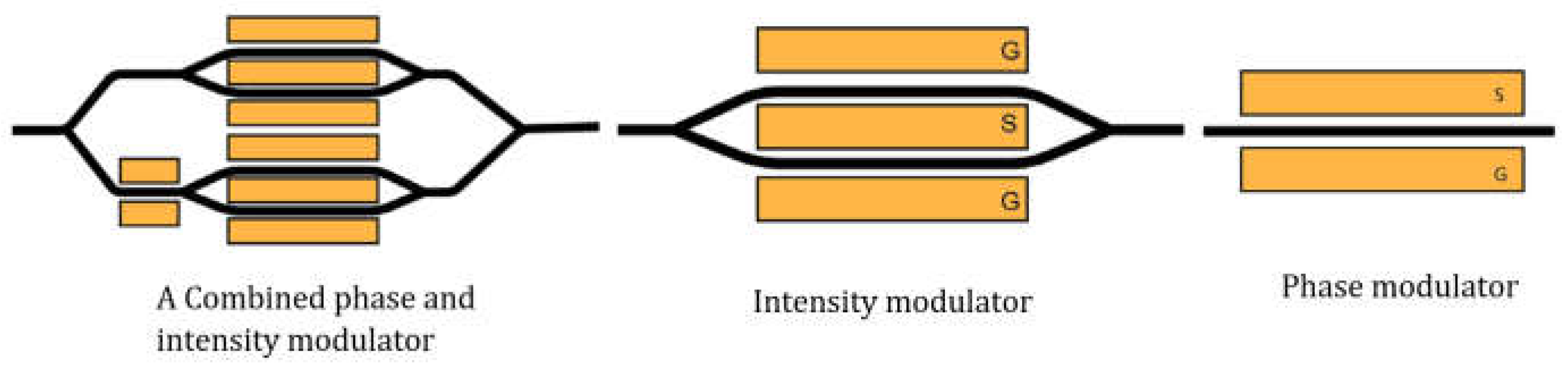
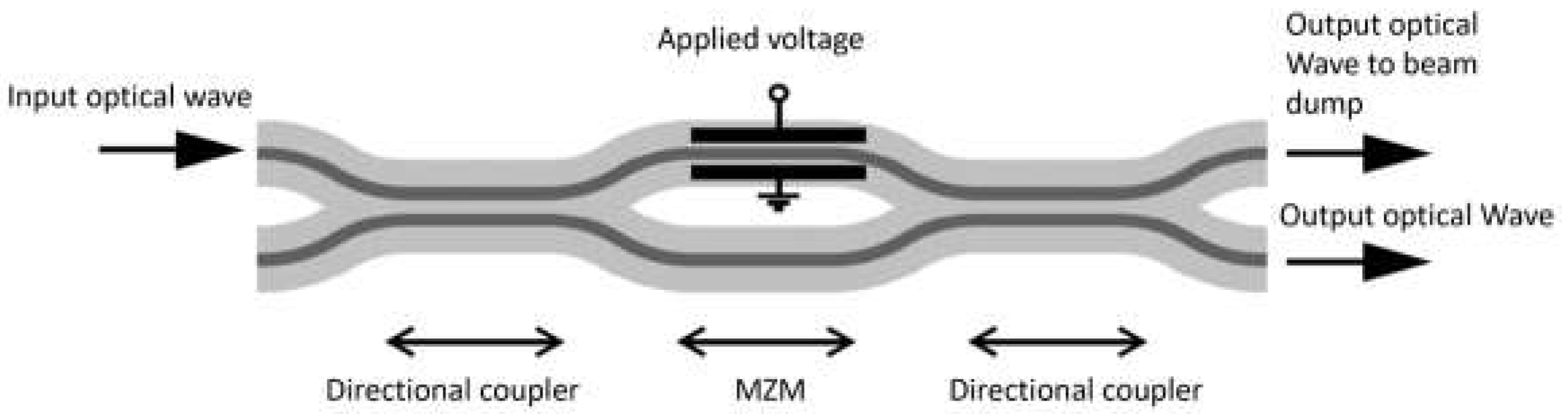
2.2. Selecting the Type and Architecture of the Modulator
2.3. Selecting the Type of Electrodes
- i.
- Case 1: The phase modulation in this case is;
- ii.
- Case 2: The phase modulation in this case is;
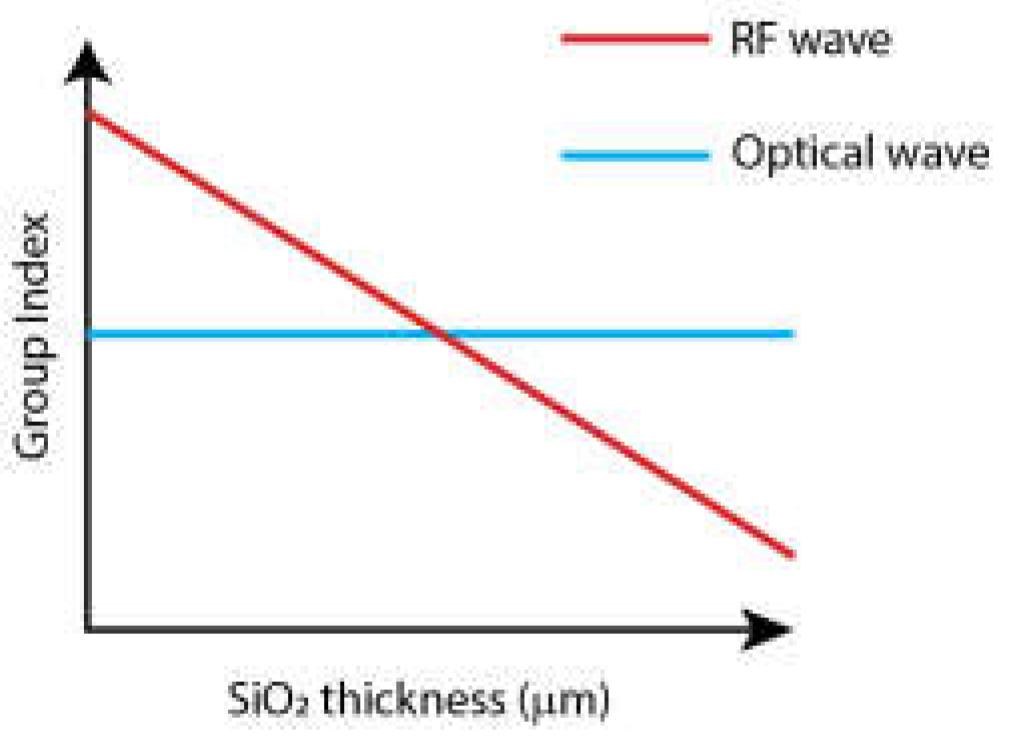
2.4. Velocity Matching between the RF and Optical Wave
2.5. The Loss Estimation Method for the RF and Optical Waves in the TW-MZM
2.6. Modeling in COMSOL Multiphysics
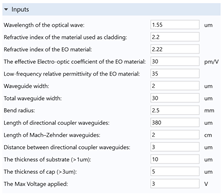
2.6.1. The Inputs of the Model
2.6.2. The Two Steps of the Model
- i.
-
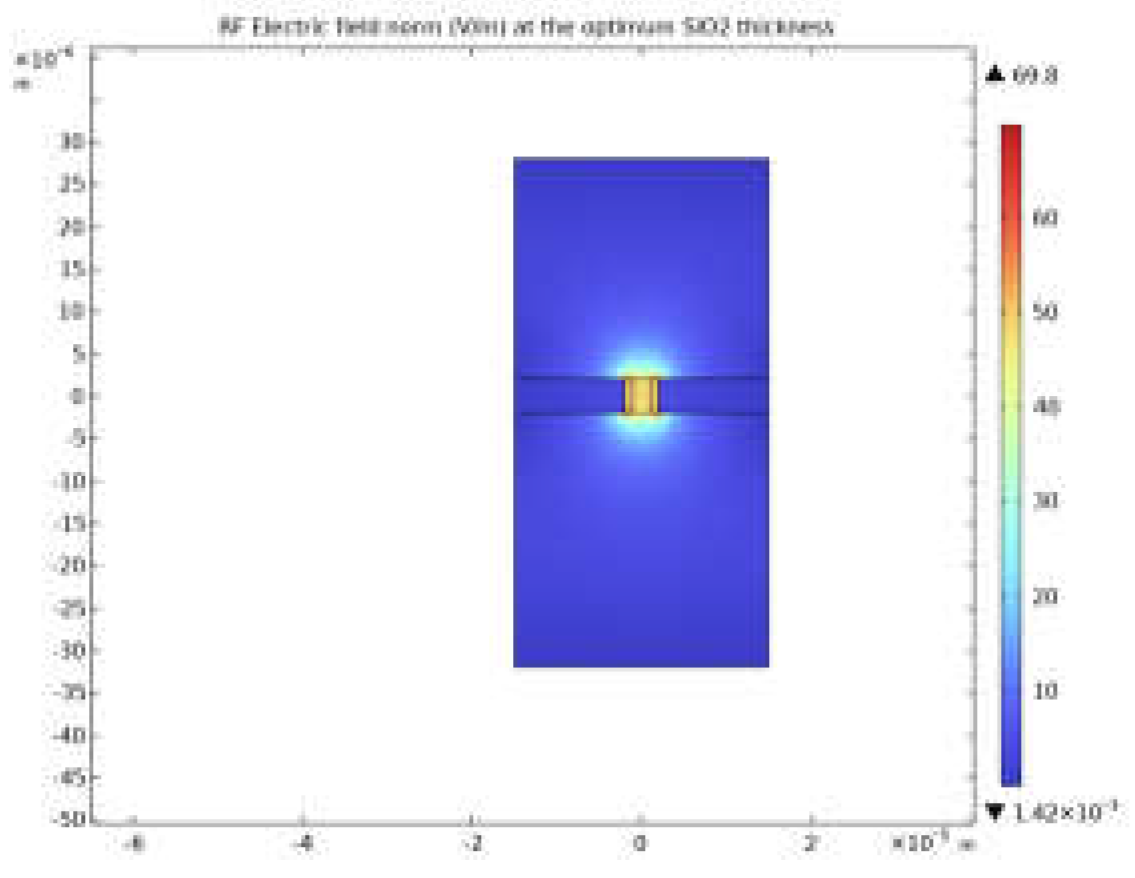
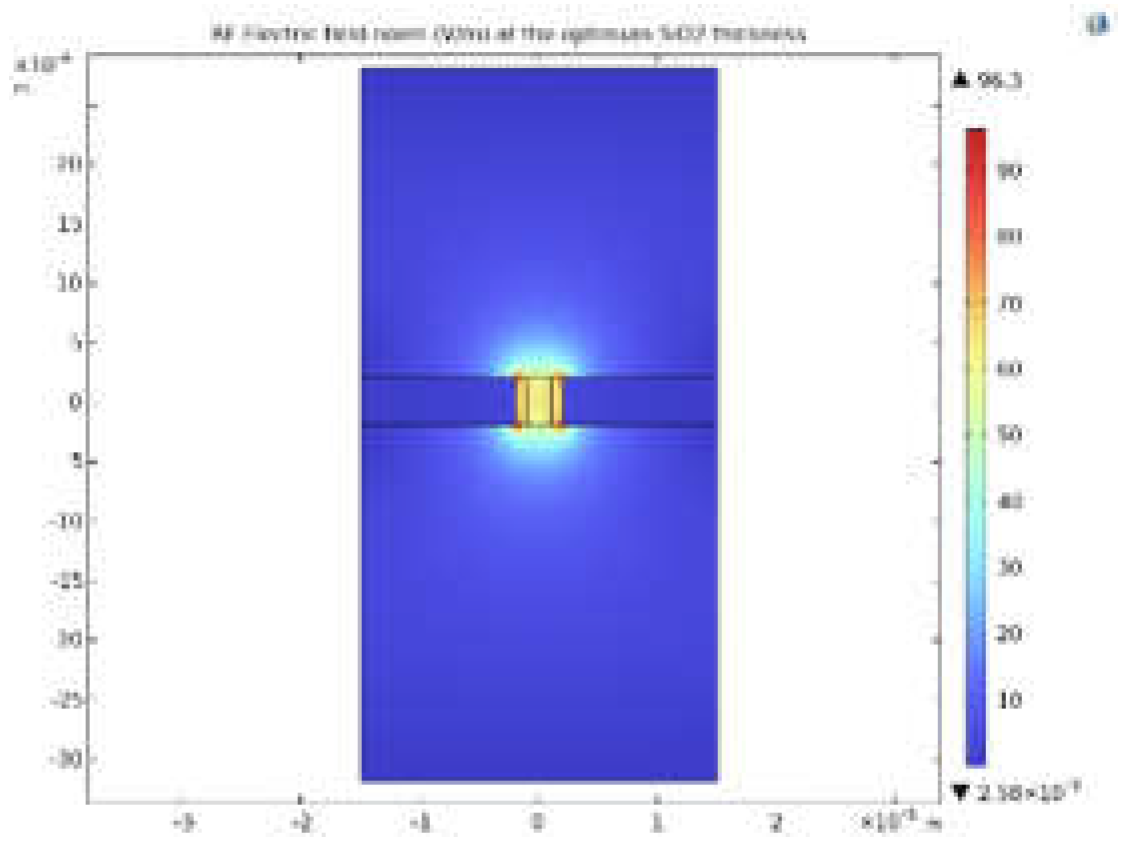
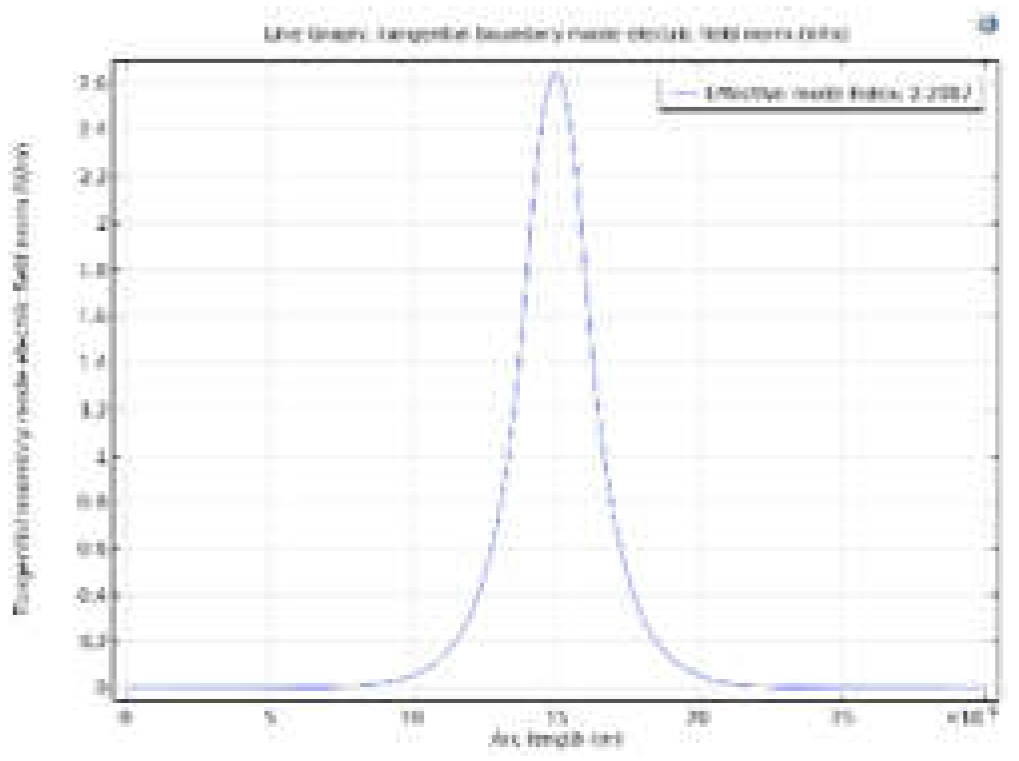
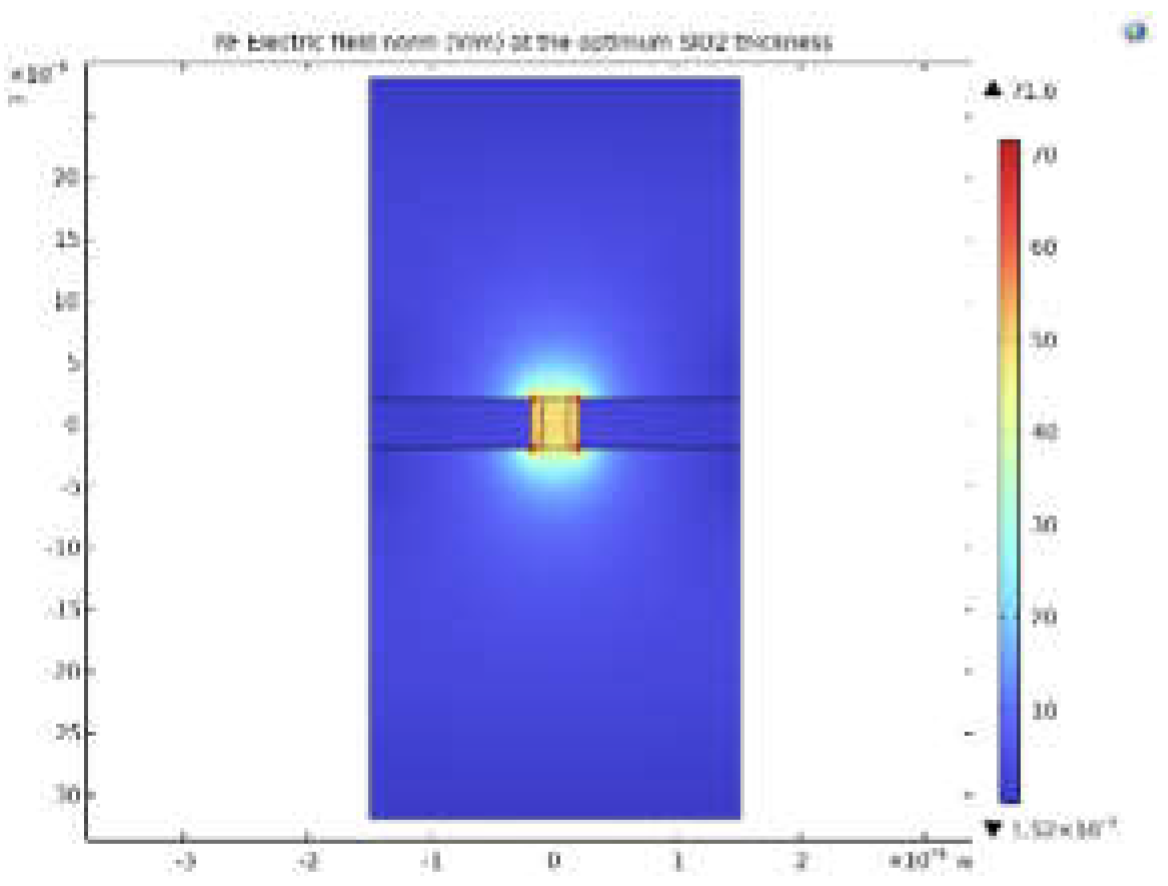
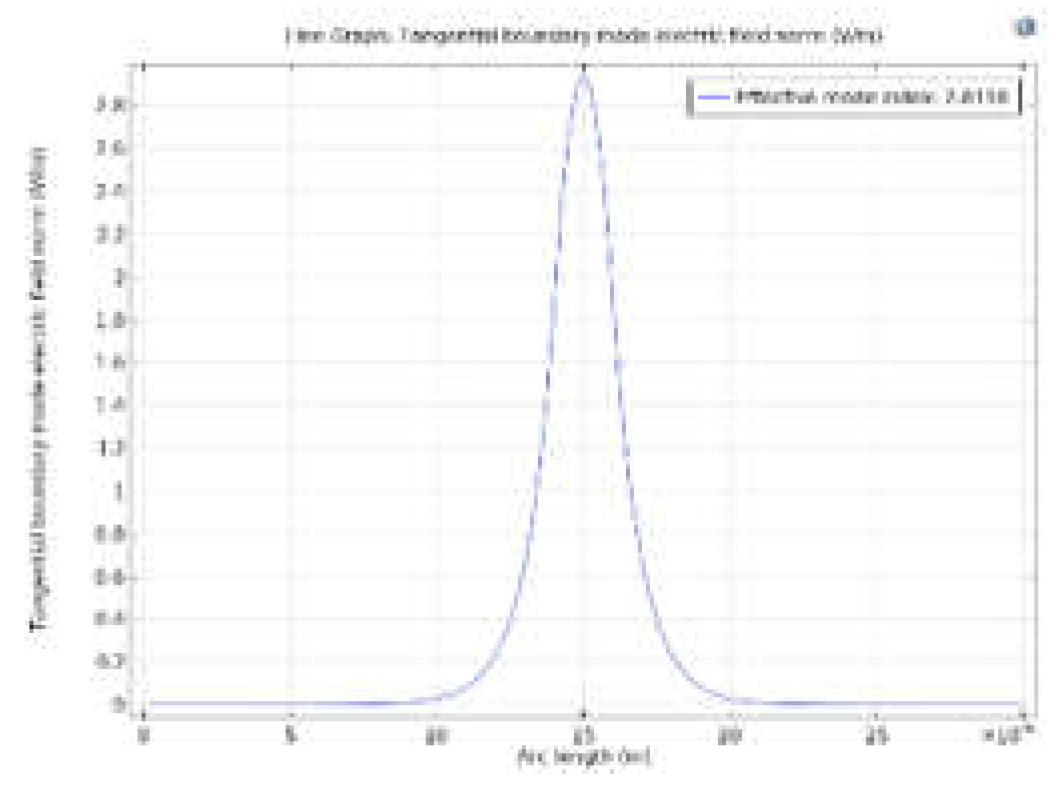
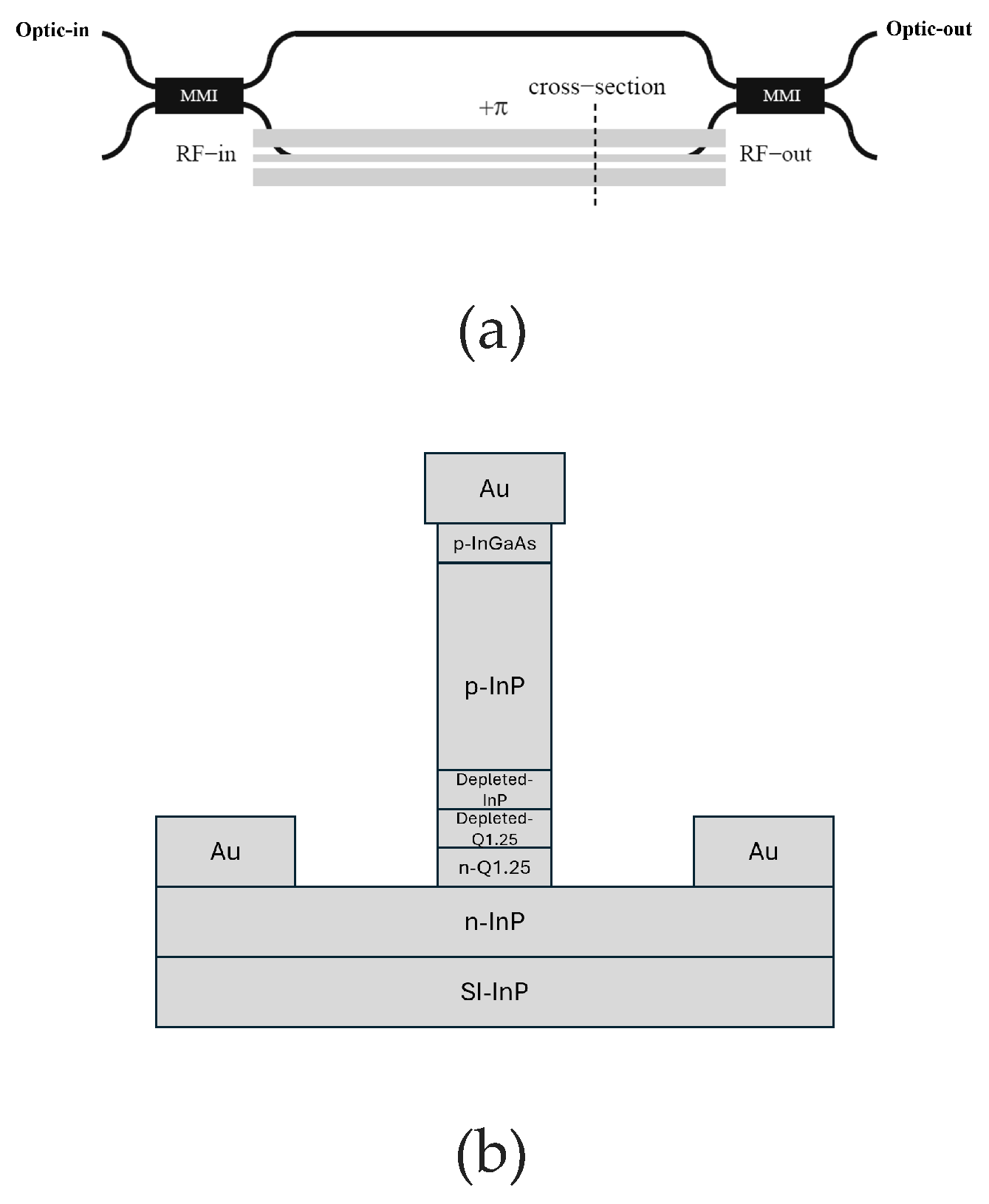
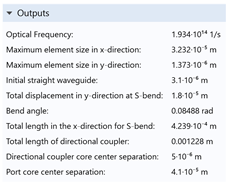
Step 1, the optical wave side: In this step, the top view of the modulator is considered (Figure 6a), and the geometry is constructed according to the inputs (Table (2)). The parameters calculated in this step are as follows;
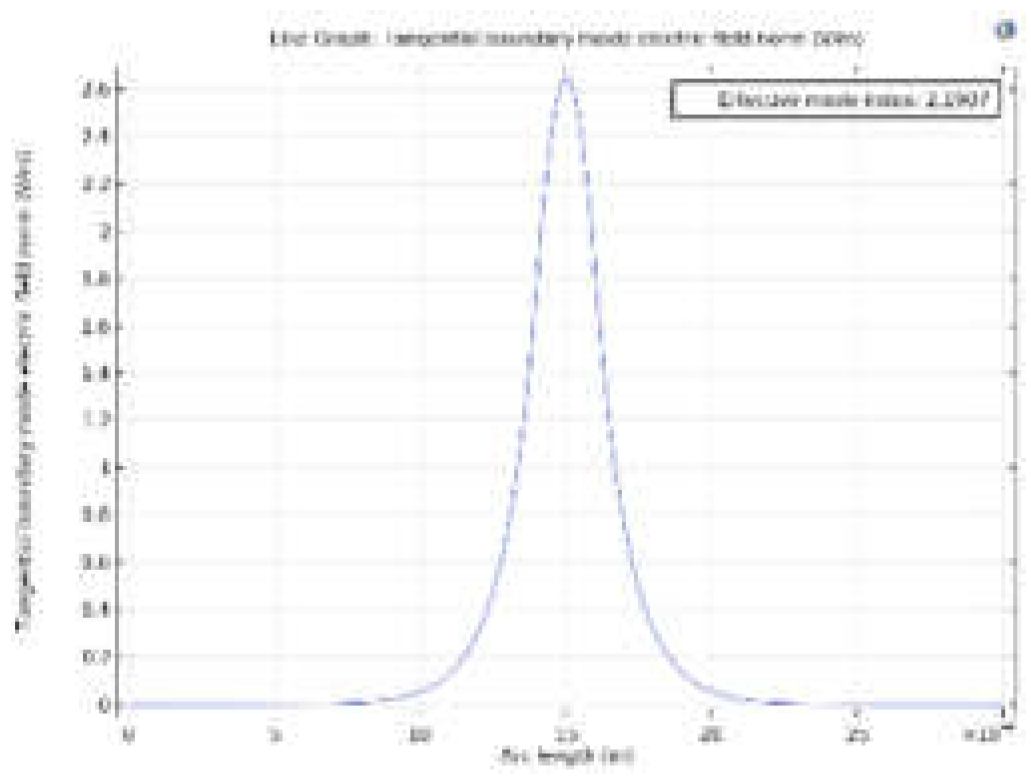
- The propagation constant of the fundamental mode for the optical wave.
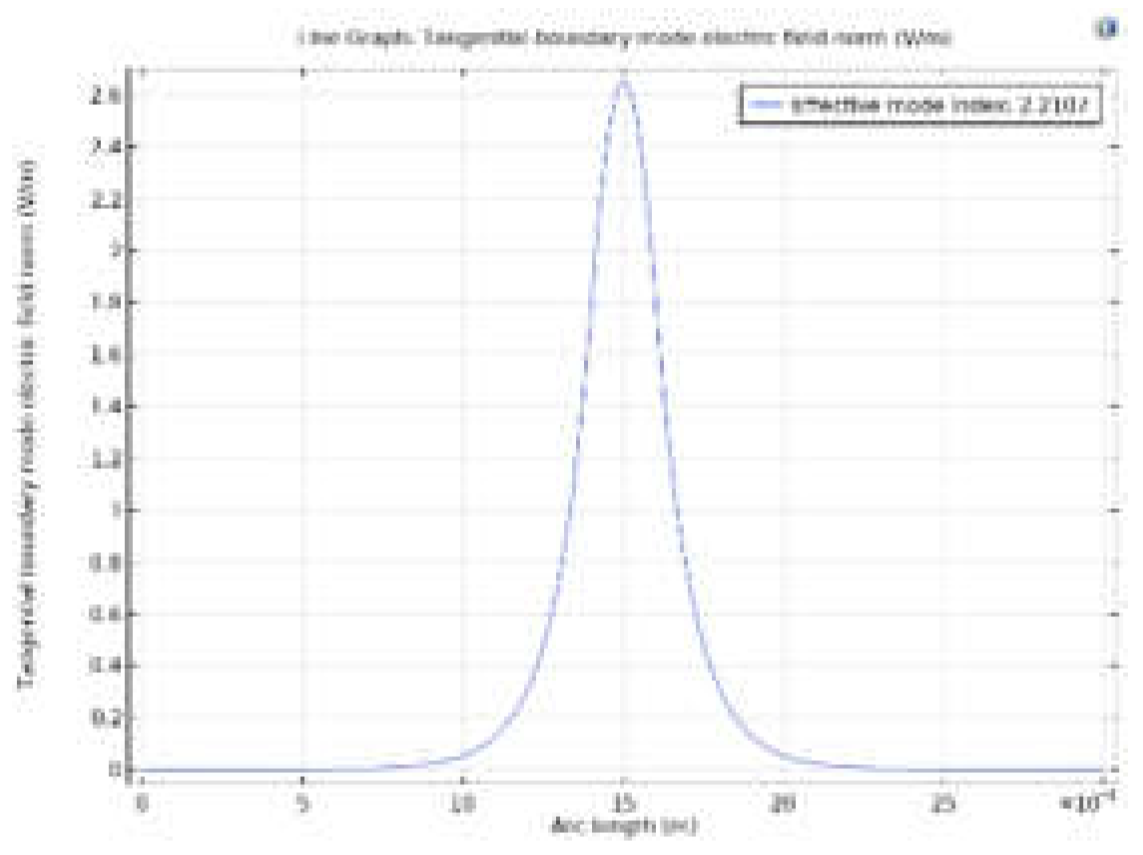
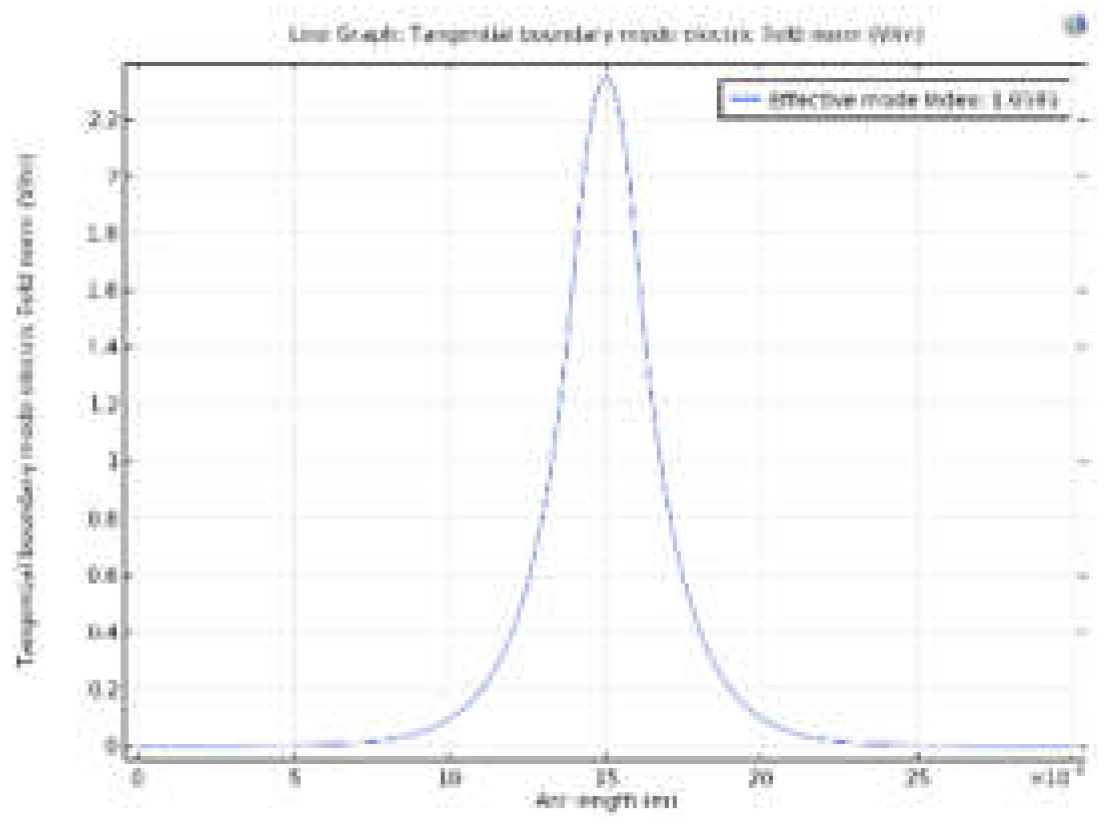
- The effective index of the fundamental mode for the optical wave.
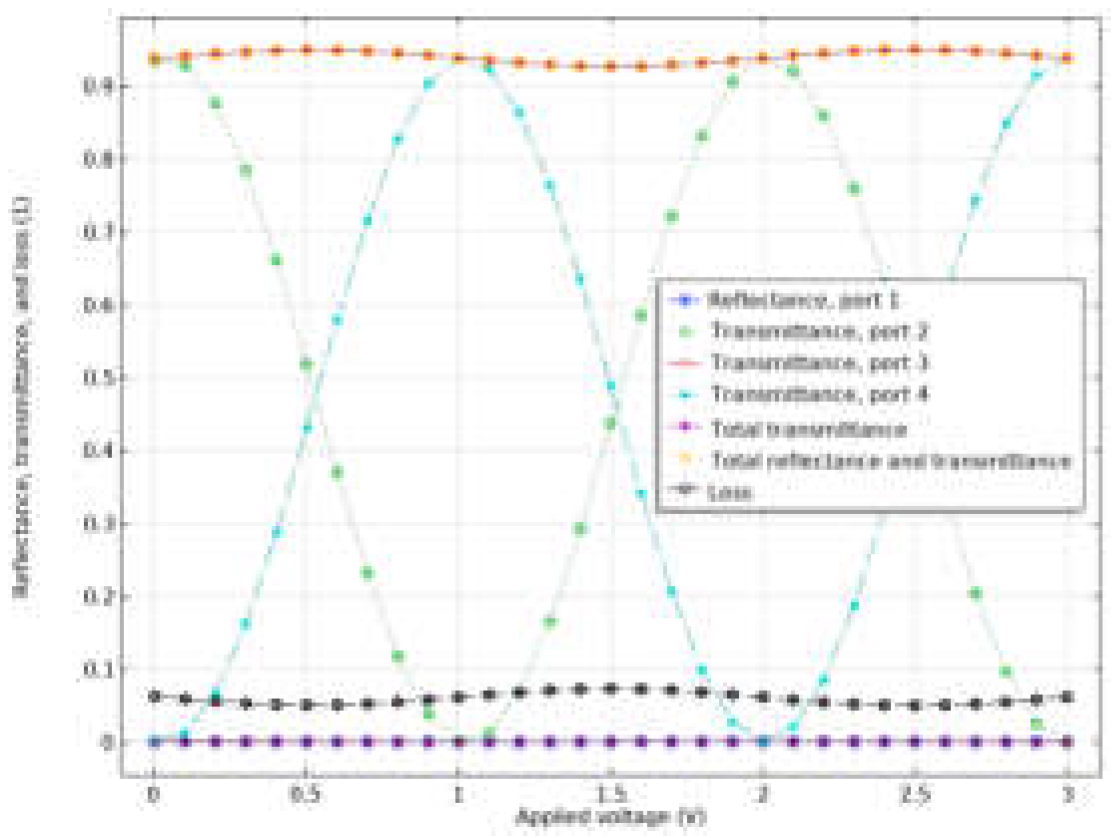
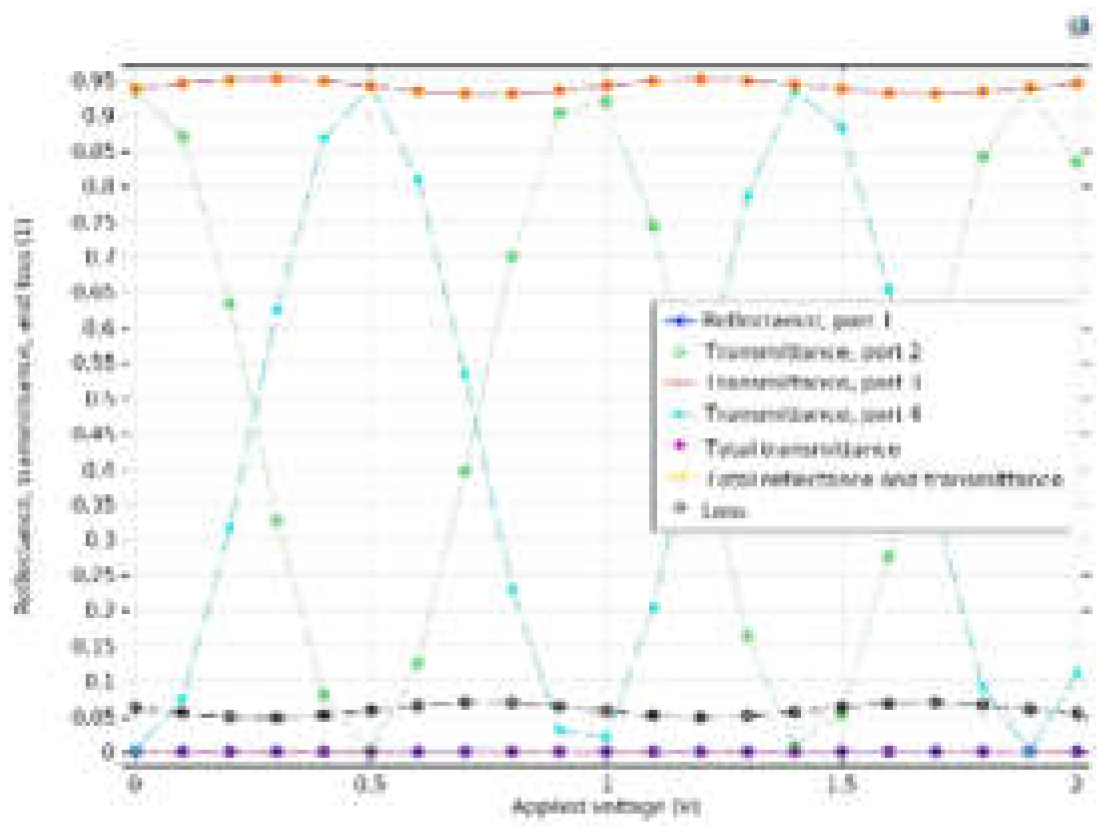
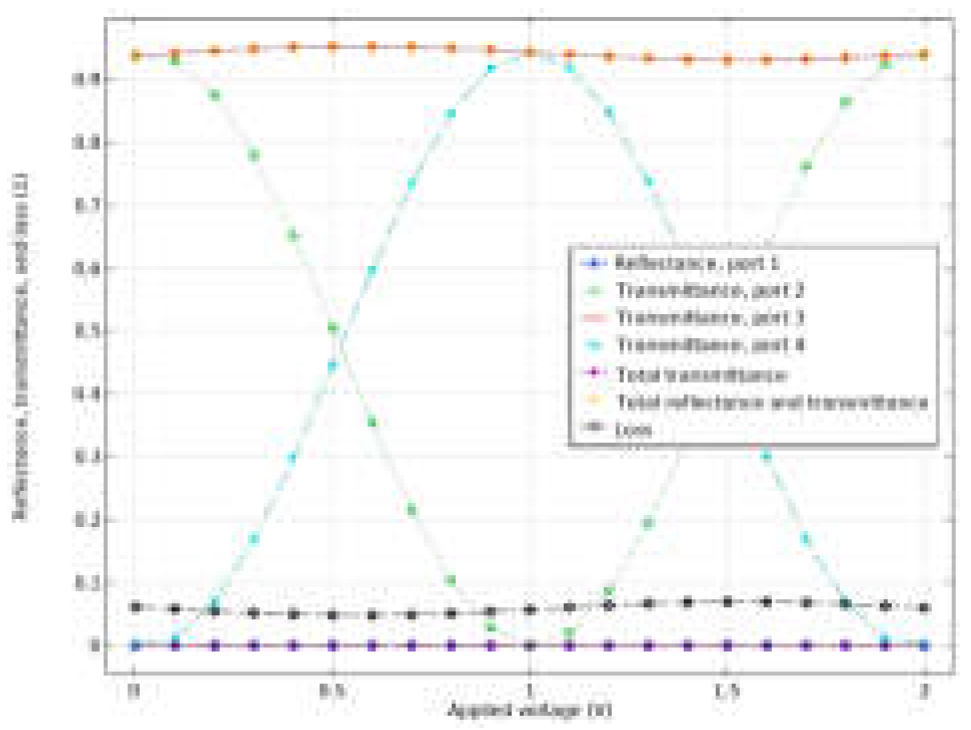
- The transmission, reflectance, and loss in all ports at the given range for the applied voltage;
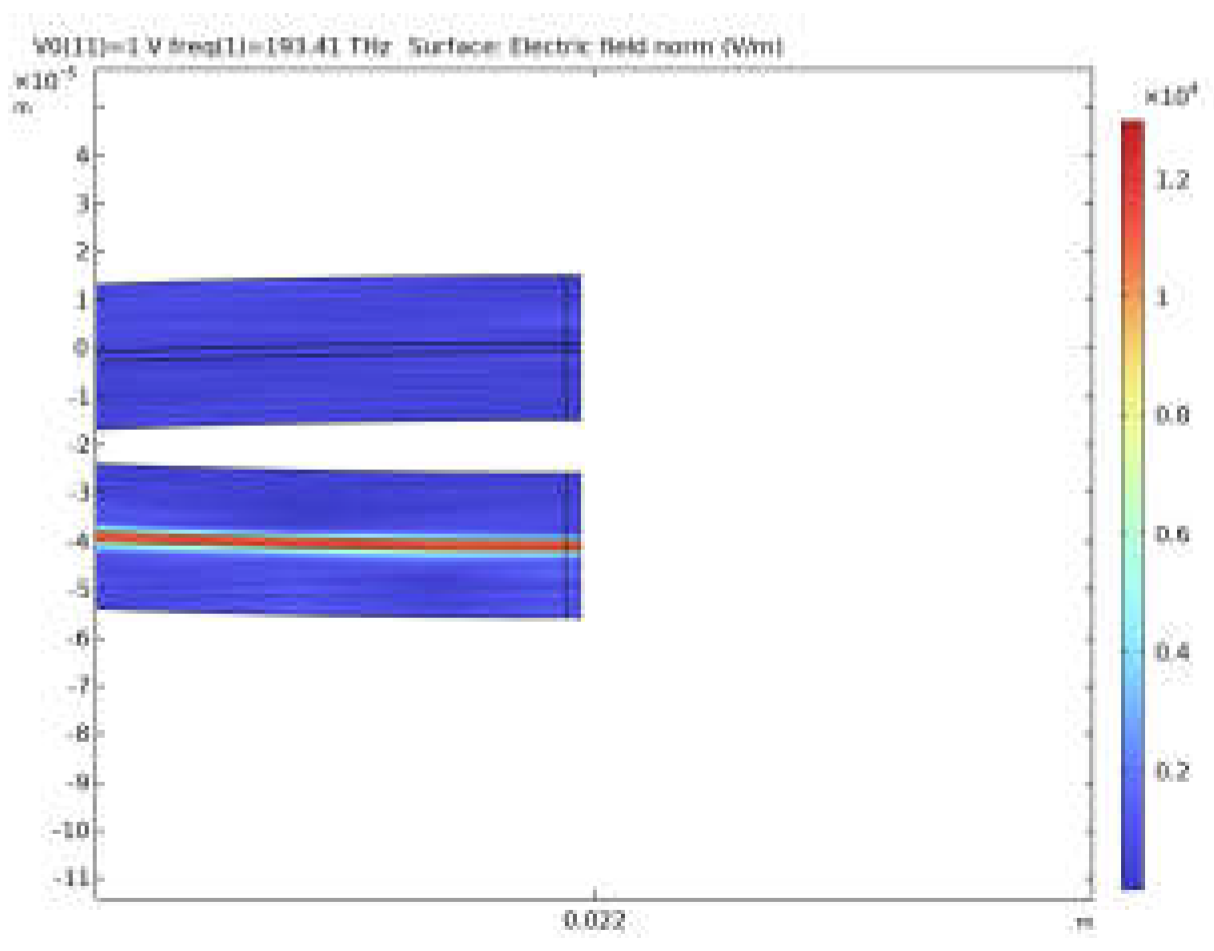
- The optical guided field at all ports under different applied voltages.
- ii.
-
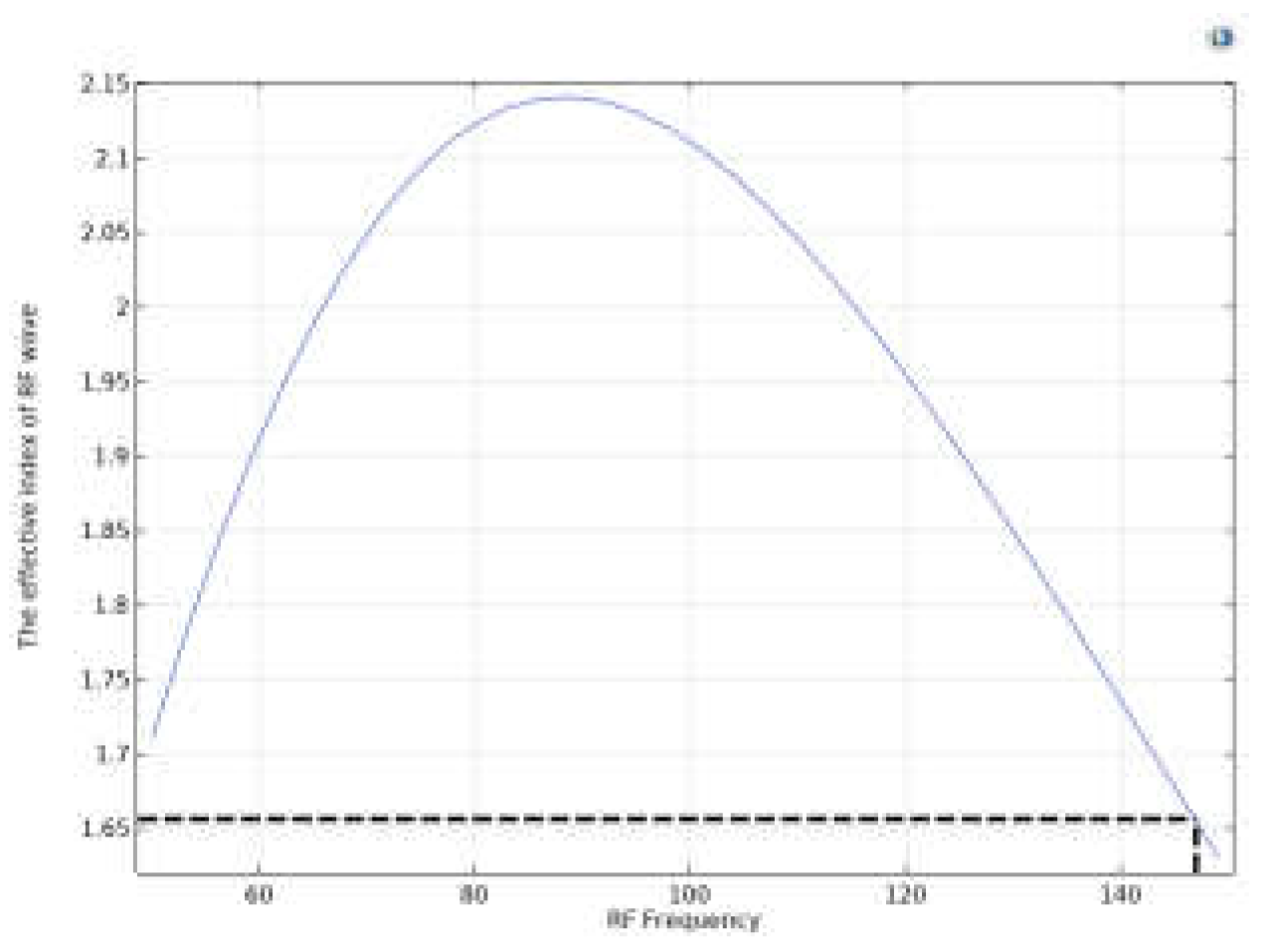
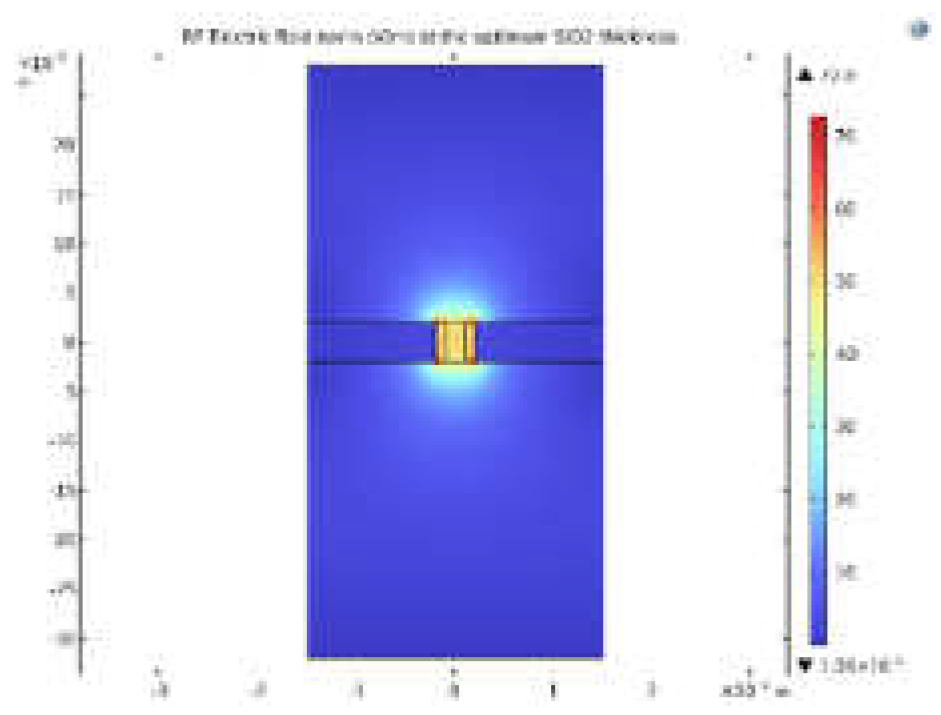
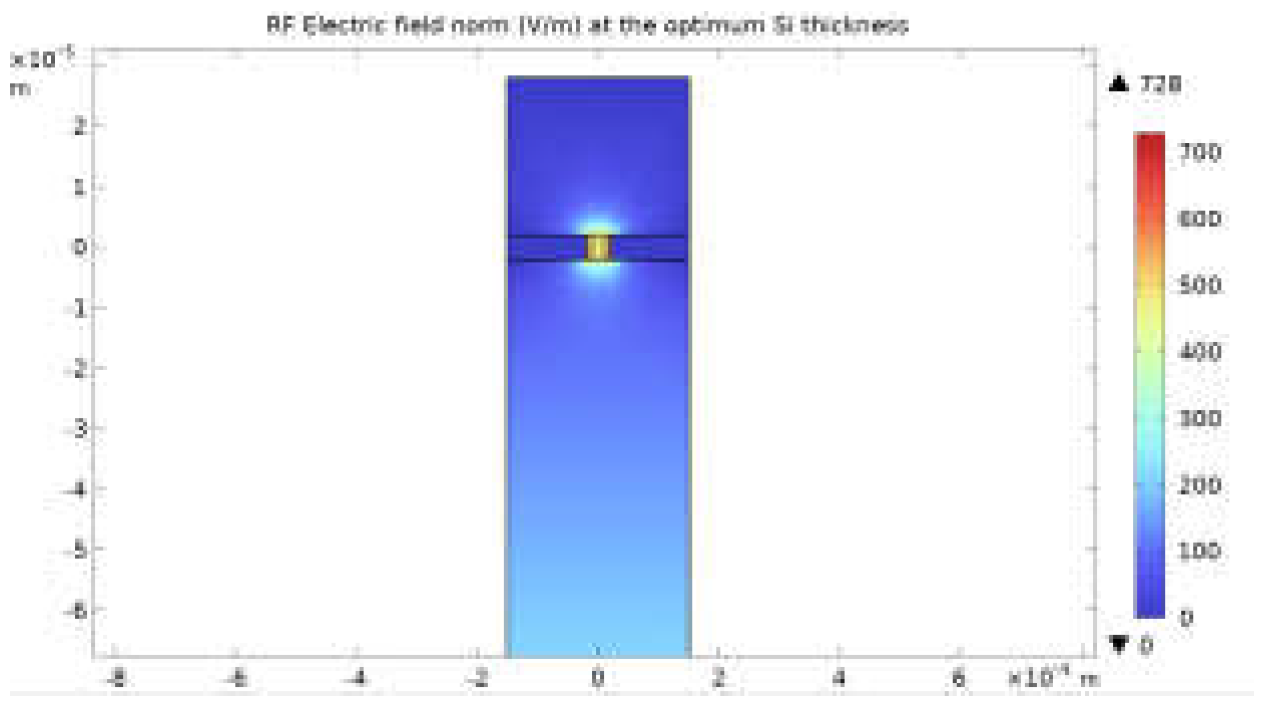
Step 2, The RF wave side: In this step, the section view of the modulator (Figure 6b) is considered, and the geometry is constructed according to the inputs. Then, the thickness of the SiO2 layer (or Si layer in the case of CdTe) is optimized for every single RF frequency in the given range to minimize the difference between the effective indices of the fundamental mode of the RF and optical waves propagating through the TW-MZM. The parameters calculated in this step are as follows;
- By optimizing the SiO2 layer (or the Si layer in the case of CdTe) thickness for every RF frequency, the propagation constant, the effective index, and the phase velocity of the RF wave at that frequency are calculated.
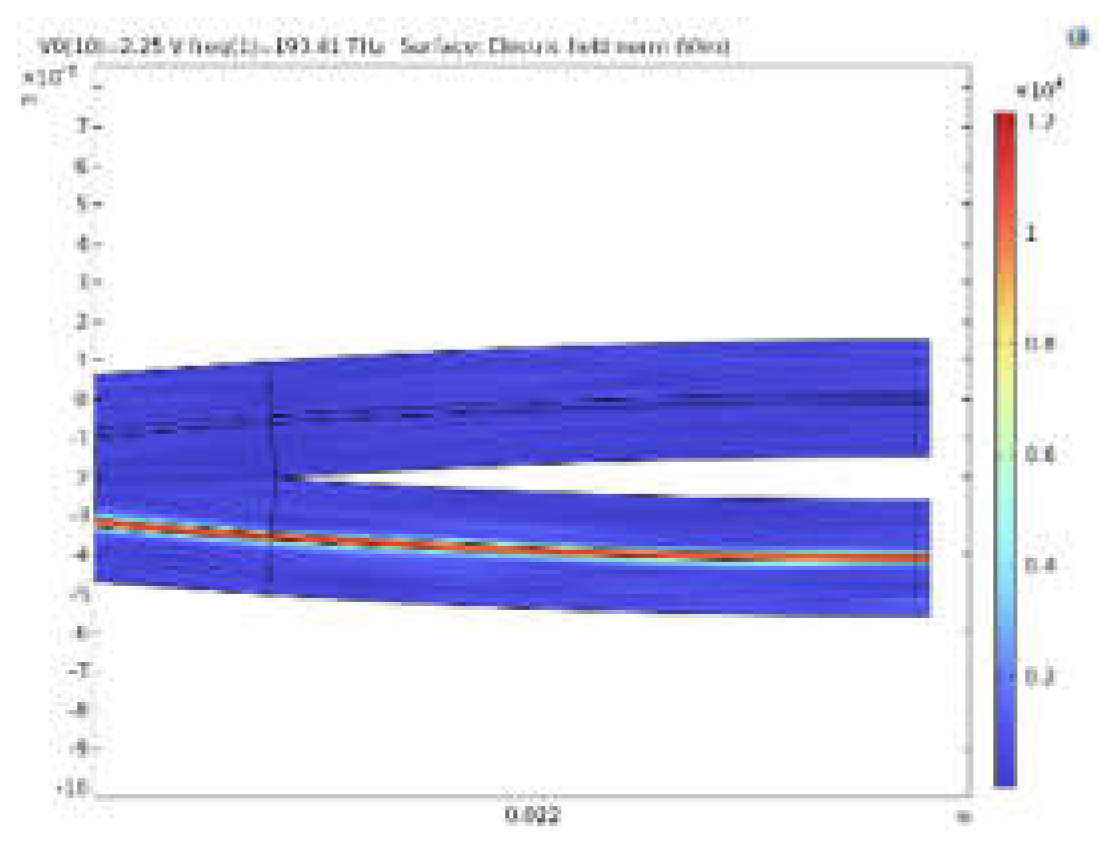
- The RF field at every frequency is evaluated by optimizing the SiO2 layer (or Si layer in the case of CdTe) thickness for every RF frequency.
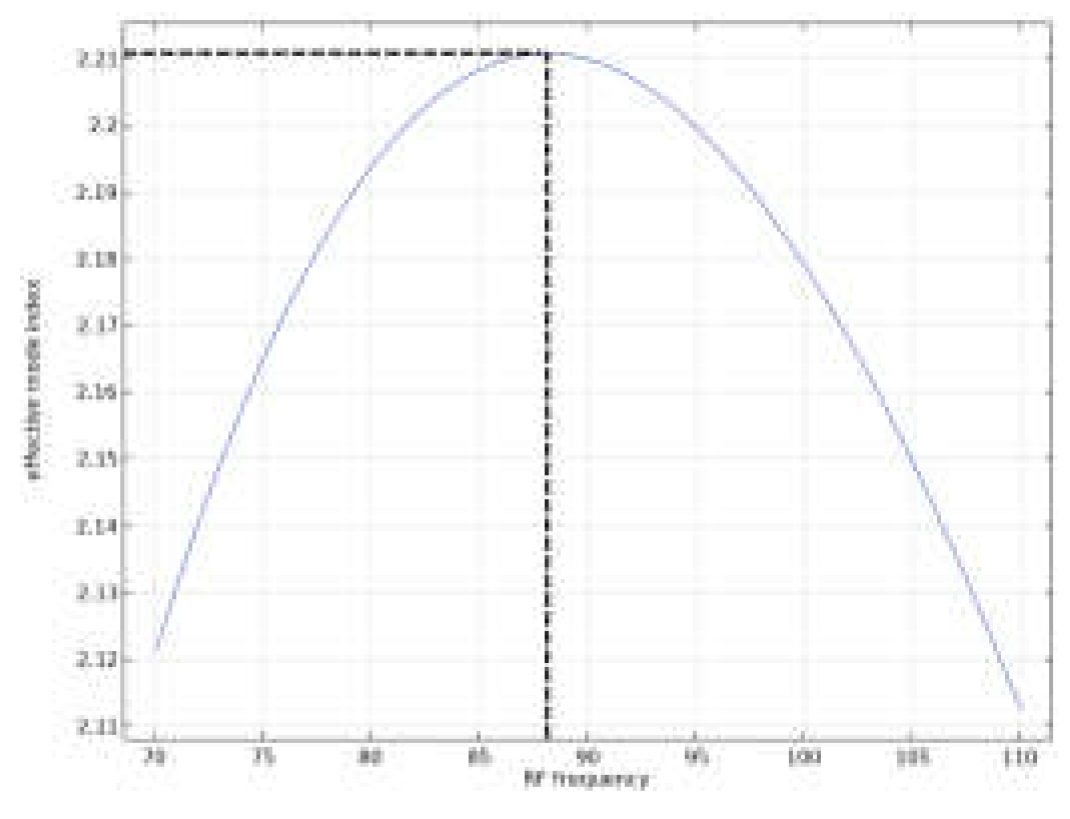
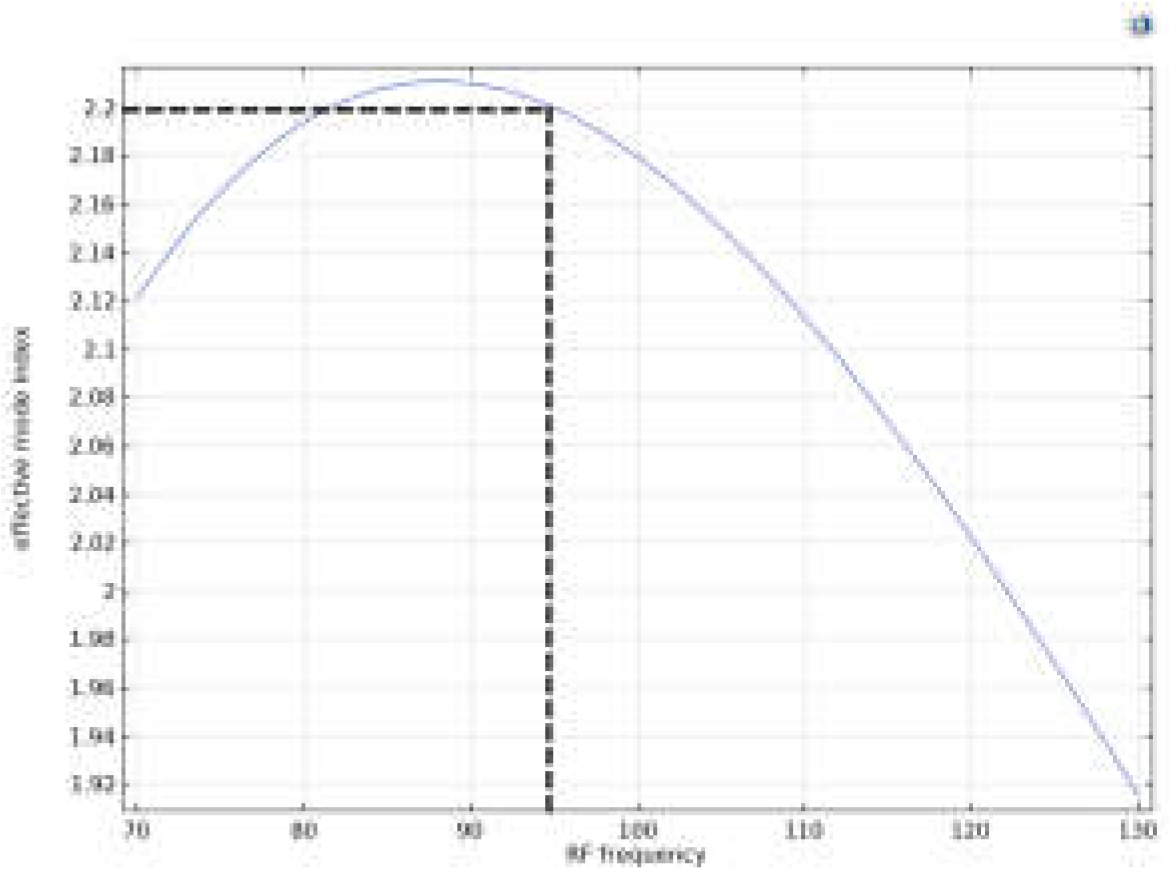
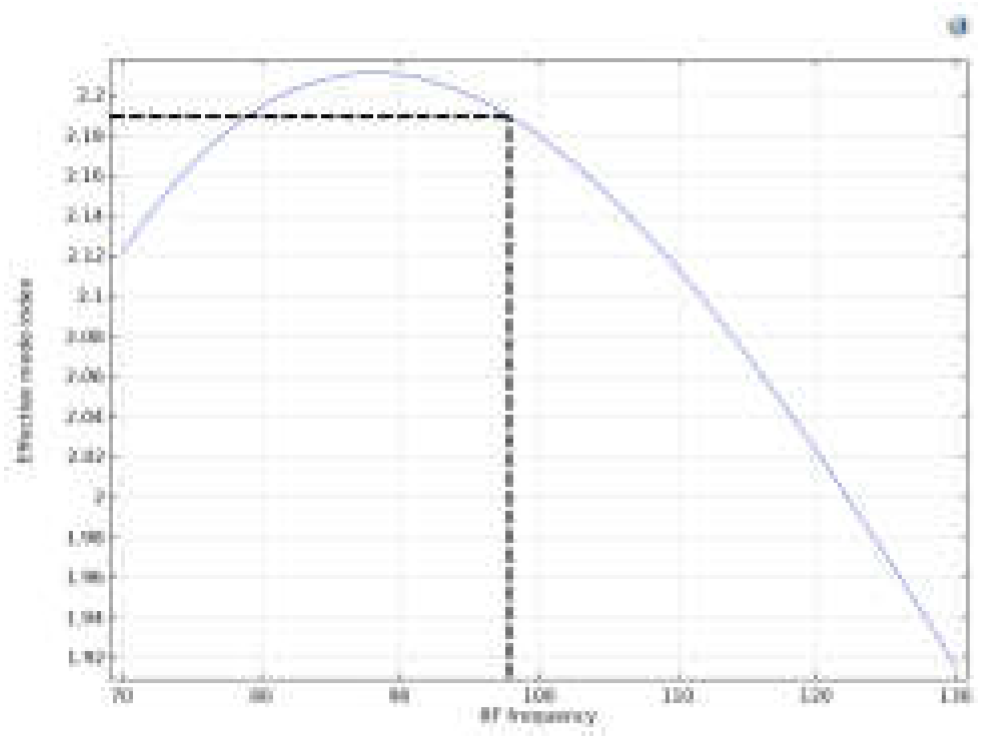
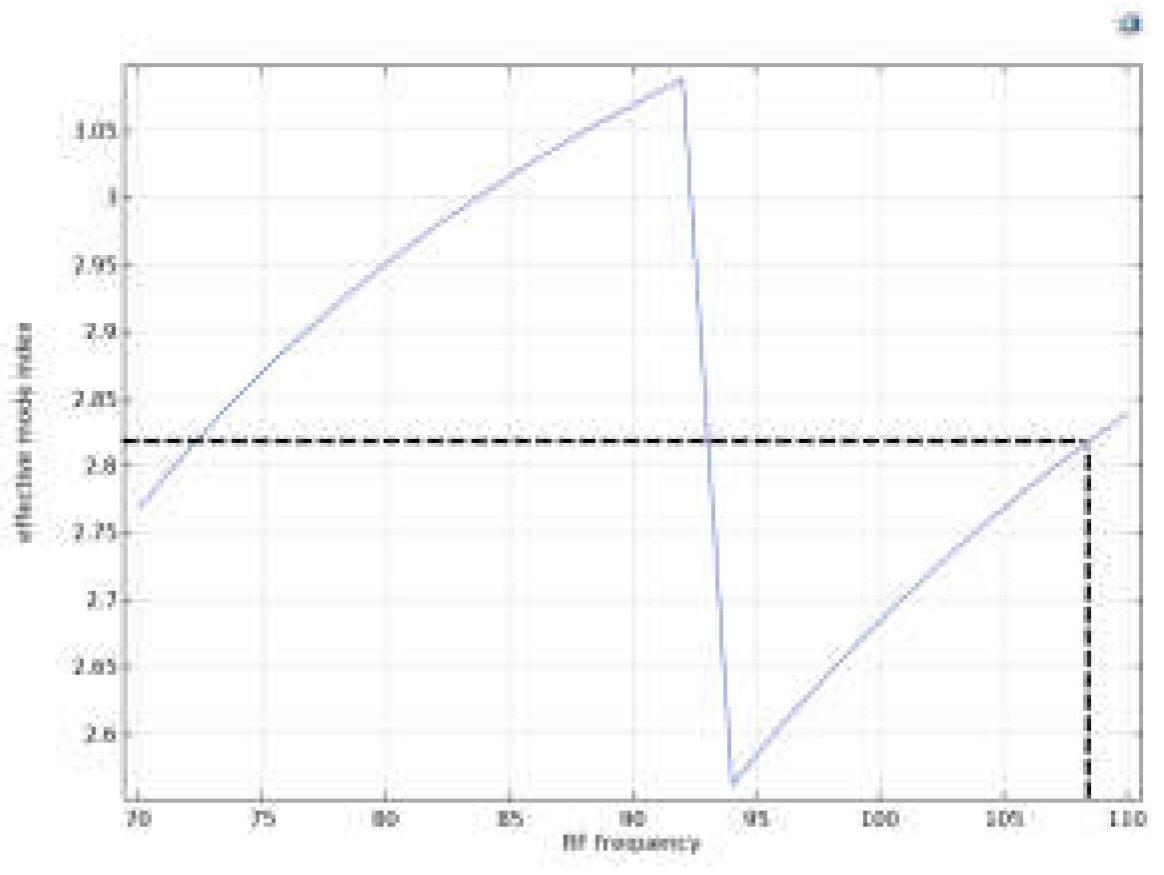
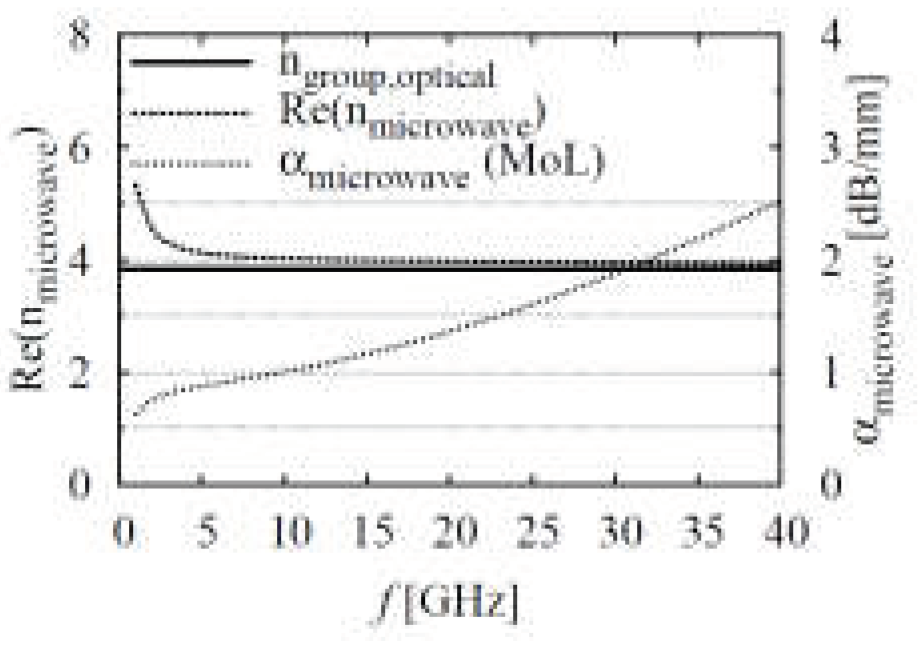
- The effective index of the fundamental mode of the RF wave after optimizing the thickness of the SiO2 is plotted versus the frequency of the RF wave.
- The maximum bandwidth of the modulation, as the frequency of the RF wave with the fundamental mode effective index matching to the optical wave’s fundamental mode effective index, is estimated.
- The RF loss coefficient is calculated using the imaginary part of the RF propagation constant resulting from the velocity matching.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. The Results of the Model for Using Lithium Niobate (LNB) as the EO Medium
3.2. The Results of the Model for Using BBO as the EO Medium
3.3. The Results of the Model for Using Potassium Niobate (KNB) as the EO Medium
3.4. The Results of the Model for Using LiTiO3 as the EO Medium
3.5. The Results of the Model for Using CdTe as the EO Medium
3.6. The Results for Using InP as the EO Medium Calculated by Pascher et al.
3.7. Comparing the Bandwidth, Optical Loss, and RF Loss of the TW-MZM Optimized for Each of the Six EO Crystals
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cong, G., et al., Silicon traveling-wave Mach–Zehnder modulator under distributed-bias driving. Optics Letters, 2018. 43(3): p. 403-406. [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M., et al., Resonantly enhanced lumped-element O-band Mach–Zehnder modulator with an ultra-wide operating wavelength range. Optics Letters, 2023. 48(21): p. 5623-5626. [CrossRef]
- Sharif Azadeh, S., et al., Power-efficient lumped-element meandered silicon Mach-Zehnder modulators. SPIE OPTO. Vol. 11285. 2020: SPIE.
- Xu, H., et al., Demonstration and Characterization of High-Speed Silicon Depletion-Mode Mach–Zehnder Modulators. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2014. 20(4): p. 23-32. [CrossRef]
- Pascher, W., et al. Modeling and Design of a Velocity-Matched Traveling-Wave Electro-Optic Modulator on InP. in Integrated Photonics Research. 2003. Washington, D.C.: Optica Publishing Group.
- Ataei, A., et al., Determining the Quadratic Electro-Optic Coefficients for Polycrystalline Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 (PMN-PT) Using a Polarization-Independent Electro-Optical Laser Beam Steerer. Applied Sciences, 2021. 11(8): p. 3313.
- Steglich, P., et al., Silicon-organic hybrid photonics: an overview of recent advances, electro-optical effects and CMOS integration concepts. Journal of Physics: Photonics, 2021. 3(2): p. 022009.
- Benea-Chelmus, I.-C., et al., Electro-optic spatial light modulator from an engineered organic layer. Nature Communications, 2021. 12(1): p. 5928. [CrossRef]
- Rahim, A., et al., Taking silicon photonics modulators to a higher performance level: state-of-the-art and a review of new technologies. Advanced Photonics, 2021. 3(2): p. 024003. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M., et al., Integrated lithium niobate electro-optic modulators: when performance meets scalability. Optica, 2021. 8(5): p. 652-667. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C., et al., Integrated lithium niobate electro-optic modulators operating at CMOS-compatible voltages. Nature, 2018. 562(7725): p. 101-104. [CrossRef]
- COMSOL Multiphysics® v. 6.2. www.comsol.com. COMSOL AB, Stockholm, Sweden.
- Ataei, A., et al., An electro-optic continuous laser beam steering device based on an SBN75 crystal. Ferroelectrics, 2023. 603(1): p. 34-51. [CrossRef]
- Baehr-Jones, T., et al., Ultralow drive voltage silicon traveling-wave modulator. Optics Express, 2012. 20(11): p. 12014-12020. [CrossRef]
- Qi, N., et al., Co-Design and Demonstration of a 25-Gb/s Silicon-Photonic Mach–Zehnder Modulator With a CMOS-Based High-Swing Driver. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2016. 22(6): p. 131-140. [CrossRef]
| Material | n | ɛ | r (pmV−1) | n3r/ɛ (pmV−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferroelectrics (room temperature) | ||||
| LiNbO3 | 2.26 | 29 | 31 | 12.339 |
| LiTaO3 | 2.23 | 43 | 31 | 7.995 |
| KNbO3 | 2.23 | 55 | 64 | 12.904 |
| BaTiO3 | 2.4 | 1800 | 1670 | 12.826 |
| SBN75 | 2.3 | 1550 | 1340 | 10.519 |
| SBN60 | 2.3 | 750 | 216 | 3.504 |
| BBO | 1.67 | 6.7 | 2.7 | 1.877 |
| Semiconductors (room temperature) | ||||
| GaAs | 3.5 | 13.2 | 1.2 | 3.898 |
| InP | 3.29 | 12.6 | 1.45 | 4.098 |
| CdTe | 2.82 | 9.4 | 6.8 | 16.223 |
| Bi12SiO20 | 2.54 | 56 | 5 | 1.463 |
| Bi12GeO20 | 2.55 | 47 | 3.4 | 1.200 |
| Cubic (varied by temperature and frequency) | ||||
| KTN | 2.3 | 14000 | 8500 | 7.387 |
| PMN-PT | 2.37 | 7000 | 3400 | 6.466 |

| Parameters | LNB | BBO | KNB | LTO | CdTe | InP1 |
| The effective index of the optical wave | 2.2107 | 1.6595 | 2.2007 | 2.1907 | 2.8118 | 3.28 |
| The operating voltage of the modulator (V) | 1 | 11 | 0.5 | 1 | 2.25 | NA |
| Maximum modulation bandwidth (GHz) | 88 | 148 | 94 | 97 | 108 | 40 |
| The optical intensity loss in the modulator (%) | 6.14 | 5.82 | 6.76 | 6.66 | 7.48 | NA |
| The RF loss in the modulator (dB/mm) | 8.8 | 8.3 | 8.8 | 8.8 | 0.6 | 2.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





