1. Introduction
The ocean mixed layer serves as an important role in the global climate dynamics due to its capacity to store vast amounts of heat compared to the atmosphere. Its variability is one of most important quantities of the upper ocean processes because it can identify the surface region that directly interacts with the atmosphere. It has a broad influence on determining the volume or mass of distributed net surface heat flux [
1], near surface navigational pulse propagation [
2] and ocean ecosystem [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. Ocean waves, surface currents and evaporation and precipitation can all cause significant mixing in the upper ocean which in turn effects changes in the mixed layer depth [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15].
The ocean mixed layer depth is generally defined as homogeneous region in upper ocean where has little variations in temperature (0.2-0.5°C [
16,
17]), or density (0.01-0.03 kg/m
3 [
16,
18]) in depth. It is predominantly determined by the process of the turbulent mixing due to the winds and heat exchange at the air-sea interface. Most notably, both military and civilian have an interest in recognizing where the MLD is exactly located for their operations. In particular, U.S. Navy operates in the MLD over the world on a daily basis, such as the activities of submarine and underwater autonomous vehicle operations. Every U.S. Navy platform will practically come across with the MLD in any case [
19]. MLD is generally derived from the oceanic profiles (e.g. temperature, density, salinity) which can be homogeneous from the water surface to a certain depth [
20]. Typically, salinity and temperature field are controlled by wind-driven processes and thermohaline circulation [
21]. They are transported and transformed by interaction with currents and turbulent mixing in the ocean, which are often driven by winds. Data show that intense winds, such as “
Shamal”- Arabian Gulf [
22],
“Mistral”- Northern Mediterranean Sea [
23],
“Bora”- Adriatic Sea [
24], lead to surface mixing, convective cooling and overturning with surface heat loss leading to significant changes in the mixed layer.
Extreme weather conditions, such as tropical cyclones and intense storms, are particularly likely to have a major impact on mixing dynamics and transport by surface forcing (e.g. wind stress, heat flux, surface wave effects, transport, etc.). However, it is not yet fully understood how the extreme weather conditions might affect the mixed layer, nor is it clear how much time it takes before the ocean returns to its former state. Several studies of Hurricanes Gilbert [
25,
26], Opal [
27], Lili [
28], Ivan [
29], Katrina and Rita [
30,
31,
32] in the Gulf of Mexico have exhibited the storm impact on the upper ocean variability by the tropical cyclone intensity. Early observations including ship-based [
33,
34], aircraft-based [
35], mooring-based [
36,
37] resulted in maximum sea surface temperature (SST) decreases of 1°C to 6°C to the right of the storm track. The temperature in upper ocean mixed layer was reduced by about 6°C [
38], 1-5°C [
31], 3-4°C [
39], 2-4.5°C [
40] and exceeded 5°C [
29,
41] by hurricanes in the Gulf of Mexico. These changes are attributed to the dynamic cooling and dissipative heating processes at the surface layer [
42,
43], which can affect the transport of heat flux and establishment of thermocline gradient [
44].
Unfortunately, the lack of temperature and salinity data with depth in any particular region inhibits the description of proper definition of MLD, so that may cause misleading information and incorrect predictions on the upper ocean mixed layer. The lack of adequate observation hinders description of thermocline, thermohaline and pycnocline processes, variations of lateral and vertical mixing and physical and oceanic processes for deducing the MLD, particularly during extreme weather events. Thus, it is also important to determine the MLD in the ocean during extreme weather conditions because it plays an important role in a wide variety of oceanic investigations [
18]. The recovery rate (or time) of MLD from strong wind and other extreme weather events will help to minimize the potential errors and incorrect predictions during humanitarian and military operations. Because of high importance of MLD in global ocean, many techniques have been used to determine the MLD. Several studies [
25,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49], including field data analysis, experiments and numerical simulations, show the influence of spatial and temporal variations of MLD on the tropical cyclones.
This study aimed to examine how extreme weather events, particularly Hurricane Katrina in 2005, impact the Mixed Layer Depth (MLD) in the Gulf of Mexico. We utilized the Delft3D modeling system, which offers advanced simulations of ocean physics like hydrodynamics and wave dynamics. This allows for a detailed understanding of processes such as wind-wave interactions and depth-induced breaking, crucial for accurately capturing the ocean’s response to severe weather. Our goal was to gain insights into how hurricanes affect ocean dynamics, temperature, salinity, and the recovery rates of the MLD. It’s worth noting that intense storms can cause regional mixing, anomalies in temperature and salinity, and variations in heat transport and the gradient of the thermocline, which impacts its recovery time. These effects can have implications for environmental health and various civilian and military operations in the affected area. While data during extreme events is limited in the Gulf of Mexico, we utilized available in-situ data to inform our modeling approach. By employing the comprehensive Delft3D system, we aimed to better understand the hydrographic responses of oceanic water columns to extreme weather events.
2. General Background and Methods
2.1. Study Area
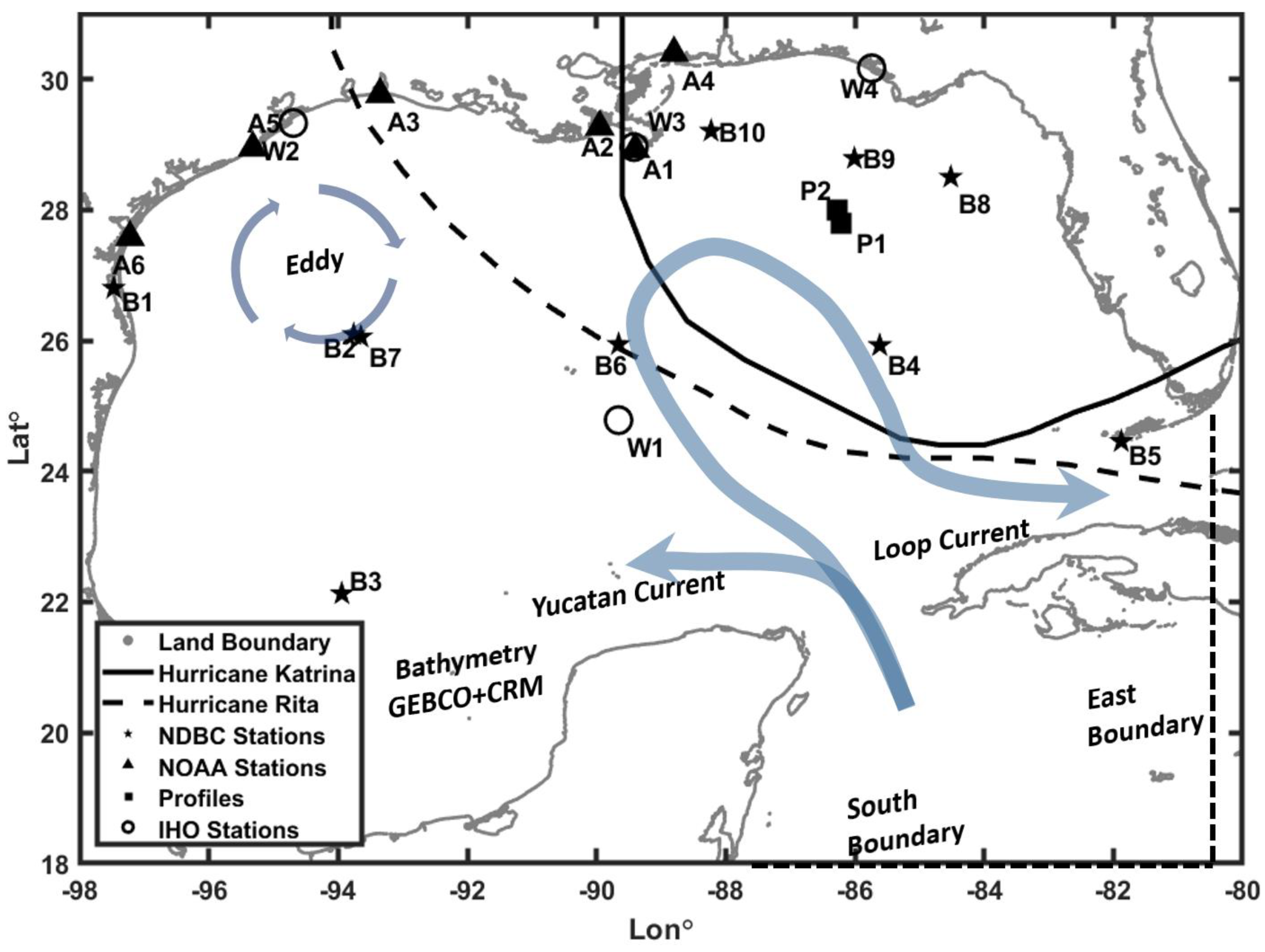
The Gulf of Mexico, situated between the Strait of Florida and the Yucatan Channel, stretches across the coordinates of 18-31° N and 99-81° W (
Figure 1), representing a vast expanse of water. Its diverse terrain includes coastal regions, continental shelves, and an abyssal plain, boasting an average depth of approximately 1,615 m over its expansive 1.6 million km
2 surface area [
50]. Economically and ecologically, the Gulf holds significant importance both regionally and globally. Its rich energy resources support a thriving industry, with oil production reaching 1.65 million barrels per day in 2017 [
51], sustaining over 55,000 jobs [
52]. Additionally, the Gulf’s diverse marine ecosystems, including vibrant coral environments, harbor a plethora of marine species, underscoring its ecological significance [
53].
The Mixed Layer Depth (MLD) within the Gulf is of considerable importance for dynamic ocean management and fisheries applications. Understanding its fluctuations aids in predicting the distribution and abundance of marine life and informs management strategies amidst global climate change [
54]. Due to the Gulf’s varied geological provinces at different depths, salinity and temperature exhibit notable seasonal variations. Salinity typically ranges between 30-36 ppt at a depth of 10 m due to coastal inflows, while deeper depths experience less variability at around 35.5-37 ppt. Likewise, sea surface temperatures vary seasonally, ranging from 28-29°C in summer to 16-18°C in the northern Gulf and 24-26°C in the southern Gulf during winter [
55]. Freshwater influx from the Mississippi river delta and other tributaries further influences salinity and temperature dynamics, particularly in the northern Gulf [
56,
57].
The Gulf’s physiographic diversity manifests in subtropical and tropical characteristics, driven by the Loop Current—a warm ocean current converging with the Yucatan and Florida currents [
58,
59,
60]. This intricate circulation pattern, along with the Loop Current’s associated eddies, significantly impacts ocean circulation patterns [
61,
62,
63], biological communities [
64,
65], and even influences the development of hurricanes. Notably, hurricanes such as Katrina and Rita in 2005, intensifying rapidly over the warm waters of the Loop Current, highlight the Gulf’s vulnerability to extreme weather events [
31,
66,
67]. Given the Gulf’s advantageous position for oceanographic and atmospheric observations, as well as its support for marine life and operational predictions across industrial, civilian, and military sectors, significant weather events like hurricanes can profoundly impact these processes and environments. Investigating the spatial and temporal variability of MLD under extreme weather events can enhance our understanding of the Gulf’s physical climate, offshore industrial operations, and the maintenance of oceanic and atmospheric observations.
2.2. Hurricane Katrina (2005)
Hurricane Katrina, the impactful storm that struck the Gulf of Mexico in 2005, stands out as a suitable case study for this work due to its notable characteristics and significant socio-economic consequences along the Gulf Coast. Katrina exhibited remarkable strength, reaching Category 5 status with maximum sustained winds of 175 mph (280 km/h) and a center pressure of 902 mbar on August 28th. The trajectory of Hurricane Katrina presents a unique opportunity to examine the hydrographic responses of thermohaline and thermocline processes to the intensification of wind forcing in the Gulf of Mexico. Initially, Katrina made landfall as a Category 1 hurricane on the southeastern coast of Florida. Subsequently, it rapidly intensified into a Category 3 hurricane within the Gulf, escalating to Category 5 status in less than 12 hours. This swift intensification, coupled with fluctuations in strength as it progressed towards the northern Gulf coast, provides a dynamic scenario for investigating oceanographic responses. Furthermore, the profound impact of Hurricane Katrina on coastal communities and infrastructure underscores the importance of understanding the underlying oceanic dynamics during extreme weather events. Through our focus on Katrina, we aim to elucidate the complex interactions between atmospheric forcing and oceanic processes, shedding light on the mechanisms driving the intensification and propagation of tropical cyclones in the Gulf of Mexico. Our selection of Hurricane Katrina for this study is motivated by its exceptional characteristics, trajectory, and socio-economic significance, which collectively provide a compelling basis for exploring the hydrographic responses of thermohaline and thermocline processes in the Gulf region.
2.3. Model Configuration
We employ the Delft3D modeling system, integrating Delft3D-FLOW and Delft3D-WAVE modules [
68], to investigate changes in thermohaline/thermocline characteristics induced by hurricanes in the Gulf of Mexico. Delft3D-FLOW, grounded in the three-dimensional Navier-Stokes Equations for incompressible fluids, utilizes the Generalized Lagrangian Mean (GLM) formulation. In 3D mode, solutions are derived via bottom following σ- or fixed level z-coordinate system, incorporating the shallow water approximation and Boussinesq approximation for buoyancy-driven flow. The model dynamically evolves hydrodynamics’ vertical structure, encompassing salinity, temperature, and resulting density gradients. Concurrently, Delft3D-WAVE module integrates the Simulating WAves Nearshore (SWAN) model, a third-generation spectral wave model, to analyze wind-wave growth, wave-current interaction, dissipation, and depth-induced breaking [
69]. This module enables FLOW to access SWAN-modeled wave information, including wave orbital velocity, wave forcing, and Stokes drift, while SWAN accesses surface currents and water levels from FLOW.
The model domain encompasses the entire Gulf of Mexico with open boundaries as shown in
Figure 1. It is a spherical rectangular grid with a resolution of 0.04°×0.04° and vertical discretization of 40 vertical mixed layers in the z-coordinate system. Layer thickness linearly increases from surface to bottom, with maximum layer thickness at 15.29% at the bottom and minimum at 0.03% at the surface. Combined bathymetry from the GEneral Bathymetric Chart of the Ocean [
70] and Coastal Relief Model [
71] is adopted in the model. In addition, we utilize the HYbrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) + Navy Coupled Ocean Data Assimilation (NCODA) GoM 1/25° Reanalysis (GOMu0.04 expt_50.1 year-2005) data to provide the initial and boundary conditions. This represents time and space (including in depth) varying boundary conditions of water level, current, salinity and temperature with high resolution (0.25° and 3 hourly) in the regional domain. A time-series of Riemann invariants along the southern open boundary and current velocity along the eastern open boundary were used to simulate a weakly reflective boundary. The wave grid has a lower-resolution of 0.1°× 0.1° and covers the hydrodynamic grid, with 24 frequency bins, ranging 0.033 to 0.5 Hz, and 36-directional components. SWAN is run in non-stationary mode with a 10 minute time-step and coupled with FLOW every 30 minutes. The coupled model simulation spans approximately 54 days from July 1
st to August 23
rd with restart files containing the hydrodynamic conditions for the subsequent model runs.
Winds from the HRD Real-Time Hurricane Wind Analysis System (H*WIND, [
72]) which provide high accuracy and resolution wind field in a 4°×4° grid around the center of the storm were combined with the winds from Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System (COAMPS, [
73,
74]) for areas not covered by the H*WIND grid. This provided a more accurate wind field during extreme weather conditions, as compared with observed data from the National Data Buoy Center (NDBC) stations (as shown in
Figure 2). The three wind drag coefficients are specified with the wind speed (0.001 at 0 m/s, 0.003 at 25 m/s, 0.00723 at 100 m/s) in Delft3D, and applied the
k-Ɛ 3D turbulence model with constant horizontal eddy viscosity and diffusivity (10 m
2/s). In addition, the Ocean Heat flux model [
75,
76] typically applied for a large body of water [
68] is used for the Gulf of Mexico. Several sources, including the COAMPS, National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR), Objectively Analyzed Air-Sea Fluxes (OAFlux), were incorporated to provide the meteorological data such as precipitation, evaporation air-temperature, humidity and cloud coverage in the Gulf for the modeling system. These represent the three-hourly meteorological data over the entire Gulf of Mexico. In addition, the other specified physical parameters are given in
Table 1.
The Multi-Directional Upwind Explicit (MDUE, [
77]) scheme and Van-Leer 2 [
78] method were used for momentum and transport solvers in Z-coordinate system, respectively. In order to avoid the computational noise, such as loss of imposing significant amplitude in steeply peaked solution, the Forester filtering technique [
79] was applied to smooth salinity and temperature variations in horizontal and vertical mixing. In addition, a slope limiter was used to prevent the large velocity gradients along the very steep bottom slopes.
2.4. Model Calibration
Multiple calibration steps were performed to achieve an optimal model configuration for thermocline and thermohaline processes. These dynamical variables are influenced by various oceanographic conditions, and expected to have strong impact on thermohaline/thermocline predictions: Key parameters include eddy viscosity and diffusivity, Secchi depth, and Dalton-Stanton number, which were selected base on values recommended in the model user’s manual or literature. Horizontal eddy viscosity and diffusivity are associated with three-dimensional turbulence eddies, horizontal motions, dispersion, and forcing not resolved by the horizontal grid [
68]. These values significantly contribute to salinity and temperature variations, affecting the characteristics of water mixing processes. Since they represent physics unresolved in the equations, they are utilized as calibration parameters. Recommended values vary widely, and we selected several sets of background horizontal eddy viscosity and diffusivity (1, 5, 10, 15 m
2/s) to assess their impact. Secchi depth [
80,
81], as a measure water transparency or turbidity in a body of water [
82], is linked to the heat flux of net incident solar radiation. In the Ocean Heat Flux model, Secchi depth is used to compute the absorption of heat in the water column, influencing vertical mixing and thermohaline/thermocline structures [
68]. The temporal and spatial-incoming energy flux may induce the vertical mixing and influence the thermohaline/thermocline structures. A number of studies [
83,
84,
85,
86,
87,
88] showed the significant effects of Secchi depth on the temperature and salinity anomalies. The Secchi depths used here follow that used by FGDC [
89]. The considered Secchi depths are: 3.5, 5, 10, 15 (m). Evaporation and heat exchange at the interface between ocean and air contribute significantly to the water temperature and salinity. Dalton and Stanton numbers are usually applied to compute the latent evaporative heat flux [
68,
90] and heat convection. In order to obtain a realistic hurricane-simulation, the ratio of enthalpy to drag coefficient,
(the range of 1.2~1.5, [
91,
92]), was applied to produce ensembles of Dalton and Stanton number in the calibration process. Where,
is the exchange coefficient of heat which is Dalton or Stanton number and
is surface drag coefficient.
Table 2 provides a summary of the physical parameters in the calibration process.
2.5. Model Skill Matrics
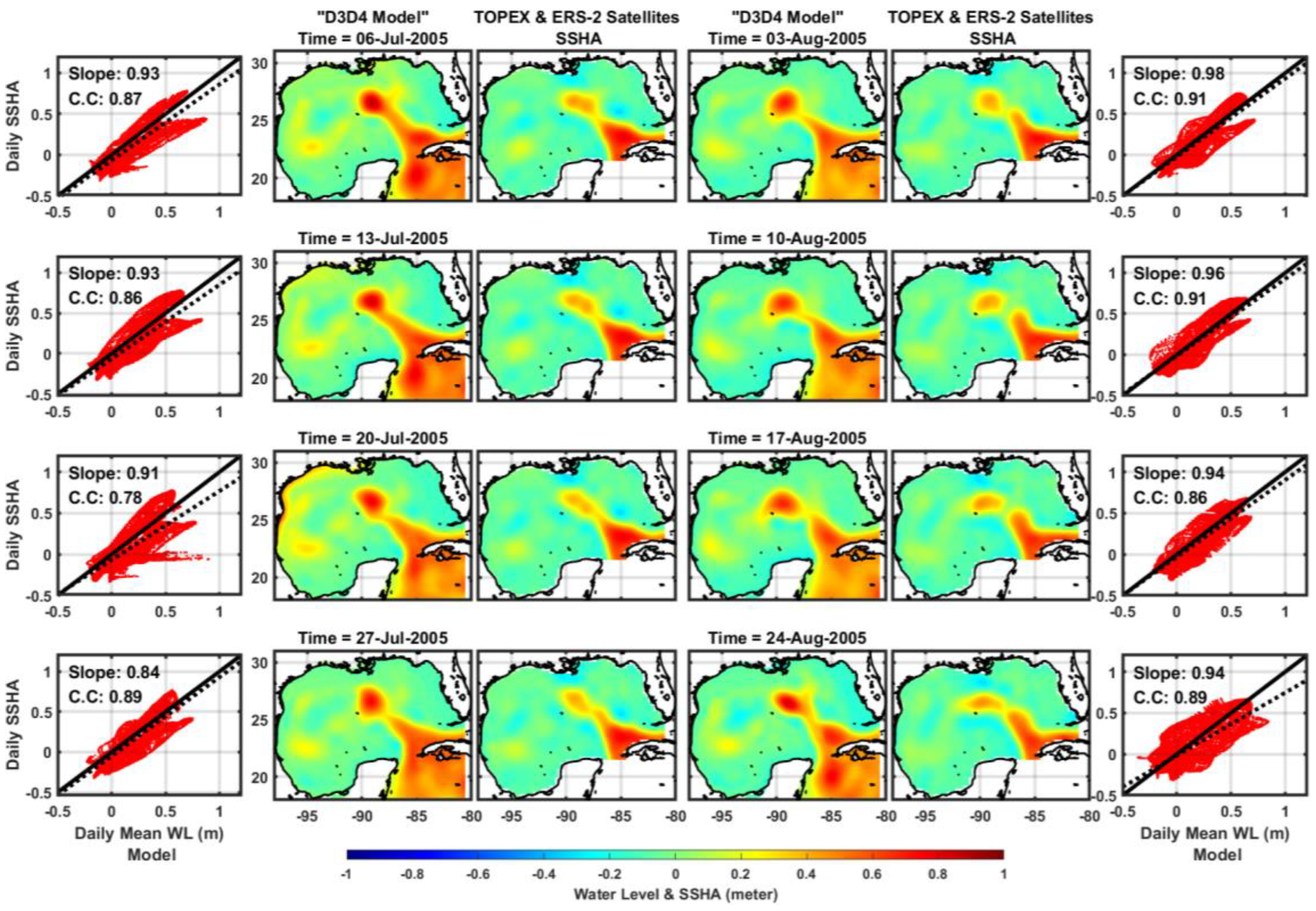
The satellite-based radar altimetry measurements of the Sea Surface Height Anomaly (SSHA) from the TOPography EXperiment (TOPEX) and European Remote Sensing Satellite (ERS-2) are used to compare with the surface water elevation from the model and to figure out whether the model (its performance) has the relevant ocean circulations and processes in the right place and with the right current strength.
Figure 3 shows the comparison between daily mean water levels from the model and daily altimetry data. The correlation between daily mean of water level and sea surface height anomaly was estimated between 0.78 to 0.91 over the Gulf of Mexico for the given period. Additionally, salinity/temperature profiles and water level observations serve as validation metrics for the model. These observations are depicted in
Figure 1. Various error statistics, including Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient (CC), and Refined Index of Agreement (RIA, [
93]) are calculated for all available observed stations using data and model predictions.
Here, n = total number of data; = predicted model value; = observed field value; c is scale constant (c = 2, preferred).
3. Results
3.1. Model Validations – Water Levels, Winds and Waves
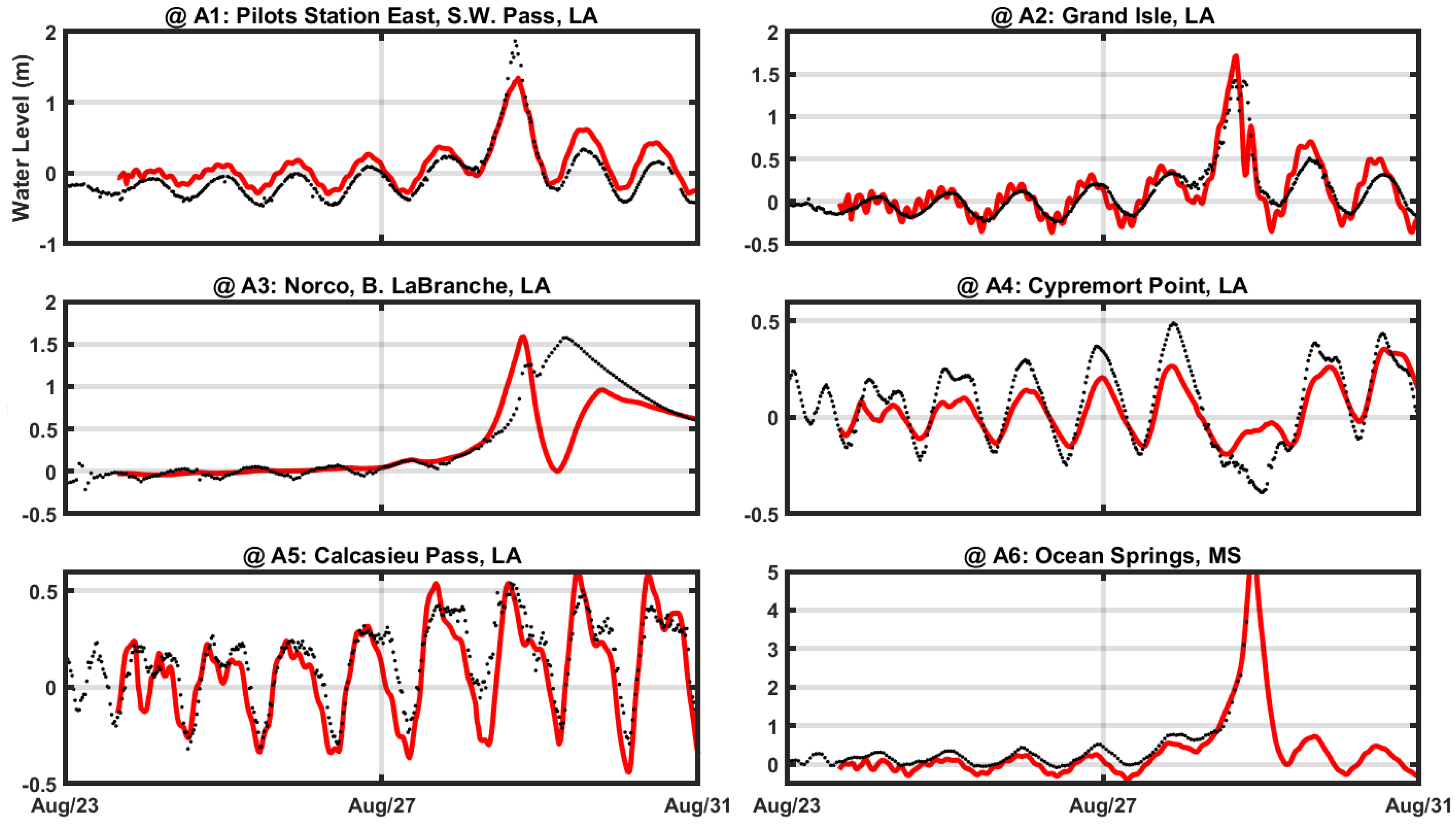
A total of six NOAA tidal stations (station locations in
Table 3) were used to compare the water elevation with the model results (as shown in
Figure 4) along the Louisiana and Mississippi coasts during the Hurricane Katrina. Water levels at stations Norco, B Labranche (#A3) and Cypremort Point (#A4) were somewhat over- and under-estimated respectively during the hurricane event, but the other four stations in open water show great agreement which boosts confidence to our model results.
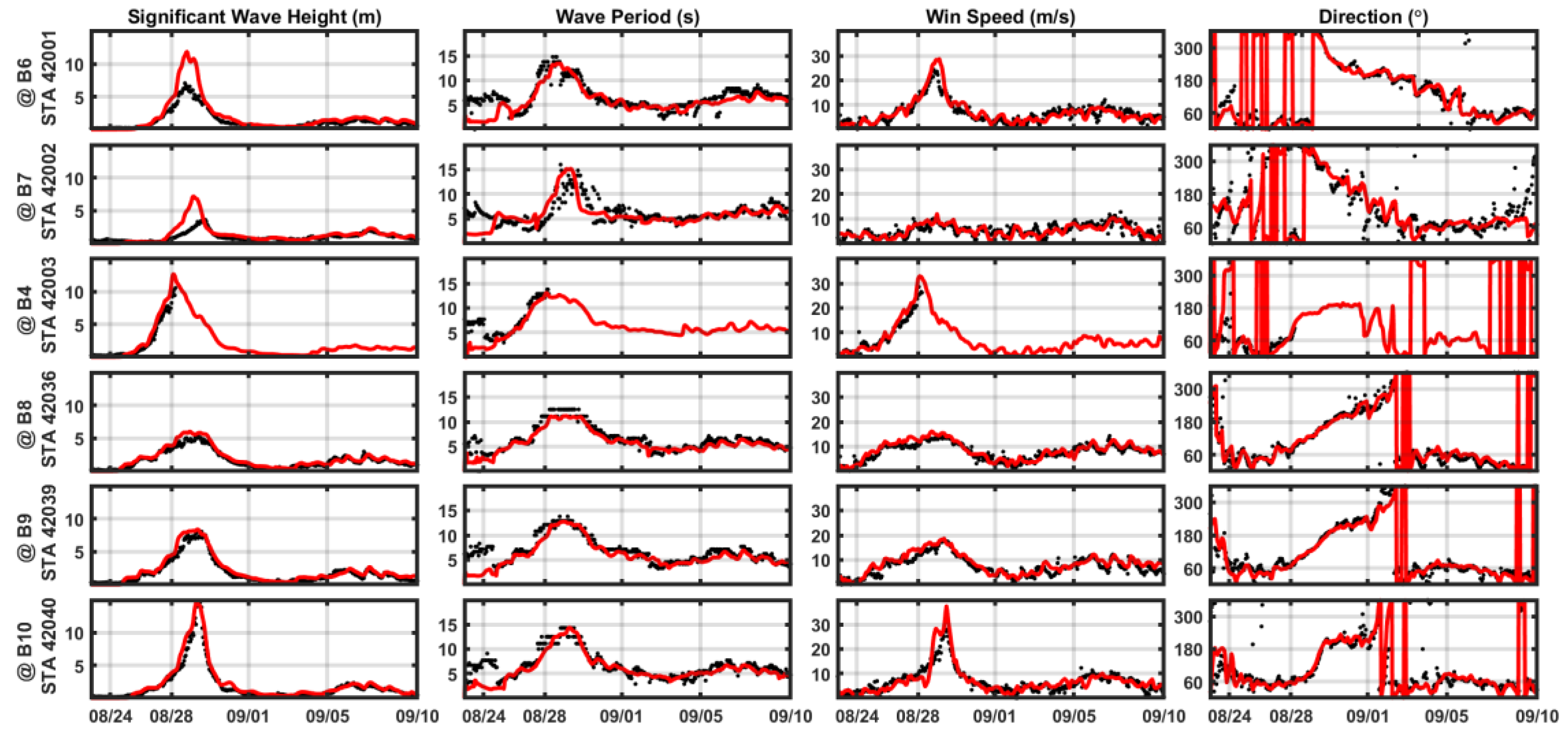
Predicted significant wave height and wave peak period were compared with observed data from NDBC stations in
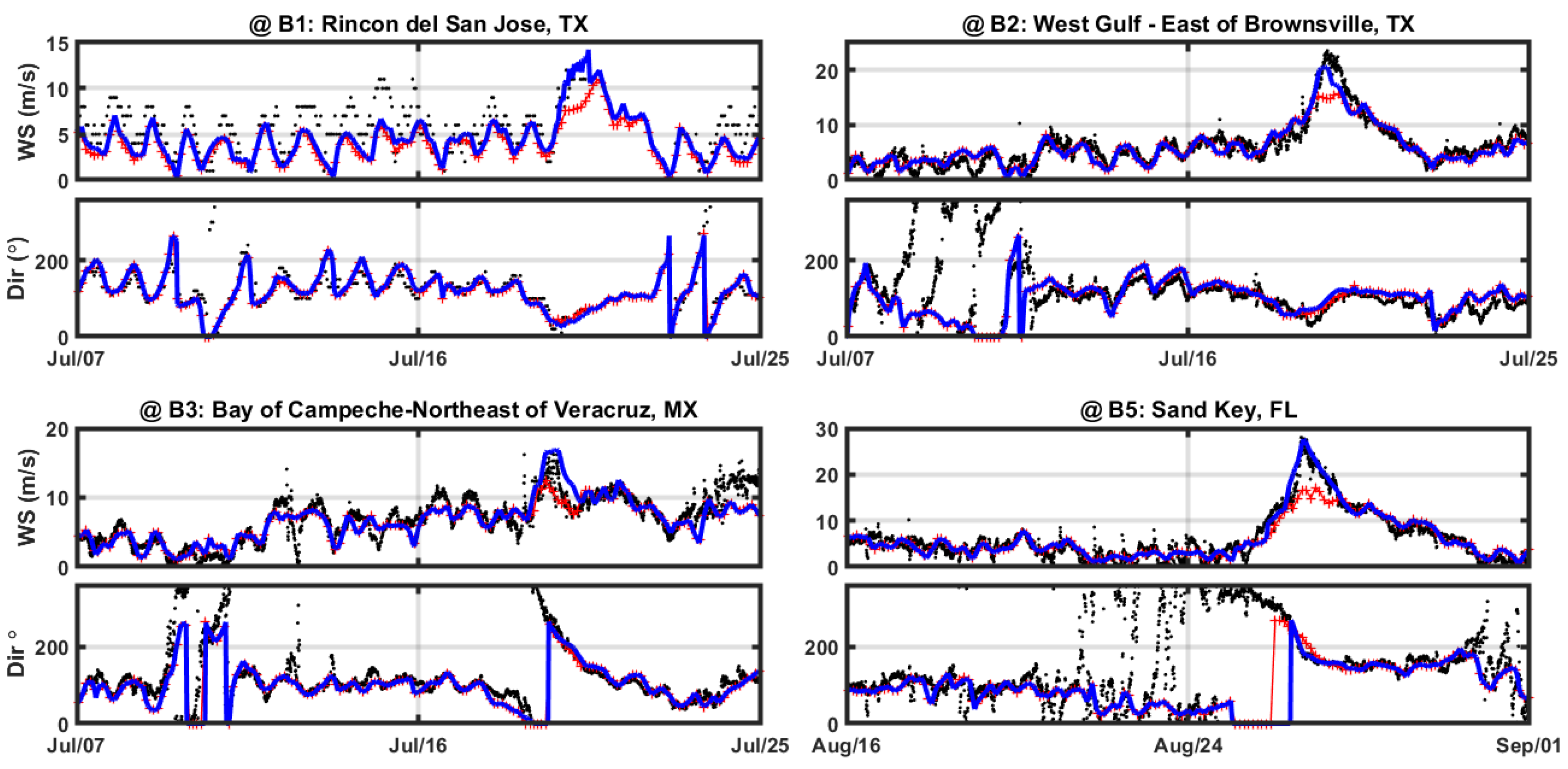
Figure 5. The model exhibits great performance over the buoy stations in the eastern Gulf (right side of storm track). Minor differences in significant wave height and peak period are attributable to wind uncertainty, currents, and bathymetry profile. However, significant wave heights observed at stations 42001 (#B6) and 42002 (#B6) are notably smaller than model results, likely due to the hurricane’s counter-clockwise rotation leads to less energetic waves to the left side of the eye because they encounter opposing winds and absorb less energy from them [
94], which is likely to have a significant impact on the development of wave height. However, this effect is not accounted for in SWAN and consequently results in larger than observed wave height predictions. Overall, the coupled model (Delft3D FLOW+WAVE) agrees well with the measured wave and wind parameters at NDBC stations as shown in
Figure 5.
Table 3 gives the summary of statistical results for water levels and vertical profiles.
3.2. Model Validations – Vertical Profiles of Salinity and Temperature
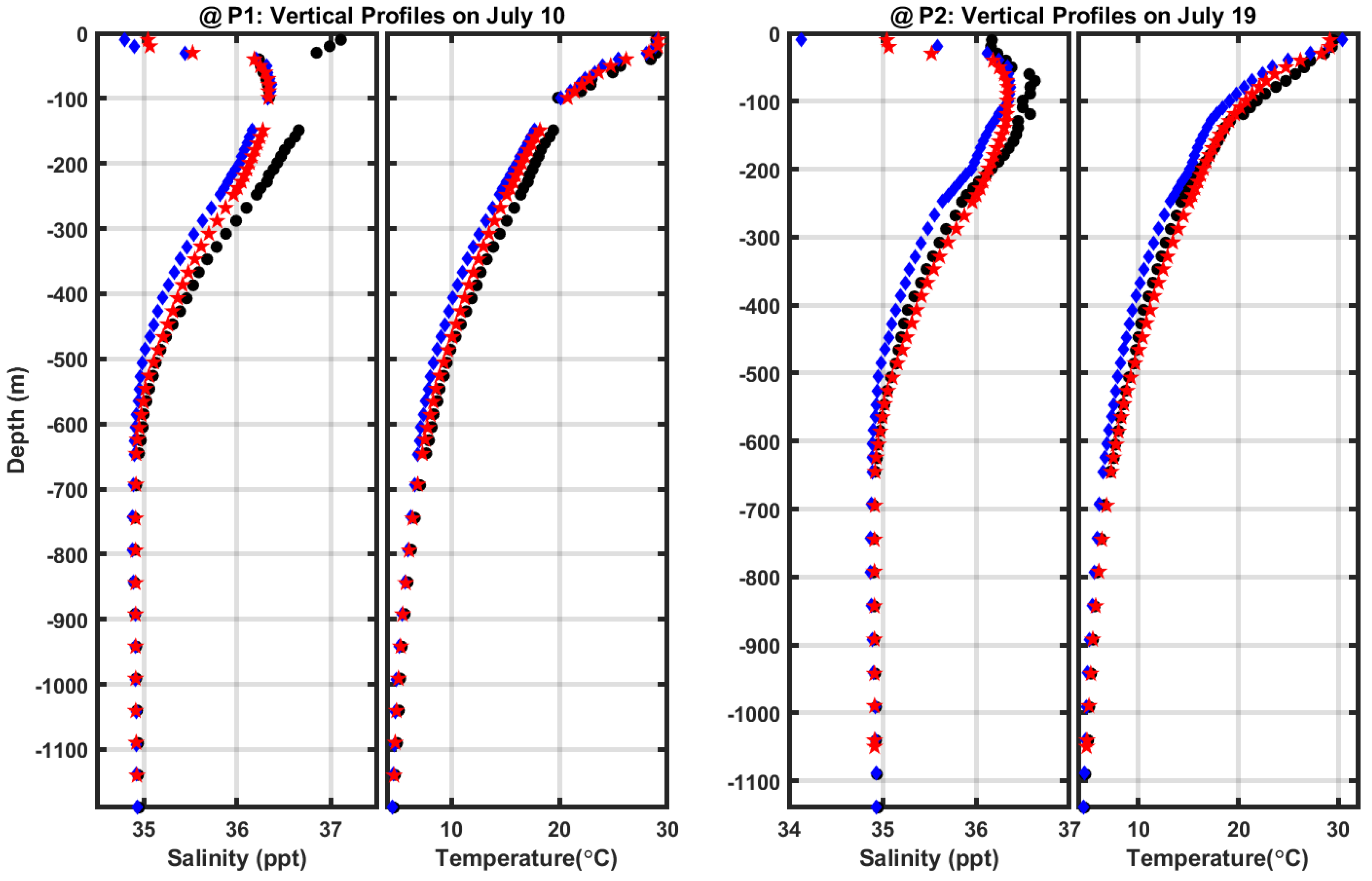
Only two observed vertical profiles (in
Figure 1) were available during July and August in 2005.
Figure 6 shows the comparisons of vertical profiles for the salinity and temperature on July 10
th and 19
th. The model demonstrates a good agreement with the observed value, except for the surface anomaly in salinity for July 10. The model results align with the HYCOM output which provided the salinity and temperature conditions initially in the entire domain and along the boundary during the simulation. RMSE was 0.46 ppt/ 0.84°C in July 10, and 0.26 ppt/ 0.7°C in July 19. One drawback in the model validation is insufficient historical profile data during the period of time in this study, but the agreement of the model results to available measurements of water levels/winds/waves lends confidence in the model. In addition, the comparison of sea surface height from the model and altimetry (shown in
Figure 3) can support whether the model accurately represents pertinent ocean circulation in terms of their spatial and temporal distribution and current intensity.
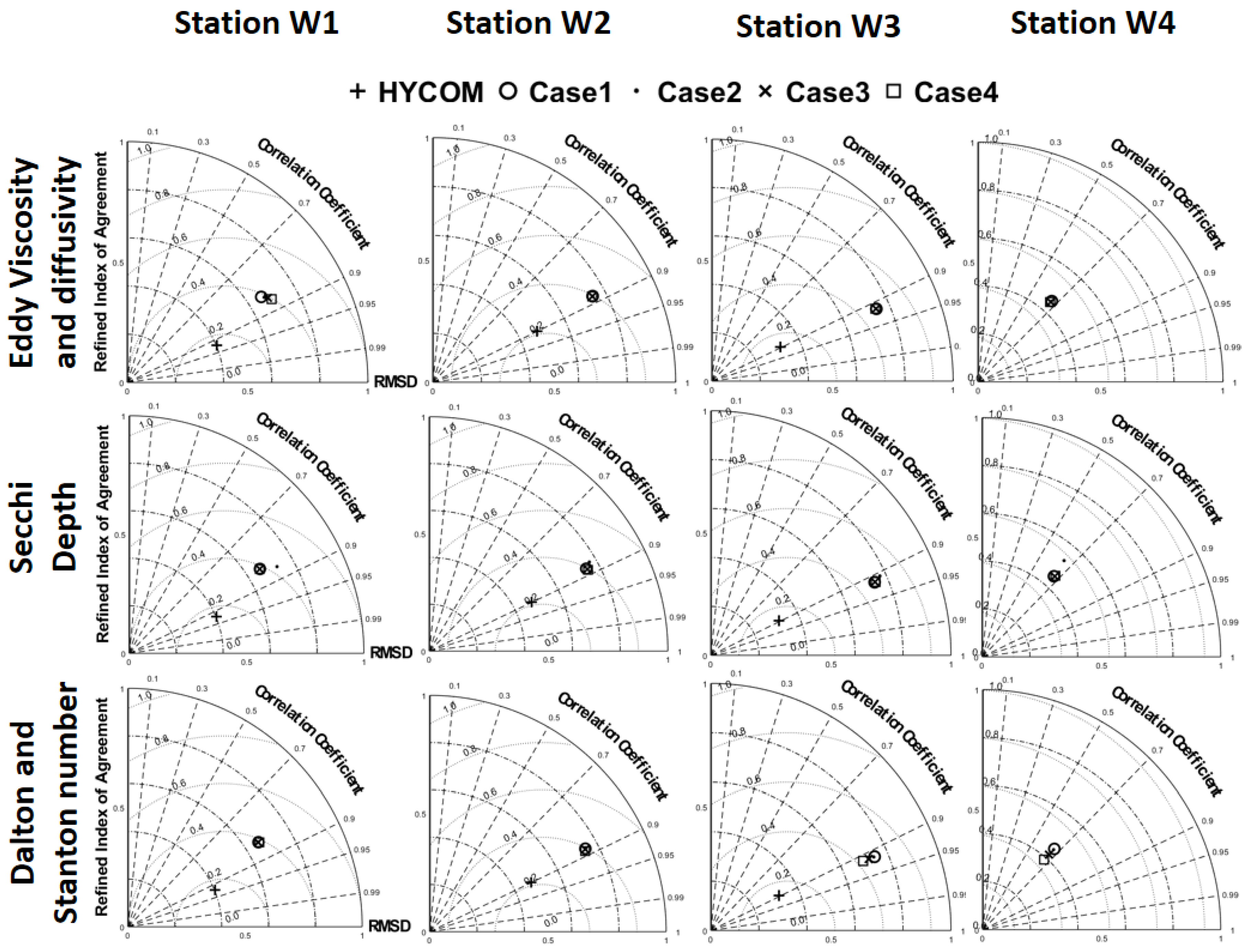
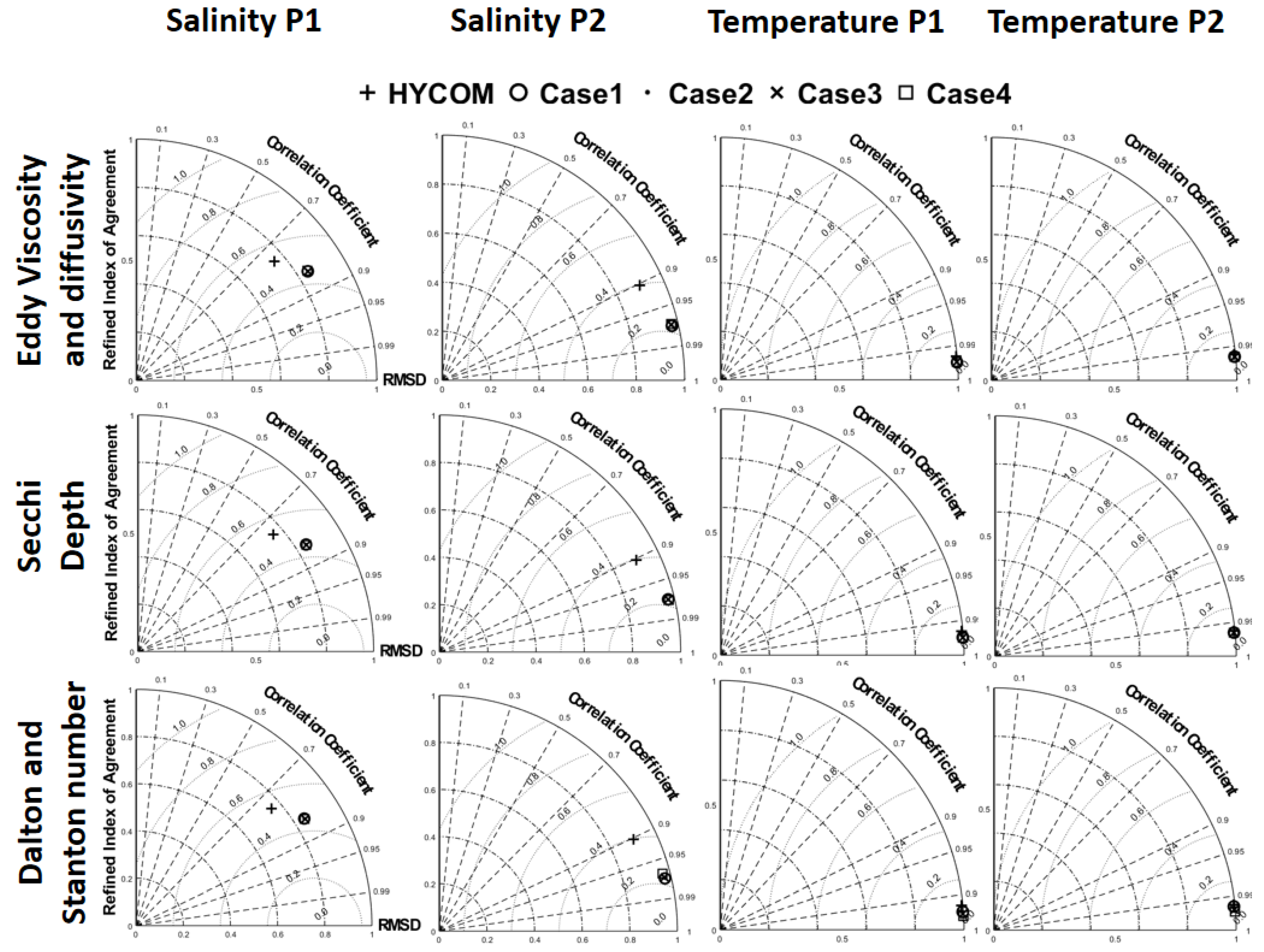
Several Taylor diagrams [
95] provide a summary of the statistical results between each model result in calibration processes and observation. Three statistics are included: the RMS error of model results is represented by the grey dashed line; Pearson’s correlation coefficient (CC), which can quantify the similarity in pattern between modeled and observed points, is depicted in dash-dotted contours; the Refined Index of Agreement (RIA), proportional to the radial distance, is shown in dashed contours. Predicted water level and vertical profiles of salinity and temperature were compared to four tidal stations, two vertical profiles and HYCOM results.
Figure 7 and
Figure 8 show the results of total error statistics for water level change and vertical profiles, respectively. Although no obvious trends emerge due to the different parameters, minimal impact is observed across the range of values chosen, even for the background eddy viscosity and diffusivity. However, certain stations tend to exhibit better performance with specific sets of values. A combination of specified forcing using the optimal parameter set, provided in the values of 10/10 (m
2/s) for eddy viscosity and diffusivity, 10 m for Secchi depth, 0.0041/0.0041 for Dalton and Stanton number (
Table 2), was utilized for the results presented in the remainder of this study.
3.3. Vertical Variability of Salinity and Temperature
Figure 9 and
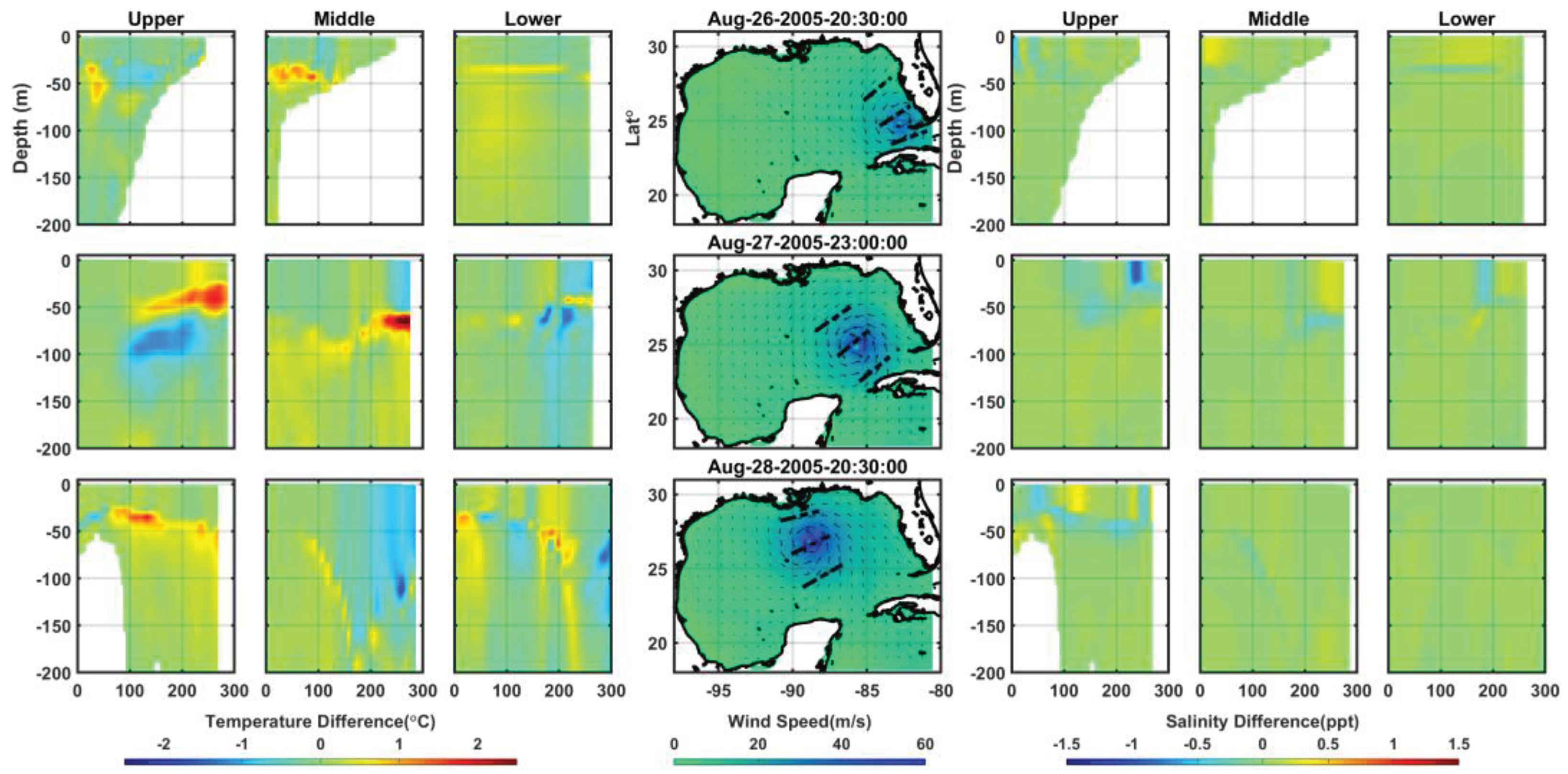
Figure 10 show the temperature and salinity differences following Hurricane Katrina’s passage, delineating the left and right side of the storm, as well as ahead-the-eye and in the wake at various times within upper 200 m in depth. In
Figure 9, the stronger wind force on the right side of the storm’s eye induces horizontal and vertical temperature changes of ± 4°C and ± 2.5 ppt in salinity, respectively, after Katrina’s passage at 20:30:00 on August 28
th. Conversely,
Figure 10 depicts spatial and temporal variations along the eye at the same time, showcasing increase and decrease of ~ ± 4°C in temperature and ~ ± 1.5 ppt in salinity due to the strong hurricane winds and influx of warm water possibly associated with the Loop Current. Temperature and salinity differences were calculated relative to a three-day mean sea state (August 21
st-23
rd) preceding the storm. In both figures, the water mass exchanges driven by the strong winds drive the various processes, such as the disturbance, mixing and transport, leading to abrupt change in temperature and salinity. The turbulence caused by the strong wind-driven current in upper-ocean can uplift colder water from the thermocline to the mixed layer, resulting in thickening and cooling [
96]. Although the likelihood of upwelling process influence is not significantly higher [
97], the combination of turbulence-driven vertical mixing and enhanced upwelling caused by geostrophic flow, such as the Loop Current and frontal cyclones [
31,
98] contributes to cooling beneath the storm. This effect is particularly pronounced on the right side of the eye, as depicted in
Figure 10. Salinity anomalies are less distinct compared to temperature. Typically, salinity increases gradually with depth. However, during Hurricane Katrina, intense vertical mixing led to salinity increases in the mixed layer due to the intense entrainment of high salinity from the subsurface layer [
25,
99,
100,
101]. Additionally, latent heat energy from the evaporation process can result in cooling at the upper ocean layer and salinization in the ocean mixed layer [
102], as observed in the results for August 28
th at 20:30:00 in
Figure 10.
4. Discussion
A simple threshold approach [
16,
103,
104,
105,
106], is utilized to identify MLD from model result, based on a temperature variation of 0.2 °C from the surface/reference depth. The strong current generated by hurricane winds, along with mixing induced by waves and turbulence in the upper ocean layer, significantly influence temperature variations during extreme weather events [
46,
49,
107,
108,
109]. Dynamic cooling and dissipative heating processes at the surface layer also drive these variations [
42,
43], subsequently affecting the transport of heat flux and the thermocline structure [
44].
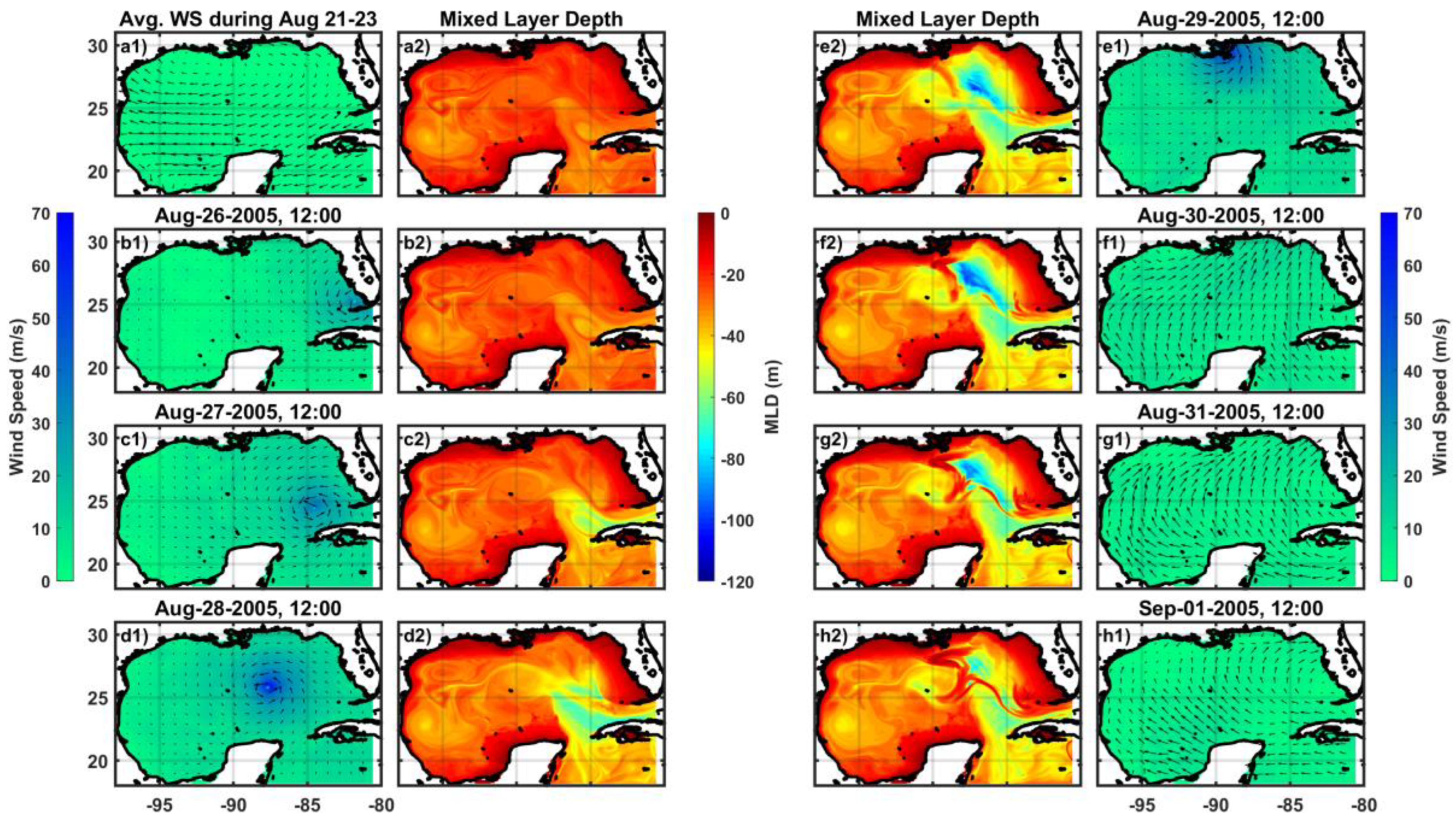
Figure 11 illustrates the distribution of daily mean mixed layer depth relative to the development of hurricane winds.
Figure 11-a1 depicts the initial phases of the wind field and the mean MLD over three days preceding the storm (August 21
st-23
rd). Utilizing a temperature variation of 0.2°C, we observe a pre-storm MLD ranging from 20-40 m (
Figure 11), consistent with seasonal values. Notably, the MLD substantially deepens to around 120 m on August 29
th-30
th in the middle of the northeastern Gulf. Although wind forcing appears particularly relevant to MLD response, there seems to be a time-lag between maximum winds and the MLD response, likely due to the complex interactions among physical inputs such as winds, hydrodynamics, thermal transport, geological features, among others. As discussed below, the MLD gradually returns to pre-hurricane conditions following the passage of Hurricane Katrina.
4.1. MLD Recovery
The recovery of MLD from storm disturbances appears to vary depending on the background climate ([
110]). Understanding the duration it takes for the MLD to revert to pre-storm levels aids in comprehending the upper ocean’s response to storms. The relative change in MLD, expressed as a percentage (%), is calculated using the equation,
where
represents the mean MLD computed over the two days preceding the storm impact, and
is the MLD at time
i after the storm passage.
Figure 12 presents the Gulf’s MLD change resulting from several hurricanes, encompassing the period from July to August (before Katrina) and extending to September 2005, based on MLD variations attributable to each storm’s impact. Mean MLD distributions during July 1
st-2
nd (a) and August 21
st-22
nd (b), serve as benchmarks for determining MLD changes induced by hurricane impacts.
Following Hurricane Cindy, a Category 1 storm with maximum winds of 33.4 m/s that traversed from south to north across the middle of the Gulf, the Gulf failed to fully return to its normal sea state due to the subsequent Hurricane Dennis. Post-Cindy, the MLD recovered to approximately 81%, but subsequently dropped to 72% following Dennis’s impact. Despite Dennis being upgraded to a Category 3-4 hurricane, it resulted in only a 9% additional decrease from Cindy’s impact, with the MLD recovering to 79% by July 16th-17th. Due to Dennis’s more eastern storm track, the shallow depth and continental shelf regions along the western side of the Florida Panhandle were likely unaffected in terms of MLD evolution.
Hurricane Emily, reaching Category 5 intensity in the Caribbean Sea, drove warm water through the Yucatan Channel, inducing anomalously high temperatures and salinity [
111], before moving west to northwest. Emily’s impact led to a significant MLD decrease to 55-57%, gradually rebounding to over 75% post-storm. Even during the interlude between Hurricanes Emily and Katrina, the Gulf’s MLD had not fully recovered, remaining below 80%. The cumulative impact of multiple storms within a short period may compromise the Gulf’s oceanic hydrodynamic resilience, altering the region’s climate background.
In
Figure 12-b, two different mean-MLD bases were utilized, computed during July 1
st-2
nd and August 21
st-22
nd. Compared to the preceding hurricanes, Katrina inflicted the most substantial MLD impact, plummeting to 37-39% using the July basis. Even three weeks later (before Hurricane Rita), the MLD level remained below 70%. Katrina’s influence was anticipated to cause significant changes in thermocline/thermohaline processes, circulation, and mixing during and post-impact. When compared to the August basis, Katrina still induced a substantial MLD change of 60%, eventually recovering to approximately 84%. The Gulf had not fully rebounded from Katrina’s impact and was subsequently affected by Hurricane Rita from September 20
th (not examined here). A longer duration may be necessary for the Gulf to recover to over 90% of its former sea state, but multiple hurricane strikes during the Atlantic hurricane season impede full recovery.
4.2. Wave Effect on MLD
The strong hurricane event is expected to have a major impact on mixing and transport via surface waves. However, the influence of waves on the thermohaline structure, and the subsequent impacts of white-capping on said structure, remain areas of ongoing investigation [
112]. To address this gap, we utilized both model results from FLOW and the coupled FLOW+WAVE to scrutinize the wind-driven wave effect on parameters such as the Mixed Layer Depth (MLD), temperature, and salinity.
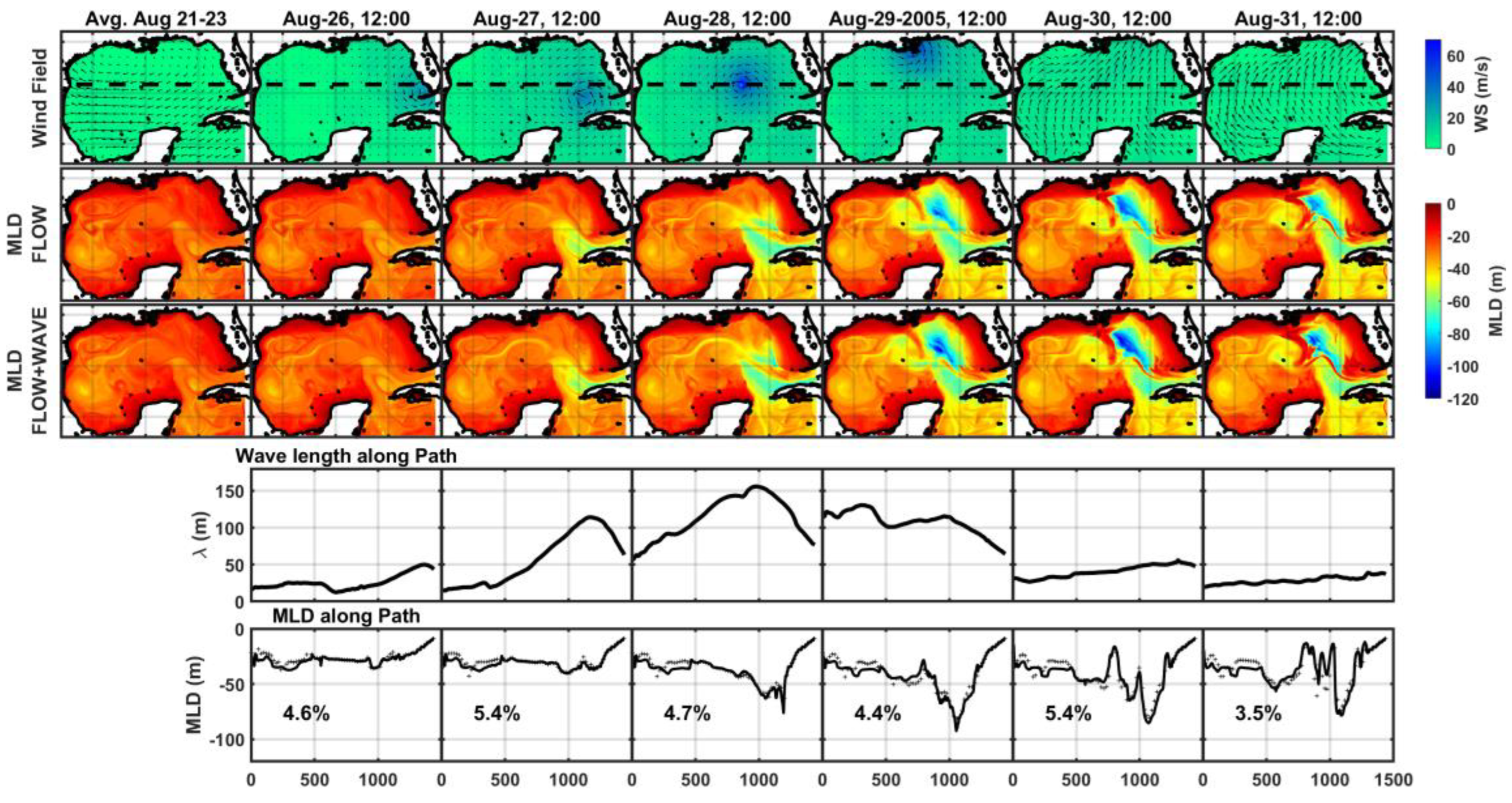
In
Figure 13, we present comparisons of daily mean MLD distributions during Hurricane Katrina, contrasting results from the FLOW and FLOW+WAVE coupled models. Additionally, we depict wave length and MLD along a cross-section down the long axis of the Gulf at each time step. During the early stages of the storm on August 26
th, the MLDs showed minimal response to the waves. However, the intense hurricane wind-driven waves on August 28
th-29
th led to more significant variations in MLD in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico compared to predictions without wave effects. Notably, on August 30
th, even as Hurricane Katrina weakened while moving inland over southern and central Mississippi, both models estimated wider and deeper MLDs, hinting at the persistent influence of the storm’s dynamics.
Various hydrodynamic and wave characteristics, such as time lag for MLD response to strong winds and wave dynamics, as well as geological features and circulations, may account for this phenomenon. Typically, wave effects penetrate to a depth of half their wavelength [
113,
114], with predicted wavelengths in ranges conducive to affecting the MLD, as depicted in
Figure 13. We observe that strong wind-driven waves result in deeper MLDs, approximately 3.5-5.4% deeper than those predicted by the FLOW model alone (
Figure 13). While this additional mixing induced by wave effects may seem minor (around 3.5~5.4%), it provides valuable insights for acoustic (sonar) systems sensitive to temperature and density variations under extreme weather conditions.
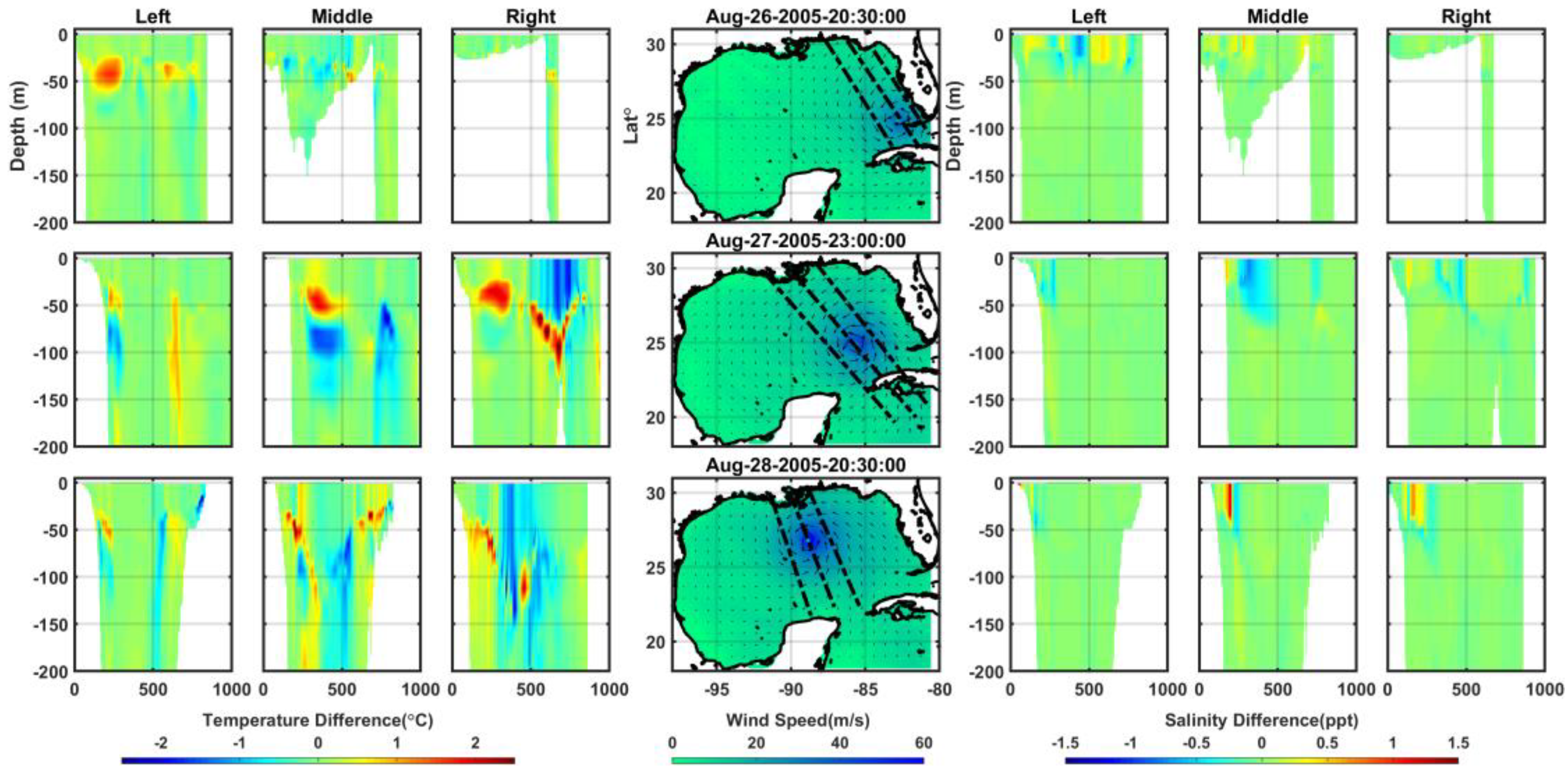
Figure 14 and
Figure 15 illustrate vertical variations in temperature and salinity caused by wind-driven wave effects during Hurricane Katrina. These figures compare differences in temperature and salinity between the coupled FLOW+WAVE model and the FLOW model cross-sections along the specified lines. The coupled model results demonstrate greater depth variations in temperature and salinity due to surface waves. While no significant changes occur in the salinity field, the coupled model reveals spatial and temporal variations, with temperature fluctuations of up to ±2.5°C and salinity fluctuations of up to ±1.5 ppt compared to FLOW model results. Additionally, strong winds on the right side of the storm track exhibit a more pronounced effect on temperature and salinity fields than those on the left side of the eye. The wave effects on the thermohaline process cross-sections, as depicted in
Figure 14 and
Figure 15, can be inferred from the model predictions between the MLDs and associated wavelengths in
Figure 13. These effects are likely attributable to dynamic cooling, dissipative heating, and wave processes acting as turbulent sources on the ocean surface [
43,
115,
116].
5. Conclusions
This study provides a comprehensive analysis of the hydrodynamic and wave effects of Hurricane Katrina on the Gulf of Mexico’s upper ocean dynamics. Utilizing a sophisticated modeling system integrating Delft3D FLOW and WAVE models, we evaluated various parameters including water elevation, vertical profiles of salinity and temperature, significant wave height, peak period, wind speed, and direction. Our findings indicate strong agreement between model predictions and observational data from NOAA, NDBC, TOPEX and ERS-2 Satellites, as well as the HYCOM model used for initial and boundary conditions.
During Hurricane Katrina, the model accurately captured spatial and temporal variations in temperature and salinity, with notable increases and decreases observed. Under the influence of extreme weather conditions, such as Hurricane Katrina, significant cooling, wind-driven mixing, and surface heat loss induce notable spatial and temporal variations in temperature (~± 4°C) and salinity (~± 2.5 ppt). MLD is strongly developed with ~120 m (or more) on August 29th~30th in middle of northeastern Gulf, compared to pre-storm conditions (~20-40 m). Recovery analysis indicates that it takes about 18 days for the MLD to rebound to approximately 84% of its pre-storm level following Hurricane Katrina. Additionally, the incorporation of surface wave effects in the coupled model results in a slightly deeper MLD (~5%) compared to the stand-alone hydrodynamic model. Our findings underscore the importance of accurate modeling in predicting and understanding the impacts of extreme weather events on ocean dynamics. These provide valuable insights for scientific understanding, environmental management, and operation applications, particularly in predicting and mitigating the impacts of extreme weather events on ocean dynamics.
Future applications should focus on incorporating denser observational data to further refine and validate the model, facilitating deeper insights into the complex responses of thermohaline structure and circulation to hurricane-induced disturbances. By leveraging advanced modeling techniques and observational data, we can deepen our understanding of marine systems and inform strategies for mitigating the impacts of climate-related disasters.
Author Contributions
W. Lee designed the concept and methodology of integrated modeling system and constructed the Delft3D model, its validations. And W. Lee analyzed the model results and provided the initial draft of the manuscript. J. Veeramony contributed to support modeling technique, discussing, editing and writing processes. All authors actively contributed to analyzing model outcomes and revisions in writing process, and agreed to publish the manuscript.
Funding
The research presented in this paper was funded by the Office of Naval Research (ONR, Grant No. N0001421WX00991).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
The authors would also like to thank Dr. Clark David Rowley and Ms. Lucy F. Smedstad of the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory for the model validation and configurations..
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that we have no conflict of interest/competing interests.
References
- Chen D, Busalacchi AJ, Rothstein LM. The roles of vertical mixing, solar radiation, and wind stress in a model simulation of the sea surface temperature seasonal cycle in the tropical Pacific Ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research. 1994 Oct 1;99:20,345-20,359. [CrossRef]
- Sutton PJ, Worcester PF, Masters G, Cornuelle BD, Lynch JF. Ocean mixed layers and acoustic pulse propagation in the Greenland Sea. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 1993 Sep 1;94[3]:1517–26. [CrossRef]
- Arrigo null, Robinson null, Worthen null, Dunbar null, DiTullio null, VanWoert null, et al. Phytoplankton community structure and the drawdown of nutrients and CO2 in the southern ocean. Science. 1999 Jan 15;283[5400]:365–7.
- Fasham MJR. Variations in the seasonal cycle of biological production in subarctic oceans: A model sensitivity analysis. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers. 1995 Jul 1;42[7]:1111–49. [CrossRef]
- Helber RW, Kara A, Barron C, Boyer T. Mixed layer depth in the Aegean, Marmara, Black and Azov Seas: Part II: Relation to the sonic layer depth. 2009; [CrossRef]
- Obata A, Ishizaka J, Endoh M. Global verification of critical depth theory for phytoplankton bloom with climatological in situ temperature and satellite ocean color data. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans. 1996;101[C9]:20657–67. [CrossRef]
- Polovina JJ, Mitchum GT, Evans GT. Decadal and basin-scale variation in mixed layer depth and the impact on biological production in the Central and North Pacific, 1960-88. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers. 1995 Oct 1;42[10]:1701–16. [CrossRef]
- Agrawal YC, Terray EA, Donelan MA, Hwang PA, Williams AJ, Drennan WM, et al. Enhanced dissipation of kinetic energy beneath surface waves. Nature. 1992;359[6392]:219–20. [CrossRef]
- Craik AD, Leibovich S. A rational model for Langmuir circulations. Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 1976;73[3]:401–26. [CrossRef]
- Large WG, McWilliams JC, Doney SC. Oceanic vertical mixing: A review and a model with a nonlocal boundary layer parameterization. Reviews of Geophysics. 1994;32[4]:363–403. [CrossRef]
- Mellor GL, Durbin PA. The structure and dynamics of the ocean surface mixed layer. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 1975;5[4]:718–28. [CrossRef]
- Pickard G, Emery W. Descriptive Physical Oceanography: an Introduction By George L. Pickard Oxford: Pergamon Press1964. Pp. viii + 199. Price 25s. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 1964 Oct;44[3]:758–758.
- Roden GI. The Depth Variability of Meridional Gradients of Temperature, Salinity and Sound Velocity in the Western North Pacific. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 1979 Jul 1;9[4]:756–67. [CrossRef]
- Skyllingstad ED, Paluszkiewicz T, Denbo DW, Smyth WD. Nonlinear vertical mixing processes in the ocean: modeling and parameterization. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena. 1996 Nov 15;98[2]:574–93. [CrossRef]
- Welander P. Mixed Layers and Fronts in Simple Ocean Circulation Models. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 1981 Feb 1;11[2]:148–52. [CrossRef]
- de Boyer Montégut C, Madec G, Fischer AS, Lazar A, Iudicone D. Mixed layer depth over the global ocean: An examination of profile data and a profile-based climatology. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans. 2004;109[C12]. [CrossRef]
- Spall MA, Weller RA, Furey PW. Modeling the three-dimensional upper ocean heat budget and subduction rate during the Subduction Experiment. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans. 2000;105[C11]:26151–66. [CrossRef]
- Thomson RE, Fine IV. Estimating Mixed Layer Depth from Oceanic Profile Data. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology. 2003 Feb 1;20[2]:319–29. [CrossRef]
- Villarreal VA. Relationship between the sonic layer depth and mixed layer depth identified from U.S. Navy sea glider data [Internet] [Thesis]. Monterey, California. Naval Postgraduate School; 2014 [cited 2021 Nov 12]. Available from: https://calhoun.nps.edu/handle/10945/44025.
- Bhaskar TU, Swain D. Sonic Layer Depth estimated from XBT temperatures and climatological salinities. Nature Precedings. 2011;1–1.
- Huang RX. Ocean circulation: wind-driven and thermohaline processes. Cambridge University Press; 2010.
- Murty TS, El-Sabh MI. Storm tracks, storm surges and sea state in the Arabian Gulf, Strait of Hormuz and the Gulf of Oman. UNESCO Report Marine Sci. 1984;28:12–24.
- Schott F, Visbeck M, Send U, Fischer J, Stramma L, Desaubies Y. Observations of deep convection in the Gulf of Lions, northern Mediterranean, during the winter of 1991/92. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 1996;26[4]:505–24. [CrossRef]
- Lee CM, Askari F, Book J, Carniel S, Cushman-Roisin B, Dorman C, et al. Northern Adriatic response to a wintertime bora wind event. Eos, Transactions american geophysical union. 2005;86[16]:157–65. [CrossRef]
- Jacob SD, Shay LK, Mariano AJ, Black PG. The 3D Oceanic Mixed Layer Response to Hurricane Gilbert. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 2000 Jun 1;30[6]:1407–29. [CrossRef]
- Shay L, Black P, Mariano A, Hawkins J, Elsberry R. Upper ocean response to Hurricane Gilbert. 1992; [CrossRef]
- Shay LK, Goni GJ, Black PG. Effects of a Warm Oceanic Feature on Hurricane Opal. Monthly Weather Review. 2000 May 1;128[5]:1366–83.
- Uhlhorn EW, Shay LK. Loop Current Mixed Layer Energy Response to Hurricane Lili (2002). Part I: Observations. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 2012 Mar 1;42[3]:400–19.
- Walker ND, Leben RR, Balasubramanian S. Hurricane-forced upwelling and chlorophyll a enhancement within cold-core cyclones in the Gulf of Mexico. Geophysical Research Letters. 2005;32[18].
- Jaimes B, Shay LK. Near-Inertial Wave Wake of Hurricanes Katrina and Rita over Mesoscale Oceanic Eddies. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 2010 Jun 1;40[6]:1320–37. [CrossRef]
- Jaimes B, Shay LK. Mixed layer cooling in mesoscale oceanic eddies during Hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Monthly Weather Review. 2009;137[12]:4188–207. [CrossRef]
- Shay LK. Upper Ocean Structure: Responses to Strong Atmospheric Forcing Events. In: Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences [Internet]. Elsevier Ltd; 2009 [cited 2021 Nov 12]. p. 192–210. Available from: http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?scp=84884459695&partnerID=8YFLogxK.
- Fedorov KN, Varfolomeev AA, Ginzburg AI. Thermal reaction of the ocean on the passage of hurricane Ella. Okeanologiya. 1979;19:992–1001.
- Leipper DF. Observed ocean conditions and Hurricane Hilda, 1964. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences. 1967;24[2]:182–6. [CrossRef]
- Black PG. Ocean temperature changes induced by tropical cyclones. Ph D Thesis. 1983;
- Brooks DA. The wake of Hurricane Allen in the western Gulf of Mexico. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 1983;13[1]:117–29. [CrossRef]
- Shay LK, Elsberry RL. Near-inertial ocean current response to Hurricane Frederic. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 1987;17[8]:1249–69. [CrossRef]
- Bender MA, Ginis I, Kurihara Y. Numerical simulations of tropical cyclone-ocean interaction with a high-resolution coupled model. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. 1993;98[D12]:23245–63. [CrossRef]
- Gierach MM, Subrahmanyam B, Thoppil PG. Physical and biological responses to Hurricane Katrina (2005) in a 1/25 nested Gulf of Mexico HYCOM. Journal of Marine Systems. 2009;78[1]:168–79.
- Davis C, Wang W, Chen SS, Chen Y, Corbosiero K, DeMaria M, et al. Prediction of Landfalling Hurricanes with the Advanced Hurricane WRF Model. Monthly Weather Review. 2008 Jun 1;136[6]:1990–2005. [CrossRef]
- Halliwell Jr GR, Shay LK, Jacob SD, Smedstad OM, Uhlhorn EW. Improving ocean model initialization for coupled tropical cyclone forecast models using GODAE nowcasts. Monthly weather review. 2008;136[7]:2576–91.
- Korty RL, Emanuel KA, Scott JR. Tropical cyclone–induced upper-ocean mixing and climate: Application to equable climates. Journal of Climate. 2008;21[4]:638–54. [CrossRef]
- Liu HL. Temperature changes due to gravity wave saturation. Journal of Geophysical Research. 2000 May 1;105:12,329-12,336. [CrossRef]
- Bueti MR, Ginis I, Rothstein LM, Griffies SM. Tropical cyclone–induced thermocline warming and its regional and global impacts. Journal of Climate. 2014;27[18]:6978–99. [CrossRef]
- Jacob SD, Shay LK. The Role of Oceanic Mesoscale Features on the Tropical Cyclone–Induced Mixed Layer Response: A Case Study. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 2003 Apr 1;33[4]:649–76. [CrossRef]
- Mao Q, Chang SW, Pfeffer RL. Influence of large-scale initial oceanic mixed layer depth on tropical cyclones. Monthly weather review. 2000;128[12]:4058–70. [CrossRef]
- McPhaden MJ, Foltz GR, Lee T, Murty VSN, Ravichandran M, Vecchi GA, et al. Ocean-Atmosphere Interactions During Cyclone Nargis. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union. 2009;90[7]:53–4. [CrossRef]
- Sutyrin GG, Khain AP. Effect of the ocean–atmosphere interaction on the intensity of a moving tropical cyclone. Atmos Oceanic Phys. 1984;20:787–94. [CrossRef]
- Toffoli A, McConochie J, Ghantous M, Loffredo L, Babanin AV. The effect of wave-induced turbulence on the ocean mixed layer during tropical cyclones: Field observations on the Australian North-West Shelf. Journal of Geophysical Research (Oceans). 2012 Nov 1;117:C00J24.
- Nipper M, Sánchez Chávez JA, Tunnell JrJWEditors. Gulf Base: Resource Database for Gulf of Mexico Research. World Wide Web electronic publication [Internet]. 2009; Available from: http://www.gulfbase.org.
- U.S Energy Information Administration. U.S. Gulf of Mexico crude oil production to continue at record highs through 2019. 2018; Available from: https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=35732.
- Hill K, Hill GN. Encyclopedia of Federal Agencies and Commissions. Infobase Publishing; 2014.
- Kennedy J. Facts About Marine Life in the Gulf of Mexico. Thought Co [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2019 Sep 13]; Available from: thoughtco.com/gulf-of-mexico-facts-2291771.
- Hobday AJ, Hartog JR. Derived Ocean Features for Dynamic Ocean Management. Oceanography. 2014;27[4]:134–45. [CrossRef]
- Baranova O, Biddle M, Boyer T. Seawater Temperature - Climatological Mean In Gulf of Mexico Data Atlas [Internet]. Stennis Space Center (MS): National Centers for Environmental Information; 2014. Available from: https://gulfatlas.noaa.gov/.
- Lane RR, Day JW, Marx BD, Reyes E, Hyfield E, Day JN. The effects of riverine discharge on temperature, salinity, suspended sediment and chlorophyll a in a Mississippi delta estuary measured using a flow-through system. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science. 2007 Aug 1;74[1]:145–54. [CrossRef]
- McDonald T, Telander A, Marcy P, Oehrig J, Geggel A, Roman H, et al. Temperature and salinity estimation in estuaries of the northern Gulf of Mexico. [Internet]. NOAA Tech Rep; 2015. Available from: https://pub-dwhdatadiver.orr. noaa.gov/ dwh-ar-documents/ 863/ DWH-AR0270936.pdf.
- Gyory J, Mariano AJ, Ryan EH. The Loop Current." Ocean Surface Currents. 2019; Available from: https://oceancurrents.rsmas.miami.edu/atlantic/loop-current.html.
- Hofmann EE, Worley SJ. An investigation of the circulation of the Gulf of Mexico. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans. 1986;91[C12]:14221–36. [CrossRef]
- Sturges W, Leben R. Frequency of Ring Separations from the Loop Current in the Gulf of Mexico: A Revised Estimate. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 2000 Jul 1;30[7]:1814–9. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Weisberg RH, Vignudelli S, Mitchum GT. Patterns of the loop current system and regions of sea surface height variability in the eastern Gulf of Mexico revealed by the self-organizing maps. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans. 2016;121[4]:2347–66. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Brunius P, Furey H, Bower A, Hamilton P, Candela J, García-Carrillo P, et al. Dominant Circulation Patterns of the Deep Gulf of Mexico. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 2018 Mar 1;48[3]:511–29. [CrossRef]
- Weisberg RH, Liu Y. On the Loop Current Penetration into the Gulf of Mexico. Journal of Geophysical Research (Oceans). 2017 Dec 1;122:9679–94. [CrossRef]
- Davis RW, Ortega-Ortiz JG, Ribic CA, Evans WE, Biggs DC, Ressler PH, et al. Cetacean habitat in the northern oceanic Gulf of Mexico. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers. 2002;49[1]:121–42. [CrossRef]
- Love M, Baldera A, Yeung C, Robbins C. The Gulf of Mexico Ecosystem: A Coastal and Marine Atlas. New Orleans, LA: Ocean Conservancy, Gulf Restoration Center. 2013.
- Keim BD, Muller RA. Hurricanes of the Gulf of Mexico. Louisiana State University Press, Baton Rouge, LA, USA; 216. 2009.
- Yablonsky RM, Ginis I. Limitation of One-Dimensional Ocean Models for Coupled Hurricane–Ocean Model Forecasts. Monthly Weather Review. 2009 Dec 1;137[12]:4410–9. [CrossRef]
- Deltares. Deft3D-Flow and -Wave user manuals. Delft, Netherlands; 2019.
- Booij N, Ris RC, Holthuijsen LH. A third-generation wave model for coastal regions: 1. Model description and validation. Journal of geophysical research: Oceans. 1999;104[C4]:7649–66.
- GEBCO Compilation Group. GEneral Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans-GEBCO 2021 grid [Internet]. 2021. Available from: https://www.gebco.net/data_and_products/historical_data_sets/#gebco_2021.
- National Geophysical Data Center. U.S. Coastal Relief Model - Central Gulf of Mexico. National Geophysical Data Center [Internet]. NOAA; 2001. [CrossRef]
- Powell M, Houston S, Amat L, Morisseau-Leroy N. The HRD real-time hurricane wind analysis system. 1998; [CrossRef]
- Doyle JD. Coupled atmosphere–ocean wave simulations under high wind conditions. Monthly Weather Review. 2002;130:3[087–3]:099. [CrossRef]
- Hodur RM. The Naval Research Laboratory’s Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System (COAMPS). Mon Wea Rev. 1997;125:1414–30. [CrossRef]
- Gill AE. Atmosphere-Ocean dynamics, vol. 30 of International Geophysics Series. Academic Press. 1982.
- Lane A. The heat balance of the North Sea. Birkenhead, Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory, 46pp. (Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory, Report No. 8). 1989.
- Eijkeren JCH, van, Haan BK de., Stelling GS, Stijn TL van. “Notes on Numerical Fluid Mechanics, Linear upwind biased methods.” In C. B. Vreugdenhil and B. Koren, eds., Numerical Methods for Advection-Diffusion Problems. Vieweg Verlag, Braunschweig. 1993;45[3]:55–91.
- van Leer B. Towards the Ultimate Conservative Difference Scheme. II. Monotonicity and Conservation Combined in a Second-order Scheme. Journal of Computational Physics. 1974 Mar 1;14:361–70.
- Forester CK. Higher order monotonic convective difference schemes. Journal of Computational Physics. 1979 Jan 1;23[1]:1–22. [CrossRef]
- Cialdi M, Secchi PA. Sur la Transparence de la Mer. Comptes Rendu de l’Acadamie des Sciences; 1865.
- Whipple GC. The Microscopy of Drinking-Water. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 73–5. 1899.
- Wernand MR. On the history of the Secchi disc. Journal of the European Optical Society - Rapid publications [Internet]. 2010 Apr 27 [cited 2021 Oct 5];5[0]. Available from: https://www.jeos.org/index.php/jeos_rp/article/view/10013s.
- Collin R, D’Croz L, Gondola P, Del Rosario JB. Climate and hydrological factors affecting variation in chlorophyll concentration and water clarity in the Bahia Almirante, Panama. In: Proceedings of the Smithsonian Marine Science Symposium. Smithsonian Institution Scholarly Press; 2009. [CrossRef]
- Löptien U, Meier HEM. The influence of increasing water turbidity on the sea surface temperature in the Baltic Sea: A model sensitivity study. Journal of Marine Systems. 2011 Nov 1;88[2]:323–31. [CrossRef]
- Raabe T, Wiltshire KH. Quality control and analyses of the long-term nutrient data from Helgoland Roads, North Sea. Journal of Sea Research. 2009;61[1]:3–16. [CrossRef]
- Testa J, Lyubchich V, Zhang Q. Patterns and Trends in Secchi Disk Depth over Three Decades in the Chesapeake Bay Estuarine Complex. Estuaries and Coasts. 2019 Apr 15;42. [CrossRef]
- Wiltshire KH, Malzahn AM, Wirtz K, Greve W, Janisch S, Mangelsdorf P, et al. Resilience of North Sea phytoplankton spring bloom dynamics: An analysis of long-term data at Helgoland Roads. Limnology and Oceanography. 2008;53[4]:1294–302. [CrossRef]
- Wiltshire KH, Kraberg A, Bartsch I, Boersma M, Franke HD, Freund J, et al. Helgoland Roads, North Sea: 45 Years of Change. Estuaries and Coasts. 2010;33[2]:295–310. [CrossRef]
- Federal Geographic Data Committee. FGDC-STD-018. Coastal and Marine Ecological Classification Standard. Reston, VA. Federal Geographic Data Committee. 2012.
- Singh VP, Xu CY. Evaluation and Generalization of 13 Mass-Transfer Equations for Determining Free Water Evaporation. Hydrological Processes. 1997;11[3]:311–23.
- Emanuel KA. Sensitivity of Tropical Cyclones to Surface Exchange Coefficients and a Revised Steady-State Model incorporating Eye Dynamics. Journal of Atmospheric Sciences. 1995 Nov 1;52:3969–76. [CrossRef]
- Janssen P. Air-sea interaction through waves, paper presented at ECMWF Workshop on Ocean-Atmosphere Interactions,. Reading, U K [Internet]. 2008;[10–12Nov 2008]. Available from: http://www.ecmwf.int/publications/.
- Willmott CJ, Robeson SM, Matsuura K. A refined index of model performance. Int J Climatol. 2012 Nov 15;32[13]:2088–94.
- Young IR. A review of the sea state generated by hurricanes. Marine Structures. 2003 May 1;16[3]:201–18. [CrossRef]
- Taylor KE. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. 2001;106[D7]:7183–92. [CrossRef]
- Ginis I. Tropical Cyclone-Ocean Interactions. Advances in Fluid Mechanics Series. 2002 Jan 1;33.
- Dietrich DE, Tseng YH, Jan S, Yau P, Lin C. Modeled Oceanic Response to Hurricane Katrina. The 16th Conference on Atmospheric and Oceanic Fluid Dynamics. 2007;10.
- Jaimes B, Shay LK. Enhanced Wind-Driven Downwelling Flow in Warm Oceanic Eddy Features during the Intensification of Tropical Cyclone Isaac (2012): Observations and Theory. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 2015 Jun 1;45[6]:1667–89. [CrossRef]
- Domingues R, Goni G, Bringas F, Lee SK, Kim HS, Halliwell G, et al. Upper ocean response to Hurricane Gonzalo (2014): Salinity effects revealed by targeted and sustained underwater glider observations. Geophysical Research Letters. 2015;42[17]:7131–8. [CrossRef]
- Maneesha K, Murty VSN, Ravichandran M, Lee T, Yu W, McPhaden MJ. Upper ocean variability in the Bay of Bengal during the tropical cyclones Nargis and Laila. 2012 [cited 2021 Oct 5]; Available from: https://drs.nio.org/xmlui/handle/2264/4202. [CrossRef]
- Ning J, Xu Q, Zhang H, Wang T, Fan K. Impact of Cyclonic Ocean Eddies on Upper Ocean Thermodynamic Response to Typhoon Soudelor. Remote Sensing. 2019 Jan;11[8]:938. [CrossRef]
- Bingham FM, Foltz GR, McPhaden MJ. Seasonal cycles of surface layer salinity in the Pacific Ocean. Ocean Science. 2010;6[3]:775–87. [CrossRef]
- D’Ortenzio F, Iudicone D, De C, de Boyer Montégut C, Testor P, Antoine D, et al. Seasonal variability of the mixed layer depth in the Mediterranean Sea as derived from in situ profiles. Geophysical Research Letters. 2005 Jun 28;32. [CrossRef]
- Kara AB, Rochford A, Hurlburt HE. Mixed layer depth variability over the global ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans [Internet]. 2003 [cited 2021 Oct 5];108[C3]. Available from: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2000JC000736. [CrossRef]
- Keerthi MG, Lengaigne M, Vialard J, de Boyer Montégut C, Muraleedharan PM. Interannual variability of the Tropical Indian Ocean mixed layer depth. Clim Dyn. 2013 Feb 1;40[3]:743–59. [CrossRef]
- Lim S, Jang CJ, Oh IS, Park J. Climatology of the mixed layer depth in the East/Japan Sea. Journal of Marine Systems. 2012 Aug 1;96–97:1–14. [CrossRef]
- DeMaria M, Kaplan J. A statistical hurricane intensity prediction scheme (SHIPS) for the Atlantic basin. Weather and Forecasting. 1994;9[2]:209–20. [CrossRef]
- Emanuel KA. The Maximum Intensity of Hurricanes. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences. 1988 Apr 1;45[7]:1143–55. [CrossRef]
- Whitney LD, Hobgood JS. The Relationship between Sea Surface Temperatures and Maximum Intensities of Tropical Cyclones in the Eastern North Pacific Ocean. Journal of Climate. 1997 Nov 1;10[11]:2921–30.
- Bitz CM, Chiang JCH, Cheng W, Barsugli JJ. Rates of thermohaline recovery from freshwater pulses in modern, Last Glacial Maximum, and greenhouse warming climates. Geophysical research letters. 2007;34[7]. [CrossRef]
- D’Sa EJ, Tehrani NC, Rivera-Monroy VH. Oceanic response around the Yucatan Peninsula to the 2005 hurricanes from remote sensing. 2011 Nov 1;8175:81750P.
- Andreas EL, Monahan EC. The role of whitecap bubbles in air–sea heat and moisture exchange. Journal of physical oceanography. 2000;30[2]:433–42. [CrossRef]
- Dean RG, Dalrymple RA. Water wave mechanics for engineers and scientists. Vol. 2. world scientific publishing company; 1991.
- Holthuijsen LH. Waves in Oceanic and Coastal Waters [Internet]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2007 [cited 2021 Oct 5]. Available from: https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/waves-in-oceanic-and-coastal-waters/F6BF070B00266943B0ABAFEAE6F54465.
- Dai D, Qiao F, Sulisz W, Han L, Babanin A. An experiment on the nonbreaking surface-wave-induced vertical mixing. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 2010;40[9]:2180–8. [CrossRef]
- Huang CJ, Qiao F, Song Z, Ezer T. Improving simulations of the upper ocean by inclusion of surface waves in the Mellor-Yamada turbulence scheme. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2021 Oct 5];116[C1]. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1029/2010JC006320. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Map of Gulf of Mexico with hurricane tracks of Katrina and Rita, NDBC buoy locations (B1-B10), NOAA water level stations (A1-A6), profile locations (P1 & P2), and IHO stations (W1-W4).
Figure 1.
Map of Gulf of Mexico with hurricane tracks of Katrina and Rita, NDBC buoy locations (B1-B10), NOAA water level stations (A1-A6), profile locations (P1 & P2), and IHO stations (W1-W4).
Figure 2.
Comparison of wind speed (m/s) and direction (°) between NDBC (●) stations, COAMPS (┼) and Blended (▬) winds (COAMPS+HWIND).
Figure 2.
Comparison of wind speed (m/s) and direction (°) between NDBC (●) stations, COAMPS (┼) and Blended (▬) winds (COAMPS+HWIND).
Figure 3.
Comparisons of 1-day mean water level (from the model) and altimeter sea surface height anomaly (from the TOPEX and ERS-2 Satellites). The scatterplots are from pointwise comparisons between both data: dashed-black line is the slope (linear fit) and Correlation Coefficients (CC) were estimated for each time span.
Figure 3.
Comparisons of 1-day mean water level (from the model) and altimeter sea surface height anomaly (from the TOPEX and ERS-2 Satellites). The scatterplots are from pointwise comparisons between both data: dashed-black line is the slope (linear fit) and Correlation Coefficients (CC) were estimated for each time span.
Figure 4.
Comparisons of water level change during Hurricane Katrina in 2005: Data (●) of NOAA stations and Delft3D model results (▬).
Figure 4.
Comparisons of water level change during Hurricane Katrina in 2005: Data (●) of NOAA stations and Delft3D model results (▬).
Figure 5.
Comparisons of wave (significant wave height and peak period) and wind (speed and direction) properties at NDBC stations. Data (●) and model results (▬).
Figure 5.
Comparisons of wave (significant wave height and peak period) and wind (speed and direction) properties at NDBC stations. Data (●) and model results (▬).
Figure 6.
Comparisons of vertical profiles in salinity and temperature on July 10 and July 19: Profiles (●), HYCOM (♦), Model results (★).
Figure 6.
Comparisons of vertical profiles in salinity and temperature on July 10 and July 19: Profiles (●), HYCOM (♦), Model results (★).
Figure 7.
Taylor diagram for error statistics of water level. Cases are referred from
Table 3. Stations W1, W2, W3, W4 are in
Figure 1. Case 1-4 indicate the values of parameters in
Table 2.
Figure 7.
Taylor diagram for error statistics of water level. Cases are referred from
Table 3. Stations W1, W2, W3, W4 are in
Figure 1. Case 1-4 indicate the values of parameters in
Table 2.
Figure 8.
Taylor diagram for error statistics of vertical profiles in salinity and temperature: Cases are referred from
Table 2. Locations of profiles P1 and P2 are in
Figure 1.
Figure 8.
Taylor diagram for error statistics of vertical profiles in salinity and temperature: Cases are referred from
Table 2. Locations of profiles P1 and P2 are in
Figure 1.
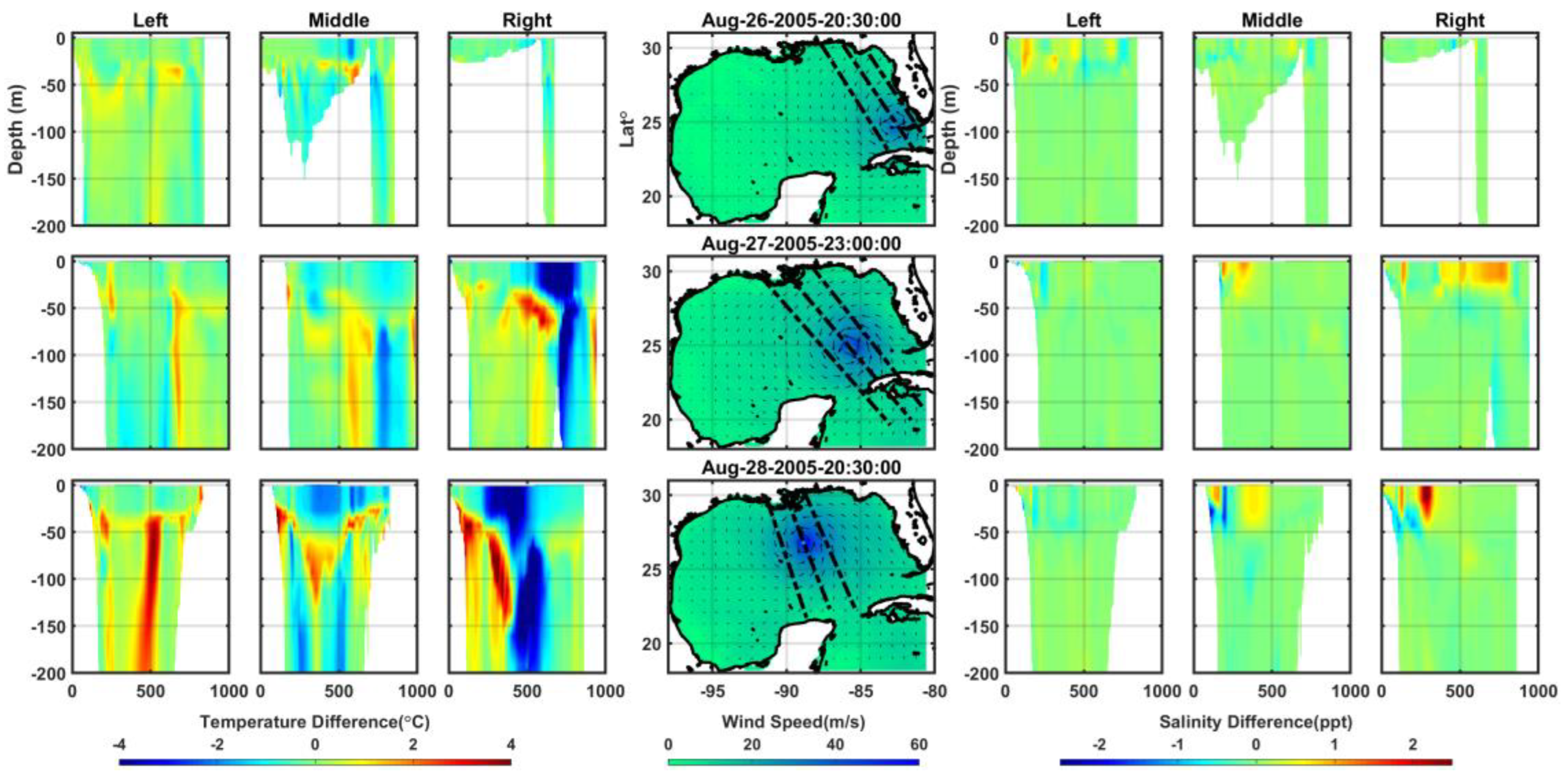
Figure 9.
Differences of vertical cross-sections (along the black dashed lines) of temperature (°C) and salinity (ppt) along the lines; left, center and right sides of storm’ eye.
Figure 9.
Differences of vertical cross-sections (along the black dashed lines) of temperature (°C) and salinity (ppt) along the lines; left, center and right sides of storm’ eye.
Figure 10.
Differences of vertical cross-sections (along the black dashed lines) of temperature (°C) and salinity (ppt) along the lines; upper, middle and lower sides of storm’s eye.
Figure 10.
Differences of vertical cross-sections (along the black dashed lines) of temperature (°C) and salinity (ppt) along the lines; upper, middle and lower sides of storm’s eye.
Figure 11.
Estimated daily mean mixed layer depths (MLD, m) and wind fields (WS, m/s) of Hurricane Katrina, ranging between August 26th and September 01st. Reference sea state and winds are averaged MLD and WS during August 21st-23rd, respectively.
Figure 11.
Estimated daily mean mixed layer depths (MLD, m) and wind fields (WS, m/s) of Hurricane Katrina, ranging between August 26th and September 01st. Reference sea state and winds are averaged MLD and WS during August 21st-23rd, respectively.
Figure 12.
a) MLD recovery (%) from July in the Gulf of Mexico, before hurricane Katrina: compared with mean-MLD during July 1st-3rd, b) MLD recovery from Hurricane Katrina: compared the MLD with mean-MLD during July 1st-3rd (►) and Aug 21st-23rd (●).
Figure 12.
a) MLD recovery (%) from July in the Gulf of Mexico, before hurricane Katrina: compared with mean-MLD during July 1st-3rd, b) MLD recovery from Hurricane Katrina: compared the MLD with mean-MLD during July 1st-3rd (►) and Aug 21st-23rd (●).
Figure 13.
Variations of MLD during Hurricane Katrina: in row 1) wind-field, 2) MLD in FLOW model, 3) MLD in coupled FLOW+WAVE model, 4) wave length along the line, 5) comparison of MLD along the black dashed line: FLOW (+) and FLOW+WAVE (▬).
Figure 13.
Variations of MLD during Hurricane Katrina: in row 1) wind-field, 2) MLD in FLOW model, 3) MLD in coupled FLOW+WAVE model, 4) wave length along the line, 5) comparison of MLD along the black dashed line: FLOW (+) and FLOW+WAVE (▬).
Figure 14.
Wave effects on the vertical cross-sections (along the black dashed lines) of temperature (°C) and salinity (ppt) along the lines; left, center and right sides of storm’s eye.
Figure 14.
Wave effects on the vertical cross-sections (along the black dashed lines) of temperature (°C) and salinity (ppt) along the lines; left, center and right sides of storm’s eye.
Figure 15.
Wave effects on the vertical cross-sections (along the black dashed lines) of temperature (°C) and salinity (ppt) along the lines; upper, middle, and lower sides of storm’s eye.
Figure 15.
Wave effects on the vertical cross-sections (along the black dashed lines) of temperature (°C) and salinity (ppt) along the lines; upper, middle, and lower sides of storm’s eye.
Table 1.
Applied the physical parameters in Delft3D modeling system.
Table 1.
Applied the physical parameters in Delft3D modeling system.
| Dalton |
0.0041 |
| Stanton |
0.0041 |
| Air Density |
1.15 kg/m3
|
| Bottom Roughness |
Manning’s Formula |
| |
Water: 0.02, Land:0.08 |
| Secchi Depth |
15 m |
| Background horizontal |
|
| Viscosity |
10 m2/s |
| Diffusivity |
10 m2/s |
Table 2.
A summary of physical parameters in calibration process.
Table 2.
A summary of physical parameters in calibration process.
| Parameter |
Value 1 |
Value 2 |
Value 3 |
Value 4 |
| Eddy Viscosity/Diffusivity (m2/s) |
01 / 01 |
05 / 05 |
10 / 10 |
15 / 15 |
| Secchi Depth (m) |
3.5 |
5.0 |
10.0 |
15.0 |
| Dalton & Stanton Number |
0.0013 / 0.0013 |
0.0014 / 0.0014 |
0.0041 / 0.0041 |
0.0098 / 0.0098 |
Table 3.
Information of NOAA Stations and profiles, and statistical results of model validation.
Table 3.
Information of NOAA Stations and profiles, and statistical results of model validation.
| Stations |
Lat |
Lon |
Parameter |
RMSE |
CC |
RIA |
| Corpus Christi, TX |
27.58 |
-97.22 |
Water level |
0.085 |
0.942 |
0.818 |
| Freeport, TX |
28.95 |
-95.32 |
ʺ |
0.081 |
0.942 |
0.831 |
| Calcasieu, LA |
29.77 |
-93.35 |
ʺ |
0.114 |
0.921 |
0.768 |
| Grand Isle, LA |
29.27 |
-89.95 |
ʺ |
0.118 |
0.855 |
0.643 |
| S.W Pass, LA |
28.93 |
-89.40 |
ʺ |
0.196 |
0.806 |
0.368 |
| Wave Land, MS |
30.28 |
-89.37 |
ʺ |
0.138 |
0.922 |
0.671 |
| Ocean Springs, MS |
30.40 |
-88.80 |
ʺ |
0.187 |
0.914 |
0.573 |
| Apalachicola, FL |
29.73 |
-84.98 |
ʺ |
0.267 |
0.848 |
0.321 |
| Tampa, FL |
27.87 |
-82.55 |
ʺ |
0.229 |
0.877 |
0.543 |
| Profile July 10 |
27.79 |
-86.20 |
Salinity/Temperature |
0.46/0.84 |
0.803/0.997 |
0.84/0.94 |
| Profile July 19 |
28.01 |
-86.28 |
ʺ |
0.26/0.70 |
0.925/0.997 |
0.94/0.96 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).