Submitted:
22 March 2024
Posted:
22 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Catalyst preparation
2.3. Catalyst characterization
2.4. Catalytic evaluation
3. Results
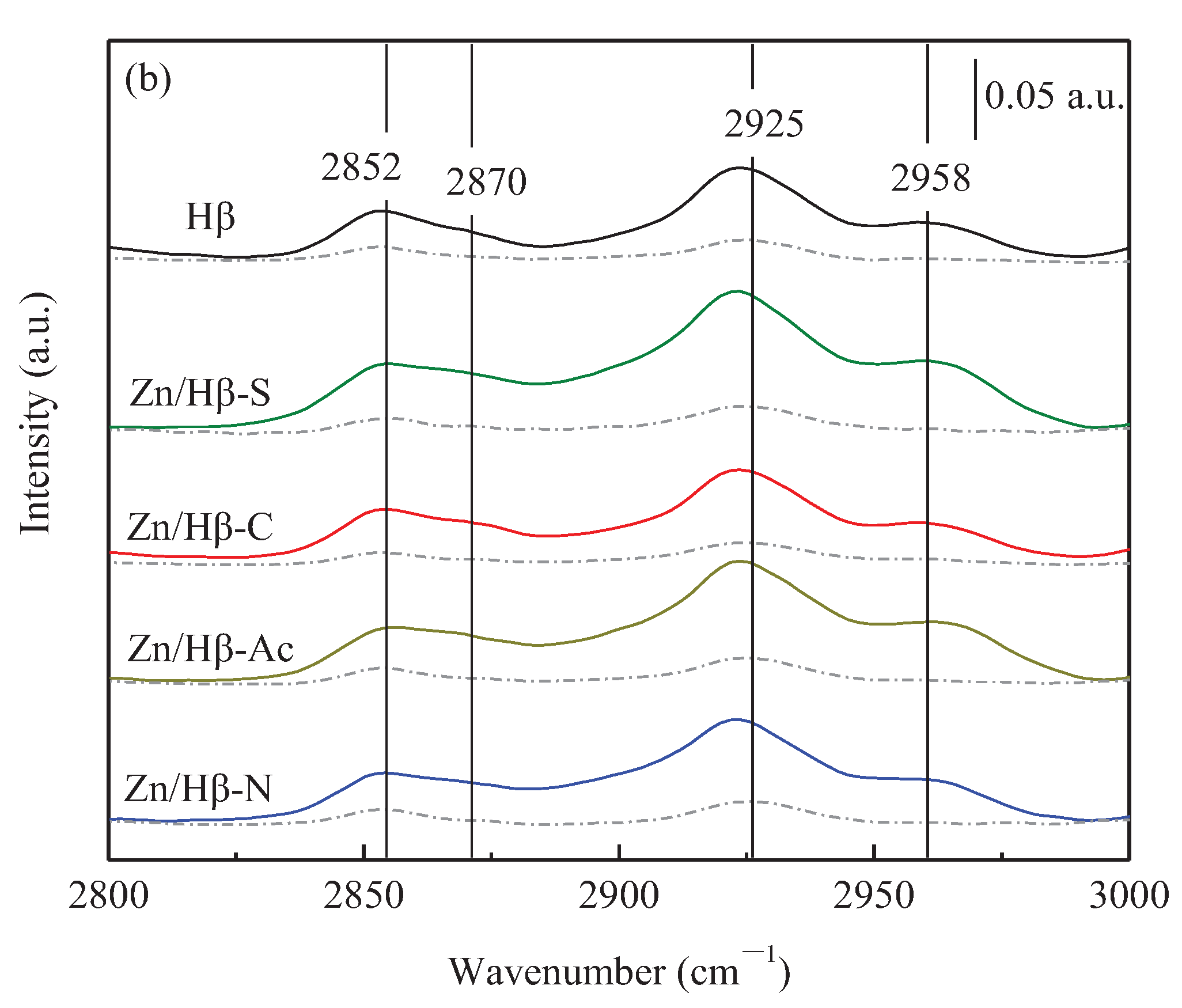
3.1. Structural and textural properties
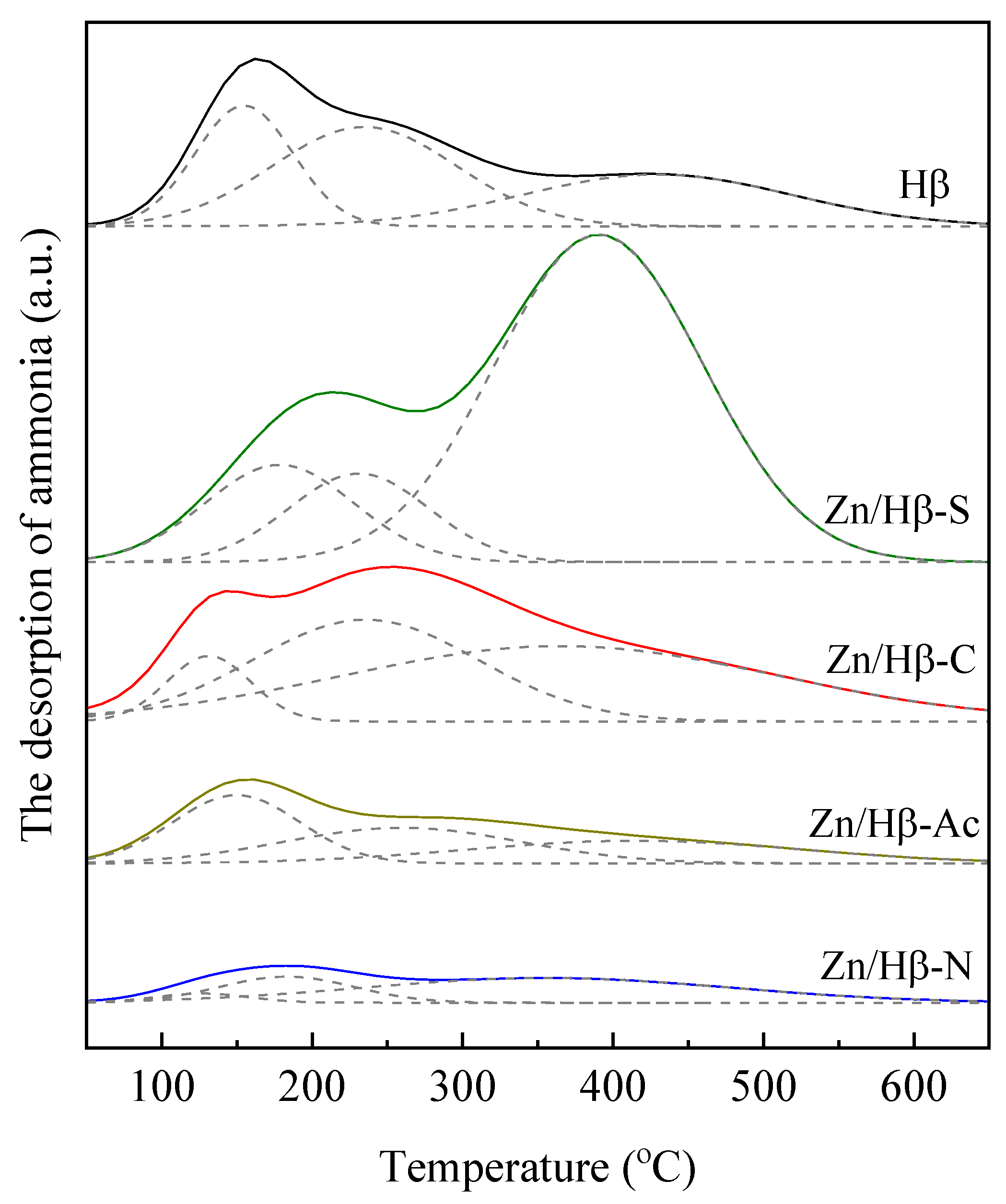
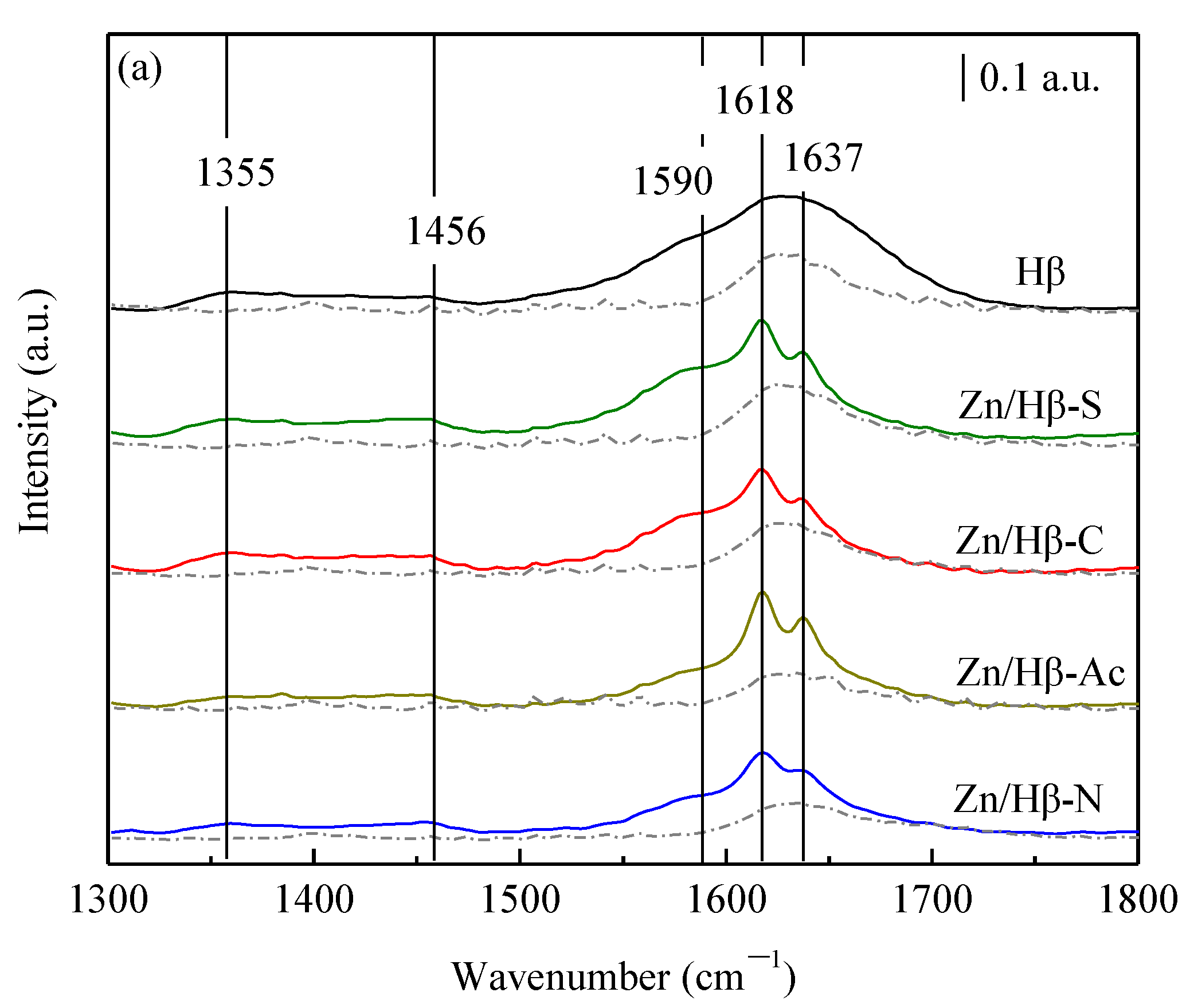
3.2. Acidic properties
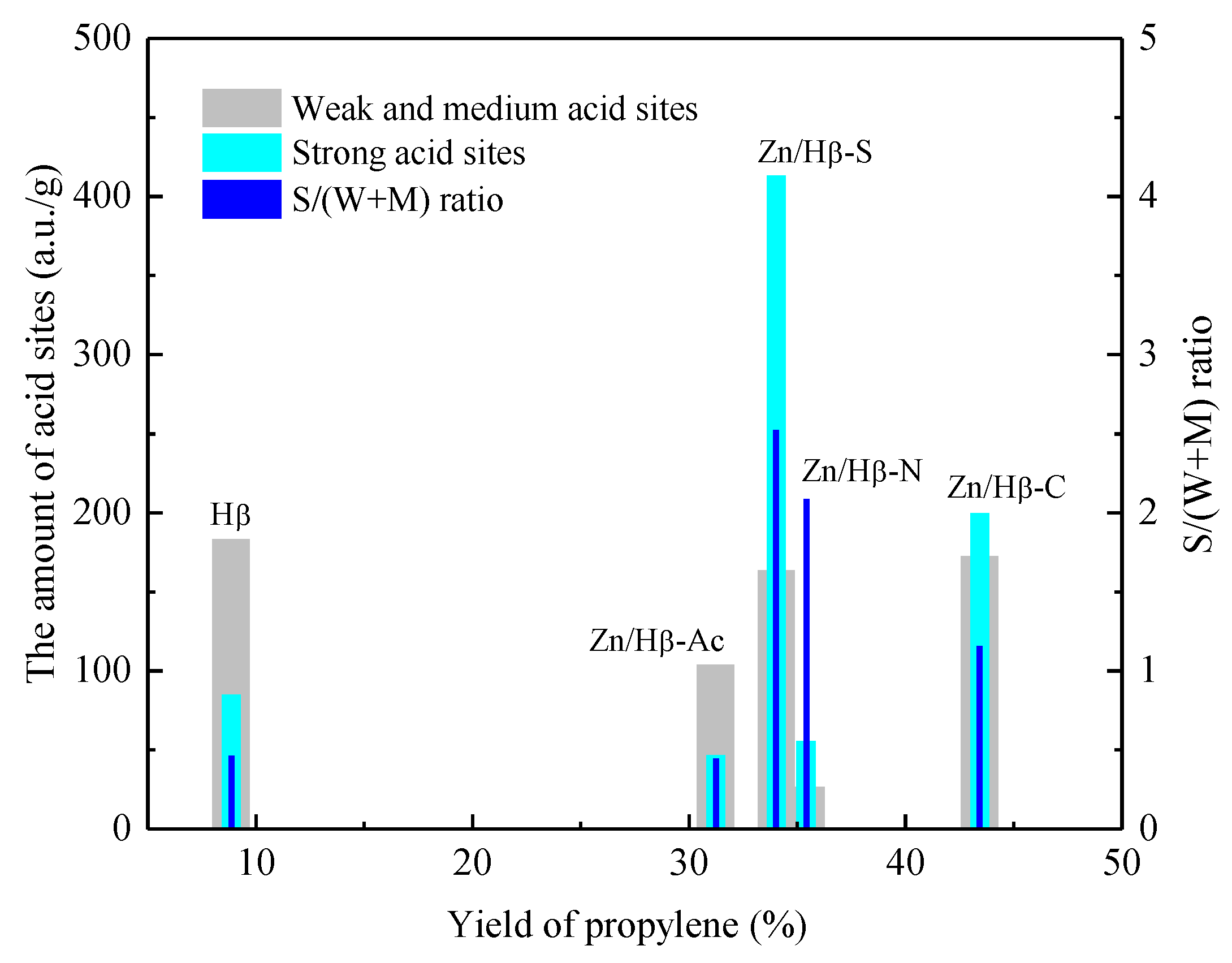
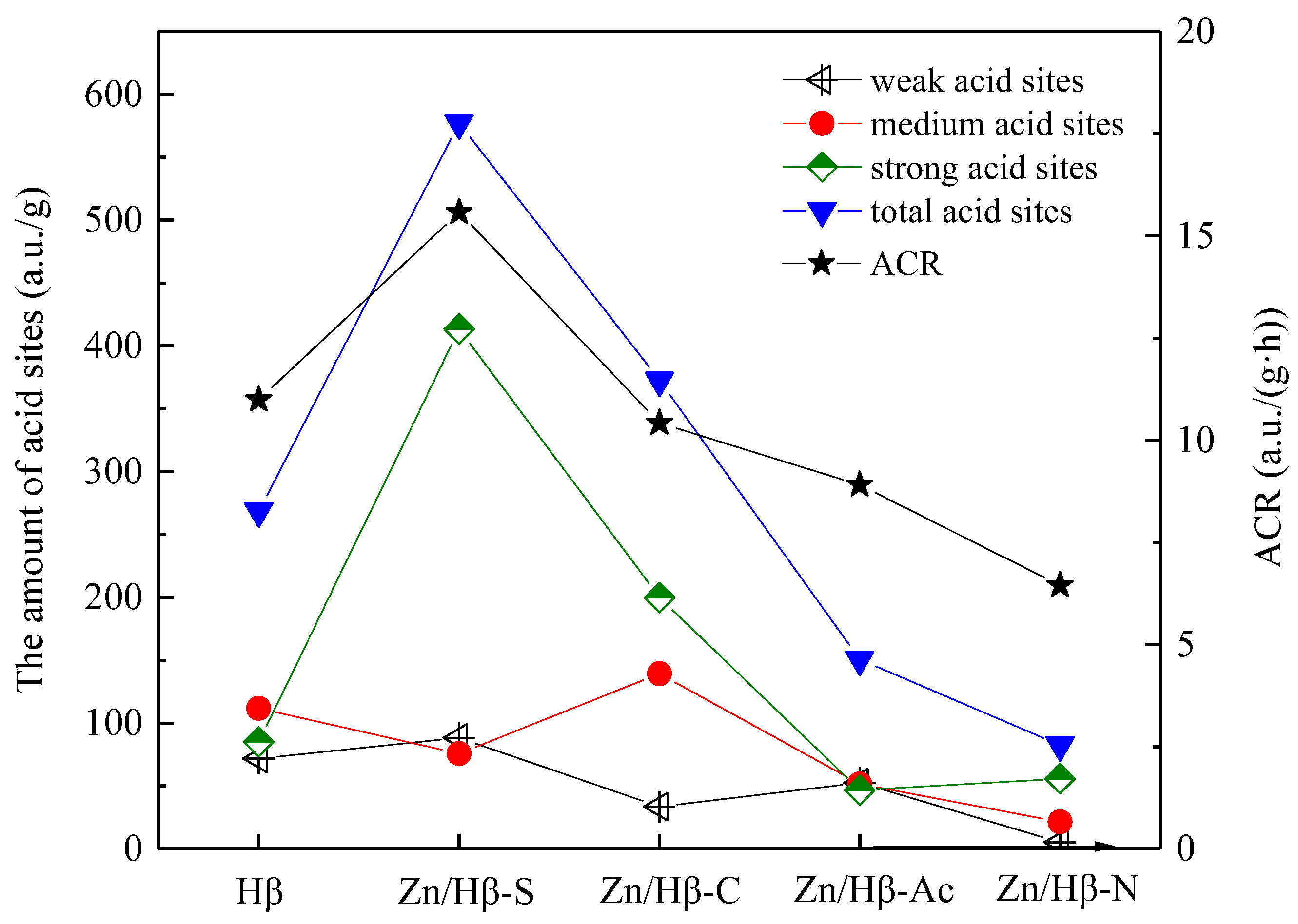
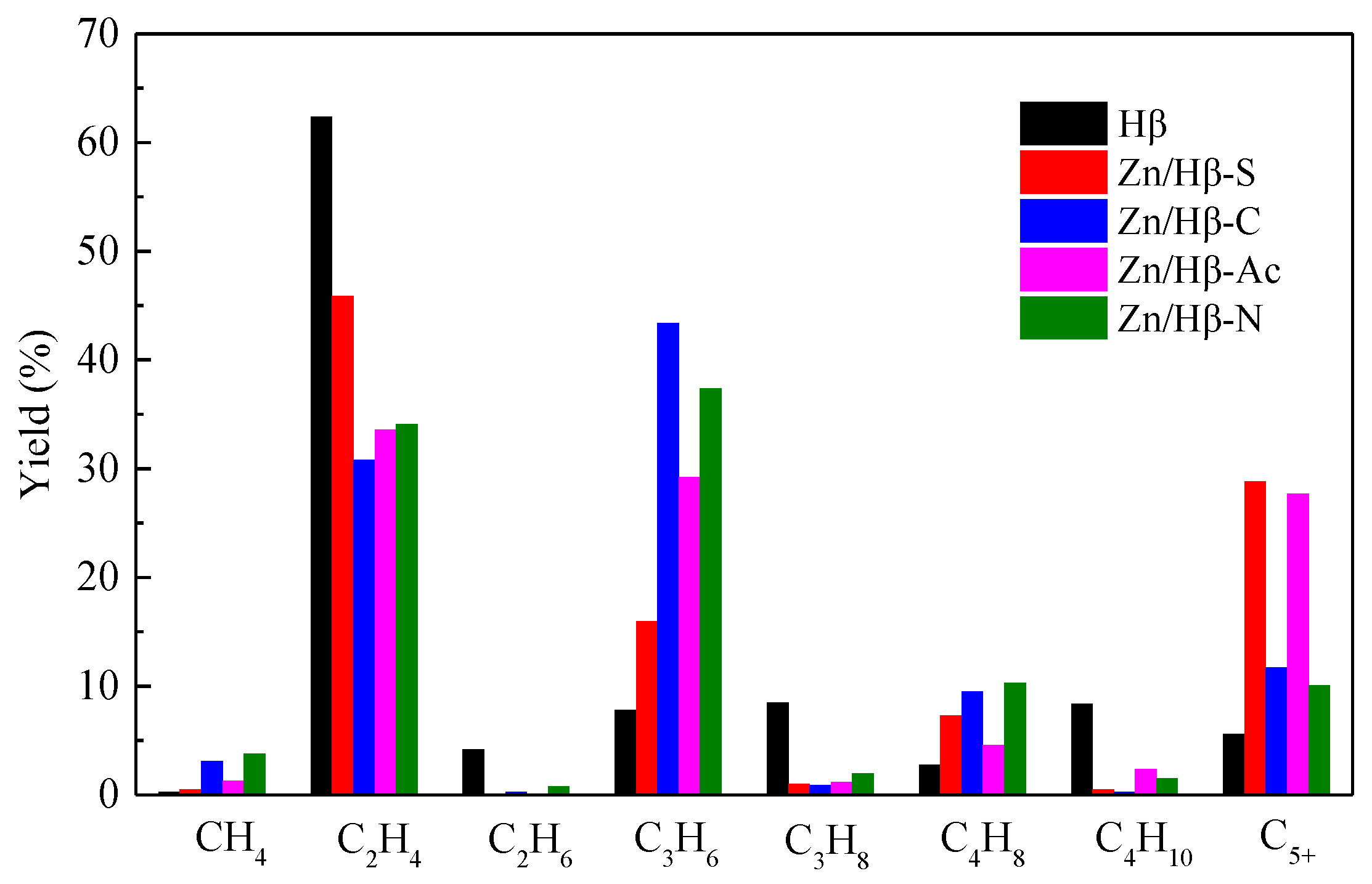
3.3. Catalytic performance
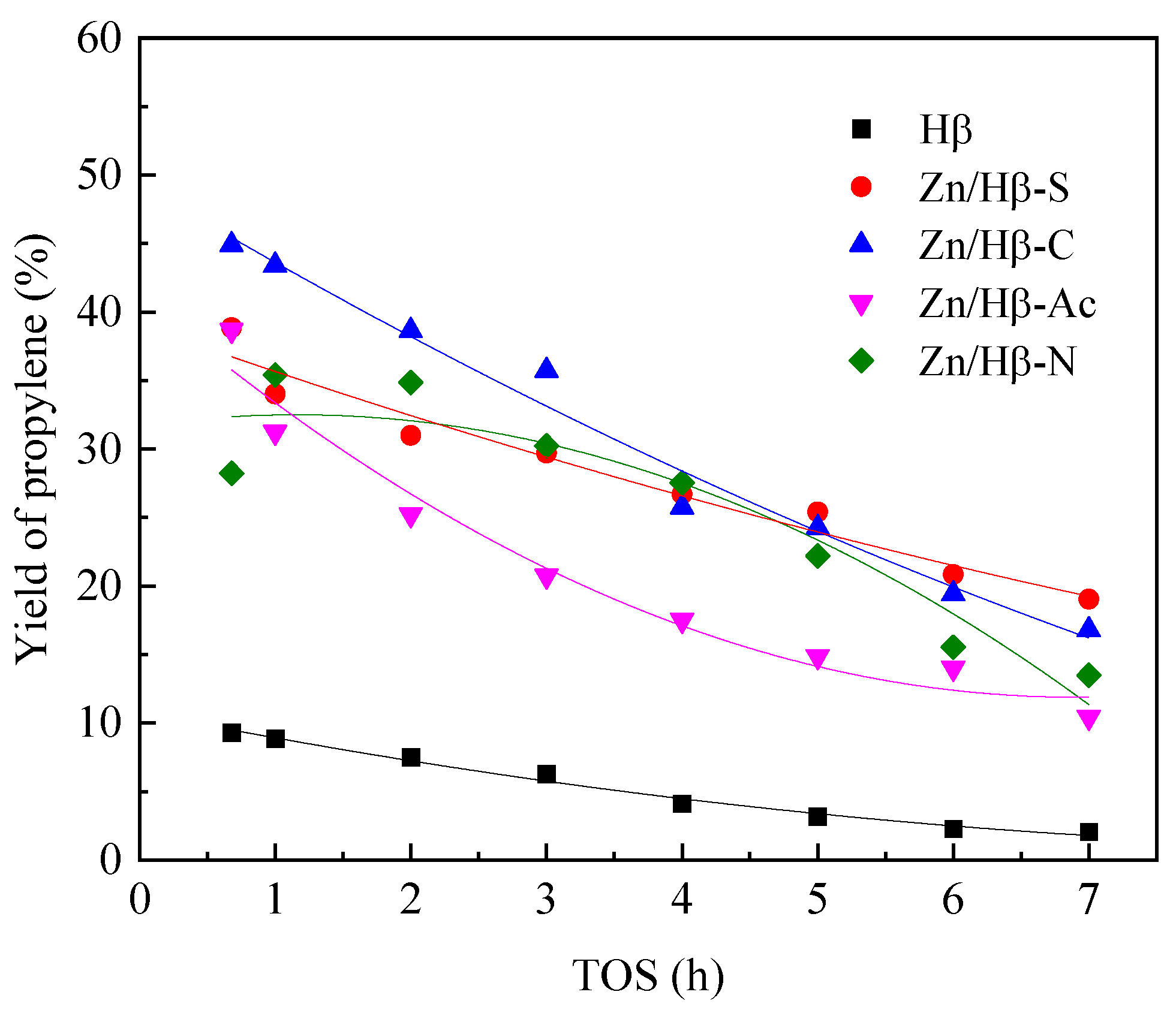
3.4. Deactivation of the catalysts
4. Discussion
4.1. Key factors effecting the catalytic activity
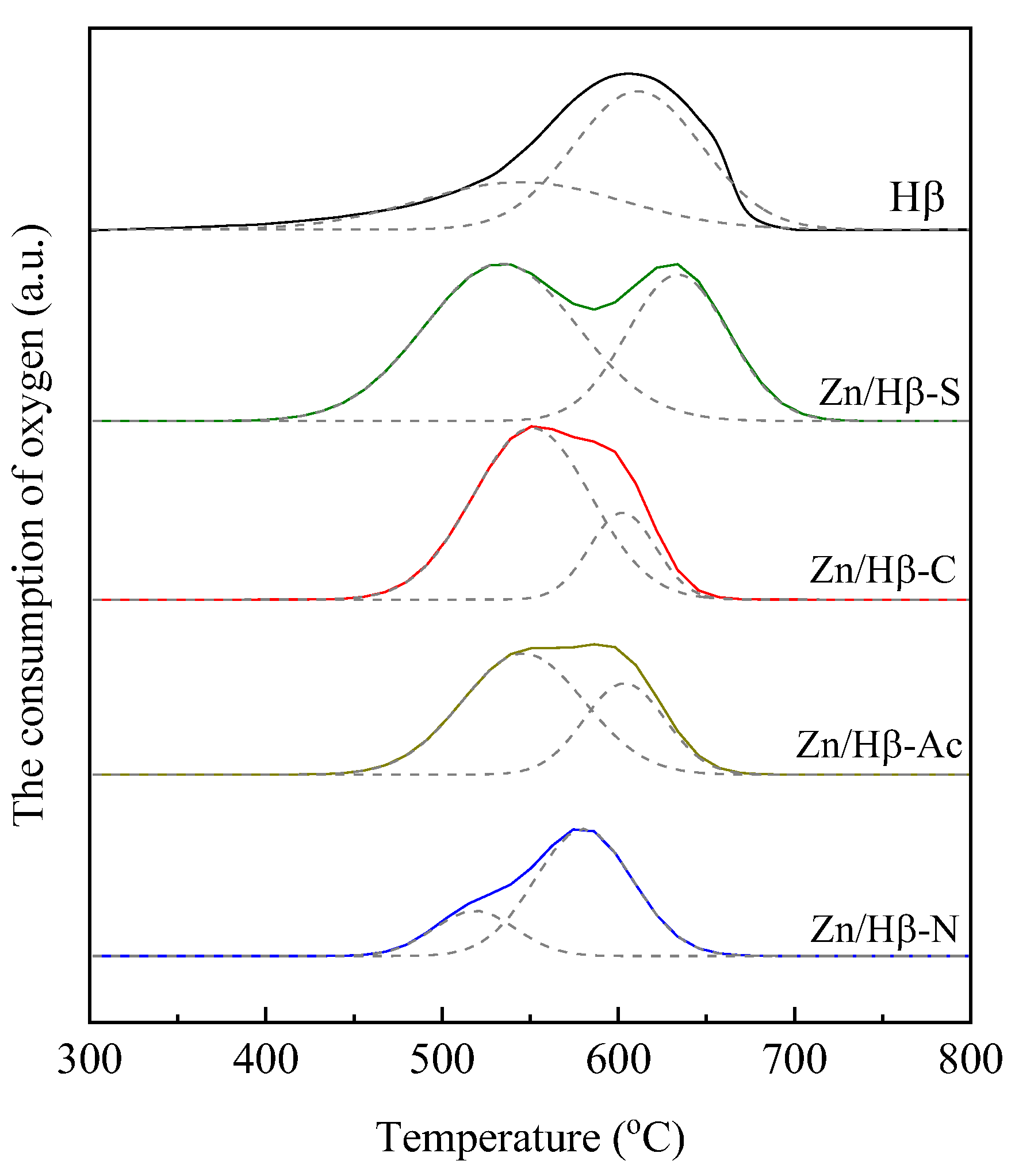
4.2. Deactivation mechanism
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Matheus CRV, Aguiar EFS. The role of MPV reaction in the synthesis of propene from ethanol through the acetone route. Catalysis Communications. 2020; 145: 106096.
- R. V. Matheus C, H. Chagas L, G. Gonzalez G, Falabella S. Aguiar E, G. Appel L. Synthesis of Propene from Ethanol: A Mechanistic Study. ACS Catalysis. 2018; 8: 7667-7678.
- Licht RB, Bell AT. A DFT Investigation of the Mechanism of Propene Ammoxidation over α-Bismuth Molybdate. ACS Catalysis. 2016; 7: 161-176.
- Hussain AI, Aitani AM, Kubů M, Čejka J, Al-Khattaf S. Catalytic cracking of Arabian Light VGO over novel zeolites as FCC catalyst additives for maximizing propylene yield. Fuel. 2016; 167: 226-239.
- Phung TK, Pham TLM, Vu KB, Busca G. (Bio)Propylene production processes: A critical review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. 2021; 9: 105673.
- Song S, Sun Y, Yang K, Fo Y, Ji X, Su H, Li Z, Xu C, Huang G, Liu J, Song W. Recent Progress in Metal-Molecular Sieve Catalysts for Propane Dehydrogenation. ACS Catalysis. 2023; 13: 6044-6067.
- Sun J, Wang Y. Recent Advances in Catalytic Conversion of Ethanol to Chemicals. ACS Catalysis. 2014; 4: 1078-1090.
- Yin J, Guo X, Sun Y, Han S, Li Q. Understanding the Nanoconfinement Effect on the Ethanol-to-Propene Mechanism Catalyzed by Acidic ZSM-5 and FAU Zeolites. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C. 2021; 125: 310-334.
- Huangfu J, Mao D, Zhai X, Guo Q. Remarkably enhanced stability of HZSM-5 zeolite co-modified with alkaline and phosphorous for the selective conversion of bio-ethanol to propylene. Applied Catalysis A: General. 2016; 520: 99-104.
- Duan C, Zhang X, Zhou R, Hua Y, Zhang L, Chen J. Comparative studies of ethanol to propylene over HZSM-5/SAPO-34 catalysts prepared by hydrothermal synthesis and physical mixture. Fuel Processing Technology. 2013; 108: 31-40.
- Xia W, Chen K, Takahashi A, Li X, Mu X, Han C, Liu L, Nakamura I, Fujitani T. Effects of particle size on catalytic conversion of ethanol to propylene over H-ZSM-5 catalysts—Smaller is better. Catalysis Communications. 2016; 73: 27-33.
- Xia W, Takahashi A, Nakamura I, Shimada H, Fujitani T. Study of active sites on the MFI zeolite catalysts for the transformation of ethanol into propylene. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical. 2010; 328: 114-118.
- Li X, Kant A, He Y, Thakkar HV, Atanga MA, Rezaei F, Ludlow DK, Rownaghi AA. Light olefins from renewable resources: Selective catalytic dehydration of bioethanol to propylene over zeolite and transition metal oxide catalysts. Catalysis Today. 2016; 276: 62-77.
- Xia W, Wang J, Wang L, Qian C, Ma C, Huang Y, Fan Y, Hou M, Chen K. Ethylene and propylene production from ethanol over Sr/ZSM-5 catalysts: A combined experimental and computational study. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2021; 294: 120242.
- Zhang N, Mao D, Zhai X. Selective conversion of bio-ethanol to propene over nano-HZSM-5 zeolite: Remarkably enhanced catalytic performance by fluorine modification. Fuel Processing Technology. 2017; 167: 50-60.
- Huang R, Fung V, Wu Z, Jiang D-e. Understanding the conversion of ethanol to propene on In2O3 from first principles. Catalysis Today. 2020; 350: 19-24.
- Hayashi F, Iwamoto M. Yttrium-Modified Ceria As a Highly Durable Catalyst for the Selective Conversion of Ethanol to Propene and Ethene. ACS Catalysis. 2012; 3: 14-17.
- Hayashi F, Tanaka M, Lin D, Iwamoto M. Surface structure of yttrium-modified ceria catalysts and reaction pathways from ethanol to propene. Journal of Catalysis. 2014; 316: 112-120.
- Wang F, Xia W, Mu X, Chen K, Si H, Li Z. A combined experimental and theoretical study on ethanol conversion to propylene over Y/ZrO2 catalyst. Applied Surface Science. 2018; 439: 405-412.
- Xia W, Wang F, Mu X, Chen K. Remarkably enhanced selectivity for conversion of ethanol to propylene over ZrO2 catalysts. Fuel Processing Technology. 2017; 166: 140-145.
- Iwamoto M, Tanaka M, Hirakawa S, Mizuno S, Kurosawa M. Pulse and IR Study on the Reaction Pathways for the Conversion of Ethanol to Propene over Scandium-Loaded Indium Oxide Catalysts. ACS Catalysis. 2014; 4: 3463-3469.
- Xue F, Miao C, Yue Y, Hua W, Gao Z. Direct conversion of bio-ethanol to propylene in high yield over the composite of In2O3 and zeolite beta. Green Chem. 2017; 19: 5582-5590.
- Xu L, Zhao R, Zhang W. One-step high-yield production of renewable propene from bioethanol over composite ZnCeOx oxide and HBeta zeolite with balanced Brönsted/Lewis acidity. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2020; 279: 119389.
- Jin H, Yue Y, Miao C, Tian C, Hua W, Gao Z. Direct and Highly Selective Conversion of Bioethanol to Propylene Over Y-CeO2 and Zeolite Beta Composite. Catal Lett. 2022; 153: 230-238.
- Xue F, Miao C, Yue Y, Hua W, Gao Z. Sc2O3-promoted composite of In2O3 and Beta zeolite for direct conversion of bio-ethanol to propylene. Fuel Processing Technology. 2019; 186: 110-115.
- Islam MJ, Granollers Mesa M, Osatiashtiani A, Taylor MJ, Manayil JC, Parlett CMA, Isaacs MA, Kyriakou G. The effect of metal precursor on copper phase dispersion and nanoparticle formation for the catalytic transformations of furfural. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2020; 273: 119062.
- Shao B, Ren K, Zhang C, Lin M, Zhou S, Li Y, Zong B. Effect of Metal Precursors on the Performance of Pt/Y Catalysts for Isobutane-Butene Alkylation Reaction-Regeneration. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 2023; 62: 19619-19628.
- Zhang B, Zhu X, Gao J, Zhu Y, Ma W. Zn modification of Beta zeolite: Effect on acid sites and propylene oxide rearrangement. Chemical Physics. 2020; 539: 110983.
- Rehman AU, Khan M, Maosheng Z. Hydration behavior of MgSO4–ZnSO4 composites for long-term thermochemical heat storage application. Journal of Energy Storage. 2019; 26: 101026.
- Kurban GVT, Rego ASC, Mello NM, Brocchi EA, Navarro RCS, Souza RFM. Thermodynamics and Kinetic Modeling of the ZnSO4·H2O Thermal Decomposition in the Presence of a Pd/Al2O3 Catalyst. Energies. 2022; 15: 548.
- Liao W, Tang C, Zheng H, Ding J, Zhang K, Wang H, Lu J, Huang W, Zhang Z. Tuning activity and selectivity of CO2 hydrogenation via metal-oxide interfaces over ZnO-supported metal catalysts. Journal of Catalysis. 2022; 407: 126-140.
- Bai T, Zhang X, Wang F, Qu W, Liu X, Duan C. Coking behaviors and kinetics on HZSM-5/SAPO-34 catalysts for conversion of ethanol to propylene. J Energy Chem. 2016; 25: 545-552.
- Sousa ZSB, Cesar DV, Henriques CA, Teixeira da Silva V. Bioethanol conversion into hydrocarbons on HZSM-5 and HMCM-22 zeolites: Use of in situ DRIFTS to elucidate the role of the acidity and of the pore structure over the coke formation and product distribution. Catalysis Today. 2014; 234: 182-191.
- Pinard L, Tayeb KB, Hamieh S, Vezin H, Canaff C, Maury S, Delpoux O, Pouilloux Y. On the involvement of radical “coke” in ethanol conversion to hydrocarbons over HZSM-5 zeolite. Catalysis Today. 2013; 218-219: 57-64.
- Ferreira Madeira F, Ben Tayeb K, Pinard L, Vezin H, Maury S, Cadran N. Ethanol transformation into hydrocarbons on ZSM-5 zeolites: Influence of Si/Al ratio on catalytic performances and deactivation rate. Study of the radical species role. Applied Catalysis A: General. 2012; 443-444: 171-180.
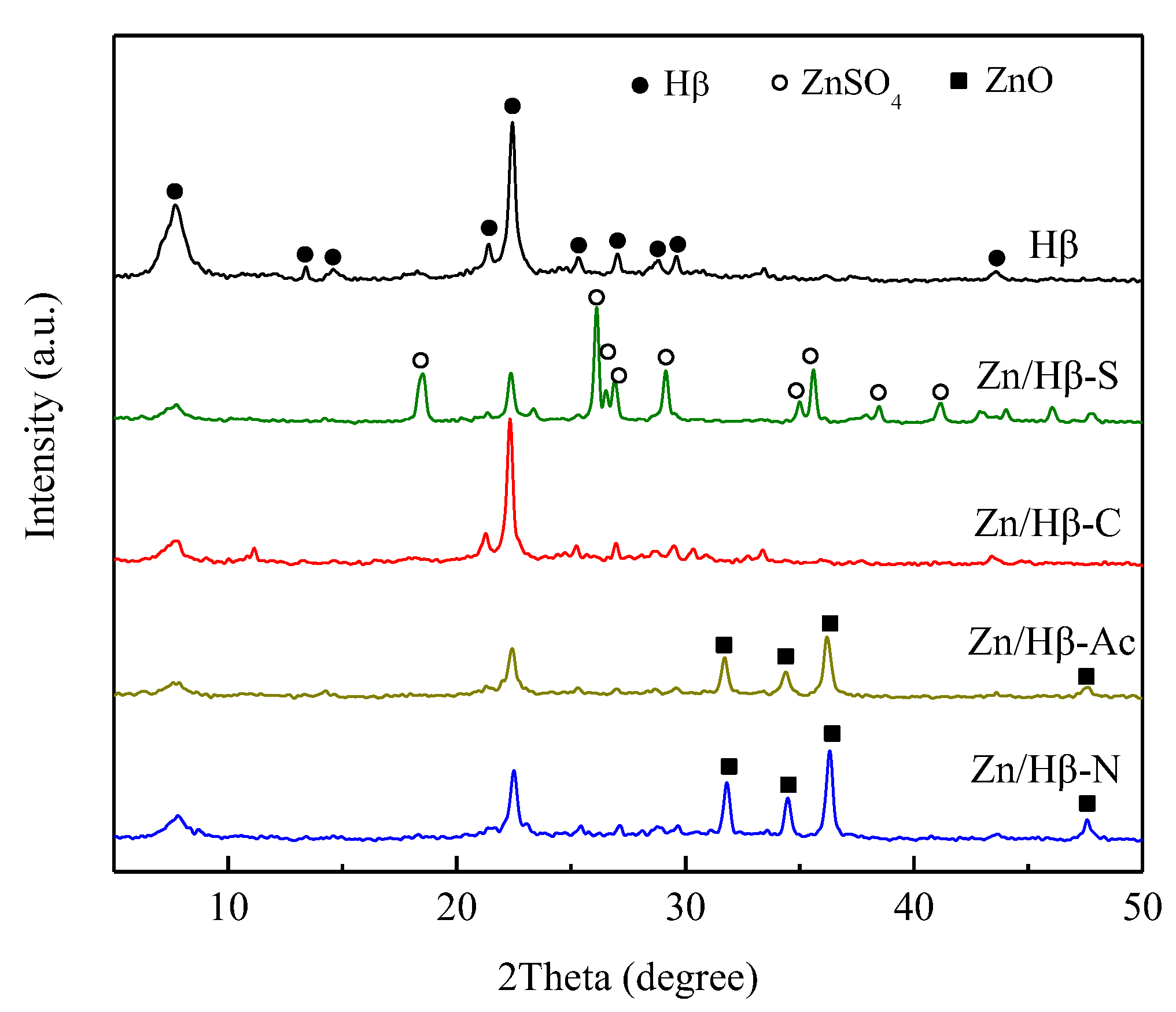
| Catalysts |
SBET (m2/g) |
Vmicro (cm3/g) | Vmeso (cm3/g) | Vtotal (cm3/g) |
| Hβ | 560.6 | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.36 |
| Zn/Hβ-S | 162.0 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.13 |
| Zn/Hβ-C | 216.7 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.20 |
| Zn/Hβ-Ac | 248.3 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.27 |
| Zn/Hβ-N | 277.2 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.24 |
| Catalysts | The amount of acid sites (a.u./g) | |||
| Weak (50-200 °C) |
Medium (200-350 °C) |
Strong (> 350 °C) |
Total | |
| Hβ | 71.8 | 111.7 | 85.1 | 268.6 |
| Zn/Hβ-S | 88.2 | 75.7 | 413.4 | 577.3 |
| Zn/Hβ-C | 33.4 | 139.3 | 199.9 | 372.6 |
| Zn/Hβ-Ac | 52.6 | 51.5 | 46.6 | 150.7 |
| Zn/Hβ-N | 5.3 | 21.4 | 55.8 | 82.5 |
| Used catalyst | Tmax (°C) | The consumption of oxygen (a.u./g) | |||
| Peak I | Peak II | Peak I | Peak II | Total | |
| Hβ | 545 | 611 | 25.8 | 47.5 | 73.3 |
| Zn/Hβ-S | 533 | 634 | 64.2 | 39.7 | 103.9 |
| Zn/Hβ-C | 551 | 602 | 54.1 | 15.4 | 69.5 |
| Zn/Hβ-Ac | 546 | 603 | 39.6 | 19.8 | 59.4 |
| Zn/Hβ-N | 518 | 580 | 9.9 | 33.1 | 43.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





