Submitted:
20 March 2024
Posted:
20 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Preprocessing
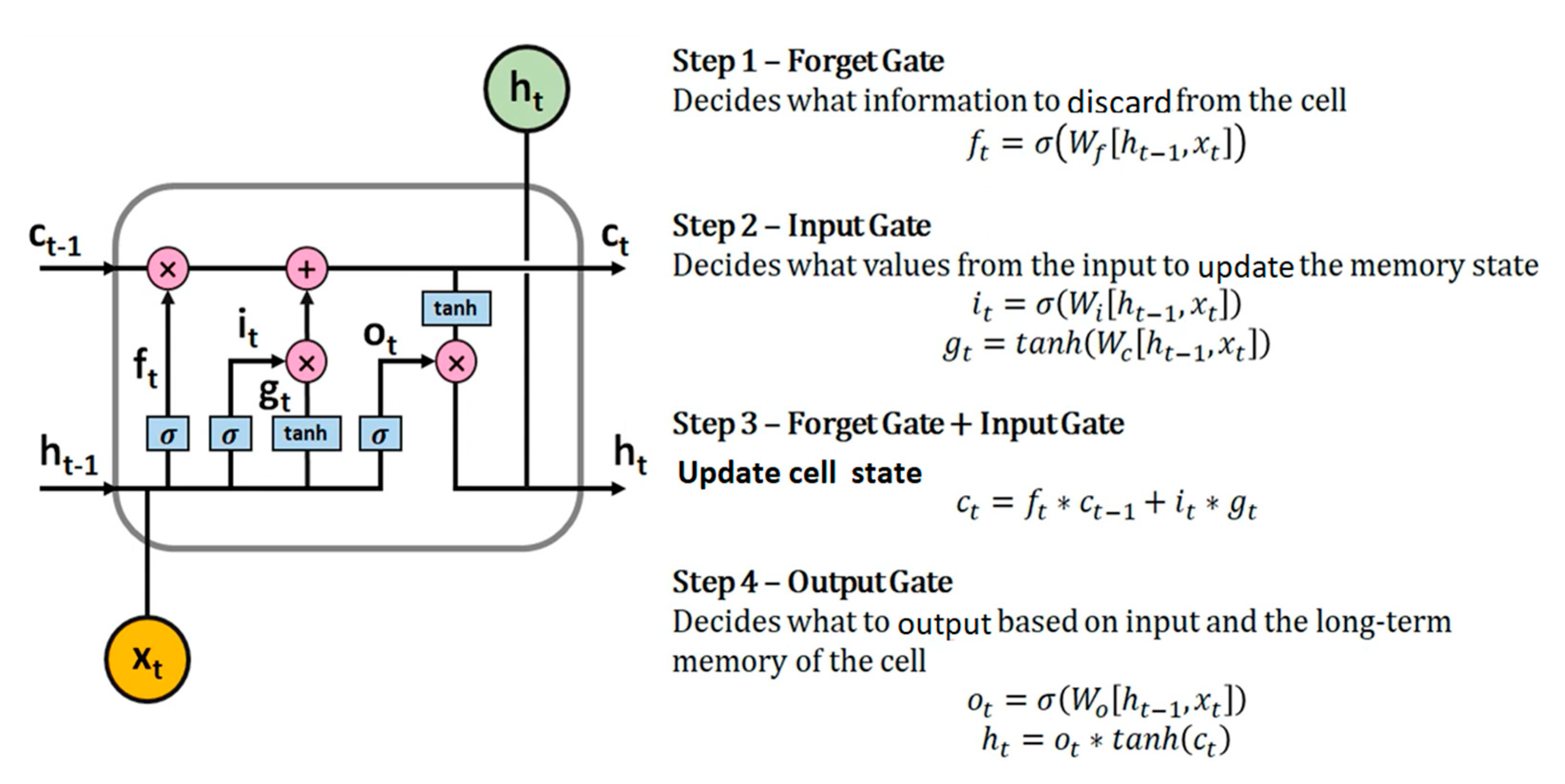
2.4. Structure of the Long Short Term Memory Model
- a)
- The forget gate
- b) Long-term state
- c) The input gate
- d) The output gate
2.5. Long Short-Term Memory Model Configuration
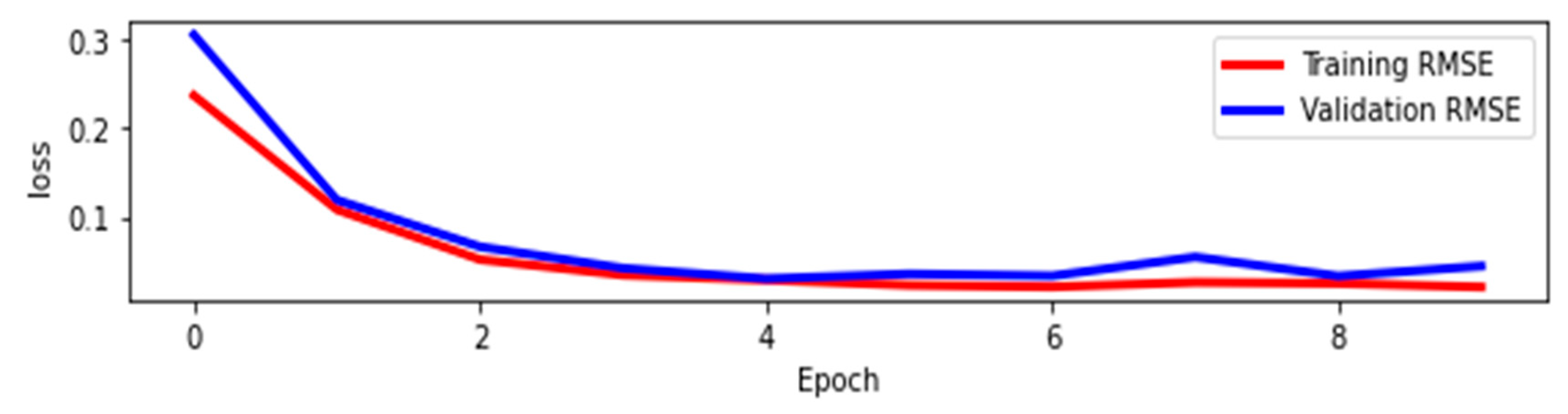
2.6. Model Performance Assessment
Results and Discussion
3.1. Variable Selection and Statistics
3.1.1. Selection of the Variables
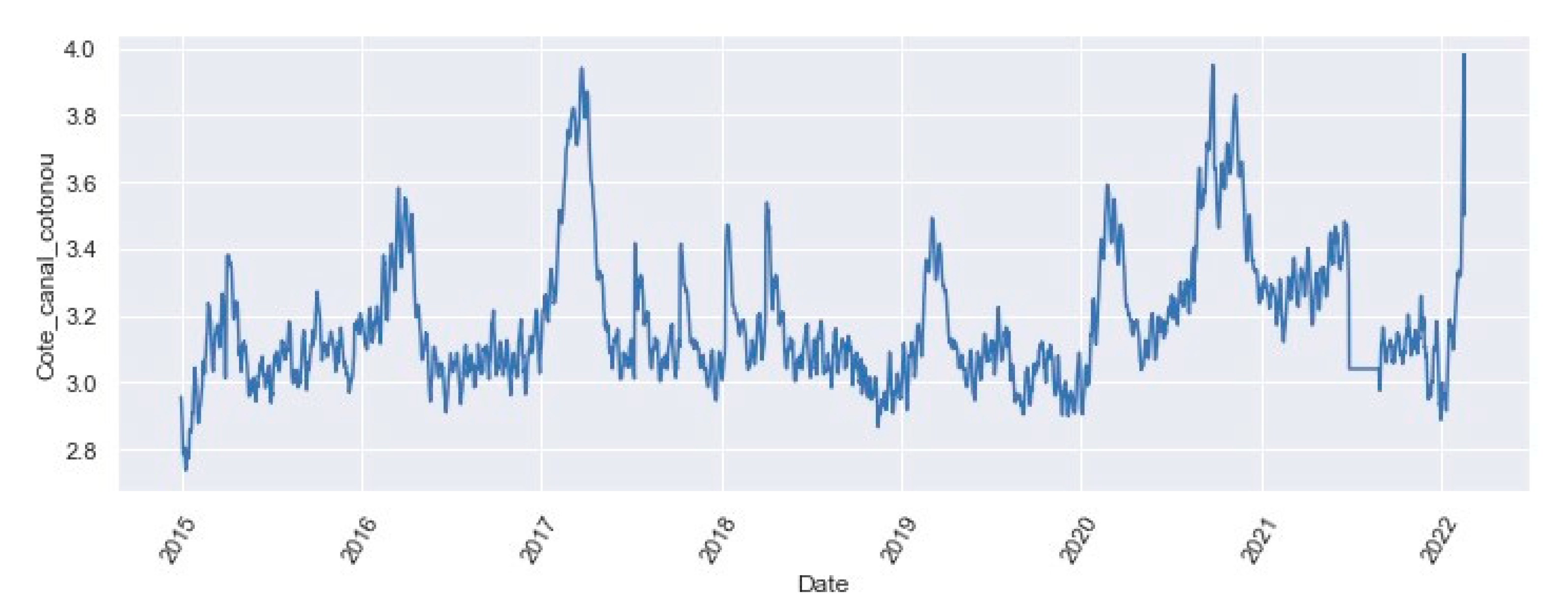
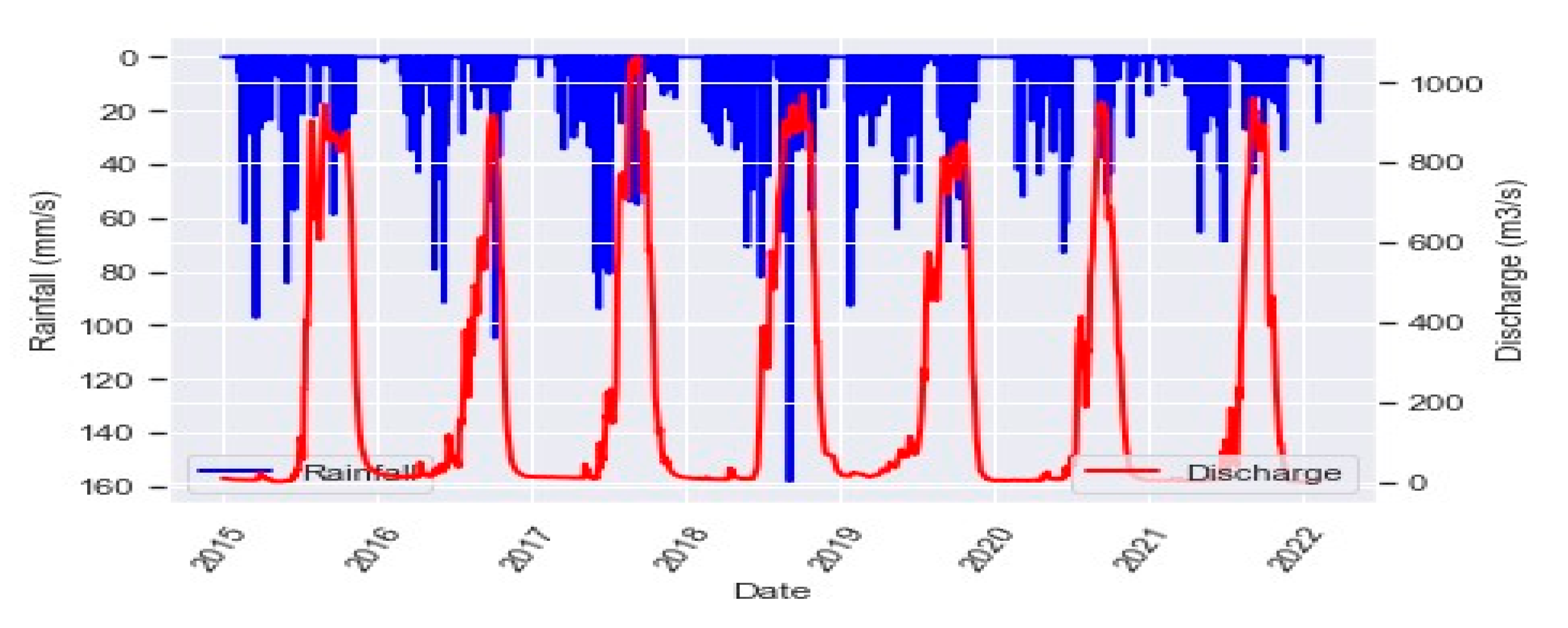
3.1.2. Statistics of the Variable
| statistics | rainfall | discharge | Water level |
|---|---|---|---|
| mean | 3.392 | 219.113 | 3.173 |
| std | 10.852 | 318.670 | 0.195 |
| min | 0.000 | 0.610 | 2.736 |
| 25% | 0.000 | 8.225 | 3.045 |
| 50% | 0.000 | 25.590 | 3.115 |
| 75% | 0.200 | 376.900 | 3.257 |
| max | 158.200 | 1064.000 | 3.981 |
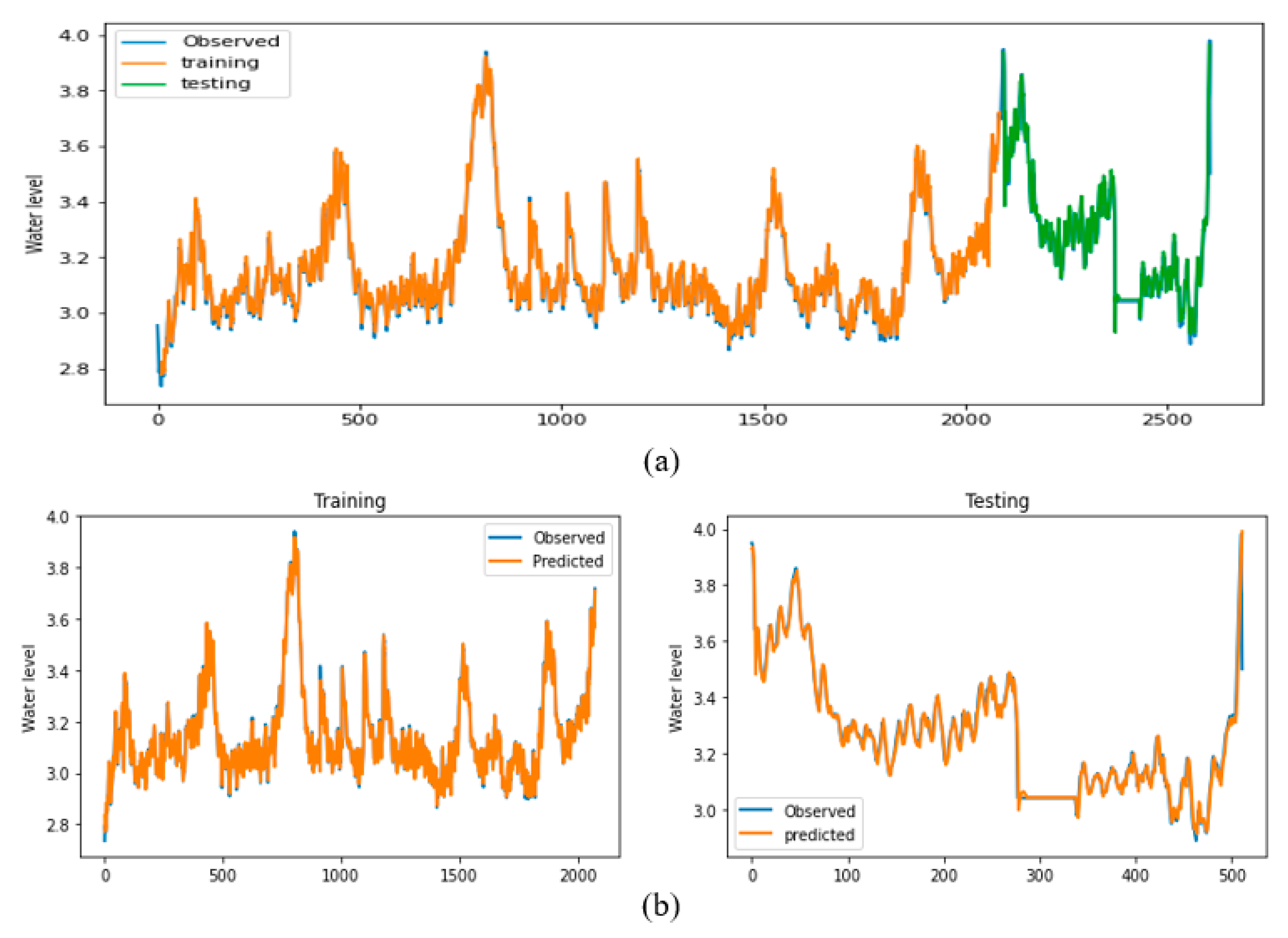
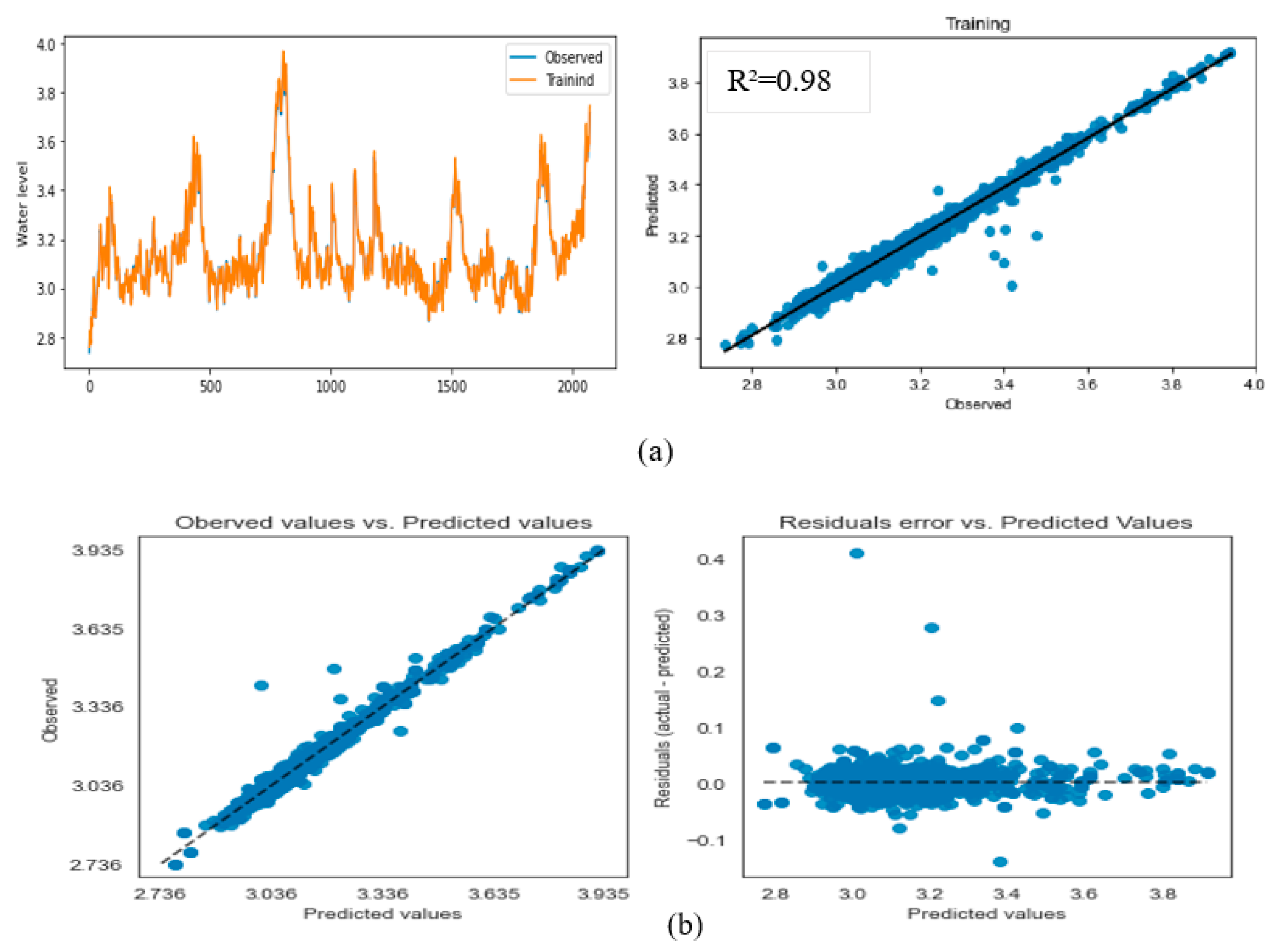
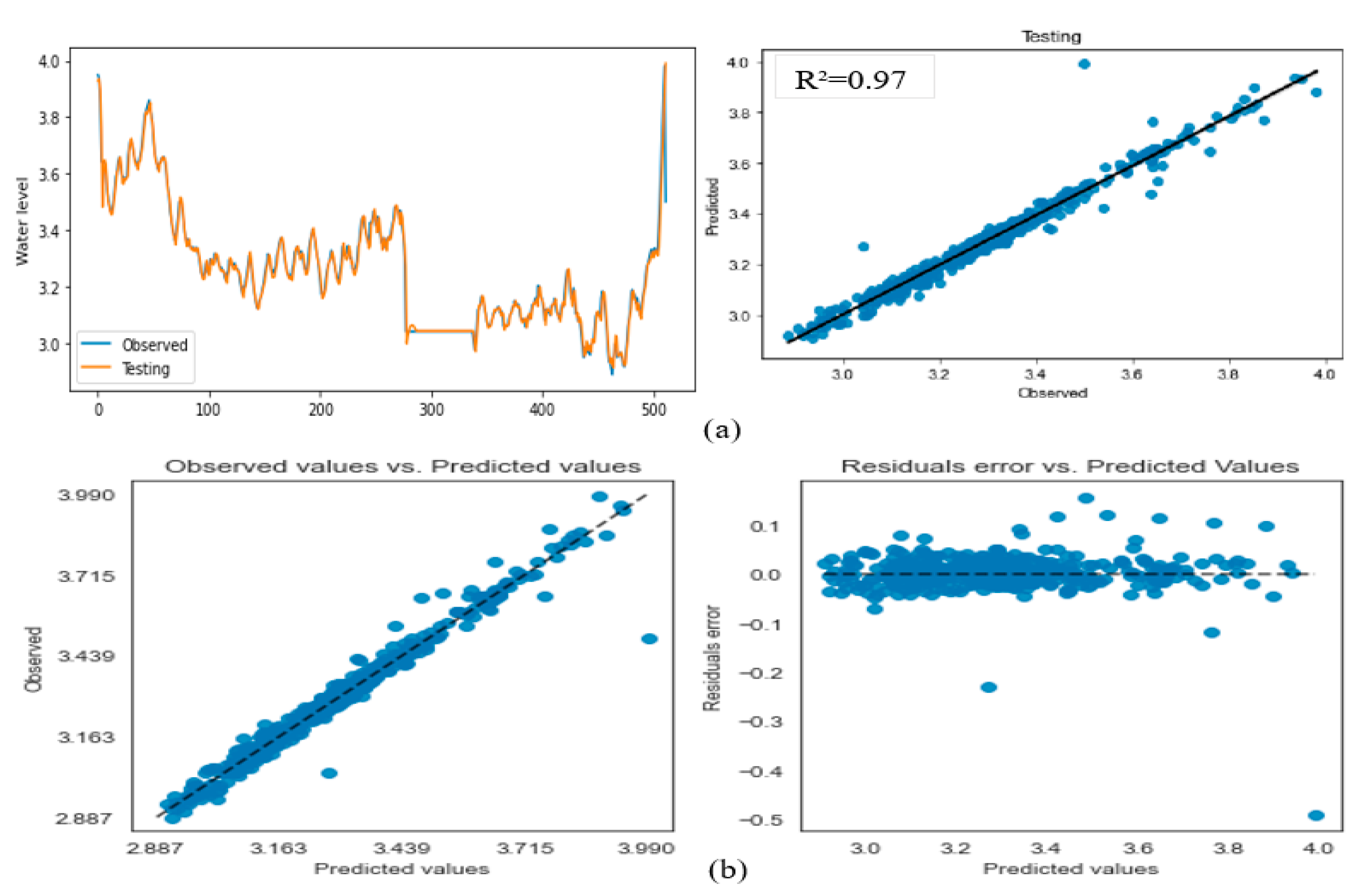
3.2. Model Performance Analysis
| Forecast horizon | Training step | Testing step | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | NSE | R² | MAE | RMSE | NSE | R² | MAE | |
|
t+1 day t+2 days t+3 days t+4 days t+5 days t+10 days |
0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 |
0.98 0.98 0.98 0.94 0.98 0.92 |
0.98 0.98 0.98 0.98 0.98 0.97 |
0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 |
0.04 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.03 0.04 |
0.97 0.97 0.97 0.96 0.97 0.90 |
0.97 0.97 0.97 0.97 0.97 0.96 |
0.03 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.03 |
Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of interest
References
- Chaigneau, A., Okpeitcha, O. V., Morel, Y., Stieglitz, T., Assogba, Morgane, B., Allamel, P., Honfos, J., Thierry Derol Awoulmbang, S., Retif, F., Duhaut, T., Peugeot, C. From seasonal flood pulse to seiche: Multi-frequency water-level fluctuations in a large shallow tropical lagoon (Nokoue Lagoon, Benin).ecss 2022, 267, 107-767.
- Ngoc, D. V. Deterministic hydrological modeling for flood risk assessment and climate change in large catchment: Application to Vu Gia Thu Bon catchment, Vietnam. Ph.D, Université Nice Sophia Antipolis, 2015.
- Rebolho, C. Modélisation conceptuelle de l’aléa inondation à l’échelle du bassin versant. Hydrology thesis doctorate, Ph.D, 2018.
- Golob, R., Štokelj, T., Grgič, D. Neural-network-based water inflow forecasting. Control Engineering Practice 1998, 6(5), 37-98.
- Ancona, M., Corradi, N., Dellacasa, A., Delzanno, G., Dugelay, J.-L., Federici, B., Gourbesville, P., Guerrini, G., La Caméra, A., Rosso, P., Stephens, J., Tacchella, A., Zolezzi, G. On the Design of an Intelligent Sensor Network for Flash Flood Monitoring, Diagnosis and Management in Urban Areas Position Paper. PCS 2014, 32, 941-946.
- Chen, L., & Singh, V. P. Flood forecasting and error simulation using copula entropy method. In P. Sharma & D. Machiwal (Éds.), Advances in Streamflow Forecasting 2021,6, 331-368.
- Chu, H., Wu, W., Wang, Q. J., Nathan, R., Wei, J. An ANN-based emulation modeling framework for flood inundation modeling: Application, challenges and future direction. envsoft 2019, 19, 104-587.
- Audrey Bornancin Plantier. Conception de modèles de prévision des crues éclair par apprentissage artificiel, informatic thesis doctorate. Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, 2013.
- Kharroubi, O., Blanpain, O., Masson, E., Lallahem, S. Application du réseau des neurones artificiels à la prévision des débits horaires : Cas du bassin versant de l’Eure, France. Hydrological Sciences Journal 2016, 61(3), 933–225. [Google Scholar]
- Peredo, D., Ramos, M.-H., Andréassian, V., Oudin, L. Investigating hydrological model versatility to simulate extreme flood events. Hydrological Sciences Journal 2022, 67(4), 628–645. [Google Scholar]
- Modeste Meliho. Spatial prediction of flood susceptible zones in the Ourika watershed of Morocco using machine learning algorithms. Aci 2022, 09, 2021-0264. [Google Scholar]
- Noor, F., Haq, S., Rakib, M., Ahmed, T., Jamal, Z., Siam, Z. S., Hasan, R. T., Adnan, M. S. G., Dewan, A., & Rahman, R. M. Water Level Forecasting Using Spatiotemporal Attention-Based Long Short-Term Memory Network. Water 2022, 14(4), 4040–612. [Google Scholar]
- Alliau, D., De Saint Seine, J., Lang, M., Sauquet, E., Renard, B. Étude du risque d’inondation d’un site industriel par des crues extrêmes : De l’évaluation des valeurs extrêmes aux incertitudes hydrologiques et hydrauliques. La Houille Blanche 2015, 101(2), 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, Y., Chaigneau, A., Okpeitcha, V. O., Stieglitz, T., Assogba, A., Duhaut, T., Rétif, F., Peugeot, C., & Sohou, Z. Terrestrial or oceanic forcing ? Water level variations in coastal lagoons constrained by river inflow and ocean tides. Hal open science 2022, 169, 104–309. [Google Scholar]
- Fathian, F. Introduction of multiple/multivariate linear and nonlinear time series models in forecasting streamflow process. In P. Sharma & D. Machiwal (Éds.), ASF 2021,12, 87-113.
- Wang, L., Dong, H., Cao, Y., Hou, D., Zhang, G. Real-time water quality detection based on fluctuation feature analysis with the LSTM model. Journal of Hydroinformatics 2023, 5, 127–305. [Google Scholar]
- Masselot, P., Dabo-Niang, S., Chebana, F., Ouarda, T. B. M. J. Streamflow forecasting using functional regression. J.Hydrol 2016, 538, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X., Yuan, X., Zhu, S., Xu, Z., Meng, L., Peng, J. A hybrid support vector regression framework for streamflow forecast. Journal of Hydrology, 2019; 568, 184–193. [Google Scholar]
- Douvinet, J., Serra-Llobet, A., Radke, J., Kondolf, M. Quels enseignements tirer des coulées de débris post-incendie survenues le 9 janvier 2018 à Montecito (Californie, USA) ? La Houille Blanche 2020, 106(6), 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M., Arnaud, P., Carreau, J., Deaux, N., Dezileau, L., Garavaglia, F., Latapie, A., Neppel, L., Paquet, E., Renard, B., Soubeyroux, J.-M., Terrier, B., Veysseire, J.-M., Aubert, Y., Auffray, A., Borchi, F., Bernardara, P., Carre, J.-C., Chambon, D., … Tramblay, Y. Résultats du projet ExtraFlo (ANR 2009-2013) sur l’estimation des pluies et crues extrêmes. La Houille Blanche 2014, 2, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Viatgé, J., Berthet, L., Marty, R., Bourgin, F., Piotte, O., Ramos, M.-H., & Perrin, C. Vers une production en temps réel d’intervalles prédictifs associés aux prévisions de crue dans Vigicrues en France. La Houille Blanche 2019, 105(2), 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein Hosseiny. A deep learning model for predicting river flood depth and extent. j.envsoft 2021, 145, 105–186. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H., Chen, Y., Fang, G., Li, Z., Duan, W., Zhang, Q. Adaptability of machine learning methods and hydrological models to discharge simulations in data-sparse glaciated watersheds. Journal of Arid Land 2021, 13(6), 549–567. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, H. R., & Dandy, G. C. Neural networks for the prediction and forecasting of water resources variables: A review of modeling issues and applications. J.envsoft 2000 15(1),101-124.
- Malik, A., Kumar, A., Tikhamarine, Y., Souag-Gamane, D., Kişi, Ö. Hybrid artificial intelligence models for predicting daily runoff. In P. Sharma, D. Machiwal (Éds.). A SF 2021, 12, 305-329.
- Barbe, Millet, Texier, Borel, Gualde. Les ressources en eaux superficielles de la République du Bénin. 1993, 540.
- Daouda Mama, Véronique Deluchat, James Bowen, Waris Chouti, Benjamin Yao, Baba Gnon,Michel Baudu. Caractérisation d’un Système Lagunaire en Zone Tropicale : Cas du lac Nokoué (Bénin). EJSR 2011, 56(4), 516–528. [Google Scholar]
- Metogbe Belfrid Djihouessi, Martin Pépin Aina. A review of hydrodynamics and water quality of Lake Nokoué: Current state of knowledge and prospects for further research. j.rsma 2018, 17, 2352-4855.
- Texier, H., Colleuil, B., Profizi, J. P., Dossou, C. (1980). Le lac Nokoué, environnement du domaine margino-littoral sud-béninois : Bathymétrie, lithofaciès, salinité, mollusque et peuplements végétaux (No 28 ; p. 115-142).
- Tore, D. B., Alamou, A. E., Obada, E., Biao, E. I., Zandagba, E. B. J. Assessment of Intra-Seasonal Variability and Trends of Precipitations in a Climate Change Framework in West Africa. ACS 2022, 12(01), 150–171. [Google Scholar]
- Sedai, A., Dhakal, R., Gautam, S., Dhamala, A., Bilbao, A., Wang, Q., Wigington, A., & Pol, S. Performance Analysis of Statistical, Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models in Long-Term Forecasting of Solar Power Production. Forecasting 2023, 5(1), 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, K., Rossi, A., Carraro, D., Visentin, A. On Forecasting Cryptocurrency Prices: A Comparison of Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Ensembles. Forecasting 2023, 5(1), 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X., Guo, H., Huang, J. J., Tian, S., Xu, W., Mai, Y. An ensemble machine learning model for water quality estimation in coastal areas based on remote sensing imagery. JEM, 2022, 323, 116–187. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, M., Ogliari, E., Nespoli, A., Simpkins, T., Leva, S. Day Ahead Electric Load Forecast: A Comprehensive LSTM-EMD Methodology and Several Diverse Case Studies. Forecasting 2023, 5(1), 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ömer Faruk, D. A hybrid neural network and ARIMA model for water quality time series prediction. EAAI 2010, 23(4), 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P., Machiwal, D. Streamflow forecasting: Overview of advances in data-driven techniques. In P. Sharma, D. Machiwal (Éds.). ASF 2021, 82(6), 1-50.
- Calèche Nehemie Nounagnon Avahouin, Henri Sourou Totin Vodounon, Ernest, Amoussou. Variabilité climatique et production halieutique du lac Nokoué dans les Aguégués au Bénin. 2018, 8(2), 51–61.
- Kawoun Alagbe Gildas, Ahamide Bernard, Chabi Amédée, Ayena Abraham, Adandedji Firminn, & Vissin Expédit. Variabilité Pluvio-Hydrologique et Incidences sur les Eaux de Surface dans la Basse Vallée de l’Ouémé au Sud-Est Bénin. IJPSAT 2020, 23(2), 52–65. [Google Scholar]
- Line Kong A Siou, Anne Johannet, Valérie Borrell, Séverin Pistre. Complexity selection of a neural network model for karst flood forecasting: The case of the Lez Basin (southern France). jhydrol 2011, 403, 367-380.
- Hu, C., Q. Wu, H. Li, S. Jian, N. Li, and Z. Lou. Deep learning with a long short-term memory networks approach for rainfall-runoff simulation. Water 2018,10 (11), 1543.
- Thapa, S.; Zhao, Z.; Li, B.; Lu, L.; Fu, D.; Shi, X.; Qi, H. Snowmelt-driven streamflow prediction using machine learning techniques (LSTM, NARX, GPR, and SVR). Water 2020, 12, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Wang, D.; Singh, V.P.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, J. Streamflow and rainfall forecasting by two long short-term memory-based models. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Fang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zang, D. Reservoir inflow prediction using a hybrid model based on deep learning. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 715, 012044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





