Submitted:
21 March 2024
Posted:
22 March 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
Table of Contents
| Abstract | 1 |
| 1. Background | 5 |
| 2. Modification strategies from CH3NH3PbI3 into many Halide Double Perovskites | 7 |
| 3. Origin of Electronic and optical property variations | 8 |
| 4.1 Effect of Polarizability and Molecular Dipoles on the dynamics of the photo-excitations | 9 |
| 4.2 Effects of tilting on the band structure and electron-hole transport | 9 |
| 5. Energy Applications of halide double perovskites | 9 |
| 6. Challenges in Lead and Tin free all-inorganic halide double perovskite solar cell | 10 |
| 6.1Discouraging power conversion efficiency. | 11 |
| 6.2 Mismatch among various interfacial layers of the device architecture | 12 |
| 6.3 Unclear charge-transport properties of these materials | 12 |
| 6.4Quantum confinement effect | 12 |
| 6.5 Low electronic dimensionality | 12 |
| 6.6 Indirect and wide bandgap | 13 |
| 6.7 Energetic disorder | 13 |
| 6.8 Geometrical constraints | 13 |
| 6.9 High processing temperature: | 14 |
| 6.10 Shortage of a broad-spectrum of speculative guidelines | 14 |
| 6.11 Lack of stoichiometric design and compatibility of various layers | 14 |
| 6.12 Incomplete order | 14 |
| 6.13 Challenges in achieving high quality films | 15 |
| 7. Suggested research roadmap engineering strategies for material and device performance improvement | 15 |
| 7.1 Engineering materials microstructure, surface and bulk properties | 16 |
| 7.2 Engineering domain wall and grain boundaries | 16 |
| 7.3 Polar order engineering | 17 |
| 7.4 Band Gap and Band Structure Engineering | 17 |
| 7.5 Crystalization process and colloidal engineering | 18 |
| 7.6 Composition engineering | 18 |
| 7.7 Engineering electronic properties | 18 |
| 7.8 Interface and defect engineering | 19 |
| 7.9 Device architectural engineering | 19 |
| 7.10 Doping engineering: | 19 |
| 7.11 Equilibrium and nonequilibrium quantum transport | 20 |
| 7.12 Microscopic physics of the ferroelectric photovoltaic effect | 20 |
| 8. Promising candidate properties to substitute Pb metal | 20 |
| 9. Concluding remark | 20 |
| 10. Reference | 22 |
1. Background
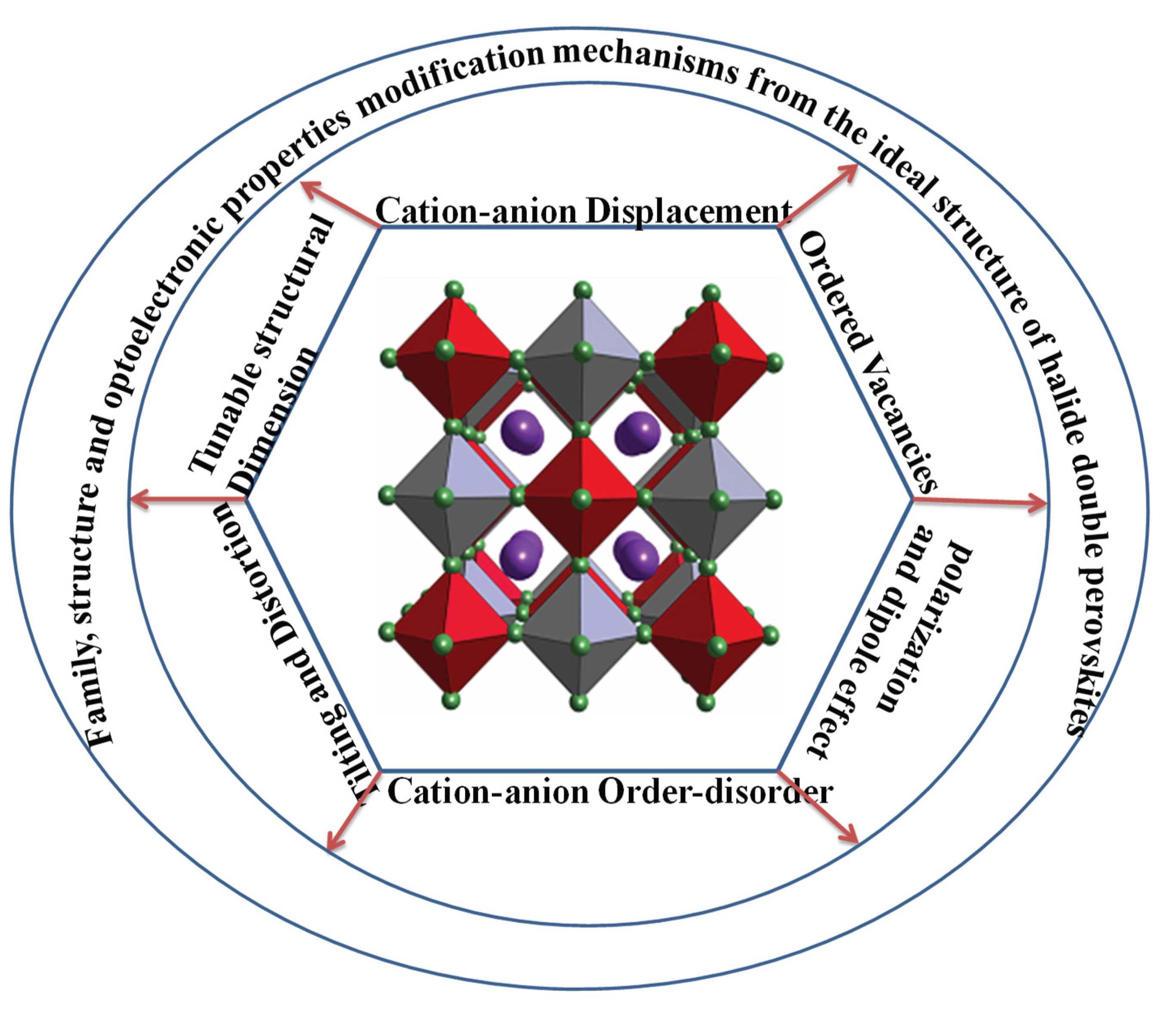
2. Modification Strategies from CH3NH3PbI3 into Many Halide Double Perovskites
3. Origin of Electronic and Optical Property Variations
4.1. Effect of Polarizability and Molecular Dipoles on the Dynamics of the Photo-Excitations
4.2. Effects of Tilting on the Band Structure and Electron-Hole Transport
5. Energy Applications of Halide Double Perovskites
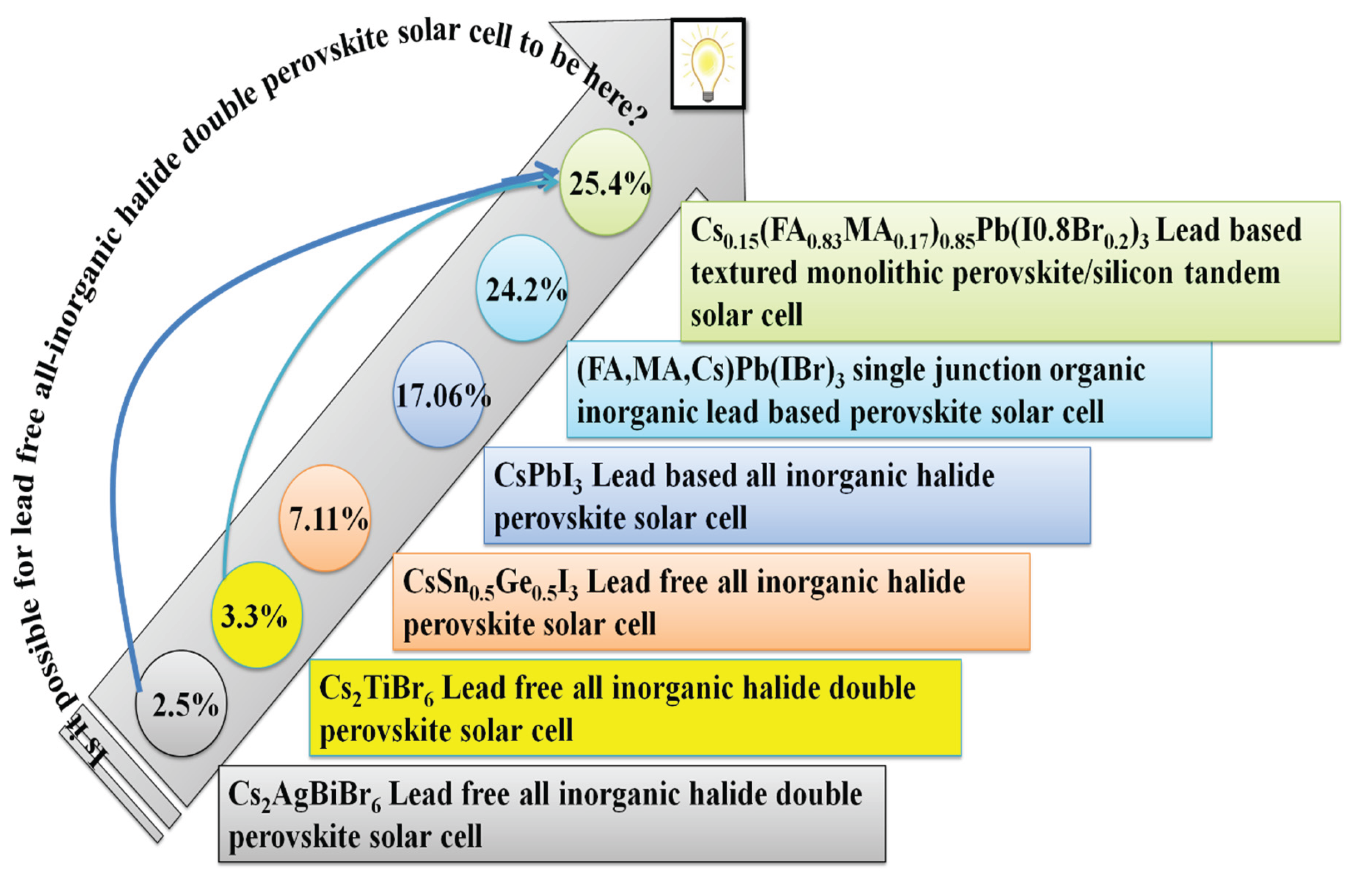
6. Challenges in Lead and Tin Free All-Inorganic Halide Double Perovskite Solar Cell
6.1. Discouraging Power Conversion Efficiency.
6.2. Mismatch among Various Interfacial Layers of the Device Architecture
6.3. Unclear Charge-Transport Properties of These Materials
6.4. Quantum Confinement Effect
6.5. Low Electronic Dimensionality
6.6. Indirect and Wide Bandgap
6.7. Energetic Disorder
6.8. Geometrical Constraints
6.9. High Processing Temperature:
6.10. Shortage of a Broad-Spectrum of Speculative Guidelines
6.11. Lack of Stoichiometric Design and Compatibility of Various Layers
6.12. Incomplete Order
6.13. Challenges in Achieving High Quality Films
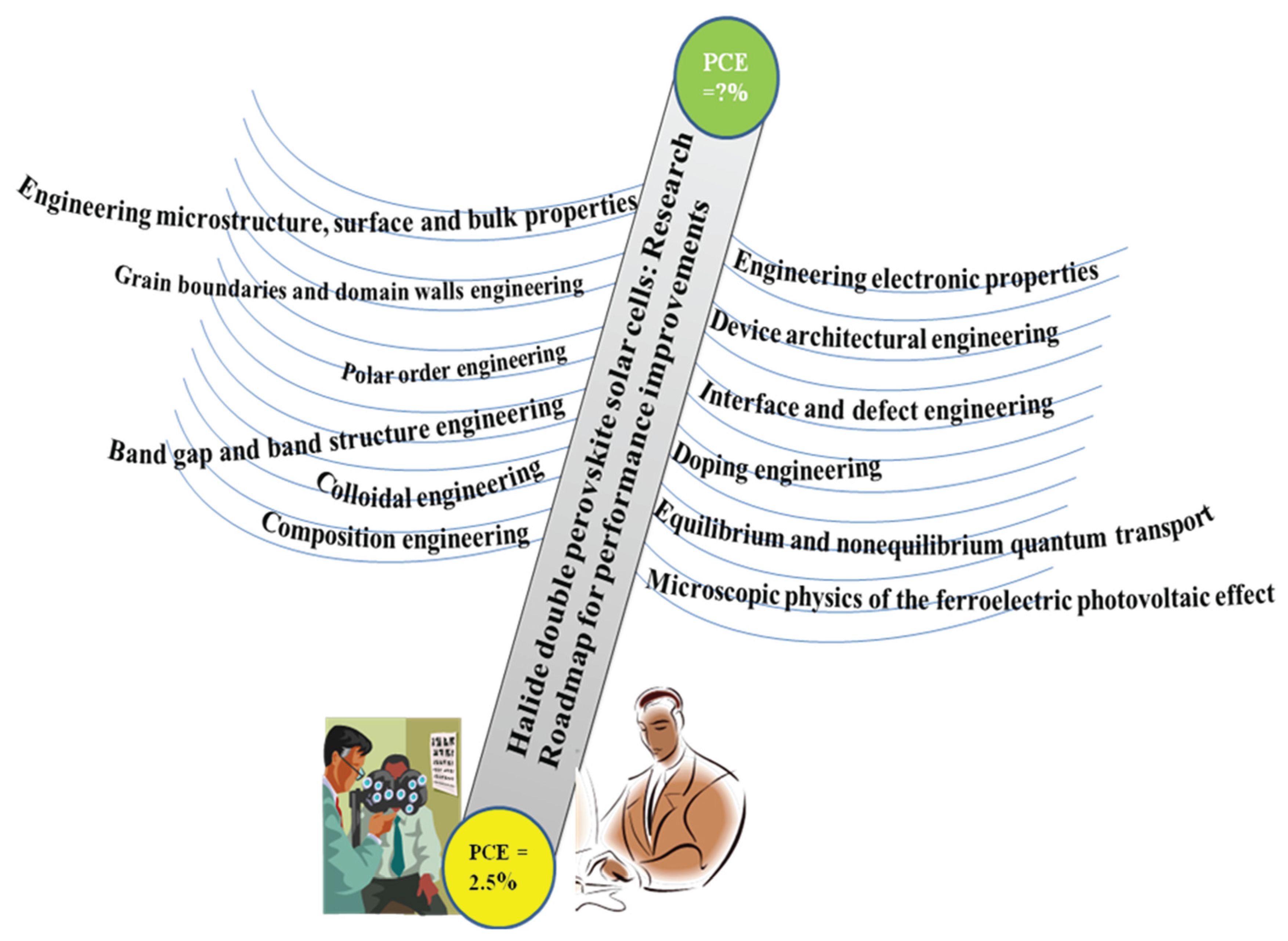
7. Suggested Research Roadmap Engineering Strategies for Material and Device Performance Improvement
7.1. Engineering Materials Microstructure, Surface and Bulk Properties
7.2. Engineering Domain Wall and Grain Boundaries
7.3. Polar Order Engineering
7.4. Band Gap and Band Structure Engineering
7.5. Crystalization Process and Colloidal Engineering
7.6. Composition Engineering
7.7. Engineering Electronic Properties
7.8. Interface and Defect Engineering
7.9. Device Architectural Engineering
7.10. Doping Engineering:
7.11. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Quantum Transport
7.12. Microscopic Physics of the Ferroelectric Photovoltaic Effect
8. Promising Candidate Properties to Substitute Pb Metal
9. Concluding Remark
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xing, G. M., N.; Lim, S.; Yantara, N.; Liu, X.; Sabba, D.; Graetzel, M.; Mhaisalkar, S.; Sum, T. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 476–480. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.-K. M., R. S.; Lai, M. L.; Docampo, P.; Higler, R.; Deschler, F.; Price, M.; Sadhanala, A.; Pazos, L. M.; Credgington, D.; Hanusch, F.; Bein, T.; Snaith, H. J.; Friend, R. H. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 687–692. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, X. Y. C., D.; Yin, J.; Bruno, A.; Soci, C. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7383. [Google Scholar]
- Boix, P. P. N., K.; Mathews, N.; Mhaisalkar, S. G. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Xin-Gang Zhao, 4 Dongwen Yang,1,4 Ji-Chang Ren,2,4 Yuanhui Sun,1 Zewen Xiao,3,* and Lijun Zhang1,*. Rational Design of Halide Double Perovskites for Optoelectronic Applications. Joule. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. & Yin, W. Recent progress in Pb-free stable inorganic double halide perovskites. Journal of Semiconductors. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M. H. D., S.; Leong, W. L.; Boix, P. P.; Prabhakar, R. R.; Baikie, T.; Shi, C.; Ding, H.; Ramesh, R.; Asta, M.; Graetzel, M.; Mhaisalkar, S. G.; Mathews, N. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, F. S., C. C.; Cao, D. H.; Chang, R. P. H.;Kanatzidis, M. G. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 489–494. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, I. L., B.; He, J.; Chang, R. P. H.; Kanatzidis, M. G. Nature 2012, 485, 486−489. 485.
- Harikesh PC, M. H. , Ghosh B, et al. Rb as an alternative cation for templating inorganic lead-free perovskites for solution processed photovoltaics. Chem Mater. 2016, 28, 7496–7504. [Google Scholar]
- Matthew, R. Linaburg, E. T. M., Jackson D. Majher, and Patrick M. Woodward*. Cs1−xRbxPbCl3 and Cs1−xRbxPbBr3 Solid Solutions: Understanding Octahedral Tilting in Lead Halide Perovskites. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 3507–3514. [Google Scholar]
- Volonakis, G. Cs2InAgCl6: A New Lead-Free Halide Double Perovskite with Direct Band Gap. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. [CrossRef]
- Zhao XG, Y. D. , Sun YH, et al. Cu-In halide perovskite solar absorbers. J Am Chem Soc. 2017, 139, 6718–6725. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ming-Gang Ju, § Min Chen,‡,§ Yuanyuan Zhou,*,‡ Hector F. Garces,‡ Jun Dai,† Liang Ma,† Nitin P. Padture,*,‡ and Xiao Cheng Zeng*,†. Earth-Abundant Nontoxic Titanium(IV)-based Vacancy-Ordered Double Perovskite Halides with Tunable 1.0 to 1.8 eV Bandgaps for Photovoltaic Applications. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 297−304. [Google Scholar]
- Pazoki M, J. M. , Zhu HM, et al. Bismuth iodide perovskite materials for solar cell applications: Electronic structure, optical transitions, and directional charge transport. J Phys Chem C. 2016, 120, 29039–29046. [Google Scholar]
- Eline, M. Hutter, †,‡ María C. Gelvez-Rueda, ́ ‡ Davide Bartesaghi,‡ Ferdinand C. Grozema,‡ and Tom J. Savenije*,‡. Band-Like Charge Transport in Cs2AgBiBr6 and Mixed Antimony−Bismuth Cs2AgBi1−xSbxBr6 Halide Double Perovskites. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 11655–11662. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, M. B. , McClure, E. T. & Woodward, P. M. Cs2AgBiBr6−xClx solid solutions – band gap engineering with halide double perovskites. Journal of Materials Chemistry C. [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.-H. , Kim, J., Debbichi, L., Kim, H. & Im, S. H. Band Gap Engineering of Cs3Bi2I9 Perovskites with Trivalent Atoms Using a Dual Metal Cation. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C. [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, A. , Dodd, M. S., Agnihotri, S., Ravera, E. & Michaelis, V. K. Cu(II)-Doped Cs2SbAgCl6 Double Perovskite: A Lead-Free, Low-Bandgap Material. Chemistry of Materials. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J. Composition design, optical gap and stability investigations of lead-free halide double perovskite Cs2AgInCl6. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L. Lead-Free Halide Double Perovskite Materials: A New Superstar Toward Green and Stable Optoelectronic Applications. Nano-Micro Letters. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y. Lead-free double halide perovskite Cs3BiBr6 with well-defined crystal structure and high thermal stability for optoelectronics. Journal of Materials Chemistry C 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J. Efficient and stable emission of warm-white light from lead-free halide double perovskites. Nature. [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E. , Mutukwa, D., Zingwe, N. & Taziwa, R. Lead-Free Halide Double Perovskites: A Review of the Structural, Optical, and Stability Properties as Well as Their Viability to Replace Lead Halide Perovskites. Metals 2018, 8, 667. [Google Scholar]
- Filip, M. R. , Liu, X., Miglio, A., Hautier, G. & Giustino, F. Phase Diagrams and Stability of Lead-Free Halide Double Perovskites Cs2BB′X6: B = Sb and Bi, B′ = Cu, Ag, and Au, and X = Cl, Br, and I. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C. [CrossRef]
- I. N. Flerova, M.V. Goreva, K.S. Aleksandrova, A. Tressaudb, J. Grannecb, M. Couzic. Phase transitions in elpasolites (ordered perovskites). Mater. Sci. Eng., R, 1998, 24, 81–151. [Google Scholar]
- Morss, L. R. , Siegal, M., Stenger, L. & Edelstein, N. Preparation of cubic chloro complex compounds of trivalent metals: Cs2NaMCl6. Inorganic chemistry. [CrossRef]
- Sasha Khalfin, Y. B. Advances in Lead-Free Double Perovskite Nanocrystals, Engineering Band-gaps and Enhancing Stability Through Composition Tunabilty. Nanoscale. [CrossRef]
- Femi Igbari, Z.-K. W. , * and Liang-Sheng Liao. Progress of Lead-Free Halide Double Perovskites. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, H. Slavney, L. L., Abraham Saldivar Valdes, Davide Bartesaghi, Tom J. Savenije, Jeffrey B. Neaton, and Hemamala Karunadasa. Small-Bandgap Halide Double Perovskites. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10.1002/anie.201807421.
- NREL Efficiency Chart. This Plot Is Courtesy of the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/pv/assets/pdfs/best-reserch-cell-efficiencies.20190411.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2019).
- Chen, B. Grain Engineering for Perovskite/Silicon Monolithic Tandem Solar Cells with Efficiency of 25.4%. Joule. [CrossRef]
- Al-Ashouri, A. Monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cell with >29% efficiency by enhanced hole extraction. Science 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M. Highly stable and efficient all-inorganic lead-free perovskite solar cells with native-oxide passivation. Nature Communications. [CrossRef]
- Nalianya, M. A. Numerical study of lead free CsSn0.5Ge0.5I3 perovskite solar cell by SCAPS-1D. Optik 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Lead free CsSn0.5Ge0.5I3 perovskite solar cell with different layer properties via SCAPS-1D simulation. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering 6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N. K. & Agarwal, A. Performance assessment of sustainable highly efficient CsSn0.5Ge0.5I3/FASnI3 based Perovskite Solar Cell: A numerical modelling approach. Optical Materials. [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.-G. Earth-Abundant Nontoxic Titanium(IV)-based Vacancy-Ordered Double Perovskite Halides with Tunable 1.0 to 1.8 eV Bandgaps for Photovoltaic Applications. ACS Energy Letters. [CrossRef]
- Saparov, B. Thin-Film Deposition and Characterization of a Sn-Deficient Perovskite Derivative Cs2SnI6. Chem.mater. 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greul, E. , Petrus, Michiel L., Binek, A., Docampo, P. & Bein, T. Highly stable, phase pure Cs2AgBiBr6 double perovskite thin films for optoelectronic applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry A. [CrossRef]
- Xiaoqing Yang, Y. C. , Pengyun Liu, Huimin Xiang, Wei Wang,* Ran Ran, Wei Zhou, and Zongping Shao*. Simultaneous Power Conversion Efficiency and Stability Enhancement of Cs2AgBiBr6 Lead-Free Inorganic Perovskite Solar Cell through Adopting a Multifunctional Dye Interlayer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2001557.
- Zhang, Z. Hydrogenated Cs2AgBiBr6 for significantly improved efficiency of lead-free inorganic double perovskite solar cell. Nature Communications 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min Chen, M.-G. J. , 2 Alexander D. Carl,3 Yingxia Zong,1 Ronald L. Grimm,3 Jiajun Gu,4 Xiao Cheng Zeng,2 Yuanyuan Zhou,1,* and Nitin P. Padture1,5,*. Cesium Titanium(IV) Bromide Thin Films Based Stable Lead-free Perovskite Solar Cells. Joule 2018, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S. , Jannat, F., Khan, M. A. K. & Alim, M. A. Numerical development of eco-friendly Cs2TiBr6 based perovskite solar cell with all-inorganic charge transport materials via SCAPS-1D. Optik. [CrossRef]
- Mercy, P. A. M. & Wilson, K. S. J. Development of environmental friendly high performance Cs2TiBr6 based perovskite solar cell using numerical simulation. Applied Surface Science Advances. [CrossRef]
- Kojima, A. , Teshima, K., Shirai, Y. & Miyasaka, T. Organometal Halide Perovskites as Visible-Light Sensitizers for Photovoltaic Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. [CrossRef]
- Ghanshyam Pilania1*, P. V. B. , Chiho Kim3 and Turab Lookman2. Finding New Perovskite Halides via Machine Learning. Finding New Perovskite Halides via Machine Learning. Frontiers in Materials ( 2016.
- Gonzalez-Pedro, V. General Working Principles of CH3NH3PbX3 Perovskite Solar Cells. Nano Letters. [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M. A. , Calabro, R. L., Kim, D.-Y. & Graham, K. R. Halide exchange and surface modification of metal halide perovskite nanocrystals with alkyltrichlorosilanes. Nanoscale 6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protesescu, L. Nanocrystals of Cesium Lead Halide Perovskites (CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, and I): Novel Optoelectronic Materials Showing Bright Emission with Wide Color Gamut. Nano Letters 3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelcu, G. Fast Anion-Exchange in Highly Luminescent Nanocrystals of Cesium Lead Halide Perovskites (CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, I). Nano Letters 5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N.J. Jeon, J. H. N., W. N.J. Jeon, J. H. N., W.S. Yang, Y.C. Kim, S. Ryu, J. Seo, S.I. Seok, Compositional engineering of perovskite materials for high-performance solar cells, Nature 517, 476-480. [CrossRef]
- Jin-Wook Lee, D.-H. K. , Hui-Seon Kim, Seung-Woo Seo, Sung Min Cho, and Nam-Gyu Park *. Formamidinium and Cesium Hybridization for Photo- and Moisture-Stable Perovskite Solar Cell. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1501310. [Google Scholar]
- Yun Hee Park, I. J. , Seunghwan Bae, Hae Jung Son, Phillip Lee, Jinwoo Lee, Chul-Ho Lee,* and Min Jae Ko*. Inorganic Rubidium Cation as an Enhancer for Photovoltaic Performance and Moisture Stability of HC(NH2)2PbI3 Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dmitry Baranov2, Z. D. , Mirko Prato3, Filippo Drago2, Maurizio Ferretti1, Valerio Pinchetti4, Marco Fanciulli4, Sergio Brovelli4, Luca De Trizio2*, Liberato Manna2* Colloidal Synthesis of Double Perovskite Cs2AgInCl6 and Mn-doped Cs2AgInCl6 Nanocrystals Federico Locardi1,2, Matilde Cirignano2. J. Am. Chem. Soc.,.
- Stoumpos, C. C. F., L.; Clark, D. J.; Kim, Y. S.; Rhim, S. H.; Freeman, A. J.; Ketterson, J. B.; Jang, J. I.; Kanatzidis, M. G. Hybrid Germanium Iodide Perovskite Semiconductors: Active Lone Pairs, Structural Distortions, Direct and Indirect Energy Gaps, and Strong Nonlinear Optical Properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 6804–6819. [Google Scholar]
- Volonakis, G. F., M. R.; Haghighirad, A. A.; Sakai, N.; Wenger, B.; Snaith, H. J.; Giustino, F. Lead-Free Halide Double Perovskites via Heterovalent Substitution of Noble Metals. J. Phys.Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slavney, A. H. H., T.; Lindenberg, A. M.; Karunadasa, H. I. A bismuth-halide double perovskite with long carrier recombination lifetime for photovoltaic applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2138–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- al., K. e. al., K. e. HALIDE DOUBLE PEROVSKITE Cs2AgBiBr6 SOLAR-CELL ABSORBER HAVING LONG CARRIER LIFETIMES. U.S. Published Patent Application US 2017/O1941 01 A1.
- Enrico Greul, a. M. L. P. , a Andreas Bineka, Pablo Docampob and Thomas Beina*. Highly stable, phase pure Cs2AgBiBr6 double perovskite thin films for optoelectronic applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 00, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao ZW, D. K. , Meng WW, et al. Intrinsic instability of Cs2In(I)M(III)X6 (M = Bi, Sb; X = Halogen) double perovskites: A combined density functional theory and experimental study. J Am Chem Soc. 2017, 139, 6054–6057. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z. Y., Y.; Shao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Dong, Q.; Bi, C.; Sharma, P.; Gruverman, A.; Huang, J. Giant Switchable Photovoltaic Effect in Organometal Trihalide Perovskite Devices. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoluzzi, L. S., R. S.; Liu, L.; Lee, J.-W.; Mas-Marza, E.; Han, H.; Park, N.-G.; Mora-Sero, I.; Bisquert, J. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 910–915. [Google Scholar]
- Snaith, H. J. A., A.; Ball, J. M.; Eperon, G. E.; Leijtens, T.; Noel, N. K.; Stranks, S. D.; Wang, J. T.-W.; Wojciechowski, K.; Zhang, W. Anomalous Hysteresis in Perovskite Solar Cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1511–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tress, W. M., N.; Moehl, T.; Zakeeruddin, S. M.; Nazeeruddin, M. K.; Gratzel, M. , Understanding the Rate-Dependent J-V Hysteresis, Slow Time Component, and Aging in Ch3nh3pbi3 Perovskite Solar Cells: The Role of a Compensated Electric Field. Energy & Environmental Science 2015, 8, 995–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Hoke, E. T. Reversible photo-induced trap formation in mixed-halide hybrid perovskites for photovoltaics. Chem. Sci. [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z. X., J.; Sun, K.; Chen, L.; Hu, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Ong, K. P.; Zeng, K.; Wang, J. ,. Ferroelectricity of Ch3nh3pbi3 Perovskite. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomas Leijtens 1, Ajay Ram Srimath Kandada1*, Giles E. Eperon2, Giulia Grancini1, Valerio D’Innocenzo1,3, James M. Ball1, Samuel D. Stranks2#, Henry J. Snaith2, and Annamaria Petrozza1*. Modulating the Electron - Hole Interaction in a Hybrid Lead Halide Perovskite with an Electric Field J. Am. Chem. Soc.,. [CrossRef]
- Metal-halide double perovskites as solar-cell absorbers Stanford University/OFFICE OF TECHNOLOGY LICENSING/http://techfinder.stanford.edu/technologies/S15-455_metal-halide-double-perovskites-as.
- et al. Enabling Flexible All-Perovskite Tandem Solar Cells. Joule. [CrossRef]
- Lei Zhou, Y.-F. X. , Bai-Xue Chen, Dai-Bin Kuang,* and Cheng-Yong Su. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Application of Stable LeadFree Cs2AgBiBr6 Perovskite Nanocrystals. Small 2018, 14, 1703762. [Google Scholar]
- Zhenzhen Zhanga, b. , Yongqi Liangb, Hanlin Huangb, Xingyi Liub, Qi Lib, Langxing Chena*, Dongsheng Xub*. Stable and Highly Efficient Photocatalysis with Lead-Free DoublePerovskite of Cs2AgBiBr6. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10.1002/anie.201900658.
- Qin, X. , Zhao, Z., Wang, Y., Wu, J., Jiang, Q., and You, J. Recent progress in stability of perovskite solar cells. Recent progress in stability of perovskite solar cells. J. Semicond. 38 01 1002.
- Berhe, T. A. Organometal halide perovskite solar cells: degradation and stability. Energy & Environmental Science. [CrossRef]
- Berhe, T. A. Identification of the physical origin behind disorder, heterogeneity, and reconstruction and their correlation with the photoluminescence lifetime in hybrid perovskite thin films. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z. , Meng, W., Wang, J., Mitzi, D.B., and Yan, Y. Searching for promising new perovskite-based photovoltaic absorbers: the importance of electronic dimensionality. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 206–216. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q. , Ting, H., Wei, S., Huang, D., Wu, C., Sun, W., Qu, B., Wang, S., Chen, Z., and Xiao, L. Recent progress in lead-free perovskite (-like) solar cells. Mater. Today Energy 2018, 8, 157–165. [Google Scholar]
- Jodlowski, A. , Rodrı’guez-Padr’n, D., Luque, R., and de Miguel, G. Alternative perovskites for photovoltaics. Adv. Energy Mater. [CrossRef]
- Liang, L. , and Gao, P. Lead-free hybrid perovskite absorbers for viable application: can we eat the cake and have it too? Adv. Sci.(Weinh) 2018, 5, 1700331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abate, A. Perovskite solar cells go lead free. Joule 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q. , Yang, D., Lv, J., Sun, Y.-Y., and Zhang, L. Perovskite solar absorbers: materials by design. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1700316. [Google Scholar]
- George Volonakis1 and Feliciano Giustino1, a. Surface properties of lead-free halide double perovskites: Possible visible-light photo-catalysts for water splitting featured. Appl. Phys. Lett. 3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavney, A. H. , Te Hu, Aaron M. Lindenberg, and Hemamala I. Karunadasa. A Bismuth-Halide Double Perovskite with Long Carrier Recombination Lifetime for Photovoltaic Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2138–2141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- al., K. e. al., K. e. HALIDE DOUBLE PEROVSKITE Cs2AgBiBr6 SOLAR-CELL ABSORBER HAVING LONG CARRIER LIFETIMES. US20170194101A1.
- Yang, Y. Top and bottom surfaces limit carrier lifetime in lead iodide perovskite films. Nature Energy 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q. Electron-hole diffusion lengths > 175 μm in solution-grown CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub>PbI<sub>3</sub> single crystals. Science. [CrossRef]
- Xing, G. Long-Range Balanced Electron- and Hole-Transport Lengths in Organic-Inorganic CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>3</sub>PbI<sub>3</sub>. Science. [CrossRef]
- Saparov, B. & Mitzi, D. B. Organic–Inorganic Perovskites: Structural Versatility for Functional Materials Design. Chemical Reviews. [CrossRef]
- Burschka, J. Sequential deposition as a route to high-performance perovskite-sensitized solar cells. Nature. [CrossRef]
- Best Research-Cell Efficiency Chart. https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-efficiency.html.
- Savory, C. N. , Walsh, A. & Scanlon, D. O. Can Pb-Free Halide Double Perovskites Support High-Efficiency Solar Cells? ACS Energy Lett. [CrossRef]
- S. Rühle. Phys. Status Solidi A.
- R. Sheng, A. W. Y. H.-B., S. Huang, M. Keevers, X. Hao, L. Jiang, Y.-B Cheng, and M. A. Green, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 3931–3934.
- Sani, F. , Shafie, S., Lim, H. N. & Musa, A. O. Advancement on Lead-Free Organic-Inorganic Halide Perovskite Solar Cells: A Review. Materials (Basel). [CrossRef]
- Filip, M. R. H., S.; Haghighirad, A. A.; Snaith, H. J.; Giustino, F. Band Gaps of the Lead-Free Halide Double Perovskites Cs2BiAgCl6 and Cs2BiAgBr6 from Theory and Experiment. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igbari, F. Composition Stoichiometry of Cs2AgBiBr6 Films for Highly Efficient Lead-Free Perovskite Solar Cells. Nano Letters 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, K. A. Compositional Engineering for Efficient Wide Band Gap Perovskites with Improved Stability to Photoinduced Phase Segregation. ACS Energy Lett. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. , Zhang, P. & Wei, S.-H. Band Structure Engineering of Cs2AgBiBr6 Perovskite through Order–Disordered Transition: A First-Principle Study. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P. , Yang, J. & Wei, S.-H. Manipulation of cation combinations and configurations of halide double perovskites for solar cell absorbers. Journal of Materials Chemistry A. [CrossRef]
- Jongseob Kim1, H. K. , Mahesh Chandran3, Seung-Cheol Lee3,a), Sang Hyuk Im4, and Ki-Ha Hong5,b). Impacts of cation ordering on bandgap dispersion of double perovskites. APL Materials 2018, 6, 084903. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z. Solution-Processed Inorganic Perovskite Flexible Photodetectors with High Performance. Nanoscale Research Letters. [CrossRef]
- Chilvery, A. , Das, S., Guggilla, P., Brantley, C. & Sunda-Meya, A. A perspective on the recent progress in solution-processed methods for highly efficient perovskite solar cells. Science and technology of advanced materials. [CrossRef]
- Seo, J. , Noh, J. H. & Seok, S. I. Rational Strategies for Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells. Acc. Chem. Res. [CrossRef]
- Arain, Z. Elucidating the dynamics of solvent engineering for perovskite solar cells. Science China Materials. [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Optimization of anti-solvent engineering toward high performance perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Res. 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, N. J. Solvent engineering for high-performance inorganic–organic hybrid perovskite solar cells. Nat. Mater. [CrossRef]
- Duan, J. Inorganic perovskite solar cells: an emerging member of the photovoltaic community. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B. Pathways toward high-performance inorganic perovskite solar cells: challenges and strategies. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P. Solvent-controlled growth of inorganic perovskite films in dry environment for efficient and stable solar cells. Nature Communications 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L. Lead-Free Halide Double Perovskite Materials: A New Superstar Toward Green and Stable Optoelectronic Applications. Vol. 11 ( 2019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volonakis, G. & Giustino, F. Surface properties of lead-free halide double perovskites: Possible visible-light photo-catalysts for water splitting. Vol. 112 (2018).
- DeHoff, R. T. Engineering of microstructures. Materials Research 1999, 2, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, H. , Mayer, S. & Scheu, C. 1-20 (2017).
- Khalfin, S. & Bekenstein, Y. Advances in lead-free double perovskite nanocrystals, engineering band-gaps and enhancing stability through composition tunability. Nanoscale. [CrossRef]
- Szuromi, P. Microstructural Engineering of Materials. Science 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. Tailoring properties of hybrid perovskites by domain-width engineering with charged walls. npj Computational Materials. [CrossRef]
- Schade, L. Structural and Optical Properties of Cs2AgBiBr6 Double Perovskite. ACS Energy Letters. [CrossRef]
- Lozhkina, O. A. Microstructural analysis and optical properties of the halide double perovskite Cs2BiAgBr6 single crystals. Chem. Phys. Lett. [CrossRef]
- Wei Liu 1, Y. L. , Ju Wang 1, Cuncun Wu 1, Congyue Liu 1, Lixin Xiao 1, Zhijian Chen 1, Shufeng Wang 1,2,* ID and Qihuang Gong 1,2. Twin Domains in Organometallic Halide Perovskite Thin-Films. Crystals 2018, 8, 216. [Google Scholar]
- Shi Liu, F. Z. , Nathan Z. Koocher, Hiroyuki Takenaka, Fenggong Wang, and Andrew M. Rappe*. Ferroelectric Domain Wall Induced Band Gap Reduction and Charge Separation in Organometal Halide Perovskites. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 693–699. [Google Scholar]
- You, L. Enhancing ferroelectric photovoltaic effect by polar order engineering. Science Advances 3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu You1*, F. Z. , Liang Fang3*, Yang Zhou1, Liang Z. Tan2, Zeyu Zhang4, Guohong Ma4, Daniel Schmidt5‡, Andrivo Rusydi5, Le Wang1§, Lei Chang1, Andrew M. Rappe2¶, Junling Wang1¶. Enhancing ferroelectric photovoltaic effect by polar order engineering Sci. Adv. 4 (2018).
- Chen, B. Interface band structure engineering by ferroelectric polarization in perovskite solar cells. Nano Energy. [CrossRef]
- Du, K. , Meng, W., Wang, X., Yan, Y. & B Mitzi, D. Bandgap Engineering of Lead-Free Double Perovskite Cs2AgBiBr6 through Trivalent Metal Alloying. (2017).
- Torkzadeh, S. , Maghsoudipour, A., Khanlarkhani, A. & Tajabadi, F. Bandgap Engineering of Mixed-Halide Perovskites, A DFT Study.
- Roknuzzaman, M. Electronic and optical properties of lead-free hybrid double perovskites for photovoltaic and optoelectronic applications. Scientific Reports. [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. High-Pressure Band-Gap Engineering in Lead-Free Cs <sub>2</sub> AgBiBr <sub>6</sub> Double Perovskite. Angewandte Chemie (International Edition) 1597. [Google Scholar]
- Shockley, W. Q., H. J. Detailed Balance Limit of Efficiency of P-N Junction Solar Cells. J. Appl. Phys. 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, H. Slavney, a., °] Linn Leppert,[b,°] Abraham Saldivar Valdes,[a] Davide Bartesaghi,[c,d] Tom J. Savenije,[c] Jeffrey B. Neaton,*[e, f, g] and Hemamala I. Karunadasa*[a]. Small-Bandgap Halide Double Perovskites. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10.1002/anie.201807421.
- Walsh, A. Principles of Chemical Bonding and Band Gap Engineering in Hybrid Organic–Inorganic Halide Perovskites. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K. Hybrid Halide Perovskite Solar Cell Precursors: Colloidal Chemistry and Coordination Engineering behind Device Processing for High Efficiency. Journal of the American Chemical Society 4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. F. Berger and J. B. Neaton. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2012, 86, 165211. [Google Scholar]
- Mcclure, E. T. B., M. R.; Windl, W.; Woodward, P. M. Cs2AgBiX6 (X = Br, Cl) -new visible light absorbing, lead-free halide perovskite semiconductors. Chem. Mater. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Creutz, S. E. , Crites, E. N., De Siena, M. C. & Gamelin, D. R. Colloidal Nanocrystals of Lead-Free Double-Perovskite (Elpasolite) Semiconductors: Synthesis and Anion Exchange To Access New Materials. Nano Lett. [CrossRef]
- Kangsabanik, J. , Sugathan, V., Yadav, A., Yella, A. & Alam, A. Double perovskites overtaking the single perovskites: A set of new solar harvesting materials with much higher stability and efficiency. Physical Review Materials. [CrossRef]
- D. Shi, V. A., R. Comin, M. Yuan, E. Alarousu, A. Buin, Y. Chen, S. Hoogland, A. Rothenberger, K. Katsiev, Y. Losovyj, X. Zhang, P. A. Dowben, O. F. Mohammed, E. H. Sargent, O. M. Bakr, Science 2015, 347, 519.
- W. Nie, H. T., R. Asadpour, J.-C. Blancon, A. J. Neukirch, G. Gupta, J. J. Crochet, M. Chhowalla, S. Tretiak, M. A. Alam, H.-L. Wang, A. D. Mohite, Science 2015, 347, 522.
- W. Zhang, G. E. E., H. J. Snaith, Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16048.
- H. Tan, A. J., O. Voznyy, X. Lan, F. P. García de Arquer, J. Z. Fan, R. Quintero-Bermudez, M. Yuan, B. Zhang, Y. Zhao, F. Fan, P. Li, L. N. Quan, Y. Zhao, Z.-H. Lu, Z. Yang, S. Hoogland, E. H. Sargent, Science 2017, 355, 722. [Google Scholar]
- N. De Marco, H. Z., Q. Chen, P. Sun, Z. Liu, L. Meng, E. P. Yao, Y. Liu, A. Schiffer, Y. Yang, Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 1009.
- D. Luo, W. Y., Z. Wang, A. Sadhanala, Q. Hu, R. Su, R. Shivanna, G. F. Trindade, J. F. Watts, Z. Xu, T. Liu, K. Chen, F. Ye, P. Wu, L. Zhao, J. Wu, Y. Tu, Y. Zhang, X. Yang, W. Zhang, R. H. Friend, Q. Gong, H. J. Snaith, R. Zhu Science 2018, 360, 1442.
- L. Liu, S. H., Y. Lu, P. Liu, Y. Zhao, C. Shi, S. Zhang, J. Wu, H. Zhong, M. Sui, H. Zhou, H. Jin, Y. Li, Q. Chen, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800544. [Google Scholar]
- Slavney, A. H. Defect-Induced Band-Edge Reconstruction of a Bismuth-Halide Double Perovskite for Visible-Light Absorption. Journal of the American Chemical Society 5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F. , Bai, S., Tress, W., Hagfeldt, A. & Gao, F. Defects engineering for high-performance perovskite solar cells. npj Flexible Electronics. [CrossRef]
- Han, T.-H. Interface and Defect Engineering for Metal Halide Perovskite Optoelectronic Devices. Interface and Defect Engineering for Metal Halide Perovskite Optoelectronic Devices. ( 2019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian Xu, J.-B. L. , * Bai-Xin Liu, Jianfeng Wang, and Bing Huang. Defect Engineering of Grain Boundaries in Lead-Free Halide Double Perovskites for Better Optoelectronic Performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ramamoorthy Ramesha, b. , c,1. Defect engineering using crystal symmetry. PNAS 9344. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, I. Functional materials, device architecture, and flexibility of perovskite solar cell. Emergent Materials. [CrossRef]
- Kopacic, I. Enhanced Performance of Germanium Halide Perovskite Solar Cells through Compositional Engineering. Enhanced Performance of Germanium Halide Perovskite Solar Cells through Compositional Engineering. Vol. 1 ( 2018. [CrossRef]
- Song, Z. , Watthage, S. C., Phillips, A. B. & Heben, M. J. Pathways toward high-performance perovskite solar cells: review of recent advances in organo-metal halide perovskites for photovoltaic applications. Vol. 6 (SPIE, 2016).
- E. Greul, M. L. P., A. Binek, P. Docampo, T. Bein, J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 19972.
- J. Luo, S. L., H. Wu, Y. Zhou, Y. Li, J. Liu, J. Li, K. Li, F. Yi, G. Niu, J. Tang, ACS Photonics 2018, 5, 398. [Google Scholar]
- Karmakar, M. S. D., S. Agnihotri, E. Ravera, V. K. Michaelis, Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 8280. [Google Scholar]
- Locardi, F. Colloidal Synthesis of Double Perovskite Cs2AgInCl6 and Mn-Doped Cs2AgInCl6 Nanocrystals. Journal of the American Chemical Society 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B. B-Site doped lead halide perovskites: synthesis, band engineering, photophysics, and light emission applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry C 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. , Li, L., Sun, Z. & Luo, J. Rational chemical doping of metal halide perovskites. Chemical Society Reviews. [CrossRef]
- Ye, T. Enhanced Charge Carrier Transport and Device Performance Through Dual-Cesium Doping in Mixed-Cation Perovskite Solar Cells with Near Unity Free Carrier Ratios. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun Zhou, X. R. , Peng Zhang, Maxim S. Molokeev, Peijia Wei, Quanlin Liu, Xiuwen Zhang,* and Zhiguo Xia*. Manipulation of Bi3+/In3+ Transmutation and Mn2+-Doping Effect on the Structure and Optical Properties of Double Perovskite Cs2NaBi1-xInxCl6. Adv. Optical Mater. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhifang Tan, J. L. , Cheng Zhang, Zha Li, Qingsong Hu, Zewen Xiao,* Toshio Kamiya, Hideo Hosono, Guangda Niu, Efrat Lifshitz, Yibing Cheng, and Jiang Tang*. Highly Efficient Blue-Emitting Bi-Doped Cs2SnCl6 Perovskite Variant: Photoluminescence Induced by Impurity Doping Adv. Funct. Mater., 1801131 (2018).
- K. Z. Du, W. M., X. Wang, Y. Yan, D. B. Mitzi, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 8158.
- T. T. Tran, J. R. P., J. R. Chamorro, J. R. Morey, T. M. McQueen, ; Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 688. [Google Scholar]
- M. R. Filip, X. L., A. Miglio, G. Hautier, F. Giustino, J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 158.
- F. Giustino, H. J. S. ACS Energy Lett. 2016, 1, 1233. [Google Scholar]
- Q. Sun, J. W., W. J. Yin, Y. Yan, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705901.
- K. -z. Du, X. W., Q. Han, Y. Yan, D. B. Mitzi, ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 2486.
- Fridkin, V. M. Bulk photovoltaic effect in noncentrosymmetric crystals. Crystallogr. Rep. 2001, 46, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng Gao1, Heng-Jui Liu3, Yen-Lin Huang3, Ying-Hao Chu3,4, Ryo Ishikawa5, Bin Feng5, Ying Jiang2,6, Naoya Shibata5, En-Ge Wang2,6 & Yuichi Ikuhara5,7,8. Atomic mechanism of polarization-controlled surface reconstruction in ferroelectric thin films. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11318. [Google Scholar]
- R. von Baltz, W. K. Theory of the bulk photovoltaic effect in pure crystals. K. Theory of the bulk photovoltaic effect in pure crystals. Phys. Rev. B 1981, 23, 5590–5596. [Google Scholar]
- S. M. Young, A. M. R. First principles calculation of the shift current photovoltaic effect in ferroelectrics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 116601. [Google Scholar]
- S. M. Young, F. Z., A. M. Rappe First-principles calculation of the bulk photovoltaic effect in bismuth ferrite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 236601. [Google Scholar]
- Padinhare Cholakkal Harikesh, B. W. , Biplab Ghosh, Rohit Abraham John, Stener Lie, Krishnamoorthy Thirumal, Lydia Helena Wong, Tze Chien Sum, Subodh Mhaisalkar, and Nripan Mathews*. Doping and Switchable Photovoltaic Effect in Lead-Free Perovskites Enabled by Metal Cation Transmutation. Adv. Mater. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- D. Lee, S. H. B., T. H. Kim, J.-G. Yoon, C. M. Folkman, C. B. Eom, T. W. Noh, Polarity control of carrier injection at ferroelectric/metal interfaces for electrically switchable diode and photovoltaic effects. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 125305. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X. , Deng, Y., Van Brackle, C. H. & Huang, J. Meniscus fabrication of halide perovskite thin films at high throughput for large area and low-cost solar panels. International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing. [CrossRef]
- Tiing, T. V. e. a. Octadecylamine-Functionalized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Facilitating the Formation of a Monolithic Perovskite Layer and Stable Solar Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 1705. [Google Scholar]
- Stoumpos, C. C. , Malliakas, C. D. & Kanatzidis, M. G. Semiconducting Tin and Lead Iodide Perovskites with Organic Cations: Phase Transitions, High Mobilities, and Near-Infrared Photoluminescent Properties. Inorganic Chemistry. [CrossRef]
- Ponseca, C. S. Organometal Halide Perovskite Solar Cell Materials Rationalized: Ultrafast Charge Generation, High and Microsecond-Long Balanced Mobilities, and Slow Recombination. Journal of American Chemical Society 5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G. Long-Range Balanced Electron- and Hole-Transport Lengths in Organic-Inorganic CH3NH3PbI3. Science. [CrossRef]
- Etgar, L. Mesoscopic CH3NH3PbI3/TiO2 Heterojunction Solar Cells. Journal of American Chemical Society 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H. Q. , Holmes, R. J., Aydil, E. S. & Gagliardi, L. Lead-free double perovskites Cs2InCuCl6 and (CH3NH3)2InCuCl6: electronic, optical, and electrical properties. Nanoscale 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankur Tayaa), P. R. , and Manish K. Kashyap. Structural, electronic and optical studies of Pb-free halide double perovskite Cs2BiAgBr6; an mBJLDA approach. AIP Conf. Proc. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. Perovskite solar cells: must lead be replaced – and can it be done? Science and Technology of Advanced Materials. [CrossRef]
- Wei, F. Synthesis and Properties of a Lead-Free Hybrid Double Perovskite: (CH3NH3)2AgBiBr6. Chem.mater. 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, J. M. , Lee, M. M., Hey, A. & Snaith, H. J. Low-temperature processed meso-superstructured to thin-film perovskite solar cells. Energy & Environmental Science. [CrossRef]
- Jeon, N. J. Solvent engineering for high-performance inorganic–organic hybrid perovskite solar cells. Nat. Mater. [CrossRef]
- Burschka, J. Sequential deposition as a route to high-performance perovskite-sensitized solar cells. Nature. [CrossRef]
- Liu, D. & Kelly, T. L. Perovskite solar cells with a planar heterojunction structure prepared using room-temperature solution processing techniques. Nat Photon. [CrossRef]
- Eperon, G. E. Formamidinium lead trihalide: a broadly tunable perovskite for efficient planar heterojunction solar cells. Energy & Environmental Science. [CrossRef]
- Hodes, G. Perovskite-Based Solar Cells. Science. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




