1. Introduction
Although the contagiousness of many diseases has been established, humans have always used substances to fight infections, as human history attests, from 2500 BC to 3000 BC, when the Chinese, Hindus, Babylonians, Sumerians, and Egyptians used medicinal plants and their derivatives to fight infections, in addition to products of animal and/or mineral origin. However, it was only from the 16th century, with the development of “alchemy”, that medicines began to be obtained by laboratory methods, but even before these, there were oils which are classified today as vegetable or fixed and essential, where they were already used to combat various diseases and infections (OLIVEIRA, 2022).
Vegetable oil is a source of energy produced by plants and is found in greater concentration in seeds and fruits. The majority (approximately 95%) of vegetable oils are composed of triglycerides. The remaining 5% are phospholipids, glycolipids, sulpholipids, waxes, hydrocarbons such as squalene, pigments in the form of carotenoids and chlorophyll, vitamin E, polyphenols and triterpenoids. The non-triglyceride fraction is called the “unsaponifiable fraction” (SARKIC; STAPPEN, 2018).
Essential oils are small, nonpolar lipophilic molecules, with volatility as one of their main characteristics. It receives this name because it has the “essence” of the olfactory characteristics of the plant from which it is extracted. They are usually extracted by steam distillation, and can be synthesized in different parts of the plant such as buds, flowers, leaves, stems, branches, seeds, fruits, roots, wood or bark. However, they can also be extracted by other methods such as hydrogenation and pressure diffusion (GUIDONI et al., 2019).
Both oils are derived from plants, but there are major differences between them, one of the main ones being the composition. Vegetable oils contain a high concentration of fatty acids in their composition, due to their properties, vegetable oils are used as emollients, which aim to hydrate and smooth the surface of the skin. There are no regulations regarding their use, but these ingredients are often used in high concentrations, depending on the product. Essential oils, on the other hand, have a high concentration of volatile molecules (mainly terpenes), which is why they are mainly used as fragrances in low concentrations (BRUNO; ALMEIDA, 2021).
Another widespread use of essential oils today is in aromatherapy, and can be utilized for their other properties, with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and calming effects (GUIDONI et al., 2019; BRUNO; ALMEIDA, 2021).
Ozone, on the other hand, has its use described for the treatment of various pathologies, among which it can be cited as an example: Autoimmune, respiratory, dermatological, gastrointestinal, ophthalmological, cardiovascular and neurological diseases (ISCO3, 2020)
Ozonated vegetable oils are well tolerated by biological tissues and the germicidal activities of ozone are attributed to its ability to destroy bacterial membranes and the viral capsid through direct oxidation of phospholipids and lipoproteins. This causes changes in the chemical structure of the cell and inhibits exchange with the environment and causes disintegration of the cell envelope causing cell lysis and death (Aghaei et al., 2019; Basile et al., 2019). Thus, they have bactericidal and fungicidal properties and favor their use topically for skin infections (Moureu et al., 2015).
Due to the instability of ozone and its toxicity, vegetable oils have proven to be very useful in ozone therapy and are enjoyed more safely (RICCO; AQUINO JÚNIOR, 2022; LESCURA; BEGA, 2020). Thus, this article aims to evaluate the sensitivity and/or resistance of the fixed oils of Buriti and Andiroba and essential oils of Mint and “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated” Clove in different concentrations against internationally known bacteria from the ATCC collection using the agar diffusion technique.
2. Methods
Investigation studies of the antibacterial activity of vegetable oils from Mauritia flexuosa (Buriti) and Carapa guaianensis (Andiroba) and essential oils from Menta piperita (Peppermint) and Eugenia caryophyllus (Cravo) were carried out at the Bioprocess Laboratory of the Federal Institute of Tocantins, Campus Araguaína – TO.
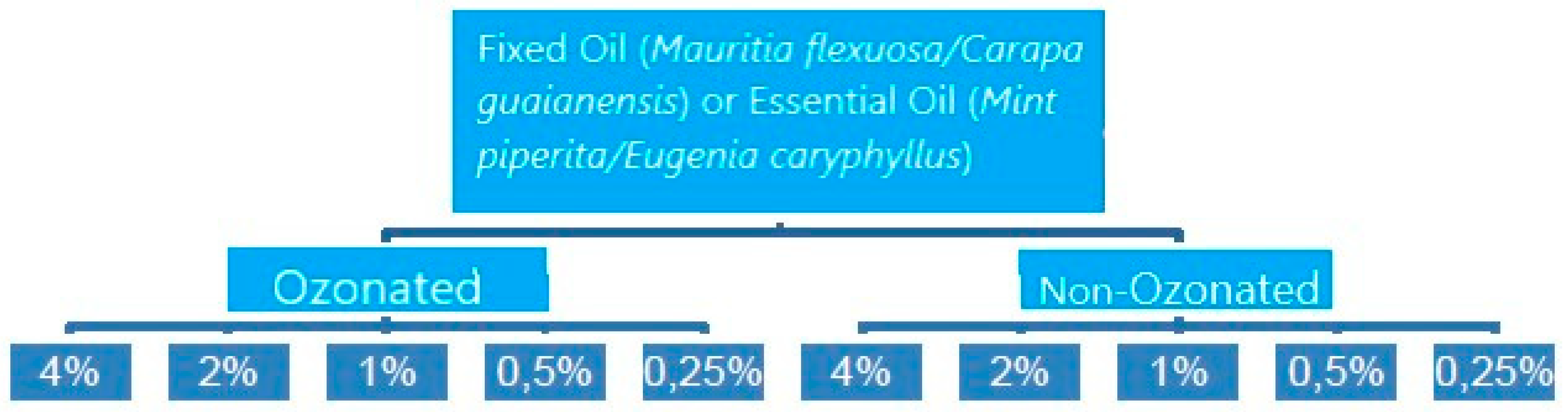
The methodology used in this research was experimental and comparative, between ozonated and non-ozonated fixed and essential oils, in 05 concentrations tested in triplicates, on 04 bacterial strains, totaling 960 observations. The flowchart below represents the treatment performed for each oil tested in each microorganism.
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the Fixed or Essential Oil Processing Methodology that were executed for the 4 types of oils used in the microbiological analyzes of the 4 microorganisms. Source: Author.
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the Fixed or Essential Oil Processing Methodology that were executed for the 4 types of oils used in the microbiological analyzes of the 4 microorganisms. Source: Author.
2.1. Vegetable Oils and Essential Oils
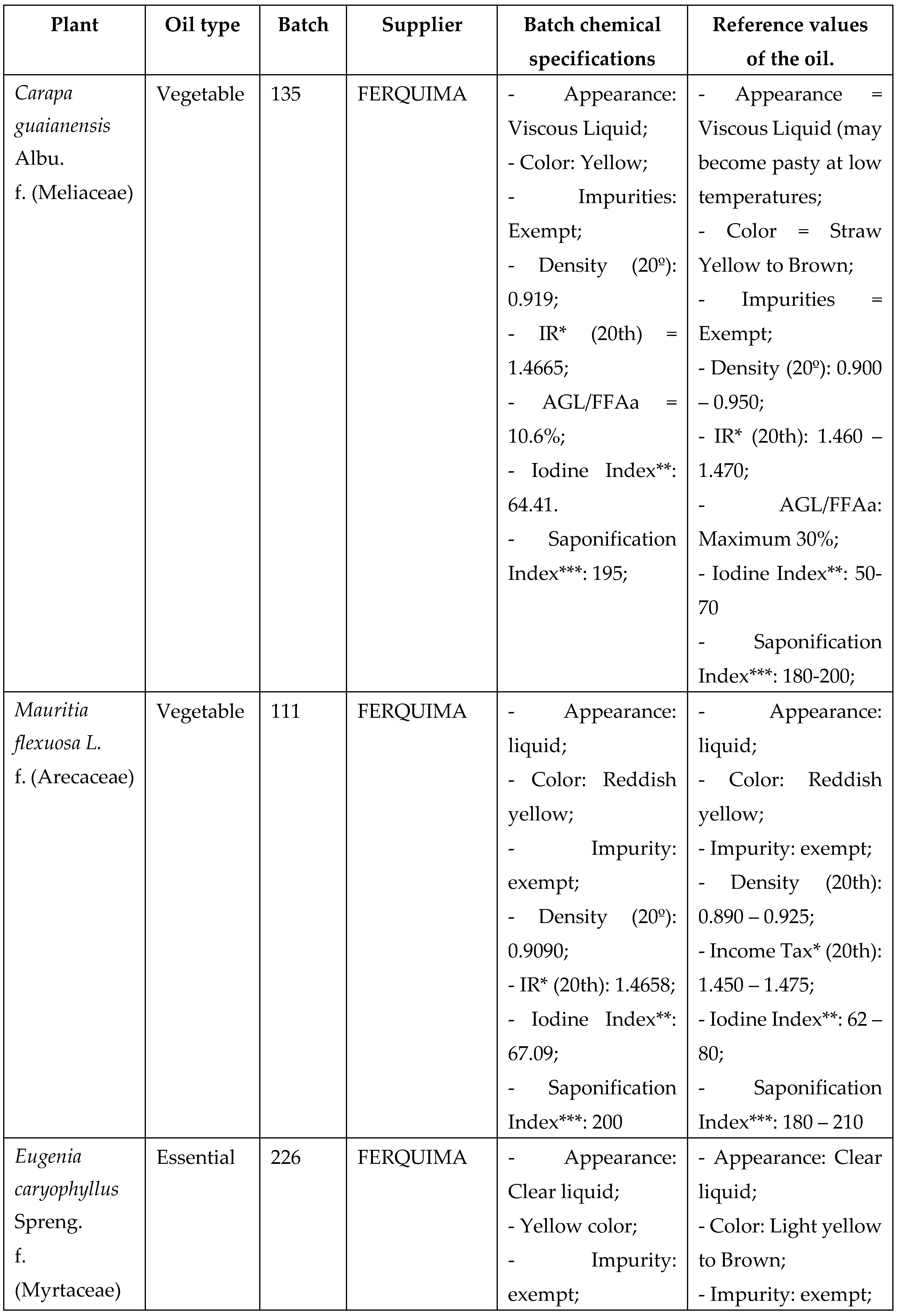
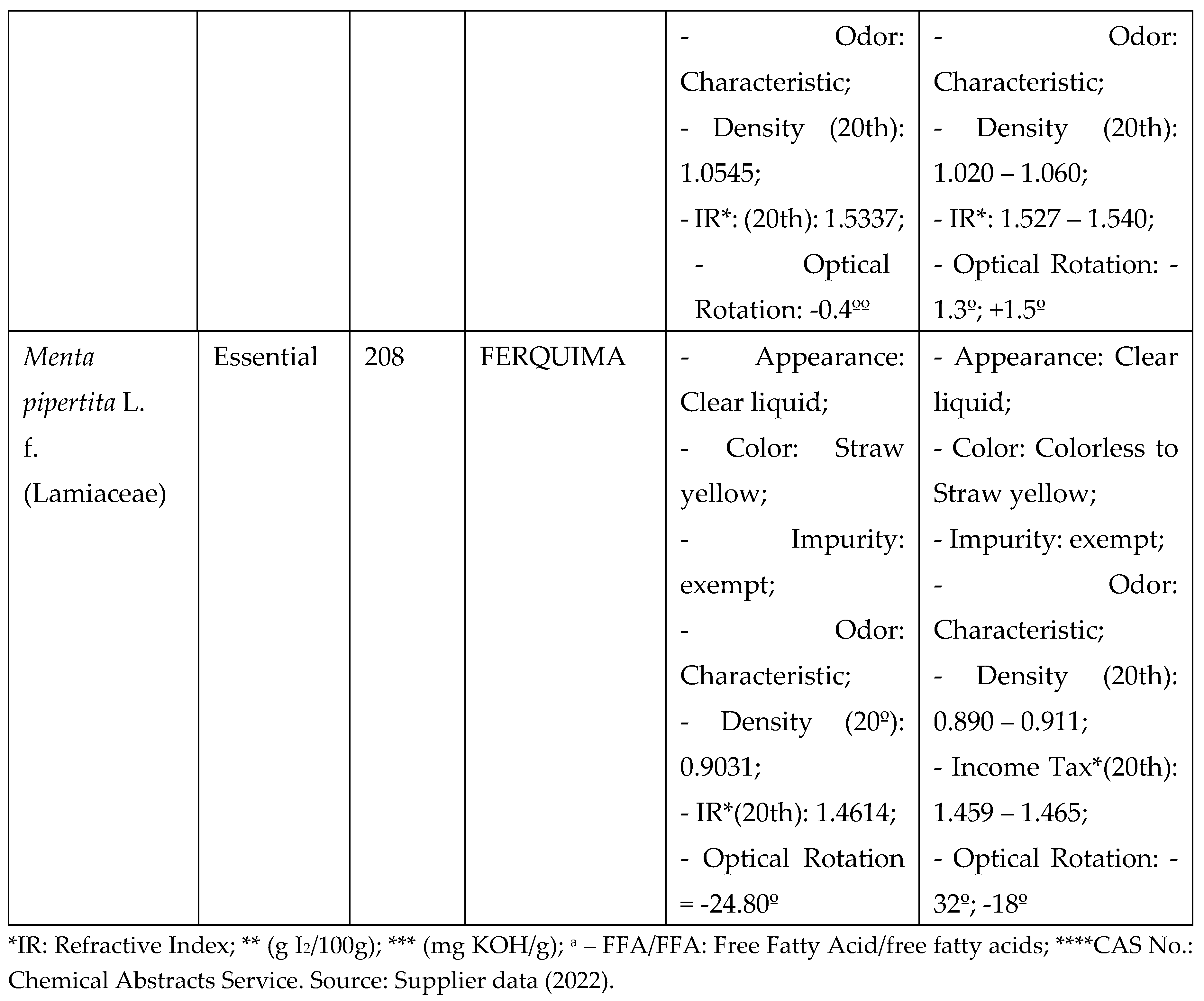
Vegetable oils from Mauritia flexuosa (Buriti) and Carapa guaianensis (Andiroba seed) and essential oils from Menta piperita (Mint) and Eugenia caryphyllus (Clove) were selected for analysis according to the vast literature reported for antimicrobial activity, as well as the use of these items (CARVALHO; ASSIS; SANTOS, 2020; SOARES, 2020), and purchased from companies specialized in selling these items, as shown in the table below, with batches of known origin and technical report, with specificities that prove their physical-chemical characteristics within the acceptability standard for oils according to the literature and legislation (Chart 1).
The vegetable oils, after acquisition, were stored at room temperature, in a cool place, with a maximum value of 24°C, while the essential oils were stored under refrigeration until use, being placed at the laboratory room temperature 30 minutes before the procedures of chemical and antimicrobial analysis Chart 1: Selected vegetable oils and essential oils with batch specifications and origin.
Chart 1.
Results of antimicrobial sensitivity of fixed oils from buriti fruit and andiroba seed and essential oils from clove and mint efflorescence.
Chart 1.
Results of antimicrobial sensitivity of fixed oils from buriti fruit and andiroba seed and essential oils from clove and mint efflorescence.
2.2. Ozonation of Oils
The vegetable oils of Mauritia flexuosa (Buriti) and Carapa guaianensis (Andiroba) and essential oils of Menta piperita (Mint) and Eugenia caryophyllus (Cravo) received ozonation through diffusion of O3, administered directly into the oil as described below.
Ozone production was carried out using a generator device, white, model MOG003, from the brand Ozone Generator, which produces electrical discharges under medicinal O2 (Corona effect), coming from an industrial cylinder, from the brand AIR GÁS Health Solution, with specifications UN 1072 oxygen, compressed 2.2 (5.1) and concentration grade 99.5% vol./vol, which supplies the device, releasing O3 at a concentration of 20 μg/ml, according to the specifications of the equipment supplied by the manufacturer, converts medical Oxygen into Ozone.
The rich O3 gas continuously produced by the device at a rate of ½ liters per minute is conducted through a silicone tube to a diffuser, which is immersed in vegetable oil or essential oil and perfused for 30 minutes. The temperature of the vegetable oils during perfusion was controlled at 25°C with an ultrathermotized bath. As for essential oils, it was perfused with ozone at a temperature of 5°C in order to reduce the loss by evaporation of essential oils.
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity
2.3.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Medium
The antimicrobial assay was conducted with Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria in standardized strains from an international collection, according to the methodology of sensitivity tests for antimicrobial agents by dilution for aerobic growth bacteria (RENTES, 2022; BATISTA, 2008).
The bacteria,
Table 1, were acquired from the Tropical Culture Collection of the André Tosello Foundation – FAT with authenticity and procedure reports (Annex B) and kept in the Bioprocesses laboratory of the IFTO Campus Araguaína – TO, as recommended by the FAT, in medium of Muelle Hinton culture. For the tests, the suspensions of the bacteria used came from the first passage (repeat) of the strains received by the IFTO laboratory.
The culture medium used was Mueller Hinton Agar, brand ION, Lot 0719/0354, the compositions of which is: Beef Infusion 300 g/L; Hydrolyzed acid casein 17.50g/L; Starch 1.5g/L; Agar 17g/L and pH 7.3 +- 0.2.
The preparation of the medium was carried out according to the instructions described by the manufacturer, in a concentration of 38 grams of the medium for 1 liter of distilled water. With the medium dissolved, it was sterilized in an autoclave at 121°C for 15 minutes and then taken for microbiological analysis.
2.3.2. Microbiological Analysis of Fixed and Essential Oils
The use of “in vitro” antimicrobial activity tests is a usual practice, standardized by Kirby and Bawer since 1966, being reviewed and modified by several authors. Currently, standardized methods are adopted by several organizations such as: NCCLS – National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, such as “Methods for Determining Bacterial Activity of Antimicrobial Agents; Approved Guideline”, standard M26-A, ISBN 1-56238-384-1 by James H. Jorgensen, 1999, which was followed by making minor adaptations as discussed below.
An aliquot of vegetable oil and essential oil was solubilized in a 1:1 solution of Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) in water and subsequently diluted, respectively obtaining a concentration of oils of 4, 2, 1, 0.5 and 0.25%. These diluted strata were submitted to microbiological tests, in sterile plates of 20x150mm, where 1mL of saline solution was deposited, containing microorganisms in suspensions (saline solution at 0.85% NaCl), standardized by tube 0.5 on the Mac Farland scale, set to 90% Transmittance (530nm). Then, 50mL of Mueller Hinton Agar solid medium was added per plate, prepared according to the manufacturer’s standards (ION), melted at 50ºC, using the “Pour Plate” technique, homogenized by the “eight” technique (MC GINNIS, 1980; BAUER et al., 1966). The microbiological analysis process in its entirety was carried out in a BSTEC exhaust hood, intending to mitigate the dangers of ozone gas aspiration, thus following international safety standards (KUME, 2020).
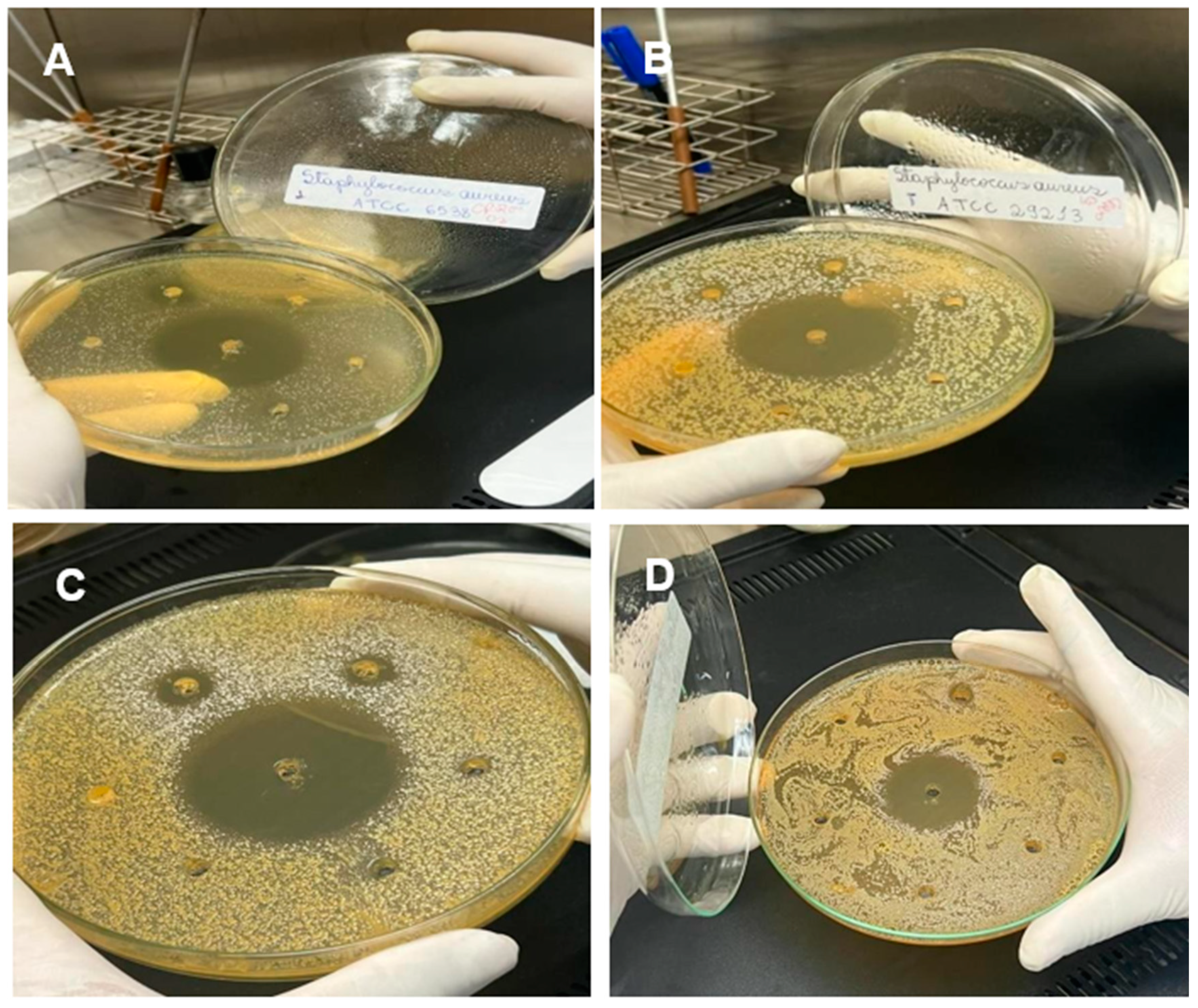
Figure 2.
Plates with antimicrobial assays of microorganisms tested with fixed and essential oils. A – Microrganismo Staphylococcus Aureus ATCC 6538; B – Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213. C - Escherichia coli ATCC 25922; D- Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853. Source: Author (2022).
Figure 2.
Plates with antimicrobial assays of microorganisms tested with fixed and essential oils. A – Microrganismo Staphylococcus Aureus ATCC 6538; B – Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213. C - Escherichia coli ATCC 25922; D- Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853. Source: Author (2022).
2.4. Chemical Analysis of “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated” Essential Oils
The analyzes were carried out using a Gas Chromatography with Mass Spectrometer (GC-MS) apparatus, at the Chemistry Laboratory of the Federal University of Norte do Tocantins, Campus Araguaína – TO. The technique was performed in triplicate to obtain the identification of the major constituents in the essential oils of clove and mint and their centesimal composition.
For this purpose, from clove and mint oils, both ozonated and non-ozonated, a 5mg/mL solution in ethyl acetate was prepared. These samples were analyzed on an Agilent Technologies 7890B Gas Chromatograph hyphenated to a 5977B Mass Spectrometer (GC-MS). The chromatograph operated with HP-5MS capillary columns (5% Phenyl Methyl Siloxane), L = 30 m, ID = 0.25 mm and film = 0.25 μm and the carrier gas used was Helium (99.999%) with flow of 1.2 mL/min. The GC-MS was used with injector temperature at 270 ºC, transferline at 250 ºC, quadrupole at 150 ºC and source at 230 ºC, with purge flow at 100 mL/min.
The analysis mode was Split in “scan” mode with a split ratio of 80:1 and a scan from 40 to 500 Da. The GC oven temperature program was initially set at 40 °C for 2 min and increased by 5 °C per minute to 170 °C, followed by an additional 25 °C per minute to 270 °C, which was maintained in isotherm for 3 minutes. In total the races lasted 35 minutes.
Figure 3.
Gas Chromatograph with Mass Spectrometer (GC-MS), Federal University North of Tocantins (UFNT). Source: Author (2022).
Figure 3.
Gas Chromatograph with Mass Spectrometer (GC-MS), Federal University North of Tocantins (UFNT). Source: Author (2022).
The mass spectra obtained were analyzed using Agilent software, MSD ChemStation F.01.03.2357 and compared with spectra from libraries: NIST 2014, NIST WEBBOOK and Adams (2017), along with the similarity index. The retention indices (RI) were determined using a homologous series of n-alkanes, C7 to C30, injected in the same method as the samples, using the equation of Van den Dool and Kratz (1963).
3. Results
3.1. Antimicrobial Activity
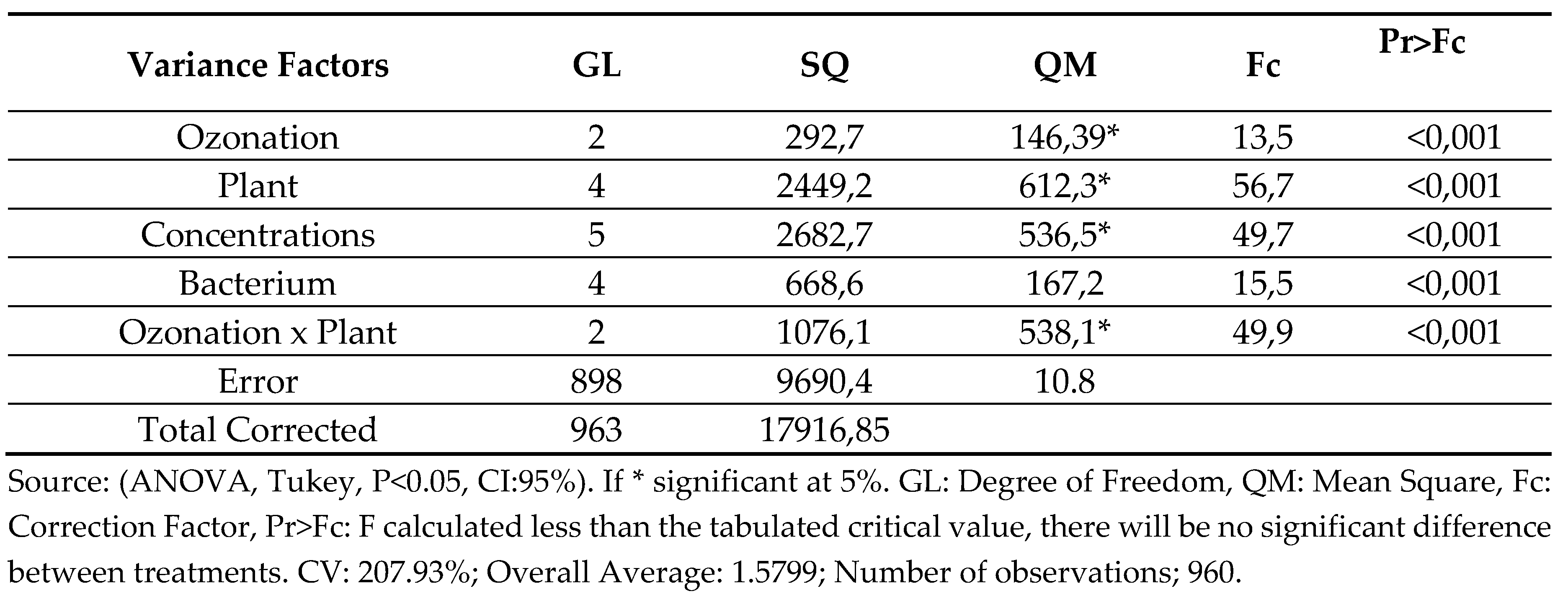
The design of this work consisted of an assessment of the sensitivity and/or resistance to fixed oils of Buriti and Andiroba and essential oils of Mint and Clove - “Ozonated” and Not “Ozonated” - in different concentrations against internationally known bacteria from the ATCC collection using the agar diffusion technique. Statistical analysis by ANOVA (analysis of variance) was significant for all possible variables used, according to PR>HR values reported in chart 1. Thus, it demonstrates that there are means with identical or approximate behaviors within the events, suggesting that the oils in the respective concentrations, ozonated or not, must be analyzed two by two, using the Tukey Test, also called Studentized Amplitude Test (MOTTA, 2006).
Chart 2.
Results of antimicrobial sensitivity of fixed oils from buriti fruit and andiroba seed and essential oils from clove and mint efflorescence.
Chart 2.
Results of antimicrobial sensitivity of fixed oils from buriti fruit and andiroba seed and essential oils from clove and mint efflorescence.
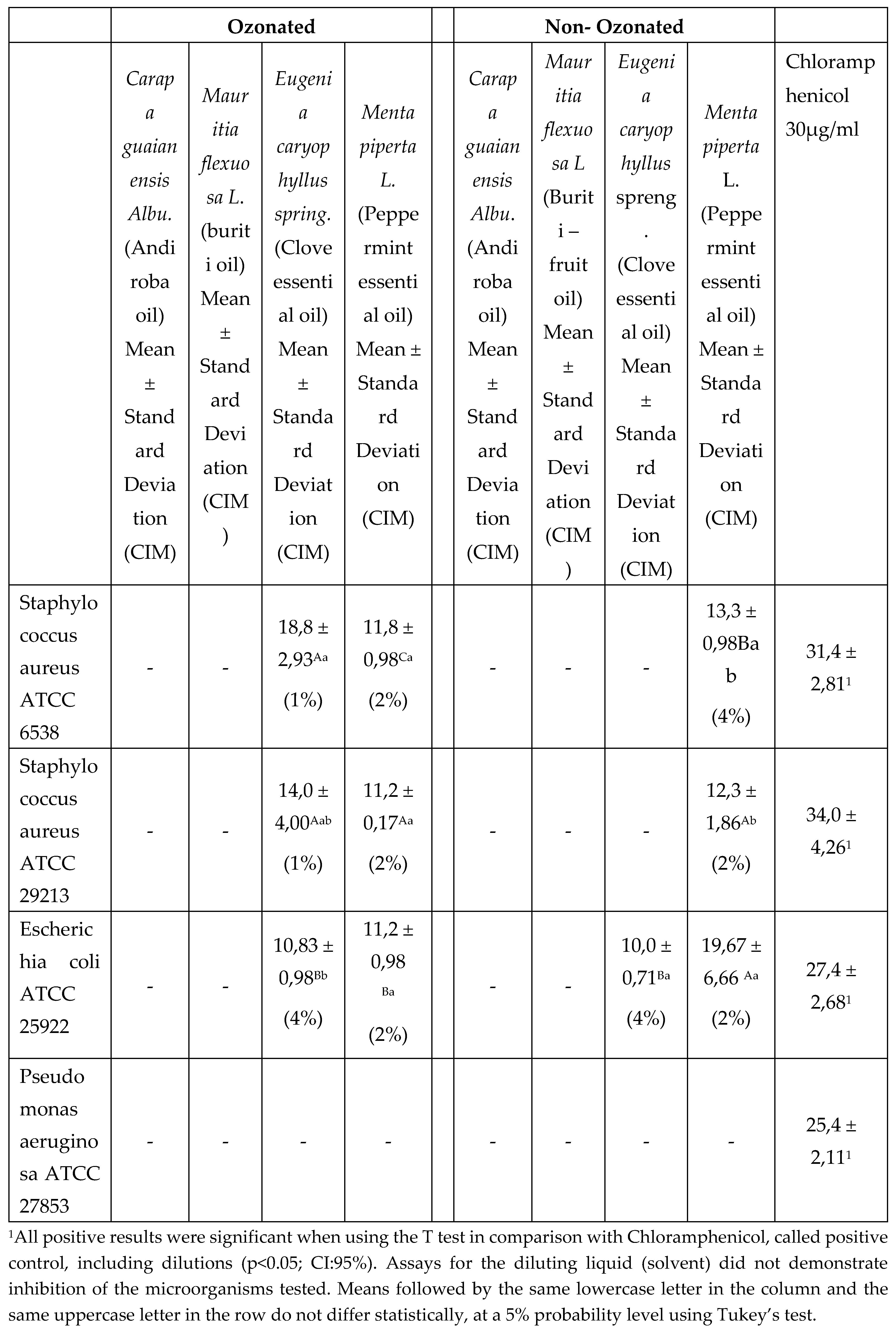
The results revealed that the process of ozonation of the fixed oils of Buriti and Andiroba did not produce additional synergistic effects inherent to the inhibition of the tested bacteria. However, the essential oils of Peppermint and Clove showed statistically inverse results in the face of the ozonation process, shown below in
Chart 3, thus confirming that each oil has a different behavior in the face of the ozonolysis process.
Chart 3.
Results of antimicrobial sensitivity of fixed oils from buriti fruit and andiroba seed and essential oils from clove and mint efflorescence.
Chart 3.
Results of antimicrobial sensitivity of fixed oils from buriti fruit and andiroba seed and essential oils from clove and mint efflorescence.
3.2. Chemical Analysis of Essential Oils
3.2.1. Chemical Analysis of Clove Essential Oil
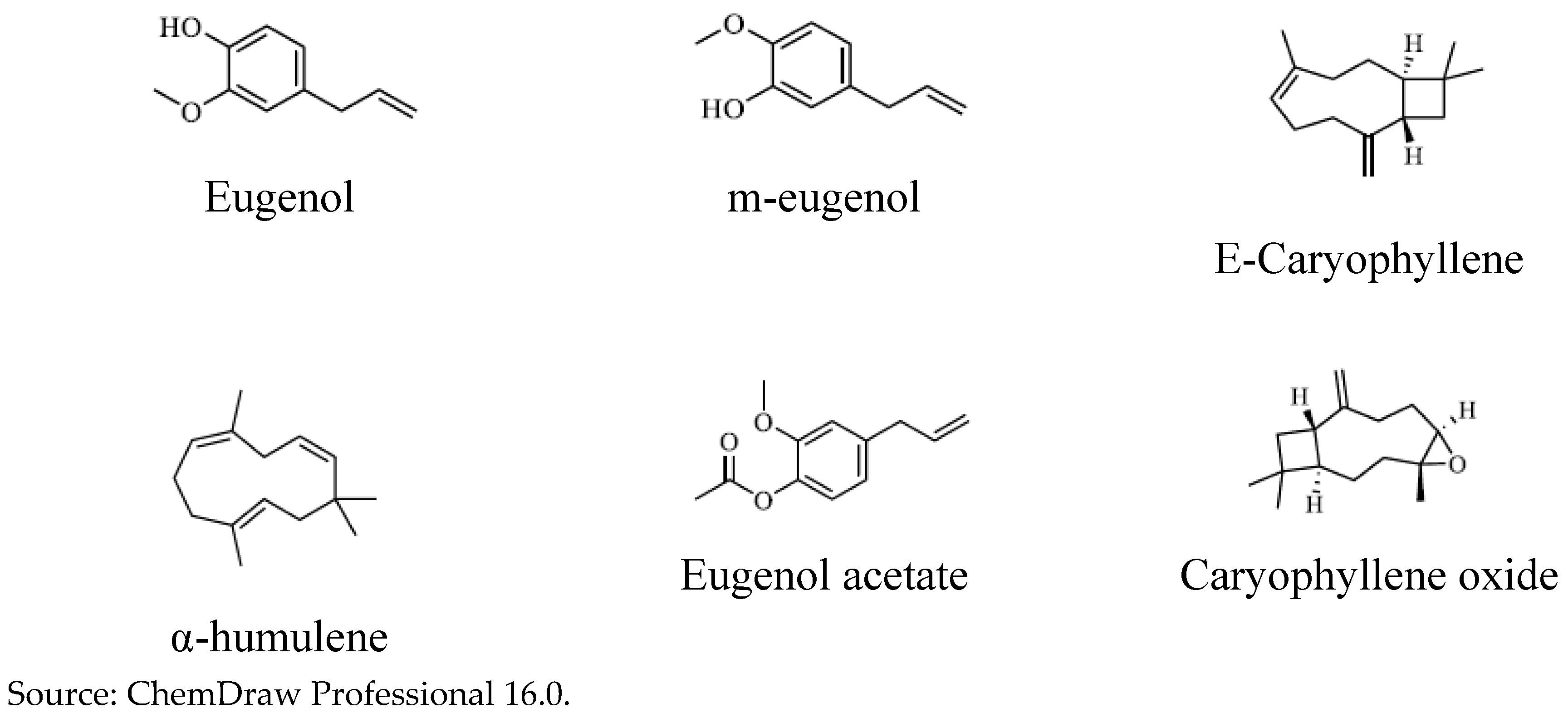
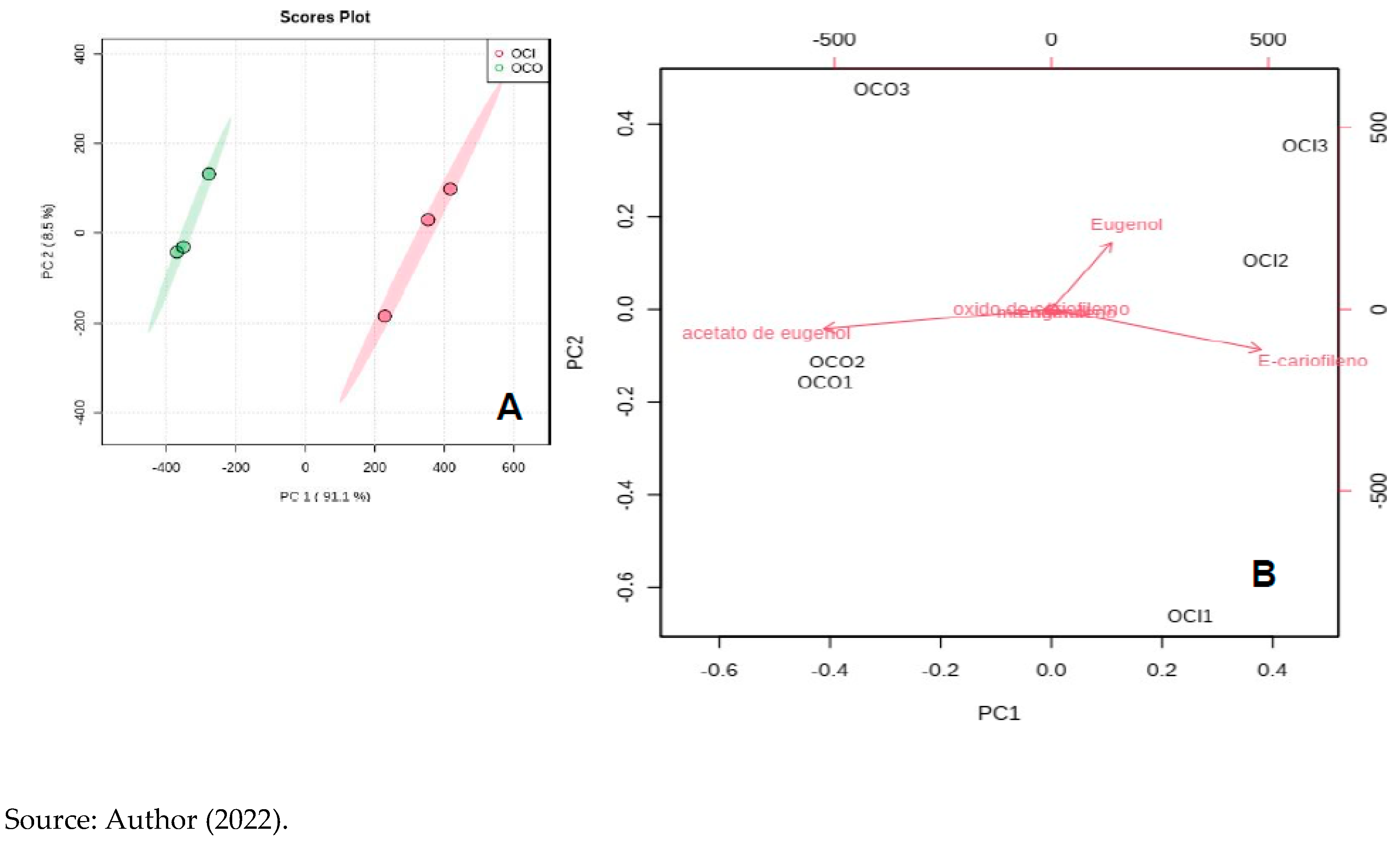
The identification of chemical compounds in samples of Clove essential oils -“Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated” - was identical. It was carried out by GC-MS, obtaining the major compounds: Eugenol; m-eugenol; eugenol acetate; E-caryophyllene; α-humulene and caryophyllene oxide.
Figure 4.
Chemical structure of the major compounds contained in “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated” Clove essential oils.
Figure 4.
Chemical structure of the major compounds contained in “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated” Clove essential oils.
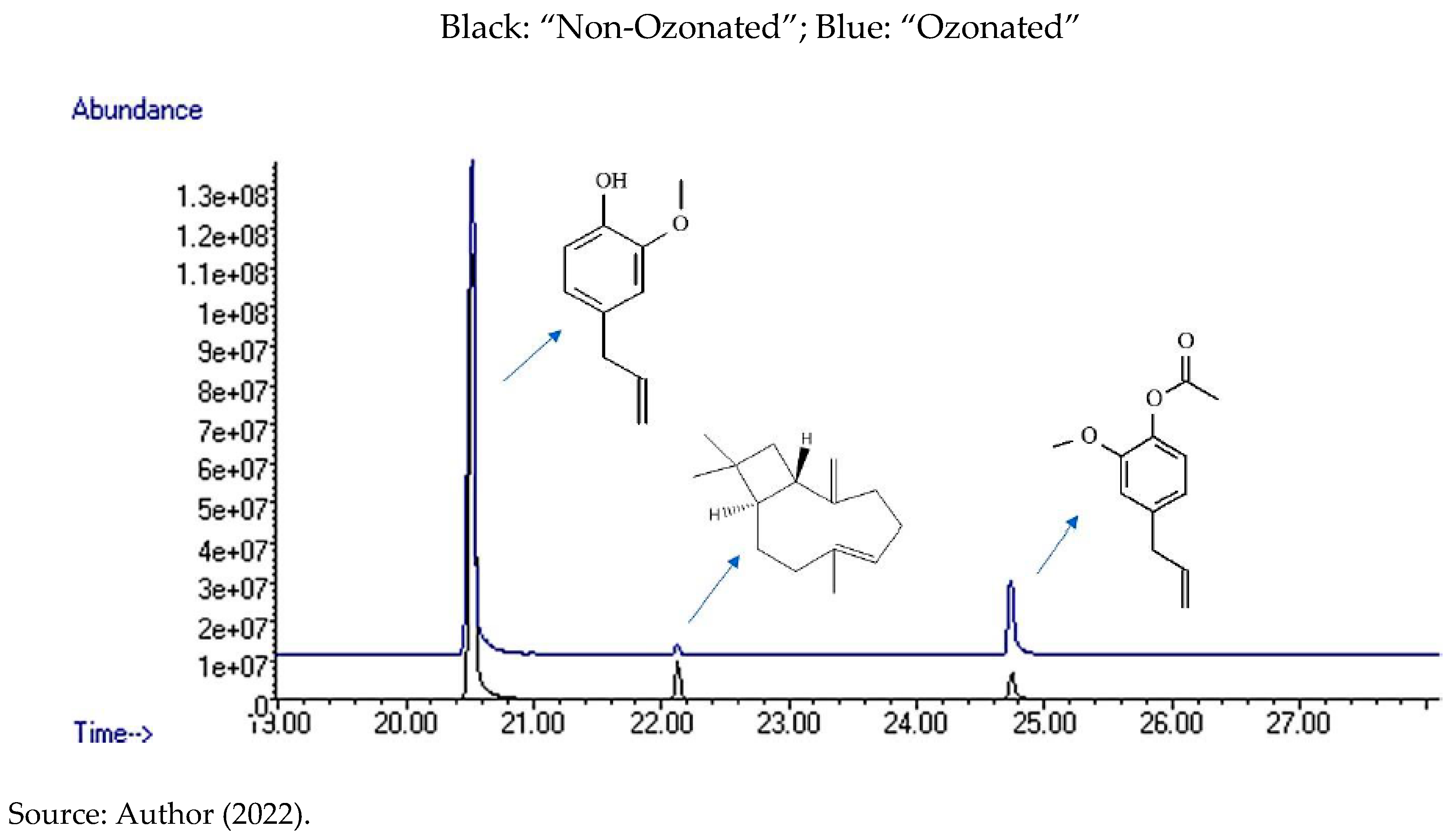
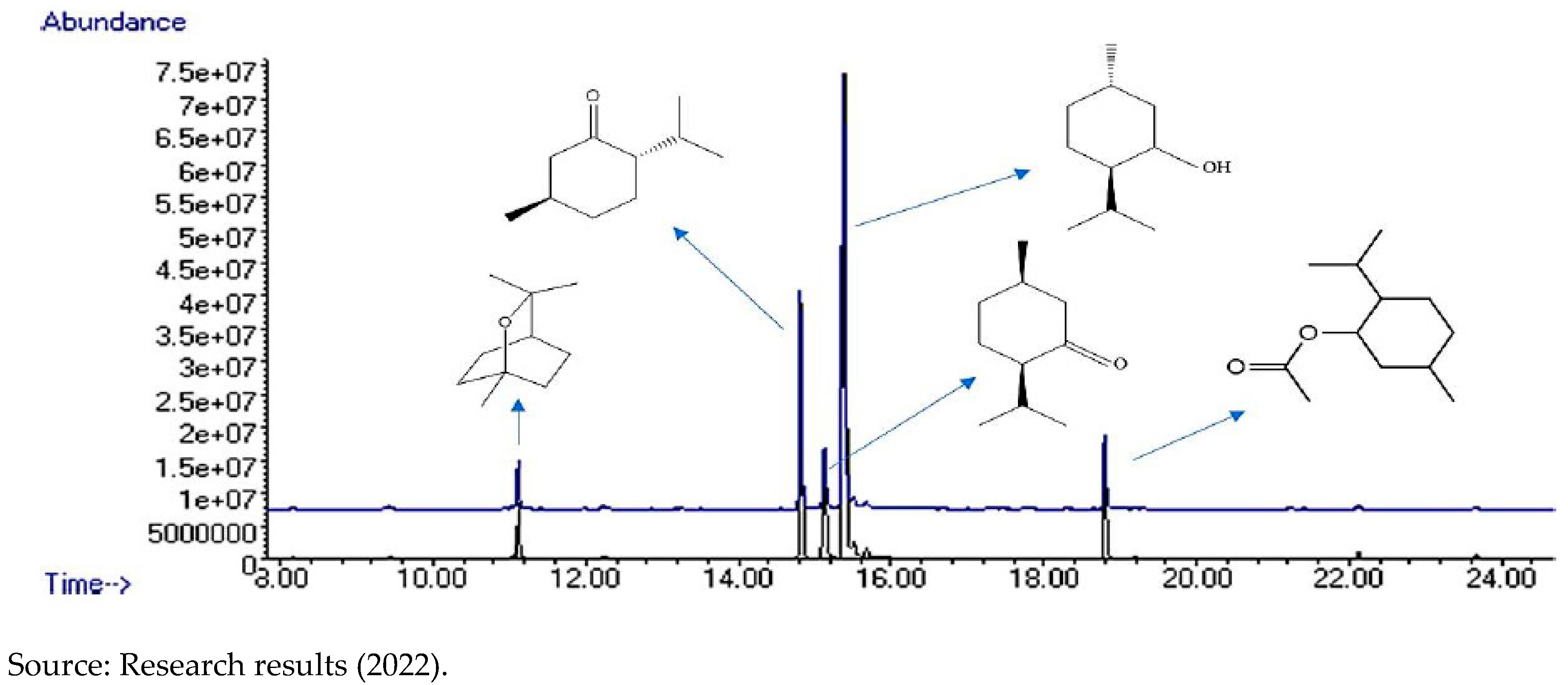
In
Figure 5, the comparison chromatogram of Clove “Non-Ozonated” essential oils, is displayed, which is shown in black and “Ozonated” represented in blue. In addition, they have the indication of the major compounds.
Figure 5.
– Comparison chromatogram of Clove essential oils - “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated” - with indication of identified compounds.
Figure 5.
– Comparison chromatogram of Clove essential oils - “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated” - with indication of identified compounds.
After being recognized, the compounds were integrated into the chromatograms area, for the detection of each one of them by peaks in the graph (
Figure 5), in order to identify the quantity and centesimal proportion of each chemical compound belonging to the essential oils of “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated Clove. The analysis determined that the essential oils have different proximate compositions, that is, ozonation modifies the composition of the essential oil, as shown in
Table 2
When comparing the average peak areas of the “ozonated” and “non-ozonated” essential oil, which corresponds to the centesimal analyzes of each oil, it is observed that they have different proportions which, when compared by the T test, confirms the differences in the amount of each compound, as shown in
Table 3.
The amount of eugenol and m-eugenol compounds did not statistically change with ozonation. The multivariate analysis of the main components - PCA showed that the essential “Ozonated” oil is statistically different from the “non-ozonated” when we observe all the compounds present, as shown in
Figure 6 below.
3.2.2. Chemical Analysis of Peppermint Essential Oil
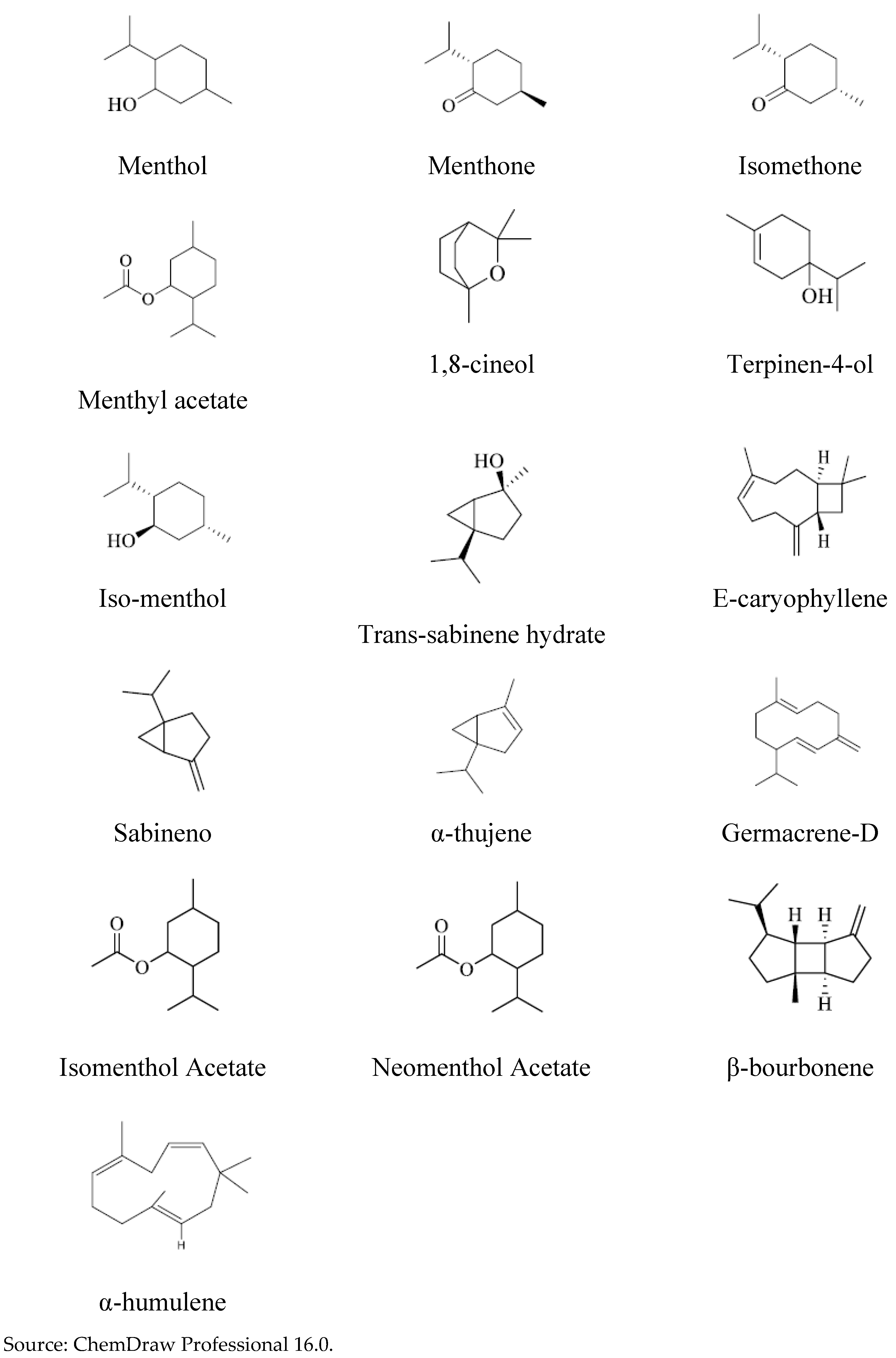
The amount of chemical compounds identified in the samples of “Ozonated and “Non-Ozonated” Peppermint oils was identical, according to analyzes carried out by GC-MS. The compounds were identified: Menthol; Menthone; Isomentone; Menthyl acetate; 1,8-cineol; terpinen-4-ol; α-thujene; Sabinene; trans-sabinene hydrate; iso-menthol; neomenthol acetate; isomenthol acetate; β-bourbonene; E-Caryophyllene and Germacrene D, whose structures are shown below:
Figure 7.
Chemical structure of the major compounds contained in “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated” Peppermint essential oils.
Figure 7.
Chemical structure of the major compounds contained in “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated” Peppermint essential oils.
In
Figure 8, the comparison chromatogram of the essential oils of Peppermint “Non-Ozonated” is displayed, which is shown in black and “Ozonated” represented in blue, in addition, they have the indication of the major compounds.
Once identified, the compounds were integrated into the chromatogram area, identifying the peak area of each compound in order to identify the amount, centesimal proportion, of Ozonated and non-Ozonated mint essential oil. The analysis determined that the mint essential oils have different proximate compositions, that is, ozonation modifies the composition of the essential oil. As shown in
Table 4.
When comparing the average of the peak areas of the essential oil of Peppermint “Ozonated “ and “Non-Ozonated” Peppermint, which corresponds to centesimal analyzes of the ozonated and non-ozonated oil, it is observed that they have different proportions which, when compared by the T test, confirms the differences in the amount of each compound, according to
Table 5.
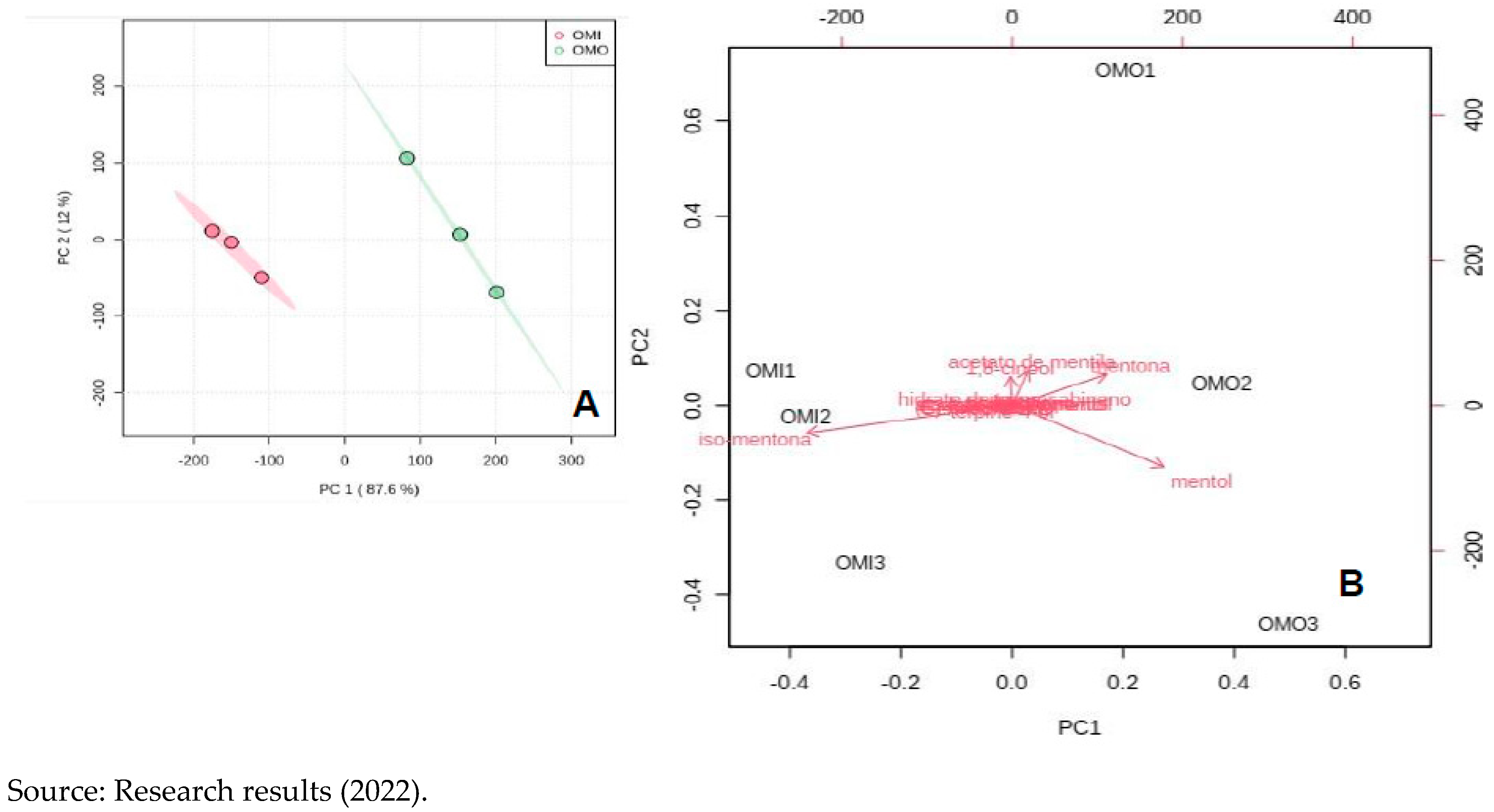
The amount of menthol compounds, 1-8 cineol and other compounds not described in the table above did not statistically change with ozonation. The multivariate analysis of the main components - PCA showed that the essential “Ozonated” oil is statistically different from the “Non-Ozonated” of Mint, when all the compounds present are verified, as shown in
Figure 9.
4. Discussion
A priori, fixed Buriti oil was ineffective in inhibiting microorganisms, which corroborates a study carried out by Nunes et al. (2021), which aimed to determine the antimicrobial activity of fixed oils extracted from native fruits of Maranhão cerrado, where Buriti oil did not obtain satisfactory inhibition against pathogenic microorganisms Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus; however, Nunes et al. (2021) explain that this oil may have antimicrobial activity against other pathogenic microorganisms, becoming antimicrobial agents.
In relation to Andiroba fixed oil, it also did not show any inhibitory activity against the microorganisms tested in this study and similar studies were not found in the literature related to this study.
The ozonation of the fixed oils did not provide antibacterial activity by the tested methodology, demonstrating that the ozone added to the oil may have dissipated during the dilution process of the fixed oils with the solvent used, since the proportion of this without ozone is greater than 96% by volume, significantly diluting the fixed ozone.
The essential oils of “Ozonated” and “Non- Ozonated” Clove showed similar inhibition activities of the microorganisms tested, however the ozonation of the oil showed greater activity in comparison to the non-ozonated one, showing inhibition capacity against 03 microorganisms, while the non-ozonated oil inhibited only one microorganism tested. Thus, the “Ozonated” essential oil of Clove was more effective to inhibit the growth of Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213, which has statistically similar behavior, while it obtained less efficiency for Escherichia coli ATCC 25922. Results similar to those presented in the research are from Baima et al. (2017), Mahendran and Rahman (2019), Badea et al. (2019) and Haro-Gonzáles et al. (2021).
Baima et al. (2017) conducted a study to evaluate the antimicrobial activity by determining the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of clove essential oil (Syzygium aromaticum) against strains of Escherichia coli – ATCC 25922 and Staphylococcus aureus – ATCC 25923 and, as a result, it was obtained that the essential oil of Cloves has antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. By determining the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), a MIC of 100 μg/mL was obtained for Escherichia coli and 200 μg/mL for Staphylococcus aureus.
Thus, reinforcing the result of this article, Haro-Gonzáles et al. (2021) explain that non-Ozonated Clove essential oil can inhibit gram-negative bacteria (E. coli, Salmonella, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Erwinia carotovora, Agrobacterium, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and gram-positive bacteria (S. aureus, Streptococcus, and L. monocytogenes), and Aspergillus fungi (A. flavus, A. parasiticus, and A. ochraceus), Penicillium, C. albicans, and yeast. It has also been observed that Clove essential oil inhibits Gram-positive bacteria to a greater extent than Gram-negative bacteria. This is attributed to a diffusible mucopeptide layer in Gram-positive bacteria that makes them susceptible to antimicrobial agents. In contrast, the complex lipopolysaccharide layer on the outer cell membrane of Gram-negative bacteria can significantly reduce the rate of diffusion of lipophilic antibacterial compounds across the cell membrane (Behbahani et al. 2019), as these pathogens have shown greater sensitivity to oil than probiotics and fungi (Shahbazi, 2019).
After the “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated” Clove essential oils are analyzed using the GC-MS method and compared in their respective chemical compositions, it is identified that both have the same major compounds; however, it is clear that the process of ozonation alters the centesimal composition of all of them, which may be a justifying factor in the difference in behavior in view of the inhibition of the analyzed bacterial strains.
As for the “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated” Peppermint essential oils, they statistically obtained the same activity for 03 of the 04 microorganisms tested (Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 and Escherichia coli ATCC 25922). The “Ozonated” Peppermint oil had inhibition behavior for sensitive microorganisms and they were statistically similar in the formation of the inhibition halo and also in the minimum inhibitory concentration. The “Non-Ozonated” Peppermint oil had greater inhibition for Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, while for Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538, it obtained less efficiency, requiring a higher concentration (4%) of oil to inhibit this strain.
In a recent study, Menta piperita essential oil was observed as a potentiating agent for the antimicrobial action of ozone, with its synergistic activity at an inhibitory concentration of 2% of essential oil (Floare et al., 2023), corroborating the values obtained by the inhibition of the ozonated and non-ozonated essential oil of this study that varied between 2 to 4% for the same selected strains. The chemical analysis of the essential oil - “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated”- of Menta, has similar composition of oxygenated monoterpenes, but with different hundredths variations between the oils of this study in relation to the oil studied by Floare et al., 2023; which only analyzed the chemical composition of non-Ozonated oil. It appears that the proportion of Menthol present in the essential oil of the cited study is lower than the 60% of the one in this study, maintaining a similar proportion of Menthone. These 02 components represent 55% of the total composition of the essential oil in the study conducted by Floare, while in this study the proportion was 75% for the Ozonated oil compared to 73% for the non-Ozonated oil.
The results obtained by this study reinforce those expressed by Badea et al. (2019) who aimed to analyze the influence of peppermint essential oil (Menta piperita), absorbed on the surface of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and its morphological, physicochemical and antimicrobial properties. Still in the study developed by Badea et al. (2019), they also investigated the antimicrobial activity against bacteria resistant to methicillin such as S. aureus (MRSA) 388, S. aureus ATCC 25923, and carbapenems E. coli C5 (carbapenemase-producing strain ), as well as S. aureus ATCC 6538, E. coli ATCC 25922, which were also tested in this study, in addition to E. faecium DSM 13590. The E. coli strain ATCC 25922 in the Badea et al. (2019) presented the largest diameter of the inhibition halo with values between 20 and 22 mm, corroborating the largest inhibition halo found for Menta piperita oil at 4% with a mean value of 19.7 mm in this study. It should be noted that the authors’ research did not use Ozonated essential oil.
Mahendran and Rahman (2019), explain in their study with Peppermint essential oil, that it showed antibacterial activity against different bacteria, including E. faecalis, S. aureus and S. dysenteria exposed the highest MIC (8.3 ± 0.2, 8.3 ± 0.1 and 5.8 ± 0.1 mg/ml) (NIKOLIC et al., 2014; BASSOLÉ et al., 2010). The study by Ceylan et al. (2014), demonstrated a maximum zone of inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus (15 mm) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (15 mm) represented by in vitro disk diffusion/dilution method. Thus, the results showed that the higher concentration of oils produced larger inhibition halos in the inoculum, which helped in the process of identifying the minimum inhibitory concentration presented.
The highest concentration of oils produced in the inoculums larger halos of inhibition, helping in the process of identifying the minimum inhibitory concentration. None of the “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated” oils inhibited the microorganism Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853. Thus, Peppermint essential oil has significant antimicrobial activity and ozonation can be a synergistic factor contributing to therapeutic and/or control antimicrobial needs
5. Final Considerations
It was evidenced in the study that Andiroba and Buriti oils in the “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated” versions were ineffective in inhibiting microorganisms.
On the other hand, the “Ozonated” Clove essential oil showed a better performance when compared to the “Non-Ozonated” version of the same, which may be related to the difference in the centesimal composition of the oils.
Peppermint essential oils, “Ozonated” and “Non-Ozonated”, showed similar antimicrobial activities, and different chemical composition after the ozonation process, although the major constituents are oxygenated monoterpenes.
Thus, the ozonation of essential oils can contribute to the synergism of antimicrobial activity and there is a need for individualized study of each type of oil produced and the species of extraction.
| 1 |
NB = Biosafety Level required for handling the strain |
References
- ABRANTES, J. A.; NOGUEIRA, J. M. da R. Resistência bacteriana aos antimicrobianos: uma revisão das principais espécies envolvidas em processos infecciosos. Revista Brasileira de Análises Clínicas. Rio de Janeiro, v. 53, n. 3, jun./set. 2021.
- ADAMS, R. P. Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectroscopy. Allured: Carol Stream, ed. 4, 2017.
- Aghaei, M.; Aghaei, S.; Sokhanvari, F.; Ansari, N.; Hosseini, S.M.; Mohaghegh, M.A.; Hejazi, H. The therapeutic effect of ozonated olive oil plus glucantime on human cutaneous leishmaniasis. 2018, 22, 25–30, . [CrossRef]
- AZEVEDO, G. M. M. Nanoencapsulação de óleo de buriti (Mauritia flexuosa) em alginato e gelatina: caracterização e avaliação da solubilidade e potencial antimicrobiano. 78f. Dissertação (Mestrado em Nutrição) - Centro de Ciências da Saúde, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Natal, 2018.
- Badea, M.L.; Iconaru, S.L.; Groza, A.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Beuran, M.; Predoi, D. Peppermint Essential Oil-Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles with Antimicrobial Properties. Molecules 2019, 24, 2169, . [CrossRef]
- BAIMA, P. T. S. et al. Atividade antimicrobiana do óleo essencial de cravo da índia (Syzygium Sromaticum) frente à cepas de Escherichia Coli (ATCC 25922) e Staphylococcus Aureus (ATCC 25923). 57º Congresso de Química. Gramado/RS 23 – 27, out. 2017.
- BARROS, B. S. Avaliação da atividade antifúngica do óleo essencial de Mentha piperita L. sobre cepas de Candida albicans. 40p. Monografia (Graduação). Universidade Federal da Paraíba. João Pessoa, 2017. Available at: Accessed on: 31 out. 2022.
- Basile, A.A.; Cendali, M.; Mandelli, G.; Fioretto, G. Anti-inflammatory effect of an eye drops solution based on liposomal ozonated oil in different corneal and anterior segment human diseases. Ozone Ther. 2019, 4, . [CrossRef]
- BASSOLÉ, I. H. et al. Composition and antimicrobial activities of Lippia multiflora Moldenke, Mentha piperita L. and Ocimum basilicum L. Essential oils and their major monoterpene alcohols alone and in combination. Molecules, v.15, pp.7825-7839. 2010. [CrossRef]
- BATISTA, H. L. Atividade antimicrobiana de extratos vegetais de plantas do Estado de Tocantins. Dissertação (Mestrado em Farmacologia Clínica). 154 f. Universidade Federal do Ceará, Fortaleza. 2008.
- BAUER, A. W. Teste de suscetibilidade a antibióticos por um método padronizado de disco único. American Journal Clinical Pathology. v. 45, n. 4, p. 493. 1966.
- BEHBAHANI, B. A.; NOSHAD, M.; FALAH, F. Estudo da estrutura química, antimicrobiana, citotóxica e mecanismo de ação do óleo essencial de Syzygium aromaticum sobre patógenos de origem alimentar. Potravin. Slovak J. Food Sci. v.13, p. 875–883, set./nov. 2019. [CrossRef]
- BRITO, A. D.; COELHO, R. D. F. R.; ROSAL, L. F. Os extrativistas de andiroba em projetos de assentamentos agroextrativistas (PAEX) da Várzea de Igarapé-Miri, Pará, Brasil. Revista Agroecossistemas, v.11, n 2, pp.82-101. 2020. Available at: https://periodicos.ufpa.br/index.php/agroecossistemas/article/view/7303. Accessed on: 22 out. 2022.
- BRUNO, C. M. A.; ALMEIDA, M. R. Óleos essenciais e vegetais: matérias-primas para fabricação de bioprodutos nas aulas de química orgânica experimental. Química Nova., v. 44, n. 7, pp. 899-907. 2021. Accessed on: 12 out. 2022. [CrossRef]
- CEYLAN, O. The antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of Mentha × piperita L. essential oil. Journal of BioScience and Biotechnology, pp. 23-27. 2014.
- CARDOSO, I. da C. C. et al. Potencial antimicrobiano de óleos vegetais ozonizados contra espécies bacterianas: uma revisão integrativa. Investigação, Sociedade e Desenvolvimento, v. 10, n. 2, 2021. Available at: https://rsdjournal.org/index.php /rsd/article/view/12451. Accessed on: 3 dez. 2022.
- Cordeiro, K.S.; Galeno, L.S.; Mendonça, C.d.J.S.; Carvalho, I.A.; Costa, F.N. Ocorrência de bactérias patogênicas e deteriorantes em sashimi de salmão: avaliação de histamina e de susceptibilidade a antimicrobianos. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2020, 23, . [CrossRef]
- CARVALHO, S. C.; ASSIS, M. W. V.; SANTOS, T. T. Propriedades químicas, medicinais e nutricionais da polpa e do óleo de buriti (Mauritia flexuosa L.). Revista Desafios. v. 7, n. 3, 2020.
- FIGUEIREDO, A. R. de; SILVA, L. R. da; MORAIS, L. A. S. de. Bioatividade do óleo essencial de Eugenia caryophyllus sobre Cladosporium herbarum, agente etiológico da verrugose em maracujá. Scientia Plena, v. 17, n. 2, 2021. Available at: https://scientiaplena.org.br/sp/article/view/5834. Accessed on: 3 dez. 2022.
- FILHO, P. R. C. F. R et al. Avaliação da lubricidade do óleo de coco (orbignya phalerata mart) e do óleo de andiroba (carapa guianensis aubl) por ensaio de desgaste. Revista Brasileira de Energias Renováveis, v.8, v.1. 2019.
- Floare, A.-D.; Dumitrescu, R.; Alexa, V.T.; Balean, O.; Szuhanek, C.; Obistioiu, D.; Cocan, I.; Neacsu, A.-G.; Popescu, I.; Fratila, A.D.; et al. Enhancing the Antimicrobial Effect of Ozone with Mentha piperita Essential Oil. Molecules 2023, 28, 2032, . [CrossRef]
- Accessed on: 26 mar. 2023.
- GONÇALVES, F. C. M. Menta (Mentha x piperita L.) cultivada com aplicação de ácido salicílico: avaliações fotossintéticas e bioquímicas. 2017. 129 f. Dissertação (Mestrado Agronomia-Horticultura) -Universidade Estadual Paulista. Botucatu, 2017. Available at: . Accessed on: 03 abr. 2021.
- Guidoni, M.; Scherer, M.d.C.; Figueira, M.; Schmitt, E.; de Almeida, L.; Scherer, R.; Bogusz, S.; Fronza, M. Fatty acid composition of vegetable oil blend and in vitro effects of pharmacotherapeutical skin care applications. Braz. J. Med Biol. Res. 2019, 52, e8209, . [CrossRef]
- HARO-GONZÁLEZ, J. N. et al. Clove Essential Oil (Syzygium aromaticum L. Myrtaceae): Extraction, Chemical Composition, Food Applications, and Essential Bioactivity for Human Health. Molecules, v. 26, p. 63 - 87. 2021. Accessed on: 12 nov. 2022. [CrossRef]
- HORVAT, E. Atividade antimicrobiana e desinfecção hospitalar com extrato de cravo-da-índia (syzygium aromaticun e/ou caryophyllus aromaticus l.). Ensaios USF, v. 3, n. 2, p. 1–13, 2019. Available at: https://ensaios.usf.emnuvens.com.br/ ensaios/article/view/133. Accessed on: 3 dez. 2022.
- ISCO3. Declaração de Madri sobre Ozonoterapia, 3rd ed. Madrid. Comitê Científico Internacional de Ozonioterapia. www.isco3.org. mar. 2020.
- JAIN, N.; SHARMA, M. Topical application of Eugenia caryophyllusoil against ringworm infection of human beings. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. v. 12, n. 7, pp. 153- 157, jul. 2019.
- Kume, J.E.P.; Junior, R.A.; Di-Tanno, M.F.P.; Kozusny-Andreani, D.I. Uso de óleos essenciais in natura e ozonizados no controle in vitro de Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, . [CrossRef]
- LESCURA, I. C. de P. S.; BEGA, A. Uso do ozônio direto em “bag” e óleo ozonizado em lesões crônicas em membros inferiores de diabéticos. REVISTA IBERO- AMERICANA DE PODOLOGIA, v. 2, n. 3, p. 260 - 269, 2020. Available at: https://www.iajp.com.br/index.php/IAJP/article/view/46. Accessed on: 18 jan. 2023.
- MAHENDRAN, G.; RAHMAN, L. U. Ethnomedicinal, phytochemical and pharmacological updates on Peppermint (Mentha × piperita L.) - A review. Phytother Res. v. 34, n. 9, pp. 2088-2139, 2020.
- MAHENDRAN, G.; RAHMAN, L. U. Ethnomedicinal, phytochemical and pharmacological updates on Peppermint (Mentha × piperita L.) - A review. Phytother Res. v. 34, n. 9, pp. 2088-2139, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Mc GINNIS, M. R. Laboratory handbook of medical mycology. Academic Press, New York. p. 643. 1980.
- MELO, W. F. et al. Propriedades físico-químicas da hortelã (Mentha piperita L.) e seus benefícios à saúde. INTESA – Informativo Técnico do Semiárido. Pombal- PB, v.12, n 2, p. 08-13, jul – dez. 2018. Available at: . Accessed on: 03 jun. 2021.
- MITTELMANN, E. C. et al. Óleos ozonizados: controle de qualidade e eficácia no tratamento da Acne vulgaris. Periódicos Univali. v. 1, n.1. 2021. Available at: https://periodicos.univali.br/index.php/QRS/article/view/18048. Accessed on: 12 nov. 2022.
- Moureu, S.; Violleau, F.; Haimoud-Lekhal, D.A.; Calmon, A. Ozonation of sunflower oils: Impact of experimental conditions on the composition and the antibacterial activity of ozonized oils. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2015, 186, 79–85, . [CrossRef]
- MOTTA, V. T. Bioestatística. 2. ed. Caxias do Sul. Editora EDUCS, p. 127-134. 2006.
- Nikolić, M.; Jovanović, K.K.; Marković, T.; Marković, D.; Gligorijević, N.; Radulović, S.; Soković, M. Chemical composition, antimicrobial, and cytotoxic properties of five Lamiaceae essential oils. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 61, 225–232, . [CrossRef]
- NUNES, V. L. N. D. Avaliação da atividade antimicrobiana dos óleos essenciais extraídos de frutas nativas Buriti e Cupuaçu do Cerrado Maranhense. Brazilian Journal of Development, Curitiba, v.7, n.7, p.67528-67537 jul. 2021.
- OLIVEIRA, G. S. Avaliação da genotoxicidade do inibidor de tripsina isolado de semente de tamarindo (Tamarindus indica L.) e do potencial antibacteriano in vitro e in silico de seus peptídeos derivados. Orientador: Ana Heloneida de Araújo Morais. 111f. Dissertação (Mestrado em Nutrição) - Centro de Ciências da Saúde, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Natal, 2022.
- PEREIRA SANTOS, F. D. R. et al. Características físico-químicas de um sérum desenvolvido à base do óleo de buriti (Mauritia flexuosa) para pele idosa. Revista Enfermagem Atual In Derme, [S. l.], v. 95, n. 33, p. 15, 2021. Available at: http://www.revistaenfermagematual.com.br/index.php/revista/article/view/912. Accessed on: 3 nov. 2022.
- REIS, J. B. et al. Avaliação da atividade antimicrobiana dos óleos essenciais contra patógenos alimentares/ Avaliação da atividade antimicrobiana dos óleos essenciais contra patógenos alimentares. Brazilian Journals. v. 3, n. 1. 2020. Available at: https://ojs.brazilianjournals.com.br/ojs/index.php/BJHR/article/view/6223. Accessed on: 03 dez. 2022.
- RENTES, B. R. Nanoemulsão de macela (Achyrocline satureioides) em óleo de linhaça (Linum usitatissimun): avaliação do potencial antimicrobiano contra bactérias gram positivas e gram negativas e efeito da liofilização sobre a estabilidade físico- química. Repositório Institucional da UFSC Acervos Campus Florianópolis.PROPESQ. Programa de Iniciação Científica e Tecnológica da UFSC Seminário de Iniciação Científica e Tecnológica da UFSC ,2022.
- RIBEIRO, C. D. B. et al. The medicinal use of Carapa guianensis Abul. (Andiroba). Research, Society and Development, v. 10, n. 15, 2021. Available at: https://rsdjournal.org/index.php/rsd/article/view/22815. Accessed on: 26 out. 2022.
- RICCO, F. G.; AQUINO JÚNIOR, D. S. Uso de óleo ozonizado em feridas: Relato de caso. Pubvet. v. 16 n. 01 p. 191. 2022. Available at: https://www.pubvet.com.br/ artigo/8910/ uso de oleo ozonizado em feridas relato de caso. Accessed on: 18 jan. 2023.
- RODRIGUES, C. B. Óleos essenciais como antimicrobianos naturais em pós-colheita de frutos. Repositório Institucional UFSCar. 28, jul. 2022. Available at: https://repositorio.ufscar.br/handle/ufscar/16539. Accessed on: 12 jan. 2023.
- Sarkic, A.; Stappen, I. Essential Oils and Their Single Compounds in Cosmetics—A Critical Review. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 11, . [CrossRef]
- SERRA, J. L. et al. Fontes alternativas de óleos e gorduras de plantas amazônicas: ácidos graxos, metil tocois, carotenóides totais e composição química. Food Research International, v. 116, pp. 12-19. 2019. [CrossRef]
- SHAHBAZI, Y. Propriedades antioxidantes, antibacterianas e antifúngicas da nanoemulsão de óleo essencial de cravo. Nanomedicina Res. J. v. 4, p. 204–208. dez. 2019. [CrossRef]
- SILVA, I. N. et al. Qualidade fisiológica de sementes de arroz tratadas com óleos essenciais e extratos vegetais. v. 11, n. 13, 2019. Destaques Acadêmicos. Available at: http://www.meep.univates.br/revistas/index.php/destaques/article/ view/2333. Accessed on: 12 out. 2022.
- SILVA, J. J. et al. Desenvolvimento de embalagem de ativo antimicrobiano natural conciliado com refrigeração ou congelamento para conservação de morangos. 79.
- Investigação, Sociedade e Desenvolvimento, v. 9, n. 11, 2020. Available at: https://rsdjournal.org/index.php/rsd/article/view/9595. Accessed on: 3 dez. 2022.
- SILVEIRA, M. P. Desempenho antifúngico de óleos essenciais de canela, cravo e louro em bolores de pães de forma integrais. Dissertação (Mestrado em Ciência e Tecnologia de Alimentos) – Programa de Pós-graduação em Ciência e Tecnologia de Alimentos, Universidade Federal dos Vales do Jequitinhonha e Mucuri, Diamantina, 143 p. 2019.
- SOARES, J. F. et al. Caracterização do óleo de buriti produzido na região norte de Minas Gerais: parâmetros de qualidade, perfil de ácidos graxos e teor de carotenoides. Investigação, Sociedade e Desenvolvimento, v. 10, n. 3, p. 9, 2021. Available at: https://rsdjournal.org/index.php/rsd/article/view/13734. Accessed on: 3 out. 2022.
- TORMIN, S. C.; NAVARINI, A.; ALMEIDA, J. O. C. F. de.; TRAVASSOS, L. H. R.; NEGRI; M. V. de G.; SILVA, R. A. Análise do efeito bactericida do ozônio sobre bactérias multirresistentes. Revista de Arquivos Médicos Hospital Faculdade Ciências Médicas da Santa Casa, São Paulo, v. 61, n. 138 p. 41, abr./nov. 2016.
- VAN DEN DOOL, H.; KRATZ, P. D. A Generalization of the Retention Index System Including Linear Temperature Programmed Gas-Liquid Partition Chromatography. Journal Chromatography A. v. 11, p. 463-471, 1963.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).