Submitted:
18 March 2024
Posted:
19 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The Evolution of DNA Sequencing
3. What Is Whole Genomic Sequencing?
4. AI-Powered Whole Genomic Sequencing
5. Pharmacogenomic Deep Learning Models
6. Exploring AI-Powered Genomics in Multi-Omics Research
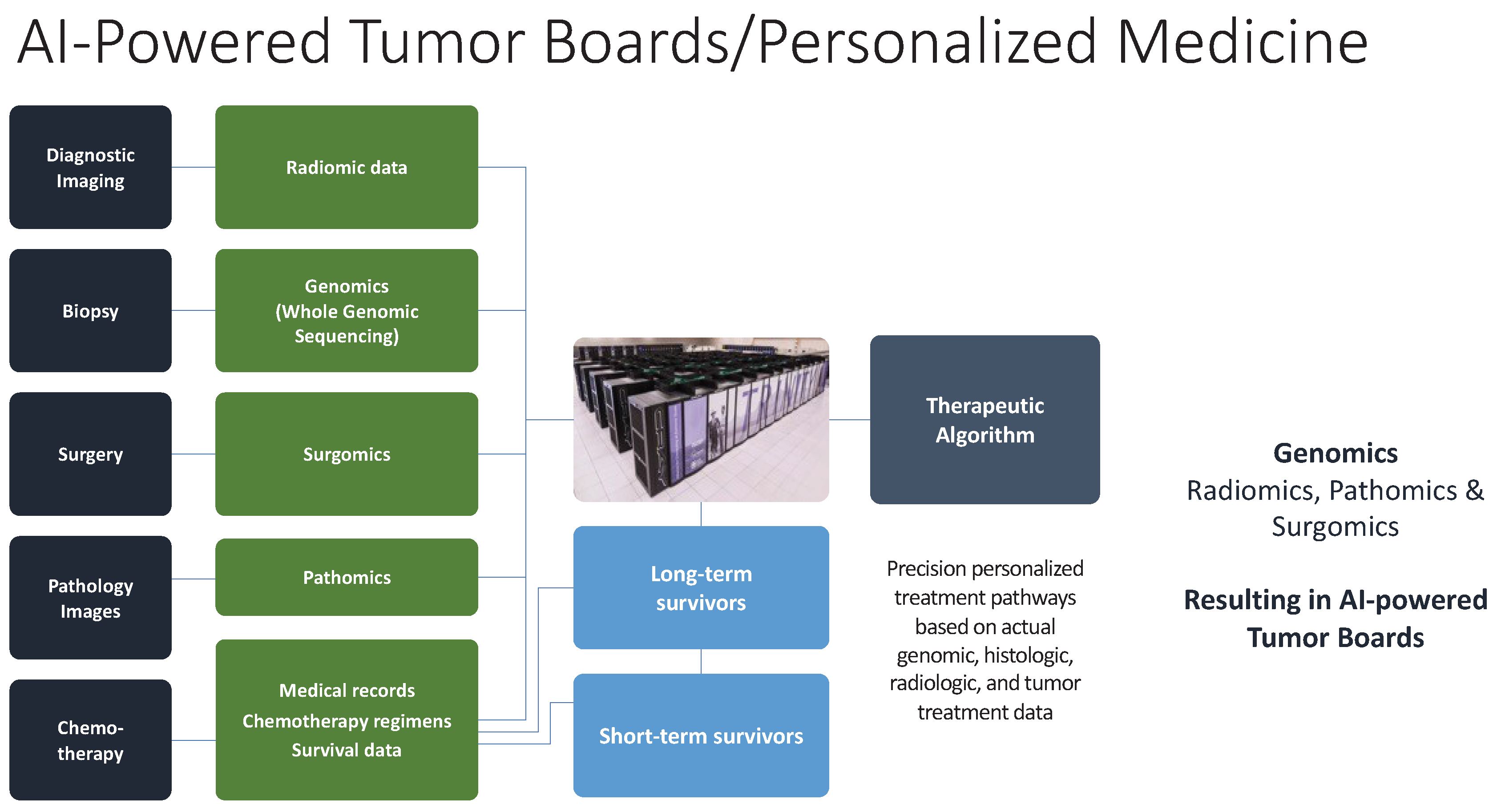
6.1. Radiomics, Pathomics and Surgomics
6.2. Proteomics, Transcriptomics and Genomics
7. Conclusion
References
- Sanger, F.; Coulson, A.R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. Journal of molecular biology 1975, 94, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoudi-Nejad, A.; Narimani, Z.; Hosseinkhan, N. (2013). Next generation sequencing and sequence assembly: methodologies and algorithms (Vol. 4). Springer Science & Business Media.
- El-Metwally, S.; Ouda, O.M.; Helmy, M. (2014). Next generation sequencing technologies and challenges in sequence assembly (Vol. 7). Springer Science & Business.
- Sanger, F.; Coulson, A.; Barrell, B.G.; Smith AJ, H.; Roe, B.A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. Journal of molecular biology 1980, 143, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative genomeanalysis@ tgr. org genomeanalysis@ gsf. de. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. nature 2000, 408, 796–815. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goff, S.A.; Ricke, D.; Lan, T.H.; Presting, G.; Wang, R.; Dunn, M.; Briggs, S.; et al. A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica). Science 2002, 296, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rm, D. A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature 2010, 467, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Kchouk, M.; Gibrat, J.F.; Elloumi, M. Generations of sequencing technologies: from first to next generation. Biology and Medicine 2017, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Maxam, A.M.; Gilbert, W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1977, 74, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi-Nejad, A.; Narimani, Z.; Hosseinkhan, N. (2013). Next generation sequencing and sequence assembly: methodologies and algorithms (Vol. 4). Springer Science & Business Media.
- Bayés, M.; Heath, S.; Gut, I.G. Applications of second generation sequencing technologies in complex disorders. Behavioral Neurogenetics 2012, 321–343. [Google Scholar]
- Mardis, E.R. Next-generation DNA sequencing methods. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2008, 9, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, N.; He, Y.; Pong, R.; Law, M.; et al. Comparison of next-generation sequencing systems. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Metwally, S.; Ouda, O.M.; Helmy, M. (2014). Next generation sequencing technologies and challenges in sequence assembly (Vol. 7). Springer Science & Business.
- Reuter, J.A.; Spacek, D.V.; Snyder, M.P. High-throughput sequencing technologies. Molecular cell 2015, 58, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loman, N.J.; Misra, R.V.; Dallman, T.J.; Constantinidou, C.; Gharbia, S.E.; Wain, J.; Pallen, M.J. Performance comparison of benchtop high-throughput sequencing platforms. Nature biotechnology 2012, 30, 434–439. [Google Scholar]
- Kulski, J.K. Next-generation sequencing—an overview of the history, tools, and “Omic” applications. Next generation sequencing-advances, applications and challenges 2016, 10, 61964. [Google Scholar]
- Mardis, E.R. Next-generation DNA sequencing methods. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2008, 9, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alic, A.S.; Ruzafa, D.; Dopazo, J.; Blanquer, I. Objective review of de novo stand-alone error correction methods for NGS data. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Molecular Science 2016, 6, 111–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi-Nejad, A.; Narimani, Z.; Hosseinkhan, N. (2013) Next generation sequencing and sequence assembly. Methodologies and algorithms. Springer.
- Masoudi-Nejad, A.; Narimani, Z.; Hosseinkhan, N. (2013). Next generation sequencing and sequence assembly: methodologies and algorithms (Vol. 4). Springer Science & Business Media.
- Bentley, D.R.; Balasubramanian, S.; Swerdlow, H.P.; Smith, G.P.; Milton, J.; Brown, C.G.; Roe, P.M.; et al. Accurate whole human genome sequencing using reversible terminator chemistry. nature 2008, 456, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Eid, J.; Fehr, A.; Gray, J.; Luong, K.; Lyle, J.; Otto, G.; Turner, S.; et al. Real-time DNA sequencing from single polymerase molecules. Science 2009, 323, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braslavsky, I.; Hebert, B.; Kartalov, E.; Quake, S.R. Sequence information can be obtained from single DNA molecules. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2003, 100, 3960–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, T.D.; Buzby, P.R.; Babcock, H.; Beer, E.; Bowers, J.; Braslavsky, I.; Xie, Z.; et al. Single-molecule DNA sequencing of a viral genome. Science 2008, 320, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, R.C.; Taylor, R.W.; Blauwkamp, T.A.; Kelley, J.L.; Kertesz, M.; Pushkarev, D.; Fiston-Lavier, A.S.; et al. Illumina TruSeq synthetic long-reads empower de novo assembly and resolve complex, highly-repetitive transposable elements. PloS one 2014, 9, e106689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoads, A.; Au, K.F. PacBio sequencing and its applications. Genomics, proteomics & bioinformatics 2015, 13, 278–289. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, N.; He, Y.; Pong, R.; Law, M.; et al. Comparison of next-generation sequencing systems. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.S.; Peluso, P.; Sedlazeck, F.J.; Nattestad, M.; Concepcion, G.T.; Clum, A.; Schatz, M.C.; et al. Phased diploid genome assembly with single-molecule real-time sequencing. Nature methods 2016, 13, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulski, J.K. Next-generation sequencing—an overview of the history, tools, and “Omic” applications. Next generation sequencing-advances, applications and challenges 2016, 10, 61964. [Google Scholar]
- Koren, S.; Schatz, M.C.; Walenz, B.P.; Martin, J.; Howard, J.T.; Ganapathy, G.; Phillippy, A.M.; et al. Hybrid error correction and de novo assembly of single-molecule sequencing reads. Nature biotechnology 2012, 30, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikheyev, A.S.; Tin, M.M. A first look at the Oxford Nanopore MinION sequencer. Molecular ecology resources 2014, 14, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laehnemann, D.; Borkhardt, A.; McHardy, A.C. Denoising DNA deep sequencing data—high-throughput sequencing errors and their correction. Briefings in bioinformatics 2016, 17, 154–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laver, T.; Harrison, J.; O’neill, P.A.; Moore, K.; Farbos, A.; Paszkiewicz, K.; Studholme, D.J. Assessing the performance of the oxford nanopore technologies minion. Biomolecular detection and quantification 2015, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, C.L.; Loose, M.; Tyson, J.R.; de Cesare, M.; Brown, B.L.; Jain, M.; Reference, Consortium; et al. MinION Analysis and Reference Consortium: Phase 1 data release and analysis. F1000Research 2015, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Behjati, S.; Tarpey, P.S. What is next generation sequencing? Archives of Disease in Childhood-Education and Practice 2013, 98, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grada, A.; Weinbrecht, K. Next-generation sequencing: methodology and application. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2013, 133, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatko, B.E.; Gardner, A.F.; Ausubel, F.M. Overview of next-generation sequencing technologies. Current protocols in molecular biology 2018, 122, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podnar, J.; Deiderick, H.; Huerta, G.; Hunicke-Smith, S. Next-Generation sequencing RNA-Seq library construction. Current protocols in molecular biology 2014, 106, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, H.; Fujita, M. Whole genome sequencing analysis for cancer genomics and precision medicine. Cancer science 2018, 109, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poplin, R.; Chang, P.C.; Alexander, D.; Schwartz, S.; Colthurst, T.; Ku, A.; DePristo, M.A.; et al. A universal SNP and small-indel variant caller using deep neural networks. Nature biotechnology 2018, 36, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Sedlazeck, F.J.; Lam, T.W.; Schatz, M.C. A multi-task convolutional deep neural network for variant calling in single molecule sequencing. Nature communications 2019, 10, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Wu, Y.; Gao, J. DeepSV: accurate calling of genomic deletions from high-throughput sequencing data using deep convolutional neural network. BMC bioinformatics 2019, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Bhatia, P. Intelli-NGS: Intelligent NGS, a deep neural network-based artificial intelligence to delineate good and bad variant calls from IonTorrent sequencer data. bioRxiv 2019, 2019–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gurovich, Y.; Hanani, Y.; Bar, O.; Nadav, G.; Fleischer, N.; Gelbman, D.; Gripp, K.W.; et al. Identifying facial phenotypes of genetic disorders using deep learning. Nature medicine 2019, 25, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S., Min, S., Choi, H., & Yoon, S. (2016). deepMiRGene: Deep neural network based precursor microrna prediction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1605.00017.Boudellioua I, Kulmanov M, Schofield PN, Gkoutos GV, Hoehndorf R. DeepPVP: phenotype-based prioritization of causative variants using deep learning. BMC Bioinform. 2019;20(1):65. [CrossRef]
- Trieu, T.; Martinez-Fundichely, A.; Khurana, E. DeepMILO: a deep learning approach to predict the impact of non-coding sequence variants on 3D chromatin structure. Genome biology 2020, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudellioua, I.; Kulmanov, M.; Schofield, P.N.; Gkoutos, G.V.; Hoehndorf, R. DeepPVP: phenotype-based prioritization of causative variants using deep learning. BMC bioinformatics 2019, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Theesfeld, C.L.; Yao, K.; Chen, K.M.; Wong, A.K.; Troyanskaya, O.G. Deep learning sequence-based ab initio prediction of variant effects on expression and disease risk. Nature genetics 2018, 50, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.C.; Mensah, M.A.; Pantel, J.T.; Aguilar, D.; Bar, O.; Bayat, A.; Krawitz, P.M.; et al. PEDIA: prioritization of exome data by image analysis. Genetics in Medicine 2019, 21, 2807–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravasio, V.; Ritelli, M.; Legati, A.; Giacopuzzi, E. Garfield-ngs: Genomic variants filtering by deep learning models in NGS. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3038–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arloth, J.; Eraslan, G.; Andlauer, T.F.; Martins, J.; Iurato, S.; Kühnel, B.; Mueller, N.S.; et al. DeepWAS: Multivariate genotype-phenotype associations by directly integrating regulatory information using deep learning. PLoS computational biology 2020, 16, e1007616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, D.R.; Snoek, J.; Rinn, J.L. Basset: learning the regulatory code of the accessible genome with deep convolutional neural networks. Genome research 2016, 26, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quang, D.; Xie, X. DanQ: a hybrid convolutional and recurrent deep neural network for quantifying the function of DNA sequences. Nucleic acids research 2016, 44, e107–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Yang, Y.; Póczos, B.; Ma, J. Predicting enhancer-promoter interaction from genomic sequence with deep neural networks. Quantitative Biology 2019, 7, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, R. Integrating distal and proximal information to predict gene expression via a densely connected convolutional neural network. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkatawi, M.; Magana-Mora, A.; Jankovic, B.; Bajic, V.B. DeepGSR: an optimized deep-learning structure for the recognition of genomic signals and regions. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaganathan, K.; Panagiotopoulou, S.K.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Farh KK, H.; et al. Predicting splicing from primary sequence with deep learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Jia, P.; Dai, Y.; Tao, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhi, D. Gene2vec: distributed representation of genes based on co-expression. BMC genomics 2019, 20, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movva, R.; Greenside, P.; Marinov, G.K.; Nair, S.; Shrikumar, A.; Kundaje, A. Deciphering regulatory DNA sequences and noncoding genetic variants using neural network models of massively parallel reporter assays. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0218073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaikkonen, M.U.; Lam, M.T.; Glass, C.K. Non-coding RNAs as regulators of gene expression and epigenetics. Cardiovascular research 2011, 90, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Troyanskaya, O.G. Predicting effects of noncoding variants with deep learning–based sequence model. Nature methods 2015, 12, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.C.; Chen HI, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, S.; Gorthi, A.; Wang, L.J.; Chen, Y.; et al. Predicting drug response of tumors from integrated genomic profiles by deep neural networks. BMC medical genomics 2019, 12, 143–155. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; He, S.; Song, X.; Bo, X.; Zhang, Z. Deep learning-based transcriptome data classification for drug-target interaction prediction. BMC genomics 2018, 19, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Bharathwaj, M.; Rosas, N.C.; Leier, A.; Akutsu, T.; Song, J.; et al. DeepBL: a deep learning-based approach for in silico discovery of beta-lactamases. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2021, 22, bbaa301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, L.; Govindaraj, R.G.; Lemoine, J.M.; Wu, H.C.; Brylinski, M. DeepDrug3D: classification of ligand-binding pockets in proteins with a convolutional neural network. PLoS computational biology 2019, 15, e1006718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuenzi, B.M.; Park, J.; Fong, S.H.; Sanchez, K.S.; Lee, J.; Kreisberg, J.F.; Ideker, T.; et al. Predicting drug response and synergy using a deep learning model of human cancer cells. Cancer cell 2020, 38, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuer, K.; Lewis, R.P.; Hochreiter, S.; Bender, A.; Bulusu, K.C.; Klambauer, G. DeepSynergy: predicting anti-cancer drug synergy with Deep Learning. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, W.S.; Rashid, M. A review of deep learning applications in human genomics using next-generation sequencing data. Human Genomics 2022, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbs, A.A.; Croner, R.; Abu-Hilal, M.; Bannone, E.; Ishizawa, T.; Spolverato, G.; Frigerio, I.; Siriwardena, A.; Messaoudi, N. Surgomics and the Artificial intelligence, Radiomics, Genomics, Oncopathomics and Surgomics (AiRGOS) Project. Art Int Surg 2023, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, M.; Ueda, D.; Matsumoto, T.; Shinkawa, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Shiba, M.; Okada, T.; Tani, N.; Tanaka, S.; Kimura, K.; Ohira, G.; Nishio, K.; Tauchi, J.; Kubo, S.; Ishizawa, T. Deep Learning Model Based on Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography Imaging to Predict Postoperative Early Recurrence after the Curative Resection of a Solitary Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2023, 15, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auffray, C.; Chen, Z.; Hood, L. Systems medicine: the future of medical genomics and healthcare. Genome Med [Internet]. 2009, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caudai, C.; Galizia, A.; Geraci, F.; Le, L.; Morea, V.; Salerno, E.; et al. AI applications in functional genomics. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021, 19, 5762–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, M.; Kumar, C.; Zeng, W.; Strauss, M.T. Perspective Artificial intelligence for proteomics and biomarker discovery. Cell Syst. 2021, 12, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiechle, F.L.; Holland-Staley, C.A. Genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and numbers. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003, 127, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, R.; Shirley, N.; Bleackley, M.; Dolan, S.; Shafee, T. Transcriptomics technologies. 2017;(Fig 1):1–23.
- Supplitt, S.; Karpinski, P.; Sasiadek, M.; Laczmanska, I. Current Achievements and Applications of Transcriptomics in Personalized Cancer Medicine. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, Y.; He, X.; Yu, J.; Jing, J. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Transcriptomic Analysis to Advance Cancer Immunotherapy. 2023. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




