1. Introduction
1.1. Review
With the development of stealth technology and aircraft technology, there has been a large number of high-speed airborne maneuvering targets with weak echoes. How to enhance the echoes of such targets and achieve effective detection has become a research hotspot in the field of radar signal processing [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. Long-time coherent integration is an effective means to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of pulse Doppler radar reception and enhance target detection capability [
10,
11]. However, for high-speed maneuvering targets, within a long integration time, the target’s movement distance will span multiple range cells, leading to the range migration (RM) effect. This will result in the spread of the target peak energy and the decrease of SNR in the coherent integration results, thereby affecting the radar’s detection capability. Therefore, the appropriate methods is needed to mitigate the RM effect.
In [
12,
13,
14], the envelope alignment method is used to correct RM, but it requires a relatively high SNR. The Radon Fourier Transform (RFT) [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19] can effectively overcome the coupling between RM and phase modulation by jointly searching along the range and velocity directions of the moving target, but it has the problem of large search computation. The adjacent cross correlation function (ACCF) [
20,
21] is a fast non-searching motion estimation method, which uses iterative adjacent cross correlation operations to eliminate RM. However, it requires a relatively high SNR. In comparison, the Keystone transform (KT) is applicable even at low SNR, with algorithm parameters depending only on system parameters rather than the motion parameters of the detected targets when there is no velocity ambiguity or when the velocity ambiguity number is known. It can simultaneously perform linear RM compensation on multiple targets. These advantages make it a commonly used method for RM compensation.
The KT was originally proposed by Perry [
22] and widely used in synthetic aperture radar [
23,
24,
25,
26]. In [
27,
28,
29], KT was applied to the ISAR imaging field. Zhang
et al.[
30] introduced it into the long-time target detection field of pulse radar, proposing a weak target detection method based on KT, where the signal is converted to the fast time frequency dimension and then interpolates along the slow time dimension to achieve KT. In order to facilitate hardware implementation, a KT method using complex multiplication and FFT was developed in [
31]. On this basis, a method based on the Chirp-z transform (CZT) for implementation was proposed in [
32], which has lower computational complexity and is a commonly used implementation for KT. The computational efficiency of CZT in hardware has been further improved in [
33]. In [
34], a second-order KT was presented to eliminate the second-order RM.
1.2. Motivation
Although KT has achieved numerous results after more than twenty years of research, there are still issues worth further investigation in specific implementations. For pulse Doppler radar, the width of Doppler band compensated by KT is the size of one pulse repetition frequency (PRF), and the echo of high speed target often has Doppler ambiguity. Therefore, KT generally needs to be used in conjunction with the Doppler ambiguity compensation function. KT has the following issues: (1) KT implemented by sinc interpolation suffers from serious performance loss at the junctions of the compensation bands. Since these positions are near the “half-blind velocity (HBV)” points, this issue is referred to as the “half-blind-velocity” effect (HBVE) [
35,
36]. (2) When the narrow Doppler frequency range (NDFR) of targets crosses two adjacent compensation Doppler bands, it results in a large amount of computation for performing KT twice. Both of these issues are closely related to the fixed setting of compensation Doppler bands. Detailed issues will be discussed in
Section 2 of this paper. To address the issues in KT, this paper proposes a variable Doppler starting point Keystone transform (VDSPKT) method, which changes the compensated ambiguity number from a fixed value to a value set as needed. The advantages of the proposed approach can mainly be reflected as follows:
The compensation flexibility of KT is improved by transforming the Doppler ambiguity compensation function from an integer form to a fractional form, allowing the compensation bands to be adjusted as needed.
The HBVE in sinc interpolation is efficiently addressed by defining the effective gain portion in compensation Doppler bands as new bands through changing their connection points.
The efficiency of KT in compensating for NDFRs is significantly improved by adjusting the compensation band to cover a NDFR, reducing the calculation times from two to one when the NDFR spans two compensation Doppler bands.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: In
Section 2, the issues in KT are detailed. In
Section 3, the theoretical principles of the VDSPKT are introduced. In
Section 4, the effectiveness and efficiency of the method are verified through simulation experiments. Finaly, the conclusion is presented in
Section 5.
2. Comprehensive Analysis of Issues in KT
2.1. Signal Model and Keystone Transform
2.1.1. Signal Model
Suppose that the radar transmits a linear frequency modulated (LFM) signal, i.e.,
where
means the rectangular window function,
denotes the pulse duration,
represents the frequency modulated rate of LFM signal.
Assuming there is a moving target in space, with a distance
from the radar and a radial velocity
, the equation describing the variation of the distance
between it and the radar is given by
where
is the slow time,
denotes the pulse repetition time.
The received baseband echoes can be stated as
where
is the fast time,
represents the amplitude of echo,
c denotes the light speed,
is the carrier frequency.
After pulse compression (PC), the compressed signal can be expressed as
where
represents the amplitude,
denotes the bandwidth of the transmitted signal.
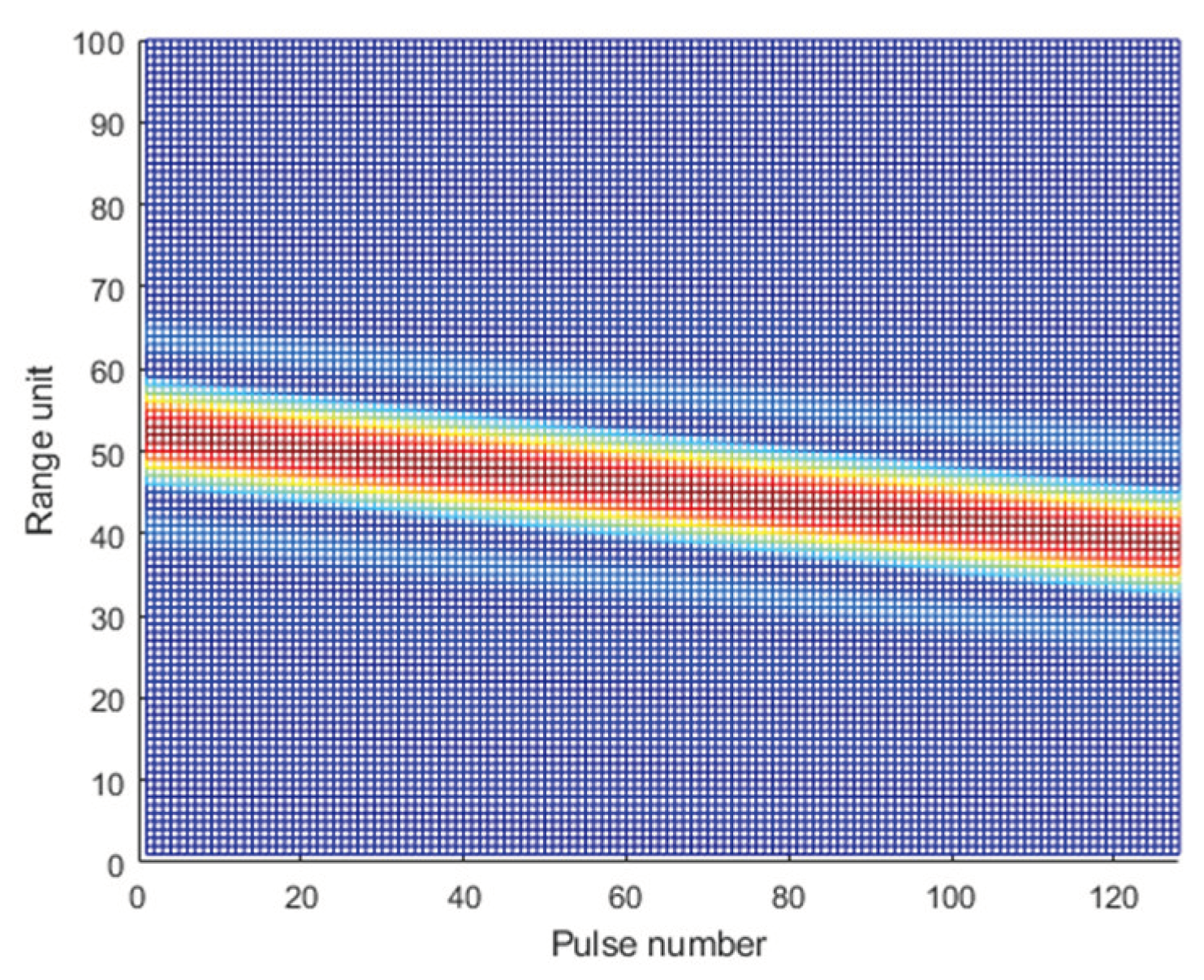
Equation (4) indicates that the center position of the pulse envelope shifts with slow time offset. When the envelope offset exceeds the distance unit, range migration occurs. The RM phenomenon in the PC result is shown in
Figure 1.
According to the principle of stationary phase, the fast-time-frequency domain signal of equation (4) is obtained as follows:
where
and
represent the fast-time frequency and the carrier frequency respectively.
stands for the amplitude. As observed from equation (5) there is coupling between the fast-time frequency
and the slow time
, corresponding to the envelope migration in the time domain. The faster the target velocity and the longer the integration time, the more severe the range migration issue becomes, which limits the coherent integration gain. The RM causes spreading of the peak energy of the target in the coherent integration result and leads to a decrease in the SNR, thus affecting the target detection performance of the radar.
2.1.2. Keystone Transform
KT is an effective method for compensating RM. The principle of KT is to perform scale transformation on the slow-time signal. Using KT formula
, we can substitute variables in equation (5), and the signal spectrum becomes
where
means the transformed slow time and
represents the amplitude of signal after KT. The spectrum of the signal, as represented in equation (6), shows that the fast-time frequency is decoupled from the slow time, thereby addressing the RM issue. Furthermore, by applying the Inverse Fast Fourier Transform (IFFT) to the fast-time dimension of equation (6), we obtain the time-domain representation of the signal after KT.
where
represents the amplitude of the signal after KT. From equation (7), it can be seen that for different pulses, the peak position of the signal remains constant at
,which no longer changes with the pulse. The echo corrections originally located in different distance units are adjusted to the same distance unit, compensating for RM.
In the formulas provided, time and frequency are both represented as continuous variables. However, in digital radar systems, these parameters need to be converted into discrete form. Let the discrete sampling order of fast time
t be represented by
l, the discrete sampling order of slow time
be denoted as
n, the digital representation of fast-time frequency
f be represented by
, and the index of slow-time frequency be denoted as
k. After converting the variables from continuous form to discrete form, formula (5) becomes
In practical radar signal processing, the implementation of KT relies on methods such as sinc interpolation and CZT.
2.2. Issues of “Half-Blind-Velocity” Effect
2.2.1. Sinc Interpolation
Sinc interpolation is a classical method for implementing KT. However, at the points near HBV, its performance will significantly degrade, an effect referred to as the HBVE. The formula for implementing KT based on sinc interpolation can be expressed as
where
N denotes the number of integration pulses,
is the index of the sampled points in the transformed slow-time domain,
is the number for compensating Doppler ambiguity. For a target with velocity
v, its Doppler centroid can be expressed as
where
is the wavelength,
is the PRF,
represents the real Doppler ambiguity number for the targets in sinc interpolation. Only when compensating with the Doppler ambiguity number
equaling to
, can equation (9) accurately compensate for RM caused by the target. Otherwise, there may be compensation mismatch, leading to a decrease in compensation gain.
2.2.2. “Half-Blind-Velocity” Effect
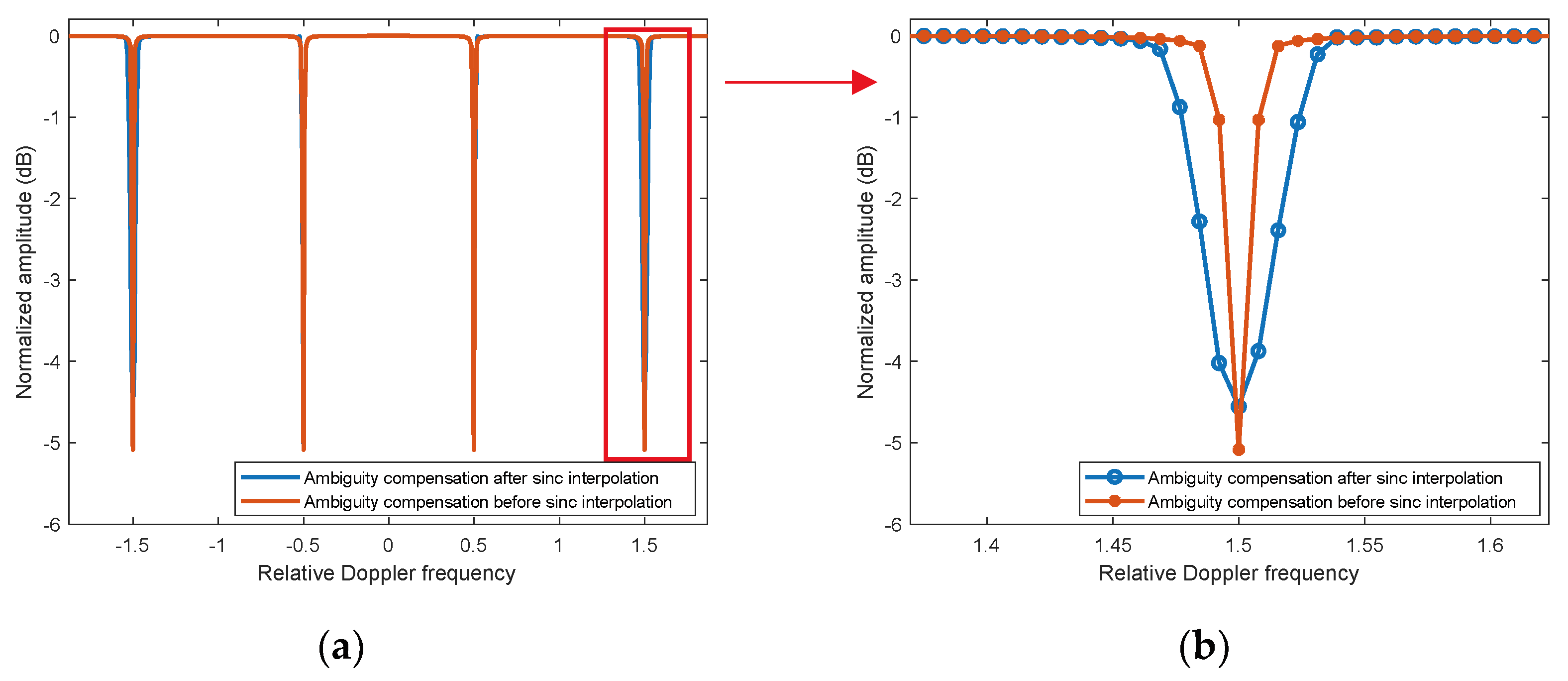
RM compensation gain of sinc interpolation for targets with different velocities is shown by the blue curve in
Figure 2. When the target velocity is near
, the compensation gain will decrease significantly.
Since the Doppler frequency generated by a target has a bandwidth. At the boundary of the compensation Doppler bands, some of the Doppler frequency enter the next compensation band, leading to a decrease in compensation gain. Therefore, the velocity bands where HBVE occurs can be derived as
The bands represented by equation (11) is referred to as the HBV bands. The width of HBV bands increases with the ambiguity number
. This problem can be suppressed by compensating for the ambiguity before sinc interpolation [
33]. Formula (9) can be converted as
Using formula (12) to calculate the compensation gain, as shown by the orange curve in
Figure 1b, it can be observed that each HBV band becomes the same width.
2.2.3. Existing Methods to Address the HBVE
In [
35], an additional calculation is performed after sinc interpolation calculation. For each HBV band, a modulation is applied to the PC data
using a compensation function
, which can shift the signal’s Doppler centroid from
to
. Then, another sinc interpolation calculation is performed, replacing the data in the HBV bands with the corresponding data from the additional calculation result. This method is referred to as the Doppler shift. While this method can solve the HBVE, it doubles the computation time, significantly increasing the computational load.
In [
36], the method of compensating for the ambiguity before sinc interpolation is performed. The ambiguity compensation function
is used to correct RM of all values in HBV bands approximately. Then the same replacement operation is performed. This method is referred to as the approximately compensating. Although it avoids the additional sinc interpolation calculation, reducing the computational load to some extent, it still requires an additional ambiguity compensation and Doppler filtering calculation, and the compensation effect is not ideal for points not located at the centers of HBV bands.
2.3. Issues Related to Narrow Doppler Frequency Range
Here, the issues of large computational complexity arises when compensating for targets with a NDFR using KT. This problem exists for all KT implementations, and here CZT is used for illustration.
2.3.1. Chirp-z Transform
CZT is more efficient and commonly used in engineering. KT can be achieved by performing a discrete Fourier transform (DFT) along the slow-time dimension of
with a frequency spacing of
, where
M here refers to the number of DFT points. CZT, using spiral sampling to calculate the z-transform, is a fast algorithm for computing the
M-point samples under non-uniform sampling conditions. The formula of CZT for implementing KT is
Then, by performing an IFFT calculation on the fast-time dimension of , the fast-time Doppler data is obtained, completing the RM correction.
Unlike sinc interpolation, the compensation Doppler band of CZT is
. For targets with Doppler exceeding this band, the Doppler ambiguity compensation function needed is given by
where
denotes the number of compensated Doppler ambiguity. The real Doppler ambiguity number of target is defined as
, where
represents the floor function. When
, the Doppler ambiguity can be accurately compensated. The transformation formula with ambiguity compensation is
By using equation (17), the compensation Doppler band of CZT becomes .
2.3.2. Narrow Doppler Frequency Range
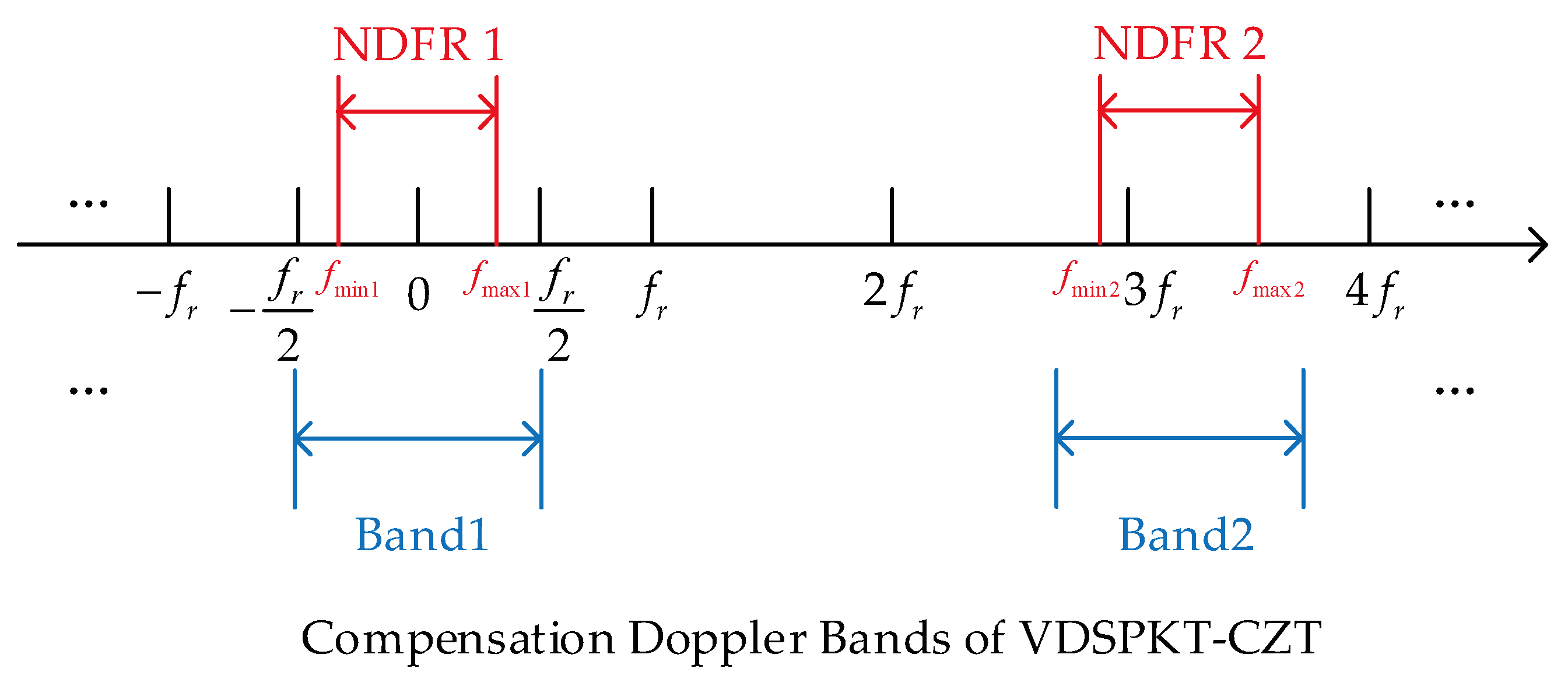
Assuming there are multiple targets in space with similar velocities, their Doppler frequencies are also close. When the difference between the maximum and minimum Doppler frequencies, and , is less than , this range is defined as the narrow Doppler frequency range, which is the precise definition of NDFR in this paper.
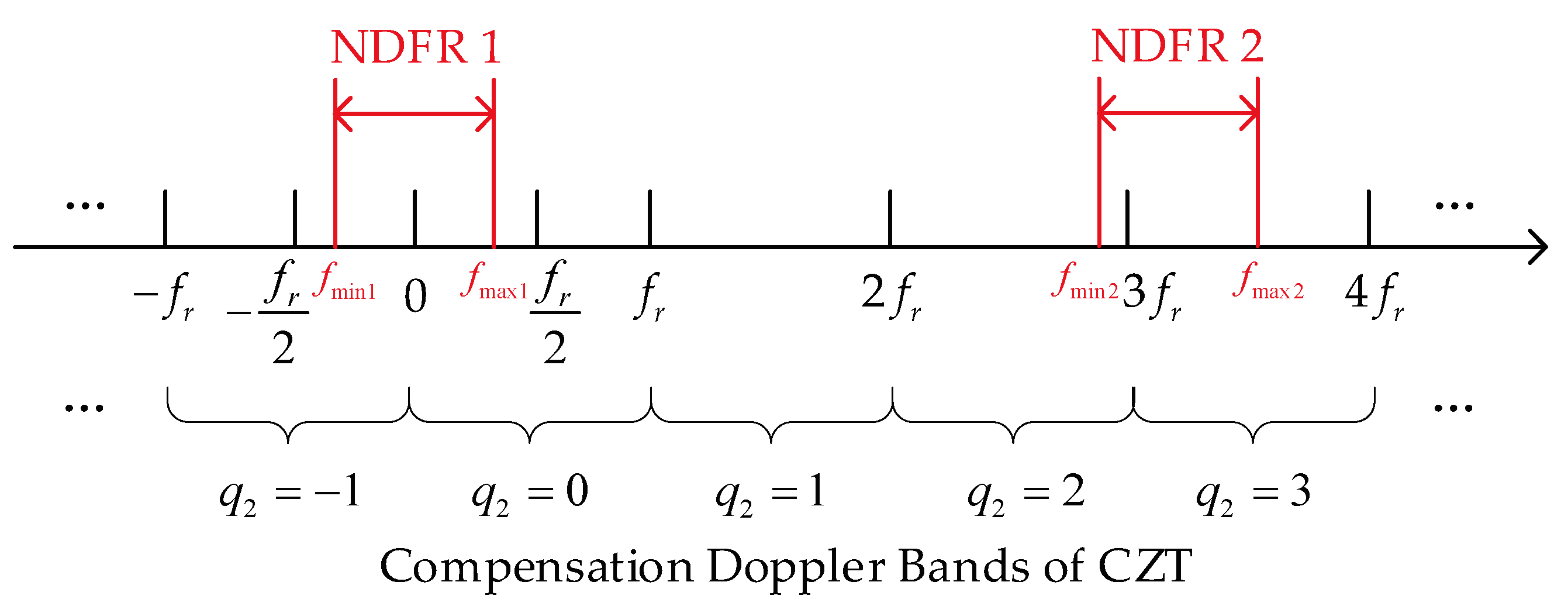
Although the width of NDFR is less than that of a Doppler compensation band, when NDFR spans two compensation bands, two corresponding Doppler ambiguity numbers need to be set, and two CZT calculations need to be performed to compensate for all targets’ RM. This issue is illustrated in
Figure 3.
In
Figure 3, the horizontal axis represents Doppler frequency, and the ranges marked by curly braces are the compensation Doppler bands. The band corresponding to the Doppler ambiguity number
is
, and the band corresponding to
is
.The red bands are 2 examples of NDFR. Within NDFR 1, CZT with
is needed to correct the RM of targets with Doppler between
, and CZT with
is required to compensate the RM of targets with Doppler between
. RM correction for all targets within this NDFR is completed.
Similarly, in NDFR 2, correction using CZT with is required for the RM of targets with Doppler between , while CZT with is needed for targets with Doppler between .
When NDFR spans two compensation Doppler bands, two CZT calculations are required to correct all targets’ RM. The total width of the two compensation bands is , while the width of NDFR is less than , which is less than half of the former, resulting in a serious waste of computation.
3. The Proposed VDSPKT Method
In
Section 2, two main issues were analyzed in detail. (1) The HBVE associated with sinc interpolation. (2) The computational complexity when a NDFR spans two compensation Doppler bands. Both of them are fundamentally related to the fixed setting of the compensation Doppler bands.
In this section, the principle of proposed VDSPKT is elaborated. By changing the Doppler compensation starting point, this method transforms the position of the compensation Doppler bands from fixed values to values that can be changed as needed, thereby addressing the issues raised.
3.1. VDSPKT Implemented by Sinc Interpolation (VDSPKT-SI)
The ambiguity number used for Doppler ambiguity compensation is an integer, resulting in a fixed set of compensation Doppler bands. Therefore, the position of compensation Doppler bands can be adjusted by changing the ambiguity number used. Further, based on equation (12), the formula for VDSPKT-SI is constructed as follows
where
, an integer, represents the parameter of the Doppler starting point, which shifts the starting point compensation Doppler band to
. Then the compensation Doppler band becomes
.
It is worth noting that, theoretically, replacing the integer ambiguity number
with other real numbers can also shift the starting point to a different frequency. However, the definition in this paper has its advantages. Generally, setting the total number of transformation points
M to a power of 2 facilitates FFT computation of the slow-time signal for Doppler filtering after. For convenience, in this paper, the number of points in the Doppler filtering is also defined as
M. When the ambiguity number is 0, the frequency points in the Doppler spectrum are
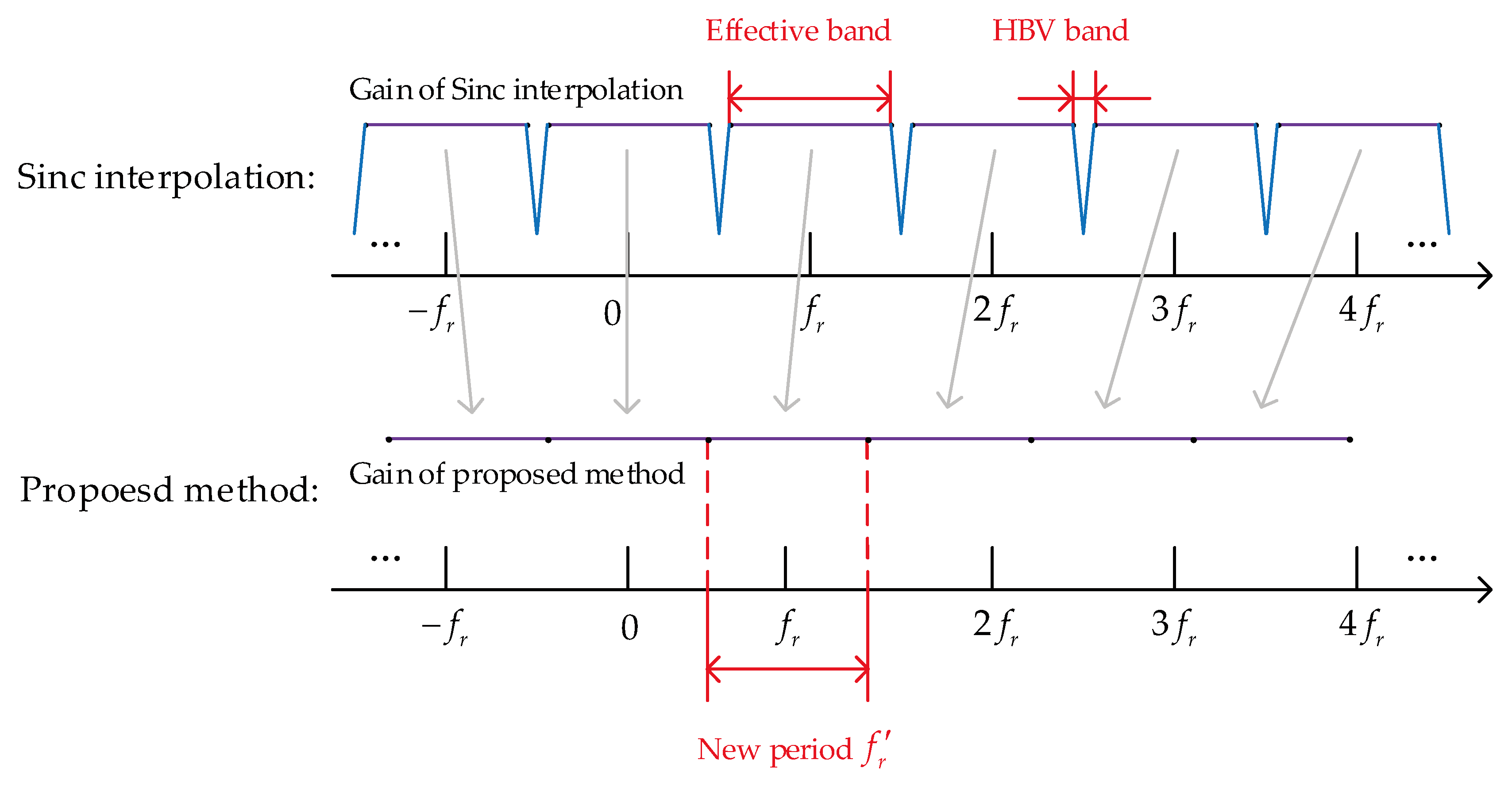
. This paper’s definition ensures continuity between the frequency points in the Doppler spectrum after VDSPKT and those obtained when the ambiguity number is 0. Further, the process of addressing HBVE using VDSPKT-SI is illustrated in
Figure 4.
According to the conclusion in
Section 2.2, by compensating ambiguity before sinc interpolation, the widths of the HBV bands under each ambiguity number become the same. The Doppler range excluding the HBV bands are defined as the effective bands. Taking the ambiguity number 0 as an example, the effective compensation Doppler band is given by
Since the Doppler value obtained from signal processing corresponds to the value at the frequency points in the Doppler spectrum, the frequency corresponding to the point in the Doppler spectrum is . Further, the smallest value of k that satisfies is defined as , and the largest value of k that satisfies is defined as . Therefore, the frequency corresponding to falls within the effective compensation Doppler band. And the number of points in the band is .
The width of effective bands is taken as the new Doppler compensation period. The new ambiguity number with is represented by , which is set in equation (18) to ensure the continuity of each effective band, i.e., the frequency difference between adjacent points of two neighboring effective bands is .This approach ensures that there is no longer HBVE in the new compensation Doppler bands.
3.2. VDSPKT Implemented by CZT (VDSPKT-CZT)
The principle of the VDSPKT has been explained in
Section 3.1. For CZT, by modifying the ambiguity compensation function in equation (17), we obtain the formula for the VDSPKT-CZT
The simplified equation is obtained by combining the two exponential terms to be
The compensation Doppler band of CZT becomes .
The illustration of VDSPKT addressing the issue of large computational complexity when the NDFR of targets spans two compensation Doppler bands is shown in
Figure 5. To ensure that the compensation Doppler band 1 includes NDFR 1, the value of
is set to satisfy
and
. Additionally, in order to leave some margin, the center of Band 1 is aligned as much as possible with the center of NDFR 1. Similarly, the value of
is set to satisfy
and
to make sure that the Band 2 covers NDFR 2. Likewise, the center of Band 2 is set to be aligned with the center of NDFR as far as possible.
For targets with NDFR spanning two compensation Doppler bands, the VDSPKT-CZT can include the compensation band in NDFR, reducing the CZT calculation times from two to one, which significantly reduces the computational complexity.
4. Simulation Experiments
Here, the effectiveness of the VDSPKT is validated through simulation experiments. The radar parameters for simulation are shown in
Table 1.
4.1. Effectiveness in Addressing the HBVE
Under the current radar parameter settings, the parameters of the effective compensation Doppler bands is calculated. According to equation (19), we calculate the minimum value of k such that , resulting in ,and calculate the maximum value of k such that , resulting in . When the ambiguity number is 0, the range of the frequency points indices in the Doppler spectrum that fall within the effective compensation Doppler band is . The new unambiguous Doppler frequency point cycle is calculated as .
4.1.1. Effectiveness for HBV Points
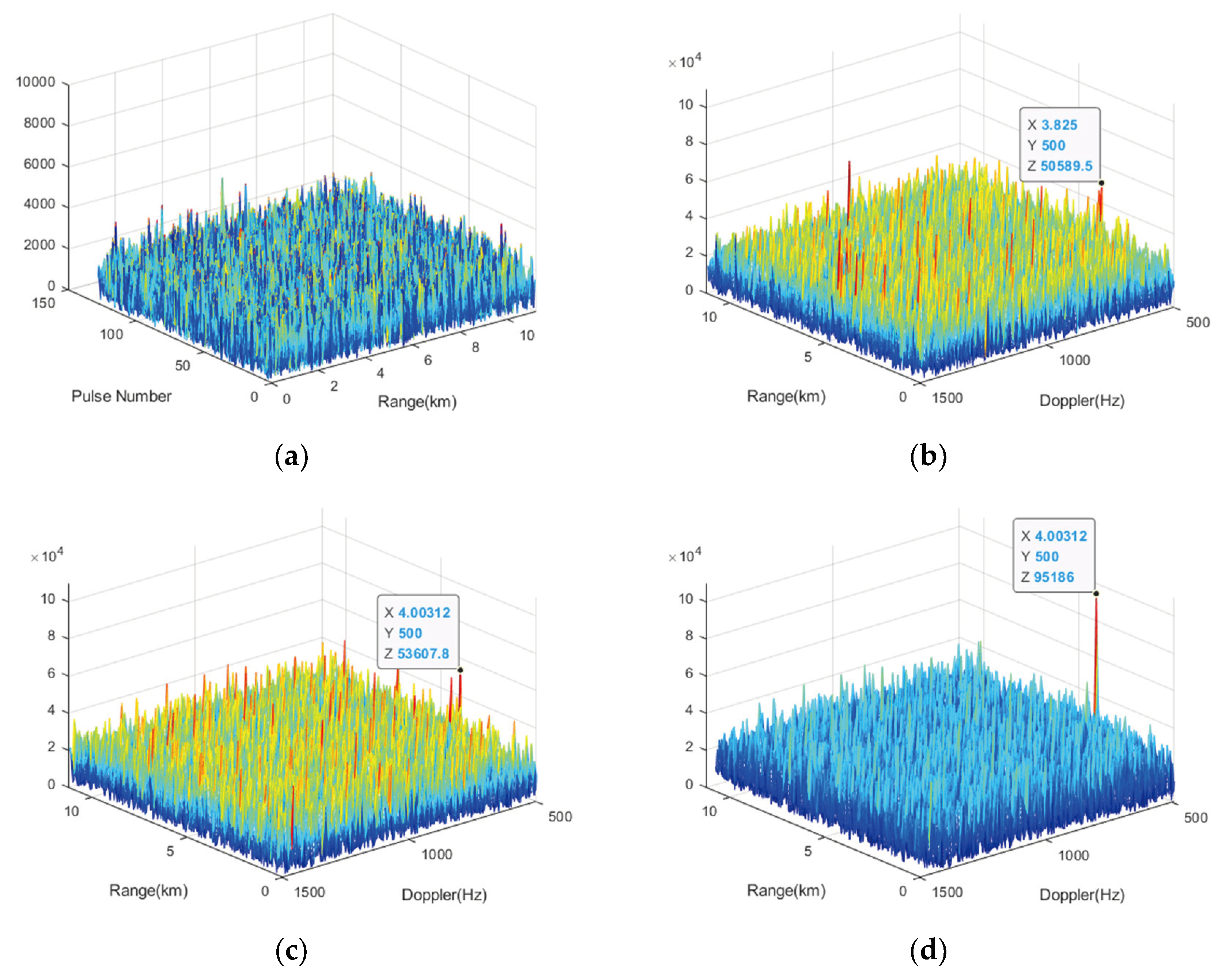
A point target is set in the detection space, with a distance of 0.4 km from the radar. The maximum unambiguous velocity of the radar is , therefore, the target velocity is set to , which lies at a HBV point. The SNR of echo is -35dB. Simulated coherent target echoes are generated.
The signal processing results are shown in
Figure 6.
Figure 6a shows the result after PC, where the target is not yet discernible due to RM and low SNR.
Figure 6b shows the result after Doppler filtering, where the target’s peak amplitude is low due to target motion causing energy spread.
Figure 6c shows the result of the traditional sinc interpolation, which compensates for RM to some extent but is affected by the HBVE, resulting in only a 0.5dB improvement in the SNR.
When using the VDSPKT-SI, setting the Doppler starting point parameter
(
can be set to other values that meet the requirements) ensures that the target’s Doppler falls within the effective band. It overcomes the HBVE, resulting in a target SNR increase of 5.5dB, which is shown in
Figure 6d.
4.1.2. Effectiveness in Solving the HBVE
In
Section 2.2, two other methods, Doppler shift and approximate compensation, for solving the HBVE were introduced. In the following simulations, these two methods are compared with the proposed method in terms of their effectiveness.
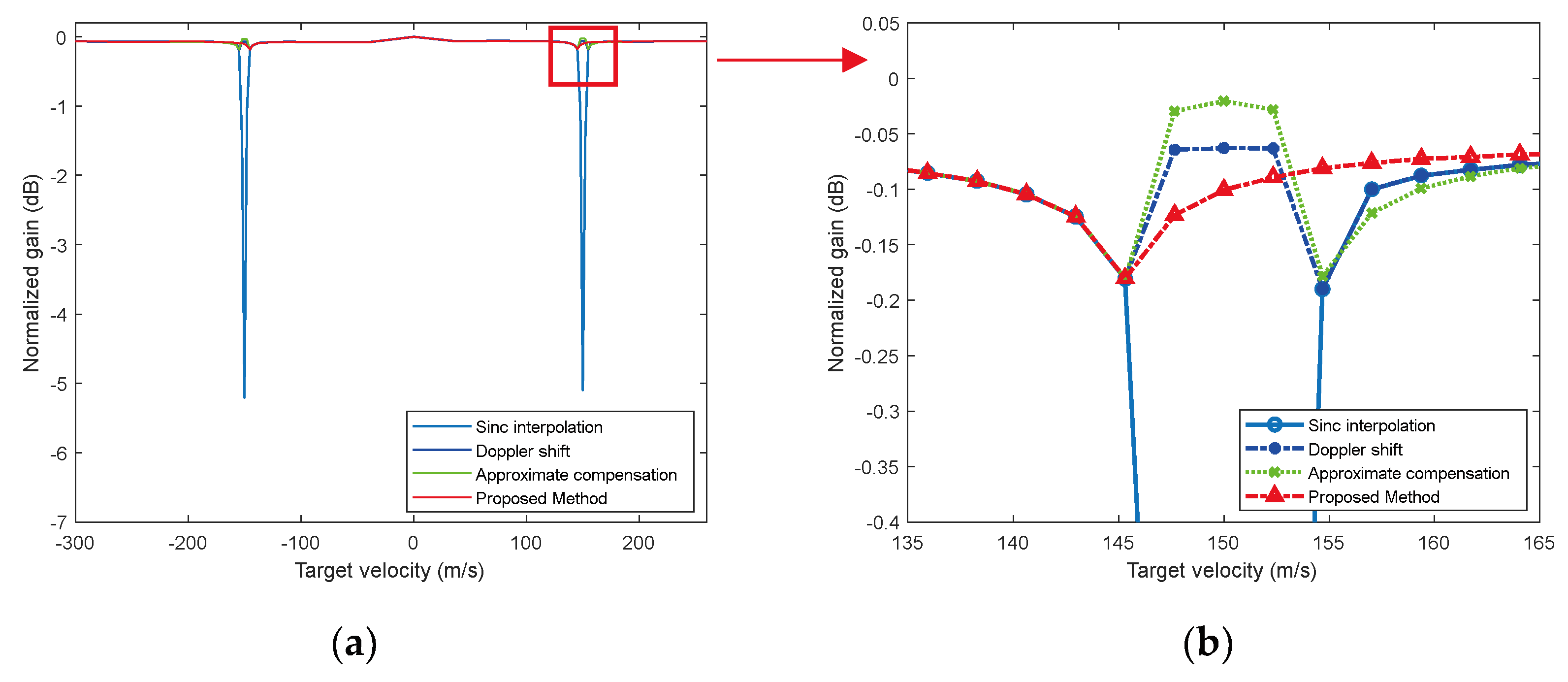
The velocity range is set to , within which there are two HBV bands centered at -150 m/s and 150 m/s. According to the previous calculation, use proposed method with the Doppler starting point parameter .
The traditional sinc interpolation and three improved methods is used to correct RM of targets within the preset velocity range, and the peak of the processing results is recorded to obtain the gain curves, which is shown in
Figure 7. Due to the shape of sinc interpolation filter, there are slight losses in gain for points near the HBV bands, which fall within an acceptable range. Because the proposed method does not involve replacement operations, the gain range is smoother near the HBV bands compared to the other two methods. Furthermore, the smoothness can be further improved by reducing the value of
.
4.1.3. Computational Complexity
In this subsection, the number of complex multiplications is used to compare the computational complexity. The number of complex multiplications for compensating a period with a Doppler ambiguity number of 0 using sinc interpolation is . For periods requiring Doppler ambiguity compensation, using the method of Doppler ambiguity compensation first, the number of complex multiplications is . For processing at one HBV band: (1) the number of complex multiplications for shifting is , and the number of complex multiplications for sinc interpolation is ; (2) the number of complex multiplications for the approximate compensation is ; (3) the computational complexity of the VDSPKT-SI within one period is . The number of multiplications for Doppler filtering of the result obtained by sinc interpolation is .
The number of complex multiplications of three improved methods for different compensation Doppler ranges is shown in
Figure 8. It can be observed that the proposed method requires much less computation than the Doppler shift, and is almost the same as the approximate compensation.
When compensating for the Doppler range including the HBV band, which corresponds to the part in the
Figure 8 where the relative Doppler is greater than a certain value (slightly less than 1), the HBVE needs to be addressed. The proposed method exhibits lower computational complexity than the approximate compensation method at the majority of points, and the computational load is reduced by 50% compared to the traditional Doppler shift method at all points. Therefore, considering both effectiveness and computational complexity, the proposed approach outperforms the other two methods in addressing the HBVE.
4.2. The Effectiveness of VDSPKT-CZT
Here, we simulate example 1 in
Section 3.2 to verify the effectiveness of VDSPKT-CZT. NDFR 1 is set to
, and 3 point targets is placed within it. The target parameters are shown in
Table 2. In addition, to make the comparison between the results before and after RM correction clearer,
is set. The SNR of echo is -20dB.
The simulated echoes are processed with frequency-domain PC to obtain the compressed results in the fast-frequency domain, denoted as
. Then, a
M-point FFT is applied to the slow-time dimension of
to obtain the Doppler filtering result
, as shown in
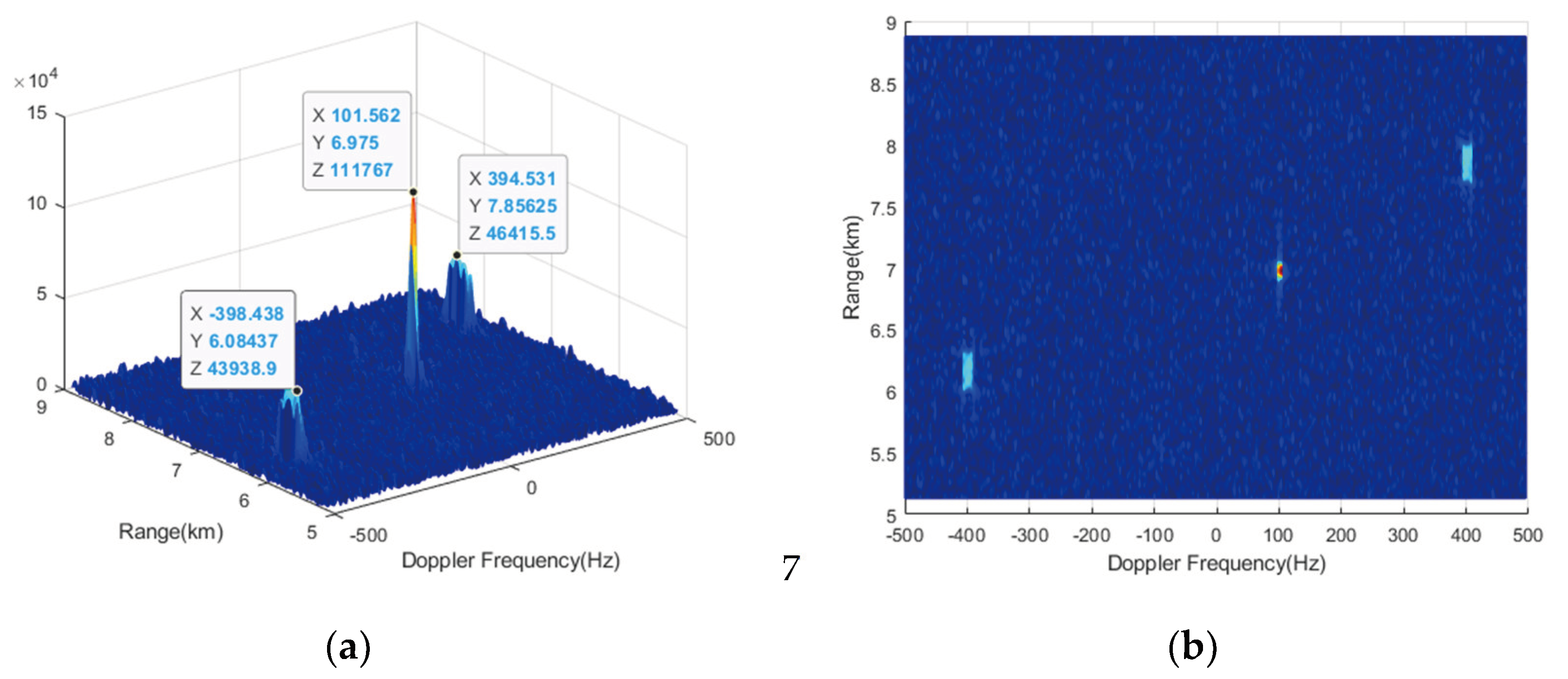
Figure 9. The data are affected by RM, causing the target energy to spread to surrounding cells. Since the velocity of Target 2 is relatively small, and the impact of RM is not significant.
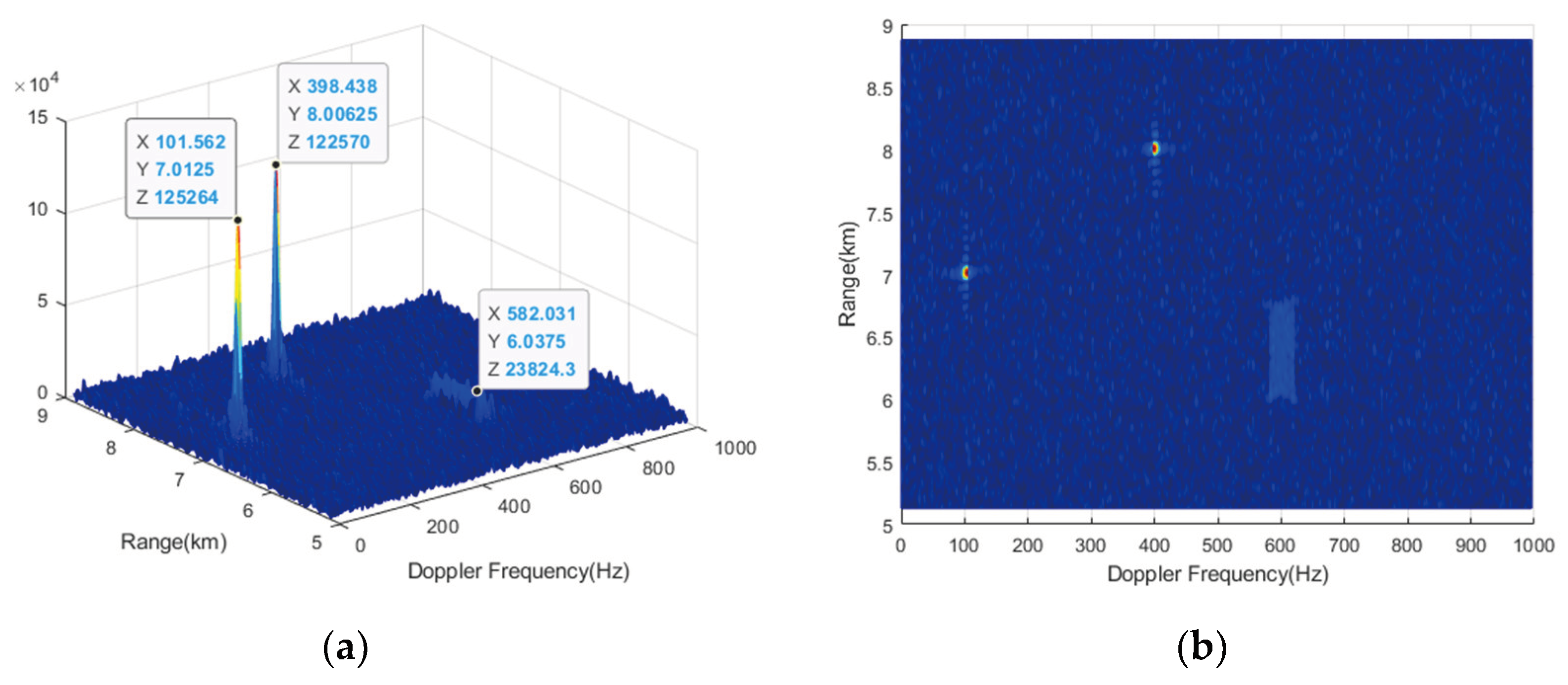
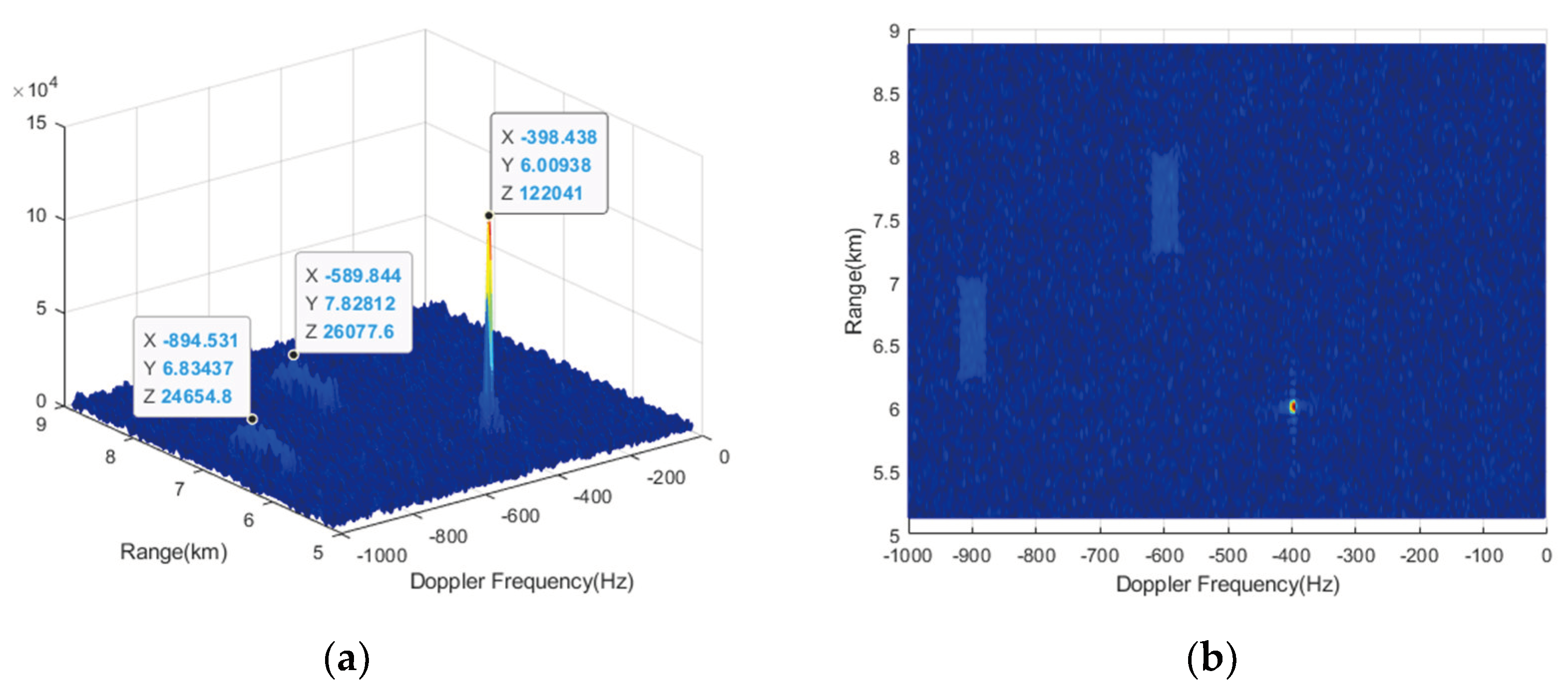
RM compensation is performed using CZT formula (17) with ambiguity numbers
and
, respectively. The results are shown in
Figure 10 and
Figure 11. From
Figure 10, it can be observed that only the RM of target 1 and target 2 can be effectively compensated, while that of target 3 cannot be compensated, leading to further energy diffusion conversely. Because when the compensation ambiguity number is 0, the compensation Doppler band is
and the Doppler of target 3 is not within it. Similarly, when the compensation ambiguity number is -1, the compensated Doppler band is
, and only target 3 can be effectively compensated. When using traditional CZT, a total of two compensation operations is required to complete the RM correction for all 3 targets in the NDFR.
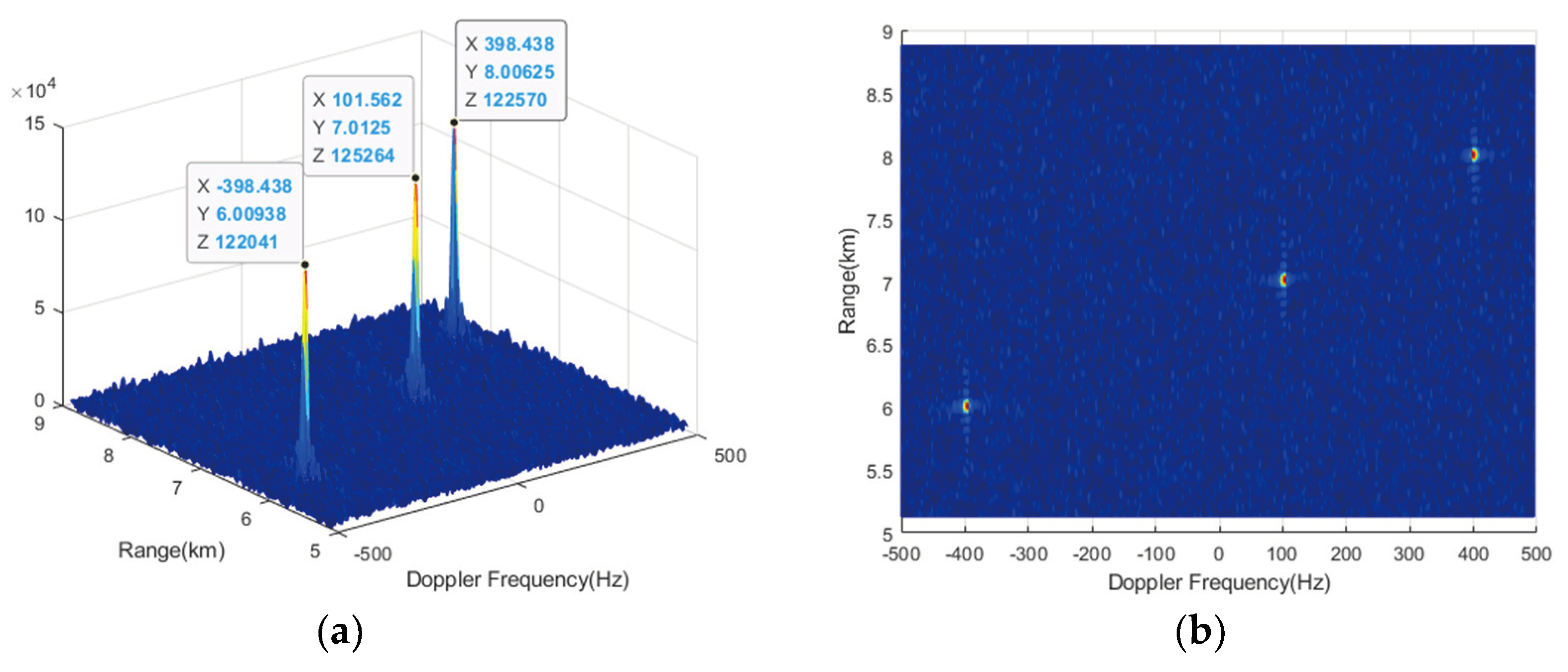
Using the proposed VDSPKT-CZT, the Doppler starting point
is set to
, so that the compensation Doppler band becomes
, covering the NDFR where targets are located and aligning its center with the center of the NDFR. The result is shown in the
Figure 12. It can be observed that after VDSPKT-CZT, RM of the 3 targets is effectively compensated simultaneously, the energy of the targets is more concentrated, the peak amplitudes are higher, and the gain of integration for the three targets is increased by 8.4 dB, 1 dB, and 8.9 dB, respectively, compared to the result of Doppler filtering.
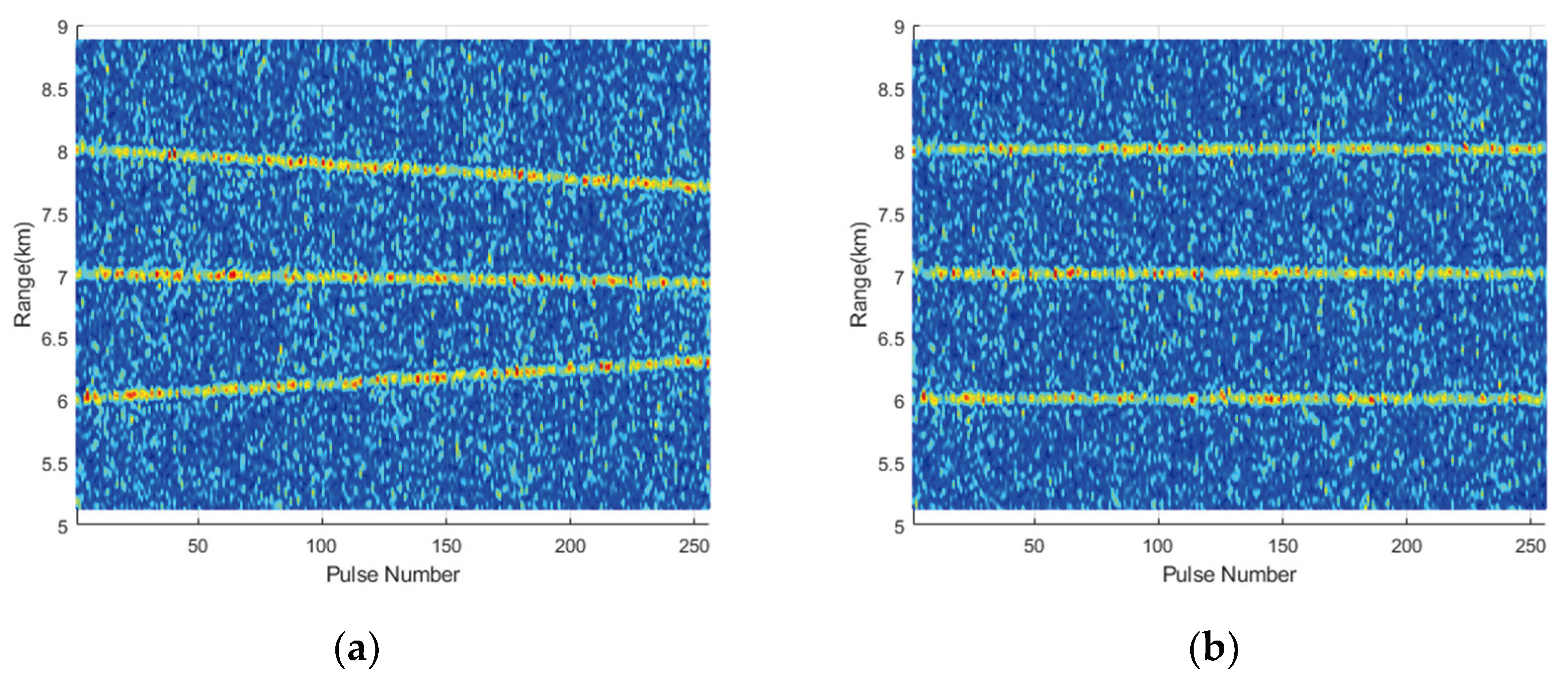
Finally, PC results before and after the RM correction are compared. An IFFT calculation is performed on the fast-time frequency dimension of
to obtain the fast-time domain PC result, as shown in
Figure 13a. It can be seen that the positions of the targets echo envelope change continuously with the slow time. A
M-point IFFT is performed on the range-Doppler matrix
obtained after VDSPKT-CZT in the Doppler dimension to calculate the PC result after RM correction, as shown in
Figure 13b. The positions of the target signal envelope no longer change with slow time, indicating effective compensation for RM.
The proposed VDSPKT-CZT in this paper only needs to perform one calculation to complete the RM correction of targets with NDFR spanning two compensation Doppler bands, which improves computational efficiency. Compared to traditional CZT, this approach reduces computational complexity by approximately 50%.
5. Conclusion
In this paper, we proposed the VDSPKT, which transformed the Doppler ambiguity compensation function from an integer form to a fractional form. This transformation enabled the starting point of compensation Doppler bands in KT to be adjusted as needed thus enhancing the flexibility. For the HBVE in sinc interpolation, a solution based on VDSPKT-SI was proposed. This approach effectively addressed the HBVE problem by changing the position and connection points of the compensation Doppler band. Moreover, it reduced the computational complexity by approximately 50% compared to the traditional Doppler shift method. Furthermore, to improve the computational efficiency of KT in RM compensating for targets with NDFR, using CZT as an illustration, VDSPKT-CZT was introduced. This approach changed the position of the compensation Doppler band, enabling it to encompass a NDFR. As a result, the CZT calculation times were reduced from two to one, greatly improving the computational efficiency. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithms was validated through simulation experiments.
Since we only consider the first-order range migration of moving targets in this paper. In the future, it will be interesting to study how to combine this approach with Doppler frequency migration correction methods and apply it to more scenarios.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.J. and T.S.; methodology, W.J. and Y.F.; software, W.J. and X.Q.; validation, W.J. and T.W.; formal analysis, W.J. and T.S.; resources, T.W.; writing—original draft preparation, W.J.; writing—review and editing, W.J., T.S. and X.Q.; supervision, Y.F.; funding acquisition, T.S. and Y.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant No.62171029 and 61931015.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
References
- Xiaolong, C.; Jian, G.; Jibin, Z.; Yue, Z.; Xiaohan, Y. Radar Fast Long-Time Coherent Integration via TR-SKT and Robust Sparse FRFT. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2023, 34, 1116–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, G.; Yeo, T.S. Coherent Integration and Parameter Estimation for High-Speed Target Detection With Bistatic MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Du, X.; Liu, Q.H. Radar High-Speed Maneuvering Target Detection Based on Three-Dimensional Scaled Transform. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2821–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Liao, G.; Yang, Z.; Xia, X.-G.; Ma, J.-T.; Ma, J. Long-Time Coherent Integration for Weak Maneuvering Target Detection and High-Order Motion Parameter Estimation Based on Keystone Transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 4013–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Su, T.; Liu, H.; Liao, G.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Q.H. Radar High-Speed Target Detection Based on the Frequency-Domain Deramp-Keystone Transform. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Li, X.; Cui, G.; Yi, W.; Yang, Y. Coherent Integration Algorithm for a Maneuvering Target With High-Order Range Migration. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 4474–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Cui, W.; Wu, S. A Novel Method for Parameter Estimation of Space Moving Targets. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Xing, M.; Xia, X.-G.; Wu, Y.; Bao, Z. Robust Ground Moving-Target Imaging Using Deramp–Keystone Processing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 966–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, B.D.; Evans, E.D.; Wilson, S.L. Search Radar Detection and Track with the Hough Transform. I. System Concept. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xu, J.; Peng, Y. Performance Analysis of Long-Time Coherent Integration for Moving Targets. In Proceedings of the 2009 2nd Asian-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar; IEEE: Xian, Shanxi, China, October 2009; pp. 197–200.
- Wang, D.; Bao, Q.; Niu, Z.; Chen, Z. Long Time Coherent Integration Method for Frequency Agile Radar. In Proceedings of the 2014 11th European Radar Conference; IEEE: Italy, October 2014; pp. 553–556.
- Wang, G. The Minimum Entropy Criterion of Range Alignment in ISAR Motion Compensation.; IET: Edinburgh, UK, 1997; pp. 236–239. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-C.; Andrews, H. Target-Motion-Induced Radar Imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1980, AES-16, 2–14. [CrossRef]
- Delisle, G.Y. ; Haiqing Wu Moving Target Imaging and Trajectory Computation Using ISAR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yu, J.; Peng, Y.-N.; Xia, X.-G. Radon-Fourier Transform for Radar Target Detection, I: Generalized Doppler Filter Bank. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 1186–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yu, J.; Peng, Y.-N.; Xia, X.-G. Radon-Fourier Transform for Radar Target Detection (II): Blind Speed Sidelobe Suppression. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 2473–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xu, J.; Peng, Y.-N.; Xia, X.-G. Radon-Fourier Transform for Radar Target Detection (III): Optimality and Fast Implementations. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 48, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia Xu; Xiang-Gen Xia; Shi-Bao Peng; Ji Yu; Ying-Ning Peng; Li-Chang Qian Radar Maneuvering Target Motion Estimation Based on Generalized Radon-Fourier Transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 6190–6201. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Cui, G.; Yeo, T.S. Multi-Frame Integration Method for Radar Detection of Weak Moving Target. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 3609–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, G.; Yi, W.; Kong, L. A Fast Maneuvering Target Motion Parameters Estimation Algorithm Based on ACCF. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Yi, W.; Cui, G.; Kong, L. Detection of Maneuvering Target with Complex Motions Based on ACCF and FRFT. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf); IEEE: Seattle, WA, USA, May, 2017; pp. 0017–0020. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, R.P.; DiPietro, R.C.; Fante, R.L. SAR Imaging of Moving Targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1999, 35, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungang, Y.; Xiaotao, H.; Tian, J.; Thompson, J.; Zhimin, Z. New Approach for SAR Imaging of Ground Moving Targets Based on a Keystone Transform. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xia, X.-G.; Peng, Y.-N. Doppler Keystone Transform: An Approach Suitable for Parallel Implementation of SAR Moving Target Imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xia, X.-G.; Peng, Y.-N. Doppler Keystone Transform for SAR Imaging of Moving Targets. In Proceedings of the 2008 Congress on Image and Signal Processing; IEEE: Sanya, China, 2008; pp. 716–719. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Wu, R.; Xing, M.; Bao, Z. Approach for Single Channel SAR Ground Moving Target Imaging and Motion Parameter Estimation. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2007, 1, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongyin, S.; Yue, L.; Jianwen, G.; Mingxin, L. ISAR Autofocus Imaging Algorithm for Maneuvering Targets Based on Deep Learning and Keystone Transform. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2020, 31, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, K.; Liu, Y.; Hu, J.; Jiang, W.; Li, X. A Novel Imaging Method for Fast Rotating Targets Based on the Segmental Pseudo Keystone Transform. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xing, M.; Su, J.; Quan, Y.; Bao, Z. A New Algorithm of ISAR Imaging for Maneuvering Targets with Low SNR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2013, 49, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shun-sheng Zhang; Tao Zeng; Teng Long; Hai-peng Yuan Dim Target Detection Based on Keystone Transform. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Radar Conference, 2005.; IEEE: Arlington, VA, USA, 2005; pp. 889–894.
- Zhu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z. A Keystone Transform Without Interpolation for SAR Ground Moving-Target Imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongbo Zhao; Juan Wang; Lei Huang; Rui Yang Low Complexity Keystone Transform without Interpolation for Dim Moving Target Detection. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar; IEEE: Chengdu, China, October 2011; pp. 1745–1748.
- Shan, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.D.; Amin, M.G.; Tao, R.; Feng, Y. Efficient Architecture and Hardware Implementation of Coherent Integration Processor for Digital Video Broadcast-based Passive Bistatic Radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2016, 10, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, D. Imaging Moving Targets Using the Second-Order Keystone Transform. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2011, 5, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xu, J.; Tang, J.; Peng, Y. An Improved Keystone-Transform Based Method for Long-Time Coherent Integration of Radar Target. Radar Sci. Technol. 2008, 6, 454–458. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, J.; Qin, G. The Suppression and Elimination of Half Blind Velocity Effect Associated with Keystone Transform. 36 2014, 1, 175–180. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).