Submitted:
26 March 2024
Posted:
27 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction

- A dynamic patch-based framework, mainly consisting of two threads running in parallel that estimate motion fields in a coarse-to-fine manner, adapting to the inherent challenges posed by nonrigid deformations.
- A patch-based rigid registration module is designed for efficiently solving a set of coarse transformation fields, which are defined and solved for each non-overlapped patch independently.
- A deformation optimization module is employed and integrated to refine the coarse transformation fields, yielding more accurate and consistent transformation fields with the embedded deformation graph.
- Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed approach is able to dynamically track and reconstruct deformable surfaces, offering a more accurate representation of their evolving shapes.
2. Related Works
2.1. Rigid Registration
2.2. Patch-Based Approaches for 3D Reconstruction
2.3. Deformable Object Tracking
2.4. RGB-D Tracking and Reconstruction
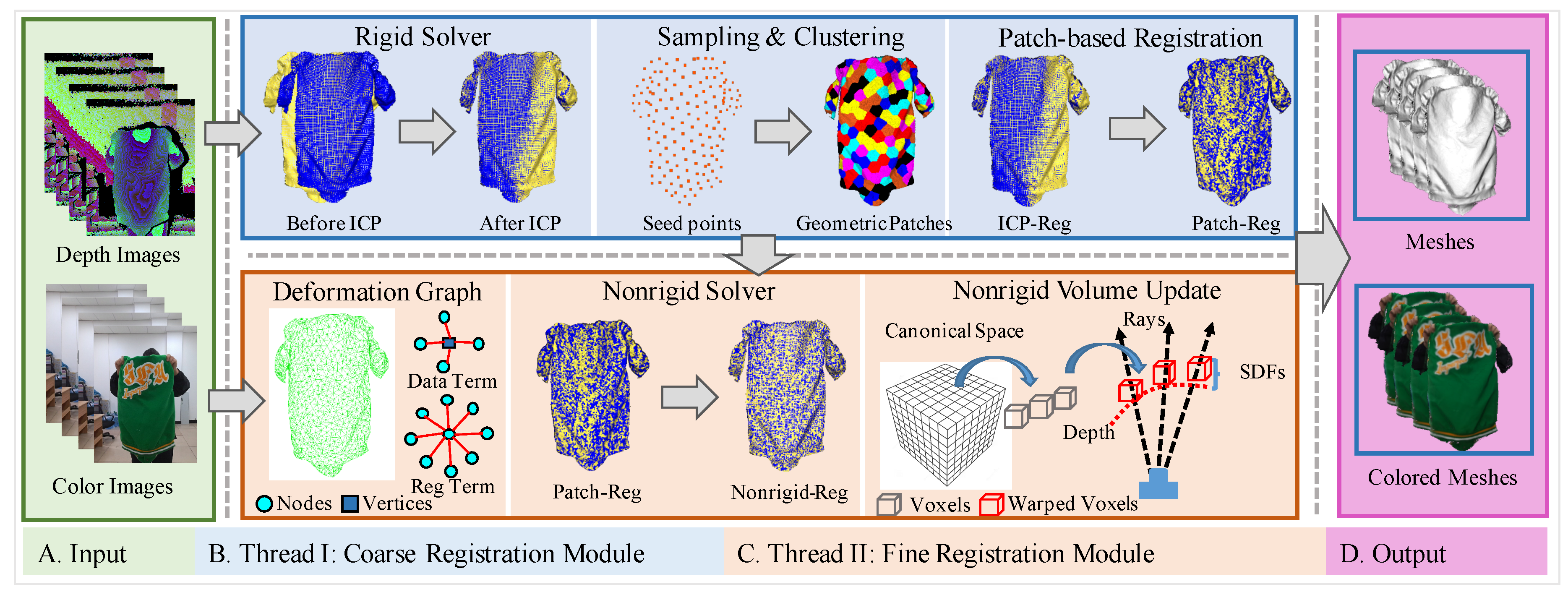
3. System Overview
3.1. Definition of Variables
- - depth image at time t; - color image at time t.
- - pixel location; - homogeneous coordinate of .
- - depth value at .
- - continuous point in ; - dehomogenised coordinate of in .
- - perspective projection of the depth camera.
- - perspective projection of the color camera.
- K - intrinsic matrix of depth camera.
- - extrinsic matrix between depth camera and color camera.
- - rigid transformation matrix of i-th node.
- - unknown parameter vector of all nodes.
- - parametrized vector of .
- - canonical mesh at frame t; - warped mesh at frame t.
- - rendered vertex map of that is predicted-to-be-visible.
- - vertex in from ; - corresponding vertex of ; - warped vertex of .
- - embedded deformation graph consisting of nodes and edges.
- - rigid transformation matrix from canonical coordinate frame to camera coordinate frame.
- - influence weights; - influence radius.
- - K-NN nodes of used in data term.
- - K-NN nodes of node used in regularization term.
3.2. System Architecture
4. Methods
4.1. Preliminaries
4.2. Nonrigid Alignment as Energy Optimization
4.3. Patch-Based Rigid Alignment
4.4. Local-to-Global Fusion
4.5. Implicit Surface and Rasterization
5. Experiments
5.1. Experiment Setup
5.1.1. Dataset
5.1.2. Evaluation Metrics
5.1.3. Implementation Details
5.2. Quantative Analysis
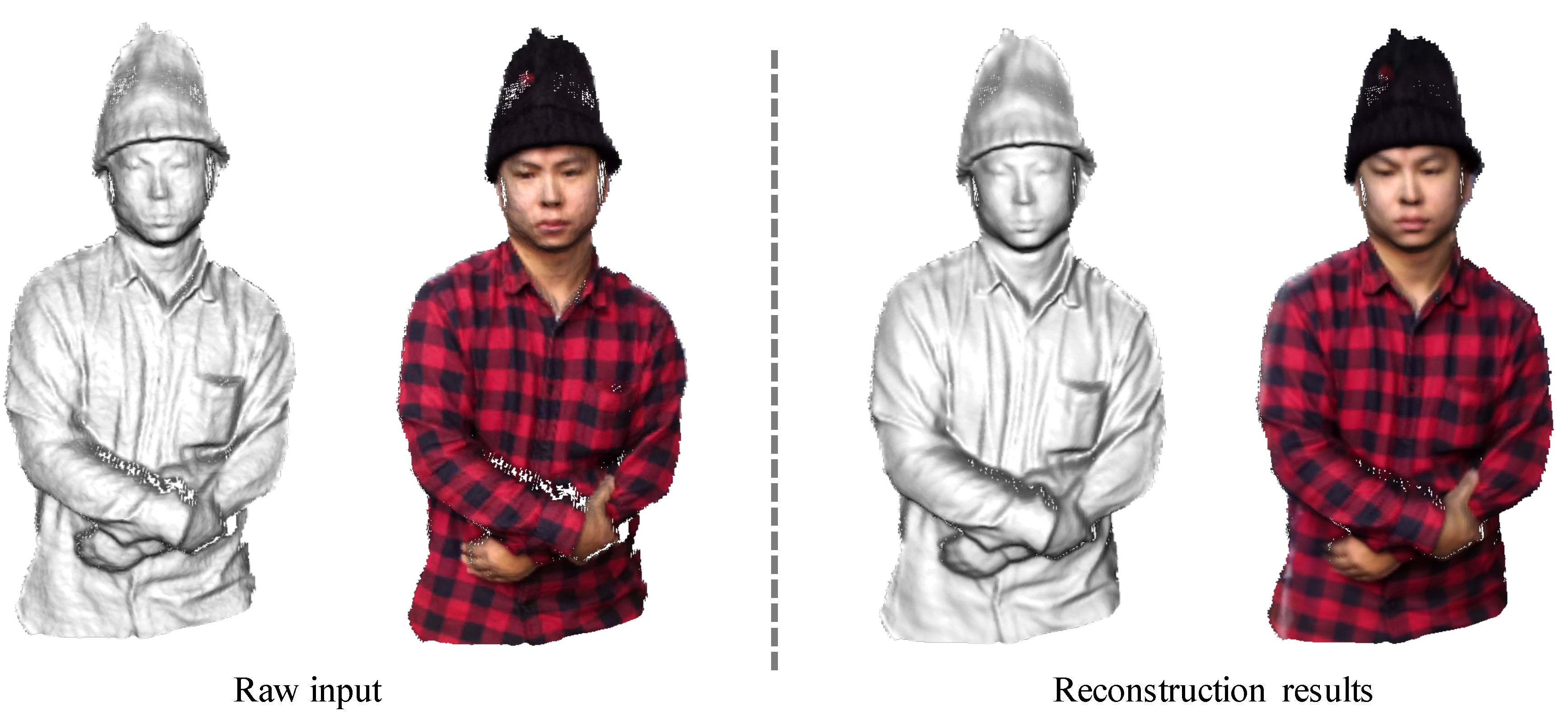
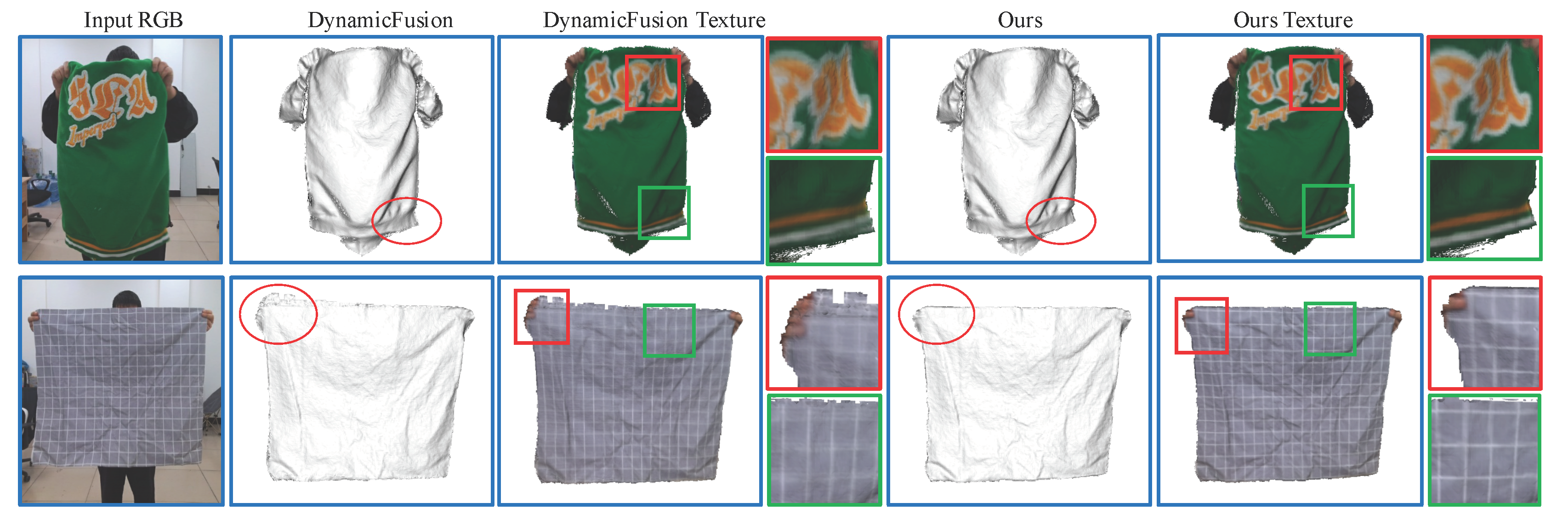
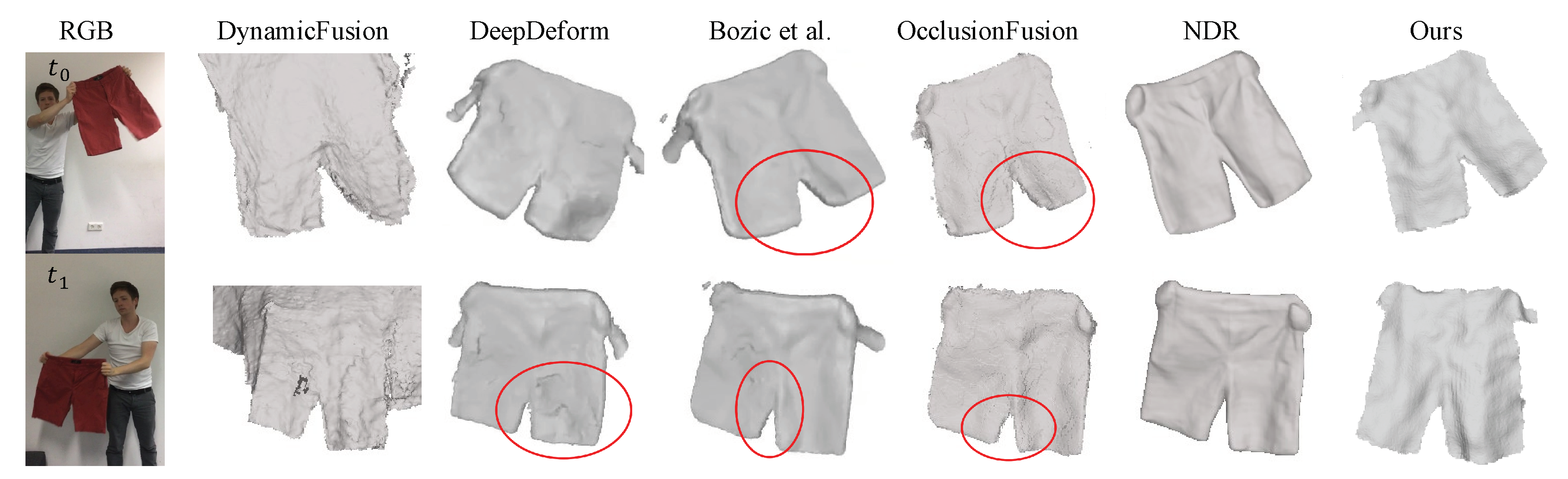
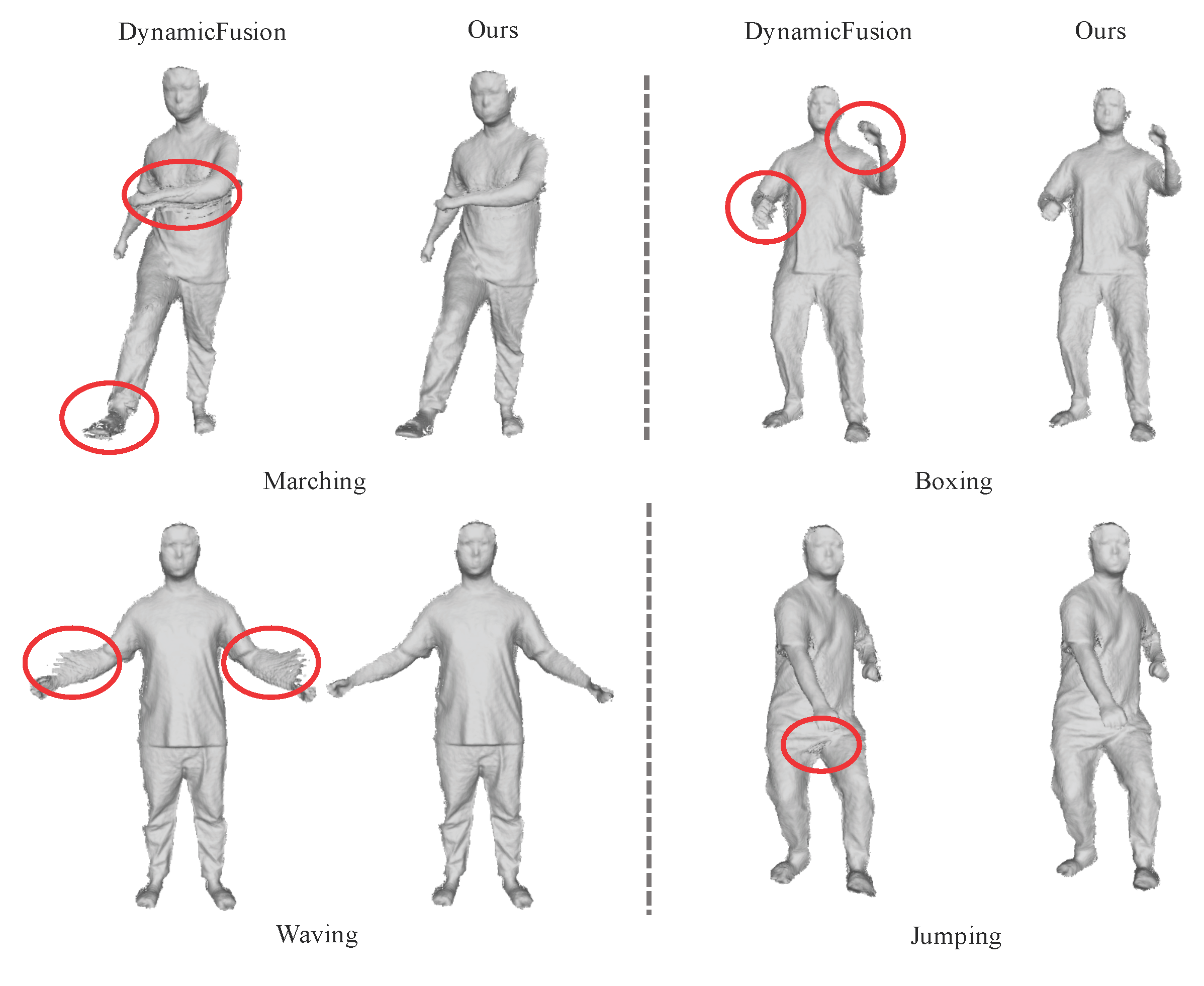
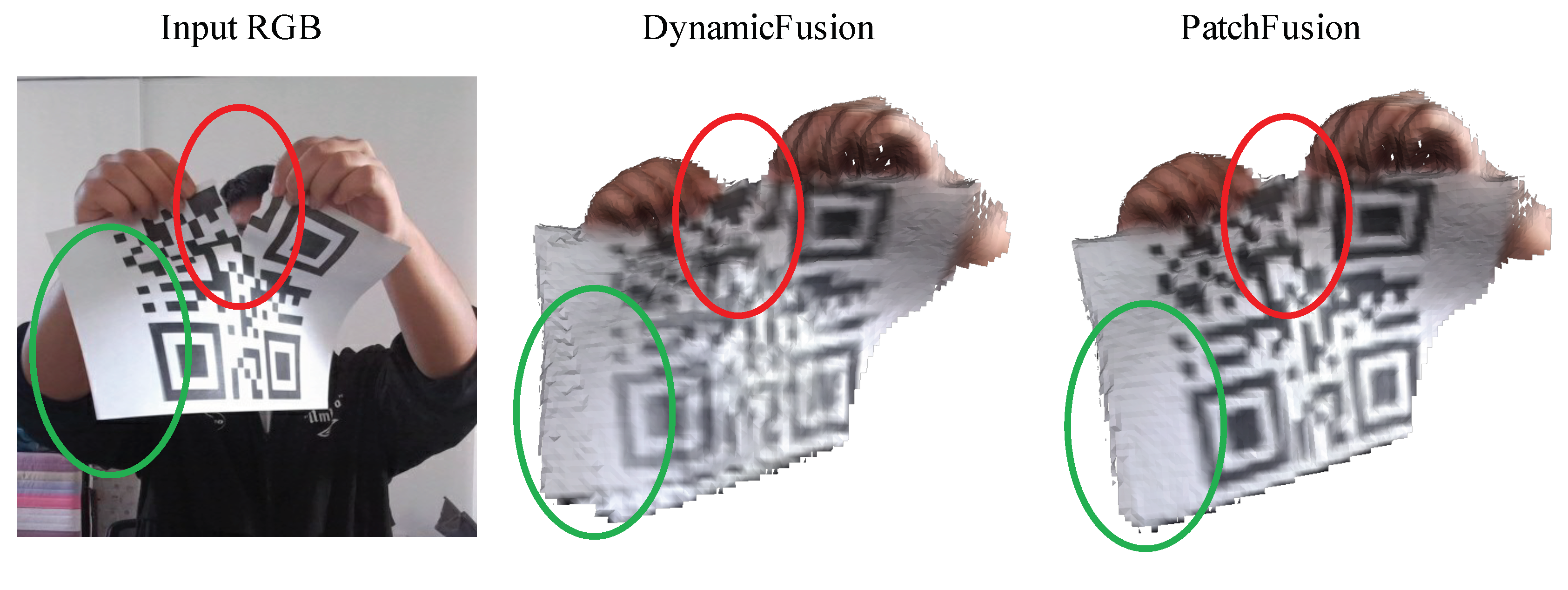
5.3. Qualitative Comparison Results
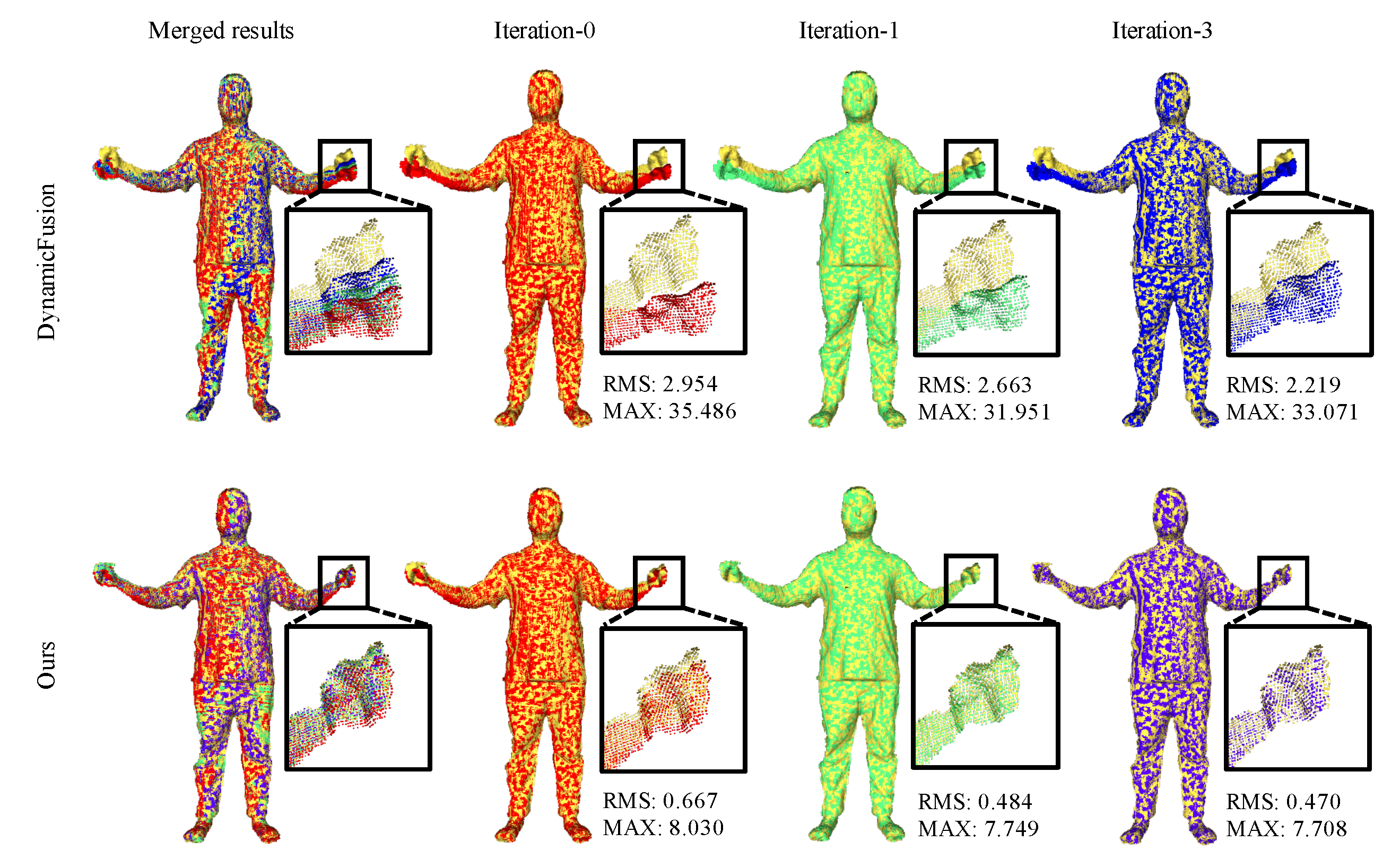
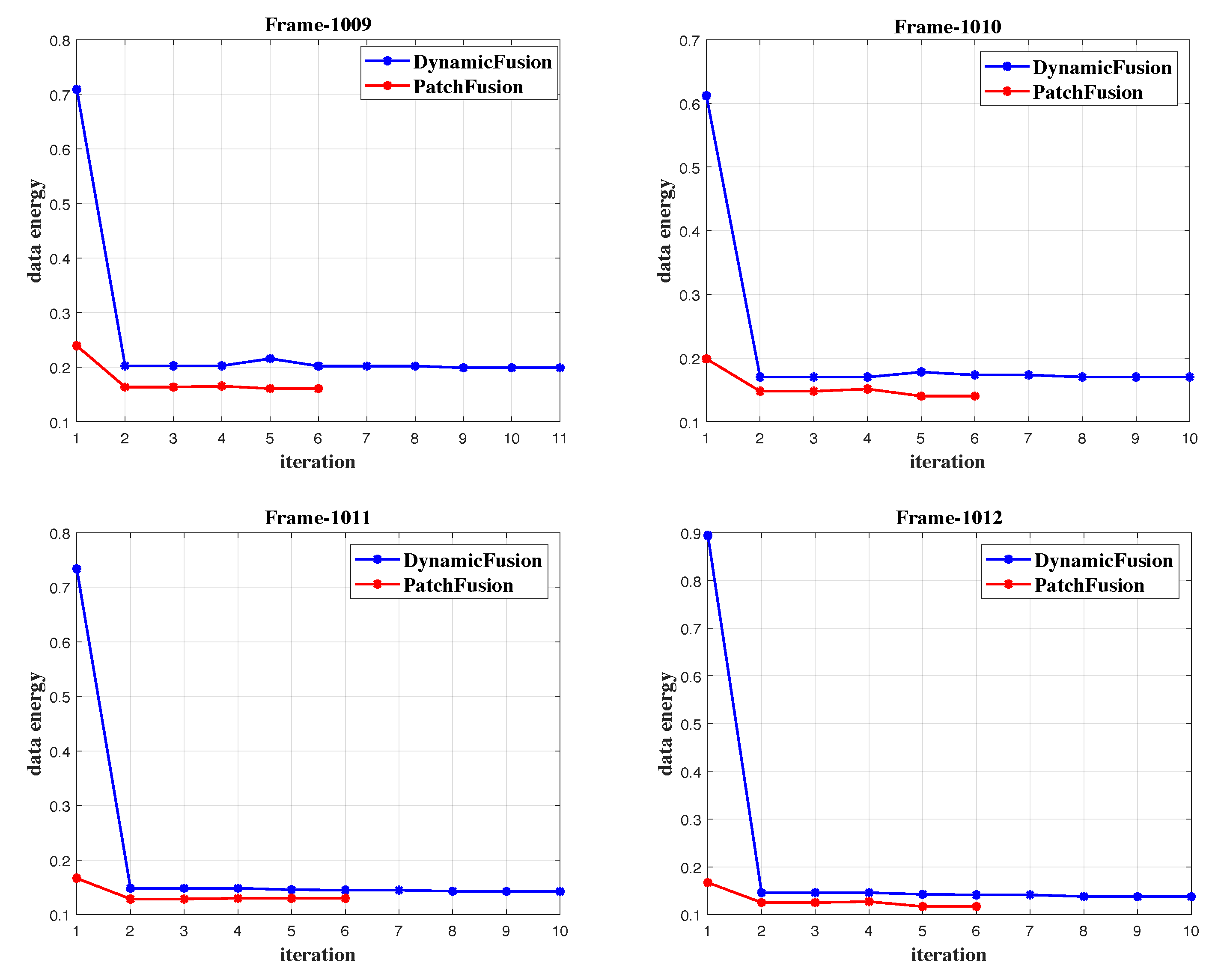
5.4. Ablations of Patch-Based Registration
5.5. System Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
References
- Fuster-Guilló, A.; Azorin-Lopez, J.; Saval-Calvo, M.; Castillo-Zaragoza, J.M.; Garcia-D’Urso, N.; Fisher, R.B. RGB-D-based framework to acquire, visualize and measure the human body for dietetic treatments. Sensors 2020, 20, 3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, W.; Tang, S.; Li, W.; Chen, W. A new calibration method for commercial RGB-D sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, C.; Chen, H.; Zeng, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Qiao, Z.; Qu, Y.; Li, L.; Li, L. A Smart Cane Based on 2D LiDAR and RGB-D Camera Sensor-Realizing Navigation and Obstacle Recognition. Sensors 2024, 24, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollhöfer, M.; Nießner, M.; Izadi, S.; Rehmann, C.; Zach, C.; Fisher, M.; Wu, C.; Fitzgibbon, A.; Loop, C.; Theobalt, C.; others. Real-time non-rigid reconstruction using an RGB-D camera. ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG) 2014, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcombe, R.A.; Fox, D.; Seitz, S.M. Dynamicfusion: Reconstruction and tracking of non-rigid scenes in real-time. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2015, pp. 343–352.
- Innmann, M.; Zollhöfer, M.; Nießner, M.; Theobalt, C.; Stamminger, M. Volumedeform: Real-time volumetric non-rigid reconstruction. European conference on computer vision. Springer, 2016, pp. 362–379.
- Guo, K.; Xu, F.; Yu, T.; Liu, X.; Dai, Q.; Liu, Y. Real-time geometry, albedo, and motion reconstruction using a single rgb-d camera. ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG) 2017, 36, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curless, B.; Levoy, M. A volumetric method for building complex models from range images. Proceedings of the 23rd annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques, 1996, pp. 303–312.
- Sumner, R.W.; Schmid, J.; Pauly, M. Embedded deformation for shape manipulation. In ACM siggraph 2007 papers; 2007; p. 80–es. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Pollefeys, M. A factorization-based approach for articulated nonrigid shape, motion and kinematic chain recovery from video. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2008, 30, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, S.; Hu, Q.; Cai, Q.; Li, M.; Bai, Y.; Wu, K.; Xiang, B. GFOICP: Geometric Feature Optimized Iterative Closest Point for 3D Point Cloud Registration. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Jiao, Y. 6D Object Pose Estimation Based on Cross-Modality Feature Fusion. Sensors 2023, 23, 8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Geng, C.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S. Point Cloud Registration Method Based on Geometric Constraint and Transformation Evaluation. Sensors 2024, 24, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y. Nrtnet: An unsupervised method for 3d non-rigid point cloud registration based on transformer. Sensors 2022, 22, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Du, C.; Chen, H. Nbr-net: A nonrigid bidirectional registration network for multitemporal remote sensing images. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2022, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besl, P.J.; McKay, N.D. Method for registration of 3-D shapes. Sensor fusion IV: control paradigms and data structures. Spie, 1992, Vol. 1611, pp. 586–606.
- Maken, F.A.; Ramos, F.; Ott, L. Stein ICP for uncertainty estimation in point cloud matching. IEEE robotics and automation letters 2021, 7, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.D.; Raettig, R.M.; Larson, J.; Nykl, S.L.; Taylor, C.N.; Wischgoll, T. Delaunay walk for fast nearest neighbor: accelerating correspondence matching for ICP. Machine Vision and Applications 2022, 33, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinkiewicz, S. A symmetric objective function for ICP. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 2019, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, Y.; Deng, B. Fast and robust iterative closest point. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2021, 44, 3450–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagniart, C.; Boyer, E.; Ilic, S. Free-form mesh tracking: a patch-based approach. 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2010, pp. 1339–1346.
- Zhao, B.; Lin, W.; Lv, C. Fine-grained patch segmentation and rasterization for 3-d point cloud attribute compression. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 2021, 31, 4590–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiong, R.; Liu, D.; Ma, S.; Wu, F.; Gao, W. Image denoising via low rank regularization exploiting intra and inter patch correlation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 2017, 28, 3321–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ha, H.; Dong, Y.; Tong, X.; Kim, M.H. Texturefusion: High-quality texture acquisition for real-time rgb-d scanning. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020, pp. 1272–1280.
- Kwon, J.; Lee, K.M. Highly nonrigid object tracking via patch-based dynamic appearance modeling. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2013, 35, 2427–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayad, J.; Agapito, L.; Del Bue, A. Piecewise quadratic reconstruction of non-rigid surfaces from monocular sequences. European conference on computer vision. Springer, 2010, pp. 297–310.
- Locher, A.; Perdoch, M.; Van Gool, L. Progressive prioritized multi-view stereo. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016, pp. 3244–3252.
- Zhang, J.; Yao, Y.; Quan, L. Learning signed distance field for multi-view surface reconstruction. 2021 IEEE. CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2021, pp. 6505–6514.
- Huang, M.; Li, X.; Hu, J.; Peng, H.; Lyu, S. Tracking Multiple Deformable Objects in Egocentric Videos. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2023, pp. 1461–1471.
- Tang, T.; Fan, Y.; Lin, H.C.; Tomizuka, M. State estimation for deformable objects by point registration and dynamic simulation. 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). IEEE, 2017, pp. 2427–2433.
- Yu, T.; Guo, K.; Xu, F.; Dong, Y.; Su, Z.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Dai, Q.; Liu, Y. Bodyfusion: Real-time capture of human motion and surface geometry using a single depth camera. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017, pp. 910–919.
- Yu, T.; Zheng, Z.; Guo, K.; Zhao, J.; Dai, Q.; Li, H.; Pons-Moll, G.; Liu, Y. Doublefusion: Real-time capture of human performances with inner body shapes from a single depth sensor. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2018, pp. 7287–7296.
- Zuo, X.; Wang, S.; Zheng, J.; Yu, W.; Gong, M.; Yang, R.; Cheng, L. Sparsefusion: Dynamic human avatar modeling from sparse rgbd images. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 2020, 23, 1617–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcombe, R.A.; Izadi, S.; Hilliges, O.; Molyneaux, D.; Kim, D.; Davison, A.J.; Kohi, P.; Shotton, J.; Hodges, S.; Fitzgibbon, A. Kinectfusion: Real-time dense surface mapping and tracking. 2011 10th IEEE international symposium on mixed and augmented reality. Ieee, 2011, pp. 127–136.
- Ondrúška, P.; Kohli, P.; Izadi, S. Mobilefusion: Real-time volumetric surface reconstruction and dense tracking on mobile phones. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics 2015, 21, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavcheva, M.; Baust, M.; Cremers, D.; Ilic, S. Killingfusion: Non-rigid 3d reconstruction without correspondences. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017, pp. 1386–1395.
- Loper, M.; Mahmood, N.; Romero, J.; Pons-Moll, G.; Black, M.J. SMPL: A Skinned Multi-Person Linear Model. ACM Trans. Graphics (Proc. SIGGRAPH Asia) 2015, 34, 248:1–248:16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorensen, W.E.; Cline, H.E. Marching cubes: A high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. In Seminal graphics: pioneering efforts that shaped the field; 1998; pp. 347–353.
- Cignoni, P.; Callieri, M.; Corsini, M.; Dellepiane, M.; Ganovelli, F.; Ranzuglia, G. MeshLab: an Open-Source Mesh Processing Tool. Eurographics Italian Chapter Conference; Scarano, V.; Chiara, R.D.; Erra, U., Eds. The Eurographics Association, 2008. [CrossRef]
- Dou, M.; Khamis, S.; Degtyarev, Y.; Davidson, P.; Fanello, S.R.; Kowdle, A.; Escolano, S.O.; Rhemann, C.; Kim, D.; Taylor, J.; others. Fusion4d: Real-time performance capture of challenging scenes. ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG) 2016, 35, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozic, A.; Zollhofer, M.; Theobalt, C.; Nießner, M. Deepdeform: Learning non-rigid rgb-d reconstruction with semi-supervised data. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020, pp. 7002–7012.
- Bozic, A.; Palafox, P.; Zollhöfer, M.; Dai, A.; Thies, J.; Nießner, M. Neural non-rigid tracking. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2020, 33, 18727–18737. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Zheng, C.; Yong, J.H.; Xu, F. Occlusionfusion: Occlusion-aware motion estimation for real-time dynamic 3d reconstruction. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022, pp. 1736–1745.
- Cai, H.; Feng, W.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Neural surface reconstruction of dynamic scenes with monocular rgb-d camera. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2022, 35, 967–981. [Google Scholar]
- Zampogiannis, K.; Fermüller, C.; Aloimonos, Y. Topology-aware non-rigid point cloud registration. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2019, 43, 1056–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, X. Topology-change-aware volumetric fusion for dynamic scene reconstruction. Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part XVI 16. Springer, 2020, pp. 258–274.
Short Biography of Authors
 |
Mingyuan Zhao received the M.S. degree from Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, in 2018. He is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree with National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China. His research interests include image/video/point cloud compression and processing, and 3D reconstruction. |
 |
Xuexin Yu received the Ph.D. degree in astronomical technology and methods from the National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, in 2022. Currently, he is a Postdoc with the Department of Automation, Tsinghua University. His current research interests include deep learning and computer vision. |
 |
Long Xu (Senior Member, IEEE) received his M.S. degree in applied mathematics from Xidian University, Xi’an, China, in 2002, and the Ph.D. degree from the Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China. He was a Postdoc with the Department of Computer Science, City University of Hong Kong, the Department of Electronic Engineering, Chinese University of Hong Kong, from July Aug. 2009 to Dec. 2012. From Jan. 2013 to March 2014, he was a Postdoc with the School of Computer Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore. Currently, he is with the Key Laboratory of Solar Activity, National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences. His research interests include image/video processing, solar radio astronomy, wavelet, machine learning, and computer vision. He was selected into the 100-Talents Plan, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014. |
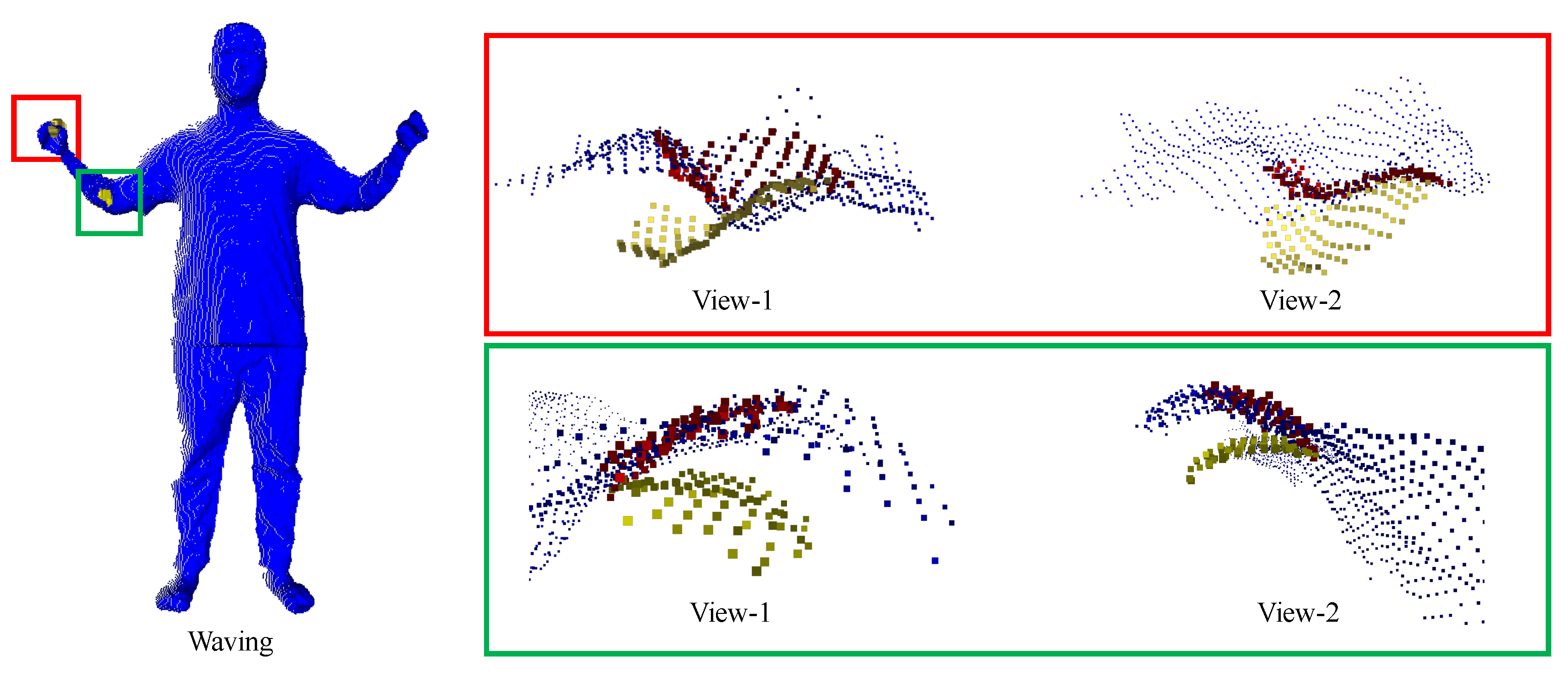

| Input | ICP | Nonrigid-ICP | Patch-ICP | Ours | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| max↓ | RMS↓ | max↓ | RMS↓ | max↓ | RMS↓ | max↓ | RMS↓ | |
| Marching | 17.610 | 2.306 | 18.950 | 1.366 | 15.244 | 1.382 | 16.081 | 1.230 |
| Boxing | 23.210 | 3.955 | 19.227 | 1.642 | 22.014 | 1.774 | 20.723 | 1.597 |
| Waving | 33.528 | 3.850 | 20.086 | 1.406 | 18.886 | 1.622 | 17.196 | 1.241 |
| Jumping | 27.100 | 1.816 | 26.761 | 1.464 | 24.475 | 1.390 | 23.819 | 1.316 |
| Jacket | 16.127 | 1.817 | 15.895 | 0.911 | 14.460 | 0.939 | 13.663 | 0.869 |
| Tablecloth | 23.575 | 3.915 | 16.165 | 1.099 | 16.576 | 1.201 | 15.989 | 1.013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





