Submitted:
19 March 2024
Posted:
19 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
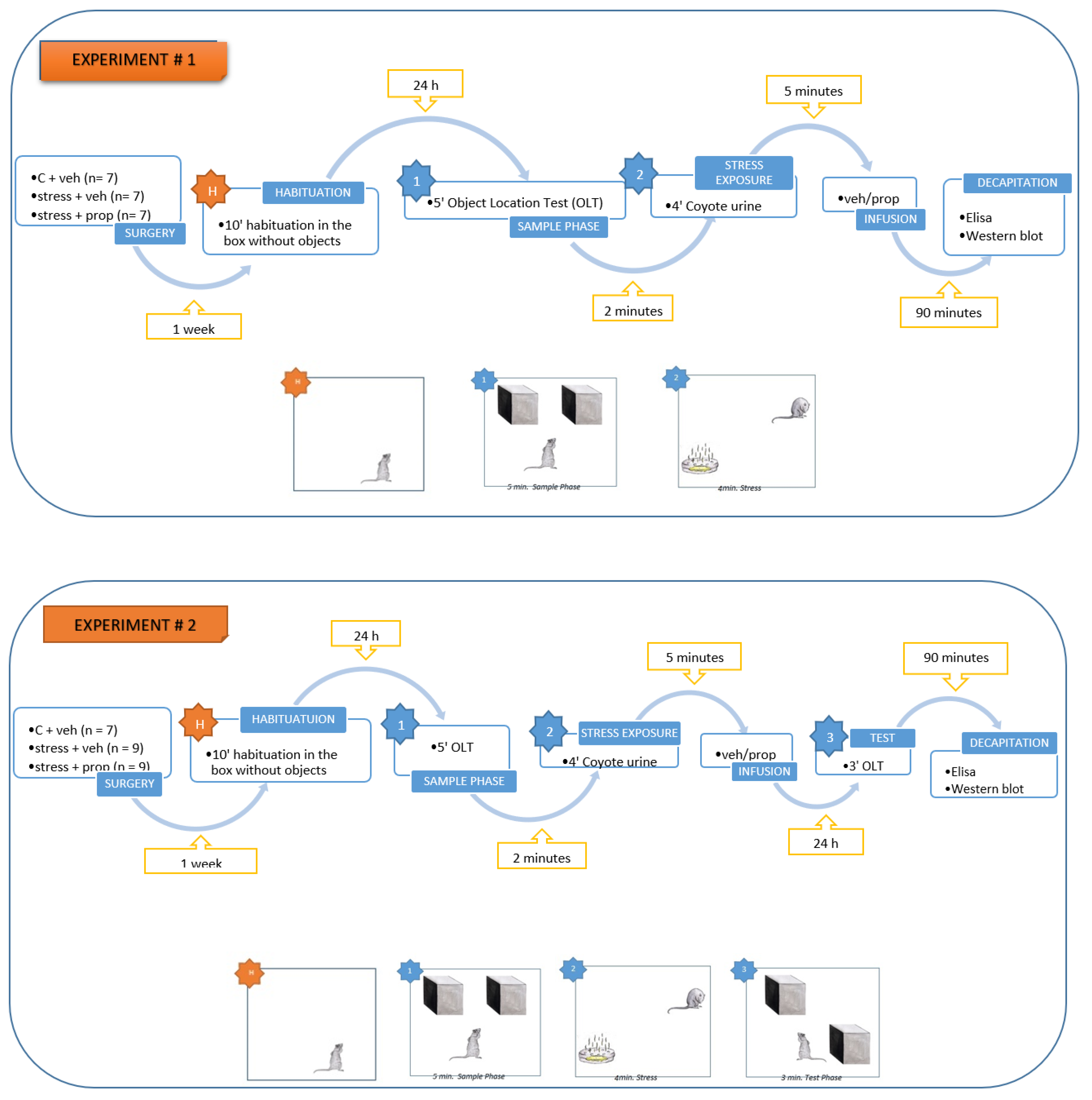
2.1. Experiment #1
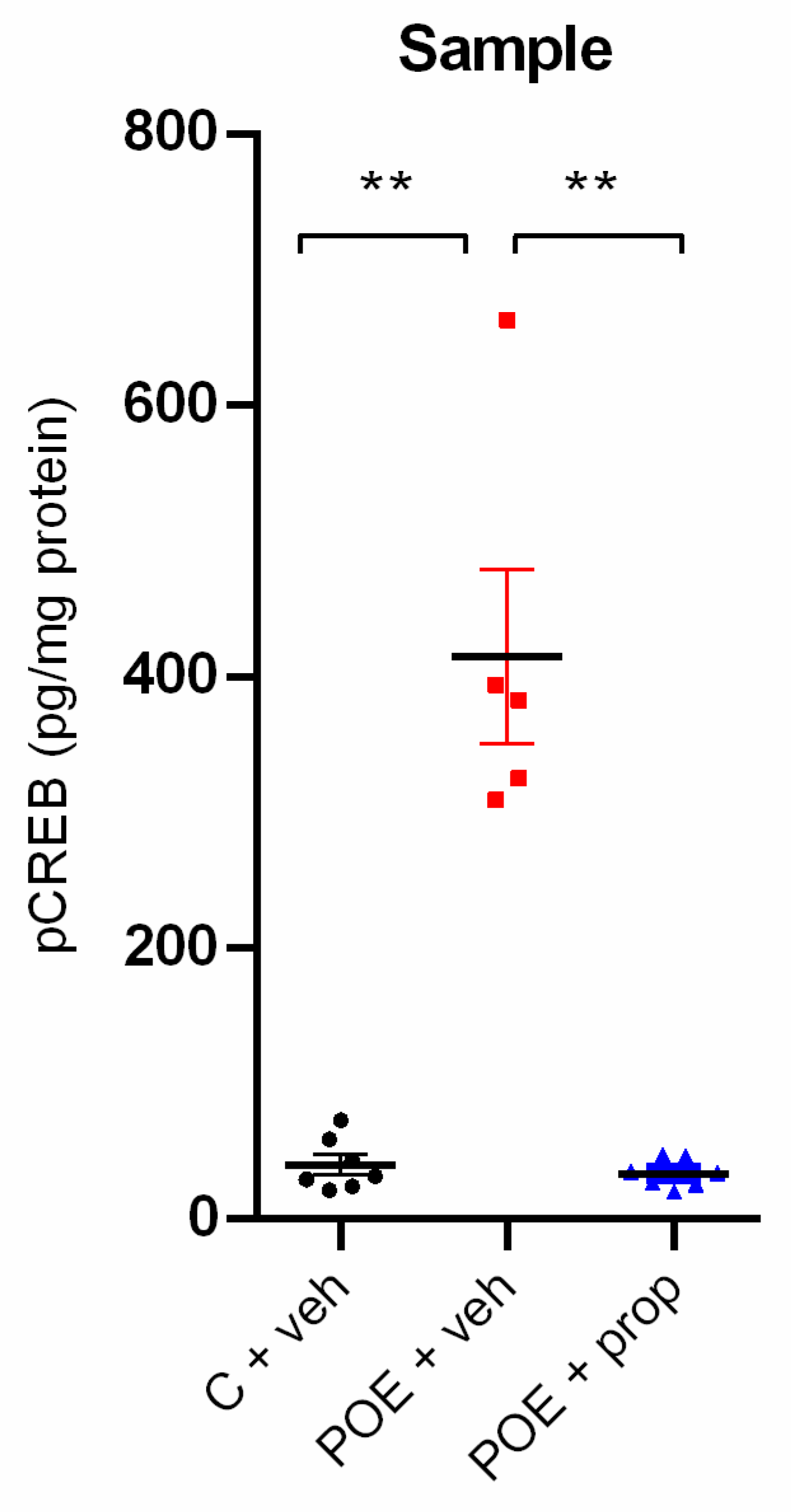
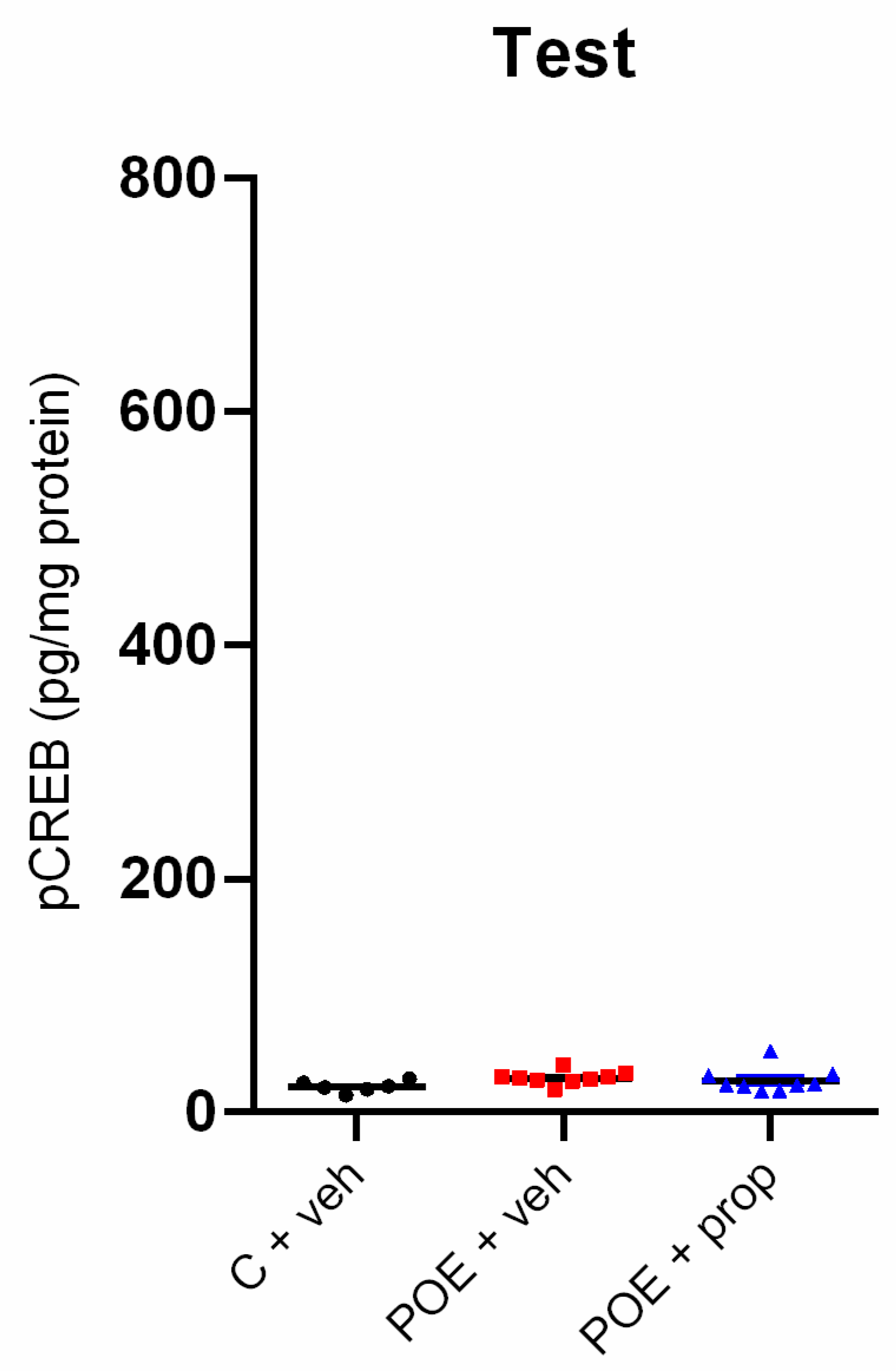
2.1.1. Post-Training Propranolol Infusion Suppresses the Effect of the Exposure to a Natural Aversive Stimulus (Coyote Urine) on Hippocampal pCREB Expression
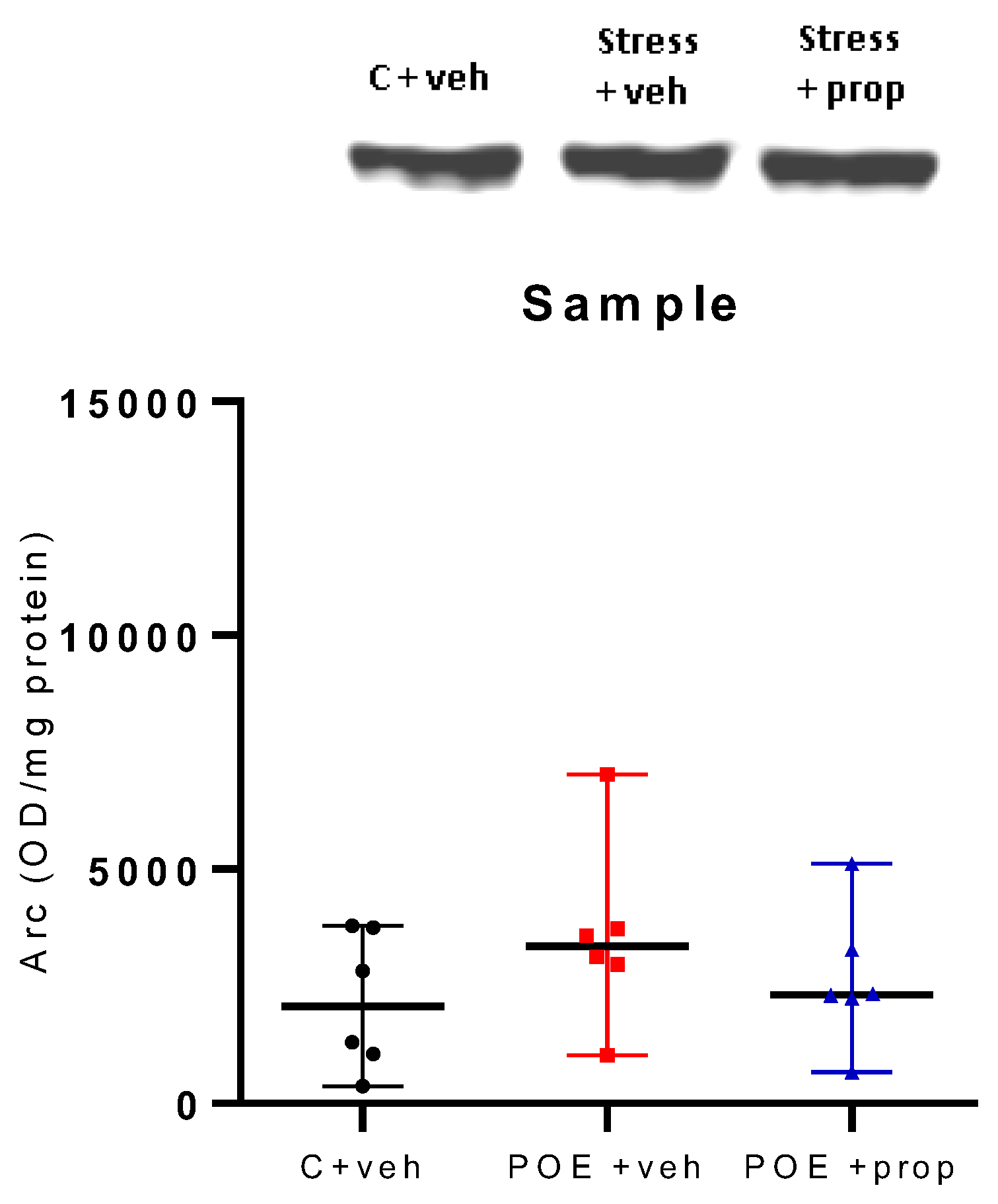
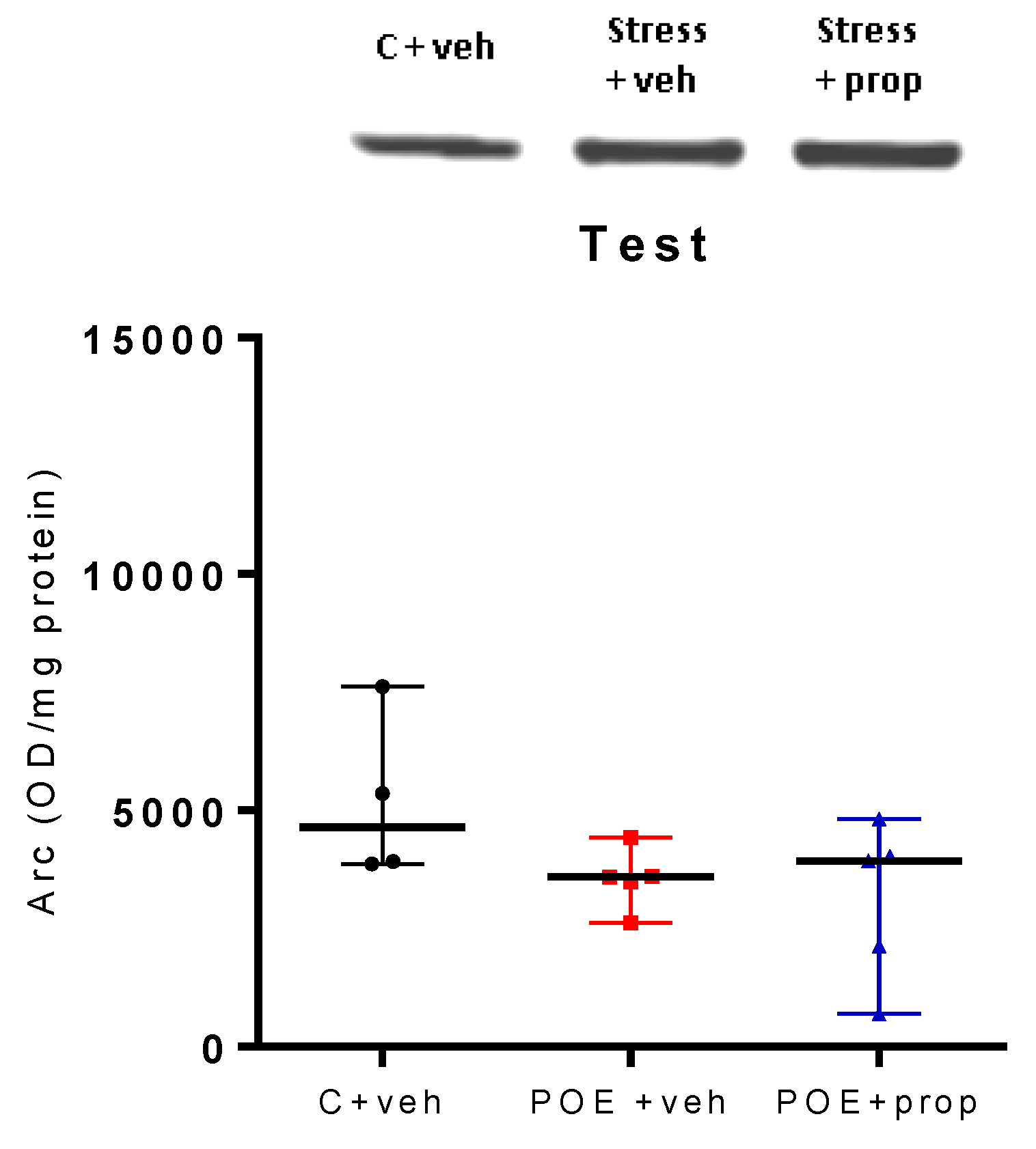
2.1.2. The Arc Expression in the Hippocampus Showed a Tendency for Elevation as a Sequence of Post-Training Exposure to a Natural Aversive Stimulus (Coyote Urine)
2.2. Experiment # 2
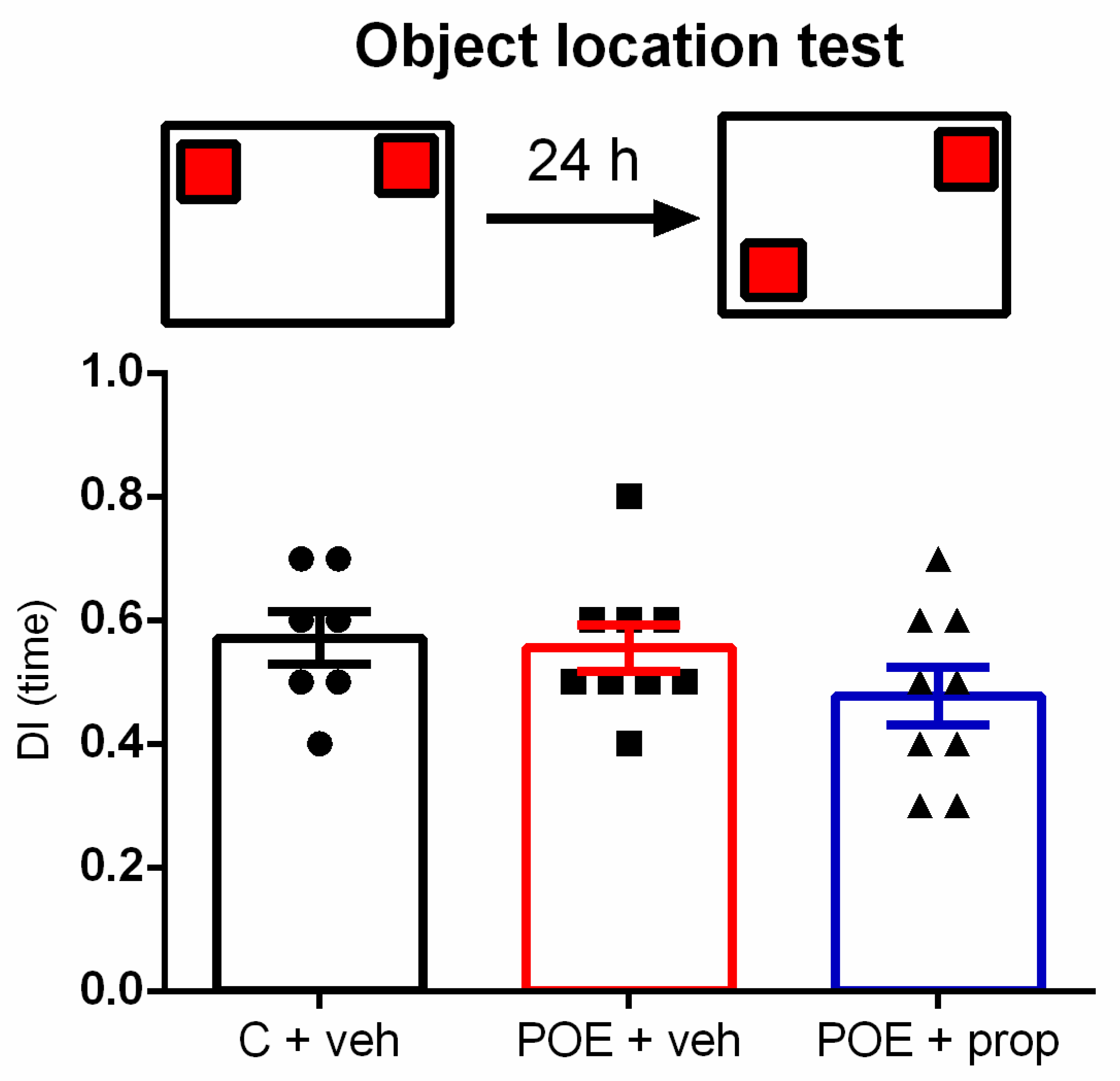
2.2.1. Acute Post-Training Exposure to a Natural Aversive Stimulus (Coyote Urine) Did Not Affect the Performance of Rats on the Object Location Task
2.2.2. Acute Post-Training Exposure to a Natural Aversive Stimulus (Coyote Urine) and Propranolol Infusion Did Not Change the pCREB Expression in the Hippocampus in the Retention Phase
2.2.3. Acute Post-Training Exposure to Predator Odor and Propranolol Infusion Did Not Change the Arc Expression in the Hippocampus in the Retention Phase
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Object Localization Test
4.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Test
4.5. Western Blot Test
Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sugar, J.; Moser, M. Episodic Memory: Neuronal Codes for What, Where, and When. Hippocampus 2019, 29, 1190–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T. A.; Fortin, N. J. The Evolution of Episodic Memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2013, 110 (Suppl. S2), 10379–10386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanselow, M. S.; Dong, H.-W. Are the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus Functionally Distinct Structures? Neuron 2010, 65, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenbaum, H. Hippocampus. Neuron 2004, 44, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, K.; Højgaard, K.; Privitera, L.; Bayraktar, G.; Takeuchi, T. Initial Memory Consolidation and the Synaptic Tagging and Capture Hypothesis. Eur J of Neuroscience 2021, 54, 6826–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisman, J.; Grace, A. A.; Duzel, E. A neoHebbian Framework for Episodic Memory; Role of Dopamine-Dependent Late LTP. Trends in Neurosciences 2011, 34, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P. V.; Connor, S. A. Noradrenergic Regulation of Hippocampus-Dependent Memory. CNSAMC 2019, 19, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finsterwald, C.; Alberini, C. M. Stress and Glucocorticoid Receptor-Dependent Mechanisms in Long-Term Memory: From Adaptive Responses to Psychopathologies. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 2014, 112, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaLumiere, R. T.; McGaugh, J. L.; McIntyre, C. K. Emotional Modulation of Learning and Memory: Pharmacological Implica-tions. Pharmacol Rev 2017, 69, 236–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, G.; Morris, R. G. M. Memory, Novelty and Prior Knowledge. Trends in Neurosciences 2018, 41, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunsmoor, J. E.; Murty, V. P.; Clewett, D.; Phelps, E. A.; Davachi, L. Tag and Capture: How Salient Experiences Target and Rescue Nearby Events in Memory. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 2022, 26, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, M. J.; Kulesza, A.; Werkle-Bergner, M.; Mather, M. Declining Locus Coeruleus–Dopaminergic and Noradrenergic Modulation of Long-Term Memory in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2023, 153, 105358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duszkiewicz, A. J.; McNamara, C. G.; Takeuchi, T.; Genzel, L. Novelty and Dopaminergic Modulation of Memory Persistence: A Tale of Two Systems. Trends in Neurosciences 2019, 42, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, N. The Longevity of Hippocampus-Dependent Memory Is Orchestrated by the Locus Coeruleus-Noradrenergic System. Neural Plasticity 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redondo, R. L.; Morris, R. G. M. Making Memories Last: The Synaptic Tagging and Capture Hypothesis. Nat Rev Neurosci 2011, 12, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncada, D.; Ballarini, F.; Viola, H. Behavioral Tagging: A Translation of the Synaptic Tagging and Capture Hypothesis. Neural Plasticity 2015, 2015, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, S.; Raisuddin, S.; Parvez, S. Behavioral Tagging: A Novel Model for Studying Long-Term Memory. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2016, 68, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballarini, F.; Moncada, D.; Martinez, M. C.; Alen, N.; Viola, H. Behavioral Tagging Is a General Mechanism of Long-Term Memory Formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2009, 106, 14599–14604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, S.; Raisuddin, S.; Parvez, S. Behavioral Tagging: Role of Neurotransmitter Receptor Systems in Novel Object Recognition Long-Term Memory. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 11587–11595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada, D.; Ballarini, F.; Martinez, M. C.; Frey, J. U.; Viola, H. Identification of Transmitter Systems and Learning Tag Molecules Involved in Behavioral Tagging during Memory Formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2011, 108, 12931–12936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, K. R.; Da Rosa, A. C. D. S.; Picua, S. S.; E Silva, S. S.; Soares, N. M.; Mello-Carpes, P. B. Novelty Promotes Recognition Memory Persistence by D1 Dopamine Receptor and Protein Kinase A Signalling in Rat Hippocampus. Eur J of Neuroscience 2022, 55, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes Da Cunha, P.; Villar, M. E.; Ballarini, F.; Tintorelli, R.; Ana María Viola, H. Spatial Object Recognition Memory Formation under Acute Stress. Hippocampus 2019, 29, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes Da Cunha, P.; Tintorelli, R.; Correa, J.; Budriesi, P.; Viola, H. Behavioral Tagging as a Mechanism for Aversive-memory Formation under Acute Stress. Eur J of Neuroscience 2022, 55, 2651–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janak, P. H.; Tye, K. M. From Circuits to Behaviour in the Amygdala. Nature 2015, 517, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-H.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Holmes, A.; Pan, B.-X. Amygdala Circuit Substrates for Stress Adaptation and Adversity. Biological Psychiatry 2021, 89, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockett, A. T.; Vázquez, D.; Roesch, M. R. Prediction Errors and Valence: From Single Units to Multidimensional Encoding in the Amygdala. Behavioural Brain Research 2021, 404, 113176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatelli, M.; Beyeler, A. Valence Coding in Amygdala Circuits. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences 2019, 26, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesler, R.; Parent, M. B.; LaLumiere, R. T.; McIntyre, C. K. Amygdala-Hippocampal Interactions in Synaptic Plasticity and Memory Formation. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 2021, 184, 107490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergado, J. A.; Lucas, M.; Richter-Levin, G. Emotional Tagging—A Simple Hypothesis in a Complex Reality. Progress in Neurobiology 2011, 94, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, E. J.; Battaglia, F. P.; Atsak, P.; De Voogd, L. D.; Fernández, G.; Roozendaal, B. How the Amygdala Affects Emotional Memory by Altering Brain Network Properties. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 2014, 112, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozendaal, B.; McEwen, B. S.; Chattarji, S. Stress, Memory and the Amygdala. Nat Rev Neurosci 2009, 10, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paré, D.; Headley, D. B. The Amygdala Mediates the Facilitating Influence of Emotions on Memory through Multiple Interacting Mechanisms. Neurobiology of Stress 2023, 24, 100529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manns, J. R.; Bass, D. I. The Amygdala and Prioritization of Declarative Memories. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 2016, 25, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roesler, R.; McGaugh, J. L. The Entorhinal Cortex as a Gateway for Amygdala Influences on Memory Consolidation. Neuroscience 2022, 497, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz, R.; Pare, D. Physiological Basis for Emotional Modulation of Memory Circuits by the Amygdala. Current Opinion in Neurobiology 2013, 23, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, D. I.; Nizam, Z. G.; Partain, K. N.; Wang, A.; Manns, J. R. Amygdala-Mediated Enhancement of Memory for Specific Events Depends on the Hippocampus. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 2014, 107, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, D. I.; Partain, K. N.; Manns, J. R. Event-Specific Enhancement of Memory via Brief Electrical Stimulation to the Basolateral Complex of the Amygdala in Rats. Behavioral Neuroscience 2012, 126, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, M. L.; Miller, R. L.; Deisseroth, K.; Moorman, D. E.; LaLumiere, R. T. Posttraining Optogenetic Manipulations of Basolateral Amygdala Activity Modulate Consolidation of Inhibitory Avoidance Memory in Rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2013, 110, 3597–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozendaal, B.; Okuda, S.; Van Der Zee, E. A.; McGaugh, J. L. Glucocorticoid Enhancement of Memory Requires Arousal-Induced Noradrenergic Activation in the Basolateral Amygdala. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2006, 103, 6741–6746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McReynolds, J. R.; Donowho, K.; Abdi, A.; McGaugh, J. L.; Roozendaal, B.; McIntyre, C. K. Memory-Enhancing Corticosterone Treatment Increases Amygdala Norepinephrine and Arc Protein Expression in Hippocampal Synaptic Fractions. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 2010, 93, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, C. K.; Miyashita, T.; Setlow, B.; Marjon, K. D.; Steward, O.; Guzowski, J. F.; McGaugh, J. L. Memory-Influencing Intra-Basolateral Amygdala Drug Infusions Modulate Expression of Arc Protein in the Hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005, 102, 10718–10723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McReynolds, J. R.; Anderson, K. M.; Donowho, K. M.; McIntyre, C. K. Noradrenergic Actions in the Basolateral Complex of the Amygdala Modulate Arc Expression in Hippocampal Synapses and Consolidation of Aversive and Non-Aversive Memory. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 2014, 115, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsegyan, A.; McGaugh, J. L.; Roozendaal, B. Noradrenergic Activation of the Basolateral Amygdala Modulates the Consolidation of Object-in-Context Recognition Memory. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McReynolds, J. R.; Carreira, M. B.; McIntyre, C. K. Post-Training Intra-Basolateral Complex of the Amygdala Infusions of Clenbuterol Enhance Memory for Conditioned Place Preference and Increase ARC Protein Expression in Dorsal Hippocampal Synaptic Fractions. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 2021, 185, 107539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korb, E.; Finkbeiner, S. Arc in Synaptic Plasticity: From Gene to Behavior. Trends in Neurosciences 2011, 34, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaienko, O.; Patil, S.; Eriksen, M. S.; Bramham, C. R. Arc Protein: A Flexible Hub for Synaptic Plasticity and Cognition. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology 2018, 77, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramham, C. R.; Alme, M. N.; Bittins, M.; Kuipers, S. D.; Nair, R. R.; Pai, B.; Panja, D.; Schubert, M.; Soule, J.; Tiron, A.; Wibrand, K. The Arc of Synaptic Memory. Exp Brain Res 2010, 200, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, R. Neuronal Plasticity in the Amygdala Following Predator Stress Exposure. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, D. M.; Lemon, J. K.; Fluegge, D.; Pashkovski, S. L.; Korzan, W. J.; Datta, S. R.; Spehr, M.; Fendt, M.; Liberles, S. D. Detection and Avoidance of a Carnivore Odor by Prey. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2011, 108, 11235–11240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes-Marco, L.; Lanuza, E.; Martinez-Garcia, F. Of Pheromones and Kairomones: What Receptors Mediate Innate Emotional Responses? The Anatomical Record 2013, 296, 1346–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. E.; Fraize, N. P.; Yin, L.; Yuan, R. K.; Petsagourakis, D.; Wann, E. G.; Muzzio, I. A. Differential Roles of the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus in Predator Odor Contextual Fear Conditioning. Hippocampus 2013, 23, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, R. K.; Hebert, J. C.; Thomas, A. S.; Wann, E. G.; Muzzio, I. A. HDAC I Inhibition in the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus Differentially Modulates Predator-Odor Fear Learning and Generalization. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestas-Olguin, C. R.; Parish, M. M.; Pentkowski, N. S. Coyote Urine, but Not 2-Phenylethylamine, Induces a Complete Profile of Unconditioned Anti-Predator Defensive Behaviors. Physiology & Behavior 2021, 229, 113210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, J.-P.; Guzmán-Ramos, K.; Bermudez-Rattoni, F. New Insights on Retrieval-Induced and Ongoing Memory Consolidation: Lessons from Arc. Neural Plasticity 2015, 2015, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberini, C. M.; Kandel, E. R. The Regulation of Transcription in Memory Consolidation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2015, 7, a021741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberini, C. M. Transcription Factors in Long-Term Memory and Synaptic Plasticity. Physiological Reviews 2009, 89, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabitzke, P. A.; Silva, L.; Wiedenmayer, C. Norepinephrine Mediates Contextual Fear Learning and Hippocampal pCREB in Juvenile Rats Exposed to Predator Odor. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 2011, 96, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada, D.; Viola, H. Phosphorylation State of CREB in the Rat Hippocampus: A Molecular Switch between Spatial Novelty and Spatial Familiarity? Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 2006, 86, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazma, M. A.; Shields, G. S.; Yonelinas, A. P. The Effects of Post-Encoding Stress and Glucocorticoids on Episodic Memory in Humans and Rodents. Brain and Cognition 2019, 133, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliaro, M. Effects on Behavior by Different Exposure Durations of Predator Scent Stress. aip 2020, 10, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




