Submitted:
25 March 2024
Posted:
26 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of C. sativa Burrs (CSB) Extract
2.3. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.4. Total Flavonoid Content (TFC)
2.5. Determination of Reducing Power
2.6. ABTS∙+ Free-Radical Scavenging Activity
2.7. DPPH∙+ Free-Radical Scavenging Activity
2.8. UPLC-MS-MS
2.9. In vitro Cytotoxicity and Anti-Inflammatory Activity
2.9.1. Cell Cultures
2.9.2. NIH3T3 Cytotoxicity
2.9.3. Cell Viability
2.9.4. Cell Stimulation
2.9.5. Quantification of Intracellular ROS Formation
2.9.6. Determination of NO Production
2.9.7. Protein Extraction
2.9.8. Western Blotting
2.9.9. Immunofluorescence Study
2.10. Mutagenicity Assay: Ames Test
2.11. Statistical Analysis
2.12. In Silico Studies
2.12.1. Structural Optimization and Resources
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Capacity of C. sativa Extract
3.2. NIH3T3 Viability and Proliferation
3.3. CSB Inhibits LPS-Induced ROS Generation
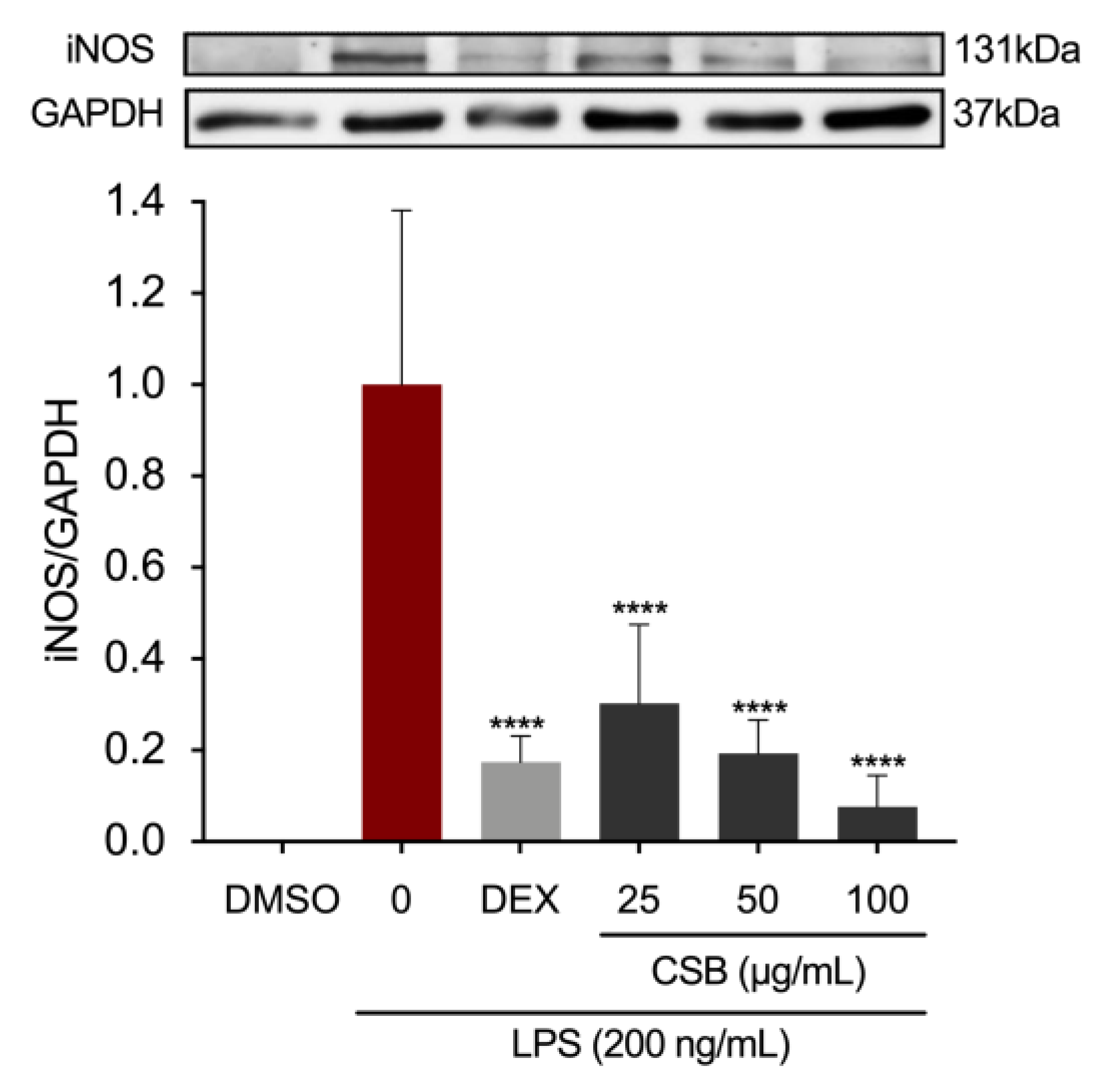
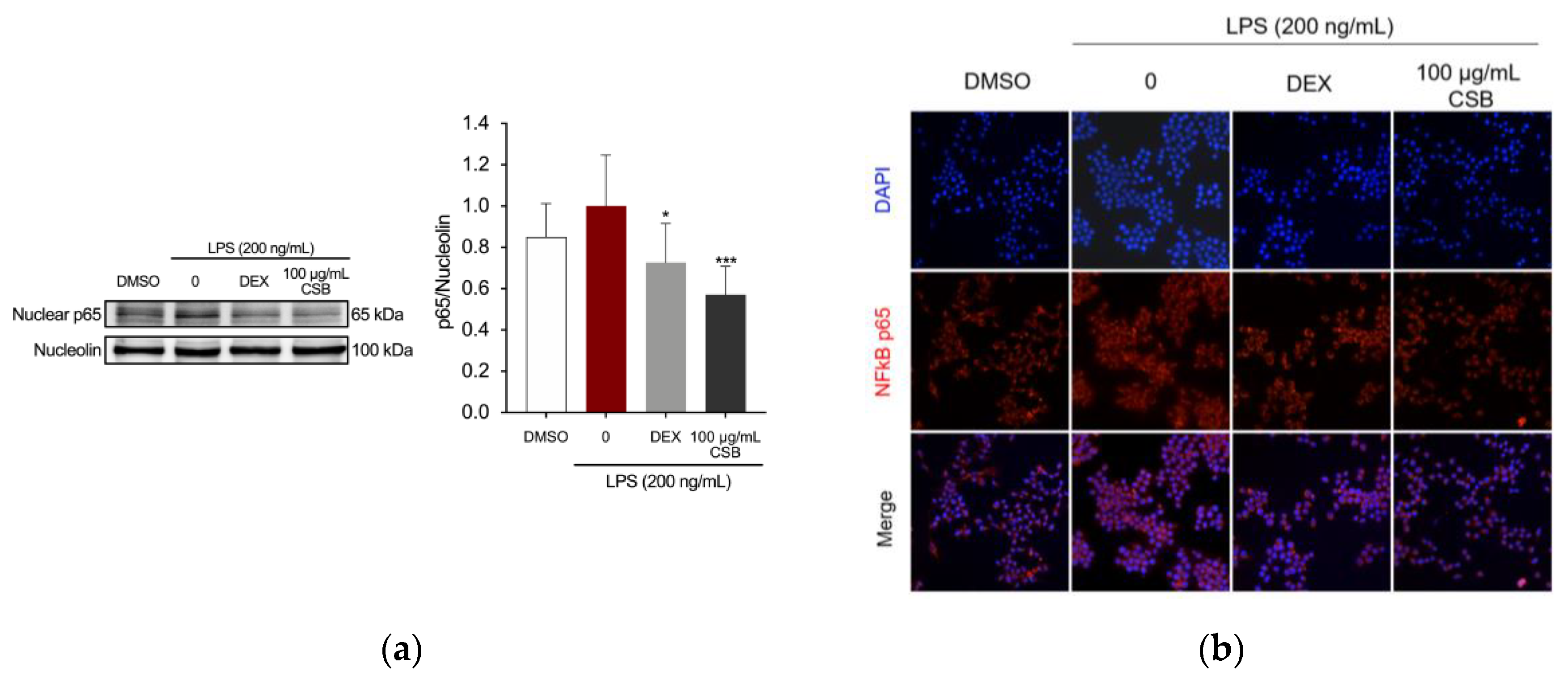
3.4. CSB Reduced LPS-Induced Inflammation in RAW 264.7 Cells
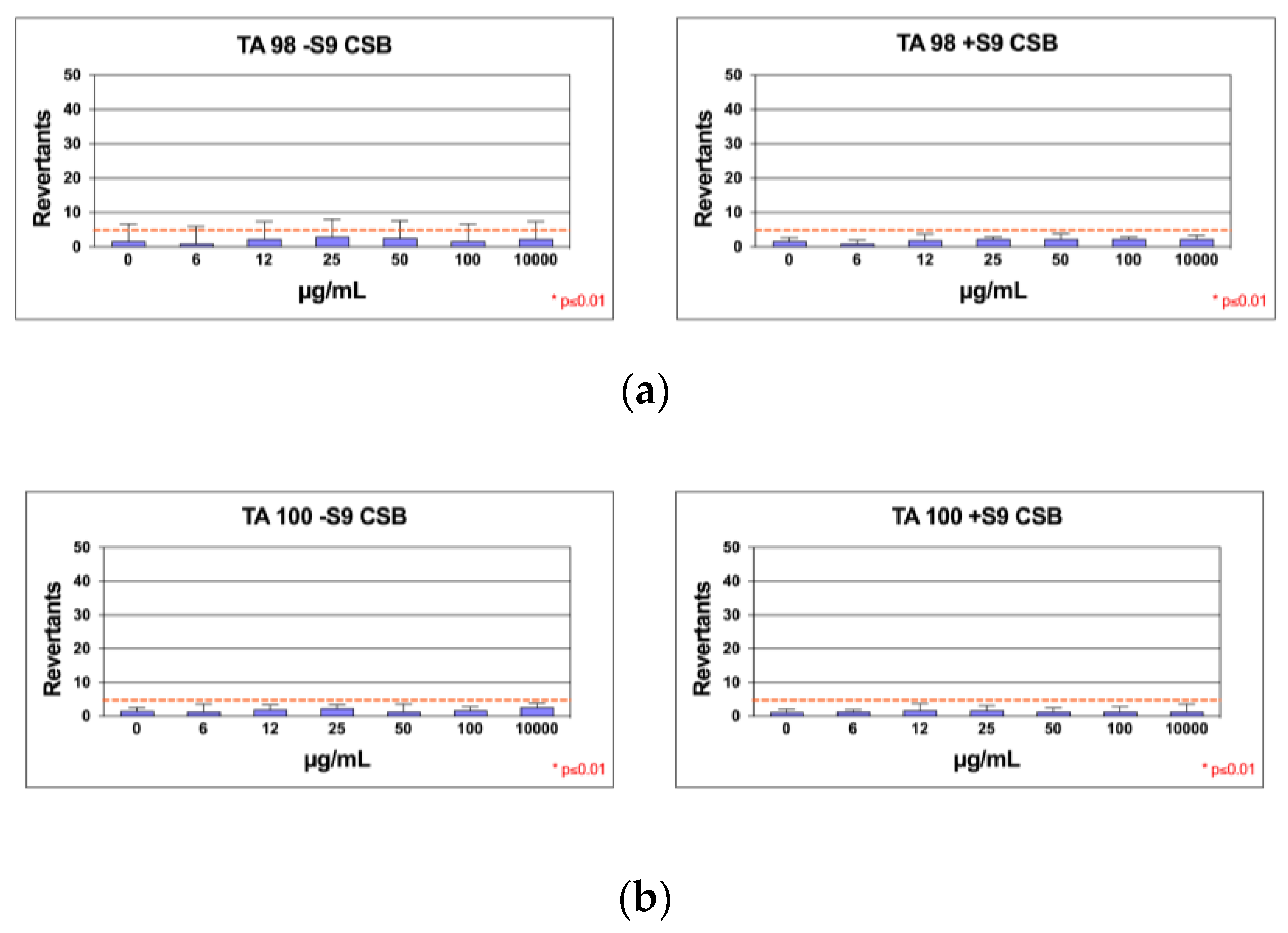
3.5. Mutagenicity Assay: Ames Test
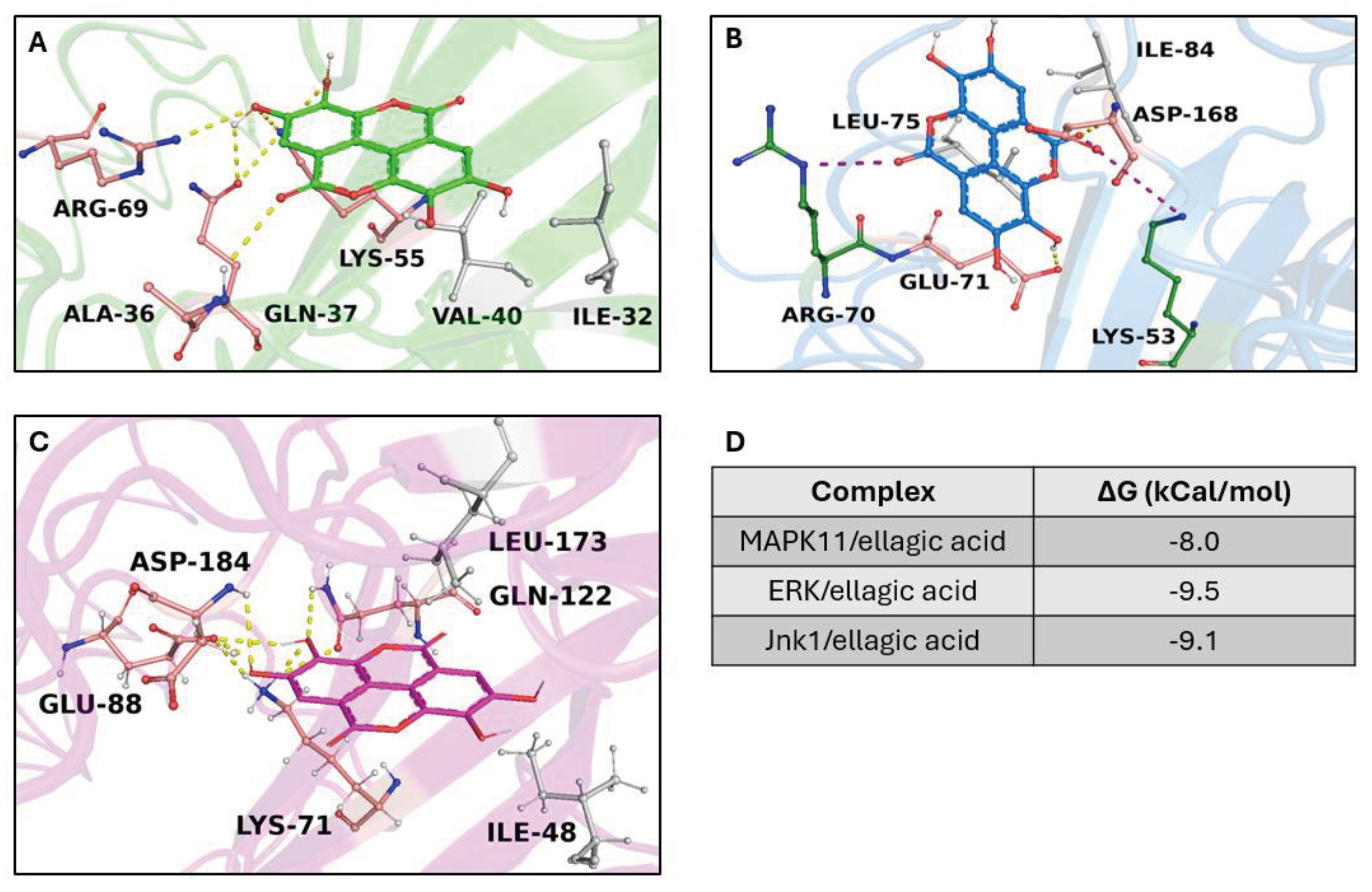
2.2. In Silico Results
2.2.1. Target/Compound Virtual Screening
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Squillaci, G.; Apone, F.; Sena, L.M.; Carola, A.; Tito, A.; Bimonte, M.; Lucia, A. De; Colucci, G.; Cara, F. La; Morana, A. Chestnut ( Castanea Sativa Mill.) Industrial Wastes as a Valued Bioresource for the Production of Active Ingredients. Process Biochemistry 2018, 64, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Braga, N.; Silva, A.M.; Costa, P.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Rodrigues, F. Chestnut. In Valorization of Fruit Processing By-products; Elsevier, 2020; pp. 127–144. [Google Scholar]
- Battisti, A.; Benvegnù, I.; Colombari, F.; Haack, R.A. Invasion by the Chestnut Gall Wasp in Italy Causes Significant Yield Loss in Castanea Sativa Nut Production. Agric For Entomol 2014, 16, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchenko, T.; Degtyaryov, E.; Radzyukevich, Y.; Buryak, V. Therapeutic Potential of Plant Oxylipins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, Vol. 23, Page 14627 2022, 23, 14627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Https://Www.Marketgrowthreports.Com/Global-Biomedical-Materials-Market-21051012.
- Li, L.; Peng, P.; Ding, N.; Jia, W.; Huang, C.; Tang, Y. Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Gut Dysbiosis: What Can Polyphenols Do in Inflammatory Bowel Disease? Antioxidants 2023, 12, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.Y. Regulation of the Gut Microbiome by Inflammasomes. Free Radic Biol Med 2017, 105, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillo, S.; Saleh, M. Inflammasomes in Cancer Progression and Anti-Tumor Immunity. Front Cell Dev Biol 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Braga, N.; Rodrigues, F.; Oliveira, M. Castanea Sativa Bur: An Undervalued By-Product but a Promising Cosmetic Ingredient. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Rodrigues, F.; Braga, N.; Santos, J.; Pimentel, F.B.; Palmeira-de-Oliveira, A.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. The Castanea Sativa Bur as a New Potential Ingredient for Nutraceutical and Cosmetic Outcomes: Preliminary Studies. Food Funct 2017, 8, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.M.; Costa, P.C.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Rodrigues, F. Assessment of a Formulation Containing a Castanea Sativa Shells Extract on Skin Face Parameters: In Vivo Evaluation. Processes 2022, 10, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nema, N.; Rajan, N.; Babu, M.; Sabu, S.; Khamborkar, S.; Sarojam, S.; Sajan, L.; Peter, A.; Chacko, B.; Jacob. Viju Plant Polyphenols as Nutraceuticals and Their Antioxidant Potentials. In Polyphenols; Wiley, 2023; pp. 21–44. [Google Scholar]
- Squillaci, G.; Apone, F.; Sena, L.M.; Carola, A.; Tito, A.; Bimonte, M.; Lucia, A. De; Colucci, G.; Cara, F. La; Morana, A. Chestnut ( Castanea Sativa Mill.) Industrial Wastes as a Valued Bioresource for the Production of Active Ingredients. Process Biochemistry 2018, 64, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiocchio, I.; Prata, C.; Mandrone, M.; Ricciardiello, F.; Marrazzo, P.; Tomasi, P.; Angeloni, C.; Fiorentini, D.; Malaguti, M.; Poli, F.; et al. Leaves and Spiny Burs of Castanea Sativa from an Experimental Chestnut Grove: Metabolomic Analysis and Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity. Metabolites 2020, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, A.L.; Duarte, M.P.; Vatsanidou, A.; Alexopoulou, E. Environmental Aspects of Fiber Crops Cultivation and Use. Ind Crops Prod 2015, 68, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Zuazo, V.H.; Rodríguez, B.C.; García-Tejero, I.F.; Ruiz, B.G. Suitability and Opportunities for Cannabis Sativa L. as an Alternative Crop for Mediterranean Environments. In Current Applications, Approaches, and Potential Perspectives for Hemp; Elsevier, 2023; pp. 3–47. [Google Scholar]
- Song, F.L.; Gan, R.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Kuang, L.; Li, H. Bin Total Phenolic Contents and Antioxidant Capacities of Selected Chinese Medicinal Plants. Int J Mol Sci 2010, 11, 2362–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-C.; Yang, M.-H.; Wen, H.-M.; Chern, J.-C. Estimation of Total Flavonoid Content in Propolis by Two Complementary Colometric Methods. J Food Drug Anal 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Singh, R.P.; Sakariah, K.K. Antioxidant Activity of Grape Seed (Vitis Vinifera) Extracts on Peroxidation Models in Vitro. Food Chem 2001, 73, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyasov, I.R.; Beloborodov, V.L.; Selivanova, I.A.; Terekhov, R.P. ABTS/PP Decolorization Assay of Antioxidant Capacity Reaction Pathways. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamponi, S. Preliminary In Vitro Cytotoxicity, Mutagenicity and Antitumoral Activity Evaluation of Graphene Flake and Aqueous Graphene Paste. Life 2022, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, N.; Ooi, L. A Simple Microplate Assay for Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Rapid Cellular Protein Normalization. Bio Protoc 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feoktistova, M.; Geserick, P.; Leverkus, M. Crystal Violet Assay for Determining Viability of Cultured Cells. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2016, 2016, pdbprot087379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortelmans, K.; Zeiger, E. The Ames Salmonella/Microsome Mutagenicity Assay. Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis 2000, 455, 29–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A Major Update to the DrugBank Database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouillard, A.D.; Gundersen, G.W.; Fernandez, N.F.; Wang, Z.; Monteiro, C.D.; McDermott, M.G.; Ma’ayan, A. The Harmonizome: A Collection of Processed Datasets Gathered to Serve and Mine Knowledge about Genes and Proteins. Database 2016, 2016, baw100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, A.; Martin, M.J.; O’Donovan, C.; Magrane, M.; Alpi, E.; Antunes, R.; Bely, B.; Bingley, M.; Bonilla, C.; Britto, R.; et al. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res 2017, 45, D158–D169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Zaretskaya, I.; Raytselis, Y.; Merezhuk, Y.; McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. NCBI BLAST: A Better Web Interface. Nucleic Acids Res 2008, 36, W5–W9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janson, G.; Paiardini, A. PyMod 3: A Complete Suite for Structural Bioinformatics in PyMOL. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 1471–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A Program to Check the Stereochemical Quality of Protein Structures. J Appl Crystallogr 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; van der Spoel, D.; van Drunen, R. GROMACS: A Message-Passing Parallel Molecular Dynamics Implementation. Comput Phys Commun 1995, 91, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A Web-based Graphical User Interface for CHARMM. J Comput Chem 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebel, M.R.; Schmadeke, G.; Posner, R.G.; Sirimulla, S. AutoDock VinaXB: Implementation of XBSF, New Empirical Halogen Bond Scoring Function, into AutoDock Vina. J Cheminform 2016, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2019 Update: Improved Access to Chemical Data. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47, D1102–D1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An Open Chemical Toolbox. J Cheminform 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusi, F.; Trezza, A.; Spiga, O.; Sgaragli, G.; Bova, S. Ca v 1.2 Channel Current Block by the PKA Inhibitor H-89 in Rat Tail Artery Myocytes via a PKA-Independent Mechanism: Electrophysiological, Functional, and Molecular Docking Studies. Biochem Pharmacol 2017, 140, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusi, F.; Durante, M.; Spiga, O.; Trezza, A.; Frosini, M.; Floriddia, E.; Teodori, E.; Dei, S.; Saponara, S. In Vitro and in Silico Analysis of the Vascular Effects of Asymmetrical N,N-Bis(Alkanol)Amine Aryl Esters, Novel Multidrug Resistance-Reverting Agents. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2016, 389, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adasme, M.F.; Linnemann, K.L.; Bolz, S.N.; Kaiser, F.; Salentin, S.; Haupt, V.J.; Schroeder, M. PLIP 2021: Expanding the Scope of the Protein–Ligand Interaction Profiler to DNA and RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, W530–W534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carullo, G.; Ahmed, A.; Trezza, A.; Spiga, O.; Brizzi, A.; Saponara, S.; Fusi, F.; Aiello, F. A Multitarget Semi-Synthetic Derivative of the Flavonoid Morin with Improved in Vitro Vasorelaxant Activity: Role of CaV1.2 and KCa1.1 Channels. Biochem Pharmacol 2021, 185, 114429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, Scalable Generation of High-quality Protein Multiple Sequence Alignments Using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, O.; Bolshakov, V.N.; Raines, S.; Newham, P.; Perkins, N.D. Transcriptional Profiling of the LPS Induced NF-ΚB Response in Macrophages. BMC Immunol 2007, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trezza, A.; Geminiani, M.; Cutrera, G.; Dreassi, E.; Frusciante, L.; Lamponi, S.; Spiga, O.; Santucci, A. A Drug Discovery Approach to a Reveal Novel Antioxidant Natural Source: The Case of Chestnut Burr Biomass. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreira, J.C.M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Pereira, J.A. Antioxidant Potential of Chestnut (Castanea Sativa L.) and Almond (Prunus Dulcis L.) By-Products. Food Science and Technology International 2010, 16, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Agulló, A.; Freire, M.S.; Antorrena, G.; Pereira, J.A.; González-Álvarez, J. Effect of the Extraction Technique and Operational Conditions on the Recovery of Bioactive Compounds from Chestnut ( Castanea Sativa ) Bur and Shell. Sep Sci Technol 2014, 49, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Falco, V.; Dias, M.I.; Barros, L.; Silva, A.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Amaral, J.S.; Igrejas, G.; C. F. R. Ferreira, I.; et al. Evaluation of the Phenolic Profile of Castanea Sativa Mill. By-Products and Their Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity against Multiresistant Bacteria. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, F.; Santos, J.; Pimentel, F.B.; Braga, N.; Palmeira-de-Oliveira, A.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Promising New Applications of Castanea Sativa Shell: Nutritional Composition, Antioxidant Activity, Amino Acids and Vitamin E Profile. Food Funct 2015, 6, 2854–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vella, F.M.; Laratta, B.; La Cara, F.; Morana, A. Recovery of Bioactive Molecules from Chestnut ( Castanea Sativa Mill.) by-Products through Extraction by Different Solvents. Nat Prod Res 2018, 32, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, N.; Rodrigues, F.; P.P. Oliveira, M.B. Castanea Sativa by-Products: A Review on Added Value and Sustainable Application. Nat Prod Res 2015, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flórez-Fernández, N.; Torres, M.D.; Gómez, S.; Couso, S.; Domínguez, H. Potential of Chestnut Wastes for Cosmetics and Pharmaceutical Applications. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 4721–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadau, S.; Gault, M.; Berthelemy, N.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Danoux, L.; Pelletier, N.; Goudounèche, D.; Pons, C.; Leprince, C.; André-Frei, V.; et al. An Inflamed and Infected Reconstructed Human Epidermis to Study Atopic Dermatitis and Skin Care Ingredients. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 12880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bioactive Compounds in Underutilized Fruits and Nuts; Murthy, H.N., Bapat, V.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; ISBN 978-3-030-30181-1. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Dzah, C.S.; Zandile, M.; Duan, Y.; Ma, H.; Luo, X. Advances in Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Cash Crops – A Review. Ultrason Sonochem 2018, 48, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Rombaut, N.; Sicaire, A.-G.; Meullemiestre, A.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.-S.; Abert-Vian, M. Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Food and Natural Products. Mechanisms, Techniques, Combinations, Protocols and Applications. A Review. Ultrason Sonochem 2017, 34, 540–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerulli, A.; Napolitano, A.; Hošek, J.; Masullo, M.; Pizza, C.; Piacente, S. Antioxidant and In Vitro Preliminary Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Castanea Sativa (Italian Cultivar “Marrone Di Roccadaspide” PGI) Burs, Leaves, and Chestnuts Extracts and Their Metabolite Profiles by LC-ESI/LTQOrbitrap/MS/MS. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, K.; Zhang, Y.; Leahy, K.; Hauser, S.; Masferrer, J.; Perkins, W.; Lee, L.; Isakson, P. Pharmacological and Biochemical Demonstration of the Role of Cyclooxygenase 2 in Inflammation and Pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994, 91, 12013–12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, R.; Vodovotz, Y.; Billiar, T.R. Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase and Inflammatory Diseases. Molecular Medicine 2000 6:5 2000, 6, 347–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchin, B.M.; dos Reis, G.O.; Vieira, G.N.; Mohr, E.T.B.; da Rosa, J.S.; Kretzer, I.F.; Demarchi, I.G.; Dalmarco, E.M. Inflammatory Biomarkers on an LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Cell Model: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Inflammation Research 2022, 71, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Quispe, C.; Castillo, C.M.S.; Caroca, R.; Lazo-Vélez, M.A.; Antonyak, H.; Polishchuk, A.; Lysiuk, R.; Oliinyk, P.; De Masi, L.; et al. Ellagic Acid: A Review on Its Natural Sources, Chemical Stability, and Therapeutic Potential. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.-H.; Shiao, H.-Y.; Tu, C.-H.; Liu, P.-M.; Hsu, J.T.-A.; Amancha, P.K.; Wu, J.-S.; Coumar, M.S.; Chen, C.-H.; Wang, S.-Y.; et al. Protein Kinase Inhibitor Design by Targeting the Asp-Phe-Gly (DFG) Motif: The Role of the DFG Motif in the Design of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors. J Med Chem 2013, 56, 3889–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arter, C.; Trask, L.; Ward, S.; Yeoh, S.; Bayliss, R. Structural Features of the Protein Kinase Domain and Targeted Binding by Small-Molecule Inhibitors. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2022, 298, 102247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, C.; Hou, Y.; Ai, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, X. Gallic Acid: Pharmacological Activities and Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Inflammation-Related Diseases. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2021, 133, 110985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mard, S.A.; Mojadami, S.; Farbood, Y.; Kazem, M.; Naseri, G.; Ali, S.; Phd, M. The Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Gallic Acid against Mucosal Inflammation- and Erosions-Induced by Gastric Ischemia-Reperfusion in Rats. Veterinary Research Forum 2015, 6, 305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chagas, M. do S.S.; Behrens, M.D.; Moragas-Tellis, C.J.; Penedo, G.X.M.; Silva, A.R.; Gonçalves-de-Albuquerque, C.F. Flavonols and Flavones as Potential Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Antibacterial Compounds. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Heo, M.Y.; Kim, H.P. Flavonoids: Broad Spectrum Agents on Chronic Inflammation. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 2019, 27, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; -Ji, M.; * -Qin; -Gu, Z.; -Liu, Y.; -Sikandar; -Iqbal, M.F.; -Javeed, A. PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING, TOTAL PHENOLIC AND FLAVONOIDS CONTENTS AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITIES OF CITRULLUS COLOCYNTHIS L. AND CANNABIS SATIVA L. [CrossRef]
- Mkpenie, V.N.; Essien, E.E.; Udoh, I.I. Effect of Extraction Conditions on Total Polyphenol Contents, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Cannabis Sativa L. Electronic Journal of Environmental, Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2012, 11, 300–307. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.-M.; Cheng, M.-Y.; Xun, M.-H.; Zhao, Z.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, W.; Cheng, J.; Ni, J.; Wang, W. Possible Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress-Induced Skin Cellular Senescence, Inflammation, and Cancer and the Therapeutic Potential of Plant Polyphenols. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernarelli, J.A.; Lambert, J.D. Flavonoid Intake Is Inversely Associated with Obesity and C-Reactive Protein, a Marker for Inflammation, in US Adults. Nutrition & Diabetes 2017 7:5 2017, 7, e276–e276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre-Arbogast, S.; Gaudout, D.; Bensalem, J.; Letenneur, L.; Dartigues, J.F.; Hejblum, B.P.; Féart, C.; Delcourt, C.; Samieri, C. Pattern of Polyphenol Intake and the Long-Term Risk of Dementia in Older Persons. Neurology 2018, 90, e1979–e1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; He, F.; Wu, C.; Li, P.; Li, N.; Deng, J.; Zhu, G.; Ren, W.; Peng, Y. Betaine in Inflammation: Mechanistic Aspects and Applications. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, M.K.; Paal, M.C.; Donohue, T.M.; Ganesan, M.; Osna, N.A.; Kharbanda, K.K. Beneficial Effects of Betaine: A Comprehensive Review. Biology 2021, Vol. 10, Page 456 2021, 10, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, E.K.; Jung, K.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Yu, B.P.; Chung, H.Y. Betaine Suppresses Proinflammatory Signaling During Aging: The Involvement of Nuclear Factor- B via Nuclear Factor-Inducing Kinase/I B Kinase and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2005, 60, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
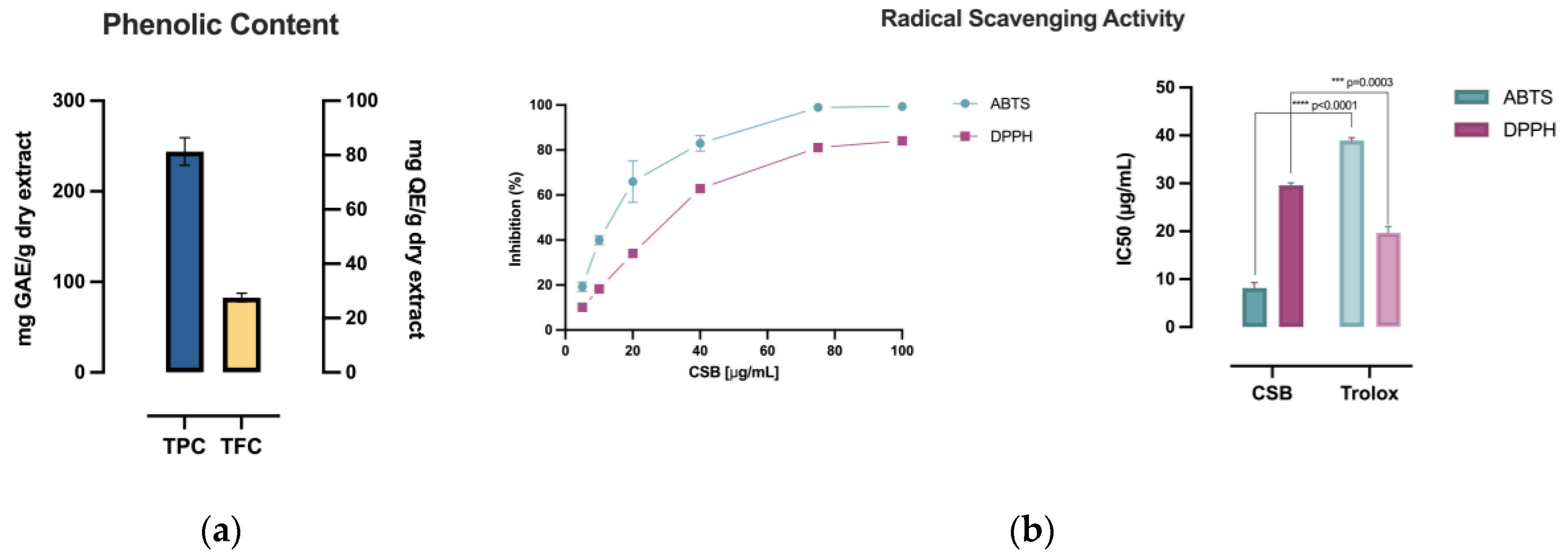
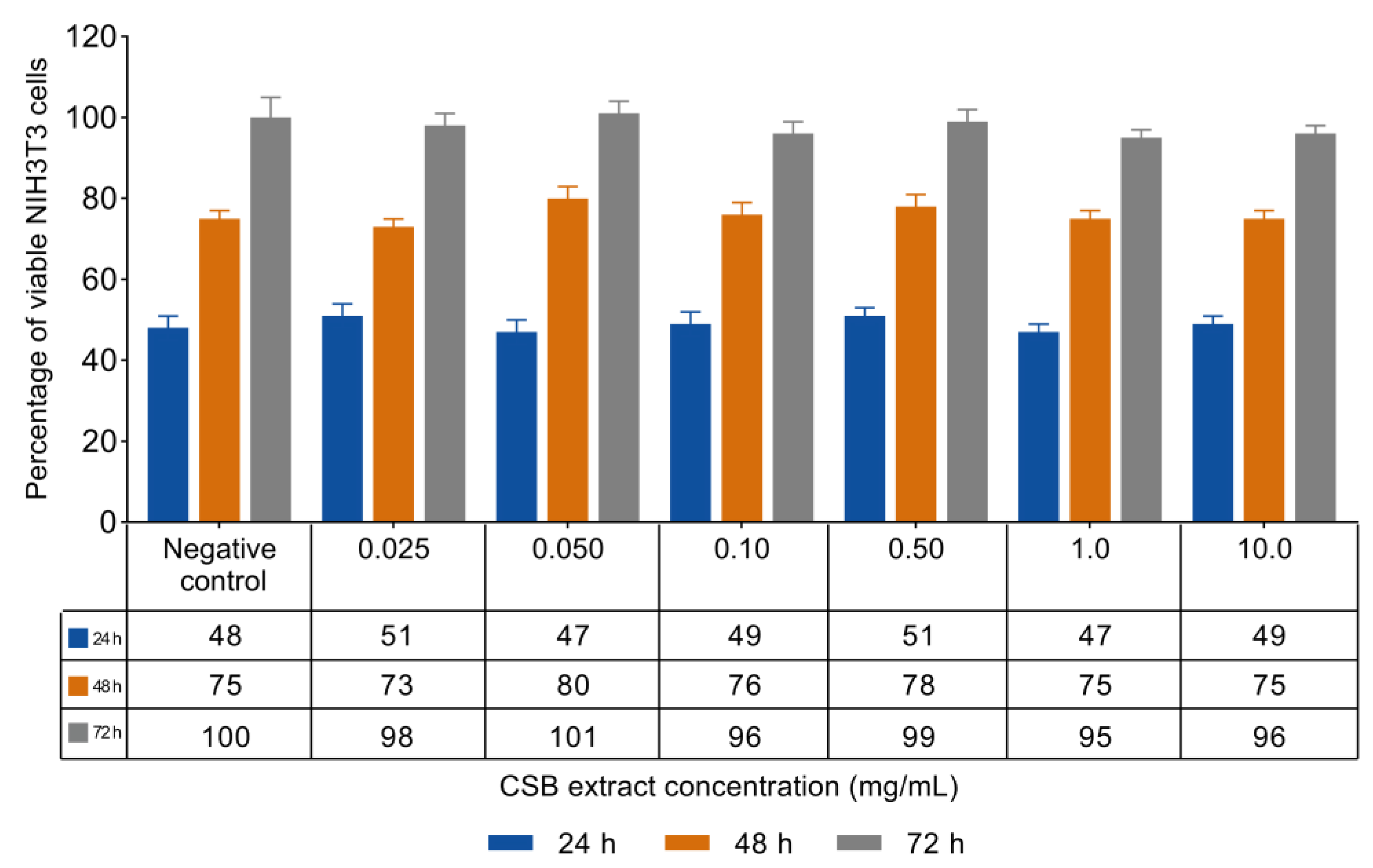
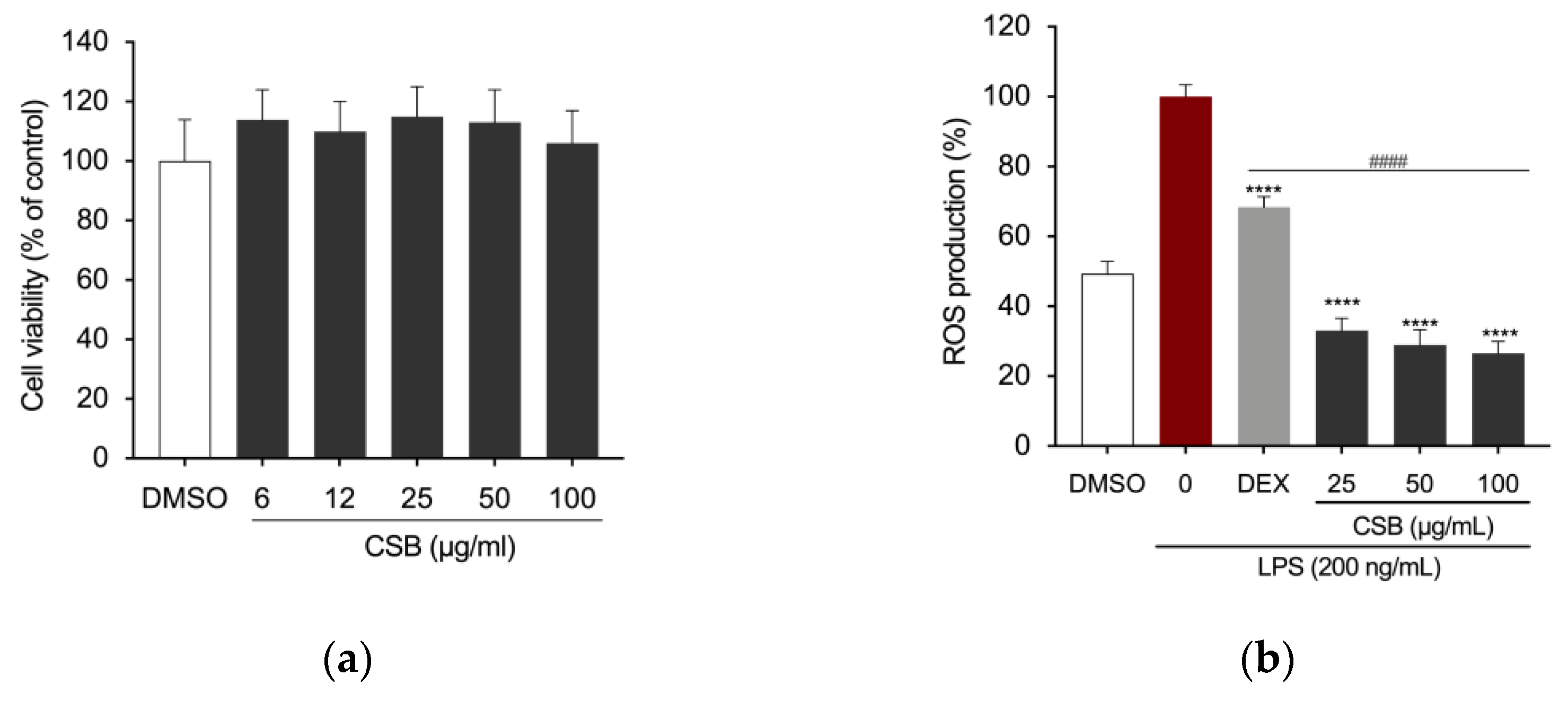
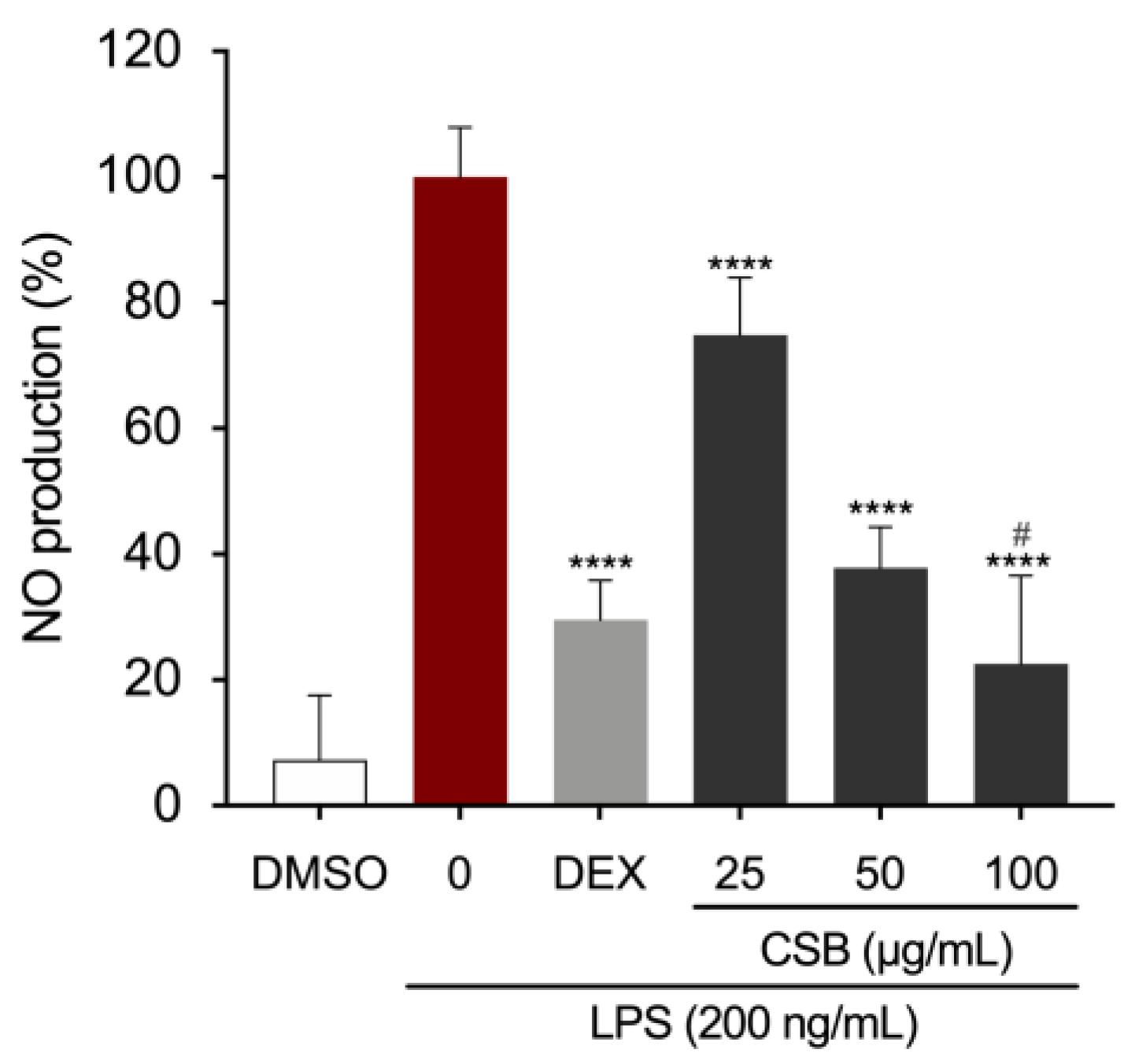
| Antioxidant Capacity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPC (mg GAE/g) |
TFC (mg QE/g) |
TRP (mg AAE/g) |
ABTS•+ (IC50 µg/mL) |
DPPH (IC50 µg/mL) |
|
| CSB | 243.98±17.77 | 27.54±0.60 | 272.12±4.64 | 8.16±1.11 | 29.57±0.57 |
| Chemical class | % of CSB |
|---|---|
| Phenolic compounds | 71.43 |
| Polyphenols | 54.01 |
| Flavonoids | 16.95 |
| Phenolic aldehydes | 0.47 |
| Amino acids | 22.0 |
| Plant hormones | 3.64 |
| Terpenes | 1.69 |
| Others | tr.* |
| No. | Name | Retention time (min) | Formula | Calculated MW |
Theoretical m/z |
Reference ion |
Mass error (ppm) | Area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ellagic acid | 15.388 | C14H6O8 | 302.00617 | 300.9988 | [M-H]-1 | -0.33 | 51.7 |
| 2 | Betaine | 1.863 | C5H11NO2 | 117.07923 | 118.0865 | [M+H]+1 | 2.17 | 22.0 |
| 3 | 5,7-dihydroxy-3.8-dimethoxy-2-phenyl-4h-chromen-4-one | 29.172 | C17H14O6 | 314.07985 | 315.0871 | [M+H]+1 | 2.59 | 15.8 |
| 4 | Mollioside | 25.285 | C26H40O10 | 512.26256 | 513.2698 | [M+H]+1 | 0.81 | 1.7 |
| 5 | (±)-(2e)-abscisic acid | 11.733 | C15H20O4 | 264.13625 | 265.1435 | [M+H]+1 | 0.34 | 1.6 |
| 6 | 3,8-di-o-methylellagic acid | 21.233 | C16H10O8 | 330.03838 | 331.0457 | [M+H]+1 | 2.46 | 1.4 |
| 7 | 12-hydroxyjasmonic acid | 18.885 | C12H18O4 | 226.12108 | 227.1284 | [M+H]+1 | 2.53 | 0.9 |
| 8 | Epi-jasmonic acid | 15.442 | C12H18O3 | 210.12618 | 211.1335 | [M+H]+1 | 2.77 | 0.7 |
| 9 | Protocatechuic aldehyde | 6.164 | C7H6O3 | 138.03177 | 139.0391 | [M+H]+1 | 0.56 | 0.4 |
| 10 | Gibberellin A2 o-beta-d-glucoside | 23.076 | C25H36O11 | 512.22551 | 513.2328 | [M+H]+1 | -0.49 | 0.3 |
| 11 | Sinapaldehyde | 21.782 | C11H12O4 | 208.07372 | 209.081 | [M+H]+1 | 0.76 | 0.3 |
| 12 | 12-hydroxyjasmonic acid 12-o-beta-d-glucoside | 19.078 | C19H30O8 | 386.1931 | 387.2004 | [M+H]+1 | -2.5 | 0.3 |
| 13 | 5,7-dihydroxy-3’,4’,5’-trimethoxyflavanone | 18.774 | C18H18O7 | 346.10628 | 347.1136 | [M+H]+1 | 2.97 | 0.2 |
| 14 | (+)-Gibberellic acid | 16.236 | C19H22O6 | 346.14242 | 347.1497 | [M+H]+1 | 2.25 | 0.2 |
| 15 | N-propyl galiate | 10.343 | C10H12O5 | 212.06876 | 235.058 | [M+Na]+1 | 1.35 | 0.2 |
| 16 | Syringaldehyde | 12.269 | C9H10O4 | 182.05821 | 183.0655 | [M+H]+1 | 1.68 | 0.2 |
| 17 | Retusin (flavonol) | 18.648 | C19H18O7 | 358.10628 | 359.1136 | [M+H]+1 | 2.87 | 0.2 |
| 18 | Acaciin | 11.453 | C28H32O14 | 592.17833 | 593.1856 | [M+H]+1 | -1.48 | 0.2 |
| 19 | Kaempferol | 17.111 | C15H10O6 | 286.04805 | 287.0553 | [M+H]+1 | 1.1 | 0.2 |
| 20 | Scopoletin | 16.019 | C10H8O4 | 192.04282 | 193.0501 | [M+H]+1 | 2.91 | 0.2 |
| 21 | Isorhamnetin 3-rhamnosyl-(1->2)-gentiobiosyl- (1->6) -glucoside | 28.24 | C40H52O26 | 948.27548 | 949.2828 | [M+H]+1 | 0.84 | 0.1 |
| 22 | 5,7-methoxyflavanone | 12.653 | C17H16O4 | 284.10549 | 285.1128 | [M+H]+1 | 2.21 | 0.1 |
| 23 | 4’.5.7-trimethoxyflavone | 20.486 | C18H16O5 | 312.10053 | 313.1079 | [M+H]+1 | 2.44 | 0.1 |
| 24 | Ethyl gallate | 13.29 | C9H10O5 | 198.05319 | 199.0605 | [M+H]+1 | 1.87 | 0.1 |
| 25 | 2-(2,6-dimethoxyphenyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-4h-chromen-4-one (zapotin) | 16.541 | C19H18O6 | 342.11131 | 343.1186 | [M+H]+1 | 2.85 | 0.1 |
| 26 | Helichrysoside | 20.13 | C30H26O14 | 610.13403 | 633.1237 | [M+Na]+1 | 2.91 | 0.1 |
| 27 | 1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-(2-pyrrolidinyl)-2-quinolinecarboxylic acid | 17.834 | C14H14N2O3 | 258.10066 | 259.1079 | [M+H]+1 | 0.86 | 0.1 |
| 28 | Afrormosin | 16.195 | C17H14O5 | 298.08489 | 299.0922 | [M+H]+1 | 2.56 | 0.1 |
| 29 | Gibberellin A17 | 6.043 | C20H26O7 | 378.16813 | 377.1609 | [M-H]-1 | 0.75 | 0.1 |
| 30 | Quercetin | 17.258 | C15H10O7 | 302.04329 | 303.0506 | [M+H]+1 | 2.11 | 0.1 |
| 31 | 1,3-bis-(5-carboxypentyl)-urea | 11.099 | C13H24N2O5 | 288.16887 | 289.1762 | [M+H]+1 | 1.21 | 0.1 |
| 32 | 5-carboxyvanillic acid | 13.026 | C9H8O6 | 212.0318 | 211.0245 | [M-H]-1 | -1.37 | tr. |
| 33 | 3-hydroxyflavone | 18.639 | C15H10O3 | 238.06363 | 239.0709 | [M+H]+1 | 2.68 | tr. |
| 34 | Coniferaldehyde | 19.593 | C10H10O3 | 178.0632 | 179.0705 | [M+H]+1 | 1.18 | tr. |
| 35 | Gibberellin A1/A34 | 39.565 | C19H24O6 | 348.15815 | 349.1654 | [M+H]+1 | 2.47 | tr. |
| 36 | Isorhamnetin 3-o-alpha-l-[6’’’’-p-coumaroyl-beta-d-glucopyranosyl-(1->2)-rhamnopyranoside] | 20.825 | C37H38O18 | 770.20801 | 793.1978 | [M+Na]+1 | 2.85 | tr. |
| 37 | Gibberellin A53 | 38.444 | C20H28O5 | 348.19405 | 349.2013 | [M+H]+1 | 1.07 | tr. |
| 38 | 2’,5-digalloylhamamelofuranose | 12.064 | C20H20O14 | 484.08397 | 485.0913 | [M+H]+1 | -2.76 | tr. |
| 39 | (+)-Catechin 7-o-beta-d-xyloside | 18.011 | C20H22O10 | 422.12248 | 445.1117 | [M+Na]+1 | 2.81 | tr. |
| 40 | Digallic acid | 2.807 | C14H10O9 | 322.03294 | 321.0257 | [M-H]-1 | 1.43 | tr. |
| 41 | (E)-ferulic acid | 29.676 | C10H10O4 | 194.05788 | 195.0652 | [M+H]+1 | -0.16 | tr. |
| 42 | 1,3-dibutyl-1,3-dimethylurea | 13.625 | C11H24N2O | 200.18829 | 199.181 | [M-H]-1 | -2.86 | tr. |
| 43 | Kaempferol-3-o-(6’’’-trans-p-coumaroyl-2’’-glucosyl)rhamnoside | 21.66 | C36H36O17 | 740.19518 | 741.2025 | [M+H]+1 | -0.1 | tr. |
| 44 | Tomentosin | 15.583 | C15H20O3 | 248.14121 | 249.1487 | [M+H]+1 | -0.15 | tr. |
| 45 | Catechin gallate. (-)- | 18.618 | C22H18O10 | 442.08926 | 443.0965 | [M+H]+1 | -1.68 | tr. |
| 46 | Coniferyl aldehyde | 24.95 | C10H10O3 | 178.0632 | 179.0705 | [M+H]+1 | 1.18 | tr. |
| 47 | Quercetin-3-o-(6’’’-trans-p-coumaroyl-2’’-glucosyl)rhamnoside | 18.932 | C36H36O18 | 756.19158 | 779.1812 | [M+Na]+1 | 1.87 | tr. |
| 48 | Gibberellin A24 | 37.98 | C20H26O5 | 346.17818 | 347.1855 | [M+H]+1 | 0.45 | tr. |
| 49 | Glucogallin | 3.747 | C13H16O10 | 332.07488 | 331.0676 | [M-H]-1 | 1.61 | tr. |
| 50 | 5’-desgalloylstachyurin | 11.878 | C34H24O22 | 784.0757 | 783.0684 | [M-H]-1 | -0.29 | tr. |
| 51 | Gibberellin A12 | 44.209 | C20H28O4 | 332.19787 | 333.2052 | [M+H]+1 | -2.67 | tr. |
| 52 | (+)-Gallocatechin | 2.929 | C15H14O7 | 306.07341 | 305.0661 | [M-H]-1 | -1.78 | tr. |
| 53 | Isorhamnetin | 23.872 | C16H12O7 | 316.05908 | 315.0518 | [M-H]-1 | 2.47 | tr. |
| 54 | Myricetin-3-o-glucoside | 8.465 | C21H20O13 | 480.09172 | 479.0844 | [M-H]-1 | 2.77 | tr. |
| 55 | 1,6-bis-o-galloyl-beta-d-glucose | 8.974 | C20H20O14 | 484.0862 | 483.0789 | [M-H]-1 | 1.84 | tr. |
| 56 | Castalagin/vescalagin | 15.21 | C41H26O26 | 934.06952 | 933.0623 | [M-H]-1 | -1.83 | tr. |
| Tot | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





