1. Introduction
Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) has a tripartite, single-stranded, positive-sense RNA genome (Palukaitis and García-Arenal, 2003; Jacquemond, 2012). RNA1 encodes the 110 kDa 1a protein which functions as a methyltransferase and RNA helicase. RNA2 is the translation template for the 97 kDa 2a protein which functions as an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, and RNA2 also encodes the multifunctional 2b protein, which is translated from the RNA2-derived subgenomic RNA4A (Ding et al.; 1994; Li and Ding, 2006; Jacquemond, 2012). RNA3 is the translation template for the movement protein, while the coat protein is expressed from the RNA3-derived subgenomic RNA4 (Palukaitis and García-Arenal, 2003; Jacquemond, 2012). CMV has a very wide host range, comprising plants of 1071 species, belonging to 521 genera (Yoon et al.; 2019), and the virus is transmitted in the stylet-borne nonpersistent manner by aphid vectors from over 80 species (Hull, 2013; Krenz et al.; 2015; Fereres and Perry, 2019).
Taxonomically, Cucumber mosaic virus is the type species of the Cucumovirus genus (family Bromoviridae) (Yoon et al.; 2019), which also contains the species Gayfeather mild mottle virus, Peanut stunt virus and Tomato aspermy virus (TAV) (Bujarski et al.; 2019). However, CMV is the most diverse of the cucumoviruses. Most of the many strains and isolates of CMV can be assigned to one of three Subgroups (IA, IB and II) based on RNA sequence similarity (Palukaitis and García-Arenal, 2003; Balaji et al.; 2008; Jacquemond, 2012).
The multifunctional CMV 2b protein suppresses antiviral RNA silencing by binding to double-stranded short-interfering RNAs (siRNAs), and it also inhibits micro(mi)RNA-directed cleavage of host transcripts by Argonaute (AGO)1 and AGO4, AGO1-mediated regulation of mRNA translation, and AGO4-mediated effects on plant genomic DNA methylation (reviewed by Carr and Murphy, 2019). The CMV 2b protein also inhibits plant defensive signaling pathways regulated by the phytohormones jasmonic acid and salicylic acid, and it influences interactions between host plants and the aphid vectors of CMV (Carr and Murphy, 2019). In Arabidopsis thaliana the 2b protein’s effects on miRNA-directed AGO1 activity are mediated by a direct physical interaction (Zhang et al.; 2006; González et al.; 2010). The extent to which AGO1 activity is inhibited differs between 2b proteins encoded by CMV strains belonging to different Subgroups, with 2b proteins of Subgroup II having a weaker inhibitory effect on miRNA-directed mRNA cleavage than orthologues encoded by most Subgroup IA and IB CMV strains (Lewsey et al.; 2007). However, recent work suggests that this is not due to an inability of Subgroup II CMV 2b protein orthologues to form 2b-AGO1 complexes; rather, it is due to differences in intracellular localization. Specifically, AGO1-2b complexes for Subgroup II orthologues (such as the 2b protein encoded by LS-CMV) accumulate almost exclusively in nuclei, but for Subgroup IA and IB 2b orthologues these complexes also occur in the cytoplasm, consistent with the localization of the pool of AGO1 molecules mediating miRNA-mediated mRNA cleavage (Crawshaw et al.; 2023).
The more efficient inhibition of AGO1 mRNA cleavage by 2b protein orthologues encoded by Subgroup IA or IB CMV strains helps explain why these strains generally induce more severe symptoms than strains belonging to Subgroup II (Lewsey et al.; 2007, 2009; Du et al.; 2014). However, unrestricted binding of the 2b protein to AGO1 can trigger effects that are directly or indirectly deleterious to the virus. For example, in A. thaliana the inhibition of miR403-directed cleavage of AGO2 mRNA, permits increased AGO2 protein synthesis, which fosters RNA silencing-mediated resistance against CMV (Harvey et al.; 2011). Additionally, inhibition of AGO1 activity by the 2b protein can induce strong resistance against aphid vectors. During infection both effects are circumvented by the intervention of the CMV 1a protein, which binds to and re-localizes 2b protein molecules to processing bodies (P-bodies), which decreases the proportion of the 2b protein pool available for 2b-AGO1 complex formation (Watt et al.; 2020).
Despite its important consequences for the success of CMV infection and for vector-mediated transmission of the virus, the interaction between the 2b protein and AGO1 is not understood in detail. For example, whereas specific amino acid residues involved in double-stranded RNA binding and RNA silencing suppression, or intracellular localization have been definitively characterized (reviewed by Carr and Murphy, 2019), no specific 2b protein residues have been shown to be indispensable for the CMV 2b protein-AGO1 interaction to occur. Furthermore, it is unknown if specific 2b protein residue(s) are responsible for interaction with the CMV 1a protein, or if the same amino acids are involved in 2b-AGO1 complex formation.
Early studies that revealed, using site-directed mutagenesis, several functional domains in the 2b protein of the Subgroup IA strain Fny-CMV, including those responsible for nuclear localization, protein phosphorylation, RNA binding and RNA silencing suppression, did not find a residue or domain for binding to AGO1 or to AGO4 (González et al.; 2010, 2012) (
Figure 1A). A subsequent study using the SD-CMV 2b protein employed a strategy of larger scale deletions and led to certain regions of the 2b protein being ruled out as being important in AGO1 binding, but it was inferred that the sequence(s) responsible for 2b-AGO1 complex formation most likely lay somewhere in a broad region spanning residues 38 through 94 (Duan et al.; 2012) (
Figure 1a). However, so far as we are aware no specific AGO1-binding residues or discrete sequence domains have been pinpointed. In this study, we set out to identify sequences within the 2b protein that enable it to interact with AGO1 and that condition its regulation by the CMV 1a protein. In the process we found that some of the 2b protein’s properties may potentially be explainable by possession of intrinsically disordered regions.
2. Results
2.1. Construction of 2b Protein Deletion Mutants
To test the importance of different sequences of the Fny-CMV 2b protein in interactions with the CMV 1a protein and with AGO1, a series of cDNA clones encoding mutant versions of the protein were generated, in which regions with already known or currently unknown biological functions were deleted (
Figure 1b). These included reconstruction of previously examined protein variants truncated in the N-terminal 17 (2b
D1-17) or the C-terminal 16 (2b
Δ95-110) amino acids (Lewsey et al.; 2009), deletion of 55 N-terminal amino acids (2b
Δ1-55), as well as mutants encoding 2b variants with more extensive deletions starting from the C-terminus. These were deletions of 26 (2b
Δ85-110), 28 (2b
Δ83-110), 37 (2b
Δ74-110), 42 (2b
Δ69-110), 46 (2b
Δ65-110), 50 (2b
Δ61-110) or 55 (2b
Δ56-110) amino acids. There was a focus on deletions of the C-terminal/proximal sequences since we initially hypothesized that the C-terminal domain of the 2b protein might be involved in its interaction with the CMV 1a protein. The rationale for this was that the interaction between the CMV 1a and CMV 2b proteins ameliorates the 2b-induced symptom-like phenotype in transgenic plants (Westwood et al.; 2013; Watt et al.; 2020), and that the 2b protein C-terminal domain is associated with symptom severity (Lewsey et al.; 2009).
To investigate the potential roles of internal 2b protein sequences, in-frame internal deletions of residues 83 to 93 (2b
Δ83-93), 56 to 65 (2b
Δ56-65), 56 to 60 (2b
Δ56-60), and 39 to 48 (2b
Δ39-48) were constructed, as well as alanine substitution mutations replacing the native Fny-CMV 2b sequence at residues 56 through 65 with ten alanine residues (2b
56aaa65) and 56 through 60 with five alanine residues (2b
56aaa60). Lastly, two chimeric CMV 2b proteins were generated: one in which residues 83-93 of the Fny-CMV 2b sequence were introduced into the LS-CMV 2b sequence (2b
LS/Fny83-93), and in the second two point mutations (Y58H and Q59G) into the Fny-CMV 2b protein sequence to recapitulate the LS-CMV 2b protein sequence between residues 56 and 60 (2bFny/LS56-60) (
Figure 1b).
2.2. Residues 56-60 of the Fny-CMV 2b Protein Are Required for Interaction with the CMV 1a Protein
Complex formation between the CMV 1a and 2b proteins causes the bound 2b protein to be re-localized into P-bodies (Watt et al.; 2020). Monitoring whether this change in localization occurred was used as an initial means to assess whether mutant 2b proteins had lost the ability to interact with the 1a protein. Confocal laser scanning microscopy was used to examine the distribution of 2b-derived and 1a-derived C-terminal RFP and GFP fusion proteins (
Figure 2).
Deletion of the N-terminal 17 or C-terminal 16 residues did not abolish co-localization of the 2b protein with the 1a protein (
Figure 2), although the C-terminal deletion caused an apparent decrease in the proportion of 2b protein co-localizing with the 1a protein (
Figure S1). More extensive deletions (of residues 85 to 110, and 56 to110, which bisected the 2b protein), as well as in-frame deletions of residues 83 to 93 and 56 to 60, resulted in abolition of co-localization with the 1a protein (
Figure 2). Replacement of residues 56-60 with alanine (mutant 2b
56aaa60) also abolished co-localization with the CMV 1a protein, whilst replacement of residues 56-60 of the Fny-CMV 2b with the corresponding sequence from the LS-CMV 2b protein did not completely abolish co-localization with the CMV 1a protein. This was puzzling since LS-CMV 2b protein is unable to interact with the Fny-CMV 1a protein (Crawshaw et al.; 2023).
The region between residues 83-93 in the Fny-CMV 2b protein has no equivalent sequence in the LS-CMV 2b protein (
Figure 1;
Figure S2). Thus, we hypothesized that this sequence or residues lying within it might govern the interaction of the Fny-CMV 2b protein with the Fny-CMV 1a protein. However, the chimeric 2b
LS/Fny83-93 protein created by insertion of these amino acids into the LS-CMV 2b protein backbone showed no co-localization with the Fny-CMV 1a protein (
Figure 2). This indicates that the residues 83-93 of Fny-CMV 2b do not facilitate the 2b-1a interaction.
The effect of C-terminal deletions on 2b-localization likely relates to a loss of a recently described nuclear export sequence (NES) between residues 77-87 (Kim et al.; 2022). The N-terminal mutant from residues 1-17 did not appear to impact nuclear localization but deletion of residues from 1-55 which includes the NLS domain caused a reduction in nuclear localization (
Figure S3). The results are confirmatory of previous findings with the Fny-CMV 2b protein (Lewsey et al.; 2009).
To authenticate that observed decreases in, or abolition of, co-localization between 2b-derived and 1a-derived C-terminal RFP and GFP fusion proteins reflected genuine losses of direct interactions bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays were carried out. To facilitate this, N- and C-terminal domains of the yellow fluorescent protein (YFPn or YFPc) were fused to the C-termini of mutant CMV 2b proteins and wild-type Fny-CMV 1a protein. In contrast to the co-localization results obtained with the deletion mutant 2b
Δ83-93 protein but in agreement with the co-localization results obtained with the chimeric 2b
LS/Fny83-93 protein (
Figure 2), deletion of residues 83-93 did not abolish the physical interaction between the 2b and 1a proteins, however, more extensive deletions of residues in the C-terminus did (
Figure 3).
According to BiFC assays, deletion of the 2b protein residues from 61 or 65 to the C-terminal residue 110 diminished the interaction with CMV 1a proteins and deletion of residues from 56 to 110 abolished the interaction completely (
Figure 3). In-frame deletions of residues 56-65 or 56-60 also abolished 1a-2b protein complex formation, as did substitution of the authentic amino acids at positions 56 to 65 and 56 to 60 with alanine residues (respectively, mutants 2b
56aaa65 and 2b
56aaa60:
Figure 1b) (
Figure 3). Mutation of the sequence 56 to 60 of the Fny-CMV 2b protein (PF
YQV) to recapitulate the corresponding sequence of the LS-CMV 2b protein (PF
HGV) did not completely abolish the 2b-1a protein-protein interaction although it appeared to be weaker (
Figure 3), suggesting that while this domain is the major determinant of binding other Fny-CMV 2b sequence(s) may play some role(s).
Co-immunoprecipitation assays confirmed the importance of residues 56-60 of the Fny-CMV 2b protein in mediating complex formation with the 1a protein (
Figure 4). In agroinfiltrated leaves of
N. benthamiana, GFP-tagged Fny-CMV 1a protein was co-expressed with RFP-tagged Fny-CMV 2b protein mutants. RFP-tagged wild-type and mutant 2b proteins were immunoprecipitated from leaf homogenates using magnetic agarose beads coated with anti-RFP and analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-GFP to detect Fny-CMV 1a proteins complexed with 2b-RFP fusion proteins. The Fny-CMV 1a protein-GFP fusion co-immunoprecipitated with the wild-type 2b-RFP fusion protein and the RFP tagged variant of the chimeric 2b
LS/Fny56-60 protein but not with the RFP fusion protein variants of the 2b
D56-60 or 2b
56aaa60 mutants (
Figure 4), in line with results from the BiFC assays (
Figure 3).
2.3. Residues 56-60 Are Important for the Interaction of the Fny-CMV 2b Protein with AGO1 as well as with the CMV 1a Protein
The effects of mutation of the CMV 2b protein on its interactions with AGO1 were examined. Deletions of residues 1-17 or 83-93 had no impact on the co-localization of AGO1 with the 2b protein (
Figure 5). However, progressively larger deletions of residues beginning at the C-terminus (95-110, 85-110, 74-110, 56-110, 48-110 and 44-110) diminished AGO1-2b protein co-localization (
Figure 5). To determine if these changes in localization resulted from losses of physical interaction between the two proteins, BiFC was carried out (
Figure 6). Deletion of residues 1-17, 95-110, 85-110 or 74-110 had no impact on the interaction the 2b protein with AGO1. However, marked decreases in the ability of the 2b protein to interact with AGO1 occurred after deletion of residues 61-110, 56-110 or 48-110. In-frame deletions of residues 56-60 or 39-48 weakened the interaction with AGO1, as did replacement of amino acids in the Fny-CMV 2b protein to match residues 56-60 of the LS-CMV 2b protein (the chimeric 2b
LS/Fny56-60 protein). Substitution of residues 56-60 with alanine residues (mutants 2b
56aaa60) also decreased interaction with AGO1.
Interestingly, the CMV 2b mutant protein lacking residues between 1-55 still interacted with AGO1 but its localization was predominantly cytoplasmic likely due to loss of the NLS region. Thus, both C- and N-proximal 2b protein sequences may facilitate the interaction with AGO1. Our evidence for the importance of sequences between residues 39 and 60 in the Fny 2b sequence is not inconsistent with previous work (Duan et al.; 2012) but it throws doubt on whether there is a single discrete region of the 2b protein that is alone sufficient for AGO1 interaction.
Co-immunoprecipitation assays confirmed the importance of residues 56-60 in mediating the interaction of the Fny-CMV 2b and AGO1 proteins (
Figure 7). RFP-tagged mutant versions of the Fny-CMV 2b protein were co-expressed with GFP-tagged AGO1 protein, immunoprecipitated using anti-RFP agarose magnetic beads and analyzed by western immunoblotting using anti-GFP antibodies to detect any AGO1 proteins complexed with the mutant 2b-RFP proteins. The AGO1-GFP fusion co-immunoprecipitated with the full length 2b-RFP protein and the chimeric 2b
LS/Fny56-60-RFP protein but not with the 2b
D56-60-RFP or 2b
56aaa60-RFP proteins (
Figure 7), in line with results from the BiFC assays.
2.4. In Silico Prediction of Intrinsic Disorder in the 2b Protein
The importance of residues 56-60 in the 1a-2b interaction and residues 39-60 in the AGO1-2b interaction (which overlaps with the sequence needed for 1a-2b complex formation) suggests that larger regions of the 2b protein structure are required for these interactions. Such effects can occur when two or more proteins with intrinsically disordered structures interact (Okoye et al.; 2022) and may also explain 1a-2b protein complex formation in P-bodies (Wallmann and Kesten, 2020).
The IUPred3 (Erdős et al.; 2021) and ParSe v2 (Ibrahim et al.; 2023) programs were applied to the full-length sequence of the Fny-CMV 2b protein. Both systems predicted that the Fny-CMV 2b protein contains two intrinsically disordered regions between residues 20-44 and 70-88 (
Figure 8). Additionally, the ANCHOR2 algorithm (Dosztányi et al.; 2009) predicted the presence of two regions capable of binding another molecule thereby forming a more ordered structure (
Figure 8a). Predictions using the CIDER server (
http://pappulab.wustl.edu/CIDER/about/) suggest that the 2b protein has a ‘Janus’ region with a highly context-dependent structure (
Figure S4). Interestingly, the 2b protein of the mild CMV strain LS-CMV (Subgroup II) was predicted to have a more ordered structure with only one potential region of intrinsic disorder between residues 28-38 (
Figure 8B). The 2b protein orthologs encoded by Subgroup IB CMV strains showed an intermediate level of disorder in their structure with the same predicted region of disorder between residues 20-44 but a smaller disordered region between residues 83-90 and only one predicted disordered binding domain between residues 1-20 (
Figure 8B). The disordered nature of the CMV 1a and AGO1 proteins was also predicted using the same algorithms. These results indicate that the 1a protein from Fny contains a region of disorder between residues 539-565 and LS 2b contains a much smaller region of disorder between residues 556-565. AGO1 also contains disordered regions at its N- and C-termini (as has previously been predicted: Chakrabortee et al.; 2016).
A common feature of intrinsically disordered proteins is the ability to undergo phase-separation. The key determinant of whether an intrinsically disordered protein will phase transition is the balance between residues driving cohesive intramolecular interactions and the polar residues driving solvent interactions (Pak et al.; 2016; Murthy et al.; 2019; Schuster et al.; 2020). There have been several methods developed to predict sequences which drive separation (Vernon and Forman-Kay, 2019; Pancsa et al.; 2021). One such tool is ParSe v2 which uses sequence hydrophobicity to identify intrinsically disordered protein regions followed by subsequent sorting into intrinsically disordered protein regions which phase transition and those which do not (Ibrahim et al.; 2023). ParSe v2 predicted that both CMV 1a and 2b proteins contain residues promoting phase separation (
Figure S5). Similarly, the AGO1 protein contains residues promoting it to undergo phase separation (
Figure S5).
2.5. Circular Dichroism and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Results Differ with Respect to the Disordered-Ness of the 2b Protein
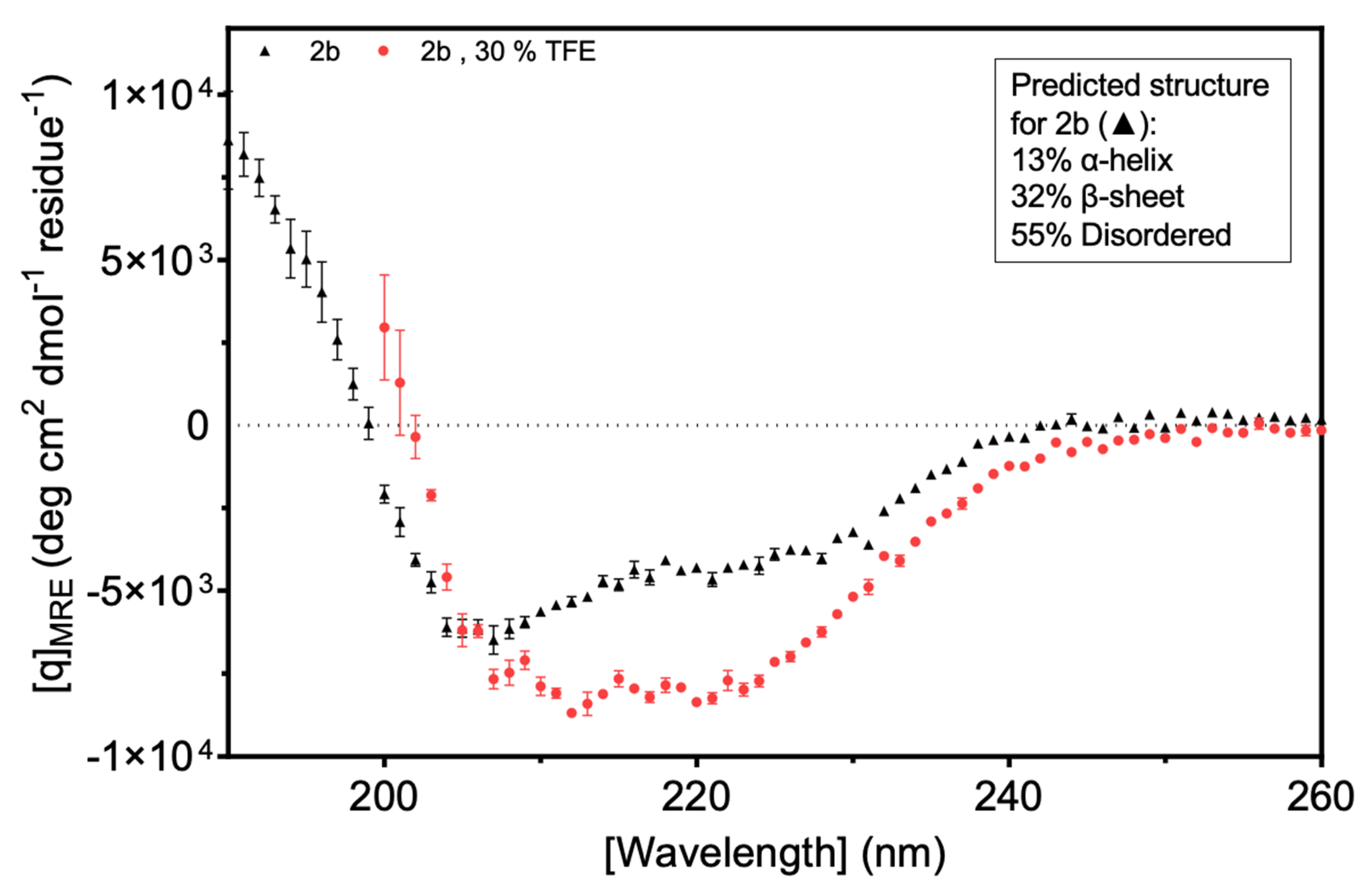
Circular dichroism (CD) was used to explore secondary structure composition. The results suggested that more than 50% of the Fny-CMV 2b protein is intrinsically disordered. The CDSSTR (abbreviation) program was used and the best fit of the data predicted that the protein was 13% α-helix, 32% β-sheet, and 55% disordered (
Figure 9;
Figure S6;
Figure S7). The indication of a large component of β-sheet from the CD analysis was an unexpected finding since it had been assumed that the 2b protein is mainly α-helical. This assumption was based on X-ray crystallography results for the resolvable portion of orthologous TAV 2b protein and on modeling by Gellèrt et al. (2012). However, the TAV 2b protein shares only 58% sequence identity with CMV 2b protein (
Figure S2), and structural studies for a CMV 2b protein have not been conducted before. Folding predictions also suggest a largely α-helical N-terminal half of the protein with no β-sheet structure present (
Figure S8).
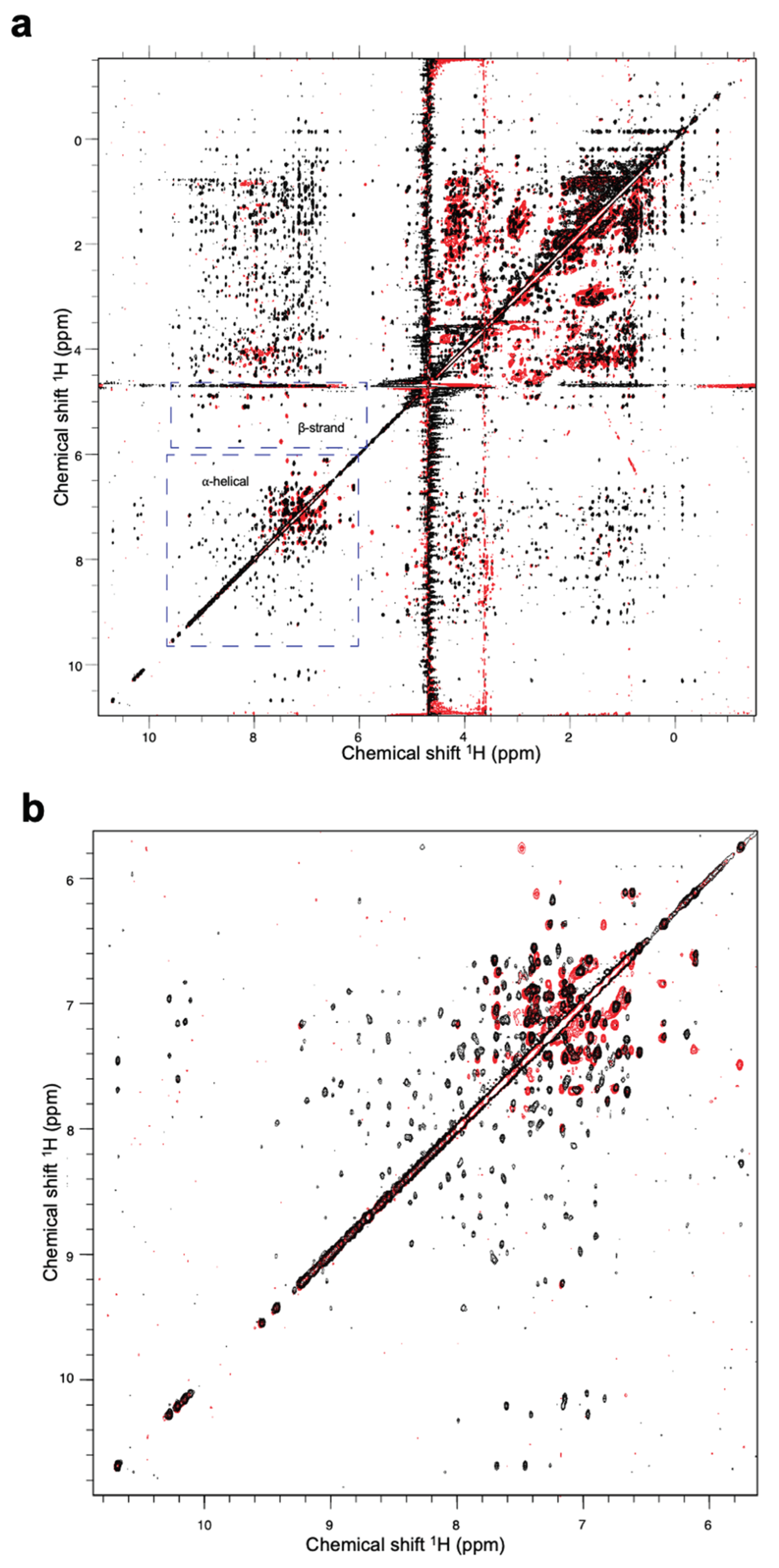
However, the results from
1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy indicated that a high proportion of the Fny-CMV 2b protein adopts α-helical structure with other regions forming β-sheet. The spectra are consistent with a typical globular protein with at least 40 residues arranged in a-helices. There was also evidence for at least 20 residues forming a b-sheet region (
Figure 10). In contrast to the secondary structure composition indicated by CD, NMR detected few signals indicative of intrinsically disordered regions of within the Fny-CMV 2b protein (
Figure 10).
3. Discussion
3.1. Controlling Interactions of the CMV 2b Protein with the CMV 1a Protein and AGO1
The CMV 2b protein interaction with AGO1 can trigger AGO2-mediated antiviral RNA silencing against CMV (Harvey et al.; 2011), as well as a form of resistance against its aphid vectors (Westwood et al.; 2013). Presumably, inhibition of AGO1 is somehow still advantageous for the virus, despite these potentially deleterious effects, which may explain why the ability of 2b to complex with AGO1 has been conserved, and why a mechanism has evolved by which the 1a protein interacts with the 2b protein sufficiently to diminish but not to abolish its effects on AGO1. Meanwhile, and despite the likely importance of the interaction, no specific amino acids have been identified as being responsible for the 2b protein’s interaction with AGO1 (or with AGO4). Generally, only broad inferences have been made regarding the central region of the 2b protein suggesting that it may be involved (González et al.; 2010; Duan et al.; 2012; Zhou et al.; 2014). In some ways this is puzzling since, despite the smallness of the 2b protein, many specific residues and sequence domains have been identified that control other activities carried out by this highly multifunctional protein. A potential conclusion is that it may not be possible to pinpoint a single domain of the CMV 2b protein which governs its interaction with AGO1, and that multiple sequences, or larger regions of the protein may be involved. A possibility that our work raises is that 2b-AGO1 complex formation may be controlled by intrinsically disordered regions within the 2b protein’s secondary structure. If correct, this might help explain aspects of 2b-1a complex formation, and why so many other interactors have been described for the CMV 2b protein.
3.2. Residues 56 to 60 of the CMV 2b Protein Are Involved in Its Interaction with Both the CMV 1a Protein and AGO1
With respect to complex formation between the 1a and 2b proteins of CMV, since the N- and C-terminal domains of the 2b protein had been implicated in enhancement and inhibition of symptoms respectively (Ding et al.; 1996; Lewsey et al.; 2009), we hypothesized that the C-terminal domain may play a role in mediating the interaction of the CMV 2b proteins with CMV 1a proteins. However, while deletion of the C-terminal domain reduced the interaction of the 2b protein with the 1a protein it did not abolish it. Similarly, mutation of residues 83-93 decreased the strength of interaction between CMV 1a and 2b proteins but did not abolish it. Our results suggest that residues 56-60 are necessary for interaction between CMV 1a and 2b proteins to occur. Mutation of these residues also weakened interactions with AGO1, and perhaps this overlap may contribute to the competition between AGO1 and 1a for binding to the Fny-CMV 2b protein (Watt et al.; 2020). However, it was not possible to attribute AGO-2b interactions to a discrete amino acid sequence within the 2b protein, and this prompted us to investigate if the folding of the CMV 2b protein rather than its primary sequence might condition it interactions with other proteins.
3.3. Modeling the Secondary Structure of the Fny-CMV 2b Protein
To our knowledge, it has not been possible to date to determine the structure of a CMV 2b protein using X-ray crystallography. However, a crystal structure has been determined to a resolution of 2.82 Å for a dimer of the orthologous 2b protein of the cucumovirus TAV complexed with a 19 base-pair double-stranded RNA molecule (Chen et al.; 2008). Unfortunately, this crystallographic structure is incomplete. Absent from the model are regions of the TAV 2b, including its N-terminal four amino acids and its C-terminal residues, which the authors considered to be unstructured (Chen et al.; 2008). At the present time, the most detailed published insights into the three-dimensional structures of the CMV 2b protein have come from modeling; in particular, a model developed by Gellèrt et al. (2012), which predicted that the C-terminal domain of the CMV 2b protein is potentially unstructured with only a single short stablea-helix between residues 68-76.
Intrinsically disordered proteins are characterized by the absence of stable structures, and they exist instead as conformational ensembles (Dunker and Obradović, 2001; Holmes, 1983). Our modeling suggested there are marked differences in the numbers of disorder-promoting residues between 2b orthologs of Subgroup IA compared with Subgroup II CMV strains. The 2b ORFs of Subgroup IA CMV strains typically encode products 10 residues longer than Subgroup II CMV strains. Our alignment of the Fny-CMV (Subgroup IA) and LS-CMV (Subgroup II) 2b proteins placed this ‘missing’ sequence between residues 83 and 93 (based on the Fny-CMV 2b protein coordinates). However, there was a prediction of intrinsic disorder over a larger region of dissimilarity between residues 62 and 93 in 2b proteins encoded by Subgroup IA and IB CMV strains. In addition to modeling predictions, a number of observations point towards the disordered nature of the Fny-CMV 2b protein such as the difficulties of obtaining X-ray crystallographic structures, toxicity following overexpression of the full-length 2b protein in bacteria (Gellért et al.; 2012; Sueda et al.; 2010), and differences between the predicted mass of the 2b protein and its apparent mass according to sodium dodecyl-sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, are all hallmarks of intrinsically disordered proteins (Nadassy et al.; 1999; Ebert et al.; 2008; Vavouri et al.; 2009; Oldfield et al.; 2013). The possibility of intrinsic disorder in the Fny-CMV 2b protein led us to experimentally investigate its secondary structure.
3.4. Experimental Investigations of the Folding of the 2b Protein
To our knowledge, the CD and NMR data presented here are the first obtained for the CMV 2b protein. The CD data broadly supported the modeling predictions that the C-terminal 50% of the protein is largely disordered. The CD analysis also suggests there are both α-helical structures and b-sheet structures but surprisingly the b-sheet content appeared to be greater than suggested by either our modeling or that of Gellèrt and colleagues (2012). The NMR data suggested the Fny-CMV 2b protein is mainly α-helical, which is in line with the structure predictions based on the crystallography-derived structure for the TAV 2b (Chen et al.; 2008). Contrastingly, we found less evidence for the intrinsically disordered nature of the Fny-CMV 2b protein from our NMR results, which conflicted with modeling predictions as well as with the CD data. The NMR analysis also indicates a greater abundance of b-sheet than we had anticipated from our modeling, the previous modeling of the CMV2b proteins such as that of Gellèrt et al. (2012), or the partly solved X-ray crystallographic structure of the TAV2 protein (Chen et al.; 2008).
3.5. New Questions on the CMV 2b Protein Secondary Structure and Its Functional Effects
A possible explanation for the differing conclusions reached with NMR compared to those reached using computational approaches and CD measurements could be that NMR was carried out with 2b protein in phosphate buffered saline (containing 137 mM NaCl and 2.7 mM KCl) whereas CD was conducted in the absence of salt. The diagram of states generated as part of our modeling indicated that the Fny-CMV 2b sequence is a ‘Janus’ protein, i.e.; possessing a highly context-dependent secondary structure that can dramatically and reversibly adopt different conformations in response to factors in its environment including, inter alia, salt concentration. Interestingly, Gellèrt et al. (2012) proposed that the interactions of metal ions with negatively charged residues in the 2b protein C-terminal domain would participate in b-sheet formation. The 2b protein is known to dimerize and form higher-order assemblies with itself (Chen et al.; 2008; González et al.; 2010; Xu et al.; 2013). Although the mechanism has not been investigated, it is not based on the formation of disulfide bridges and another explanation is required. This could be the emergence of structure from the interactions of intrinsically disordered domains within the interaction partners (Dunker et al.; 1998, 2005; Wright and Dyson, 1999; Tompa and Fuxreiter, 2008; Ulrich et al.; 2008; Okoye et al.; 2022). It is plausible that in low salt environments the Fny-CMV 2b protein is monomeric or not interacting with positive ions and forms a more unstructured state while in higher salt environments the Fny-CMV-2b protein formed a more structured state due to self-interaction.
3.6. An Intrinsically Disordered Structure: An Intriguing Possibility That May Explain Several Properties of the CMV 2b Protein
At this point we cannot be certain that the 2b protein possesses intrinsically disordered regions and, if it does, under what conditions disorder will manifest itself. Further investigation of this possibility is warranted since it could explain several of its properties and in particular those that cannot be ascribed to discrete residues or domains. For example, a key feature of intrinsically disordered proteins is their ability to interact with multiple partners (Okoye et al.; 2022; Sipko et al.; 2024). This multivalency could explain variously reported interactions (in addition to those explored in this paper) with: DNA (Ham et al.; 1999; Sueda et al.; 2010), a catalase (Inaba et al.; 2011) and a calmodulin-like factor in tobacco (Nakahara et al.; 2012), cucumber RNA-directed RNA polymerase 1 (Kumari et al.; 2021), an A. thaliana zinc finger protein HB27 (Rattan et al.; 2022), and A. thaliana jasmonate ZIM-domain (JAZ) proteins 1, 3, 6 and 10 (Wu et al.; 2017). Intrinsically disordered proteins, including at least one plant viral protein (the p26 movement protein of pea enation mosaic virus 2), can phase separate and enter membrane-free organelles composed of protein-rich droplets (Brangwynne et al.; 2009; Brady et al.; 2017; Mitrea and Kriwacki, 2016; Wallmann and Kesten, 2020; Brown et al.; 2021). The 2b protein of Fny-CMV localizes to two membrane-free organelles, P-bodies (Watt et al.; 2020) and nucleoli (González et al.; 2010), indicating it can phase-separate. Nevertheless, however plausible it may seem that the CMV 2b is functioning as an intrinsically disordered protein, further work using a wider range of conditions will be required to confirm this.
4. Methods
4.1. Plant Growth and in Planta Transient Expression of Recombinant Proteins
Nicotiana benthamiana Domin. (accession RA-4: Wylie et al.; 2015) plants were grown from seed in a Conviron (Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada) growth room at 22°C, 60% relative humidity, 200 μmol.m-2.s-1 of photosynthetically-active radiation, and 16 h light and 8 h dark. Cells of Agrobacterium tumefaciens (GV3101) carrying constructs for transient expression were incubated with shaking overnight at 28°C in 50 ml LB medium (Sambrook et al.; 1989) containing appropriate antibiotics. Cultures were centrifuged at 5000 g for 15 min and pellets re-suspended and diluted to an OD600 of 0.5 in 10 mM MgCl2, 10 mM 4-morpholineethanesulfonic acid pH 5.6, and 100 μM acetosyringone, and infiltrated into the abaxial side of the third or fourth true leaves of four-week-old N. benthamiana plants using a needle-less syringe.
4.2. Cloning and Mutagenesis
Constructs used for the expression of fluorescently tagged CMV 1a (pMDC32 background for RFP or GFP fusions and pROK background for sYFP fusions) or AGO1 proteins (pSITE background for RFP or GFP fusions and pROK background for sYFP fusions) and have been previously described (Watt et al.; 2020; González et al.; 2010). New constructs used in this study were derived from the Fny strain of CMV accession NC002035 (Roossinck and Palukaitis, 1990). Full length and mutant versions of the Fny-CMV 2b sequence were incorporated into pSITE vectors (Chakrabarty et al.; 2007; Martin et al.; 2009) to yield constructs encoding CMV 2b fusions with red fluorescent protein (RFP), green fluorescent protein (GFP) and N- or C-terminal split yellow fluorescent protein (YFPn or YFPc) tags fused to the C-termini. Plasmids encoding fluorescently tagged mutant CMV 2b proteins were generated using Gateway
® cloning following the protocol provided (Invitrogen, Thermo-Fisher Scientific, Paisley UK) with
attB-flanked DNA fragments cloned into the pDONR221 donor plasmid, verified by sequencing before transfer into pSITE destination plasmids. The various
2b mutants used in this study were constructed using the primers detailed in
Table S1. Truncated versions of the CMV 2b protein were generated using mutagenic primers containing attB sequences to yield PCR products compatible with Gateway
® cloning for insertion into destination vectors. In-frame deletions and substitutions were generated using a Q5 Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (New England Biolabs, Hitchen UK) using the primers listed in
Table S1. Constructs were authenticated by automated Sanger sequencing (Sanger et al.; 1977; Smith et al.; 1986) conducted by Source BioScience (Cambridge UK).
4.3. RNA Silencing Suppression Assays and Fluorescence Imaging
For RNA silencing suppressor activity assays,
N. benthamiana leaves were co-infiltrated with
A. tumefaciens cells carrying plasmids expressing free GFP and cells carrying plasmids encoding wild-type or mutant CMV 2b proteins as described previously (Watt et al.; 2020). Leaves were imaged at 4, 8 and 12 days after agroinfiltration. For other imaging of fluorophores, imaging was at 4 days post-agroinfiltration. GFP, RFP or re-constituted YFP fluorophores were imaged by laser excitation at 488, 561 or 514 nm, respectively, using a Leica Model SP5 confocal laser scanning microscope (Leica Microsystems, Heidelberg Germany). The intensity of fluorescence quantified using Image J. The R statistical package 3.2.2 (CRAN-Ma, Imperial College London, UK,
www.R-project.org.) was used to perform an ANOVA and Tukey’s HSD
post hoc test to assess statistical significance of differences in intensity.
4.4. Protein Extraction, Coimmunoprecipitation and Western Immunoblot Analysis
Total protein was extracted from 100 mg of agroinfiltrated N. benthamiana leaf tissue. Samples were frozen and pulverized in liquid nitrogen before homogenization in 25 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 200 mM NaCl, 1 mM ethylenediaminotetraacetic acid (EDTA), 0.15% IGEPAL® CA-630, 10% glycerol, 10 mM dithiothreitol, and protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche, West Sussex UK). Crude extract was pelleted by centrifugation at 12,000 g for 4 minutes at 4 °C and the clarified supernatant collected. Coimmunoprecipitation of GFP- or RFP-tagged proteins from total leaf protein extract by incubation with GFP- or RFP-Trap magnetic agarose beads (ChromoTek, Planegg-Martinsried Germany) was performed as previously reported (Azevedo et al.; 2010; Watt et al.; 2020). Proteins were resolved on 10% polyacrylamide denaturing gels (Laemmli, 1970) and electrophoretically transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane (Towbin et al.; 1979). For immunological detection, membranes were probed with primary antibodies anti-GFP (1:1000) or anti-RFP (1:2000) (Chromotek) for 1 h, followed by incubation with horseradish peroxidase conjugated secondary antibodies. Antibody binding was detected on X-ray film with Pierce ECL Substrate (Thermo-Fisher Scientific) or signals were directly captured in a G:BOX Chemi XRQ machine (Syngene, Cambridge, UK).
4.5. In Silico Analysis of Intrinsically Disordered Protein Sequences
IUPred3, ANCHOR2 and ParSe v2 prediction algorithms were used to assess the disordered nature of protein sequences for Fny-CMV 2b (accession: NC002035), LS-CMV 2b (accession: AF416900), Fny-CMV 1a (accession: D00356), LS-CMV 1a (accession: AF416899) and
A. thaliana AGO1 (UID: 841262). The IUPred3 server (Erdős et al.; 2021) is a combined web interface which uses neural network strategies, educated with experimental data, to predict regions of disorder. The ANCHOR2 prediction algorithm (Dosztányi et al.; 2009) identifies context-dependent protein disorder, where the transition between the unstructured and the structured states is initiated by the presence of an appropriate protein partner. The ParSe v2 uses sequence hydrophobicity to identify intrinsically disordered protein sequences followed by subsequent sorting into intrinsically disordered protein sequences that phase transition and those which do not (Ibrahim et al.; 2022). The secondary structure of the Fny-CMV 2b protein was also predicted using the online RoseTTAFold server
https://robetta.bakerlab.org/ (Baek et al.; 2021).
4.6. Structural Analysis of the 2b Protein Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Circular Dichroism
Synthesis of the Fny-CMV 2b protein was carried out by LifeTein protein expression services (Somerset NJ USA). His-tagged Fny-CMV 2b protein was expressed in E. coli under a T7 promoter and purified using Ni-NTA nickel affinity beads (Qiagen, Hilden Germany). Purified protein was dissolved in PBS solution and lyophilized. The 2b protein open reading frame (ORF) expressed matched the amino acid sequence of Fny-CMV 2b protein (accession NC002035) with a single amino acid substitution replacing glutamate at position 104 with lysine (E104G) to mitigate the toxic effects of the 2b protein in E. coli (Sueda et al.; 2010) yielding the following synthetic polypeptide as analysed by mass spectrometryRoyal Society:
MELNVGAMTNVELQLARMVEAKKQRRRSHKQNRRERGHKSPSERARSNLRLFRFLPFYQVDGSELTGSCRHVNVAELPESEASRLELSAEDHDFDDTDWFAGNKWAEGAFLEHHHHHH.
The 1H NMR spectra were acquired at 25 °C using 600 ml of 200 µM protein in phosphate-buffered saline (137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, 1.8 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.4) amended with 1 mM DTT. The protein sample was subjected to 2-dimensional nuclear Overhauser enhancement spectroscopy (2D NOESY) (800 MHz, 298K, mixing time = 150 ms) and 2-dimensional total correlation spectroscopy (2D TOCSY) (800 MHz, 298K, mixing time = 32 ms) using an Avance III AV800 Spectrometer (Bruker, Billerica MA USA) equipped with a 5 mm TXI cryoprobe.
For CD analysis a sample of the synthetic 2b protein was buffer exchanged into 10 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4 with 1 mM 1,4-dithioerythritol using a PD MidiTrap™ G-25 column (Cytiva,UK). Far-UV CD spectra were obtained at 25 °C for 13.5 mM sample of protein solution using a 1 mm path length quartz cuvette in a Chirascan CD spectrometer (Applied Photophysics, Leatherhead UK). The CD spectrum was averaged across five scans recorded in the far-UV region (190–240 nm). CD data were analyzed using the K2D2 (Perez-Iratxeta and Andrade-Navarro, 2008), CONTINSP175 (Whitmore and Wallace, 2004) and CDSSTR (Sreerama and Woody, 2000) programs which use reference data sets to predict protein secondary structures. A combination of different data sets was used including a new reference dataset, IDP175, which is suitable for analyses of proteins containing significant proportions of disordered secondary structure (Miles et al.; 2023).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Initial conceptualization, SC, AMM, and JPC; investigation, SC, AMM, PJER, DN; formal analysis, SC, PJER, DN, JPC; writing—original draft preparation, SC; writing—review and editing, SC, JPC, PJER13, DN and LSI; funding acquisition, JPC, LSI, DN. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
SC received a studentship from the UK Biotechnological and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)-Cambridge University Doctoral Training Program (BB/M011194/1). AMM was supported by grants from the BBSRC (21ROMITIGATIONFUND CAMBRIDGE BB/W510609/1), The Royal Society (ICA\R1\201221) and from The Leverhulme Trust (RPG-2022-134). We thank the Isaac Newton Trust for funding to PJER.
Acknowledgments
We thank Adrienne E. Pate for expert technical assistance, and Tomás Canto and Lewis G Watt for useful discussions and provision of DNA constructs.
References
- Baek, M.; DiMaio, F.; Anishchenko, I.; Dauparas, J.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Lee, G.R.; Wang, J.; Cong, Q.; Kinch, L.N.; Schaeffer, R.D.; Millán, C.; Park, H.; Adams, C.; Glassman, C.R.; DeGiovanni, A.; Pereira, J.H.; Rodrigues, A.V.; van Dijk, A.A.; Ebrecht, A.C. and Opperman, D.J. Accurate prediction of protein structures and interactions using a three-track neural network. Science 2021, 373, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, S.; Bhat, A.I. and Eapen, S.J. A phylogenetic re-examination of Cucumber mosaic virus isolates based on 1a, 2a, 3a and 3b proteins. Indian Journal of Virology 2008, 19, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, J.P.; Farber, P.J.; Sekhar, A.; Lin, Y.-H.; Huang, R.; Bah, A.; Nott, T.J.; Chan, H.S.; Baldwin, A.J.; Forman-Kay, J.D. and Kay, L.E. Structural and hydrodynamic properties of an intrinsically disordered region of a germ cell-specific protein on phase separation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2017, 114, E8194–E8203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brangwynne, C.P.; Eckmann, C.R.; Courson, D.S.; Rybarska, A.; Hoege, C.; Gharakhani, J.; Jülicher, F. and Hyman, A.A. Germline P granules are liquid droplets that localize by controlled dissolution/condensation. Science 2009, 324, 1729–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.L.; Garrison, D.J. and May, J.P. Phase separation of a plant virus movement protein and cellular factors support virus-host interactions. PLoS Pathogens 2021, 17, e1009622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujarski, J.; Gallitelli, D.; García-Arenal, F.; Pallás, V.; Palukaitis, P.; Reddy, M.K. and Wang, A. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Bromoviridae. Journal of General Virology 2019, 100, 1206–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.P. and Murphy, A.M. Chapter 12: Suppression of Plant Defense. In: Cucumber Mosaic Virus. Palukaitis, P. and García-Arenal, F.; editors. St Paul MN: American Phytopathological Society Press. 2019; Pp.133-144.
- Chakrabarty, R.; Banerjee, R.; Chung, S.M.; Farman, M.; Citovsky, V.; Hogenhout, S.A.; Tzfira, T. and Goodin, M. pSITE vectors for stable integration or transient expression of autofluorescent protein fusions in plants: probing Nicotiana benthamiana-virus interactions. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 2007, 20, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabortee, S.; Kayatekin, C.; Newby, G.A.; Mendillo, M.L.; Lancaster, A. and Lindquist, S. Luminidependens (LD) is an Arabidopsis protein with prion behavior. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2016, 113, 6065–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Yang, J.; Lin, C. and Yuan, Y.A. Structural basis for RNA silencing suppression by Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b. EMBO Reports 2008, 9, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawshaw, S.; Watt, L.G.; Murphy, A.M. and Carr, J.P. Strain- specific differences in interactions of the cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein with the viral 1a and host Argonaute 1 proteins. (In revision for Journal of Virology) 2023, BioRxiv ID: BIORXIV/2023/555694.
- Ding, S. -W.; Anderson, B.J.; Haase, H.R. and Symons, R.H. New overlapping gene encoded by the cucumber mosaic virus genome. Virology 1994, 198, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.-W.; Shi, B.J.; Li, W.X. and Symons, R.H. An interspecies hybrid RNA virus is significantly more virulent than either parental virus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1996, 93, 7470–7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosztányi, Z.; Meszaros, B. and Simon, I. ANCHOR: web server for predicting protein binding regions in disordered proteins. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2745–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Chen, A.; Chen, W.; Westwood, J.H.; Baulcombe, D.C. and Carr, J.P. Using a viral vector to reveal the role of miR159 in disease symptom induction by a severe strain of Cucumber mosaic virus. Plant Physiology 2014, 164, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.G.; Fang, Y.Y.; Zhou, B.J.; Zhao, J.H.; Hou, W.N.; Zhu, H.; Ding, S.W.; and Guo, H.S. Suppression of Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE1-mediated slicing, transgene- induced RNA silencing, and DNA methylation by distinct domains of the Cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunker, A.K.; Cortese, M.S.; Romero, P.; Iakoucheva, L.M. and Uversky, V.N. Flexible nets. The roles of intrinsic disorder in protein interaction networks. FEBS Journal. 2015, 272, 5129–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunker, A.K.; Garner, E.; Guilliot, S.; Romero, P.; Albrecht, K.; Hart, J.; Obradovic, Z.; Kissinger, C. and Villafranca, J.E. Protein disorder and the evolution of molecular recognition: theory, predictions and observations. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 1998, 473–484. [Google Scholar]
- Dunker, A.K. and Obradović, Z. The protein trinity—linking function and disorder. Nature Biotechnology 2001, 19, 805–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, M.-O.; Bae, S.-H.; Dyson, H.J. and Wright, P.E. NMR relaxation study of the complex formed between CBP and the activation domain of the nuclear hormone receptor coactivator ACTR. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdős, G.; Pajkos, M. and Dosztányi, Z. IUPred3: prediction of protein disorder enhanced with unambiguous experimental annotation and visualization of evolutionary conservation. Nucleic Acids Research 2021, 49, W297–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereres, A. and Perry, K.L. Chapter 15: Movement between plants: Horizontal transmission. In: Cucumber Mosaic Virus. Palukaitis, P. and García-Arenal, F.; editors. St Paul MN: American Phytopathological Society Press. 2019. Pp. 173–184.
- Gellért, Á.; Nemes, K.; Kádár, K.; Salánki, K. and Balázs, E. The C-terminal domain of the 2b protein of Cucumber mosaic virus is stabilized by divalent metal ion coordination. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling 2012, 38, 446–454. [CrossRef]
- González, I.; Martínez, L.; Rakitina, D.V.; Lewsey, M.G.; Atencio, F.A.; Llave, C.; Kalinina, N.O.; Carr, J.P.; Palukaitis, P. and Canto, T. Cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein subcellular targets and interactions: their significance to RNA silencing suppressor activity. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 2010, 23, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, I.; Rakitina, D.; Semashko, M.; Taliansky, M.; Praveen, S.; Palukaitis, P.; Carr, J.P.; Kalinina, N. and Canto, T. RNA binding is more critical to the suppression of silencing function of Cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein than nuclear localization. RNA 2012, 18, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, B.K.; Lee, T.H.; You, J.S.; Nam, Y.W.; Kim, J.K. and Paek, K.H. Isolation of a putative tobacco host factor interacting with cucumber mosaic virus-encoded 2b protein by yeast two-hybrid screening. Molecules and Cells 1999, 9, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, J.J.W.; Lewsey, M.G.; Patel, K.; Westwood, J.; Heimstädt, S.; Carr, J.P. and Baulcombe, D.C. An antiviral defense role of AGO2 in plants. PLoS One 2011, 6, 14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, K.C. Flexibility in tobacco mosaic virus. Ciba Foundation Symposium 1983, 93, 116–138. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, R. Chapter 12: Plant to Plant Movement. In: Plant Virology 5th edition. Hull, R. editor. Academic Press Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 2014. Pp. 669-751.
- Ibrahim, A.; Khaodeuanepheng, N.; Amarasekara, D.L.; Correia, J.J.; Lewis, K.A.; Fitzkee, N.C.; Hough, L.E. and Whitten, S.T. Intrinsically disordered regions that drive phase separation form a robustly distinct protein class. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2023, 299, 102801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, J.; Kim, B.M.; Shimura, H. and Masuta, C. Virus-induced necrosis is a consequence of direct protein-protein interaction between a viral RNA-silencing suppressor and a host catalase. Plant Physiology 2011, 156, 2026–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquemond, M. Cucumber mosaic virus. Advances in Virus Research 2012, 84, 439–504. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Shimura, H.; Sueda, K. and Masuta, C. Importin/exportin-mediated nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein is required for 2b’s efficient suppression of RNA silencing. PLoS Pathogens 2022, 18, 1010267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenz, B.; Bronikowski, A.; Lu, X.; Ziebell, H.; Thompson, J.R. and Perry, K.L. Visual monitoring of Cucumber mosaic virus infection in Nicotiana benthamiana following transmission by the aphid vector Myzus persicae. Journal of General Virology 2015, 96, 2904–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Kumar, S.; Leibman, D.; Abebie, B.; Shnaider, Y.; Ding, S.W. and Gal-On, A. Cucumber RDR1s and Cucumber mosaic virus suppressor protein 2b association directs host defence in cucumber plants. Molecular Plant Pathology 2021, 22, 1317–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewsey, M.; Robertson, F.C.; Canto, T.; Palukaitis, P. and Carr, J.P. Selective targeting of miRNA-regulated plant development by a viral counter-silencing protein. Plant Journal 2007, 50, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewsey, M.; Surette, M.; Robertson, F.C.; Ziebell, H.; Choi, S.H.; Ryu, K.H.; Canto, T.; Palukaitis, P.; Payne, T.; Walsh, J.A. and Carr, J.P. The role of the Cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein in viral movement and symptom induction. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 2009, 22, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F. and Ding, S.-W. Virus counter defense: Diverse strategies for evading the RNA- silencing immunity. Annual Review of Microbiology 2006, 60, 503–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.; Kopperud, K.; Chakrabarty, R.; Banerjee, R.; Brooks, R. and Goodin, M.M. Transient expression in Nicotiana benthamiana fluorescent marker lines provides enhanced definition of protein localization, movement and interactions in planta. Plant Journal 2009, 59, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, A.J.; Drew, E.D. and Wallace, B.A. DichroIDP: a method for analyses of intrinsically disordered proteins using circular dichroism spectroscopy. Communications Biology 2023, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrea, D.M. and Kriwacki, R.W. Phase separation in biology; functional organization of a higher order. Cell Communication & Signaling 2016, 14, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Murthy, A.C.; Dignon, G.L.; Kan, Y.; Zerze, G.H.; Parekh, S.H.; Mittal, J. and Fawzi, N.L. Molecular interactions underlying liquid−liquid phase separation of the FUS low- complexity domain. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 2019, 26, 637–648. [Google Scholar]
- Nadassy, K.; Wodak, S.J.; Janin, J. Structural features of protein–nucleic acid recognition sites. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 1999–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, K.S.; Masuta, C.; Yamada, S.; Shimura, H.; Kashihara, Y.; Wada, T.S.; Meguro, A.; Goto, K.; Tadamura, K.; Sueda, K.; Sekiguchi, T.; Shao, J.; Itchoda, N.; Matsumura, T.; Igarashi, M.; Ito, K.; Carthew, R.W. and Uyeda, I. Tobacco calmodulin-like protein provides secondary defense by binding to and directing degradation of virus RNA silencing suppressors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2012, 109, 10113–10118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.N.; Rowling, P.J.E.; Itzhaki, L.S. and Lindon, C. Counting degrons: Lessons from multivalent substrates for targeted protein degradation. Frontiers in Physiology 2022, 13, 913063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldfield, C.J.; Xue, B.; Van, Y.-Y.; Ulrich, E.L.; Markley, J.L.; Dunker, A.K. and Uversky, V.N. Utilization of protein intrinsic disorder knowledge in structural proteomics. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Proteins and Proteomics 2013, 1834, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pak, C.W.; Kosno, M.; Holehouse, A.S.; Padrick, S.B.; Mittal, A.; Ali, R.; Yunus, A.A.; Liu, D.R.; Pappu, R.V. and Rosen, M.K. Sequence determinants of intracellular phase separation by complex coacervation of a disordered protein. Molecular Cell 2016, 63, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palukaitis, P. and García-Arenal, F. Cucumoviruses. Advances in Virus Research 2003, 62, 241–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pancsa, R.; Vranken, W. and Mészáros, B. Computational resources for identifying and describing proteins driving liquid–liquid phase separation. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2021, 22, bbaa408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Iratxeta, C. and Andrade-Navarro, M.A. K2D2: Estimation of protein secondary structure from circular dichroism spectra. BMC Structural Biology 2008, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattan, U.K.; Kumar, S.; Kumari, R.; Bharti, M. and Hallan, V. Homeobox 27, a homeodomain transcription factor, confers tolerances to CMV by associating with cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein. Pathogens 2022, 11, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roossinck, M.J. and Palukaitis, P. Rapid induction and severity of symptoms in zucchini squash (Cucurbita pepo) map to RNA 1 of cucumber mosaic virus. Molecular Plant- Microbe Interactions 1990, 3, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F. and Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, NY, USA 1989.
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S. and Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, B.S.; Dignon, G.L.; Tang, W.S.; Kelley, F.M.; Ranganath, A.K.; Jahnke, C.N.; Simpkins, A.G.; Regy, R.M.; Hammer, D.A.; Good, M.C. and Mittal, J. Identifying sequence perturbations to an intrinsically disordered protein that determine its phase-separation behavior. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2020, 117, 11421–11431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipko, E.L.; Garrett, G.F. and Berlow, R.B. Multivalency emerges as a common feature of intrinsically disordered protein interactions. Current Opinion in Structural Biology 2024, 84, 102742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.M.; Sanders, J.Z.; Kaiser, R.J.; Hughes, P.; Dodd, C.; Connell, C.R.; Heiner, C.; Kent, S.B.H. and Hood, L.E. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature 1986, 321, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreerama, N. and Woody, R.W. Estimation of protein secondary structure from circular dichroism spectra: comparison of CONTIN, SELCON, and CDSSTR methods with an expanded reference set. Analytical Biochemistry 2000, 287, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueda, K.; Shimura, H.; Meguro, A.; Uchida, T.; Inaba, J. and Masuta, C. The C- terminal residues of the 2b protein of Cucumber mosaic virus are important for efficient expression in Escherichia coli and DNA-binding. FEBS Letters 2010, 584, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompa, P. and Fuxreiter, M. Fuzzy complexes: polymorphism and structural disorder in protein–protein interactions. Trends in Biochemical Science 2008, 33, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towbin, H.; Staehlin, T. and Gordon, J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1979, 76, 4350–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, E.L.; Akutsu, H.; Doreleijers, J.F.; Harano, Y.; Ioannidis, Y.E.; Lin, J.; Livny, M.; Mading, S.; Maziuk, D.; Miller, Z.; Nakatani, E.; Schulte, C.F.; Tolmie, D.E.; Kent Wenger, R.; Yao, H. and Markley, J.L. BioMagResBank. Nucleic Acids Research 2008, 36, D402–D408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavouri, T.; Semple, J.I.; Garcia-Verdugo, R. and Lehner, B. Intrinsic protein disorder and interaction promiscuity are widely associated with dosage sensitivity. Cell 2009, 138, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon, R.M. and Forman-Kay, J.D. First-generation predictors of biological protein phase separation. Current Opinion in Structural Biology 2019, 58, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallmann, A. and Kesten, C. Common functions of disordered proteins across evolutionary distant organisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, L.G.; Crawshaw, S.; Rhee, S.-J.; Murphy, A.M.; Canto, T. and Carr, J.P. The cucumber mosaic virus 1a protein regulates interactions between the 2b protein and ARGONAUTE 1 while maintaining the silencing suppressor activity of the 2b protein. PLoS Pathogens 2020, 16, 1009125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, J.H.; Groen, S.C.; Du, Z.; Murphy, A.M.; Anggoro, D.T.; Tungadi, T.; Luangin, V.; Lewsey, M.G.; Rossiter, J.T.; Powell, G.; Smith, A.G. and Carr, J.P. A trio of viral proteins tunes aphid-plant interactions in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS One 2013, 8, 83066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmore, L. and Wallace, B.A. DICHROWEB, an online server for protein secondary structure analyses from circular dichroism spectroscopic data. Nucleic Acids Research 2004, 32, W668–W673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.E. and Dyson, H.J. Intrinsically unstructured proteins: re-assessing the protein structure–function paradigm. Journal of Molecular Biology 1999, 293, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Qi, T.; Li, W.-X.; Tian, H.; Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Ge, J.; Yao, R.; Ren, C.; Wang, X.-B.; Liu, Y.; Kang, L.; Ding, S.-W. and Xie, D. Viral effector protein manipulates host hormone signalling to attract insect vectors. Cell Research 2017, 27, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, S.J.; Zhang, C.; Long, V.; Roossinck, M.J.; Koh, S.H.; Jones, M.G.; Iqbal, S. and Li, H. Differential responses to virus challenge of laboratory and wild accessions of Australian species of Nicotiana, and comparative analysis of RDR1 gene sequences. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0121787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; Liao, Q.; Chen, J.; Carr, J.P. and Du, Z. Self- interaction of the cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein plays a vital role in the suppression of RNA silencing and the induction of viral symptoms. Molecular Plant Pathology 2013, 14, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.Y.; Palukaitis, P. and Choi, S.K. Chapter 1: Host Range. In: Cucumber Mosaic Virus. Palukaitis, P. and García-Arenal, F.; editors. St Paul MN: American Phytopathological Society Press. 2019. Pp.15–18.
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y.R.; Pei, Y.; Lin, S.-S.; Tuschl, T.; Patel, D.J. and Chua, N.-H. Cucumber mosaic virus-encoded 2b suppressor inhibits Arabidopsis Argonaute 1 cleavage activity to counter plant defense. Genes & Development 2006, 20, 3255–3268. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Murphy, A.M.; Lewsey, M.G.; Westwood, J.H.; Zhang, H.; González, I.; Canto, T. and Carr, J.P. Domains of the cucumber mosaic virus 2b silencing suppressor protein affecting inhibition of salicylic acid-induced resistance and priming of salicylic acid accumulation during infection. Journal of General Virology 2014, 95, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Mutational analysis of the cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) 2b protein. a Previously determined or inferred functional residues or domains of the 2b protein are indicated on a map of the 110 amino acid Fny-CMV 2b ortholog. Sequences longer than one amino acid are depicted as gray boxes: the N- and C-terminal domains; the RNA-binding domain; the KSPSE phosphorylation sequence; the GSEL and RHV sequences, and nuclear export sequence (NES). However, the N-terminal MEL sequence and nuclear localization sequence (NLS) 1 and 2 are shaded in darker gray to indicate that they overlap with the N-terminal and RNA-binding domains, respectively. Single amino acid residues with known biological effects are indicated by arrowheads: S28, which is an additional phosphorylation site (Kim et al.; 2022); L55, which is required for 2b self-interaction (Xu et al.; 2013), and E104 which causes cytotoxicity in E. coli due to DNA binding (Sueda et al.; 2010), suggestive of a biological function. Biological roles of sequences or residues are indicated on the left. The region spanning residues 38 to 94 of the 2b protein, inferred to contain amino acid residue(s) required for interaction with Argonaute 1 (AGO1) is indicated by a dashed line and was proposed by Duan et al. (2012). The map is updated from a previous iteration (Carr and Murphy, 2019) to include more recent information (Kim et al.; 2022). b Deletion mutations are indicated by gray lines below the amino acid sequences for the Fny-CMV and LS-CMV 2b proteins, while insertions or substitution mutations are indicated above. Numbers refer to the residues of the 110 amino acid Fny-CMV 2b protein. Mutant 2b proteins truncated from the N-terminus of the first 17 (2bD1-17) or 55 (2bΔ1-55) amino acids. Truncations were also made from the C-terminus, deleting 16 (2bΔ95-110), 26 (2bΔ85-110), 28 (2bΔ83-110), 37 (2bΔ74-110), 42 (2bΔ69-110), 46 (2bΔ65-110), 50 (2bΔ61-110), and 55 (2bΔ56-110) amino acids. In-frame internal deletions were also made between residues 83 to 93 (2bΔ83-93), 56 to 65 (2bΔ56-65), 56 to 60 (2bΔ56-60), and 39 to 48 (2bΔ39-48). Alanine substitution mutations were also made to replace the Fny-CMV 2b sequence from residues 56 to 65 with ten alanine residues (2b56aaa65) and residues 56 to 60 with five alanine residues (2b56aaa60). Two chimeric 2b proteins were generated. In 2bFny/LS56-60 the mutations Y58H and Q59G were introduced into the Fny-CMV 2b sequence to recapitulate the sequence of the LS-CMV 2b ortholog between residues 56 and 60. The chimeric protein 2bLS/Fny83-93 was created by introducing residues 83-93 from the Fny-CMV 2b protein into the LS-CMV 2b protein background. Note that the wild-type LS-CMV 2b protein does not contain a corresponding sequence.
Figure 1.
Mutational analysis of the cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) 2b protein. a Previously determined or inferred functional residues or domains of the 2b protein are indicated on a map of the 110 amino acid Fny-CMV 2b ortholog. Sequences longer than one amino acid are depicted as gray boxes: the N- and C-terminal domains; the RNA-binding domain; the KSPSE phosphorylation sequence; the GSEL and RHV sequences, and nuclear export sequence (NES). However, the N-terminal MEL sequence and nuclear localization sequence (NLS) 1 and 2 are shaded in darker gray to indicate that they overlap with the N-terminal and RNA-binding domains, respectively. Single amino acid residues with known biological effects are indicated by arrowheads: S28, which is an additional phosphorylation site (Kim et al.; 2022); L55, which is required for 2b self-interaction (Xu et al.; 2013), and E104 which causes cytotoxicity in E. coli due to DNA binding (Sueda et al.; 2010), suggestive of a biological function. Biological roles of sequences or residues are indicated on the left. The region spanning residues 38 to 94 of the 2b protein, inferred to contain amino acid residue(s) required for interaction with Argonaute 1 (AGO1) is indicated by a dashed line and was proposed by Duan et al. (2012). The map is updated from a previous iteration (Carr and Murphy, 2019) to include more recent information (Kim et al.; 2022). b Deletion mutations are indicated by gray lines below the amino acid sequences for the Fny-CMV and LS-CMV 2b proteins, while insertions or substitution mutations are indicated above. Numbers refer to the residues of the 110 amino acid Fny-CMV 2b protein. Mutant 2b proteins truncated from the N-terminus of the first 17 (2bD1-17) or 55 (2bΔ1-55) amino acids. Truncations were also made from the C-terminus, deleting 16 (2bΔ95-110), 26 (2bΔ85-110), 28 (2bΔ83-110), 37 (2bΔ74-110), 42 (2bΔ69-110), 46 (2bΔ65-110), 50 (2bΔ61-110), and 55 (2bΔ56-110) amino acids. In-frame internal deletions were also made between residues 83 to 93 (2bΔ83-93), 56 to 65 (2bΔ56-65), 56 to 60 (2bΔ56-60), and 39 to 48 (2bΔ39-48). Alanine substitution mutations were also made to replace the Fny-CMV 2b sequence from residues 56 to 65 with ten alanine residues (2b56aaa65) and residues 56 to 60 with five alanine residues (2b56aaa60). Two chimeric 2b proteins were generated. In 2bFny/LS56-60 the mutations Y58H and Q59G were introduced into the Fny-CMV 2b sequence to recapitulate the sequence of the LS-CMV 2b ortholog between residues 56 and 60. The chimeric protein 2bLS/Fny83-93 was created by introducing residues 83-93 from the Fny-CMV 2b protein into the LS-CMV 2b protein background. Note that the wild-type LS-CMV 2b protein does not contain a corresponding sequence.
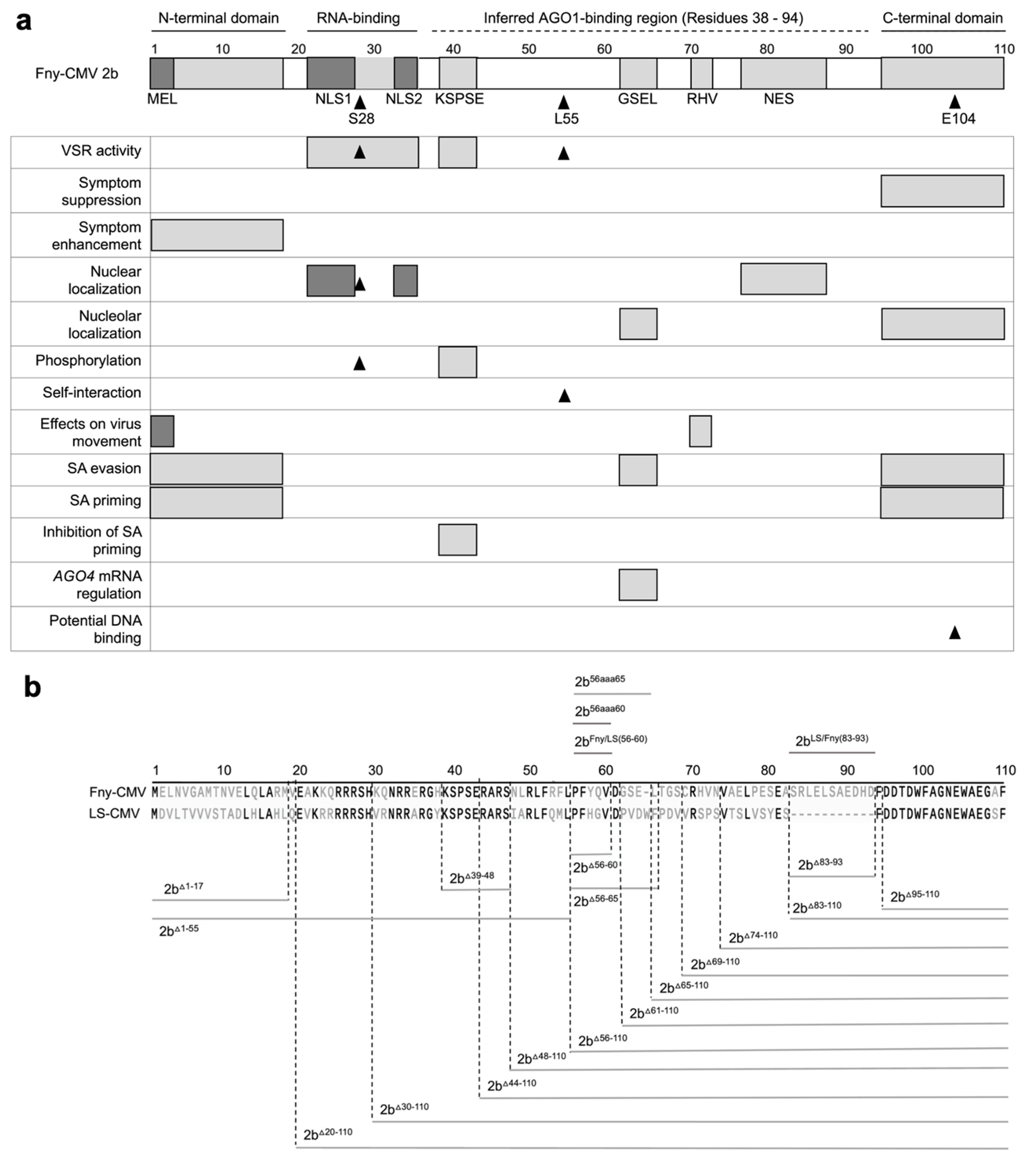
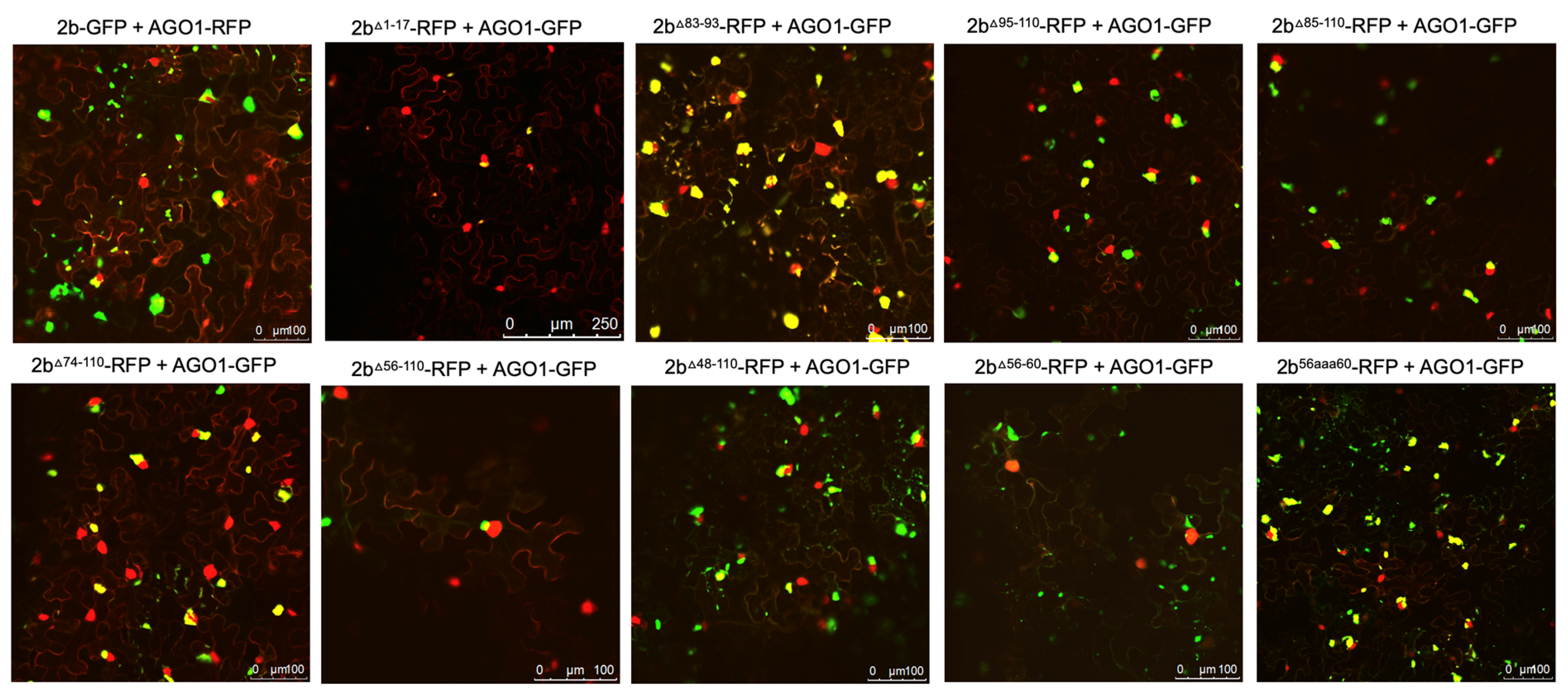
Figure 2.
Subcellular localization of mutant 2b proteins and the full length 1a protein. Using agroinfiltration, C-terminal RFP or GFP fusion proteins derived from full length 2b proteins (WT 2b-RFP) or 2b proteins lacking residues between 1-17, 95-110, 85-110, 56-110, 83-93, 56-60 or substitutions LS/Fny(83-93), 56aaa60 or Fny/LS(56-60) were co-expressed with RFP- or GFP-1a fusion proteins in N. benthamiana leaves in the combinations shown. Fluorescent signals were imaged using confocal scanning laser microscopy. Fny 2b-RFP accumulated in the nucleus and cytoplasm, with a proportion co-localizing with the 1a-GFP (merged signal shown as yellow), consistent with previous results (Watt et al.; 2020). Deletion of the N-terminal 17 residues (1-17) in the 2b sequence or the 15 C-terminal residues (95-110) did not disrupt the co-localization of 2b and 1a proteins. Deletions from 83-110, 74-110 and 56-110 all resulted in an apparent loss of co-localization with the 1a protein. Smaller in-frame deletions of residues 83-93 and 56-60 also both resulted in an apparent loss of co-localization between mutant 2b proteins and 1a proteins.
Figure 2.
Subcellular localization of mutant 2b proteins and the full length 1a protein. Using agroinfiltration, C-terminal RFP or GFP fusion proteins derived from full length 2b proteins (WT 2b-RFP) or 2b proteins lacking residues between 1-17, 95-110, 85-110, 56-110, 83-93, 56-60 or substitutions LS/Fny(83-93), 56aaa60 or Fny/LS(56-60) were co-expressed with RFP- or GFP-1a fusion proteins in N. benthamiana leaves in the combinations shown. Fluorescent signals were imaged using confocal scanning laser microscopy. Fny 2b-RFP accumulated in the nucleus and cytoplasm, with a proportion co-localizing with the 1a-GFP (merged signal shown as yellow), consistent with previous results (Watt et al.; 2020). Deletion of the N-terminal 17 residues (1-17) in the 2b sequence or the 15 C-terminal residues (95-110) did not disrupt the co-localization of 2b and 1a proteins. Deletions from 83-110, 74-110 and 56-110 all resulted in an apparent loss of co-localization with the 1a protein. Smaller in-frame deletions of residues 83-93 and 56-60 also both resulted in an apparent loss of co-localization between mutant 2b proteins and 1a proteins.
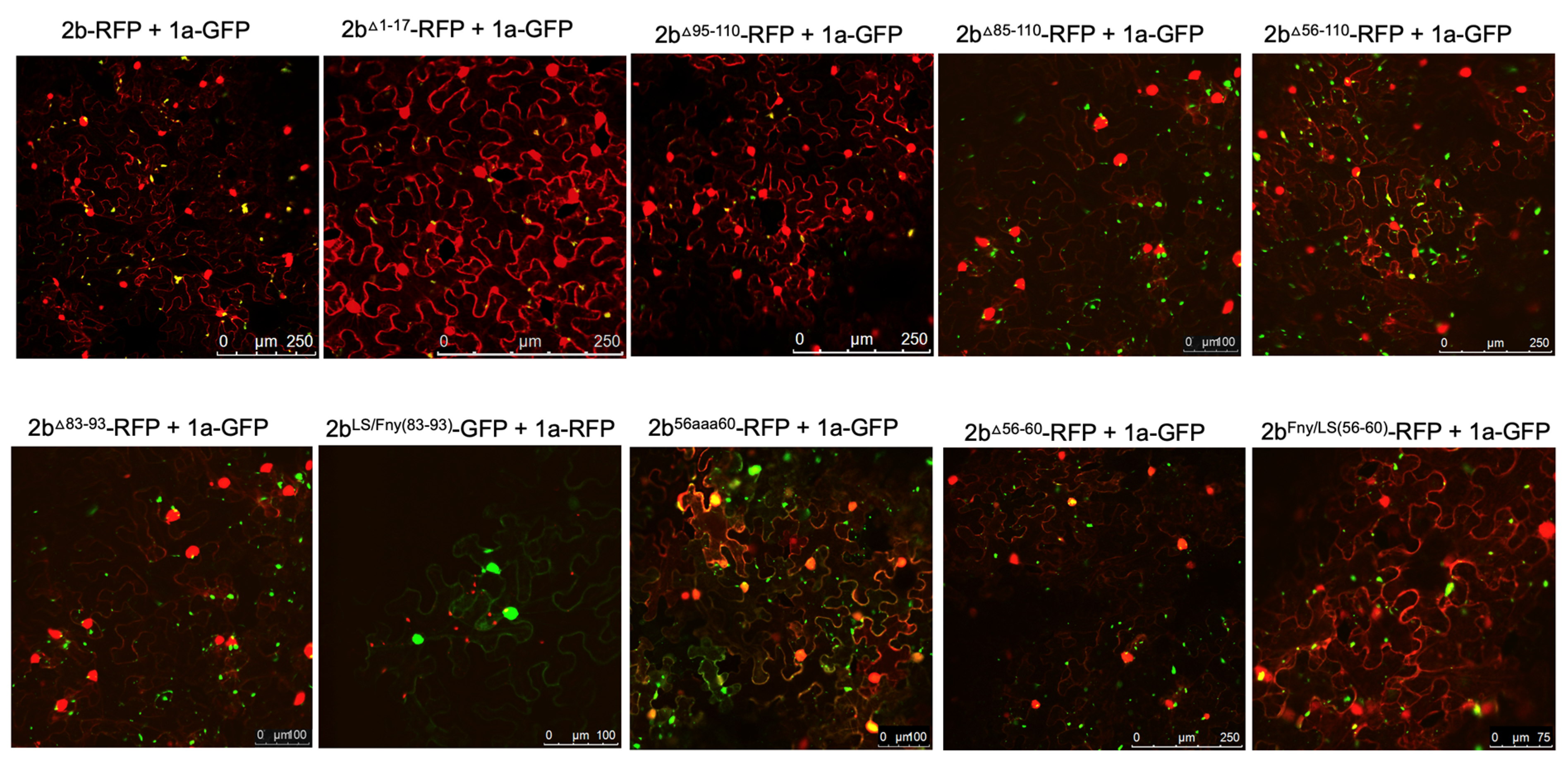
Figure 3.
Interactions of mutant versions of Fny-CMV 2b proteins with the 1a protein. Mutant versions of the 2b protein were fused at their C-termini with the C-terminal domain of split yellow fluorescent protein. Using agroinfiltration in N. benthamiana leaves, these fusion proteins were co-expressed with YFP N-proximal domain fusion proteins with the 1a proteins of Fny-CMV. Direct protein-protein interactions in vivo were revealed by bimolecular fluorescence complementation and resulting fluorescence imaged by confocal laser scanning microscopy. The data shows that the 2b mutants lacking residues 83-93, 74-110 and 69-110 mutants retained their ability to interact with 1a proteins. Truncations between residues 65-110 and 61-110 had progressively fewer instances of interaction with 1a proteins and deletion of residues 56-110 was seen to abolish the interaction completely. In-frame deletions between residues 56-65 or 56-60 or alanine substitutions between these residues also resulted in no interaction between 2b and 1a proteins. However, substitution of the Fny-CMV sequence with that of LS-CMV between residues 56-60 did not abolish the interaction with the 1a protein (although the amount of 2b-1a interaction was seemingly decreased).
Figure 3.
Interactions of mutant versions of Fny-CMV 2b proteins with the 1a protein. Mutant versions of the 2b protein were fused at their C-termini with the C-terminal domain of split yellow fluorescent protein. Using agroinfiltration in N. benthamiana leaves, these fusion proteins were co-expressed with YFP N-proximal domain fusion proteins with the 1a proteins of Fny-CMV. Direct protein-protein interactions in vivo were revealed by bimolecular fluorescence complementation and resulting fluorescence imaged by confocal laser scanning microscopy. The data shows that the 2b mutants lacking residues 83-93, 74-110 and 69-110 mutants retained their ability to interact with 1a proteins. Truncations between residues 65-110 and 61-110 had progressively fewer instances of interaction with 1a proteins and deletion of residues 56-110 was seen to abolish the interaction completely. In-frame deletions between residues 56-65 or 56-60 or alanine substitutions between these residues also resulted in no interaction between 2b and 1a proteins. However, substitution of the Fny-CMV sequence with that of LS-CMV between residues 56-60 did not abolish the interaction with the 1a protein (although the amount of 2b-1a interaction was seemingly decreased).
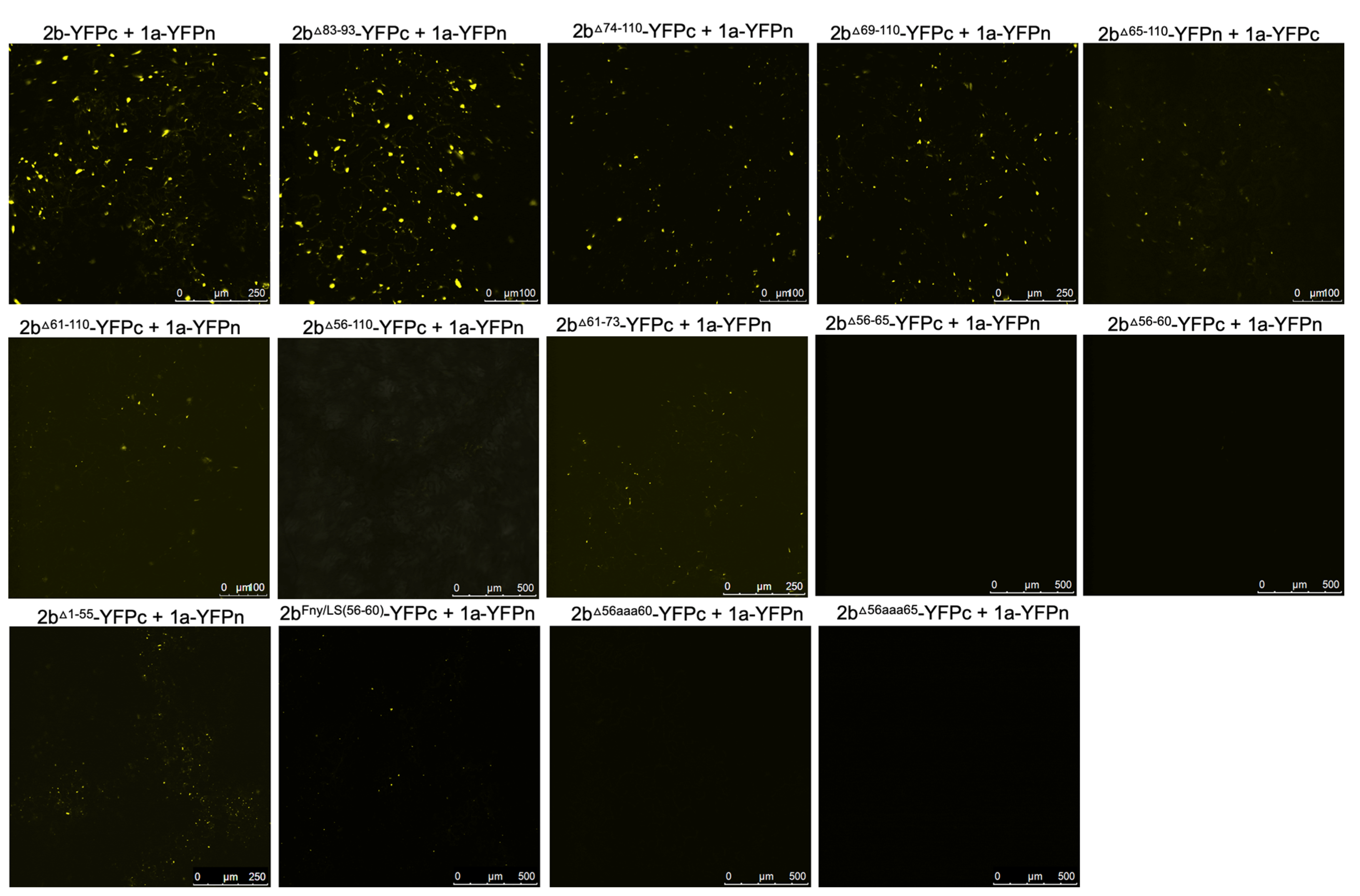
Figure 4.
Interactions of the cucumber mosaic virus 1a protein with mutant versions of the CMV 2b protein
in planta examined by co-immunoprecipitation. Using agroinfiltration into
N. benthamiana leaves, a GFP fusion protein derived from CMV 1a was coexpressed with RFP fusion proteins derived from full length 2b proteins (WT 2b-RFP) or mutant 2b sequences with deletions between residues 56-60 (2b
Δ56-60-RFP), alanine substitutions between residues 56-60 (2b
56aaa60-RFP) or replacement of the Fny-CMV 2b sequence with that of LS-CMV 2b sequence between residues 56 and 60 (2b
Fny/LS(56-60)-RFP). Total protein was extracted from leaf samples and immunoprecipitated with RFP-Trap beads (IP:RFP) followed by immunoblot analysis with anti-GFP antibodies to detect GFP-1a fusion proteins. GFP-1a was detected in all input samples with a corresponding band of approximately 138kDa. However, following RFP-pull down, GFP-1a could only be detected when co-expressed with the 2b-RFP or 2b
Fny/LS(56-60)-RFP and not with the 2b
56-60-RFP or 2b
56aaa60-RFP mutants. Original blots used to make composite image are shown in
Figure S7.
Figure 4.
Interactions of the cucumber mosaic virus 1a protein with mutant versions of the CMV 2b protein
in planta examined by co-immunoprecipitation. Using agroinfiltration into
N. benthamiana leaves, a GFP fusion protein derived from CMV 1a was coexpressed with RFP fusion proteins derived from full length 2b proteins (WT 2b-RFP) or mutant 2b sequences with deletions between residues 56-60 (2b
Δ56-60-RFP), alanine substitutions between residues 56-60 (2b
56aaa60-RFP) or replacement of the Fny-CMV 2b sequence with that of LS-CMV 2b sequence between residues 56 and 60 (2b
Fny/LS(56-60)-RFP). Total protein was extracted from leaf samples and immunoprecipitated with RFP-Trap beads (IP:RFP) followed by immunoblot analysis with anti-GFP antibodies to detect GFP-1a fusion proteins. GFP-1a was detected in all input samples with a corresponding band of approximately 138kDa. However, following RFP-pull down, GFP-1a could only be detected when co-expressed with the 2b-RFP or 2b
Fny/LS(56-60)-RFP and not with the 2b
56-60-RFP or 2b
56aaa60-RFP mutants. Original blots used to make composite image are shown in
Figure S7.
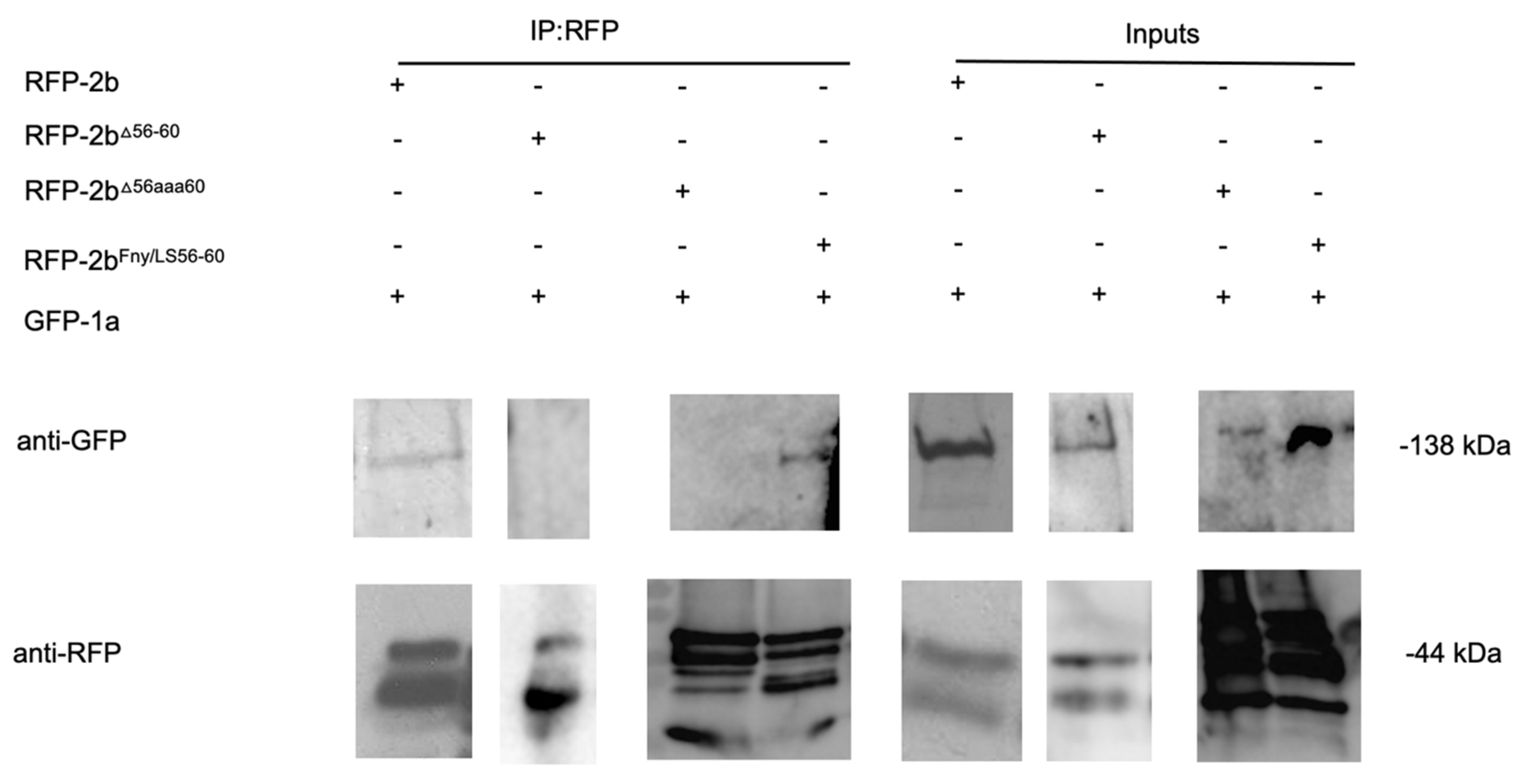
Figure 5.
Subcellular localization of mutant 2b proteins and the Argonaute 1 protein (AGO1). Using agroinfiltration, C-terminal RFP or GFP fusion proteins derived from full length 2b proteins (WT 2b-RFP) or 2b proteins were co-expressed with RFP- or GFP-AGO1 fusion proteins in N. benthamiana leaves in the combinations shown. Fluorescent signals were imaged using confocal scanning laser microscopy. Fny-CMV 2b-RFP protein accumulated in the nucleus and cytoplasm, with a proportion co-localizing with the AGO1-GFP (merged signal shown as yellow). Deletions of residues 1-17 or 83-93 had no impact on the co-localization of AGO1 and 2b signals. However, deletion of the C-terminal residues 95-110, 85-110 or 74-110 resulted in a reduction in the proportion of co-localised signal. Larger deletions in the 2b sequence between residues 56-110 and 48-110 resulted in noticeably reduced co-localization between mutant 2b proteins and AGO1 but co-localization was never completely abolished.
Figure 5.
Subcellular localization of mutant 2b proteins and the Argonaute 1 protein (AGO1). Using agroinfiltration, C-terminal RFP or GFP fusion proteins derived from full length 2b proteins (WT 2b-RFP) or 2b proteins were co-expressed with RFP- or GFP-AGO1 fusion proteins in N. benthamiana leaves in the combinations shown. Fluorescent signals were imaged using confocal scanning laser microscopy. Fny-CMV 2b-RFP protein accumulated in the nucleus and cytoplasm, with a proportion co-localizing with the AGO1-GFP (merged signal shown as yellow). Deletions of residues 1-17 or 83-93 had no impact on the co-localization of AGO1 and 2b signals. However, deletion of the C-terminal residues 95-110, 85-110 or 74-110 resulted in a reduction in the proportion of co-localised signal. Larger deletions in the 2b sequence between residues 56-110 and 48-110 resulted in noticeably reduced co-localization between mutant 2b proteins and AGO1 but co-localization was never completely abolished.
Figure 6.
Interactions of wild-type or mutant versions of Fny-CMV 2b proteins with the Argonaute 1 protein (AGO1). Mutant versions of the 2b protein were fused at their C-termini with the C-terminal domain of split yellow fluorescent protein. Using agroinfiltration in N. benthamiana leaves, these fusion proteins were co-expressed with YFP N-proximal domain fusion proteins with AGO1 proteins. Direct protein-protein interactions were revealed in vivo by bimolecular fluorescence complementation and resulting fluorescence imaged by confocal laser scanning microscopy. The data shows that deletion of residues 85-110 or 74-110 had no impact on the interaction of mutant 2b proteins with AGO1. Deletion of residues from 61-110 caused a noticeable decrease in interaction between 2b and AGO1 proteins and deletions between 56-110 or 44-110 caused an almost complete loss of interaction. In-frame deletions between residues 56-60 or 39-48 resulted in a greatly weakened interaction with AGO1. Mutation of a 56-60 sequence to match that of the LS protein also resulted in a decreased strength of interaction. Alanine substitutions between residues 56-65 or 56-60 also resulted in decreased interaction with AGO1. However, 2b proteins lacking residues between 1-55 were still able to interact with the AGO1 protein and had a predominantly cytoplasmic localization likely as a result of the loss of NLS sequences.
Figure 6.
Interactions of wild-type or mutant versions of Fny-CMV 2b proteins with the Argonaute 1 protein (AGO1). Mutant versions of the 2b protein were fused at their C-termini with the C-terminal domain of split yellow fluorescent protein. Using agroinfiltration in N. benthamiana leaves, these fusion proteins were co-expressed with YFP N-proximal domain fusion proteins with AGO1 proteins. Direct protein-protein interactions were revealed in vivo by bimolecular fluorescence complementation and resulting fluorescence imaged by confocal laser scanning microscopy. The data shows that deletion of residues 85-110 or 74-110 had no impact on the interaction of mutant 2b proteins with AGO1. Deletion of residues from 61-110 caused a noticeable decrease in interaction between 2b and AGO1 proteins and deletions between 56-110 or 44-110 caused an almost complete loss of interaction. In-frame deletions between residues 56-60 or 39-48 resulted in a greatly weakened interaction with AGO1. Mutation of a 56-60 sequence to match that of the LS protein also resulted in a decreased strength of interaction. Alanine substitutions between residues 56-65 or 56-60 also resulted in decreased interaction with AGO1. However, 2b proteins lacking residues between 1-55 were still able to interact with the AGO1 protein and had a predominantly cytoplasmic localization likely as a result of the loss of NLS sequences.
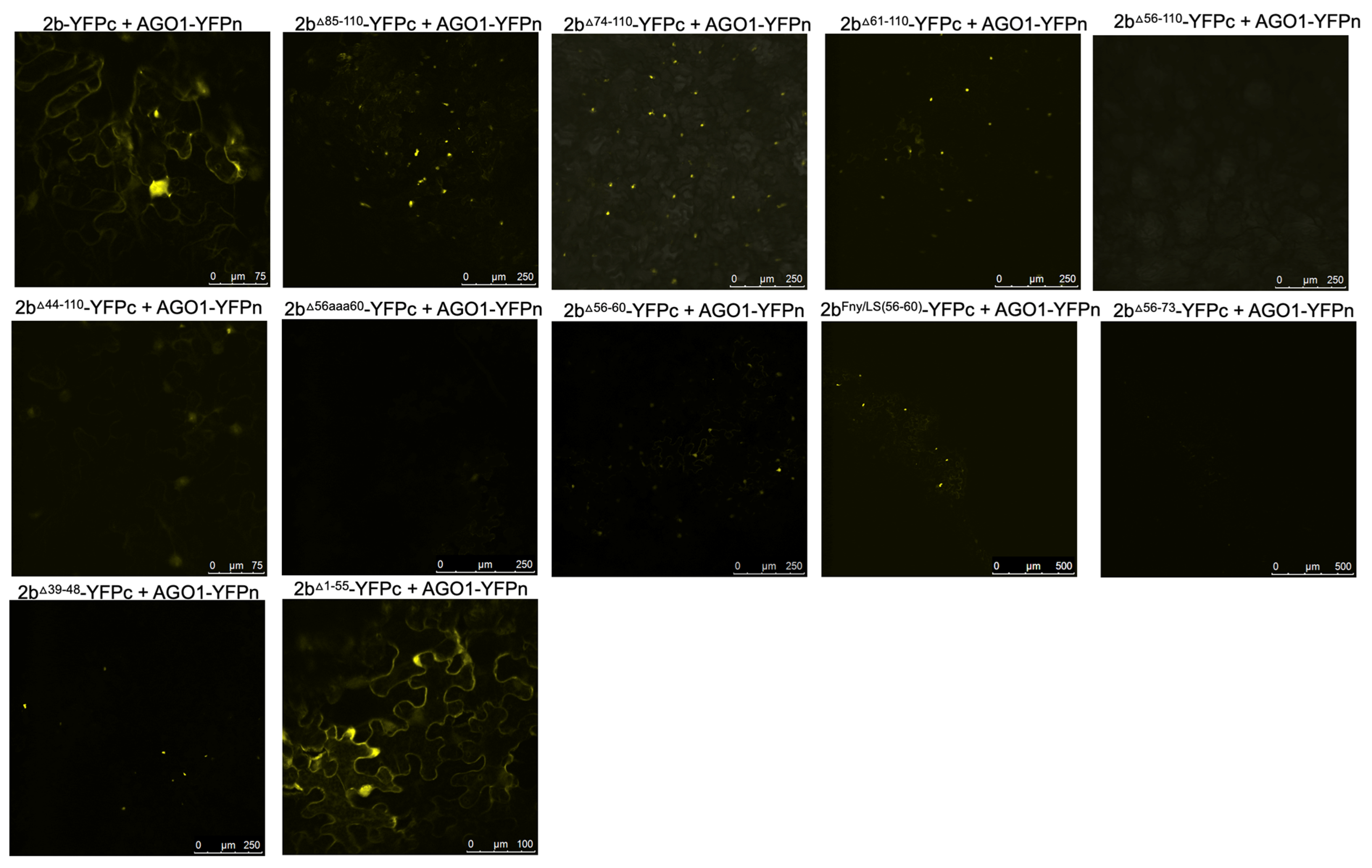
Figure 7.
CO-IP showing the mutant CMV 2b protein lacking residues 56-60 does not interact with the AGO1 protein. Using agroinfiltration into
N. benthamiana leaves, a GFP fusion protein derived from CMV 1a was coexpressed with RFP fusion proteins derived from full length 2b proteins (WT 2b-RFP) or mutant 2b sequences with deletions between residues 56-60 (2b
Δ56-60-RFP), alanine substitutions between residues 56-60 (2b
56aaa60-RFP) or replacement of the Fny-CMV 2b sequence with that of LS-CMV 2b sequence between residues 56 and 60 (2b
Fny/LS(56-60)-RFP). Total protein was extracted from leaf samples and immunoprecipitated with RFP-Trap beads (IP:RFP) followed by immunoblot analysis with anti-GFP antibodies to detect GFP-AGO1 fusion proteins. GFP-AGO1 was detected in all input samples with a corresponding band of approximately 140kDa. However, following RFP-pull down, GFP-AGO1 could only be detected when co-expressed with the 2b-RFP or 2bFny/LS(56-60)-RFP and not with the 2b56-60- RFP or 2b56aaa60-RFP mutants. Original blots used to make composite image are shown in
Figure S7.
Figure 7.
CO-IP showing the mutant CMV 2b protein lacking residues 56-60 does not interact with the AGO1 protein. Using agroinfiltration into
N. benthamiana leaves, a GFP fusion protein derived from CMV 1a was coexpressed with RFP fusion proteins derived from full length 2b proteins (WT 2b-RFP) or mutant 2b sequences with deletions between residues 56-60 (2b
Δ56-60-RFP), alanine substitutions between residues 56-60 (2b
56aaa60-RFP) or replacement of the Fny-CMV 2b sequence with that of LS-CMV 2b sequence between residues 56 and 60 (2b
Fny/LS(56-60)-RFP). Total protein was extracted from leaf samples and immunoprecipitated with RFP-Trap beads (IP:RFP) followed by immunoblot analysis with anti-GFP antibodies to detect GFP-AGO1 fusion proteins. GFP-AGO1 was detected in all input samples with a corresponding band of approximately 140kDa. However, following RFP-pull down, GFP-AGO1 could only be detected when co-expressed with the 2b-RFP or 2bFny/LS(56-60)-RFP and not with the 2b56-60- RFP or 2b56aaa60-RFP mutants. Original blots used to make composite image are shown in
Figure S7.
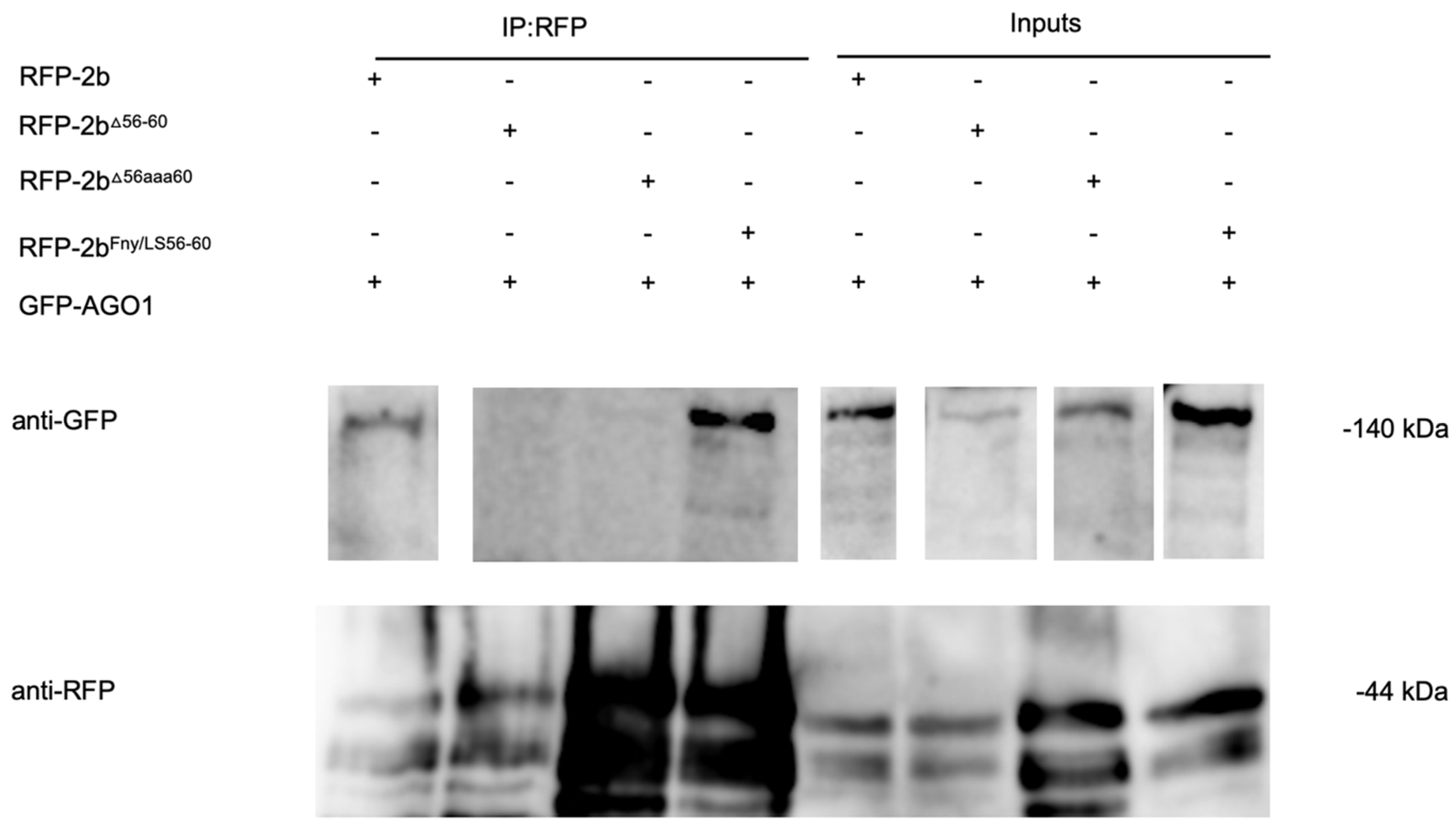
Figure 8.
Predictions of intrinsic disordered regions. a The IUPred3 program (shown in red) predicated that approximately 50% of the Fny 2b protein is likely to be intrinsically disordered with two principal disordered regions between residues 20-44 and 70-88. The ANCHOR2 algorithm (shown in blue) predicted the presence of two regions capable of binding another molecule and forming an ordered structure between residues 1-20 and residues 48-60. The 2b proteins from SD-CMV (a subgroup IB strain) had only one predicted region of disorder (between residues 20-44) but a no disordered region between residues 83-90 and only one predicted disordered binding domain between residues 1-20. The 2b protein of LS-CMV was predicted to have a much more ordered structure with only one potential region of disorder between residues 28-38 and no predicted disordered binding domains. b The ParSe v2 program yielded similar results with a greater proportion of the protein predicted to be intrinsically disordered in Subgroup IA strains than Subgroup IB strains and no sequences with 20 or more contiguous residues that are at least 90% disorder-promoting found in Subgroup II strains. Protein sequences are depicted as horizontal bars with folded regions shaded black, intrinsically disordered regions shaded red, and mixed regions shaded white. The GenBank accession numbers for the sequences used in this alignment are NC002035 for Fny-CMV, D12538 for Y-CMV, AM183118 for RI-8-CMV, AJ276480 for Mf-CMV, HE971489 for OSA3-CMV, QBH72281 for AZ14-CMV, CBG76802 for KS44-CMV, D86330 for SD-CMV, CAJ65577 for PI-1-CMV, FN552601 for 30RS-CMV, BAD15371 for TN-CMV, AF416900 for LS-CMV and Q66125 for Q-CMV.
Figure 8.
Predictions of intrinsic disordered regions. a The IUPred3 program (shown in red) predicated that approximately 50% of the Fny 2b protein is likely to be intrinsically disordered with two principal disordered regions between residues 20-44 and 70-88. The ANCHOR2 algorithm (shown in blue) predicted the presence of two regions capable of binding another molecule and forming an ordered structure between residues 1-20 and residues 48-60. The 2b proteins from SD-CMV (a subgroup IB strain) had only one predicted region of disorder (between residues 20-44) but a no disordered region between residues 83-90 and only one predicted disordered binding domain between residues 1-20. The 2b protein of LS-CMV was predicted to have a much more ordered structure with only one potential region of disorder between residues 28-38 and no predicted disordered binding domains. b The ParSe v2 program yielded similar results with a greater proportion of the protein predicted to be intrinsically disordered in Subgroup IA strains than Subgroup IB strains and no sequences with 20 or more contiguous residues that are at least 90% disorder-promoting found in Subgroup II strains. Protein sequences are depicted as horizontal bars with folded regions shaded black, intrinsically disordered regions shaded red, and mixed regions shaded white. The GenBank accession numbers for the sequences used in this alignment are NC002035 for Fny-CMV, D12538 for Y-CMV, AM183118 for RI-8-CMV, AJ276480 for Mf-CMV, HE971489 for OSA3-CMV, QBH72281 for AZ14-CMV, CBG76802 for KS44-CMV, D86330 for SD-CMV, CAJ65577 for PI-1-CMV, FN552601 for 30RS-CMV, BAD15371 for TN-CMV, AF416900 for LS-CMV and Q66125 for Q-CMV.
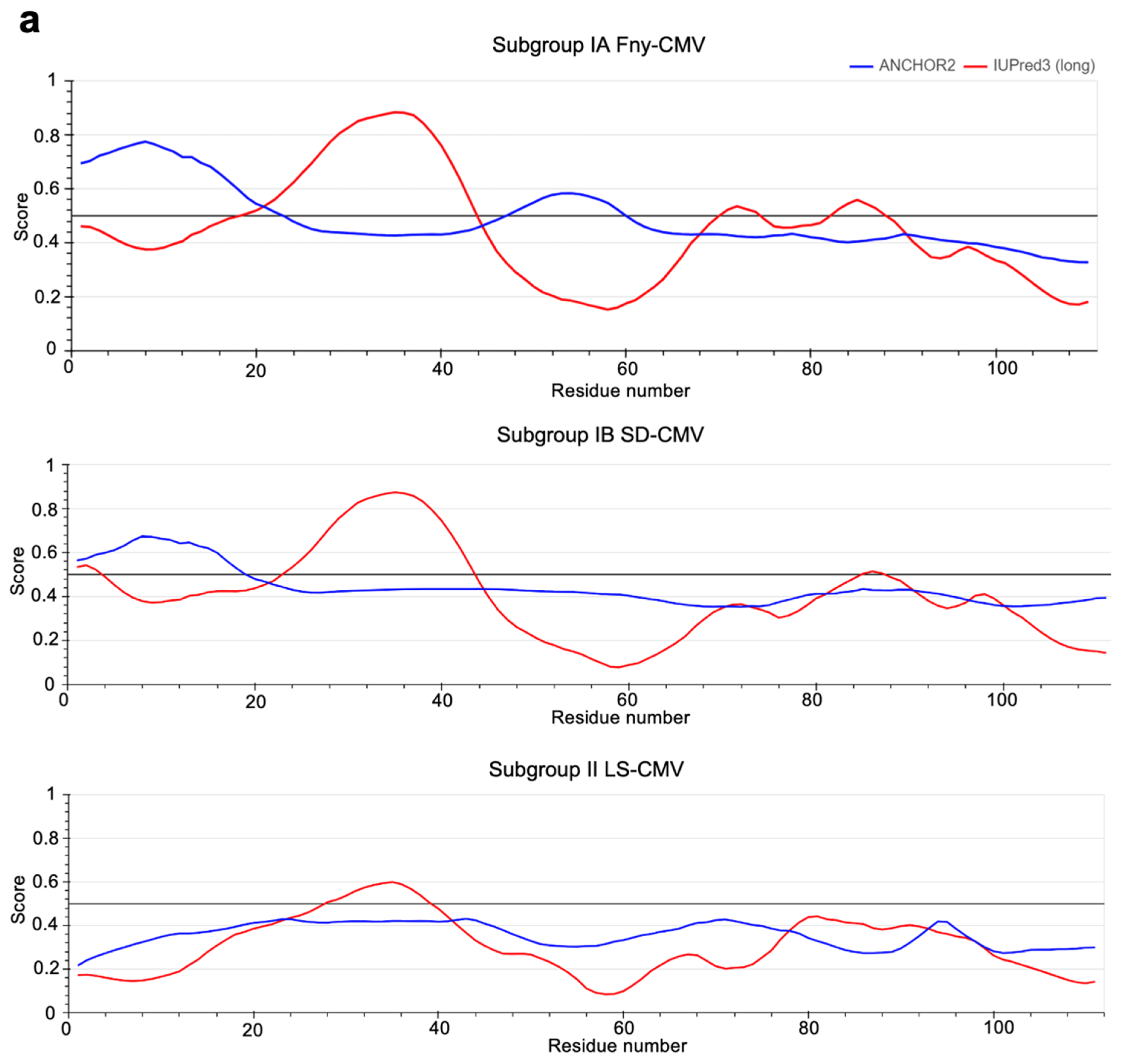
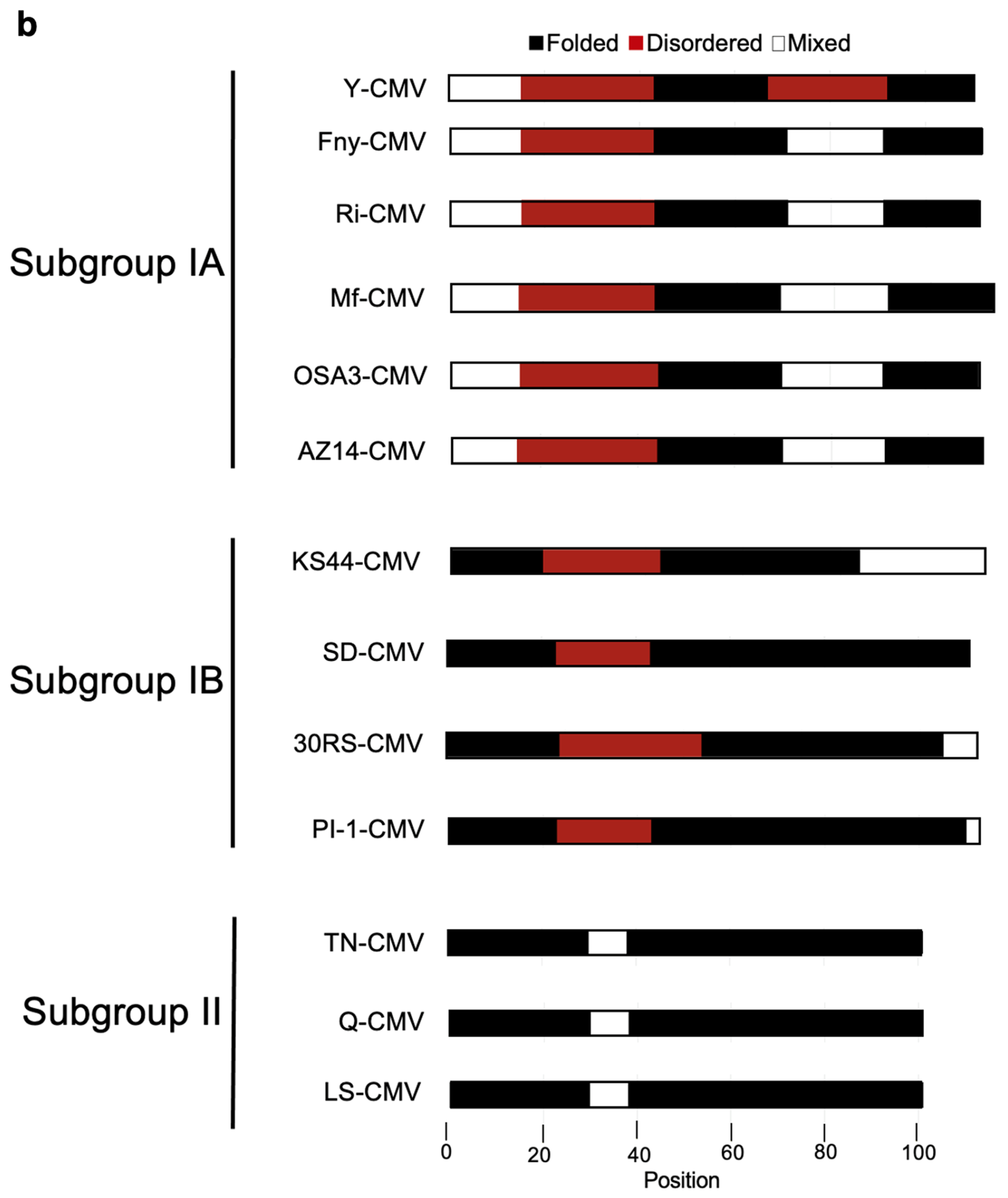
Figure 9.
Circular dichroism analysis of the Fny-CMV 2b protein. Data were obtained at a protein concentration of 13.5 μM in 10 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4 at 25 °C. The spectra were recorded between 190 nm and 240 nm and the average of five scan is shown. The data were converted to mean residue ellipticity to correct for protein size and concentration, and the spectrum was run through the CDSSTR program to assess the average secondary structure composition. The Fny-CMV 2b protein (black) shows a mix of structural motifs which when fitted by K2D shows a mainly disordered protein (55 %) with some alpha helix (13 %) and some beta-stands (32 %). Upon addition of 30 % trifluroethanol (TFE, red) there is a decrease in the amount of beta-strands (14 %) and an increase in the amount of alpha helix (31 %) with the random coil contingent remaining constant.
Figure 9.
Circular dichroism analysis of the Fny-CMV 2b protein. Data were obtained at a protein concentration of 13.5 μM in 10 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4 at 25 °C. The spectra were recorded between 190 nm and 240 nm and the average of five scan is shown. The data were converted to mean residue ellipticity to correct for protein size and concentration, and the spectrum was run through the CDSSTR program to assess the average secondary structure composition. The Fny-CMV 2b protein (black) shows a mix of structural motifs which when fitted by K2D shows a mainly disordered protein (55 %) with some alpha helix (13 %) and some beta-stands (32 %). Upon addition of 30 % trifluroethanol (TFE, red) there is a decrease in the amount of beta-strands (14 %) and an increase in the amount of alpha helix (31 %) with the random coil contingent remaining constant.
Figure 10.
Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of the Fny-CMV 2b protein. Results obtained for a 200 mM sample in phosphate-buffered saline (137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, 1.8 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.4). a Overlay of spectra from a 2D nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY) experiment (800 MHz, 298K, mixing time = 150 ms) shown in black and a 2D total correlation spectroscopy (TOCSY) experiment (800 MHz, 298K, mixing time = 32 ms) shown in red. The results suggest the presence of approximately 40 residues with an α-helical secondary structure and approximately 20 residues with a β-sheet secondary structure. b An expansion of the region between 6–11 ppm containing information relating to aromatic side chains and amide protons.
Figure 10.
Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of the Fny-CMV 2b protein. Results obtained for a 200 mM sample in phosphate-buffered saline (137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, 1.8 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.4). a Overlay of spectra from a 2D nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY) experiment (800 MHz, 298K, mixing time = 150 ms) shown in black and a 2D total correlation spectroscopy (TOCSY) experiment (800 MHz, 298K, mixing time = 32 ms) shown in red. The results suggest the presence of approximately 40 residues with an α-helical secondary structure and approximately 20 residues with a β-sheet secondary structure. b An expansion of the region between 6–11 ppm containing information relating to aromatic side chains and amide protons.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).