Submitted:
30 March 2024
Posted:
01 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
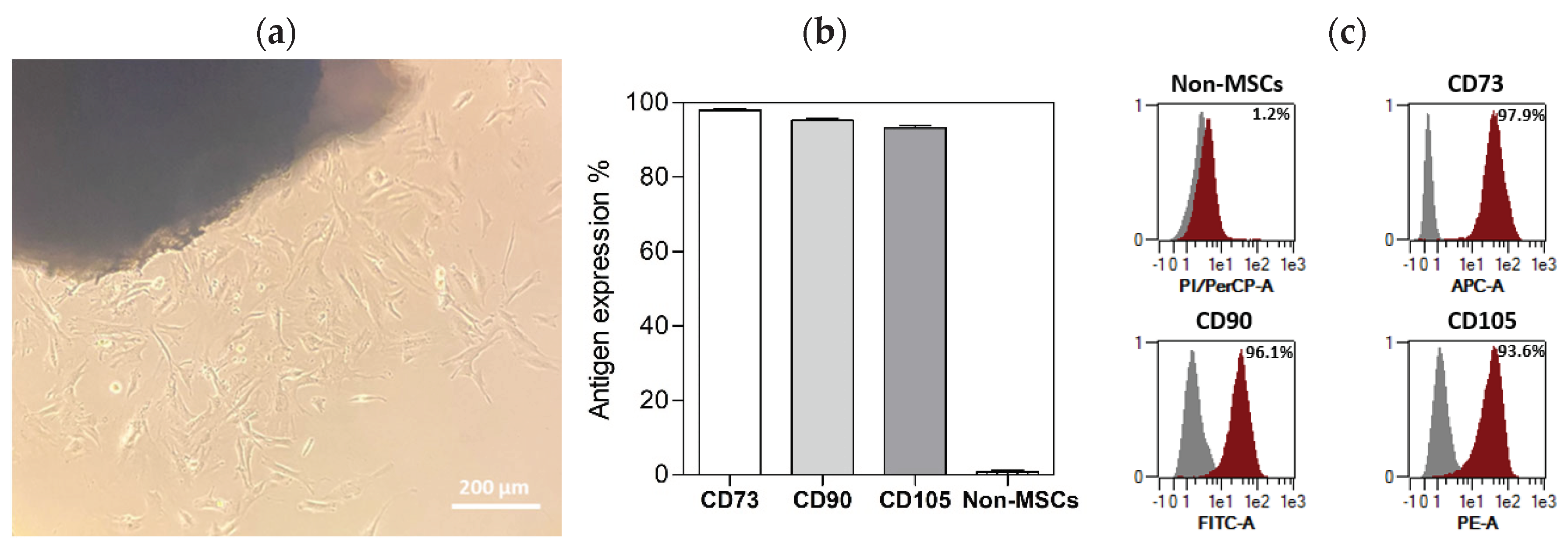
2.1. Characterisation of Isolated DPSCs populations
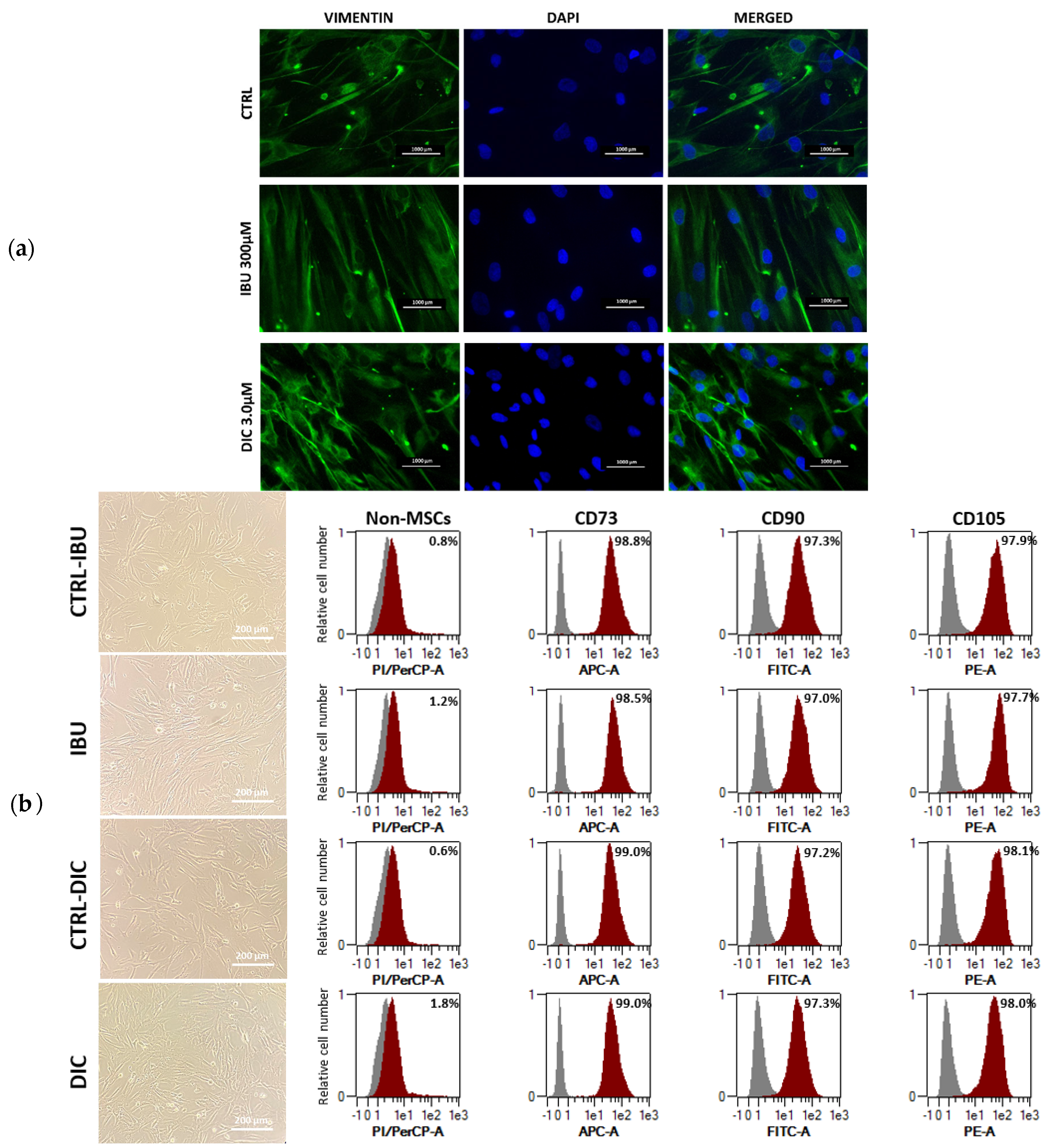
2.2. Effect of ibuprofen and diclofenac pre-treatment on characteristics, morphology and immunophenotype of DPSCs
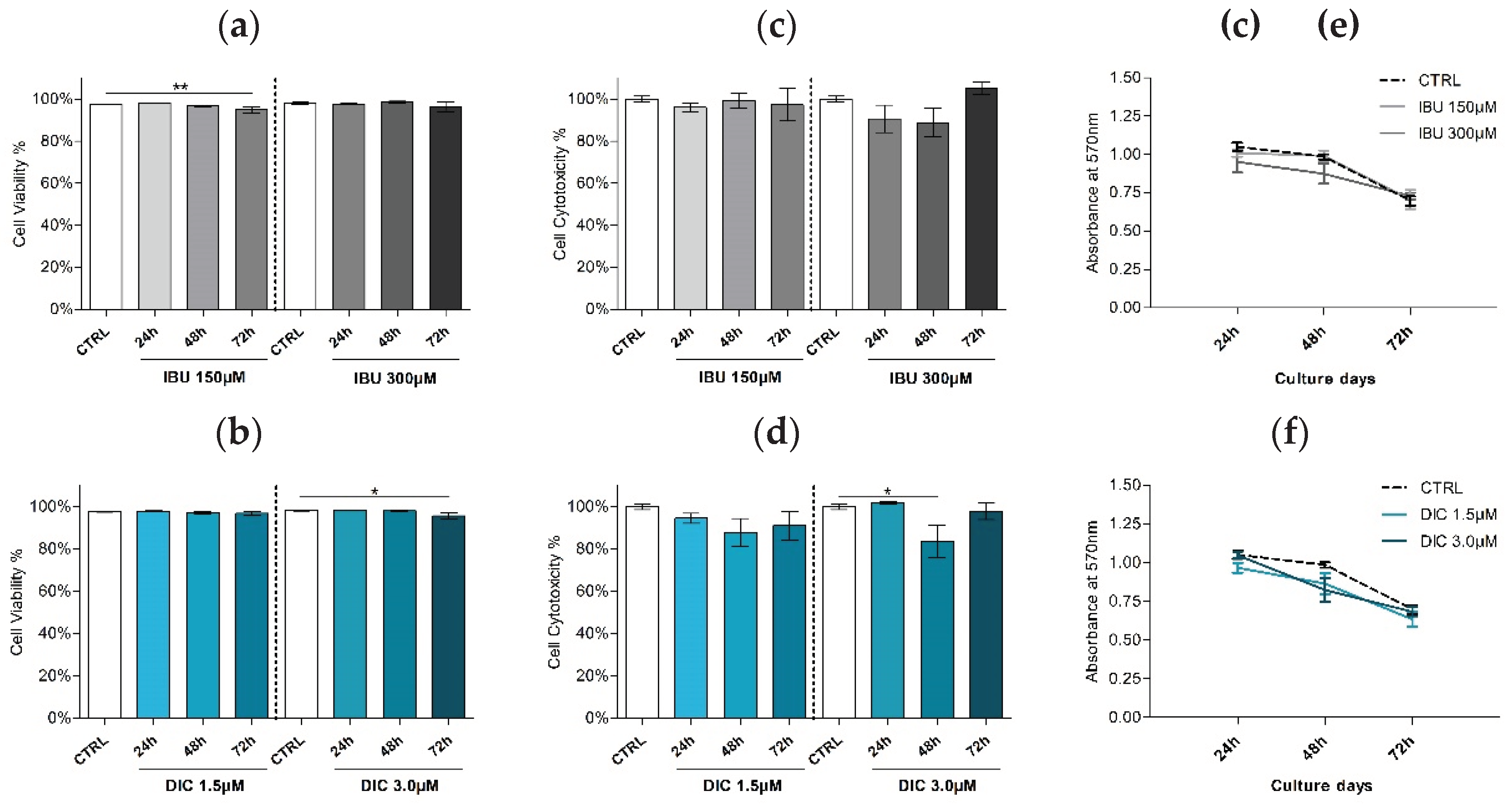
2.2. Effect of ibuprofen and diclofenac pre-treatment on viability of DPSCs
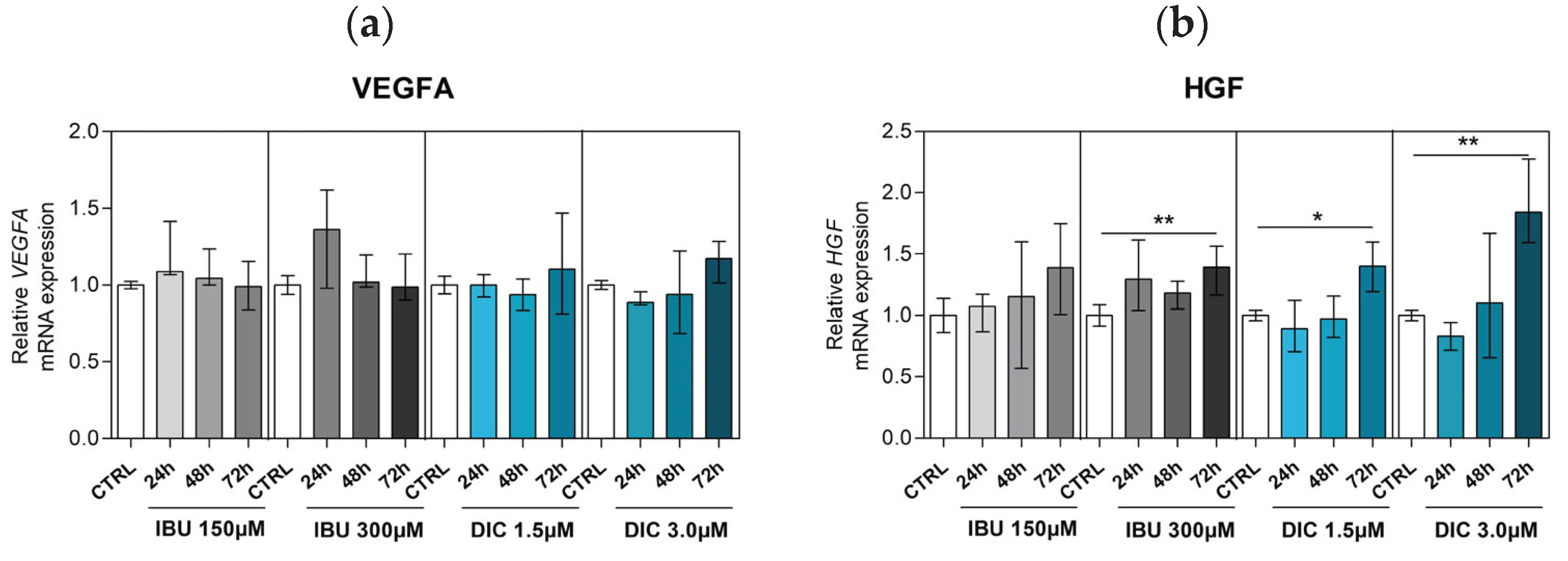
2.3. Effect of ibuprofen and diclofenac on angiogenic growth factors expression
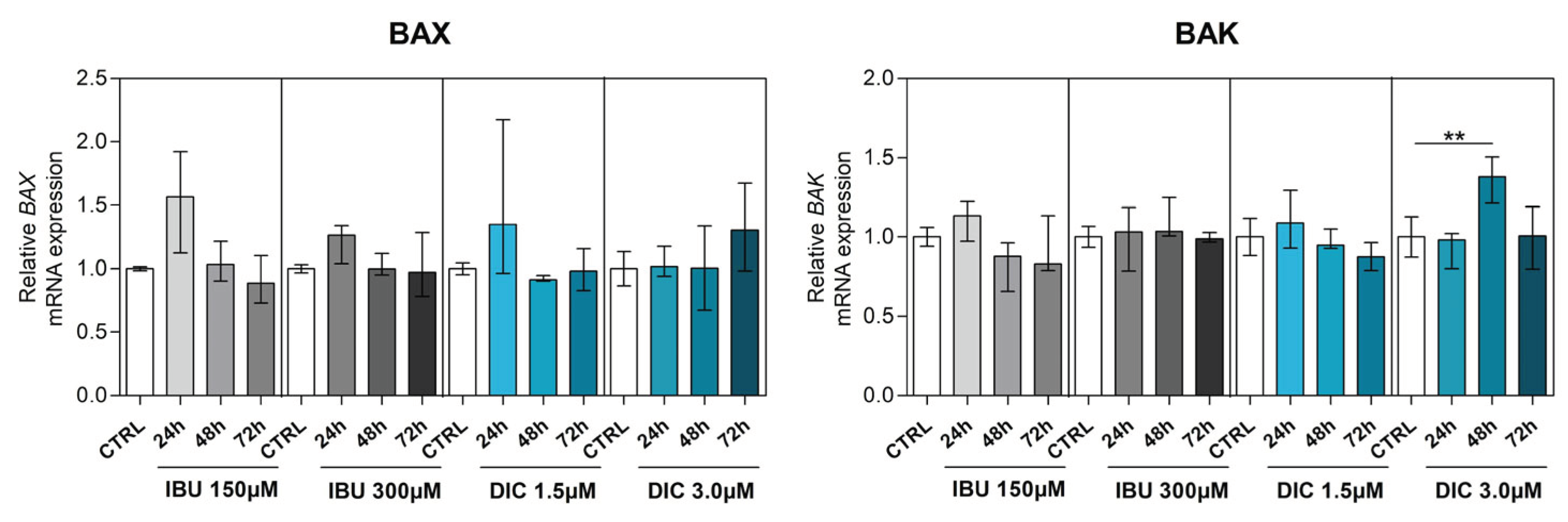
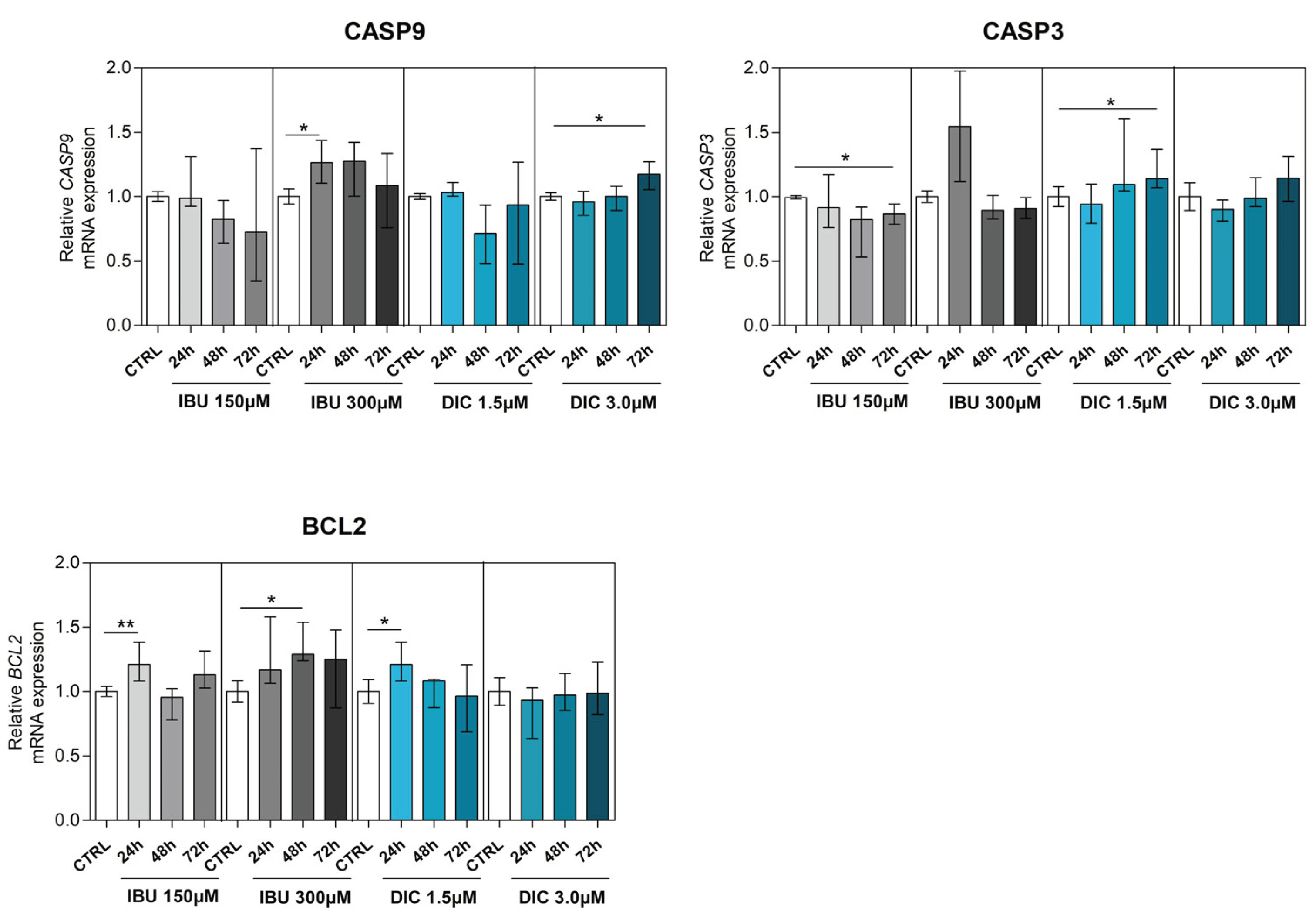
2.4. Ibuprofen and diclofenac significantly affect mRNA expression of selected genes in apoptosis signalling pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell isolation
4.3. Ibuprofen and Diclofenac Treatment
4.4. Immunofluorescence staining
4.5. MTT assay
4.6. Gene Expression
4.7. Statistical analysis
5. Conclusions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, N.; Ding, X.; Huang, R.; Jiang, R.; Huang, H.; Pan, X.; Min, W.; Chen, J.; Duan, J.-A.; Liu, P.; et al. Bone Tissue Engineering in the Treatment of Bone Defects. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Q.; Dong, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, B.; Jin, Y. Dental Stem Cell and Dental Tissue Regeneration. Front. Med. 2019, 13, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjua, O.S.; Qureshi, S.M.; Shaikh, M.S.; Alnazzawi, A.; Rodriguez-Lozano, F.J.; Pecci-Lloret, M.P.; Zafar, M.S. Autogenous Tooth Bone Grafts for Repair and Regeneration of Maxillofacial Defects: A Narrative Review. IJERPH 2022, 19, 3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, B.T.; Lee, S.; Tideman, H.; Stoelinga, P.J.W. Mandibular Reconstruction in Adults: A Review. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2008, 37, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.H. Autologous Bone Graft: Is It Still the Gold Standard? Injury 2021, 52, S18–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamieh, F.; Collignon, A.-M.; Coyac, B.R.; Lesieur, J.; Ribes, S.; Sadoine, J.; Llorens, A.; Nicoletti, A.; Letourneur, D.; Colombier, M.-L.; et al. Accelerated Craniofacial Bone Regeneration through Dense Collagen Gel Scaffolds Seeded with Dental Pulp Stem Cells. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 38814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Nakamura-Yamada, S.; Konoki, R.; Baba, S. Promising Advances in Clinical Trials of Dental Tissue-Derived Cell-Based Regenerative Medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Monjaraz, B.; Santiago-Osorio, E.; Ledesma-Martínez, E.; Alcauter-Zavala, A.; Mendoza-Núñez, V.M. Retrieval of a Periodontally Compromised Tooth by Allogeneic Grafting of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Dental Pulp: A Case Report. J Int Med Res 2018, 46, 2983–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meesuk, L.; Suwanprateeb, J.; Thammarakcharoen, F.; Tantrawatpan, C.; Kheolamai, P.; Palang, I.; Tantikanlayaporn, D.; Manochantr, S. Osteogenic Differentiation and Proliferation Potentials of Human Bone Marrow and Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on the 3D-Printed Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 19509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusuma, G.D.; Carthew, J.; Lim, R.; Frith, J.E. Effect of the Microenvironment on Mesenchymal Stem Cell Paracrine Signaling: Opportunities to Engineer the Therapeutic Effect. Stem Cells and Development 2017, 26, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oryan, A.; Kamali, A.; Moshiri, A.; Baghaban Eslaminejad, M. Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Bone Regenerative Medicine: What Is the Evidence? Cells Tissues Organs 2017, 204, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, D.M.; Pham, P.T.; Bach, T.Q.; Ngo, A.T.L.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Phan, T.T.K.; Nguyen, G.H.; Le, P.T.T.; Hoang, V.T.; Forsyth, N.R.; et al. Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Human Diseases. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, B.-D.; Hu, C.-H.; Liu, A.-Q.; Zheng, C.-X.; Xuan, K.; Jin, Y. Stem Cell-Based Bone Regeneration in Diseased Microenvironments: Challenges and Solutions. Biomaterials 2019, 196, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musiał-Wysocka, A.; Kot, M.; Majka, M. The Pros and Cons of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapies. Cell Transplant 2019, 28, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hersh, E.V.; Moore, P.A.; Grosser, T.; Polomano, R.C.; Farrar, J.T.; Saraghi, M.; Juska, S.A.; Mitchell, C.H.; Theken, K.N. Non-steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Opioids in Postsurgical Dental Pain. J Dent Res 2020, 99, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongrakpanich, S.; Wongrakpanich, A.; Melhado, K.; Rangaswami, J. A Comprehensive Review of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug Use in The Elderly. Aging Dis 2018, 9, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulesza, A.; Zielniok, K.; Hawryluk, J.; Paczek, L.; Burdzinska, A. Ibuprofen in Therapeutic Concentrations Affects the Secretion of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells, but Not Their Proliferative and Migratory Capacity. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pountos, I.; Georgouli, T.; Calori, G.M.; Giannoudis, P.V. Do Non-steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Affect Bone Healing? A Critical Analysis. ScientificWorldJournal 2012, 2012, 606404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, J.; O'Connor, J.P. Effect of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on Bone Healing. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 1668–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshiri, A.; Shahrezaee, M.; Shekarchi, B.; Oryan, A.; Azma, K. Three-Dimensional Porous Gelapin–Simvastatin Scaffolds Promoted Bone Defect Healing in Rabbits. Calcif Tissue Int 2015, 96, 552–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimetti, M.; Ferrarotti, F.; Gamba, M.N.; Giraudi, M.; Romano, F. Regenerative Treatment of Periodontal Intrabony Defects Using Autologous Dental Pulp Stem Cells: A 1-Year Follow-Up Case Series. Restorative Dentistry 2018, 38, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d'Aquino, R.; De Rosa, A.; Lanza, V.; Tirino, V.; Laino, L.; Graziano, A.; Desiderio, V.; Laino, G.; Papaccio, G. Human Mandible Bone Defect Repair by the Grafting of Dental Pulp Stem/Progenitor Cells and Collagen Sponge Biocomplexes. European Cells and Materials 2009, 18, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, K.; Li, B.; Guo, H.; Sun, W.; Kou, X.; He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, A.; Liao, L.; et al. Deciduous Autologous Tooth Stem Cells Regenerate Dental Pulp after Implantation into Injured Teeth. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaaf3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, B.-D.; Hu, C.-H.; Zheng, C.-X.; Shuai, Y.; He, X.-N.; Gao, P.-P.; Zhao, P.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.-Y.; He, T.; et al. Recipient Glycemic Micro-Environments Govern Therapeutic Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Infusion on Osteopenia. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1225–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Jin, Y. Stem Cell-Based Bone and Dental Regeneration: A View of Microenvironmental Modulation. Int J Oral Sci 2019, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjicharalambous, C.; Alpantaki, K.; Chatzinikolaidou, M. Effects of NSAIDSs on Pre-osteoblast Viability and Osteogenic Differentiation. Exp Ther Med 2021, 22, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, E.; Worthington, H.V.; van Wijk, A.; Yates, J.M.; Coulthard, P.; Afzal, Z. Ibuprofen and/or Paracetamol (Acetaminophen) for Pain Relief after Surgical Removal of Lower Wisdom Teeth. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.K.-S.; Lirk, P.; Seymour, R.A.; Jenkins, B.J. The Efficacy of Preemptive Analgesia for Acute Post-operative Pain Management: A Meta-Analysis: Anesthesia & Analgesia 2005, 100, 757–773. [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.-R.; Chamessian, A.; Zhang, Y.-Q. Pain Regulation by Non-Neuronal Cells and Inflammation. Science 2016, 354, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagi, R.; Yashoda Devi, B.K.; Rakesh, N.; Reddy, S.S.; Patil, D.J. Clinical Implications of Prescribing Non-steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Oral Health Care—a Review. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology 2015, 119, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diomede, F.; Rajan, T.S.; Gatta, V.; D’Aurora, M.; Merciaro, I.; Marchisio, M.; Muttini, A.; Caputi, S.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E.; et al. Stemness Maintenance Properties in Human Oral Stem Cells after Long-Term Passage. Stem Cells International 2017, 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, Q.; Yang, T.; Qi, Y.; Fu, M.; Yang, X.; Qiao, L.; Ling, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y. Comparative Characterization of SHED and DPSCs during Extended Cultivation In�vitro. Molecular Medicine Reports 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronthos, S.; Brahim, J.; Li, W.; Fisher, L.W.; Cherman, N.; Boyde, A.; DenBesten, P.; Robey, P.G.; Shi, S. Stem Cell Properties of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells. J Dent Res 2002, 81, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.C.; Krause, D.S.; Deans, R.J.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.J.; Horwitz, E.M. Minimal Criteria for Defining Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy Position Statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salkın, H.; Basaran, K.E. Effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (Ibuprofen) in Low and High Dose on Stemness and Biological Characteristics of Human Dental Pulp-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Connective Tissue Research 2022, 0, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.; Raabe, O.; Addicks, K.; Wenisch, S.; Arnhold, S. Effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on Proliferation, Differentiation and Migration in Equine Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell. Biol. Int. 2011, 35, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, C.; Kori, M.; Matsuzaki, K.; Yamai, K.; Nakajima, A.; Shibuya, A.; Niwa, H.; Kamisaki, Y.; Wada, K. Diclofenac Inhibits Proliferation and Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells. Biochemical Pharmacology 2003, 66, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, A.; Gallo, M.; Aldinucci, D.; Ribatti, D.; Lamura, L.; D'Alessio, A.; De Filippi, R.; Pinto, A.; Normanno, N. Role of the EGFR Ligand/Receptor System in the Secretion of Angiogenic Factors in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hankenson, K.D.; Dishowitz, M.; Gray, C.; Schenker, M. Angiogenesis in Bone Regeneration. Injury 2011, 42, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Han, Z.; Han, Z.C.; Li, Z. Proangiogenic Features of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Therapeutic Applications. Stem Cells International 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Q.; Zhang, H.; Hou, J.; Wan, L.; Cheng, W.; Wang, X.; Dong, D.; Chen, C.; Xia, J.; Guo, J.; et al. VEGF Secreted by Mesenchymal Stem Cells Mediates the Differentiation of Endothelial Progenitor Cells into Endothelial Cells via Paracrine Mechanisms. Molecular Medicine Reports 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, A.D.; Olsen, B.R. How Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A (VEGF) Regulates Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry 2014, 62, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sulpice, E.; Ding, S.; Muscatelli-Groux, B.; Bergé, M.; Han, Z.C.; Plouet, J.; Tobelem, G.; Merkulova-Rainon, T. Cross-Talk between the VEGF-A and HGF Signalling Pathways in Endothelial Cells. Biology of the Cell 2009, 101, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, A.; Kubota, T.; Taiyoh, H.; Fujiwara, H.; Okamoto, K.; Ichikawa, D.; Shiozaki, A.; Komatsu, S.; Nakanishi, M.; Kuriu, Y.; et al. HGF Regulates VEGF Expression via the C-Met Receptor Downstream Pathways, PI3K/Akt, MAPK and STAT3, in CT26 Murine Cells. International Journal of Oncology 2013, 42, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano-Moreno, F.J.; Costela-Ruiz, V.J.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; Illescas-Montes, R.; García-Martínez, O.; Ruiz, C.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J. Inhibition of VEGF Gene Expression in Osteoblast Cells by Different NSAIDSs. Archives of Oral Biology 2018, 92, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Tan, T.; Liu, P. Regulation of Autophagy by Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Cancer. CMAR 2020, Volume 12, 4595–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri, E.; Ahmadi, R.; Rostami, E. The Effects of Ibuprofen Cytoxic Dose on Caspase-3, -8 and -9 Activity Level in Cervical Cancer (Hela) Cells. JBUMS 2019, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrami, H.; Aminzadeh, S.; Fallahi, H. Inhibitory Effect of Ibuprofen on Tumor Survival and Angiogenesis in Gastric Cancer Cell. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 3237–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, R.; Bosch, B.; Brune, K.; Patrignani, P.; Young, C. Advances in NSAIDS Development: Evolution of Diclofenac Products Using Pharmaceutical Technology. Drugs 2015, 75, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, TJ. Diclofenac: An Update on Its Mechanism of Action and Safety Profile. Current medical research and opinion 2010, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosser, T.; S, F.; Ga, F. Biological Basis for the Cardiovascular Consequences of COX-2 Inhibition: Therapeutic Challenges and Opportunities. The Journal of clinical investigation 2006, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, F.; Shang, L. Advances in Antitumor Effects of NSAIDSs. Cancer Manag Res 2018, 10, 4631–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidgens, V.; Seliger, C.; Jachnik, B.; Welz, T.; Leukel, P.; Vollmann-Zwerenz, A.; Bogdahn, U.; Kreutz, M.; Grauer, O.M.; Hau, P. Ibuprofen and Diclofenac Restrict Migration and Proliferation of Human Glioma Cells by Distinct Molecular Mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiser, T.; Schepers, C.; Mück, T.; Lange, R. Pharmacokinetic Properties of Ibuprofen (IBU) From the Fixed-Dose Combination IBU/Caffeine (400/100 Mg; FDC) in Comparison With 400 Mg IBU as Acid or Lysinate Under Fasted and Fed Conditions—Data From 2 Single-Center, Single-Dose, Randomized Crossover Studies in Healthy Volunteers. Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development 2019, 8, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissy, M.; Stiff, D.D.; Kowalski, M.M.; Moore, K.A. Single-Dose Pharmacokinetic Study of Rapidly Dispersing Diclofenac Potassium Formulations in Healthy Volunteers. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2009, 25, 2423–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A New Mathematical Model for Relative Quantification in Real-Time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate Normalization of Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR Data by Geometric Averaging of Multiple Internal Control Genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, RESEARCH0034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




