Submitted:
29 March 2024
Posted:
01 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
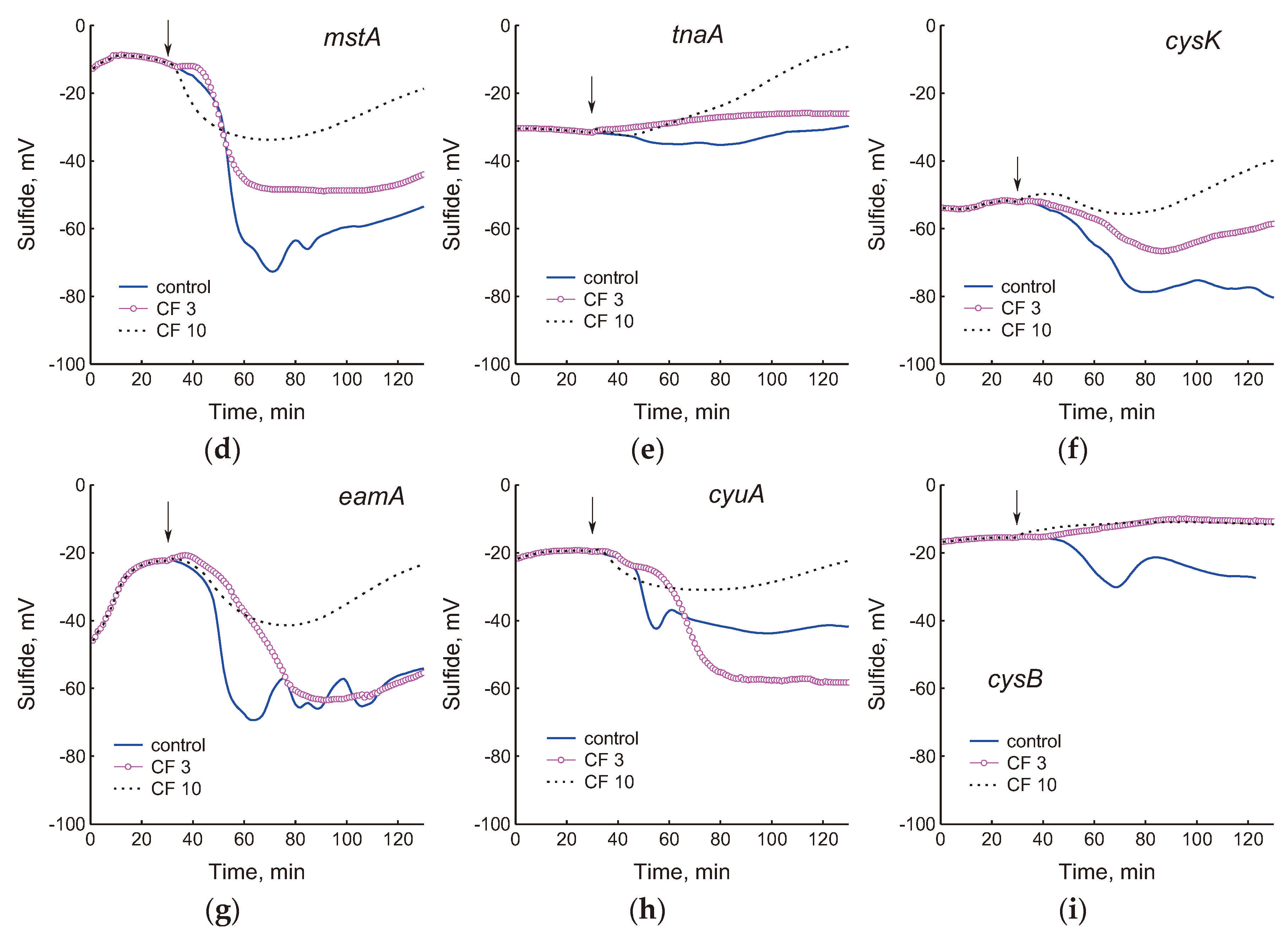
2.1. Effect of Mutations in Cysteine Homeostasis on H2S Production in the Absence and Presence of Ciprofloxacin
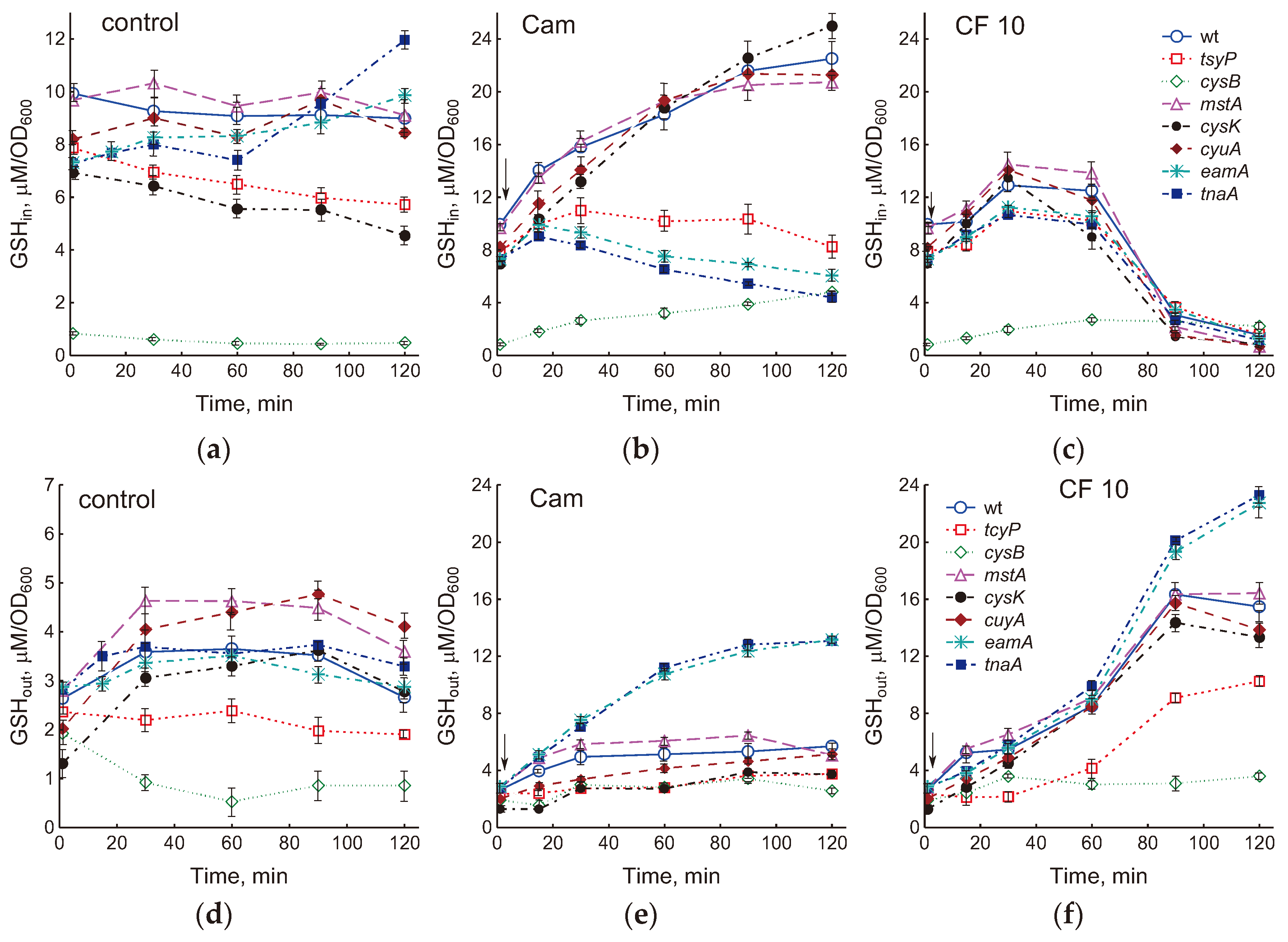
2.2. Effect of Mutations in Cysteine Homeostasis on Changes in Intra- and Extracellular Glutathione
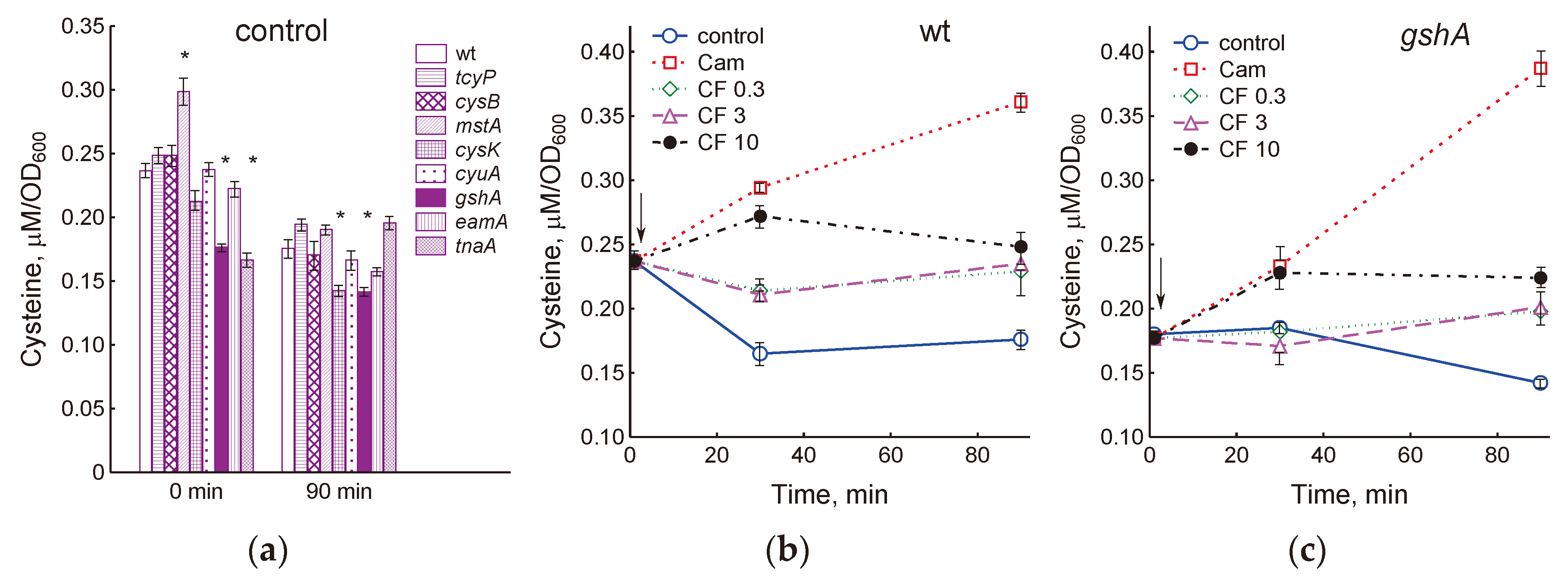
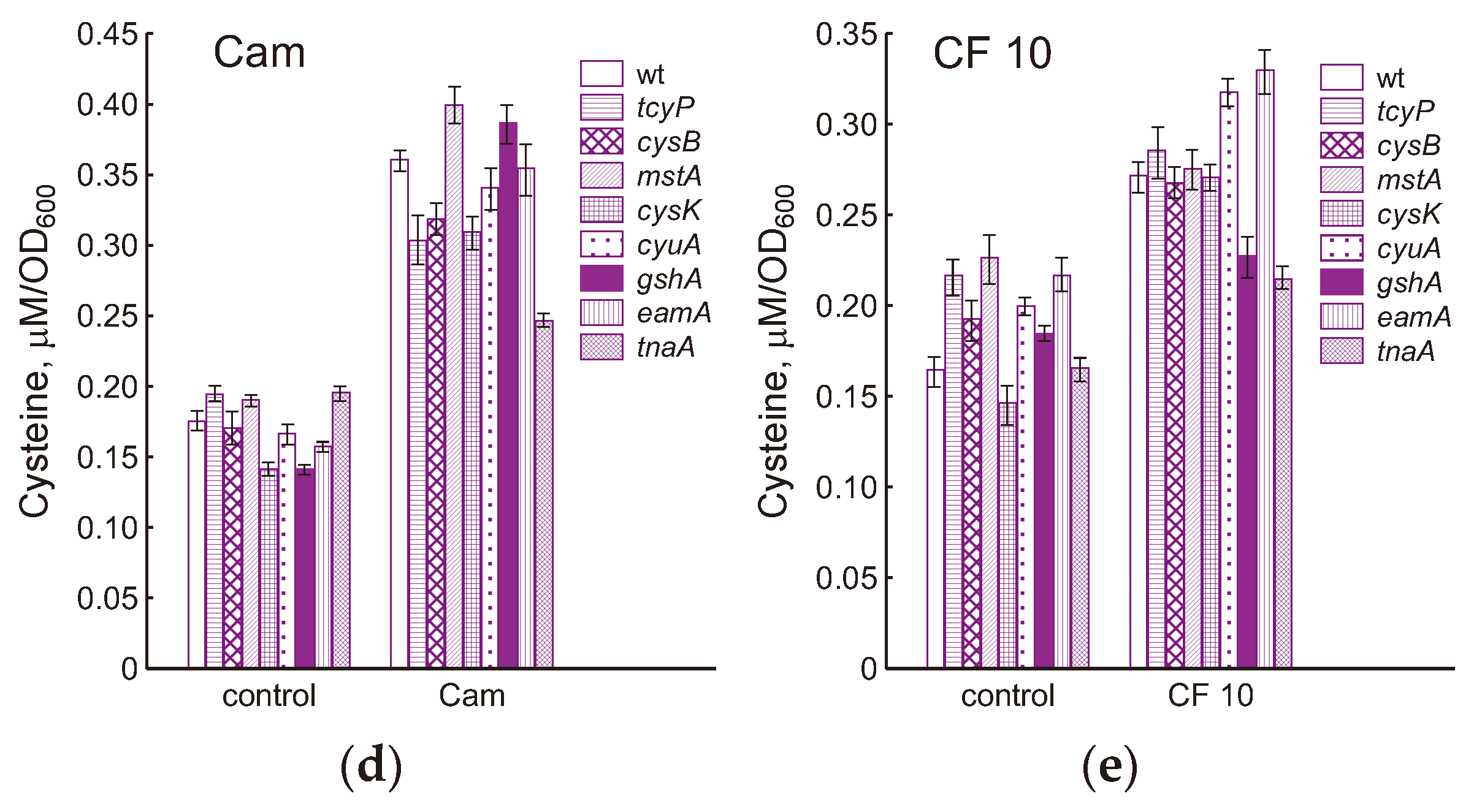
2.3. Effect of the Studied Mutations on the Level of Intracellular Cysteine during Normal Growth and Exposure to Antibiotics
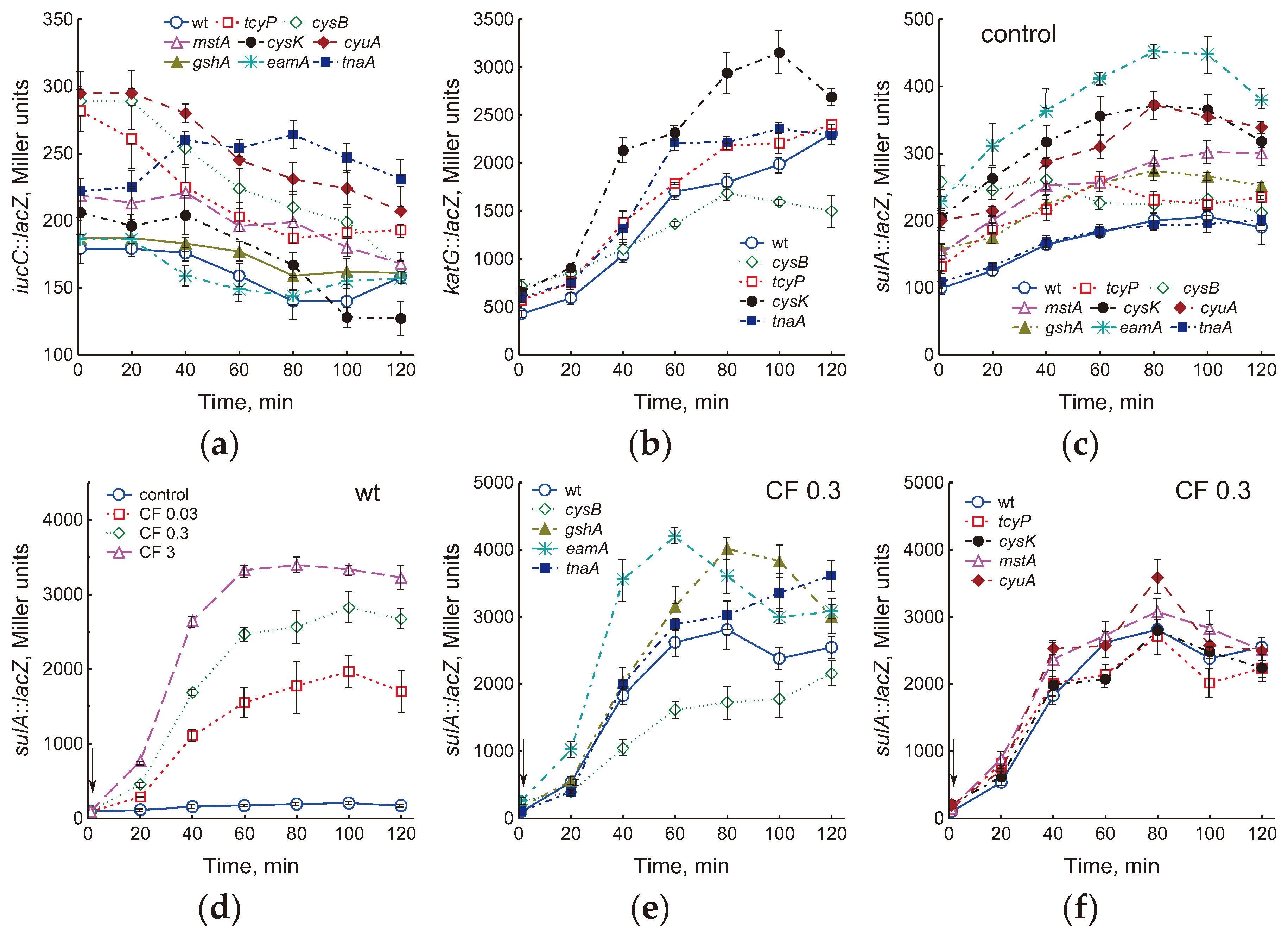
2.4. Changes in the Expression of Antioxidant Genes in the Studied Mutants
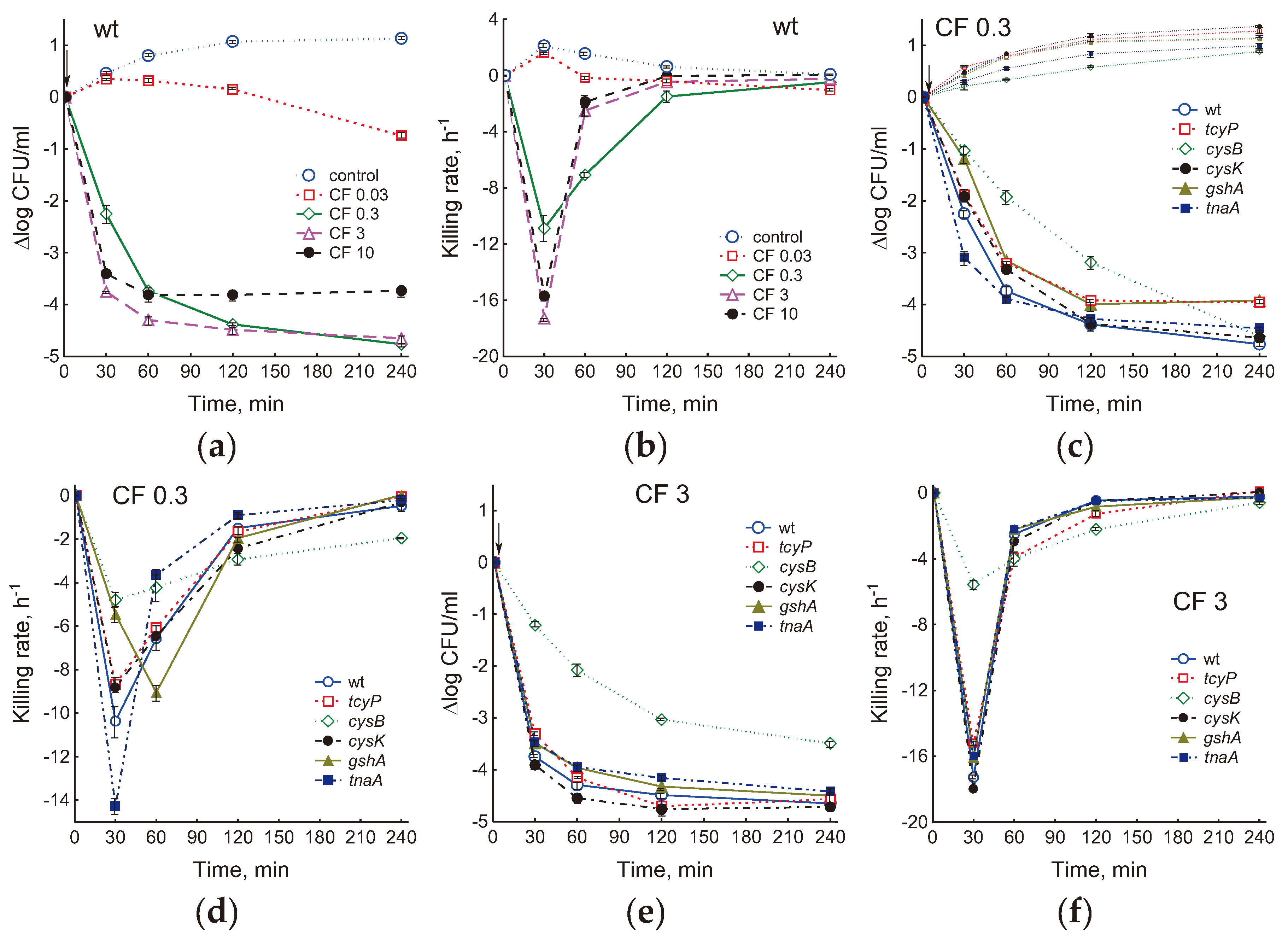
2.5. Consequence of the Studied Mutations on the Physiological Parameters of E. coli and Ciprofloxacin Sensitivity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Real-Time Monitoring of Dissolved Oxygen (dO2), pH and Sulfide
4.3. Determination of H2S, Cysteine and Glutathione
4.4. Study of Cellular Viability and Gene Expression
4.5. Statistical Analysis of the Data
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tikhomirova, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Kidd, S.P.; Fererro, R.L.; Roujeinikova, A. Cysteine and resistance to oxidative stress: implications for virulence and antibiotic resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Imlay, J.A. High levels of intracellular cysteine promote oxidative DNA damage by driving the Fenton reaction. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1942–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imlay, K.R.C.; Korshunov, S.; Imlay, J.A. Physiological roles and adverse effects of the two cystine importers of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 3629–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitzer, L. Catabolism of amino acids and related compounds. EcoSal Plus. 2005, 1, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kredich, N.M. The molecular basis for positive regulation of cys promoters in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 2747–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kredich, N. Biosynthesis of cysteine. EcoSal Plus. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, G.V.; Tyulenev, A.V.; Bezmaternykh, K.V.; Muzyka, N.G.; Ushakov, V.Y.; Oktyabrsky, O.N. Cysteine homeostasis under inhibition of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli cells. Amino Acids 2019, 51, 1577–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korshunov, S.; Imlay, K.R.C.; Imlay, J.A. Cystine import is a valuable but risky process whose hazards Escherichia coli minimizes by inducing a cysteine exporter. Mol. Microbiol. 2020, 113, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daẞler, T.; Maier, T.; Winterhalter, C.; Böck, A. Identification of a major facilitator protein from Escherichia coli involved in efflux of metabolites of the cysteine pathway. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 36, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, M.S.; Corker, H.; Wu, G.H.; Binet, M.B.; Moir, A.J.G.; Poole, R.K. Cysteine is exported from Escherichia coli cytoplasm by CydDC, an ATP-binding cassette-type transporter required for cytochrome assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49841–49849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, I.; Resch, A.; Daßler, T.; Maier, T.; Bӧck, A. YfiK from Escherichia coli promotes export of O-acetylserine and cysteine. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awano, N.; Wada, M.; Mori, H.; Nakamori, S.; Takagi, H. Identification and functional analysis of Escherichia coli cysteine desulfhydrases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4149–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Tanaka, K.; Ishihama, A. Transcription factor DecR (YbaO) controls detoxification of L-cysteine in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 2016, 162, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, G.; Takumi, K. Cysteine degradation gene yhaM, encoding cysteine desulfidase, serves as a genetic engineering target to improve cysteine production in Escherichia coli. AMB Expr. 2017, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loddeke, M.; Schneider, B.; Oguri, T.; Mehta, I.; Xuan, Z.; Reitzer, L. Anaerobic cysteine degradation and potential metabolic coordination in Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2017, 199, e00117–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatalin, K.; Shatalina, E.; Mironov, A.; Nudler, E. H2S: A universal defense against antibiotics in bacteria. Science 2011, 334, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Li, H.; Qi, H.; Qian, J.; Yan, S.; Shi, J.; Niu, W. Hydrogen sulfide from cysteine desulfurase, not 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase, contributes to sustaining cell growth and bioenergetics in E. coli under anaerobic conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyulenev, A.; Smirnova, G.; Muzyka, N.; Ushakov, V.; Oktyabrsky, O. The role of sulfides in stress-induced changes of Eh in Escherichia coli cultures. Bioelectrochem. 2018, 121, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyulenev, A.V.; Smirnova, G.V.; Muzyka, N.G.; Oktyabrsky, O.N. Study of the effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on growing bacteria Escherichia coli using electrochemical sensors. Acta biomedica scientifica. 2022, 7, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, G.V.; Tyulenev, A.V.; Bezmaternykh, K.V.; Muzyka, N.G.; Ushakov, V.Y.; Oktyabrsky, O.N. Phosphate starvation is accompanied by disturbance of intracellular cysteine homeostasis in Escherichia coli. Res. Microbiol. 2023, 174, 104108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsu, I.; Wiriyathanawudhiwong, N.; Morigasaki, S.; Nakatani, T.; Kadokura, H.; Takagi, H. The L-cysteine/L-cystine shuttle system provides reducing equivalents to the periplasm in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17479–17487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironov, A.; Seregina, T.; Nagornykh, M.; Luhachack, L.G.; Korolkova, N.; Lopes, L.E.; Kotova, V.; Zavilgelsky, G.; Shakulov, R.; Shatalin, K.; Nudler, E. Mechanism of H2S-mediated protection against oxidative stress in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6022–6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, P.; Khodade, V.S.; SharathChandra, M.; Chauhan, P.; Mishra, S.; Siddaramappa, S.; Pradeep, B.E.; Singh, A.; Chakrapani, H. “On demand” redox buffering by H2S contributes to antibiotic resistance revealed by a bacteria-specific H2S donor. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 4967–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, V.K.; Bandyopadhyay, P.; Singh, A. Hydrogen sulfide in physiology and pathogenesis of bacteria and viruses. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, V.; Chinta, K.C.; Reddy, V.P.; Glasgow, J.N.; Stein, A.; Lamprecht, D.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Truebody, B.E.; Adamson, J.H.; Kunota, T.T.R.; Bailey, S.M.; Moellering, D.R.; Lancaster, Jr. J.R.; Steyn, A.J.C. Hydrogen sulfide stimulates Mycobacterium tuberculosis respiration, growth and pathogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Kitamura, Y.; Zhang, T.; Tsutsuki, H.; Rahman, A.; Ihara, T.; Akaike, T.; Sawa, T. Cysteine hydropersulfide inactivates β-lactam antibiotics with formation of ring-opened carbothioic S-acids in bacteria. ACS Chem. Biol. 2021, 16, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatalin, K.; Nuthanakanti, A.; Kaushik, A.; Shishov, D.; Peselis, A.; Shamovsky, I.; Pani, B.; Lechpammer, M.; Vasilyev, N.; Shatalina, E.; Rebatchouk, D.; Mironov, A.; Fedichev, P.; Serganov, A.; Nudler, E. Inhibitors of bacterial H2S biogenesis targeting antibiotic resistance and tolerance. Science 2021, 372, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giedroc, D.P.; Antelo, G.T.; Fakhoury, J.N.; Capdevila, D.A. Sensing and regulation of reactive sulfur species (RSS) in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2023, 76, 102358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, G.; Tyulenev, A.; Muzyka, N.; Ushakov, V.; Samoilova, Z.; Oktyabrsky, O. Influence of growth medium composition on physiological responses of Escherichia coli to the action of chloramphenicol and ciprofloxacin. BioTech 2023, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontenot, C.R.; Ding, H. Ferric uptake regulator (Fur) binds a [2Fe–2S] cluster to regulate intracellular iron homeostasis in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maringanti, S.; Imlay, J.A. An intracellular iron chelator pleiotropically suppresses enzymatic and growth defects of superoxide dismutase-deficient Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 3792–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, A.; Miller, C.; Glinsky, G.; Eisenstark, A. Role of the rpoS(katF) in oxyR independent regulation of hydroperoxidase I in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 12, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslowska, K.H.; Makiela-Dzbenska, K.; Fijalkowska, I.J. The SOS system: a complex and tightly regulated response to DNA damage. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2019, 60, 368–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, N.G.; Diez-Santos, I.; Abbott, L.R.; Maxwell, A. Quinolones: Mechanism, lethality and their contributions to antibiotic resistance. Molecules 2020, 25, 5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, G.V.; Tyulenev, A.V.; Muzyka, N.G.; Peters, M.A.; Oktyabrsky, O.N. Ciprofloxacin provokes SOS-dependent changes in respiration and membrane potential and causes alterations in the redox status of Escherichia coli. Res. Microbiol. 2017, 168, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Xin, Y.; Xuan, G.; Zhao, R.; Liu, H.; Xia, Y.; Xun, L. Escherichia coli uses separate enzymes to produce H2S and reactive sulfane sulfur from L-cysteine. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunov, S.; Imlay, K.R.C.; Imlay, J.A. The cytochrome bd oxidase of Escherichia coli prevents respiratory inhibition by endogenous and exogenous hydrogen sulfide. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 101, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luhachack, L.; Rasouly, A.; Shamovsky, I.; Nudler, E. Transcription factor YcjW controls the emergency H2S production in E. coli. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, G.V.; Tyulenev, A.V.; Muzyka, N.G.; Oktyabrsky, O.N. Study of the contribution of active defense mechanisms to ciprofloxacin tolerance in Escherichia coli growing at different rates. Ant. Van Leeuwen. 2022, 115, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewen, P.C. Levels of glutathione in Escherichia coli. Can. J. Biochem. 1979, 57, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, A.L.; Surette, M.G. Cysteine biosynthesis, oxidative stress and antibiotic resistance in Salmonella typhimurium. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohanski, M.A.; Dwyer, D.J.; Hayete, B.; Lawrence, C.A.; Collins, J.J. A common mechanism of cellular death induced by bactericidal antibiotics. Cell 2007, 130, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, D.J.; Belenky, P.A.; Yang, J.H.; MacDonald, I.C.; Martell, J.D.; Takahashi, N.; Chan, C.T.Y.; Lobritz, M.A.; Braff, D.; Schwarz, E.G.; et al. Antibiotics induce redox-related physiological alterations as part of their lethality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E2100–E2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.H.; Bening, S.C.; Collins, J.J. Antibiotic efficacy–context matters. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 39, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren, I.; Wu, Y.; Inocencio, J.; Mulcahy, L.R.; Lewis, K. Killing by bactericidal antibiotics does not depend on reactive oxygen species. Science 2013, 339, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Imlay, J.A. Cell death from antibiotics without the involvement of reactive oxygen species. Science 2013, 339, 1210–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imlay, J.A. Diagnosing oxidative stress in bacteria: Not as easy as you might think. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 24, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Li, Q.; Gao, Q.; Xie, J.; Huang, H.; Drlica, K.; Zhao, X. Reactive oxygen species play a dominant role in all pathways of rapid quinolone-mediated killing. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, G.; Muzyka, N.; Lepekhina, E.; Oktyabrsky, O. Roles of the glutathione- and thioredoxin-dependent systems in the Escherichia coli responses to ciprofloxacin and ampicillin. Arch. Microbiol. 2016, 198, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, G.V.; Oktyabrsky, O.N. Relationship between Escherichia coli growth rate and bacterial susceptibility to ciprofloxacin. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fnx254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Fravega, J.; Rodas, P.I.; Fuentes, J.A.; Paredes-Sabja, D.; Calderon, I.L.; Gil, F. Participation of S. typhimurium cysJIH operon in the H2S-mediated ciprofloxacin resistance in presence of sulfate as sulfur source. Antibiotics 2015, 4, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodore, A.; Lewis, K.; Vulic, M. Tolerance of Escherichia coli to fluoroquinolone antibiotics depends on specific components of the SOS response pathway. Genetics 2013, 195, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fravega, J.; Alvarez, R.; Dıaz, F.; Inostroza, O.; Tejıas, C.; Rodas, P.I.; Paredes-Sabja, D.; Fuentes, J.A.; Calderon, I.L.; Gil, F. Salmonella Typhimurium exhibits fluoroquinolone resistance mediated by the accumulation of the antioxidant molecule H2S in a CysK-dependent manner. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 3409–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, T.; Ara, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Takai, Y.; Okumura, Y.; Baba, M.; et al. Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: the Keio collection. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2, 2006–0008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Ramos, H.; Cook, G.M.; Wu, G.; Cleeter, M.W.; Poole, R.K. Membrane topology and mutational analysis of Escherichia coli CydDC, an ABC-type cysteine exporter required for cytochrome assembly. Microbiology 2004, 150, 3415–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, K.; Makino, K.; Yonei, S.; Nacata, A.; Shinagawa, H. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequencing of oxyR, the positive regulatory gene of a regulon for an adaptive response to oxidative stress in Escherichia coli: homologies between OxyR protein and a family of bacterial activator proteins. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1989, 218, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkert, M.R.; Gately, F.H.; Hajec, L.I. Expression of DNA damage-inducible genes of Escherichia coli upon treatment with methylating, ethylating and propylating agents. Mutation Res. 1989, 217, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitonde, M.K. A spectrophotometric method for the direct determination of cysteine in the presence of other naturally occurring amino acids. Biochem. J. 1967, 104, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, G.; Muzyka, N.; Oktyabrsky, O. Transmembrane glutathione cycling in growing Escherichia coli cells. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 167, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically: approved standard. CLSI publication M07–A8. Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute, Wayne PA. 2009.
- Regoes, R.R.; Wiuff, C.; Zappala, R.M.; Garner, K.N.; Baquero, F.; Levin, B.R. Pharmacodynamic functions: a multiparameter approach to the design of antibiotic treatment regimens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3670–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.H. Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. 1972.



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




