Submitted:
25 March 2024
Posted:
27 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Water Supply Sources, Systems and Processes
2.1. Water Sources
2.2. Water Supply Systems
2.3. Water Treatment
2.4. Quality Control
2.4.1. Normal Requirements
2.4.2. Methods of Detection
2.5. Health Hazards and Contaminants
2.5.1. Chemical Aspects
2.5.3. Biological Aspects
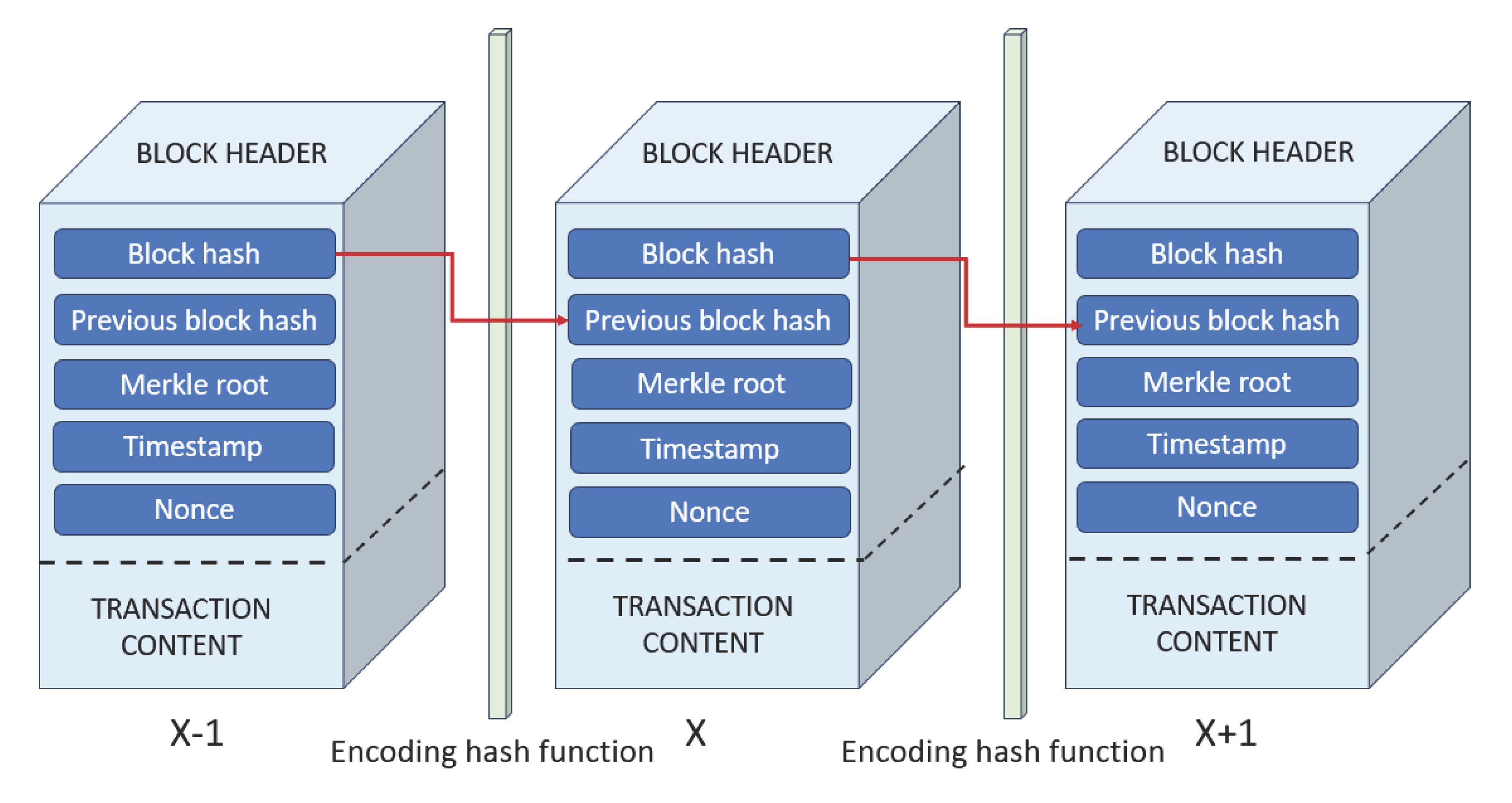
3. Blockchain Technologies
3.1. Main Elements
3.2. Applications for Water Supply
3.2.1. Smart Compliance System
3.2.2. Smart Contracts
3.2.3. Tokenisation
4. Smart Water Quality Control
4.1. Sensors, Networks, Systems
4.2. Blockchain Applications
5. Conclusion
References
- Alharbi, N., Althagafi, A., Alshomrani, O., Almotiry, A., & Alhazmi, S. (2021, July). A blockchain based secure IoT solution for water quality management. In 2021 International Congress of Advanced Technology and Engineering (ICOTEN) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
- Arnoldini, M., Heck, T., Blanco-Fernández, A., & Hammes, F. (2013). Monitoring of dynamic microbiological processes using real-time flow cytometry. PloS one, 8(11), e80117.
- Asgari, M., & Nemati, M. (2022). Application of Distributed Ledger Platforms in Smart Water Systems—A Literature Review. Frontiers in Water, 4, 848686.
- Behmel, S., Damour, M., Ludwig, R., & Rodriguez, M. J. (2016). Water quality monitoring strategies—A review and future perspectives. Science of the Total Environment, 571, 1312-1329.
- Beysens, D., & Milimouk, I. (2000). The case for alternative fresh water sources. Pour les resources alternatives en eau, Secheresse, 11(4), 1-16.
- Bratby, J. (2016). Coagulation and flocculation in water and wastewater treatment. IWA publishing.
- Clausen, C. H., Dimaki, M., Bertelsen, C. V., Skands, G. E., Rodriguez-Trujillo, R., Thomsen, J. D., & Svendsen, W. E. (2018). Bacteria detection and differentiation using impedance flow cytometry. Sensors, 18(10), 3496.
- Czyczula Rudjord, Z., Reid, M. J., Schwermer, C. U., & Lin, Y. (2022). Laboratory development of an AI system for the real-time monitoring of water quality and detection of anomalies arising from chemical contamination. Water, 14(16), 2588.
- Dodds, W. K. (2002). Freshwater ecology: concepts and environmental applications. Elsevier.
- Furones, A. R., & Monzón, J. I. T. (2023). Blockchain applicability in the management of urban water supply and sanitation systems in Spain. Journal of Environmental Management, 344, 118480.
- Gerhardt, A., Ingram, M. K., Kang, I. J., & Ulitzur, S. (2006). In situ on-line toxicity biomonitoring in water: Recent developments. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry: An International Journal, 25(9), 2263-2271.
- Gunter, H., Bradley, C., Hannah, D. M., Manaseki-Holland, S., Stevens, R., & Khamis, K. (2023). Advances in quantifying microbial contamination in potable water: Potential of fluorescence-based sensor technology. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Water, 10(1), e1622.
- Hammes, F., Berger, C., Köster, O., & Egli, T. (2010). Assessing biological stability of drinking water without disinfectant residuals in a full-scale water supply system. Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology—AQUA, 59(1), 31-40.
- Højris, B., Kornholt, S. N., Christensen, S. C. B., Albrechtsen, H. J., & Olesen, L. S. (2018). Detection of drinking water contamination by an optical real-time bacteria sensor.
- Howard, G., Bartram, J., Water, S., & World Health Organization. (2003). Domestic water quantity, service level and health.
- Hrdy, Jakub, and Petra Vasickova. "Virus detection methods for different kinds of food and water samples–The importance of molecular techniques." Food Control 134 (2022): 108764.
- Hutton, G., & Chase, C. (2017). Water supply, sanitation, and hygiene. Injury Prevention and Environmental Health. 3rd edition.
- Ighalo, J. O., Adeniyi, A. G., & Marques, G. (2021). Internet of things for water quality monitoring and assessment: a comprehensive review. Artificial intelligence for sustainable development: theory, practice and future applications, 245-259.
- Ikeda, J., & Liffiton, K. (2019). Fintech for the water Sector: Advancing financial inclusion for more equitable access to water. World Bank.
- Jackson, R. B., Carpenter, S. R., Dahm, C. N., McKnight, D. M., Naiman, R. J., Postel, S. L., & Running, S. W. (2001). Water in a changing world. Ecological applications, 11(4), 1027-1045.
- Kasahara, S., Kawahara, J., Minato, S. I., & Mori, J. (2023). DAG-Pathwidth: Graph Algorithmic Analyses of DAG-Type Blockchain Networks. IEICE TRANSACTIONS on Information and Systems, 106(3), 272-283.
- Lambrou, T. P., Anastasiou, C. C., Panayiotou, C. G., & Polycarpou, M. M. (2014). A low-cost sensor network for real-time monitoring and contamination detection in drinking water distribution systems. IEEE sensors journal, 14(8), 2765-2772.
- La Rosa, G., Pourshaban, M., Iaconelli, M., & Muscillo, M. (2010). Quantitative real-time PCR of enteric viruses in influent and effluent samples from wastewater treatment plants in Italy. Annali dell’Istituto superiore di sanita, 46, 266-273.
- Magana-Arachchi, D. N., & Wanigatunge, R. P. (2020). Ubiquitous waterborne pathogens. In Waterborne pathogens (pp. 15-42). Butterworth-Heinemann.
- Mattila, V. I. L. M. A., DWIVEDI, P., GAURI, P., & AHBAB, M. (2022). Blockchain for environmentally sustainable economies: case study on 5irechain. International Journal of Social Sciences and Management Review, 5, 50-62.
- Mays, L. W. (2000). Water distribution system handbook. McGraw-Hill Education.
- McGhee, T. J., & Steel, E. W. (1991). Water supply and sewerage (Vol. 6). New York: McGraw-Hill.
- McMeel, D., & Sims, A. (2021). Chip of the new block (chain): blockchain and the construction sector. BRANZ.
- Mills, J. E., & Cumming, O. (2016). The impact of WASH on key health & social outcomes—Review of evidence. London and New York: SHARE Consortium and United Nations Children’s Fund.
- Morabito, V. (2017). Business innovation through blockchain. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Najim, A. (2022). A review of advances in freeze desalination and future prospects. Npj clean water, 5(1), 15.
- Nemerow, N. L., Agardy, F. J., Sullivan, P. J., & Salvato, J. A. (2009). Environmental engineering: water, wastewater, soil and groundwater treatment and remediation. John Wiley & Sons.
- Oberascher, M., Rauch, W., & Sitzenfrei, R. (2022). Towards a smart water city: A comprehensive review of applications, data requirements, and communication technologies for integrated management. Sustainable Cities and Society, 76, 103442.
- Popkin, B. M., D’Anci, K. E., & Rosenberg, I. H. (2010). Water, hydration, and health. Nutrition reviews, 68(8), 439-458.
- Richards, C. E., Tzachor, A., Avin, S., & Fenner, R. (2023). Rewards, risks and responsible deployment of artificial intelligence in water systems. Nature Water, 1-11.
- Schwarzenbach, R. P., Egli, T., Hofstetter, T. B., Von Gunten, U., & Wehrli, B. (2010). Global water pollution and human health. Annual review of environment and resources, 35, 109-136.
- Shahra, E. Q., & Wu, W. (2020). Water contaminants detection using sensor placement approach in smart water networks. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 1-16.
- Sorensen, J. P., Baker, A., Cumberland, S. A., Lapworth, D. J., MacDonald, A. M., Pedley, S.,... & Ward, J. S. (2018). Real-time detection of faecally contaminated drinking water with tryptophan-like fluorescence: defining threshold values. Science of the Total Environment, 622, 1250-1257.
- Spellman, F. R. (2008). Handbook of water and wastewater treatment plant operations. CRC press.
- Stankovic, M., Hasanbeigi, A., & Neftenov, N. (2020). Use of 4IR technologies in water and sanitation in Latin America and the Caribbean.
- Stoffel, D., Rigo, E., Derlon, N., Staaks, C., Heijnen, M., Morgenroth, E., & Jacquin, C. (2022). Low maintenance gravity-driven membrane filtration using hollow fibers: Effect of reducing space for biofilm growth and control strategies on permeate flux. Science of The Total Environment, 811, 152307.
- Tinelli, S., & Juran, I. (2019). Artificial intelligence-based monitoring system of water quality parameters for early detection of non-specific bio-contamination in water distribution systems. Water Supply, 19(6), 1785-1792.
- Wlodkowic, D., & Karpiński, T. M. (2021). Live-cell systems in real-time biomonitoring of water pollution: practical considerations and future perspectives. Sensors, 21(21), 7028.
- World Health Organization. (2022). Guidelines for drinking-water quality: incorporating the first and second addenda. World Health Organization.
- World Health Organization. (2019). Water, sanitation, hygiene and health: a primer for health professionals (No. WHO/CED/PHE/WSH/19.149). World Health Organization.
- Yang, L., Driscol, J., Sarigai, S., Wu, Q., Lippitt, C. D., & Morgan, M. (2022). Towards synoptic water monitoring systems: a review of AI methods for automating water body detection and water quality monitoring using remote sensing. Sensors, 22(6), 2416.
- Yaradou, D. F., Hallier-Soulier, S., Moreau, S., Poty, F., Hillion, Y., Reyrolle, M.,... & Jarraud, S. (2007). Integrated real-time PCR for detection and monitoring of Legionella pneumophila in water systems. Applied and environmental microbiology, 73(5), 1452-1456.
| Physical contaminants |
Inorganic chemicals | Organic chemicals | Biological contaminants |
| Solid particles from nature (soil, rocks, dead trees, animal corpses, etc.) | Sodium, calcium, potassium, magnesium | trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene | Bacteria (E. Coli, Salmonella, Shigella, Legionella, etc.) |
| Organic material (algae, faeces, etc.) | Antimony, arsenic, mercury, cadmium, chromium, iron | Cyanides, phenols, volatile organic compounds, petroleum products | Viruses (Hepatitis A and E, enteroviruses, noroviruses, adenoviruses, etc.) |
| Solid particles resulting from human activity (paper, plastic, glass, etc.) | Sulfate, chloride, nitrate | Algae toxins (cylindrospermopsins, microcystins, saxitoxins) | Protozoa (lamblia, cryptosporidium, entamoeba histolytica, toxoplasma, etc.) |
| Uranium, Radon & other radioactive elements | Pesticides and fertilizers (atrazine, glyphosate, etc.) | Helminths (schistosoma, dracunculus medinensis, fasciola hepatica, etc.) |
| Water supply system management and service | Distributed ledger database | Smart contracts | Tokenization | Automatic reports to stakeholders |
| Smart water quality control | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Planned sanitary events | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Emergency sanitary events | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Supply chain management for water quality control | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Supply chain management for water delivery system | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Clean water conservation | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Auditing process | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Regulation compliance | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| End-consumer sanitary control | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





