Submitted:
30 March 2024
Posted:
01 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
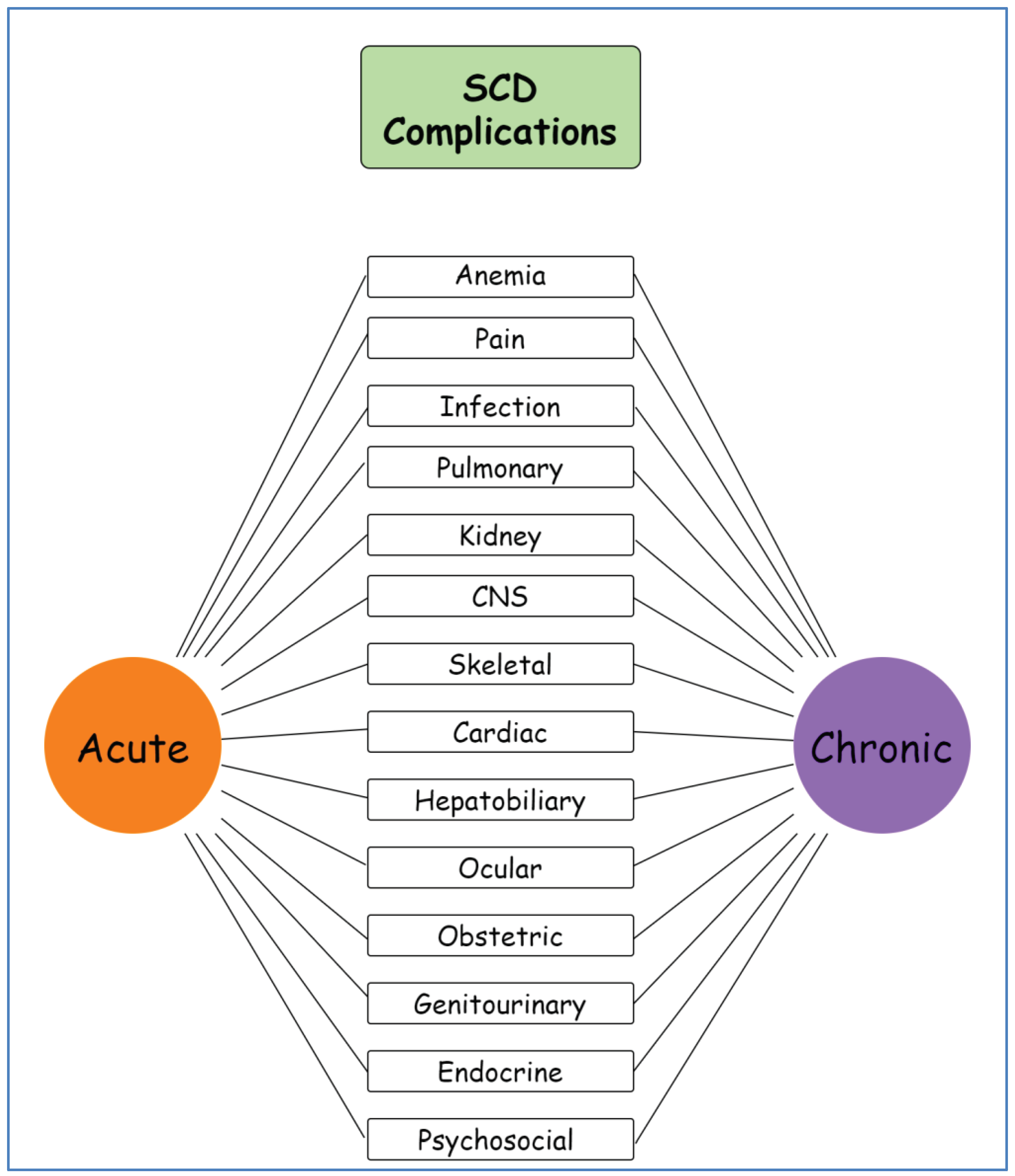
2.1. Classification of PH
- Group 1: Pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Group 2: PH due to left heart disease
- Group 3: PH due to chronic lung disease and/or hypoxemia
- Group 4: PH due to pulmonary artery obstructions (eg, chronic thromboembolic PH)
- Group 5: PH due to unclear multifactorial mechanisms (e.g., SCD, beta-thalassemia, myeloproliferative disorders, sarcoidosis, and metabolic disorders)
2.2. Clinical Presentation of PH
2.3. Diagnostic Assessment for PH
2.4. Pathophysiology
2.5. Role of Gene Polymorphisms in Pathogenesis and Prognosis of SCD-Related PH
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gladwin, M.T.; Vichinsky, E. Pulmonary Complications of Sickle Cell Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2254–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordeuk, V.R.; Castro, O.L.; Machado, R.F. Pathophysiology and treatment of pulmonary hypertension in sickle cell disease. Blood 2016, 127, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, G.J.; Steinberg, M.H.; Gladwin, M.T. Intravascular hemolysis and the pathophysiology of sickle cell disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savale, L.; Habibi, A.; Lionnet, F.; Maitre, B.; Cottin, V.; Jais, X.; Chaouat, A.; Artaud-Macari, E.; Canuet, M.; Prevot, G.; et al. Clinical phenotypes and outcomes of precapillary pulmonary hypertension of sickle cell disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1900585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 61, 2200879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klings, E.S.; Machado, R.F.; Barst, R.J.; Morris, C.R.; Mubarak, K.K.; Gordeuk, V.R.; Kato, G.J.; Ataga, K.I.; Gibbs, J.S.; Castro, O.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline: Diagnosis, Risk Stratification, and Management of Pulmonary Hypertension of Sickle Cell Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladwin, M.T.; Barst, R.J.; Gibbs, J.S.R.; Hildesheim, M.; Sachdev, V.; Nouraie, M.; Hassell, K.L.; Little, J.A.; Schraufnagel, D.E.; Krishnamurti, L.; et al. Risk Factors for Death in 632 Patients with Sickle Cell Disease in the United States and United Kingdom. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e99489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, R.F.; Hildesheim, M.; Mendelsohn, L.; Remaley, A.T.; Kato, G.J.; Gladwin, M.T. NT-pro brain natriuretic peptide levels and the risk of death in the cooperative study of sickle cell disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 154, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladwin, M.T.; Sachdev, V.; Jison, M.L.; Shizukuda, Y.; Plehn, J.F.; Minter, K.; Brown, B.; Coles, W.A.; Nichols, J.S.; Ernst, I.; et al. Pulmonary Hypertension as a Risk Factor for Death in Patients with Sickle Cell Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehari, A.; Gladwin, M.T.; Tian, X.; Machado, R.F.; Kato, G.J. Mortality in Adults With Sickle Cell Disease and Pulmonary Hypertension. JAMA 2012, 307, 1254–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liem, R.I.; Lanzkron, S.; Coates, T.D.; DeCastro, L.; Desai, A.A.; Ataga, K.I.; Cohen, R.T.; Haynes, J.J.; Osunkwo, I.; Lebensburger, J.D.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2019 guidelines for sickle cell disease: cardiopulmonary and kidney disease. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3867–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehari, A.; Alam, S.; Tian, X.; Cuttica, M.J.; Barnett, C.F.; Miles, G.; Xu, D.; Seamon, C.; Adams-Graves, P.; Castro, O.L.; et al. Hemodynamic Predictors of Mortality in Adults with Sickle Cell Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehari, A.; Igbineweka, N.; Allen, D.; Nichols, J.; Thein, S.L.; Weir, N.A. Abnormal Ventilation–Perfusion Scan Is Associated with Pulmonary Hypertension in Sickle Cell Adults. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 60, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niss, O.; Fleck, R.; Makue, F.; Alsaied, T.; Desai, P.; Towbin, J.A.; Malik, P.; Taylor, M.D.; Quinn, C.T. Association between diffuse myocardial fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction in sickle cell anemia. Blood 2017, 130, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.-L.; Tian, X.; Alam, S.; Mehari, A.; Leung, S.W.; Seamon, C.; Allen, D.; Minniti, C.P.; Sachdev, V.; Arai, A.E.; et al. Elevated transpulmonary gradient and cardiac magnetic resonance-derived right ventricular remodeling predict poor outcomes in sickle cell disease. Haematologica 2015, 101, e40–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.S.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parent, F.; Bachir, D.; Inamo, J.; Lionnet, F.; Driss, F.; Loko, G.; Habibi, A.; Bennani, S.; Savale, L.; Adnot, S.; et al. A Hemodynamic Study of Pulmonary Hypertension in Sickle Cell Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, R.F.; Anthi, A.; Steinberg, M.H.; Bonds, D.; Sachdev, V.; Kato, G.J.; Taveira-DaSilva, A.M.; Ballas, S.K.; Blackwelder, W.; Xu, X.; et al. N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels and Risk of Death in Sickle Cell Disease. JAMA 2006, 296, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthi, A.; Machado, R.F.; Jison, M.L.; Taveira-DaSilva, A.M.; Rubin, L.J.; Hunter, L.; Hunter, C.J.; Coles, W.; Nichols, J.; Avila, N.A.; et al. Hemodynamic and Functional Assessment of Patients with Sickle Cell Disease and Pulmonary Hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, C.P.; Sable, C.; Campbell, A.; Rana, S.; Ensing, G.; Dham, N.; Onyekwere, O.; Nouraie, M.; Kato, G.; Gladwin, M.T.; et al. Elevated tricuspid regurgitant jet velocity in children and adolescents with sickle cell disease: association with hemolysis and hemoglobin oxygen desaturation. Haematologica 2009, 94, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, H.F.; Nathan, D.G.; Dover, G.J.; Hebbel, R.P.; Platt, O.S.; Rosse, W.F.; Ware, R.E. Pulmonary hypertension and nitric oxide depletion in sickle cell disease. Blood 2010, 116, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, G.J.; McGowan, V.; Machado, R.F.; Little, J.A.; Taylor, J.; Morris, C.R.; Nichols, J.S.; Wang, X.; Poljakovic, M.; Morris, S.M.; et al. Lactate dehydrogenase as a biomarker of hemolysis-associated nitric oxide resistance, priapism, leg ulceration, pulmonary hypertension, and death in patients with sickle cell disease. Blood 2006, 107, 2279–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, G.J.; Gladwin, M.T.; Steinberg, M.H. Deconstructing sickle cell disease: Reappraisal of the role of hemolysis in the development of clinical subphenotypes. Blood Rev. 2007, 21, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prohaska, C.C.; Machado, R.F. The different facets of sickle cell disease-related pulmonary hypertension. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2021, 27, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B. Integrated bioinformatics analysis reveals marker genes and immune infiltration for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rother, R.P.; Bell, L.; Hillmen, P.; Gladwin, M.T. The Clinical Sequelae of Intravascular Hemolysis and Extracellular Plasma Hemoglobin. JAMA 2005, 293, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niss, O.; Quinn, C.T.; Lane, A.; Daily, J.; Khoury, P.R.; Bakeer, N.; Kimball, T.R.; Towbin, J.A.; Malik, P.; Taylor, M.D. Cardiomyopathy With Restrictive Physiology in Sickle Cell Disease. JACC: Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebbel, R.P. Reconstructing sickle cell disease: A data-based analysis of the “hyperhemolysis paradigm” for pulmonary hypertension from the perspective of evidence-based medicine. Am. J. Hematol. 2011, 86, 123–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinsheye, I.; Klings, E.S. Sickle cell anemia and vascular dysfunction: The nitric oxide connection. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 224, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jison, M.L.; Gladwin, M.T. Hemolytic Anemia–associated Pulmonary Hypertension of Sickle Cell Disease and the Nitric Oxide/Arginine Pathway. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.R.; Kato, G.J.; Poljakovic, M.; Wang, X.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Sachdev, V.; Hazen, S.L.; Vichinsky, E.P.; Morris, S.M., Jr.; Gladwin, M.T. Dysregulated Arginine Metabolism, Hemolysis-Associated Pulmonary Hypertension, and Mortality in Sickle Cell Disease. JAMA 2005, 294, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, G.J.; Wang, Z.; Machado, R.F.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Taylor, J.G.; Hazen, S.L. Endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitors in sickle cell disease: abnormal levels and correlations with pulmonary hypertension, desaturation, haemolysis, organ dysfunction and death. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 145, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmakis, D.; Aessopos, A. Pulmonary Hypertension Associated With Hemoglobinopathies. Circ. 2011, 123, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasimuzzaman, M. D.; Malik, P. Role of the coagulation system in the pathogenesis of sickle cell disease. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3170–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shet, A.S.; Lizarralde-Iragorri, M.A.; Naik, R.P. The molecular basis for the prothrombotic state in sickle cell disease. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2368–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulou, M.; Politou, M.; Stavroula, K.; Koutsouri, D.; Tsioutsias, P.; Flevari, P.; Voskaridou, E. SILENT CEREBRAL ISCHEMIA AND THROMBOEMBOLIC EVENTS IN SICKLE CELL DISEASE: ANALYSIS OF COAGULATION PARAMETERS AND THROMBOELASTOGRAPHY. Abstract release date: 05/18/17. EHA Library. Dimopoulou M. 05/18/2017; 181261; E1485.
- Tantawy, A.; El-Sherif, N.; Makkeyah, S.; Eldeen, N.S.; Farghal, N.B.E.-D.; Soliman, N.; Ebeid, F.S.E. Sleep disordered breathing and its relation to stroke and pulmonary hypertension in children with sickle cell disease: a single-center cross-sectional study. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Efird, J.T.; Knupp, C.; Kadali, R.; Liles, D.; Shiue, K.; Boettger, P.; Quan, S.F. Sleep Disorders in Adult Sickle Cell Patients. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehari, A.; Klings, E.S. Chronic Pulmonary Complications of Sickle Cell Disease. Chest 2016, 149, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley-Koch, A.E.; Elliott, L.; Kail, M.E.; De Castro, L.M.; Jonassaint, J.; Jackson, T.L.; Price, J.; Ataga, K.I.; Levesque, M.C.; Weinberg, J.B.; et al. Identification of genetic polymorphisms associated with risk for pulmonary hypertension in sickle cell disease. Blood 2008, 111, 5721–5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trembath, R.C.; Thomson, J.R.; Machado, R.D.; Morgan, N.V.; Atkinson, C.; Winship, I.; Simonneau, G.; Galie, N.; Loyd, J.E.; Humbert, M.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Genetic Features of Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K. BMPR2 mutations in pulmonary arterial hypertension with congenital heart disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 24, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klings, E.S.; A Dworkis, D.; Sedgewick, A.; Hartley, S.W.; Allison, A.-K.; Telen, M.J.; Kato, G.J.; Gladwin, M.; Sebastiani, P.; Baldwin, C.T.; et al. Genetic Polymorphisms in NEDD4L Are Associated with Pulmonary Hypertension of Sickle Cell Anemia. Blood 2009, 114, 2562–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotin, D.; Prag, G. Physiological Functions of the Ubiquitin Ligases Nedd4-1 and Nedd4-2. Physiology 2024, 39, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouraie, M.; Reading, N.S.; Campbell, A.; Minniti, C.; Rana, S.R.; Luchtman-Jones, L.; Sable, C.; Dham, N.; Ensing, G.; Kato, G.J.; et al. Cytochrome b5 Reductase T116S Mutation and Hemolysis in Sickle Cell Disease. Blood 2009, 114, 903–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordeuk, V.R.; Nouraie, M.; Niu, X.; DelBove, J.N.; Prchal, J.T. Cytochrome B5 Reductase T116S Polymorphism Is Associated with Decreased Risk of Severe Anemia Among Zambian Children with Malaria. Blood 2010, 116, 4233–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.A.; Zhou, T.; Ahmad, H.; Zhang, W.; Mu, W.; Trevino, S.; Wade, M.S.; Raghavachari, N.; Kato, G.J.; Peters-Lawrence, M.H.; et al. A Novel Molecular Signature for Elevated Tricuspid Regurgitation Velocity in Sickle Cell Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geard, A.; Pule, G.D.; Chelo, D.; Bitoungui, V.J.N.; Wonkam, A. Genetics of Sickle Cell-Associated Cardiovascular Disease: An Expert Review with Lessons Learned in Africa. OMICS: A J. Integr. Biol. 2016, 20, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogimori, K.; Hori, T.; Kawaguchi, K.; Fukui, T.; Mii, S.; Nakada, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Yamauchi, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Furukawa, K.; et al. Increased expression levels of ppGalNAc-T13 in lung cancers: Significance in the prognostic diagnosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 50, 746–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shozu, K.; Kaneko, S.; Shinkai, N.; Dozen, A.; Kosuge, H.; Nakakido, M.; Machino, H.; Takasawa, K.; Asada, K.; Komatsu, M.; et al. Repression of the PRELP gene is relieved by histone deacetylase inhibitors through acetylation of histone H2B lysine 5 in bladder cancer. Clin. Epigenetics 2022, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Yerneni, S.S.; Azambuja, J.H.; Gillespie, D.G.; Menshikova, E.V.; Jackson, E.K.; Whiteside, T.L. Tumor-derived exosomes promote angiogenesis via adenosine A2B receptor signaling. Angiogenesis 2020, 23, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Ma, S.-F.; Desai, A.A.; Saraf, S.; Miasniakova, G.; Sergueeva, A.; Ammosova, T.; Xu, M.; Nekhai, S.; et al. Hypoxic Response Contributes to Altered Gene Expression and Precapillary Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients With Sickle Cell Disease. Circ. 2014, 129, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellithy, H.N.; Yousri, S.; Shahin, G.H. Relation between glutathione S-transferase genes (GSTM1, GSTT1, and GSTP1) polymorphisms and clinical manifestations of sickle cell disease in Egyptian patients. Hematology 2015, 20, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousry, S.M.; Ellithy, H.N.; Shahin, G.H. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphisms and the risk of vasculopathy in sickle cell disease. Hematology 2016, 21, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, J.P.; Stearman, R.S.; Bull, T.M.; Calabrese, D.W.; Tripp-Addison, M.L.; Wick, M.J.; Broeckel, U.; Robbins, I.M.; Wheeler, L.A.; Cogan, J.D.; et al. Loss-of-function thrombospondin-1 mutations in familial pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 302, L541–L554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, S.A.; Novelli, E.M.; Isenberg, J.S.; Garrett, M.E.; Chu, Y.; Soldano, K.; Ataga, K.I.; Telen, M.J.; Ashley-Koch, A.; Gladwin, M.T.; et al. Thrombospondin-1 gene polymorphism is associated with estimated pulmonary artery pressure in patients with sickle cell anemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, E31–E34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, N.M.; Yao, M.; Sembrat, J.; George, M.P.; Knupp, H.; Ross, M.; Sharifi-Sanjani, M.; Milosevic, J.; Croix, C.S.; Rajkumar, R.; et al. Cellular, Pharmacological, and Biophysical Evaluation of Explanted Lungs from a Patient with Sickle Cell Disease and Severe Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2013, 3, 936–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, K.G.; Agyingi, S.E.; Nwabuobi, C.K.; Thomas, B.N. Polymorphism of the endothelin-1 gene (rs5370) is a potential contributor to sickle cell disease pathophysiology. Genes Dis. 2016, 3, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorshied, M.M.; Mohamed, N.S.; Hamza, R.S.; Ali, R.M.; El-Ghamrawy, M.K. Protein Z and Endothelin-1 genetic polymorphisms in pediatric Egyptian sickle cell disease patients. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2017, 32, e22264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, T.J.; Guindo, A.; Cullifer, L.R.; Li, Y.; Imumorin, I.G.; Diallo, D.A.; Thomas, B.N. Endothelin-1 but not Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Gene Polymorphism is Associated with Sickle Cell Disease in Africa. Gene Regul. Syst. Biol. 2014, 8, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afifi, R.A.-R.A.-A.; Sedky, Y.M.; Abd-Elkareem, H.; Botros, S.K.A. IL-Iβ +3954 C / T Polymorphism and Its Clinical Associations in Egyptian Sickle Cell Disease Patients. Int. J. Hematol. Stem Cell Res. 2019, 13, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicari, P.; Adegoke, S.A.; Mazzotti, D.R.; Cançado, R.D.; Noguti, M.A.E.; Figueiredo, M.S. Corrigendum to “Interleukin-1β and interleukin-6 gene polymorphisms are associated with manifestations of sickle cell anemia” [Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 54/3(2014), 244–249]. Blood Cells, Mol. Dis. 2015, 54, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakkakula, B. Association between MTHFR 677C>T polymorphism and vascular complications in sickle cell disease: A meta-analysis. Transfus. Clin. et Biol. 2019, 26, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prohaska, C.C.; Zhang, X.; Schwantes-An, T.L.; Stearman, R.S.; Hooker, S.; Kittles, R.A.; Aldred, M.A.; Lutz, K.A.; Pauciulo, M.W.; Nichols, W.C.; et al. RASA3 is a candidate gene in sickle cell disease-associated pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fertrin, K.Y.; Costa, F.F. Genomic polymorphisms in sickle cell disease: implications for clinical diversity and treatment. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2010, 3, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, M.H. Genetic Etiologies for Phenotypic Diversity in Sickle Cell Anemia. Sci. World J. 2009, 9, 46–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B. Integrated bioinformatics analysis reveals marker genes and immune infiltration for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountouris, P.; Stephanou, C.; Archer, N.; Bonifazi, F.; Giannuzzi, V.; Kuo, K.H.M.; Maggio, A.; Makani, J.; Mañú-Pereira, M.d.M.; Michailidou, K.; et al. The International Hemoglobinopathy Research Network (INHERENT): An international initiative to study the role of genetic modifiers in hemoglobinopathies. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, E416–E420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
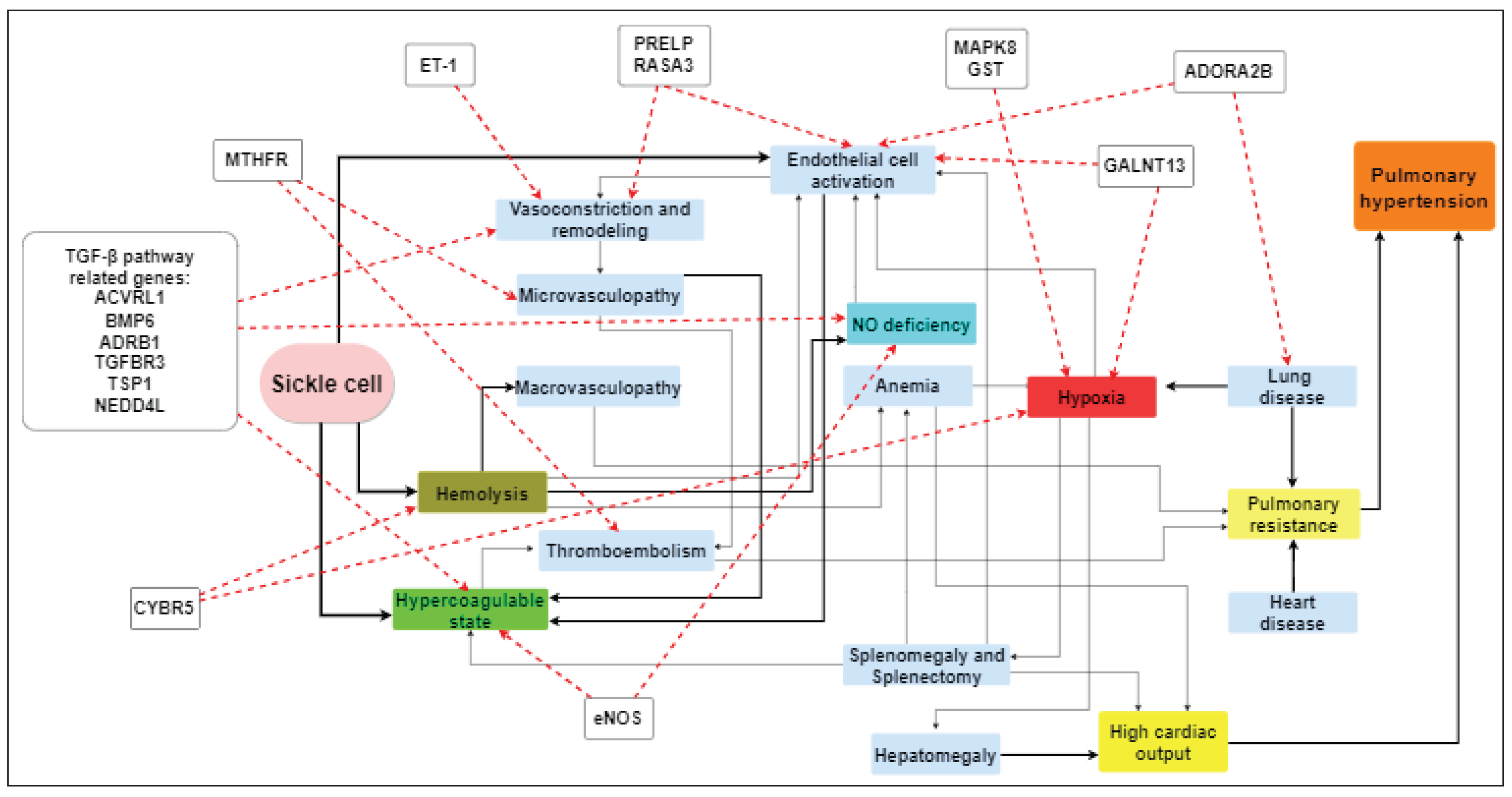
| Gene name | SNP/mutation | Study, Year | Number of patients | Ancestry | PH-related findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACVRL1 | rs3847859, rs706814 | Ashley-Koch et al., 2008 | 518 | N/A | Associated with the occurrence of PH |
| BMP6 | rs267192 | ||||
| ADRB1 | rs1801253, rs7921133 | ||||
| TGFBR3 | rs10874940 | ||||
| ARG2 | rs12587111, rs1885042 | Nominally associated with PH | |||
| NEDD4L | rs559046, rs1624292 | Klings et al., 2009 | 59 | N/A | Associated with a TRV ≥ 2.5 m/sec |
| 4 SNPs in intron 1 | 139 | Associated with elevated NT-pro-BNP levels | |||
| CYBR5 | T116S | Nouraie et al.,2009 | 261 | N/A | Heterozygosity and homozygosity for the CYBR5 T116S associated with lower TRV |
| GALNT13 | rs799813, rs10497120, rs13407922, rs16833378, rs9808145 |
Desai et al., 2012 | 27 | African American | Associated with elevated TRV |
| PRELP | rs2794452 | ||||
| ADORA2B | rs7208480 | ||||
| MAPK8 | rs10857560 | Zhang et al., 2014 | 61 | African American | Associated with precapillary PH |
| GST |
GSTM1, GSTT1, GSTP1 |
Ellithy et al., 2015 | 100 | Egyptian | Absence of both GSTM1 and GSTT1 genes significantly associated with developing PH |
| eNOS | eNOS 4a/b, eNOS 786T>C, C-4a |
Yousry et al., 2016 | 100 | Egyptian | Wild-type eNOS-4a/4b genotype seemed protective against VOC and PH. Mutant homozygous haplotype (C-4a) associated with the risk of ACS, VOC, and PH |
| TSP1 | rs1478604, rs1478605 | Jacob et al., 2017 | 406 | N/A | Associated with elevated TRV |
| ET-1 | G5665T | Khorshied et al., 2018 | 100 | Egyptian | Pulmonary dysfunction (PH and ACS) more frequent in patients with the polymorphic genotypes |
| IL-1 β | +3954 | Afifi et al.,2019 | 50 | Egyptian | Mutant genotype more prevalent in cases with PH. Mean ESPAP significantly higher among mutant genotypes. |
| Vicari et al., 2015 | 107 | Brazilian | |||
| MTHFR | 677C>T | Lakkakula et al.,2019 | 614 | N/A | Mutant genotype associated with increased risk of vascular events |
| RASA3 | rs9525228 | Prohaska et al.,2023 | 171 | African American | SNP correlated with PH risk, higher TRV and pulmonary vascular resistance and associated with precapillary PH values and decreased survival in a subgroup of the patients |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





