Submitted:
21 March 2024
Posted:
22 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Project Background and Calculation Method
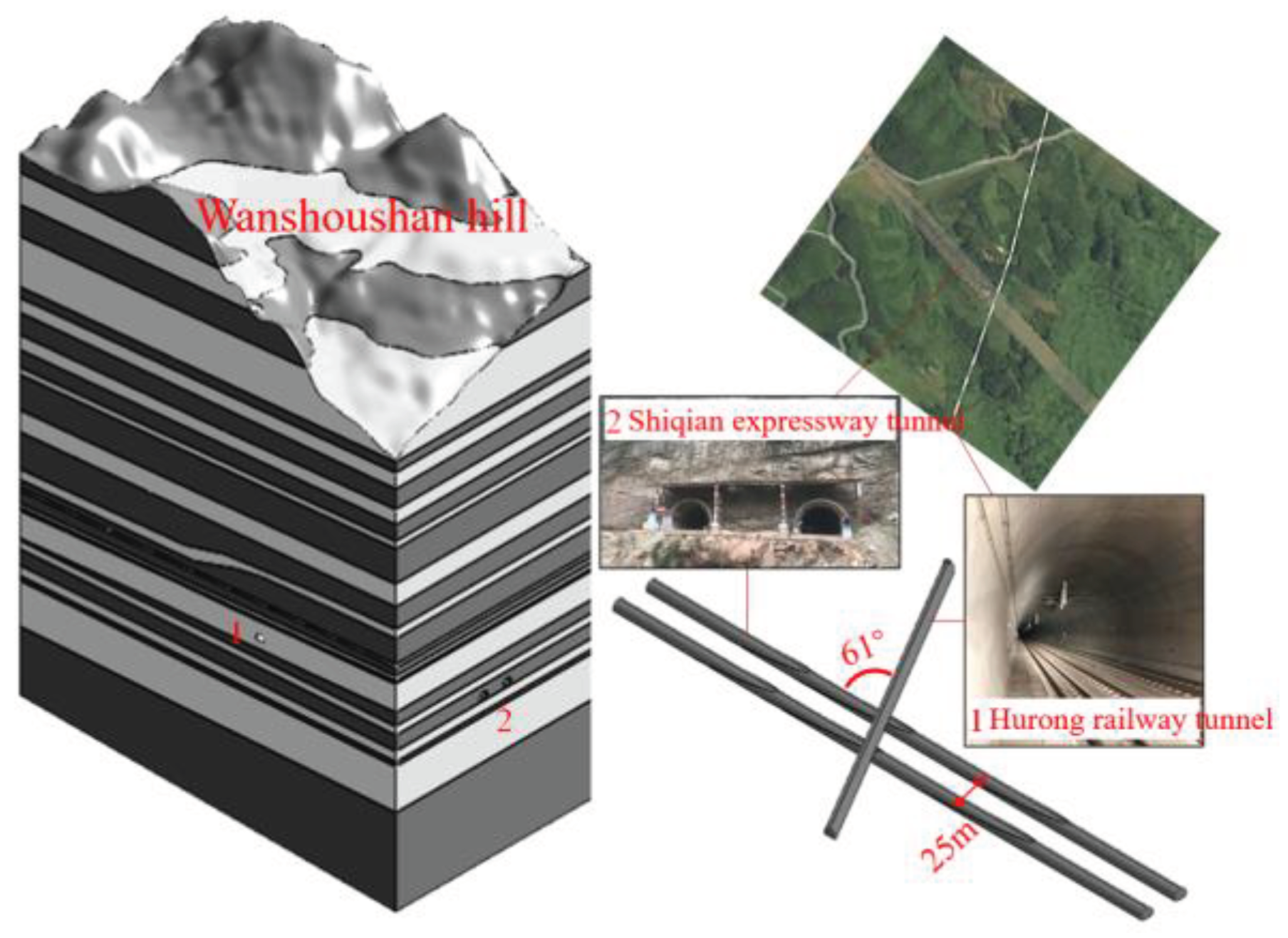
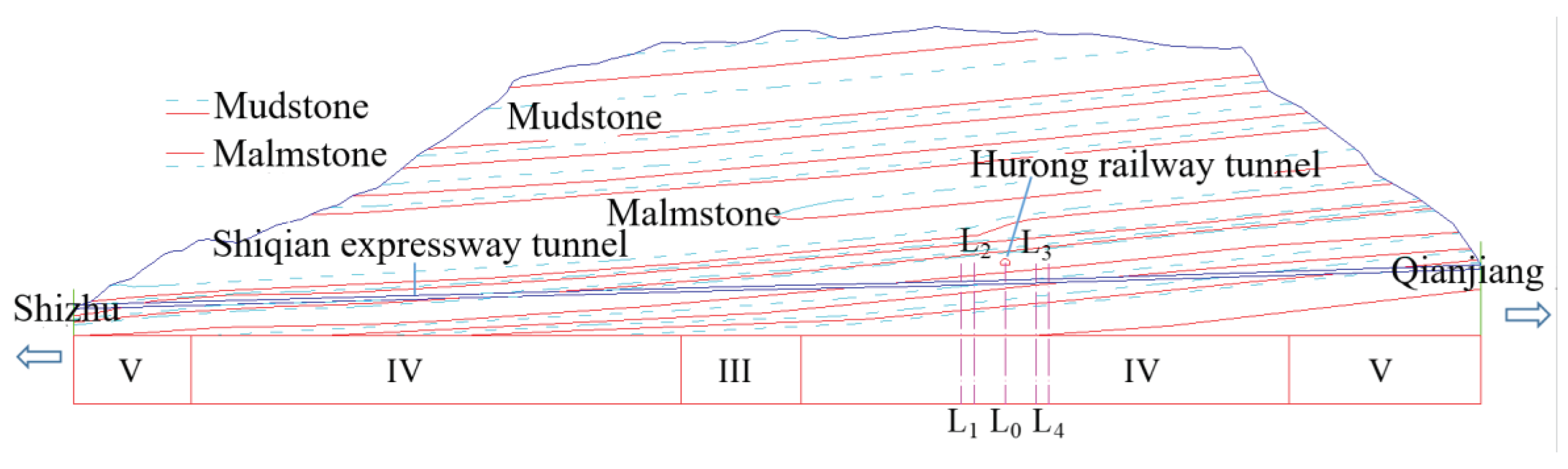
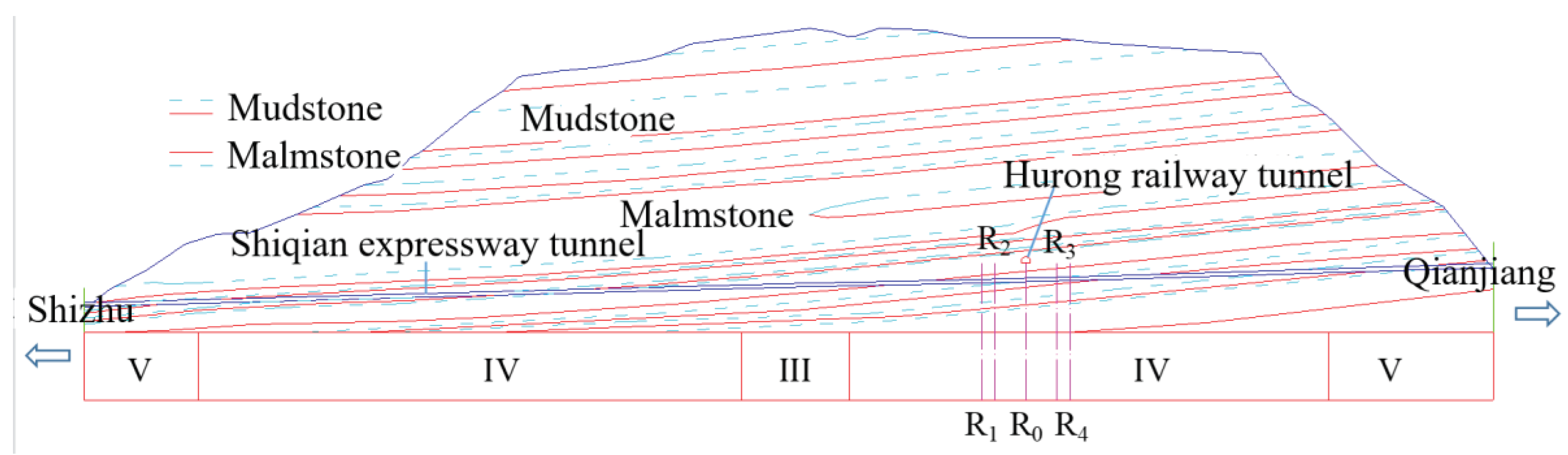
2.1. Project Background
2.2. Calculation Method
2.2.1. Hoek-Brown Guidelines
2.2.2. Determination of Rock Reduction Parameters
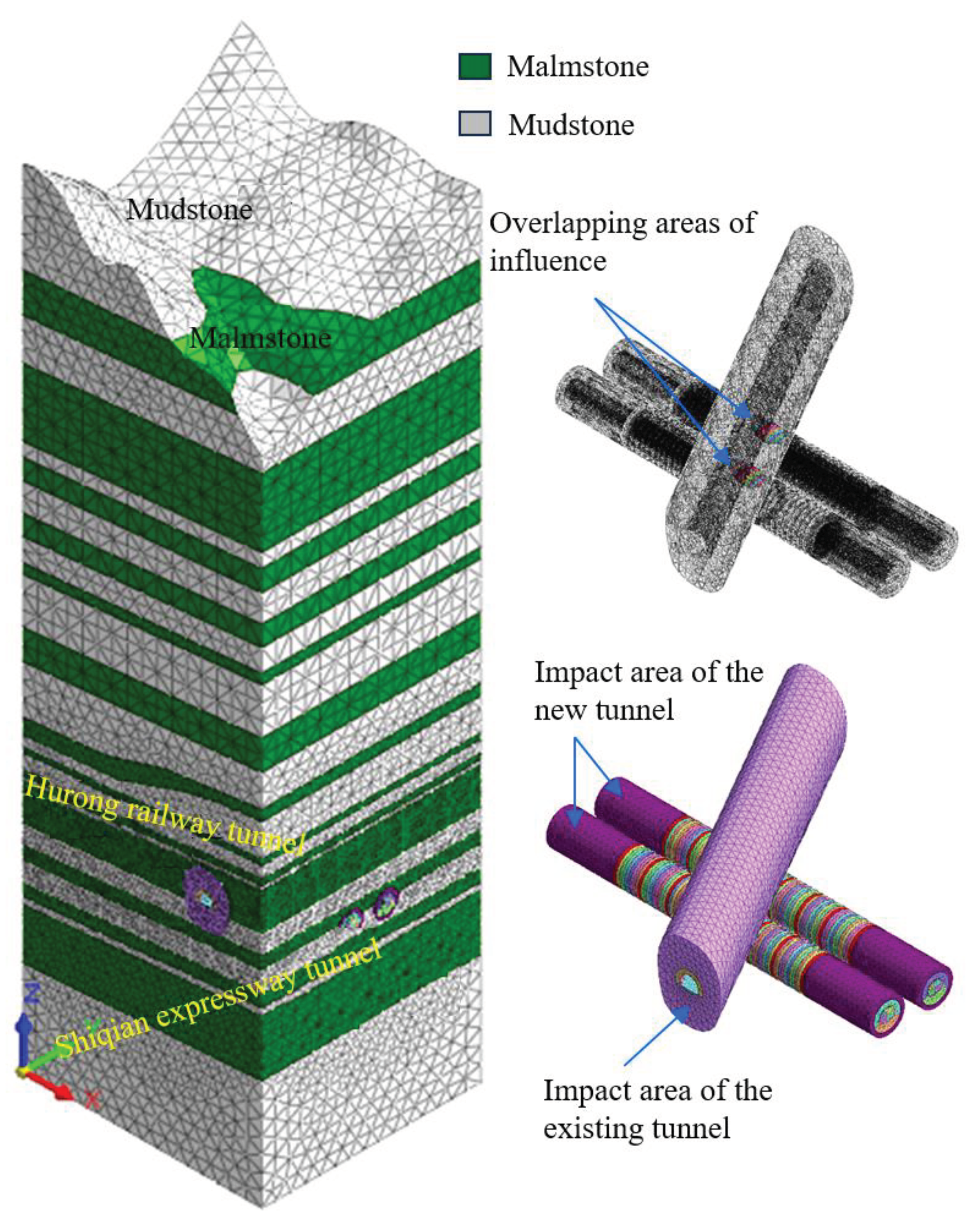
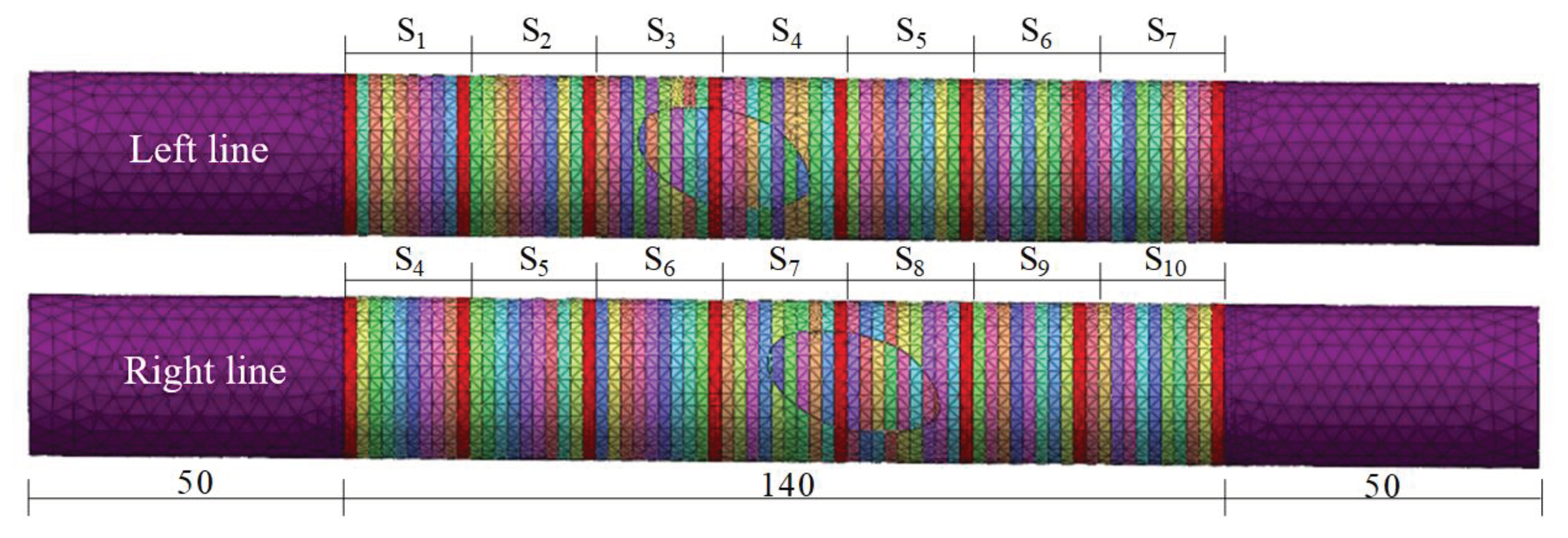
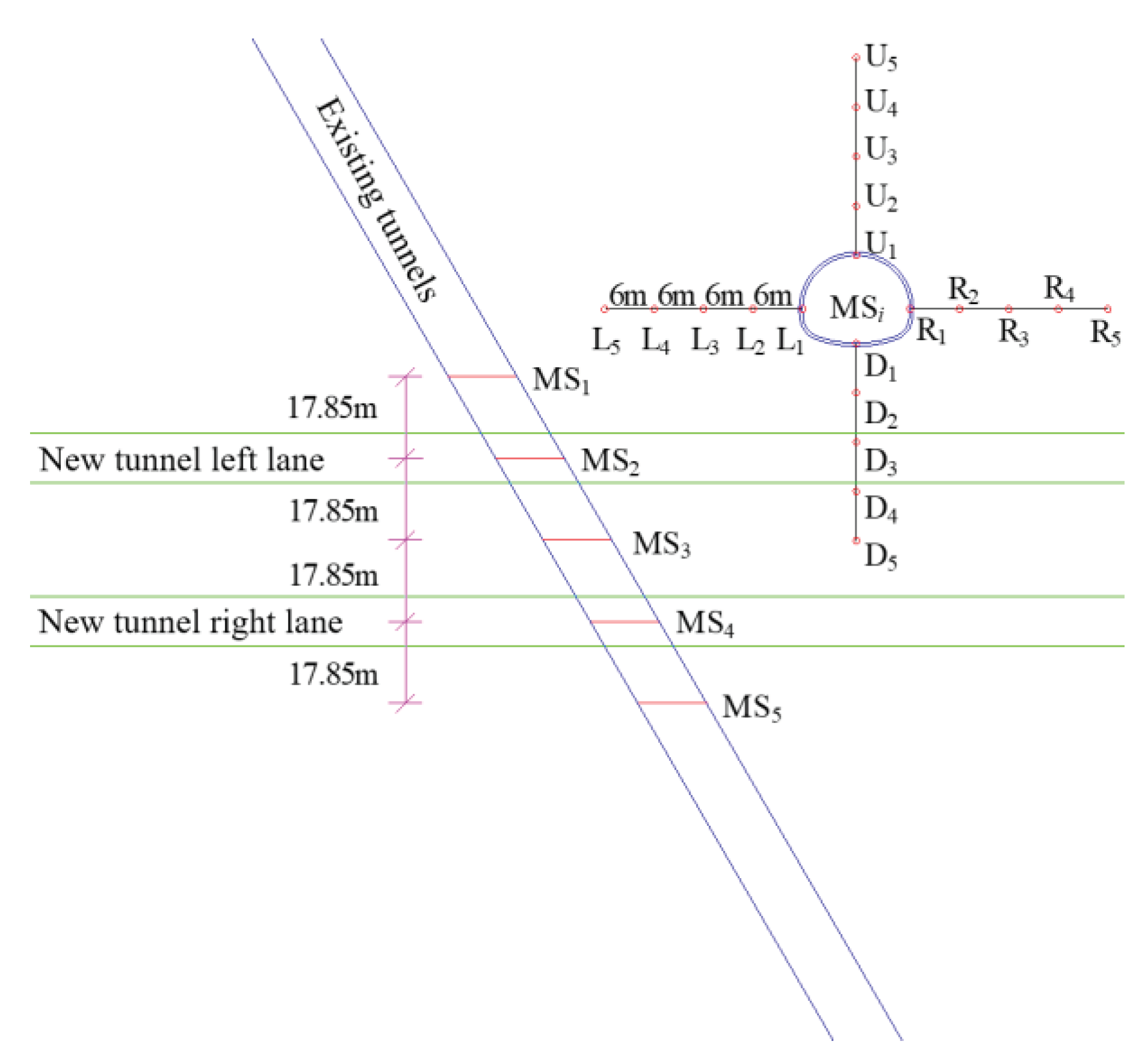
3. Three-Dimensional Numerical Model
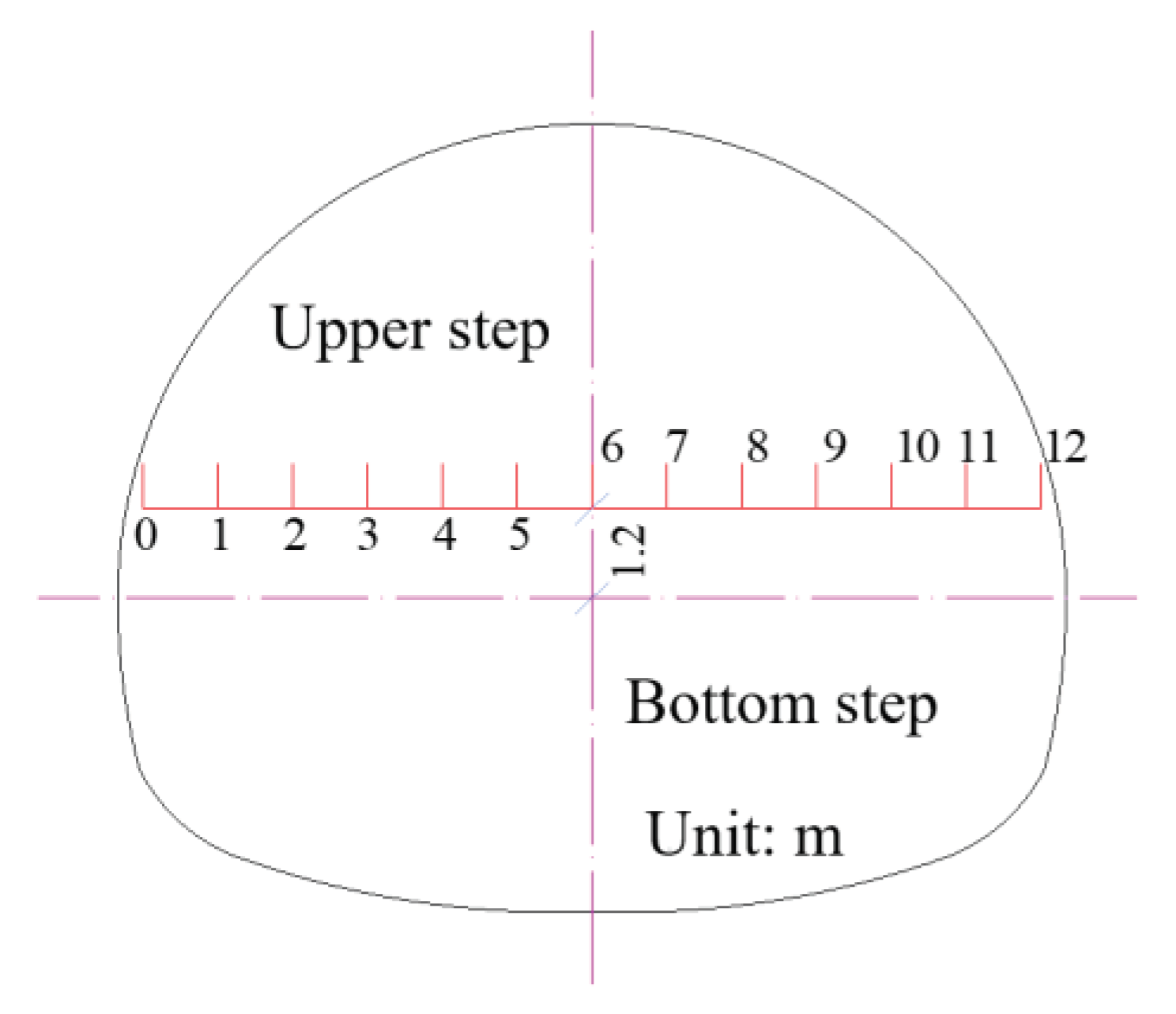
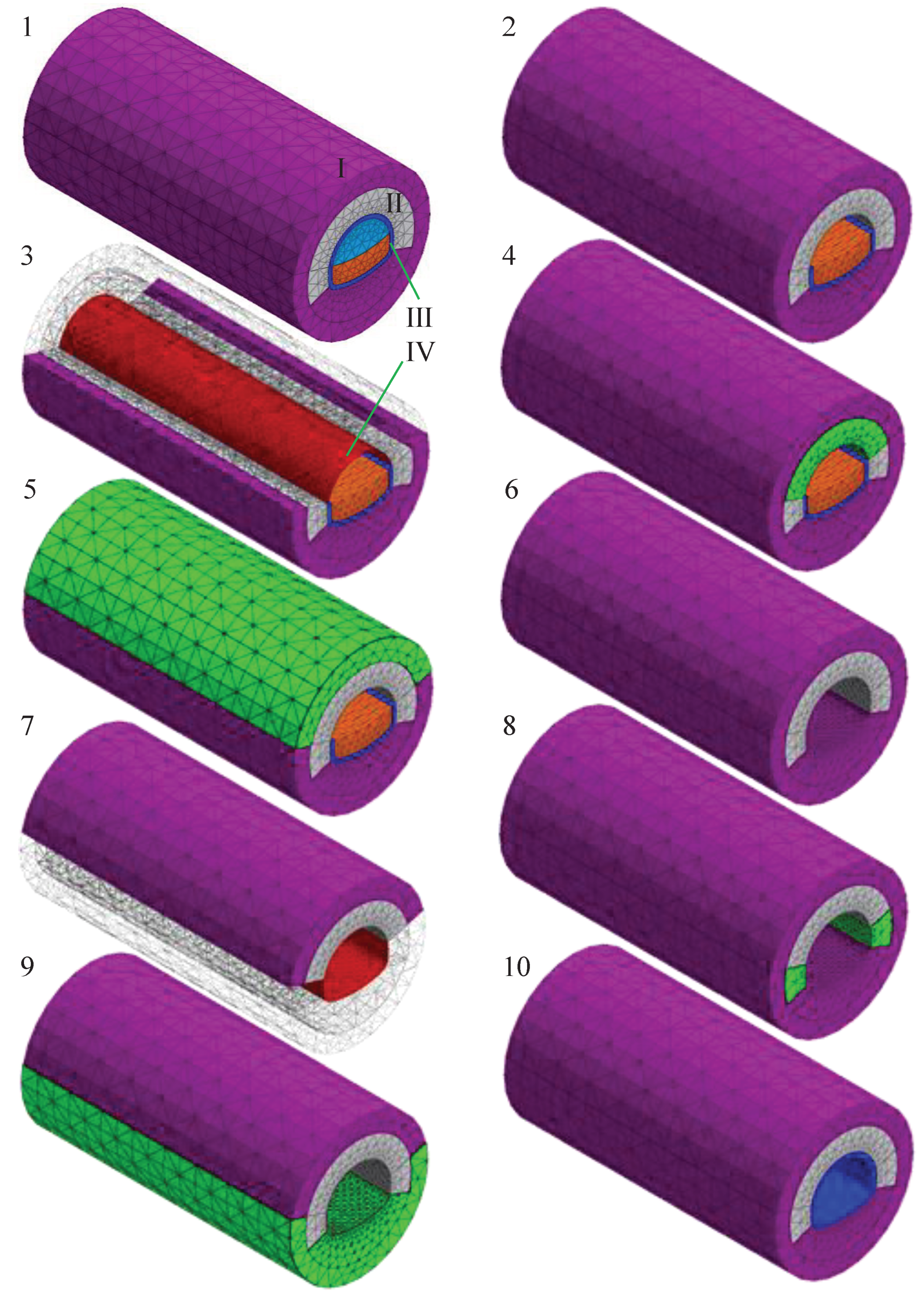
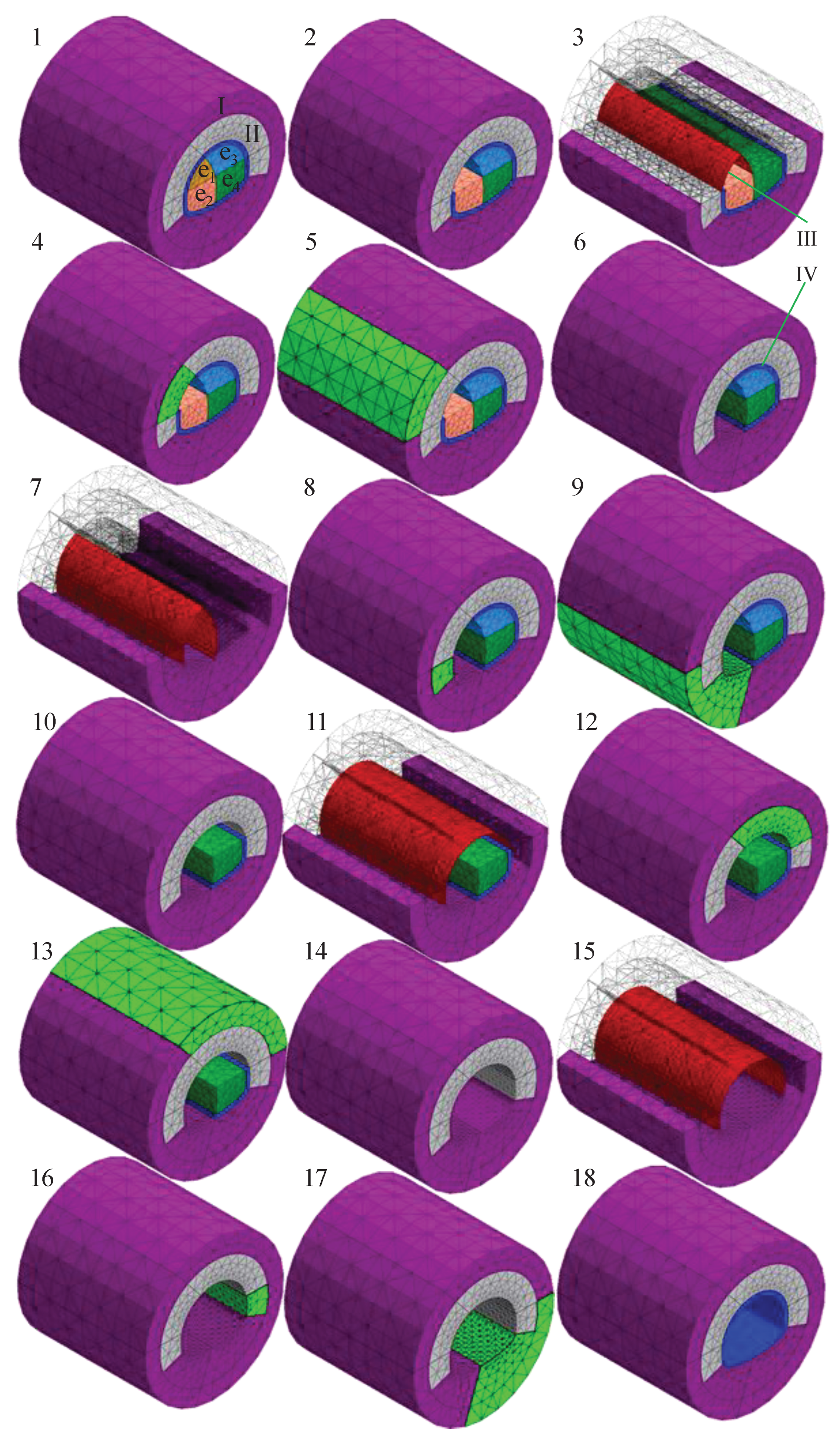
3.1. Model Building
3.2. Calculation of Working Conditions
4. Results
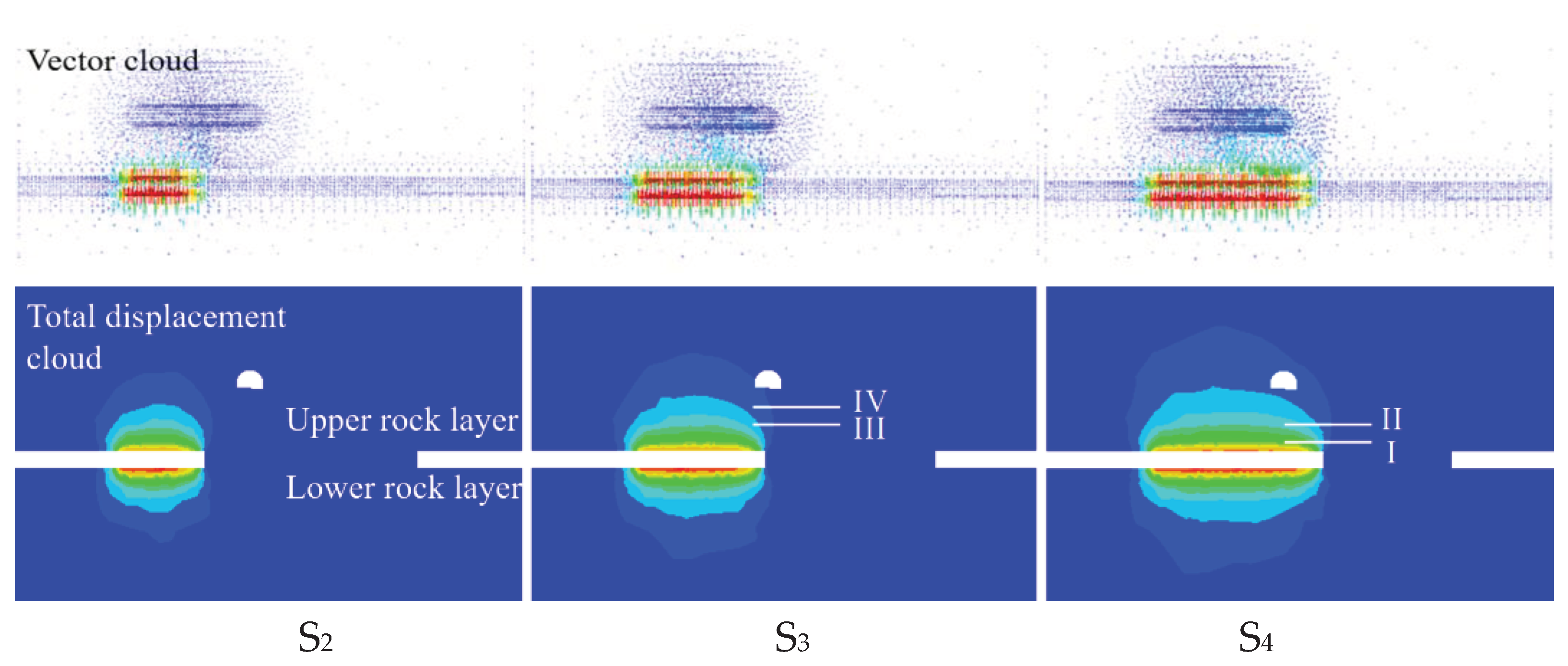
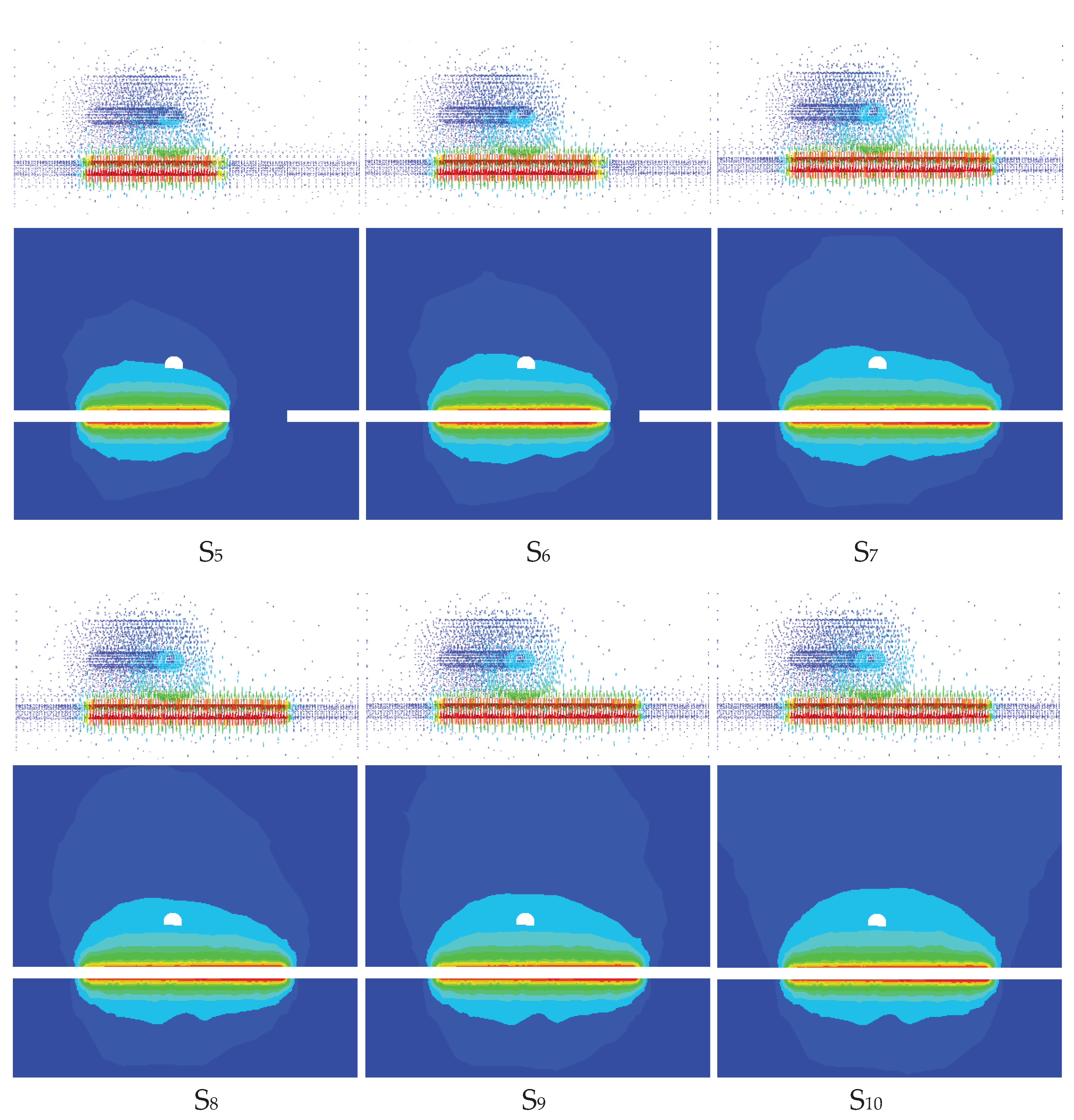
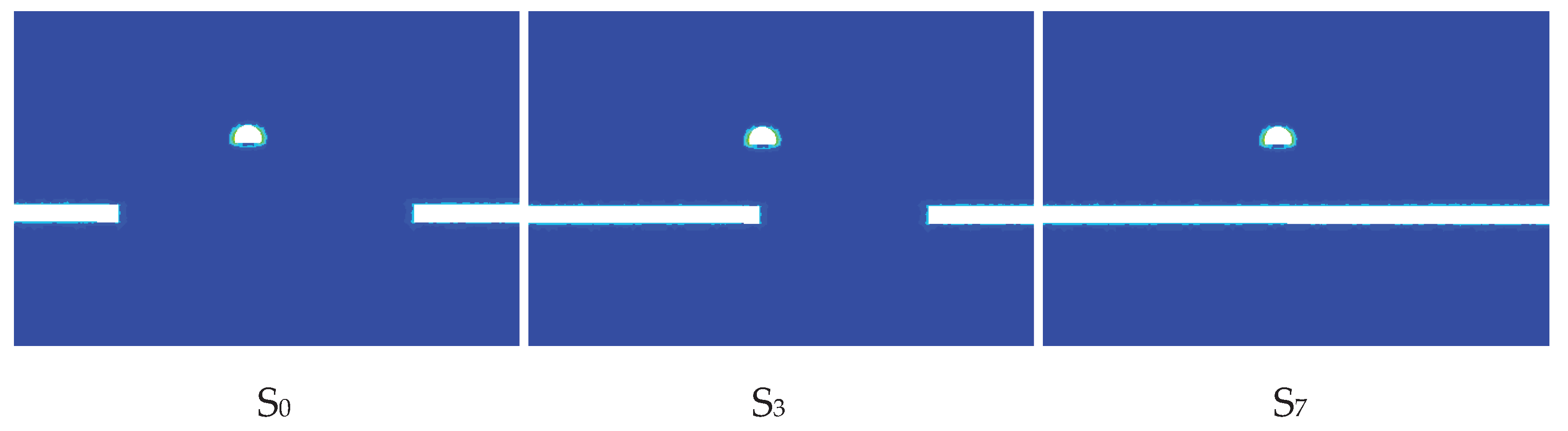
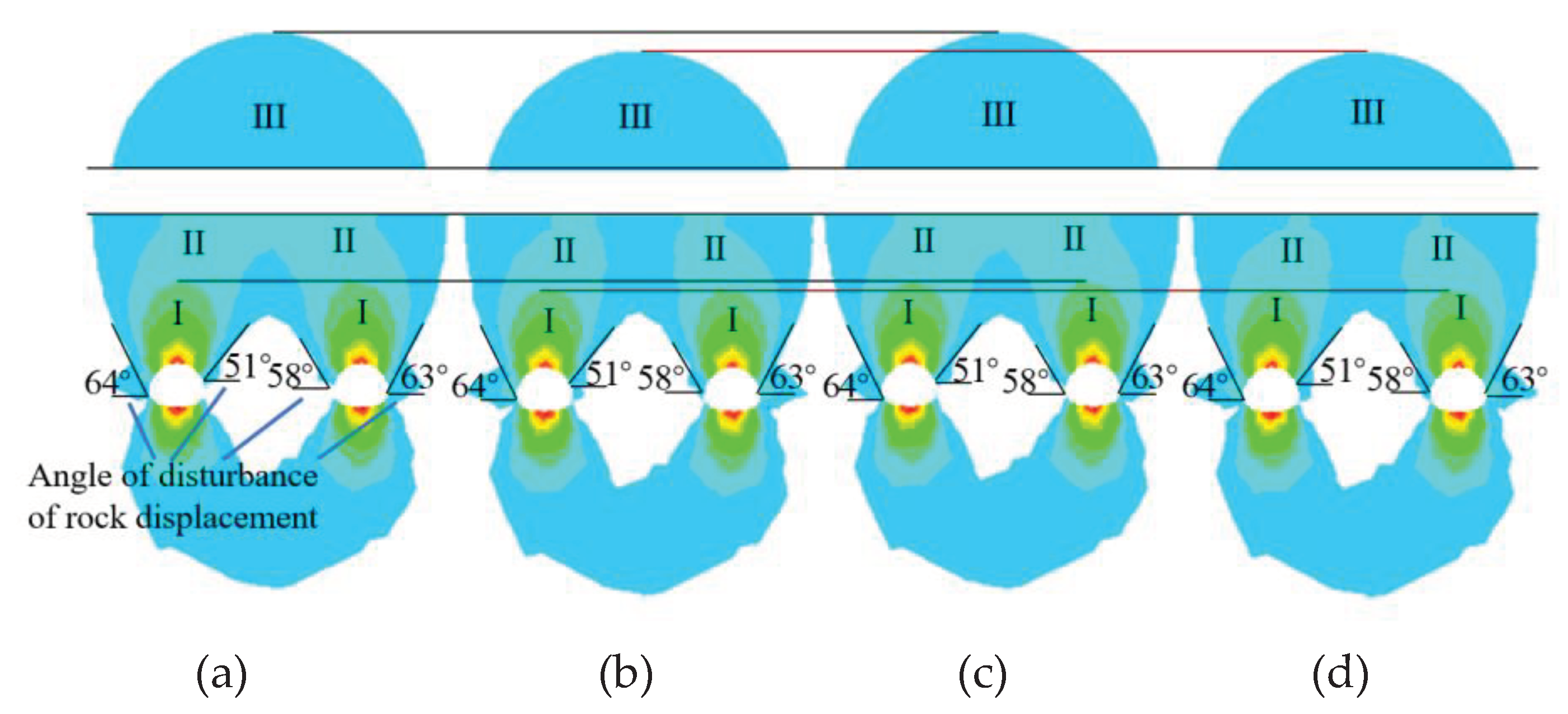
4.1. Analysis of Rock Formations in the Area of Influence
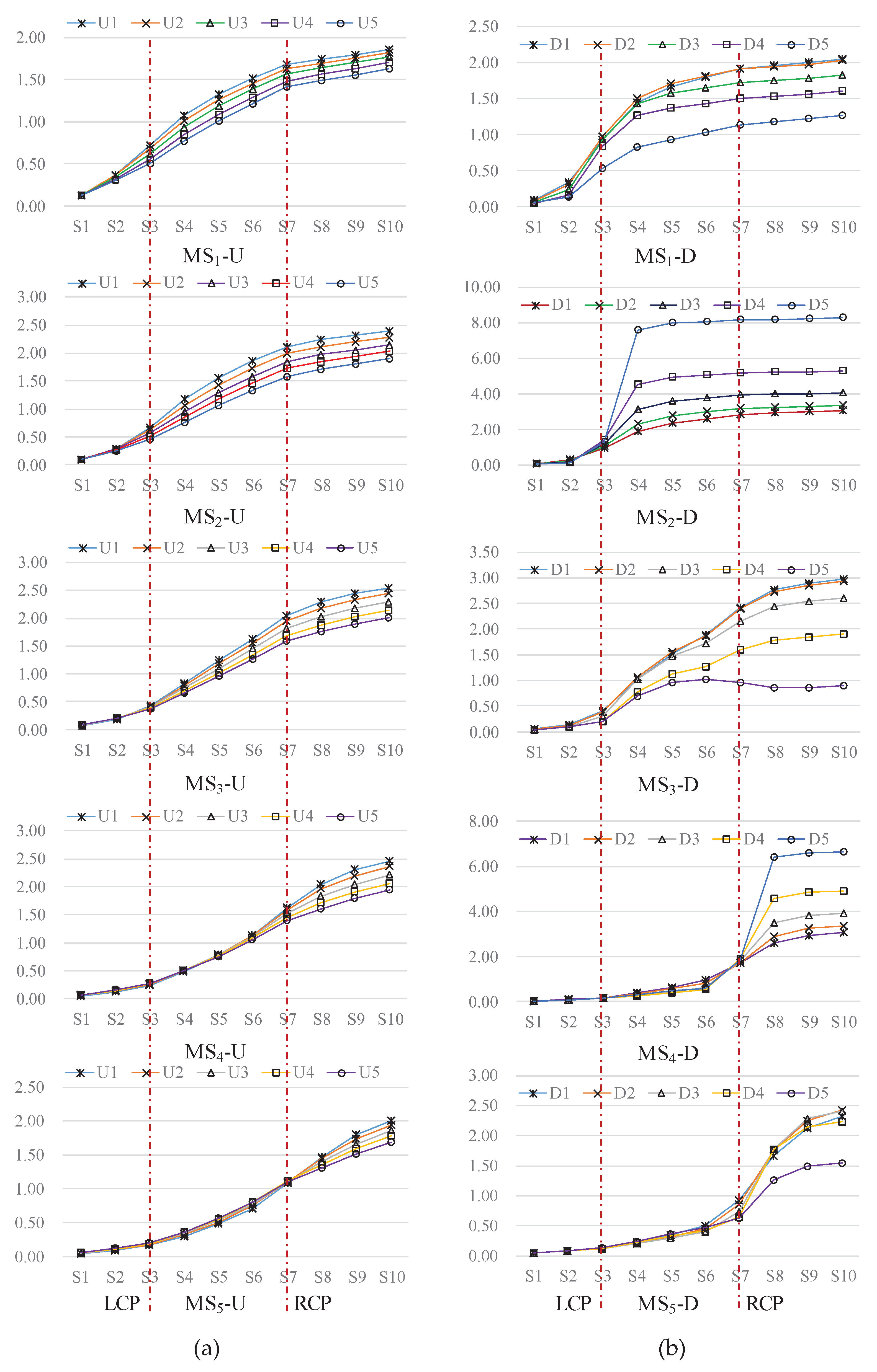
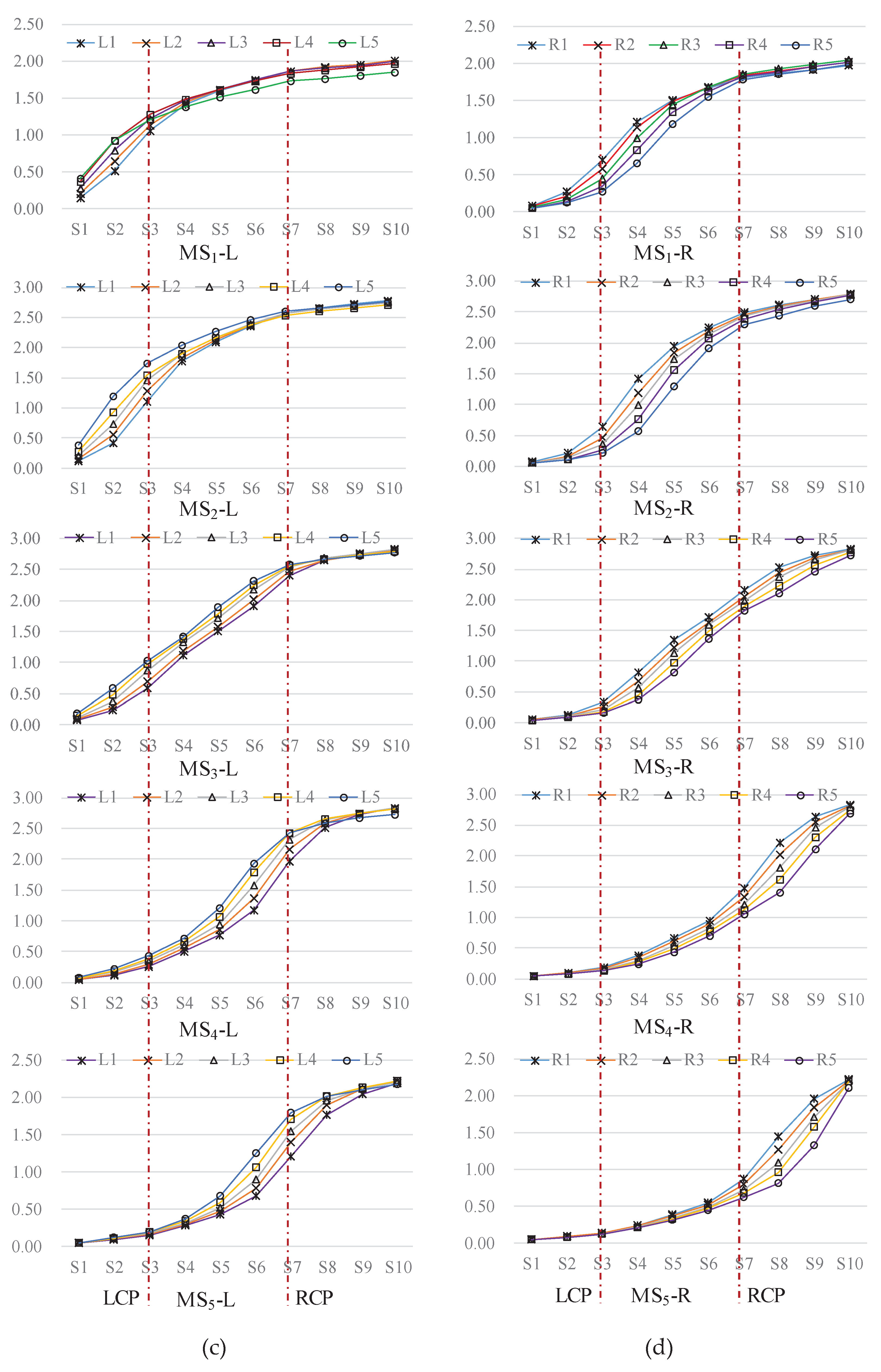
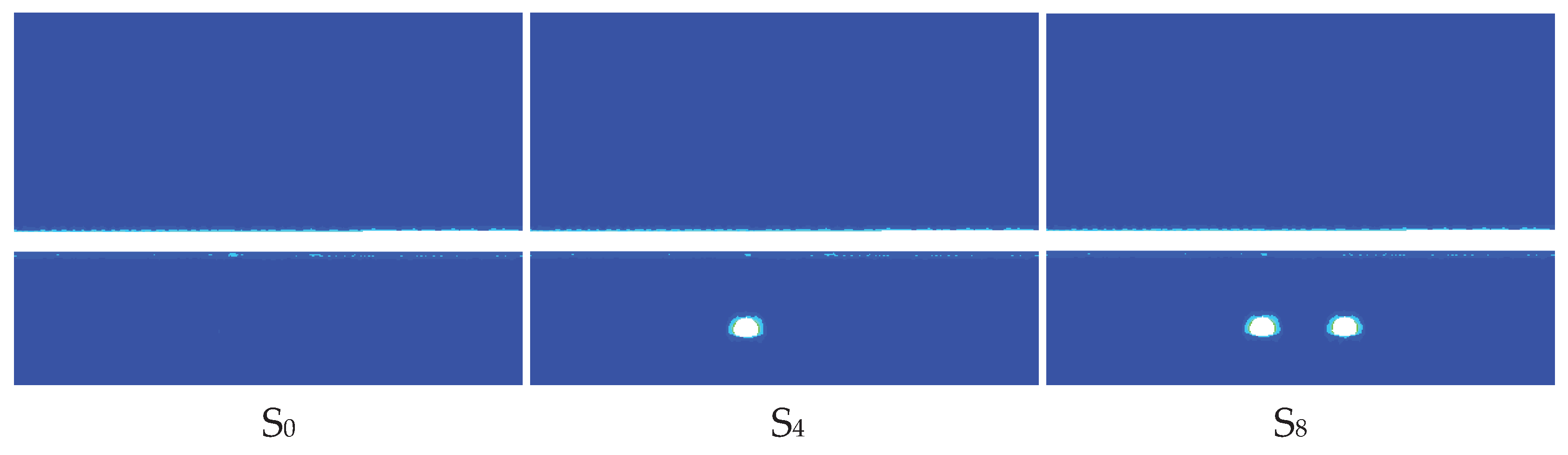
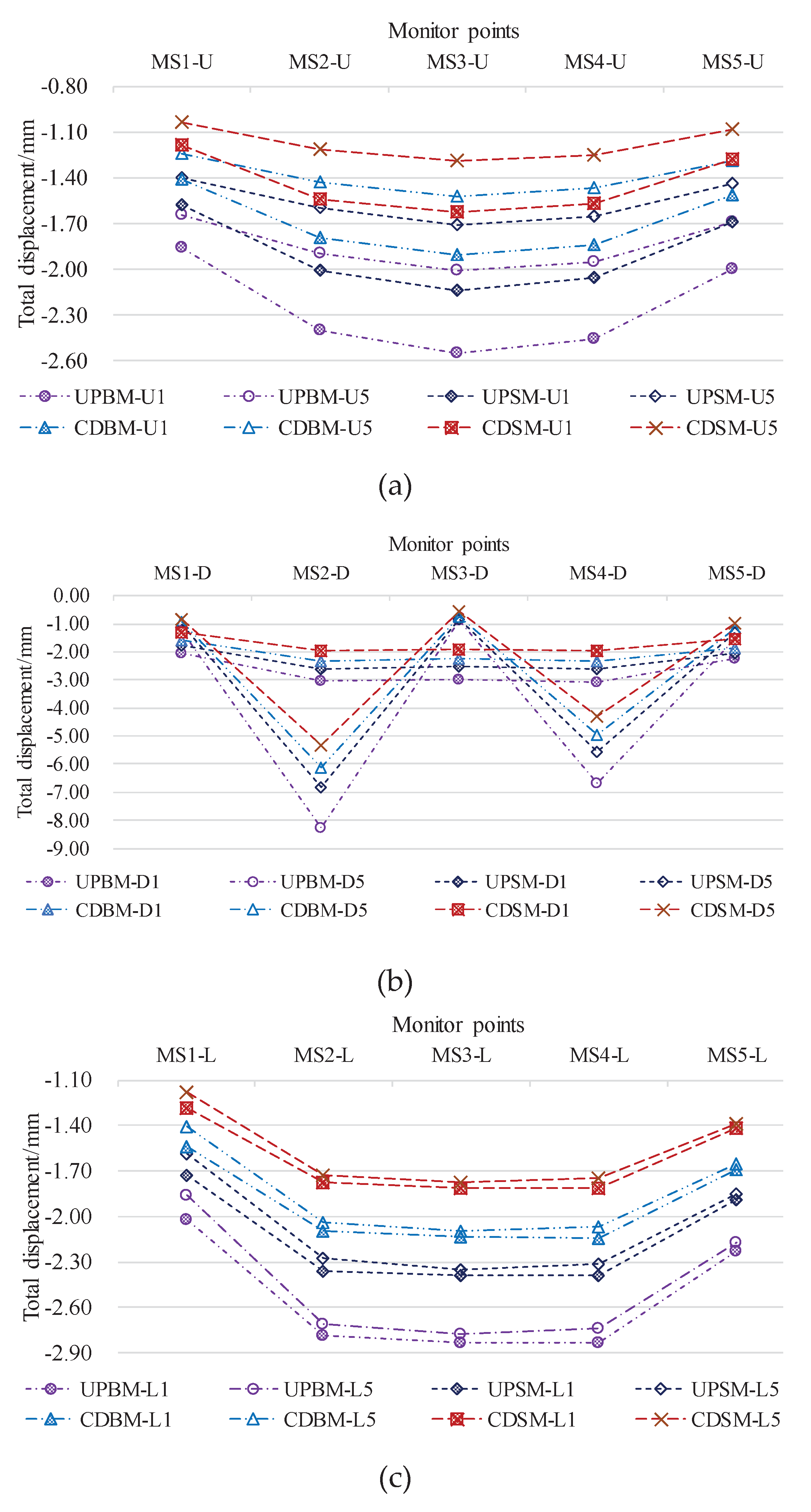
4.1.1. Total Displacement Response
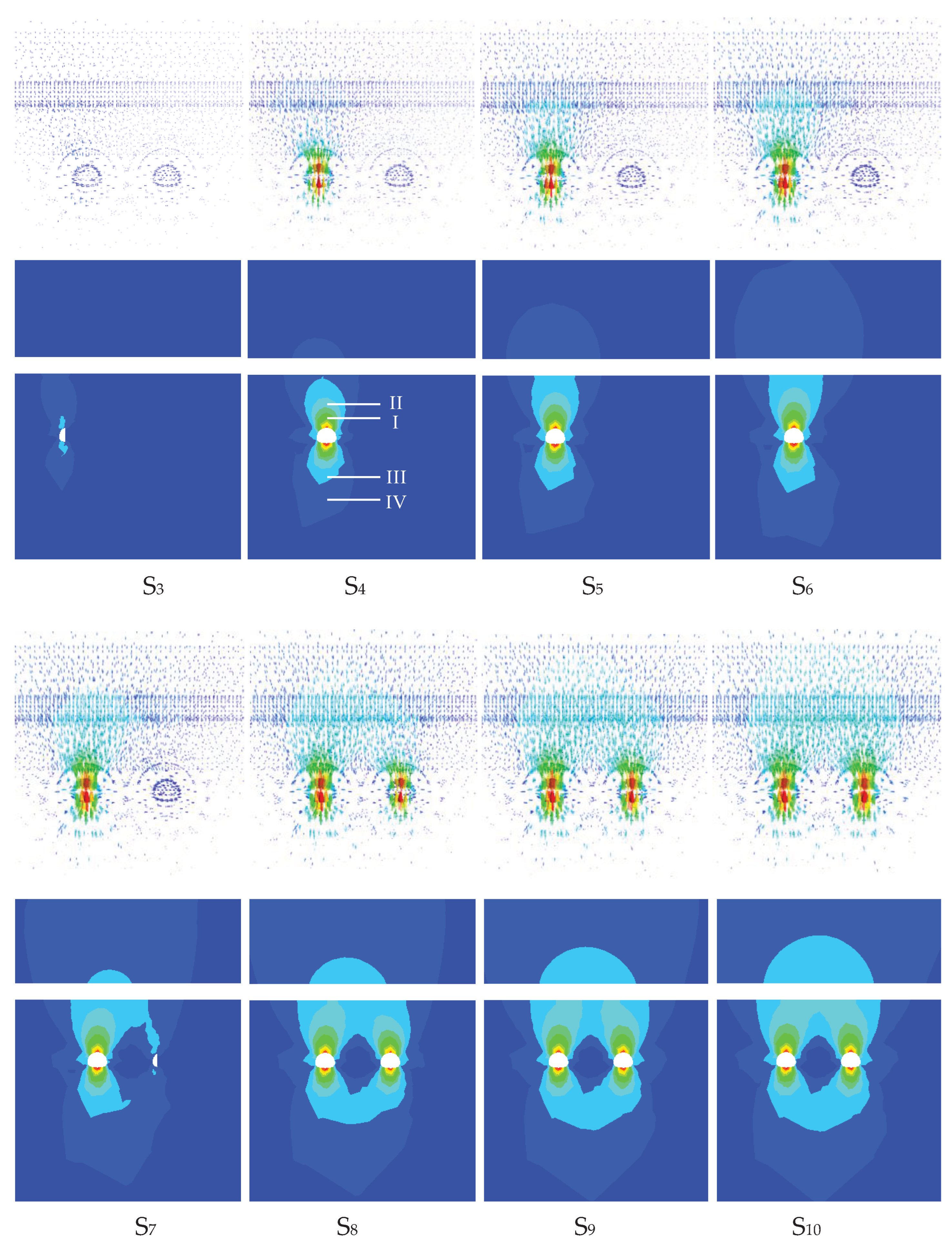
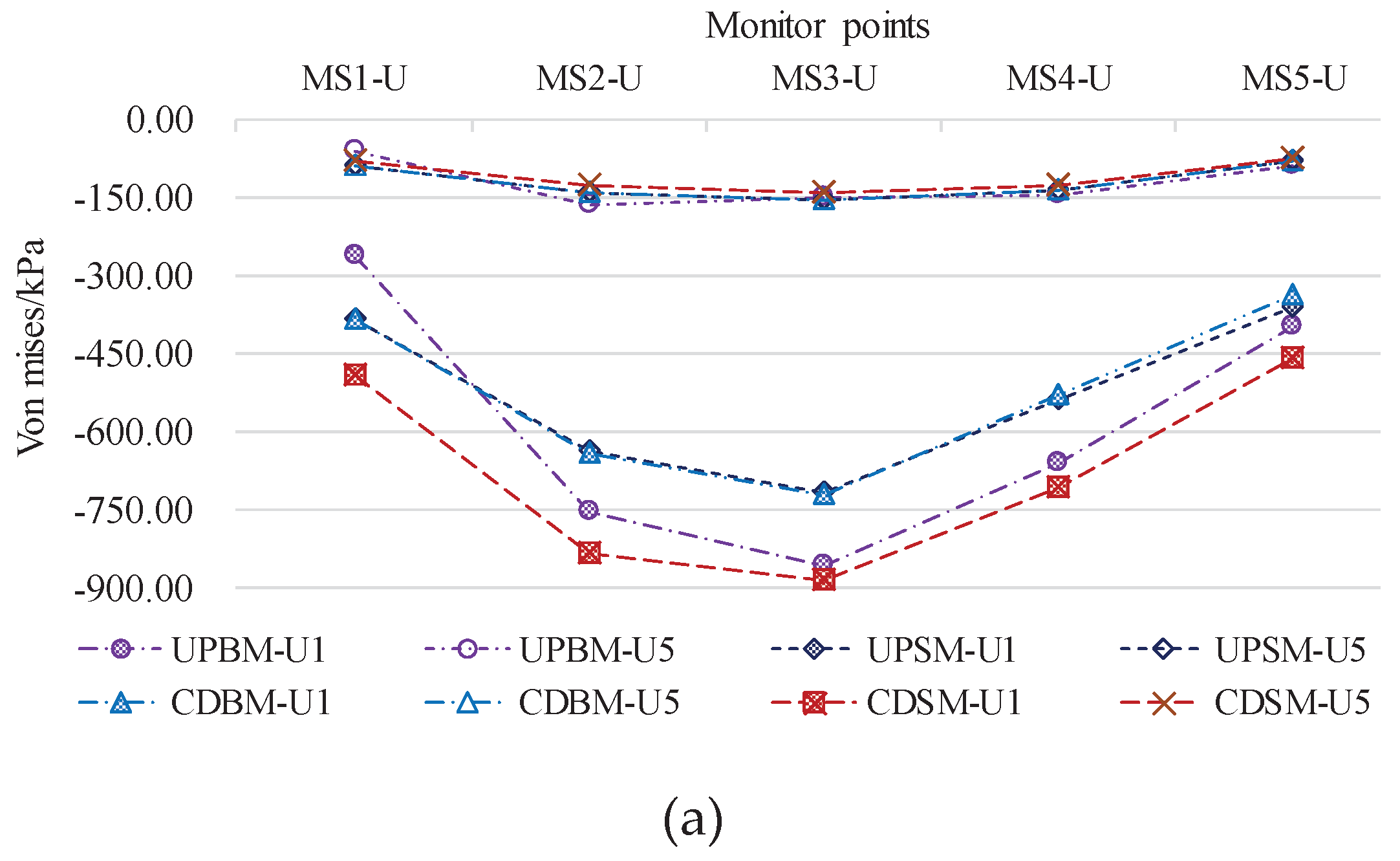
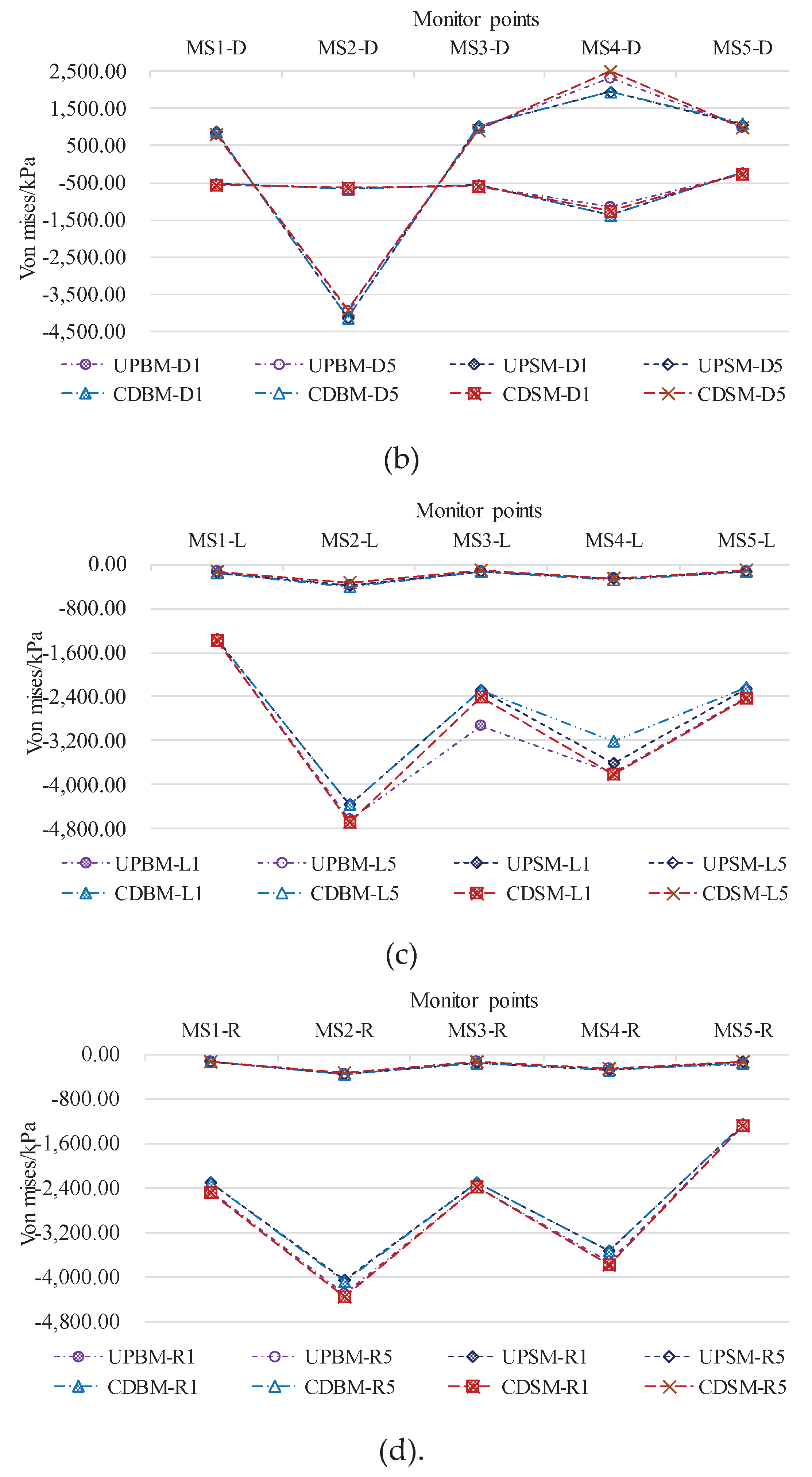
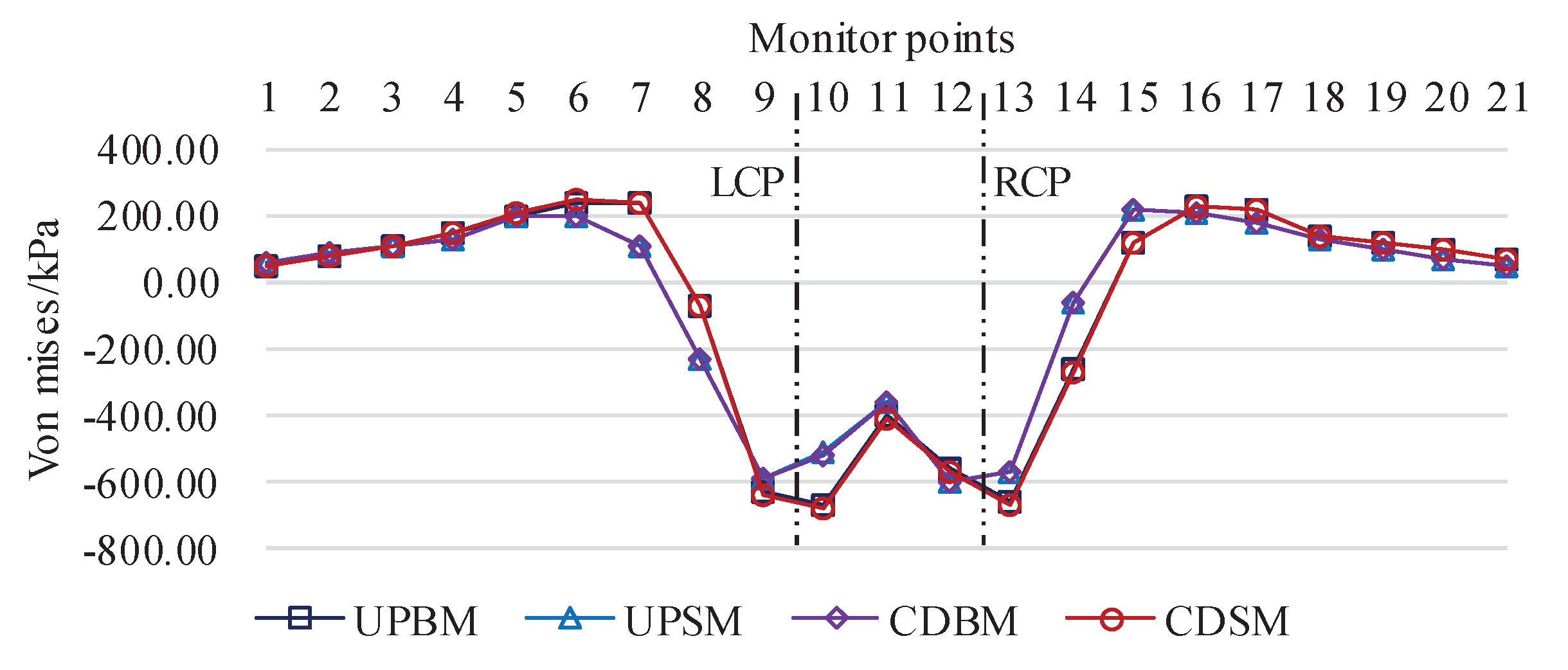
4.1.2. Von Mises Stress Response
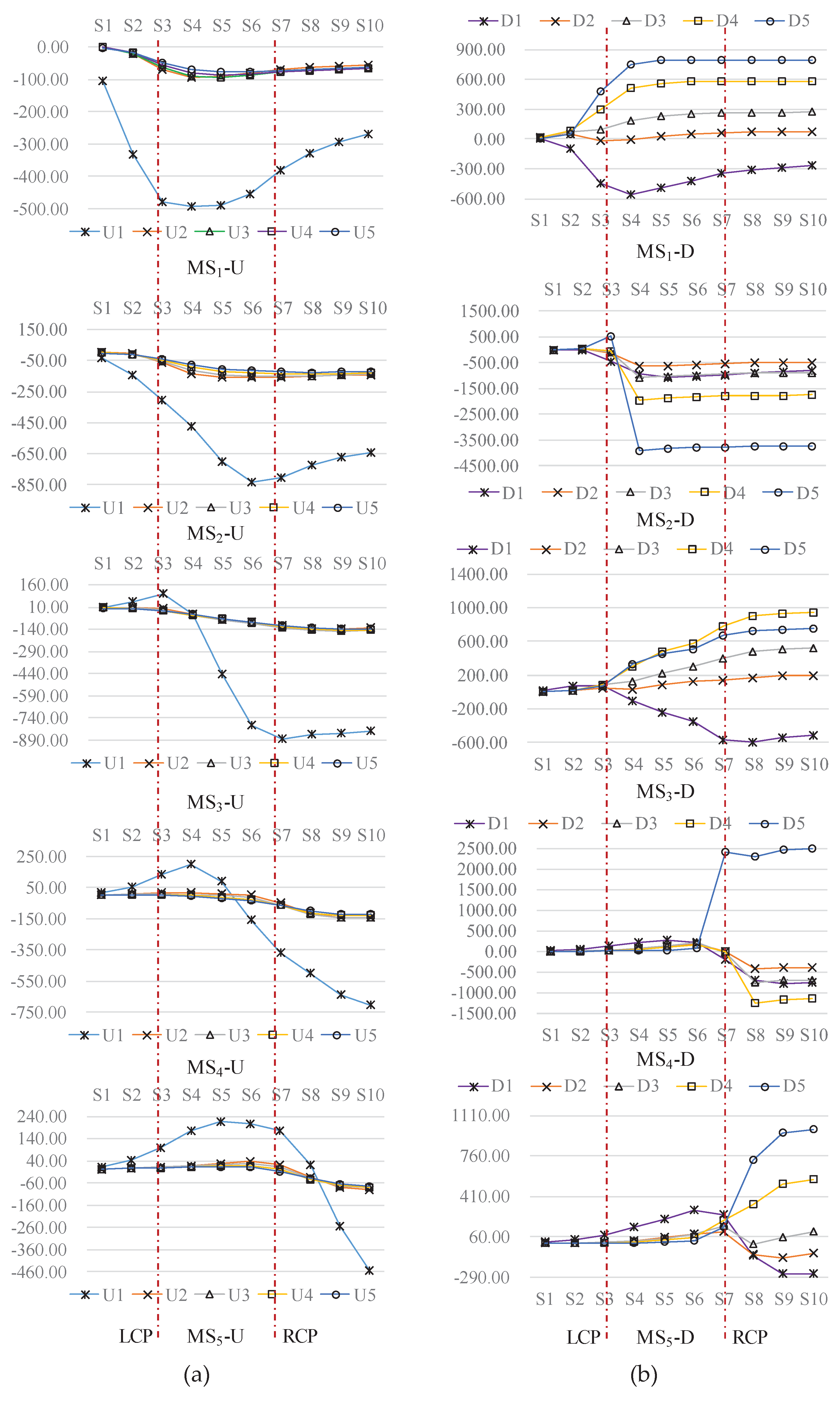
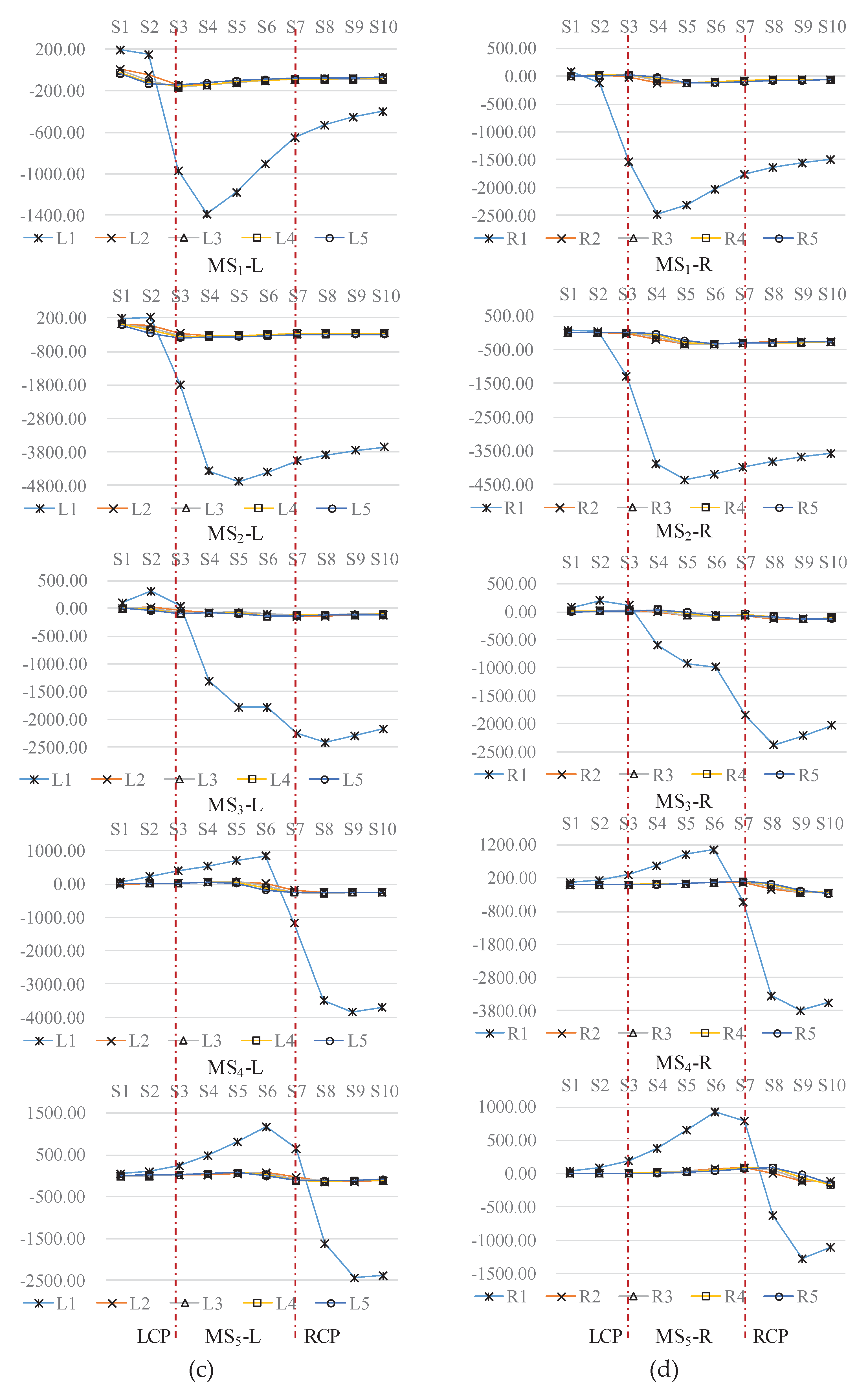
4.2. Typical Profile Analysis
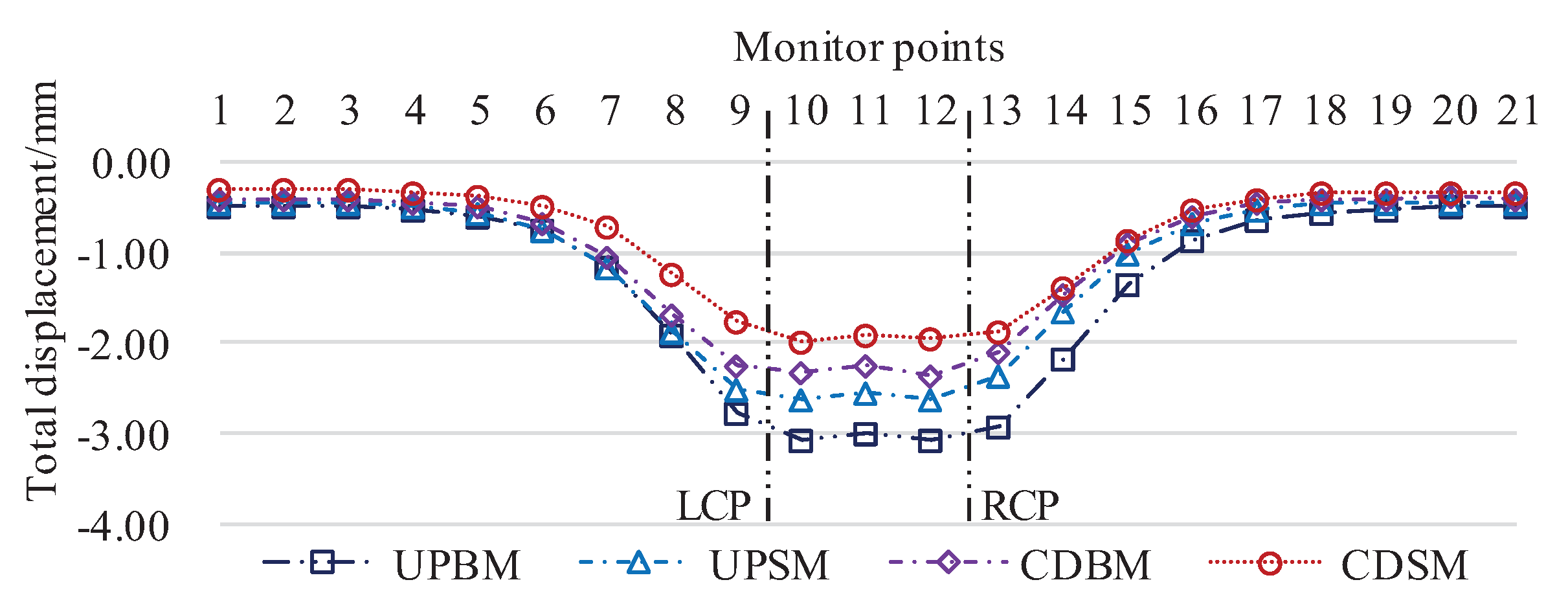
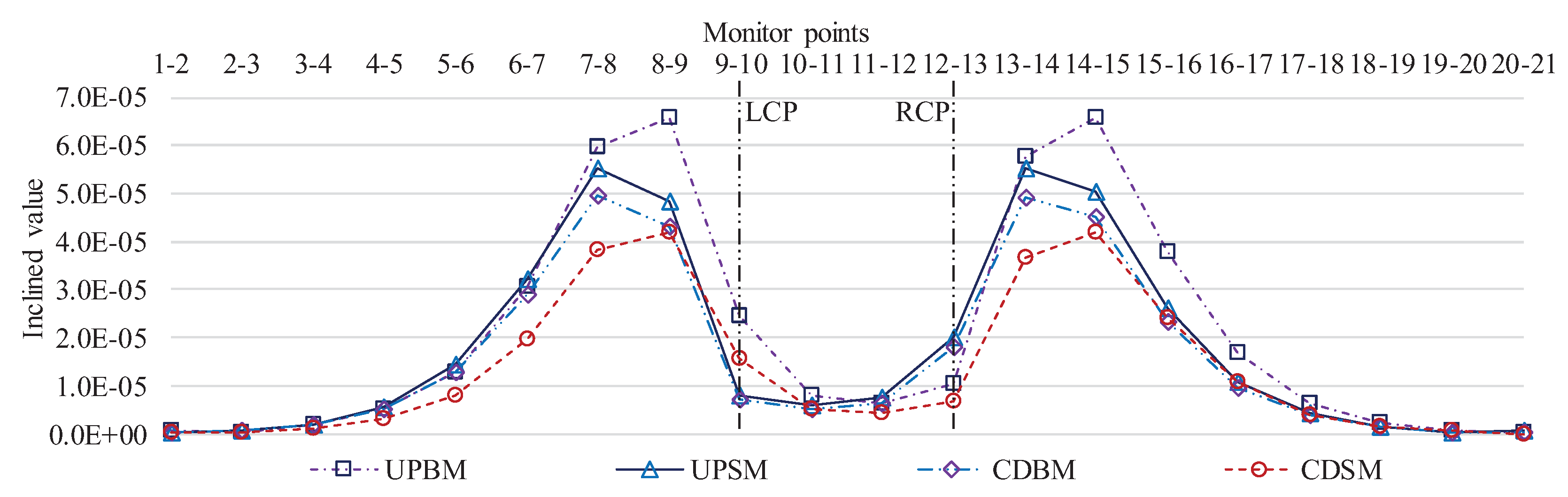
4.2.1. Total Displacement Characterization
4.2.2. Typical Point Characteristics
4.2.3. Characterization of Bottom Plate Measurement Points
4.2.4. Excavation Method Preference
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CHEN, Y.L.; CHEN, Z.L.; GUO, D.J.; et al. Underground space use of urban built-up areas in the central city of Nanjing: Insight based on a dynamic population distribution. Underground Space 2022, 7, 748–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PENG, F.L.; QIAO, Y.K.; SABRI, S.; et al. A collaborative approach for urban underground space development toward sustainable development goals: Critical dimensions and future directions. Frontiers of Structural and Civil Engineering 2021, 15, 20–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHENG, H.Z.; CHEN, R.P.; WU, H.N.; et al. General solutions for the longitudinal deformation of shield tunnels with multiple discontinuities in strata. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2021, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHEN, R.P.; SONG, X.; MENG, F.Y.; et al. Analytical approach to predict tunneling-induced subsurface settlement in sand considering soil arching effect. Computers and Geotechnics 2022, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LIU, T.; XIE, Y.; FENG, Z.H.; et al. Better understanding the failure modes of tunnels excavated in the boulder-cobble mixed strata by distinct element method. Engineering Failure Analysis 2020, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, S.B.; ZHANG, Y.G.; CAO, M.Y.; et al. Study on Excavation Sequence of Pilot Tunnels for a Rectangular Tunnel Using Numerical Simulation and Field Monitoring Method. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering 2022, 55, 3507–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QIU, J.L.; LU, Y.Q.; LAI, J.X.; et al. Failure behavior investigation of loess metro tunnel under local-high-pressure water environment. Engineering Failure Analysis 2020, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHAO, C.Y.; LEI, M.F.; SHI, C.H.; et al. Function mechanism and analytical method of a double layer pre-support system for tunnel underneath passing a large-scale underground pipe gallery in water-rich sandy strata: A case study. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2021, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHAIPANNA, P.; JONGPRADIST, P. 3D response analysis of a shield tunnel segmental lining during construction and a parametric study using the ground-spring model. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2019, 90, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LIU, B.; ZHANG, D.W.; YANG, C.; et al. Long-term performance of metro tunnels induced by adjacent large deep excavation and protective measures in Nanjing silty clay. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2020, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHANG, D.M.; XIE, X.C.; LI, Z.L.; et al. Simplified analysis method for predicting the influence of deep excavation on existing tunnels. Computers and Geotechnics 2020, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DENG, Z.Y.; LIU, X.R.; ZHOU, X.H.; et al. Field monitoring of mechanical parameters of deep-buried jacketed-pipes in rock: Guanjingkou water control project. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2022, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MA, J.F.; HE, S.H.; CUI, G.Y.; et al. Construction stability and reinforcement technology for the super-large rectangular pipe-jacking tunnel passing beneath the operational high-speed railway in composite stratum. Geomatics Natural Hazards & Risk 2023, 14. [Google Scholar]
- MA, P.; SHIMADA, H.; SASAOKA, T.; et al. Investigation on the engineering effects of the geometrical configuration of the jacking rectangular pipe. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2022, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHENF, F.; WANG, L.; ZHANG, W. Reliability assessment on stability of tunnelling perpendicularly beneath an existing tunnel considering spatial variabilities of rock mass properties. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2019, 88, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LIN, X.T.; CHEN, R.P.; WU, H.N.; et al. Deformation behaviors of existing tunnels caused by shield tunneling undercrossing with oblique angle. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2019, 89, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHEN, R.P.; ZHANG, P.; WU, H.N.; et al. Prediction of shield tunneling-induced ground settlement using machine learning techniques. Frontiers of Structural and Civil Engineering 2019, 13, 1363–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHANG, P.; WU, H.N.; CHEN, R.P.; et al. A critical evaluation of machine learning and deep learning in shield-ground interaction prediction. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2020, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHANG, P. A novel feature selection method based on global sensitivity analysis with application in machine learning-based prediction model. Applied Soft Computing 2019, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHOU, J.; SHI, X.Z.; DU, K.; et al. Feasibility of Random-Forest Approach for Prediction of Ground Settlements Induced by the Construction of a Shield-Driven Tunnel. International Journal of Geomechanics 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHEN, R.P.; LIN, X.T.; KANG, X.; et al. Deformation and stress characteristics of existing twin tunnels induced by close-distance EPBS under-crossing. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2018, 82, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LAI, H.P.; ZHENG, H.W.; CHEN, R.; et al. Settlement behaviors of existing tunnel caused by obliquely under-crossing shield tunneling in close proximity with small intersection angle. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2020, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LEI, H.Y.; LIU, Y.N.; HU, Y.; et al. Active stability of the shield tunneling face crossing an adjacent existing tunnel: transparent clay model test and DEM simulation. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 2023, 60, 864–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHENG, R.S.; CHEN, W.S.; HAO, H.; et al. A state-of-the-art review of road tunnel subjected to blast loads. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2021, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TIANX, X.; SONGZ, P.; WANGJ, B. Study on the propagation law of tunnel blasting vibration in stratum and blasting vibration reduction technology. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering 2019, 126. [Google Scholar]
- DUAN, B.F.; GONG, W.Z.; TA, G.S.; et al. Influence of Small, Clear Distance Cross-Tunnel Blasting Excavation on Existing Tunnel below. Advances in Civil Engineering 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WU, B.; CUI, Y.Z.; MENG, G.W.; et al. Research on Dynamic Response of Shallow Buried Tunnel Lining Constructed by Drilling and Blasting Method. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RUAN, J.B.; WANG, T.H.; ZHAO, Z.K.; et al. Discussion on Blasting Vibration Velocity of Deep Rock Mass Considering Thickness of Overlying Soil Layer. Periodica Polytechnica-Civil Engineering 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TIANBIN, L.I.; LUBO, M.; JIN, Z.H.U.; et al. COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS METHOD FOR ADVANCED FORECAST OF GEOLOGY IN TUNNELS. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 2009, 28, 2429–2436. [Google Scholar]
- ZHOU, Y.; ZHANG, B.; GENG, Z.; et al. STABILITY ANALYSIS OF SOFT ROCK SURROUNDING TUNNEL BASED ON HOEK-BROWN STRENGTH CRITERION. Journal of Engineering Geology 2019, 27, 980–988. [Google Scholar]
- GENG, Z.; ZHANG, B.; LI, W.; et al. COMPARISON AND ANALYSIS ON SURROUNDING ROCK STABILITY OF BIAS LARGE SPAN TUNNEL WITH DIFFERENT EXCAVATION METHODS. Journal of Engineering Geology 2018, 26, 866–873. [Google Scholar]
- HU, W.; LIU, J.; PANG, Y.; et al. CORRECTION OF STRENGTH PARAMETERS FOR ANISOTROPIC SLOPE ROCK MASS BASED ON H-B PRINCIPLES. Journal of Engineering Geology 2018, 26, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar]
- LI, S.; LIU, B.; SUN, H.; et al. STATE OF ART AND TRENDS OF ADVANCED GEOLOGICAL PREDICTION IN TUNNEL CONSTRUCTION. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 2014, 33, 1090–1113. [Google Scholar]
- LI, Y.F.; HUANG, C.F.; LU, H.J.; et al. Investigation of the Influence Area of the Excavation of a Double-Line Highway Tunnel under an Existing Railway Tunnel. Applied Sciences-Basel 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MARINOS, P.; MARINOS, V.; HOEK, E. Geological Strength Index (GSI). A characterization tool for assessing engineering properties for rock masses; proceedings of the Underground Works under Special Conditions Workshop, Lisbon, PORTUGAL, F Jul 06, 2007 [C]. 2007.
- HOEK, E.; BROWN, E.T. The Hoek-Brown failure criterion and GSI - 2018 edition. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 2019, 11, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HEPING, X.I.E.; YANG, J.U.; LIYUN, L.I.; et al. ENERGY MECHANISM OF DEFORMATION AND FAILURE OF ROCK MASSES. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 2008, 27, 1729–1740. [Google Scholar]
- WANG, Y.; YIN, J.M.; XIAO, G.Q. Three-dimensional stability analysis of stratified rock mass tunnel based on anisotropic theory; proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on In-Situ Rock Stress, Beijing, PEOPLES R CHINA, F Aug 25-27, 2010 [C]. 2010.
- GUO, F.; LIU, J.X.; LI, Y.F.; et al. Fatigue life evaluation of high-speed maglev train bogie under higher operating speed grade; proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety (ICTIS), Liverpool, ENGLAND, F Jul 14-17, 2019 [C]. 2019.
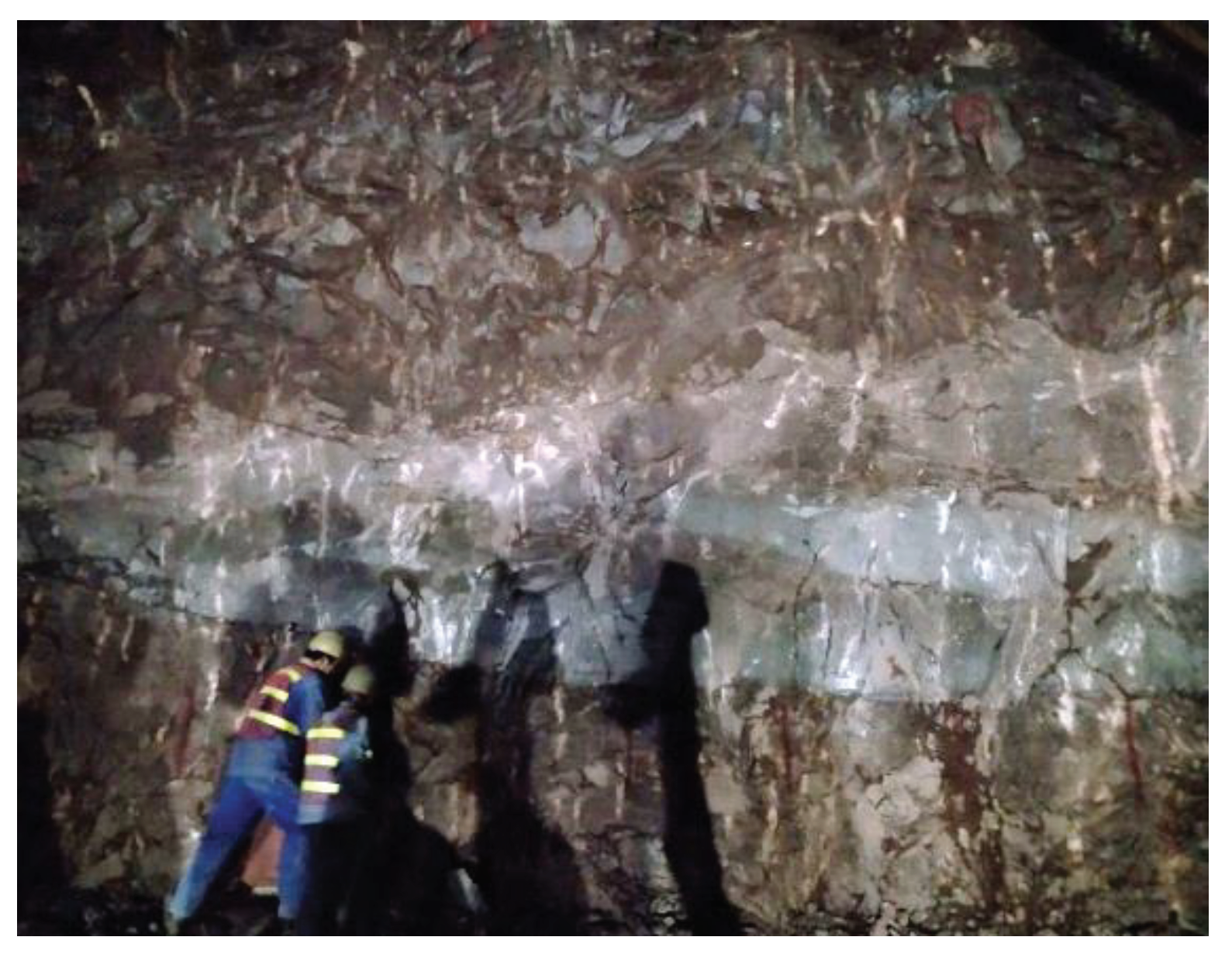
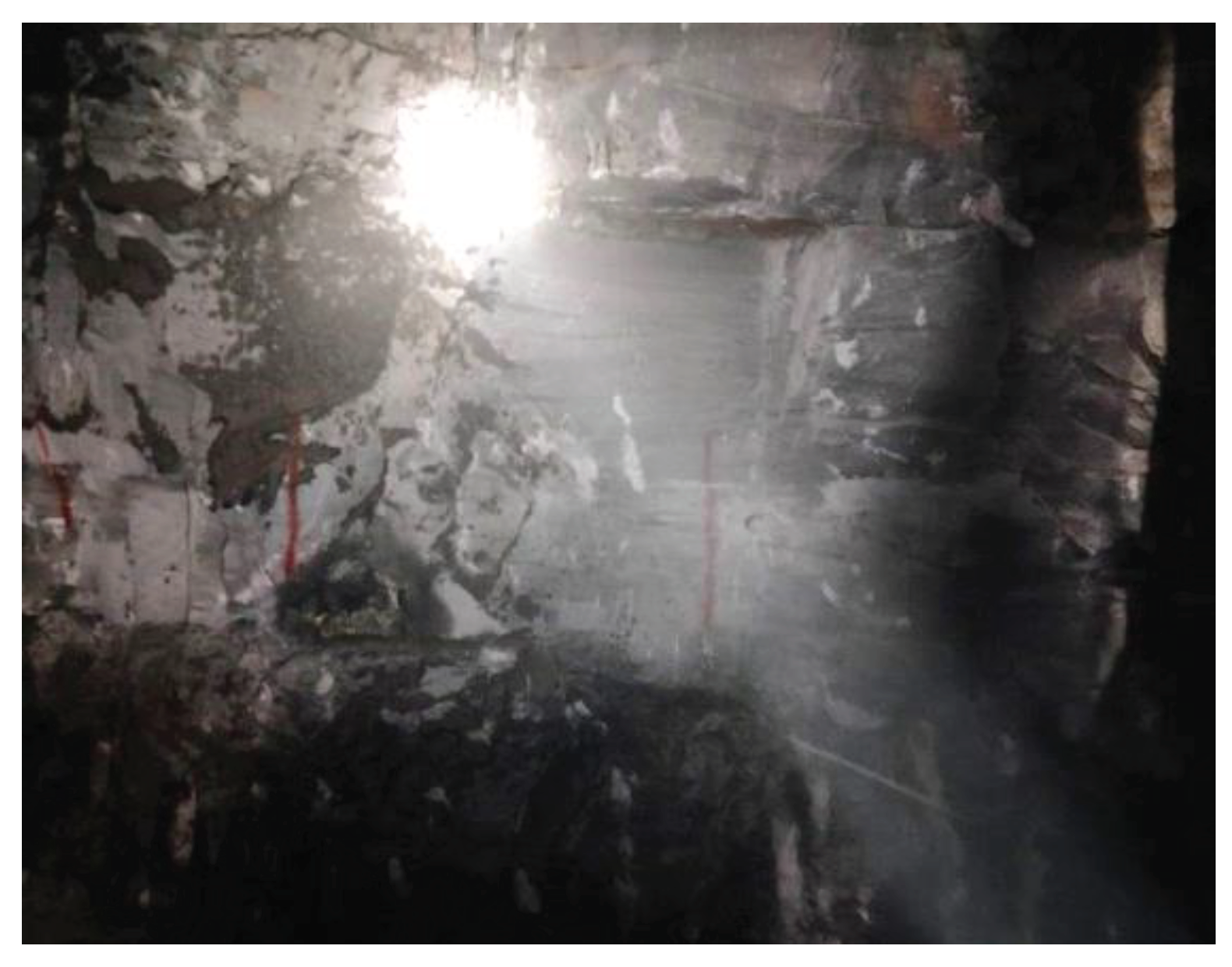
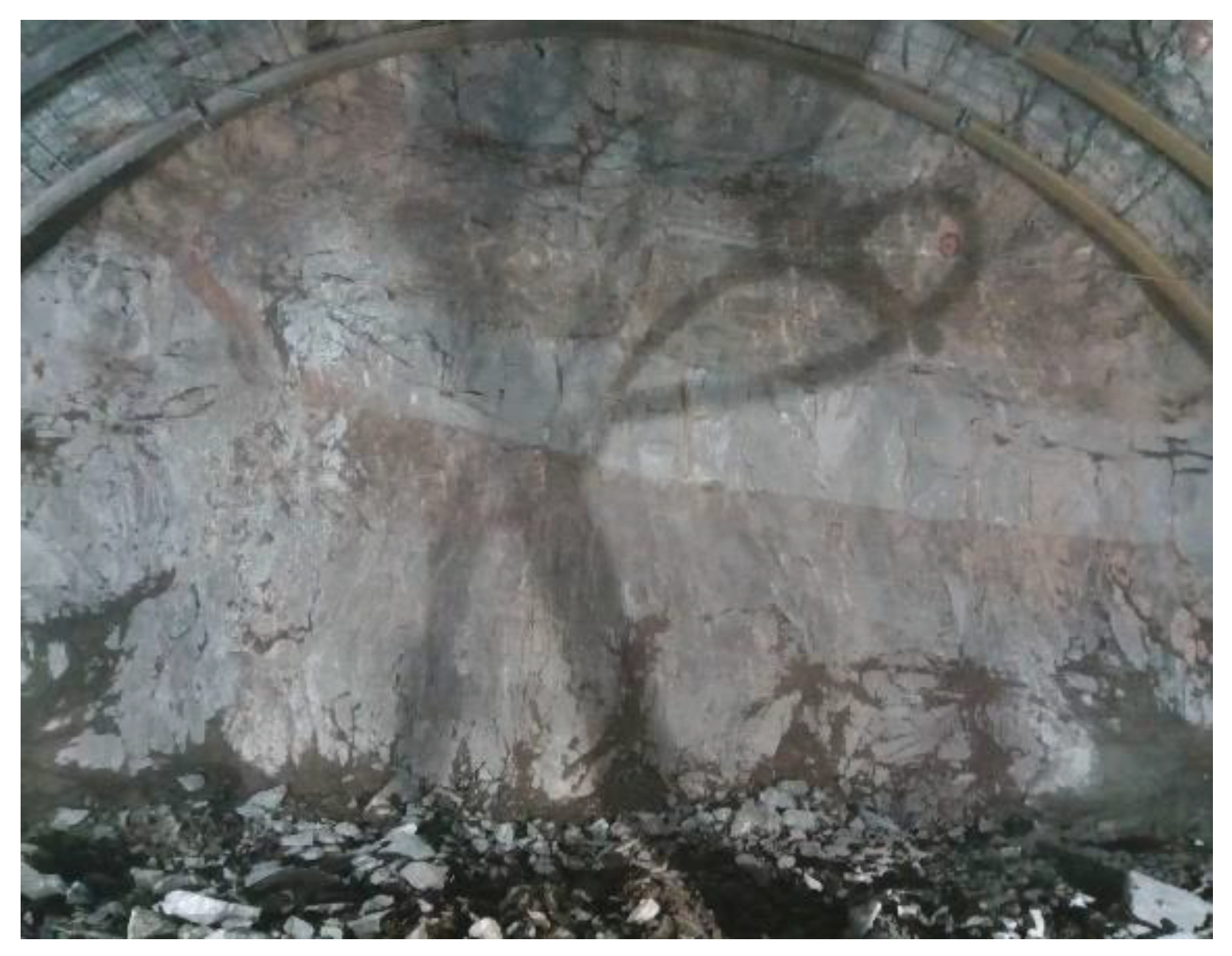
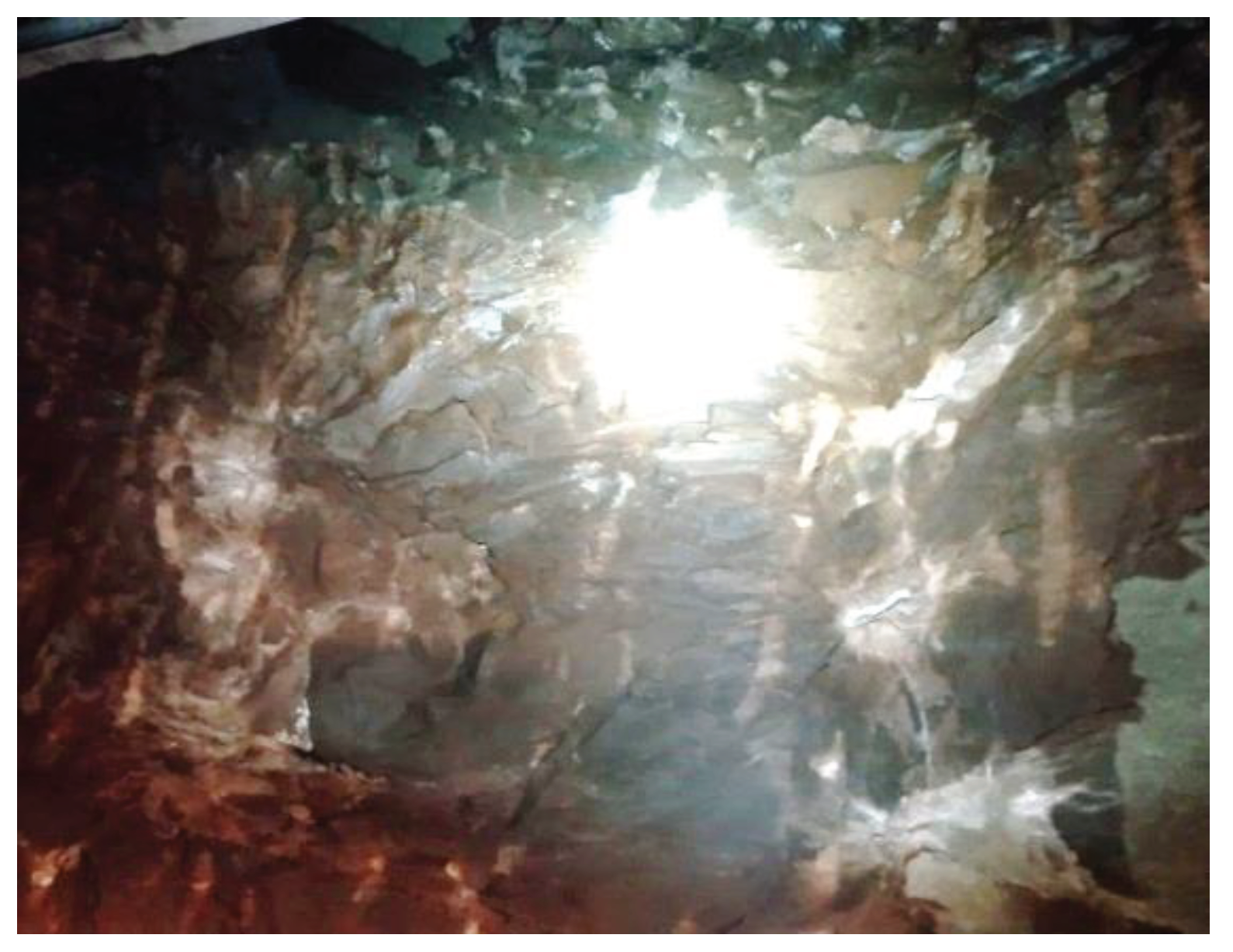









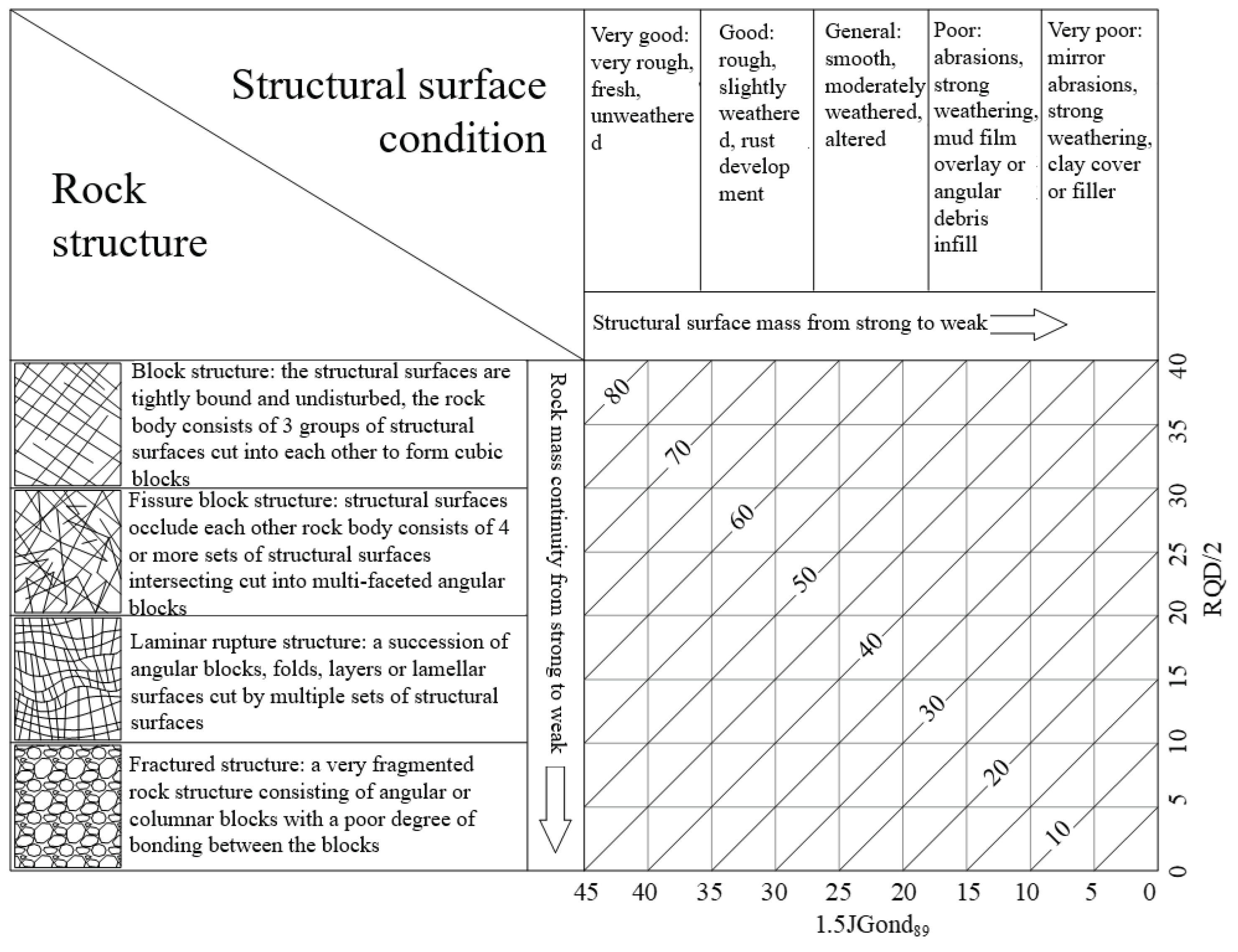

| Description of rock excavation methods and effects | D value |
| Very little disturbance, good blasting or tunnel boring machine excavation | 0 |
| Small disturbances, poor rock mass with mechanical or manual excavation | 0 |
| Large disturbances, stress concentrations causing the tunnel bottom to bulge | 0.5 |
| High disturbance, poor blasting results | 0.8 |
| Rock Type | Rock group | Rock structure | |||
| Coarse | Medium grain | Grain | Very fine grain | ||
| Sedimentary rock | Clastic rock | Conglomerate (geology) | Conglomerate (geology) | ||
| Malmstone | Malmstone | ||||
| 17±4 siltstone | 17±4 siltstone | ||||
| Non-clastic rocks | 7±2Claystone | 7±2Claystone | |||
| Carbonate rock | 4±2 | 4±2 | |||
| Non-clastic rocks | Conglomerate | Conglomerate | |||
| Metamorphic | EvaporitesNon-clastic rocks | - miscellaneous malmstones | - miscellaneous malmstones | ||
| (18±3) Shale | (18±3) Shale | ||||
| Organic Rocks | 6±2 | 6±2 | |||
| Non-fragmentary | Marl | Marl | |||
| Volcanic rock | Microfacies | (7±2) | (7±2) | ||
| Coarse crystalline limestone | Coarse crystalline limestone | ||||
| Lamellar Light-colored,dark-octidolite | (12±3) Brilliant limestone | (12±3) Brilliant limestone | |||
| (10±2) Microcrystalline limestone | (10±2) Microcrystalline limestone | ||||
| (9±2) Dolomite | (9±2) Dolomite | ||||
| Dark colored plutonic rocks | (9±2) Dolomite | (9±2) Dolomite | |||
| Gypsum rock | Gypsum rock | ||||
| Light-colored, dark-colored mafic rocks | 8±2 Hard gypsum | 8±2 Hard gypsum | |||
| Area of influence | Excavation method | Rock type | mb | s | a | /MPa | /MPa |
| New tunnels | Blasting excavation | Malmstone | 2.464 | 0.0025 | 0.504 | 1.86 | 0.514 |
| Mudstone | 0.656 | 0.0007 | 0.508 | 0.40 | 1.087 | ||
| Static excavation | Malmstone | 4.210 | 0.0067 | 0.504 | 2.46 | 0.523 | |
| Mudstone | 1.262 | 0.0022 | 0.508 | 0.57 | 1.109 | ||
| Existing tunnels | —— | Malmstone | 3.521 | 0.0047 | 0.504 | 2.24 | 0.477 |
| Mudstone | 1.015 | 0.0014 | 0.508 | 0.51 | 1.011 | ||
| Overlap zone | Blasting excavation | Malmstone | 1.772 | 0.0015 | 0.504 | 1.57 | 0.493 |
| Mudstone | 0.438 | 0.0003 | 0.508 | 0.33 | 1.040 | ||
| Static excavation | Malmstone | 3.521 | 0.0047 | 0.504 | 2.24 | 0.504 | |
| Mudstone | 1.015 | 0.0014 | 0.508 | 0.51 | 1.068 |
| Area of influence | Excavation method | Rock type | γ | E/GPa | c′/MPa | φ′/° | v |
| New tunnels | Blasting excavation | Malmstone | 23.13 | 2.98 | 0.80 | 27.90 | 0.27 |
| Mudstone | 23.89 | 1.10 | 0.33 | 13.77 | 0.38 | ||
| Static excavation | Malmstone | 23.13 | 3.98 | 0.97 | 32.23 | 0.23 | |
| Mudstone | 23.89 | 1.47 | 0.44 | 17.53 | 0.35 | ||
| Existing tunnels | —— | Malmstone | 23.13 | 3.58 | 0.86 | 31.48 | 0.24 |
| Mudstone | 23.89 | 1.32 | 0.38 | 16.72 | 0.36 | ||
| Overlap zone | Blasting excavation | Malmstone | 23.13 | 2.59 | 0.69 | 25.60 | 0.28 |
| Mudstone | 23.89 | 0.96 | 0.27 | 11.91 | 0.40 | ||
| Static excavation | Malmstone | 23.13 | 3.58 | 0.89 | 31.03 | 0.24 | |
| Mudstone | 23.89 | 1.32 | 0.39 | 16.39 | 0.36 |
| Train speed | Operational acceptance | Regular maintenance | Temporary repairs |
| 200~250km/h | 0.0002 | 0.0005 | 0.0008 |
| 250~300km/h | 0.0002 | 0.0004 | 0.0007 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




