Submitted:
20 March 2024
Posted:
20 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Cellular Senescence
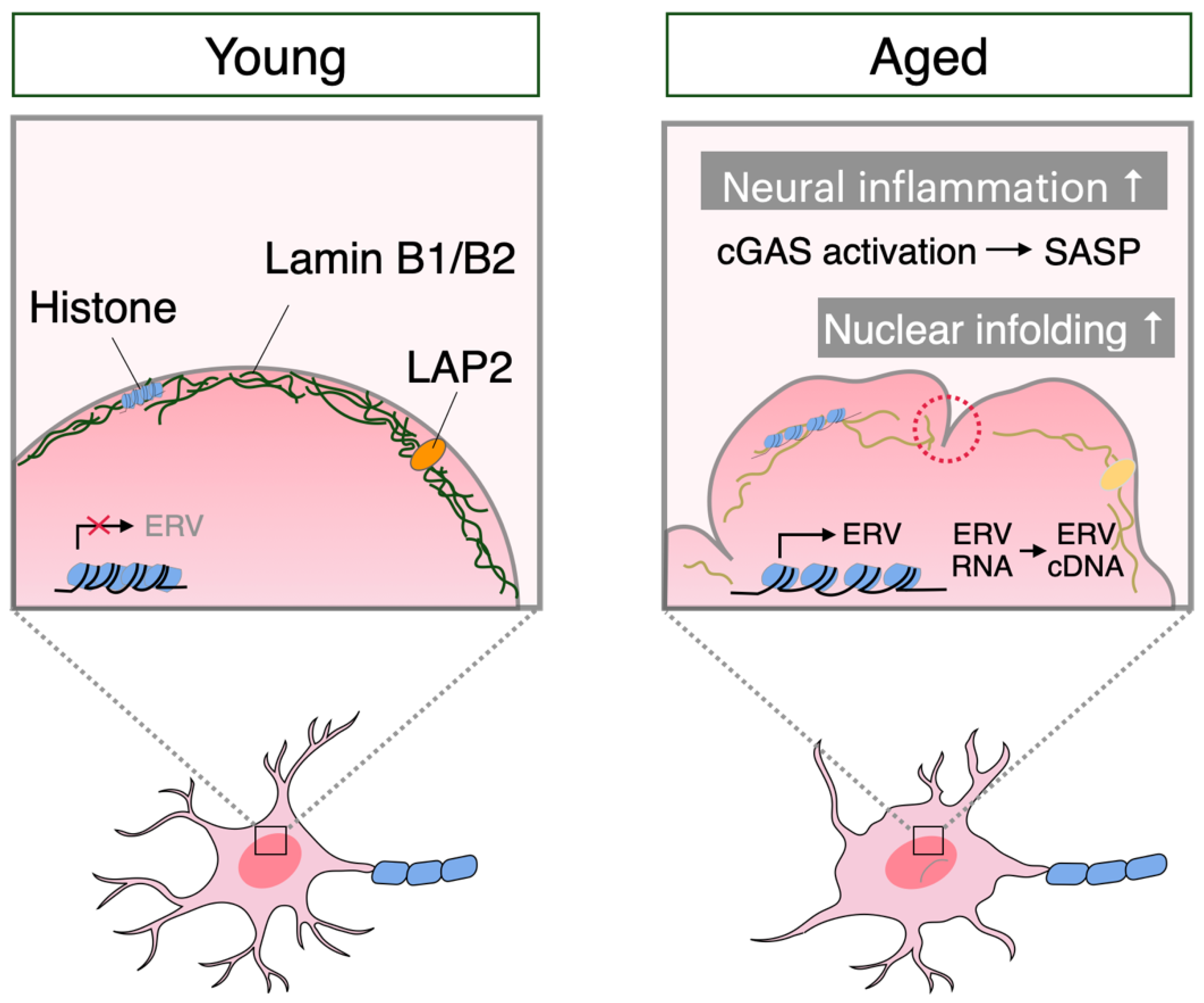
3. Neuronal Senescence
4. Microglial Senescence
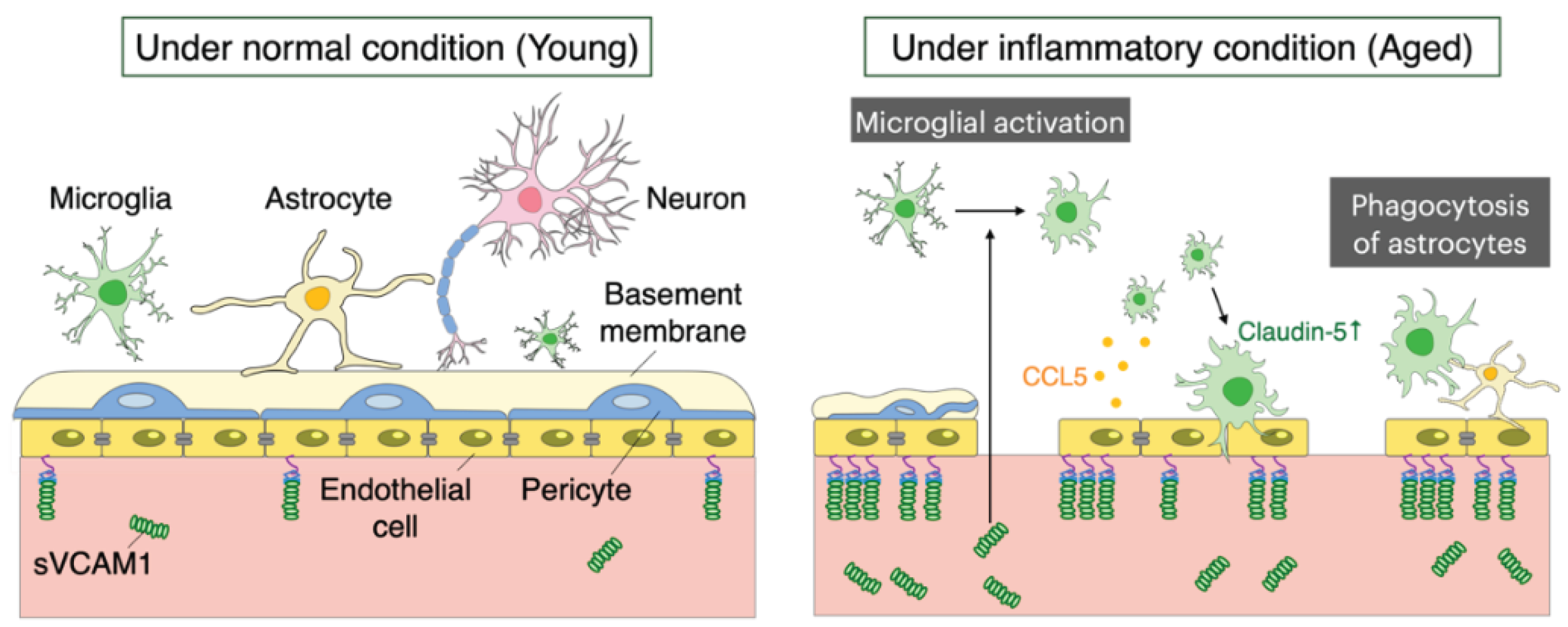
5. Aging of the Blood-Brain Barrier
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Tosato M; Zamboni V; Ferrini A; Cesari M The Aging Process and Potential Interventions to Extend Life Expectancy; Clin Interv Aging 2007, 2, 401–412.
- Mattson, M.P.; Arumugam, T. V. Hallmarks of Brain Aging: Adaptive and Pathological Modification by Metabolic States. Cell Metab 2018, 27, 1176–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Dan, X.; Babbar, M.; Wei, Y.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. Ageing as a Risk Factor for Neurodegenerative Disease. Nat Rev Neurol 2019, 15, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iadecola, C. The Neurovascular Unit Coming of Age: A Journey through Neurovascular Coupling in Health and Disease. Neuron 2017, 96, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiisen, T.M.; Lehre, K.P.; Danbolt, N.C.; Ottersen, O.P. The Perivascular Astroglial Sheath Provides a Complete Covering of the Brain Microvessels: An Electron Microscopic 3D Reconstruction. Glia 2010, 58, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Tian, G.-F.; Peng, W.; Lou, N.; Libionka, W.; Han, X.; Nedergaard, M. Astrocyte-Mediated Control of Cerebral Blood Flow. Nat Neurosci 2006, 9, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HAYFLICK, L.; MOORHEAD, P.S. The Serial Cultivation of Human Diploid Cell Strains. Exp Cell Res 1961, 25, 585–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.P.; Bartek, J. The DNA-Damage Response in Human Biology and Disease. Nature 2009, 461, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumagalli, M.; Rossiello, F.; Mondello, C.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F. Stable Cellular Senescence Is Associated with Persistent DDR Activation. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, M.; Rossiello, F.; Clerici, M.; Barozzi, S.; Cittaro, D.; Kaplunov, J.M.; Bucci, G.; Dobreva, M.; Matti, V.; Beausejour, C.M.; et al. Telomeric DNA Damage Is Irreparable and Causes Persistent DNA-Damage-Response Activation. Nat Cell Biol 2012, 14, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halazonetis, T.D.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Bartek, J. An Oncogene-Induced DNA Damage Model for Cancer Development. Science 2008, 319, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, J.; Fielder, E.; Passos, J.F. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Cell Senescence: Deciphering a Complex Relationship. FEBS Lett 2019, 593, 1566–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N. A Brief History of Autophagy from Cell Biology to Physiology and Disease. Nat Cell Biol 2018, 20, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, Y.; Schmauck-Medina, T.; Hansen, M.; Morimoto, R.I.; Simon, A.K.; Bjedov, I.; Palikaras, K.; Simonsen, A.; Johansen, T.; Tavernarakis, N.; et al. Autophagy in Healthy Aging and Disease. Nat Aging 2021, 1, 634–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukášová, E.; Kovařík, A.; Kozubek, S. Consequences of Lamin B1 and Lamin B Receptor Downregulation in Senescence. Cells 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Sen, P. The Senescent Cell Epigenome. Aging 2018, 10, 3590–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppé, J.P.; Patil, C.K.; Rodier, F.; Sun, Y.; Muñoz, D.P.; Goldstein, J.; Nelson, P.S.; Desprez, P.Y.; Campisi, J. Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotypes Reveal Cell-Nonautonomous Functions of Oncogenic RAS and the P53 Tumor Suppressor. PLoS Biol 2008, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, J.H.; Baxter, M.G. The Ageing Cortical Synapse: Hallmarks and Implications for Cognitive Decline. Nat Rev Neurosci 2012, 13, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowald, A.; Kirkwood, T.B. Accumulation of Defective Mitochondria through Delayed Degradation of Damaged Organelles and Its Possible Role in the Ageing of Post-Mitotic and Dividing Cells. J Theor Biol 2000, 202, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, S.; Sato, S.; Fukuda, T.; Tada, N.; Hattori, N. Aging-Related Motor Function and Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss in C57BL/6 Mice. Mol Brain 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Ohkubo, R.; Mu, W.C.; Chen, W.; Fan, J.L.; Song, Z.; Maruichi, A.; Sudmant, P.H.; Pisco, A.O.; Dubal, D.B.; et al. The Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response Regulates Hippocampal Neural Stem Cell Aging. Cell Metab 2023, 35, 996–1008.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, M.M.; Zheng, B.; Lu, T.; Yan, Z.; Py, B.F.; Ng, A.; Xavier, R.J.; Li, C.; Yankner, B.A.; Scherzer, C.R.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis Reveals Mechanisms Modulating Autophagy in Normal Brain Aging and in Alzheimer’s Disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 14164–14169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovács, T.; Szinyákovics, J.; Billes, V.; Murányi, G.; Varga, V.B.; Bjelik, A.; Légrádi, Á.; Szabó, M.; Sándor, S.; Kubinyi, E.; et al. A Conserved MTMR Lipid Phosphatase Increasingly Suppresses Autophagy in Brain Neurons during Aging. Sci Rep 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Blas, D.; Gorostieta-Salas, E.; Pommer-Alba, A.; Muciño-Hernández, G.; Gerónimo-Olvera, C.; Maciel-Barón, L.A.; Konigsberg, M.; Massieu, L.; Castro-Obregón, S. Cortical Neurons Develop a Senescence-like Phenotype Promoted by Dysfunctional Autophagy. Aging 2019, 11, 6175–6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Ren, J.; Liu, Q.; Bao, Z.; Sun, S.; Liu, X.; Ma, S.; Liu, Z.; et al. Nuclear Lamina Erosion-Induced Resurrection of Endogenous Retroviruses Underlies Neuronal Aging. Cell Rep 2023, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Ramanan, N. Region-Specific Heterogeneity in Neuronal Nuclear Morphology in Young, Aged and in Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Brains. Front Cell Dev Biol 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, T.; Murakami, T.; Maki, K.; Kawaue, T.; Tani, N.; Sugai, A.; Nakazawa, N.; Ishiguro, K. ichiro; Adachi, T.; Kengaku, M.; et al. Age-Associated Reduction of Nuclear Shape Dynamics in Excitatory Neurons of the Visual Cortex. Aging Cell 2023, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xie, C.; Tian, W.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; Hawes, S.; Chang, L.; Kung, J.; Ding, J.; Chen, S.; et al. Parkinson’s Disease-Related Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 Modulates Nuclear Morphology and Genomic Stability in Striatal Projection Neurons during Aging. Mol Neurodegener 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paonessa, F.; Evans, L.D.; Solanki, R.; Larrieu, D.; Wray, S.; Hardy, J.; Jackson, S.P.; Livesey, F.J. Microtubules Deform the Nuclear Membrane and Disrupt Nucleocytoplasmic Transport in Tau-Mediated Frontotemporal Dementia. Cell Rep 2019, 26, 582–593.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmut, K.; Hanisch, U.K.; Noda, M.; Verkhratsky, A. Physiology of Microglia. Physiol Rev 2011, 91, 461–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Barres, B.A. Microglia and Macrophages in Brain Homeostasis and Disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2018, 18, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry-Carroll, L.; Greulich, P.; Marshall, A.R.; Riecken, K.; Fehse, B.; Askew, K.E.; Li, K.; Garaschuk, O.; Menassa, D.A.; Gomez-Nicola, D. Microglia Colonize the Developing Brain by Clonal Expansion of Highly Proliferative Progenitors, Following Allometric Scaling. Cell Rep 2023, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, M.; Masuda, T.; Wheeler, M.A.; Quintana, F.J. Annual Review of Immunology Microglia and Central Nervous System-Associated Macrophages-From Origin to Disease Modulation. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Florent Ginhoux; Melanie Greter; Marylene Leboeuf; Sayan Nandi; Peter See; Solen Gokhan; Mark F Mehler; Simon J Conway; Lai Guan Ng; E Richard Stanley; et al. Fate Mapping Analysis Reveals That Adult Microglia Derive from Primitive Macrophages. Science (1979) 2010, 330, 841–845. [Google Scholar]
- Paolicelli, R.C.; Bolasco, G.; Pagani, F.; Maggi, L.; Scianni, M.; Panzanelli, P.; Giustetto, M.; Ferreira, T.A.; Guiducci, E.; Dumas, L.; et al. Synaptic Pruning by Microglia Is Necessary for Normal Brain Development. Science (1979) 2011, 333, 1456–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, D.P.; Lehrman, E.K.; Kautzman, A.G.; Koyama, R.; Mardinly, A.R.; Yamasaki, R.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Greenberg, M.E.; Barres, B.A.; Stevens, B. Microglia Sculpt Postnatal Neural Circuits in an Activity and Complement-Dependent Manner. Neuron 2012, 74, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.A.; Damisah, E.C.; Chen, F.; Kwan, A.C.; Grutzendler, J. Targeted Two-Photon Chemical Apoptotic Ablation of Defined Cell Types in Vivo. Nat Commun 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, C.L.; Martínez-Cerdeño, V.; Noctor, S.C. Microglia Regulate the Number of Neural Precursor Cells in the Developing Cerebral Cortex. Journal of Neuroscience 2013, 33, 4216–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, A.; Encinas, J.M.; Deudero, J.J.P.; Chancey, J.H.; Enikolopov, G.; Overstreet-Wadiche, L.S.; Tsirka, S.E.; Maletic-Savatic, M. Microglia Shape Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis through Apoptosis-Coupled Phagocytosis. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, A.; Wake, H.; Ishikawa, A.W.; Eto, K.; Shibata, K.; Murakoshi, H.; Koizumi, S.; Moorhouse, A.J.; Yoshimura, Y.; Nabekura, J. Microglia Contact Induces Synapse Formation in Developing Somatosensory Cortex. Nat Commun 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruwaka, K.; Ikegami, A.; Tachibana, Y.; Ohno, N.; Konishi, H.; Hashimoto, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Kato, D.; Ono, R.; Kiyama, H.; et al. Dual Microglia Effects on Blood Brain Barrier Permeability Induced by Systemic Inflammation. Nat Commun 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Cai, L.; Gao, S.; Liu, T.; et al. Transcriptional and Epigenetic Decoding of the Microglial Aging Process. Nat Aging 2023, 3, 1288–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketomi, T.; Tsuruta, F. Towards an Understanding of Microglia and Border-Associated Macrophages. Biology (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, T.R.; Dufort, C.; Dissing-Olesen, L.; Giera, S.; Young, A.; Wysoker, A.; Walker, A.J.; Gergits, F.; Segel, M.; Nemesh, J.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of Microglia throughout the Mouse Lifespan and in the Injured Brain Reveals Complex Cell-State Changes. Immunity 2019, 50, 253–271.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaiyan, S.; Besson-Girard, S.; Kaya, T.; Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Liu, L.; Ji, H.; Schifferer, M.; Gouna, G.; Usifo, F.; Kannaiyan, N.; et al. White Matter Aging Drives Microglial Diversity. Neuron 2021, 109, 1100–1117.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschallinger, J.; Iram, T.; Zardeneta, M.; Lee, S.E.; Lehallier, B.; Haney, M.S.; Pluvinage, J. V.; Mathur, V.; Hahn, O.; Morgens, D.W.; et al. Lipid-Droplet-Accumulating Microglia Represent a Dysfunctional and Proinflammatory State in the Aging Brain. Nat Neurosci 2020, 23, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluvinage, J. V.; Haney, M.S.; Smith, B.A.H.; Sun, J.; Iram, T.; Bonanno, L.; Li, L.; Lee, D.P.; Morgens, D.W.; Yang, A.C.; et al. CD22 Blockade Restores Homeostatic Microglial Phagocytosis in Ageing Brains. Nature 2019, 568, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnartz-Gerlach, B.; Bodea, L.G.; Klaus, C.; Ginolhac, A.; Halder, R.; Sinkkonen, L.; Walter, J.; Colonna, M.; Neumann, H. TREM2 Triggers Microglial Density and Age-Related Neuronal Loss. Glia 2019, 67, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, B.D.; Snyder, S.H.; Bohr, V.A. Signaling by CGAS–STING in Neurodegeneration, Neuroinflammation, and Aging. Trends Neurosci 2021, 44, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulen, M.F.; Samson, N.; Keller, A.; Schwabenland, M.; Liu, C.; Glück, S.; Thacker, V. V.; Favre, L.; Mangeat, B.; Kroese, L.J.; et al. CGAS–STING Drives Ageing-Related Inflammation and Neurodegeneration. Nature 2023, 620, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X. Current Strategies for Brain Drug Delivery. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatovic, S.M.; Keep, R.F.; Andjelkovic, A. V Brain Endothelial Cell-Cell Junctions: How to “Open” the Blood Brain Barrier; 2008; Vol. 6.
- Stamatovic, S.M.; Johnson, A.M.; Keep, R.F.; Andjelkovic, A. V. Junctional Proteins of the Blood-Brain Barrier: New Insights into Function and Dysfunction. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geranmayeh, M.H.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Farhoudi, M. Targeting Pericytes for Neurovascular Regeneration. Cell Communication and Signaling 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.I.; Sei, Y.J.; Park, H.J.; Kim, J.; Ryu, Y.; Choi, J.J.; Sung, H.J.; MacDonald, T.J.; Levey, A.I.; Kim, Y.T. Microengineered Human Blood–Brain Barrier Platform for Understanding Nanoparticle Transport Mechanisms. Nat Commun 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armulik, A.; Genové, G.; Mäe, M.; Nisancioglu, M.H.; Wallgard, E.; Niaudet, C.; He, L.; Norlin, J.; Lindblom, P.; Strittmatter, K.; et al. Pericytes Regulate the Blood-Brain Barrier. Nature 2010, 468, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.J.; Rönnbäck, L.; Hansson, E. Astrocyte-Endothelial Interactions at the Blood-Brain Barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci 2006, 7, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengillo, J.D.; Winkler, E.A.; Walker, C.T.; Sullivan, J.S.; Johnson, M.; Zlokovic, B. V. Deficiency in Mural Vascular Cells Coincides with Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Pathology 2013, 23, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.C.; Stevens, M.Y.; Chen, M.B.; Lee, D.P.; Stähli, D.; Gate, D.; Contrepois, K.; Chen, W.; Iram, T.; Zhang, L.; et al. Physiological Blood–Brain Transport Is Impaired with Age by a Shift in Transcytosis. Nature 2020, 583, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloway, S.; Gur, T.; Berzin, T.; Zipser, B.; Correia, S.; Hovanesian, V.; Fallon, J.; Kuo-Leblanc, V.; Glass, D.; Hulette, C.; et al. Effect of APOE Genotype on Microvascular Basement Membrane in Alzheimer’s Disease.
- Mendiola, A.S.; Yan, Z.; Dixit, K.; Johnson, J.R.; Bouhaddou, M.; Meyer-Franke, A.; Shin, M.G.; Yong, Y.; Agrawal, A.; MacDonald, E.; et al. Defining Blood-Induced Microglia Functions in Neurodegeneration through Multiomic Profiling. Nat Immunol 2023, 24, 1173–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, H.; Czupalla, C.J.; Lee, D.; Chen, M.B.; Burke, A.N.; Zera, K.A.; Zandstra, J.; Berber, E.; Lehallier, B.; Mathur, V.; et al. Aged Blood Impairs Hippocampal Neural Precursor Activity and Activates Microglia via Brain Endothelial Cell VCAM1. Nat Med 2019, 25, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Ma, N.; Zhong, J.; Yu, B.; Wan, J.; Zhang, W. Age-Associated Changes in Microglia and Astrocytes Ameliorate Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2021, 26, 970–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



