1. Introduction
The retinoblastoma (RB) transcriptional corepressor 1 (RB1) stands as the first human tumor suppressor gene described by Dr. Alfred G. Knudson, who reported his observations on 48 cases of retinoblastoma, a rare eye cancer primarily affecting children, and associated reports [
1]. Through the study of the RB1 tumor suppressor, Dr. Knudson suggested that individuals inherit one defective copy of a tumor suppressor gene (the "first hit") and acquire a second mutation in the other copy of the gene (the "second hit") over time, leading to the development of cancer. His "two-hit" hypothesis, aimed at elucidating the genetic basis of retinoblastoma, stands as a fundamental cornerstone to understanding cancer genetics.
Since the discovery of RB1 decades ago, numerous studies on retinoblastoma and related non-ocular tumors have shed light on the molecular and genetic role of RB1 in cancer development and inheritance. These findings have significantly advanced our understanding of the pivotal role RB1 plays in cancer development. For instance, RB1 serves as a crucial regulator of cell cycle progression, acting as a safeguard against uncontrolled cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Mechanistically, RB1 functions as a transcriptional repressor, fine-tuning the cell cycle by binding to and negatively regulating the function of E2F1/2/3 transcription factors (for a review, see references [
2,
3,
4,
5]). In addition to its role in modulating the cell cycle, RB1 has been discovered to play crucial roles in various processes unrelated to cell cycle control. The intricate interactions between RB1 and cellular pathways emphasize its integral role in maintaining genomic stability and curbing aberrant cell growth, positioning it as a prime target for cancer research and therapeutic interventions. Its importance is further underscored by its involvement in various cancer types, where mutations or dysregulation of RB1 contribute to the initiation and progression of diverse cancers [
6].
The RB gene family comprises three key members: RB1 (p105), RBL1 (p107), and RBL2 (p130). While RBL1 and RBL2 are infrequently mutated in human cancers, RB1 mutations are prevalent across various cancer types, such as retinoblastoma, osteosarcoma, pinealoma, and melanoma [
6]. These mutations contribute significantly to the oncogenic characteristics associated with RB1 loss of function. Research indicates that irreversible impairments in the functions of the RB1 tumor suppressor frequently predict poor prognoses in cancer patients. However, RB1 loss can also confer advantages, manifesting in diverse mechanisms and vulnerabilities during cancer development. These encompass the upregulation of RB1 targets initially functionally inactivated due to RB1 binding, the presence of genes whose inactivation leads to synthetic lethality with RB1 loss, or the simultaneous loss of neighboring genes resulting in concomitant synthetic lethality [
7,
8,
9].
In this review, we will summarize the current evidence elucidating the pivotal role of RB1 in orchestrating both biological and pathological mechanisms across diverse cancer types, which not only enhances our understanding of the intricate molecular landscape due to RB1 loss but also lays the groundwork for the rational design of targeted therapeutic drugs. Specifically, we place a particular emphasis on potential strategies for targeted therapy that exhibit superior efficacy in the treatment of RB1-deficient cancers, offering a focused exploration of promising avenues in the pursuit of precision medicine.
2. Canonical Function of RB1 Tumor Suppressor
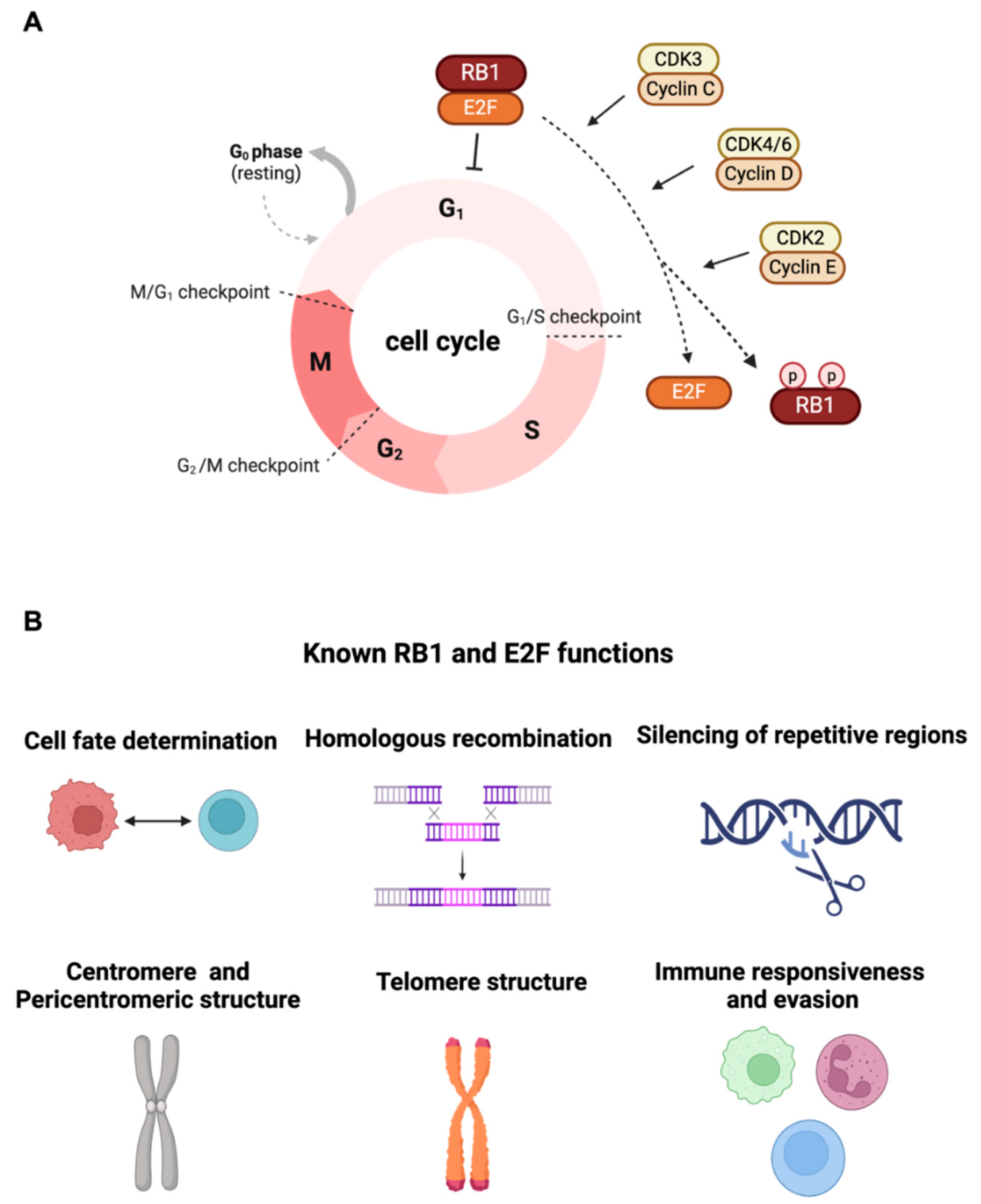
The RB1 tumor suppressor gene is initially characterized based on the germline predisposition of the pediatric eye tumor. Prior research has shown that RB1 functions as a key regulator in cell cycle progression [
2]. Functional characterization of the RB1 tumor suppressor gene was originally observed to be able to arrest cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle by inhibiting E2F1/2/3 transcription factors family activity. This suppression is abolished through the phosphorylation of pRB facilitated by Cyclin C/CDK3, Cyclin D/CDK4/6, or Cyclin E/CDK2 [
10] (
Figure 1A). There is a growing body of literature that investigates many cellular roles of RB1 besides serving as a G1 checkpoint, including a contribution of cell fate determination [
11], cellular differentiation control [
12,
13], DNA damage response [
14], cellular senescence [
15], homologous recombination [
16], silencing of repetitive regions [
17], centromere structure [
18,
19], pericentromeric structure and telomere maintenance [
20,
21,
22,
23], and Immune responsiveness and evasion [
24,
25] (
Figure 1B). Recent studies have further demonstrated RB1’s necessity in DNA double-strand break repair via canonical non-homologous end-joining (cNHEJ), wherein RB1 interacts with NHEJ components XRCC5 and XRCC6 [
26], suggesting RB1 loss as a potential driver of structural genomic instability, contributing to cancer somatic heterogeneity and evolution. Furthermore, RB1 can interact with non-E2F transcription factors such as CEBPD [
27], PU.1 [
28], and androgen receptor (AR) [
29], serving as a co-factor in modulating numerous gene expressions. While many cellular functions and binding proteins have been generally revealed, the precise pathological role of RB1 loss and its downstream effectors in distinct steps of tumorigenesis and various types of cancers largely remain unknown. It is necessary to consider the varied functions of RB1 across different cell types. While challenges such as lead optimization, pre-clinical testing, and clinical trials need to be addressed, historically, biomarker-matched drugs have exhibited high FDA approval rates. Therefore, it holds promise to target RB1/E2F downstream effectors in the treatment of RB1 mutation cancers.
3. Exploiting Vulnerabilities Stemming from RB1 Deficiency-Associated Mechanisms for Targeted Therapy
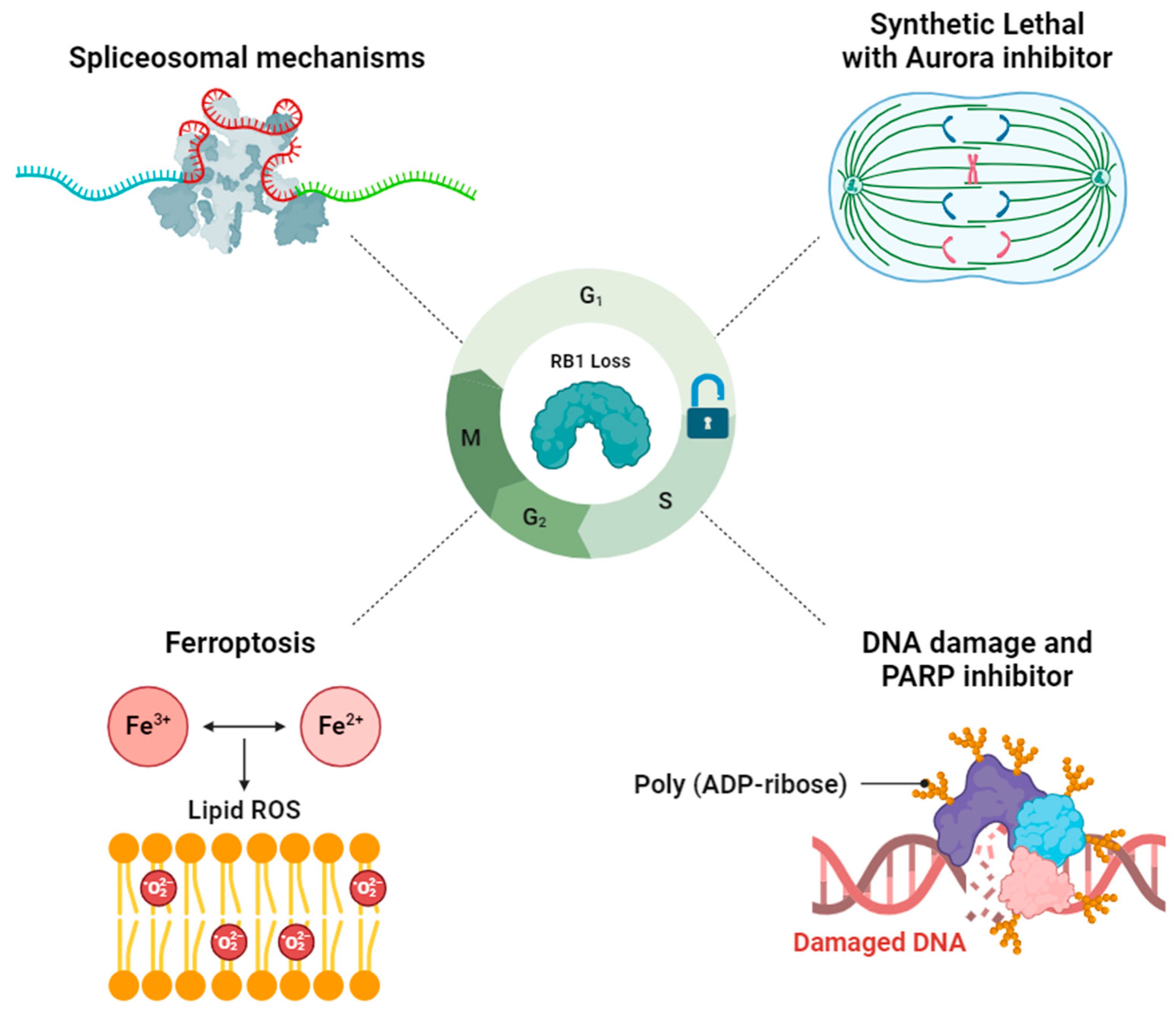
Based on the previous findings, four primary mechanisms associated with RB1 deficiency have emerged as promising candidates for targeted therapy development (
Figure 2).
3.1. RB1-Deficient Cancers Present a Vulnerability in Spliceosomal Mechanisms
Alternative RNA splicing is a crucial process for eukaryotes [
30], generating diverse RNA variants and protein isoforms from a single gene. Cancer cells often leverage the splicing machinery to create varied transcriptomes and unique splicing patterns [
31,
32]. Dysregulation of splicing factors, frequently upregulated in cancer cells, underscores the pivotal role of alternative splicing in cancer biology. Initially, RB1 is implied to be involved in spliceosome function, as indicated by the identification of the RB1/pp32 complex associating with components of the splicing machinery [
33,
34].
Tu J. et al. generated induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs; [
35]) derived from patients with hereditary retinoblastoma and utilized this platform to reveal that the RNA processing pathway is induced under conditions of oncogene stress in RB1-mutant cells [
36]. Through the analysis of transcriptomic and chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) data, they discovered that both RB1 and E2F3a co-regulate over a third of spliceosomal genes by binding to their promoters or enhancers. The clinical relevance of the RB1/E2F3a onco-spliceosome signature (REOSS) was demonstrated across various cancer types, with elevated expression observed in tumors exhibiting low RB1 and high E2F3a expression levels, which also correlated with poor prognosis in osteosarcoma (OS) patients. Significantly, pharmacological inhibition of the spliceosome using pladienolide B and SD6 in RB1-mutant cells led to widespread intron retention, reduced cellular proliferation, and compromised tumorigenesis ability, underscoring the therapeutic potential of targeting splicing dysregulation in RB1-deficient cancers. Notably, in support of the findings from Tu J. et al., the synthetic lethality screening performed by Oser MG et al. also identified that the depletion of RNA splicing factors, such as SNRPG, SNRPF, and U2AF1, leads to synthetic lethality in RB1-deficient small cell lung cancers (SCLCs) [
37]. Importantly, targeting the RNA spliceosome is considered a potential strategy for cancer treatment, as evidenced by the proposed use of spliceosome inhibitors such as H3B-8800 in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), or chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) with S3B1 mutation (clinical trial: NCT02841540) [
38,
39].
In summary, the dysregulation of alternative RNA splicing, particularly in RB1-deficient cancers, emphasizes the therapeutic potential of targeting the splicing machinery. The clinical relevance of the RB1/E2F3a onco-spliceosome signature underscores its prognostic significance across various cancer types.
3.2. Aurora Kinase Inhibitor-Induced Synthetic Lethal in RB1-Deficient Cancers
Targeting loss-of-function mutations or deletions in tumor suppressor genes is generally recognized as challenging. However, exploiting "gene-drug" synthetic lethality offers a promising opportunity for cancer therapeutic applications by identifying specific vulnerabilities that arise following the deficiency of a particular gene [
40].
Oser MG et al. utilized CRISPR/Cas9 screening methodologies to conduct synthetic lethal screening, aiming to identify therapeutic vulnerabilities in RB1-deficient SCLCs [
37]. They discovered that many of the hits encode regulators of chromosomal segregation that functionally interact, including components of condensin complexes (SMC2, NCAPG, and SMC4) and their upstream regulators (AURKB, PLK1, and INCENP). They further explored the intricate interplay between Aurora B inhibition and the transcriptional deregulation of numerous mitotic genes across various RB1-deficient SCLCs. Pharmacologically inhibiting Aurora B by AZD2811 in the SCLC mouse model not only increased polyploidy but also induced cell apoptosis, confirming that AURKB is the Achilles heel of RB1-deficient SCLCs.
Gong X et al. developed a pharmacogenomic screening assay to normalize growth rates by performing two doubling times for each assay and identified that Aurora A inhibitors, LY3295668, showed the strongest cytotoxicity in RB1-mutant SCLCs [
41]. They further demonstrated that LY3295668 has the potential to induce cell mitotic defects and cell apoptosis, as evidenced by its efficacy in an in vivo xenograft mouse model with RB1-deficient retinoblastoma [
42]. Besides, they highlighted the crucial role of spindle-assembly checkpoint (SAC) activation for the cytotoxicity of LY3295668 in malignancies lacking RB1. On the other hand, an independent study conducted by Lyu J et al., involving an RNAi library in lung cancer cells with RB1 knockout, shed light on the heightened sensitivity of these cells to Aurora A inhibition. The rationale behind this discovery lies in the E2F-mediated elevation of the microtubule destabilizer Stathmin. Inhibition of Aurora A by ENMD-2076 resulted in the activation of Stathmin by decreasing its phosphorylation, disrupting microtubule dynamics, and triggering SAC hyperactivation in RB1-deficient cells, ultimately leading to mitotic cell death [
43].
Taken together, the exploitation of synthetic lethality offers promising avenues for addressing the challenges posed by RB1 loss-of-function mutations in tumor suppressor genes. Studies investigating Aurora kinase inhibitors have shown potential in targeting RB1-deficient cancers, suggesting approaches for the development of more effective treatment strategies in oncology.
3.3. Synergistic Effect of DNA Damage and PARP Inhibitor on RB1-Deficient Cancers
As previously emphasized, loss-of-function mutations or deletions in tumor-suppressor genes are less favored as targetable driver mutations in cancer therapeutics. Therefore, a classic strategy for treating RB1-deficient malignancies involves the utilization of traditional cytotoxic chemotherapy, which specifically targets rapidly dividing cells. Despite the initial heightened sensitivity of RB1-deficient malignancies to DNA damage, strategies involving combinations of DNA-damaging agents with inhibitors of DNA damage repair, such as poly-ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors (PARPis), show promise in addressing RB1-deficient cancers [
16,
44,
45].
R. Vélez-Cruz et al. have elucidated the mechanistic rationale underlying the involvement of RB1 loss in the response to PARP inhibitors by revealing a novel, non-transcriptional function for RB1 in homologous recombination (HR) [
16]. This finding highlights that RB1 plays a pivotal role in facilitating DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair through HR and underscores the consequences of its absence, which lead to genome instability. In their investigation, it was observed that RB1 localizes to DSBs in a manner dependent on E2F1 and ATM kinase activity. This localization of RB1 is essential for the recruitment of the BRG1 ATPase to DSBs, thus enabling DNA end resection and facilitating the HR process. Depletion of RB1 in breast cancer and osteosarcoma cells results in sensitivity to DNA-damaging drugs, a sensitivity further exacerbated by the PARP inhibitor Olaparib. Supporting their findings, Pietanza MC et al. demonstrate the potential of Temozolomide in combination with the PARP inhibitor Veliparib in treating patients with relapsed-sensitive or refractory SCLCs [
44]. Additionally, Zoumpoulidou G demonstrated that RB1-deficient osteosarcoma is selectively sensitive to diverse PARP inhibitors such as Olaparib, Niraparib, and Talazoparib [
45].
Furthermore, by investigating the impact of RB1 mutation on the transcriptome and proteome, Dong Q et al. revealed that loss-of-function mutations in RB1 increase genomic instability and contribute to the accumulation of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) within the cytoplasm [
46]. Consequently, this accumulation initiates a series of events, including the upregulation of the innate immune signaling response by activating the cGAS/STING signaling pathway, elevated chemokine expression, and triggered immune cell infiltration in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). Moreover, xenograft experiments showed that treatment with PARP inhibitors reduced tumorigenesis in the A549 RB1-knockout xenograft mouse model. These findings collectively suggest that RB1 mutation mediates sensitivity to PARP inhibitors such as Olaparib, Rucaparib, and Niraparib through its crucial role in facilitating DNA DSB repair via HR and in modulating immune responses within the tumor microenvironment.
Another study conducted by Chakraborty G. et al. investigated the significance of BRCA2 and RB1 co-loss in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) [
47]. DNA damage response (DDR) gene variants are frequently observed in both the germline and as somatic abnormalities in mCRPC. Notably, a parallel investigation in prostate cancer patients underscored the significance of BRCA2 germline mutations, particularly when associated with RB1 heterozygous deletion. The co-deletion of BRCA2 and RB1 emerged as an independent genomic driver of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), contributing to an aggressive phenotype characterized by epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This transition was mediated by the induction of key EMT transcription factors such as SNAIL and SLUG, and the transcriptional co-activator PRRX1. They further highlighted the promising role of PARP inhibitors Olaparib and Talazoparib in treating cancers with DDR deficiencies, with a particular focus on the sensitivity of tumors harboring BRCA2 defects. Additionally, the research demonstrated that PARP inhibitors Olaparib and Talazoparib significantly hamper the growth of prostate cancer cell lines and organoids derived from human mCRPC exhibiting both homozygous and heterozygous co-deletion of BRCA2 and RB1 Supporting their findings, Miao C. et al. demonstrated that the loss of BRCA2 resensitizes RB1-deleted cells to PARP inhibition in RNASEH2B-deleted prostate cancer [
48].
Taken together, these findings collectively emphasize the therapeutic potential of targeting DDR pathways, especially in the context of BRCA2 and RB1 co-deletion, to combat the progression of castration-resistant prostate cancer.
3.4. Targeting RB1 Loss Cancer with Ferroptosis Inducer
Ferroptosis is a newly recognized, iron-dependent mechanism of programmed cell death, distinguished from conventional cell death pathways like apoptosis, necrosis, or autophagy [
49]. Cells die as a result of heightened lipid peroxidation induced by the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) during ferroptosis, leading to the breakdown of cell membranes and, ultimately, cell death. Long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 4 (ACSL4) and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) are two pivotal enzymes, with ACSL4 playing a positive regulatory role and GPX4 exerting a negative influence on the process of ferroptosis.
Growing evidence suggests a connection between ferroptosis and cancer cells that are resistant to therapy or drugs, observed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, small cell lung cancer, triple-negative breast cancer, etc. Wang ME et al. demonstrated that the mechanistic association of ferroptosis links to RB1 tumor suppressor loss and RB1-regulated transcription to targeted therapy [
50]. Since E2F is the primary transcription factor (mainly E2F1) driven by RB1 loss to regulate ACSL4 expression in prostate cancer, they unveiled the control of ferroptosis through the RB/E2F/ACSL4 axis, emphasizing the potential therapeutic application of inducing ferroptosis for treating prostate tumor growth driven by RB1 loss. They have reported the significance of RB1 inactivation as a genomic driver of resistance to various targeted therapies, signifying poor clinical outcomes across different cancer types. Additionally, they propose a potential solution by introducing the ferroptosis inducer JKE-1674, a highly selective and stable GPX4 inhibitor, which demonstrated selective induction of ferroptosis and lipid peroxidation in prostate cancer cells compared to normal-like prostate epithelial cells, suggesting the feasibility of ferroptosis induction as a promising cancer therapy for RB1-deficient malignancies.
3.5. Other Targets
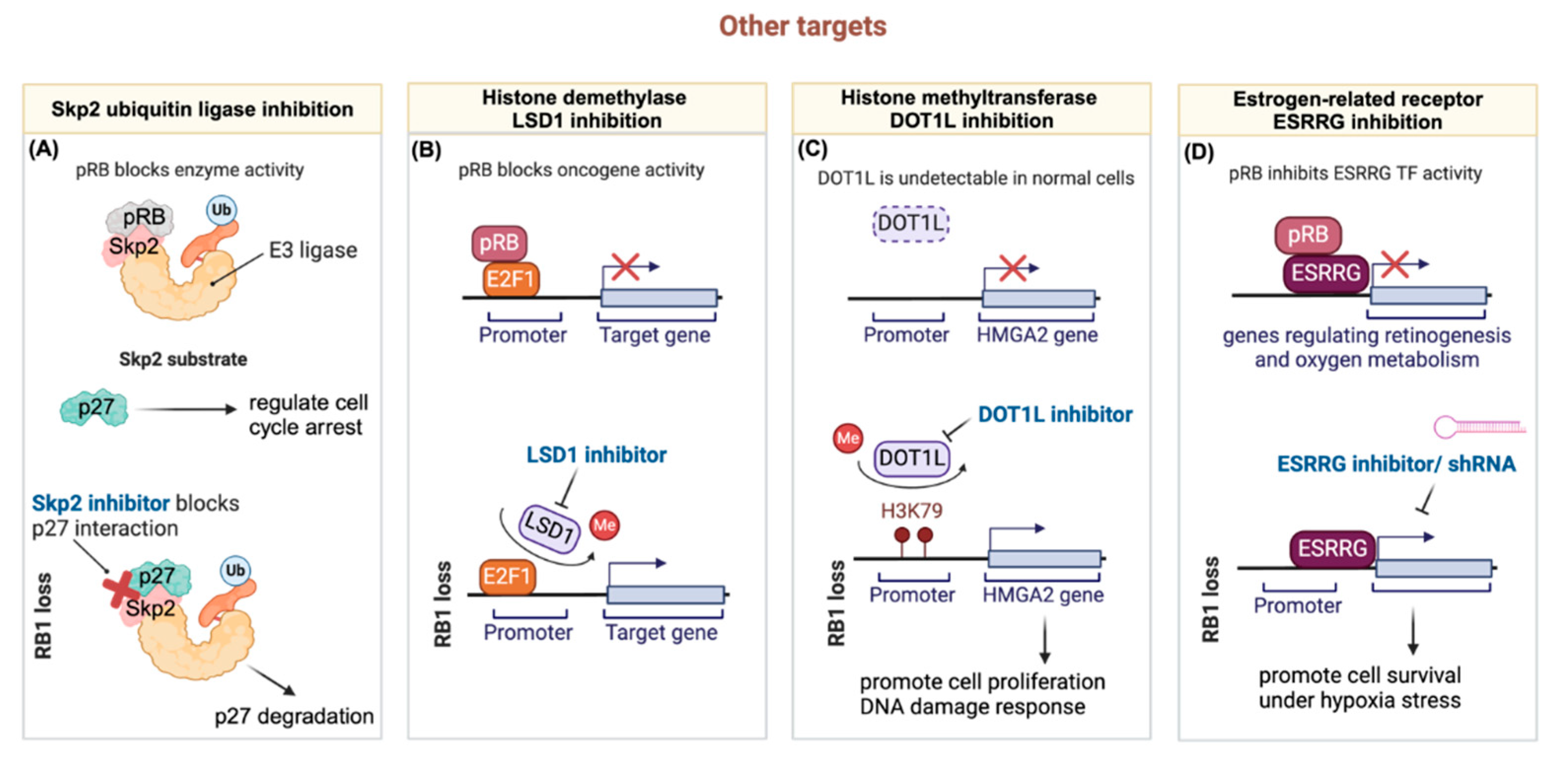
Given the widespread occurrence of loss-of-function mutations in RB1 observed across various human cancers, direct targeting of the RB1 protein presents significant challenges. Nevertheless, emerging evidence points to promising avenues for therapeutic intervention by focusing on downstream targets regulated either through transcriptional modulations or protein-protein interactions by RB1. This shift towards targeting downstream effectors holds the potential for enhancing therapeutic efficacy and achieving more precise treatment outcomes in RB1-mutated cancer patients. Here, we summarize four types of pharmacological inhibition potentially applicable in RB1-deficient cancers (
Figure 3).
3.5.1. Targeting RB1 Deficient Tumors through the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway
The intricate regulation of cell cycle progression emphasizes the pivotal role of protein ubiquitination and degradation in facilitating transitions between normal cells and transformed cells. SCF (SKP1-CUL1-Fb-ox) E3 ligase complexes utilize various F-box proteins to recognize and degrade specific substrates [
51]. Among these, SKP2, functioning as the substrate recognition F-box protein in SCFSKP1/CKS1/SKP2, acts as the E3 ligase that ubiquitinates numerous cell cycle substrates. Consequently, SKP2 plays crucial roles in cell proliferation, and differentiation, and is implicated in oncogenesis due to its overexpression in human cancers.
Multiple studies have associated SKP2 with RB1 and demonstrated that SKP2's activity is regulated by the RB1 tumor suppressor gene [
52]. This regulation involves not only mRNA expression [
53,
54] but also direct protein-protein interaction [
55] that modulates SKP2’s enzymatic activity. Loss of RB1 protein function, commonly observed through RB1 mutations in aggressive cancers, leads to dysregulation of SKP2 activity, resulting in decreased levels of p27 and compromised cell cycle control. Given SKP2’s oncogenic nature, inhibiting SKP2 either genetically or pharmacologically holds promise for therapeutic benefits in targeting RB1-deficient tumors.
Upregulation of SKP2 often correlates with the loss of the tumor suppressor RB1, suggesting that SKP2 inhibitors could be effective in tumors driven by various oncogenic drivers. Recognizing that SKP2 loss causes synthetic lethality in RB1 null cells, Aubry and colleagues explored the therapeutic potential of the SKP2 inhibitor MLN4924 in treating retinoblastoma [
56]. Their findings revealed that MLN4924 selectively impedes retinoblastoma tumor growth in vitro and in vivo, inducing G1 arrest with apoptosis and G2/M arrest with endoreplication. These results underscore the potential of developing small-molecule SKP2 inhibitors for clinical use in treating RB1-mutant cancers.
3.5.2. Targeting Hyperactive E2F through Histone Demethylase LSD1 Inhibition in RB1-Deficient Tumors
While prior research has shed light on the impact of RB1 inactivation on prostate cancer progression and lineage plasticity, there still remains a critical need to comprehensively understand the underlying mechanisms and identify therapeutic vulnerabilities in RB1-deficient CRPC. Wanting et al. explored the implications of RB1 loss in CRPC, particularly in the neuroendocrine (NE) subtype, given that genomic loss of RB1 is frequently observed in CRPC, correlating with adverse patient outcomes and neuroendocrine transdifferentiation induced by AR signaling inhibition [
57]. Intriguingly, the data suggest that the genomic background of prostate cancer cells influences the RB1-E2F transcriptional repression program, with implications for tumor behavior. Through integrated cistromic and transcriptomic analyses, Han W et al. characterized RB1 activity in multiple CRPC models, revealing distinct binding sites and targets based on genomic backgrounds. The study also identified a 49-gene RB1-target signature associated with worse survival in CRPC patients, highlighting the potential of RB1 deficiency as a prognostic marker. Importantly, their findings demonstrate that E2F1 chromatin binding and transcriptional activity in RB1-deficient CRPC is highly reliant on LSD1/KDM1A. Furthermore, RB1 inactivation sensitizes CRPC tumors to LSD1 inhibitor treatment. These findings suggest that LSD1 inhibitors could be effective in treating RB1-deficient CRPC or CRPC-NE, offering a promising avenue for therapeutic development in these aggressive cancer subtypes. This study underscores the importance of further exploring the therapeutic potential of LSD1 inhibitors in treating aggressive forms of prostate cancer characterized by RB1 loss.
3.5.3. Synergistic Chemo-Drug and Histone Methyltransferase DOT1L Inhibition for Treating Retinoblastoma
The dysregulation of epigenetic mechanisms plays a significant role in the tumorigenesis and progression of retinoblastoma [
58,
59,
60]. Despite the identification of aberrantly expressed chromatin regulators in retinoblastoma tumors compared to normal retina, their precise functions in retinoblastoma development and potential as therapeutic targets remain incompletely understood [[
61]. Mao Y. et al. explored the involvement of the histone H3K79 methyltransferase DOT1L in sensitizing retinoblastoma cells to chemotherapy [
62]. Although DOT1L is implicated in promoting leukemia development, and EPZ5676 monotherapy has shown promise in MLL-fusion leukemia, its effectiveness relies on the epigenetic repression of MLL target genes and continuous intravenous infusion to maintain therapeutic concentrations [
63]. While DOT1L was found to be expressed in most human retinoblastoma cases, its expression was undetectable in normal retina, suggesting a potential selective vulnerability for DOT1L targeting in retinoblastoma cells. However, treatment with the DOT1L inhibitor EPZ5676 alone demonstrated limited therapeutic efficacy in vitro and in vivo animal models, primarily due to the need for high doses and sustained drug availability to achieve significant anticancer effects. As DOT1L is involved in DNA damage response and repair, combination treatments of EPZ5676 with genotoxic agents were investigated. Indeed, DOT1L inhibition sensitized retinoblastoma cells to etoposide-induced apoptosis, enhancing the therapeutic effects of DNA-damaging agents. Additionally, the non-histone chromosome protein HMGA2 was identified as a novel target gene of DOT1L in retinoblastoma cells, with its expression epigenetically upregulated by DOT1L. Since HMGA2 promotes retinoblastoma cell proliferation and regulates DNA damage response, these findings suggest that DOT1L inhibition plays a dual role in chemosensitizing retinoblastoma cells by impairing early DNA damage response and downregulating HMGA2 expression.
In the clinical management of retinoblastoma, targeted therapies are not yet established, and conventional chemotherapy remains the standard treatment [
64,
65]. However, the extensive use of genotoxic drugs in young children with retinoblastoma raises concerns about potential late effects later in life. Targeting epigenetic regulators such as DOT1L may offer a means to enhance the efficacy of current chemotherapy regimens while reducing the doses of genotoxic drugs required for treatment. This approach aligns with recent findings suggesting improved chemotherapy outcomes through combination therapies targeting specific molecular pathways in retinoblastoma xenografts [
11]. Therefore, targeting epigenetic dysregulation, particularly through DOT1L inhibition, holds promise for advancing the treatment of retinoblastoma and minimizing the long-term adverse effects associated with conventional chemotherapy.
3.5.4. The Crosstalk of RB1-Loss and ESRRG
It is widely believed that further aberrations are necessary for complete malignant transformation in retinoblastoma [
66,
67]. However, none of the identified secondary drivers have yet been linked to any clinically targeted therapy. Taking advantage of a large comprehensive multi-omics analysis, Field M.G. et al. conducted a study integrating data from whole-exome sequencing (WES), whole-genome sequencing (WGS), RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), and single-cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) to identify previously unknown retinoblastoma dependencies [
68]. Their findings revealed that RB1 directly interacts with and inhibits estrogen-related receptor gamma (ESRRG). ESRRG functions as an estrogen-related orphan nuclear receptor transcription factor typically expressed in the developing retina and central nervous system and is known to regulate genes involved in various cellular processes such as development, proliferation, and oxygen metabolism [
69].
In the developing retina, a hypoxic environment arises from various factors, including the rapid proliferation of retinal precursor cells, high oxygen demand from newly formed neurons, and restricted blood supply [
70,
71]. This elevated oxygen demand is further exacerbated by the uncontrolled proliferation of tumor cells lacking RB1 [
72,
73]. As a result, the absence of RB1 disrupts the negative regulation of ESRRG by RB1, enabling cancer cells to survive under hypoxic stress. Furthermore, pharmacological inhibition by a specific inverse agonist GSK5182 or short hairpin RNA (shRNA)-mediated depletion of ESRRG results in significant RB1-loss cell death, particularly under hypoxic conditions. In clinical observations, heightened expression of ESRRG has been noted in human retinoblastoma tumor cells that infiltrate the optic nerve, a phenomenon strongly correlated with metastatic potential and dismal prognosis. These findings underscore the clinical significance of ESRRG dysregulation in the progression and aggressiveness of retinoblastoma, highlighting its potential utility as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in RB1 loss cancers.
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
The research summarized above provides the multifaceted role of RB1 in cancer biology and its implications for targeted therapy. RB1, a critical tumor suppressor gene, governs various cellular processes, including cell cycle regulation, DNA damage response, and transcriptional modulation. Mutations or dysregulation of RB1 are implicated in the development and progression of diverse cancers, making it a prime target for therapeutic intervention. The canonical function of RB1 in cell cycle control and DNA repair mechanisms underscores its significance in restraining aberrant cell growth and maintaining genomic integrity. However, the complex interplay between RB1 and either lineage-dependent or independent cellular pathways presents challenges in fully elucidating its tumor-suppressive role across different cancer types.
Exploiting vulnerabilities arising from RB1 loss-associated mechanisms offer promising avenues for targeted therapy. Studies investigating alternative RNA splicing dysregulation in RB1-deficient cancers highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting spliceosomal machinery. Furthermore, the identification of Aurora kinase inhibitors and PARP inhibitors as synthetic lethal targets in RB1-deficient malignancies provides insights into the development of more effective treatment strategies. Additionally, targeting RB1 loss-associated cancers with ferroptosis inducers represents a novel therapeutic approach. Ferroptosis induction, particularly through the RB/E2F/ACSL4 axis, emerges as a promising strategy for combating tumor growth driven by RB1 loss, offering potential clinical benefits in various cancer types.
Furthermore, targeting downstream effectors regulated by RB1 presents promising therapeutic approaches for RB1-mutated cancers, overcoming the challenges associated with direct RB1 protein targeting. We highlight four potential pharmacological inhibition strategies in RB1-deficient cancers: SKP2 ubiquitin ligase inhibition, histone demethylase LSD1 inhibition, histone methyltransferase DOT1L inhibition, and ESRRG inhibition. Each of these inhibitors has been proven effective for different RB1-deficient cancer cells, indicating that targeting downstream effectors regulated by RB1 offers promising strategies for therapeutic intervention in RB1-mutated cancers. This provides insights into potential biomarkers and avenues for precision medicine in cancer treatment.
Given the intricate network of pathways affected by RB1 deficiency and the emerging understanding of downstream effectors, future research could focus on elucidating the crosstalk between RB1 and other key regulatory molecules in cancer cells. Investigating how RB1 loss interacts with other genetic alterations or signaling pathways implicated in cancer development and progression could provide valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms driving RB1-deficient cancers. Additionally, exploring the tumor microenvironment's role in modulating the effects of RB1 deficiency and identifying potential therapeutic targets within the tumor stroma could open up new avenues for treatment. Integrating multi-omics approaches, including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, could further enhance our understanding of RB1-deficient cancers and facilitate the development of personalized treatment strategies tailored to individual patients' molecular profiles.
In summary, these findings deepen our understanding of RB1 biology in cancer and provide a foundation for the rational design of targeted therapeutic approaches. By elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying RB1 deficiency-associated vulnerabilities, these findings pave the way for the development of precision medicine strategies aimed at improving patient outcomes in RB1-deficient malignancies.
Author Contributions
M.-F.H. and Y.-X.W. Conceptualization, M.-F.H. and Y.-X.W.; writing—original draft preparation, M.-F.H., and Y.-X.W. writing—review and editing, M.-F.H., Y.-X.W., Y.-T.C., and D.-F.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
M.-F.H. was supported by the Rosalie B. Hite Fellowship and the Dr. John J. Kopchick Fellowship. Y.-X.W. was supported by the Overseas Internship Program (Taiwan Ministry of Education) and the Shen's Culture & Education Foundation Scholarship. D.-F.L. was supported by R01 CA246130 and R01 HL14270. Additionally, D.-F.L. is a CPRIT Scholar in Cancer Research.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this article are available in the references provided.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Knudson, A.G., Jr. Mutation and cancer: statistical study of retinoblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971, 68, 820–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, R.A. The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell. 1995, 81, 323–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevins, J.R. The Rb/E2F pathway and cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 2001, 10, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyson, N.J. RB1: a prototype tumor suppressor and an enigma. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Z.; Tsai, S.Y.; Leone, G. Emerging roles of E2Fs in cancer: an exit from cell cycle control. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009, 9, 785–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, P.; Zhao, Z. Characterization of Tumor-Suppressor Gene Inactivation Events in 33 Cancer Types. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Gordon, G.M.; Du, C.H.; Xu, J.; Du, W. Specific killing of Rb mutant cancer cells by inactivating TSC2. Cancer Cell. 2010, 17, 469–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, S.; Linn, P.; Nagatani, N.; Watanabe, Y.; Kumar, S.; Soga, T.; et al. Pharmacologically targetable vulnerability in prostate cancer carrying RB1-SUCLA2 deletion. Oncogene. 2020, 39, 5690–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, G.M.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, J.; Du, W. Deregulated G1-S control and energy stress contribute to the synthetic-lethal interactions between inactivation of RB and TSC1 or TSC2. J Cell Sci. 2013, 126 Pt. 9, 2004–13. [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht, B.D.; Flores, O.; Lees, J.A.; Harlow, E. Differential regulation of E2F transactivation by cyclin/cdk2 complexes. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 1772–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, A.; Pearson, J.D.; Huang, K.; Livne-Bar, I.; Ahmad, M.; Jagadeesan, M.; et al. Functional genomics identifies new synergistic therapies for retinoblastoma. Oncogene. 2020, 39, 5338–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jori, F.P.; Melone, M.A.; Napolitano, M.A.; Cipollaro, M.; Cascino, A.; Giordano, A.; et al. RB and RB2/p130 genes demonstrate both specific and overlapping functions during the early steps of in vitro neural differentiation of marrow stromal stem cells. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, C.; De Falco, G.; Tosi, G.M.; Lazzi, S.; Ferrari, F.; Morbini, G.; et al. Missing expression of pRb2/p130 in human retinoblastomas is associated with reduced apoptosis and lesser differentiation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002, 43, 3602–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dick, F.A.; Rubin, S.M. Molecular mechanisms underlying RB protein function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicas, A.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; McCurrach, M.; Zhao, Z.; Mert, O.; et al. Dissecting the unique role of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor during cellular senescence. Cancer Cell. 2010, 17, 376–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velez-Cruz, R.; Manickavinayaham, S.; Biswas, A.K.; Clary, R.W.; Premkumar, T.; Cole, F.; et al. RB localizes to DNA double-strand breaks and promotes DNA end resection and homologous recombination through the recruitment of BRG1. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 2500–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishak, C.A.; Marshall, A.E.; Passos, D.T.; White, C.R.; Kim, S.J.; Cecchini, M.J.; et al. An RB-EZH2 Complex Mediates Silencing of Repetitive DNA Sequences. Mol Cell. 2016, 64, 1074–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, A.L.; Yazinski, S.A.; Nicolay, B.; Bryll, A.; Zou, L.; Dyson, N.J. Suppression of genome instability in pRB-deficient cells by enhancement of chromosome cohesion. Mol Cell. 2014, 53, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, A.L.; Longworth, M.S.; Dyson, N.J. Loss of pRB causes centromere dysfunction and chromosomal instability. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 1364–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo, S.; Blasco, M.A. Role of Rb family in the epigenetic definition of chromatin. Cell Cycle. 2005, 4, 752–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Vasconcellos, I.; Schneider, R.; Anastasov, N.; Alonso-Rodriguez, S.; Sanli-Bonazzi, B.; Fernandez, J.L.; et al. The Rb1 tumour suppressor gene modifies telomeric chromatin architecture by regulating TERRA expression. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 42056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalo, S.; Garcia-Cao, M.; Fraga, M.F.; Schotta, G.; Peters, A.H.; Cotter, S.E.; et al. Role of the RB1 family in stabilizing histone methylation at constitutive heterochromatin. Nat Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 420–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cao, M.; Gonzalo, S.; Dean, D.; Blasco, M.A. A role for the Rb family of proteins in controlling telomere length. Nat Genet. 2002, 32, 415–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kansara, M.; Leong, H.S.; Lin, D.M.; Popkiss, S.; Pang, P.; Garsed, D.W.; et al. Immune response to RB1-regulated senescence limits radiation-induced osteosarcoma formation. J Clin Invest. 2013, 123, 5351–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Ding, D.; Yan, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Ma, L.; et al. Phosphorylated RB Promotes Cancer Immunity by Inhibiting NF-kappaB Activation and PD-L1 Expression. Mol Cell. 2019, 73, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, R.; Zoumpoulidou, G.; Luczynski, M.T.; Rieger, S.; Moquet, J.; Spanswick, V.J.; et al. Direct involvement of retinoblastoma family proteins in DNA repair by non-homologous end-joining. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 2006–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.L.; Riley, D.J.; Chen, Y.; Lee, W.H. Retinoblastoma protein positively regulates terminal adipocyte differentiation through direct interaction with C/EBPs. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 2794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemeier, C.; Bannister, A.J.; Cook, A.; Kouzarides, T. The activation domain of transcription factor PU.1 binds the retinoblastoma (RB) protein and the transcription factor TFIID in vitro: RB shows sequence similarity to TFIID and TFIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993, 90, 1580–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.; Miyamoto, H.; Nishimura, K.; Kang, H.; Ludlow, J.; Hsiao, P.; et al. Retinoblastoma, a tumor suppressor, is a coactivator for the androgen receptor in human prostate cancer DU145 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998, 248, 361–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. Mechanistic insights into precursor messenger RNA splicing by the spliceosome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 655–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveen, A.; Kilpinen, S.; Ruusulehto, A.; Lothe, R.A.; Skotheim, R.I. Aberrant RNA splicing in cancer; expression changes and driver mutations of splicing factor genes. Oncogene. 2016, 35, 2413–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Marabti, E.; Younis, I. The Cancer Spliceome: Reprograming of Alternative Splicing in Cancer. Front Mol Biosci. 2018, 5, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlander, J.; Bosco, G. The RB/E2F pathway and regulation of RNA processing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009, 384, 280–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegbola, O.; Pasternack, G.R. A pp32-retinoblastoma protein complex modulates androgen receptor-mediated transcription and associates with components of the splicing machinery. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005, 334, 702–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gingold, J.; Zhou, R.; Lemischka, I.R.; Lee, D.F. Modeling Cancer with Pluripotent Stem Cells. Trends Cancer. 2016, 2, 485–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Huo, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Xu, A.; Huang, M.F.; et al. Hereditary retinoblastoma iPSC model reveals aberrant spliceosome function driving bone malignancies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022, 119, e2117857119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oser, M.G.; Fonseca, R.; Chakraborty, A.A.; Brough, R.; Spektor, A.; Jennings, R.B.; et al. Cells Lacking the RB1 Tumor Suppressor Gene Are Hyperdependent on Aurora B Kinase for Survival. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 230–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, M.; Yoshimi, A.; Darman, R.; Chan, B.; Keaney, G.; Thomas, M.; et al. H3B-8800, an orally available small-molecule splicing modulator, induces lethality in spliceosome-mutant cancers. Nat Med. 2018, 24, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steensma, D.P.; Wermke, M.; Klimek, V.M.; Greenberg, P.L.; Font, P.; Komrokji, R.S.; et al. Phase I First-in-Human Dose Escalation Study of the oral SF3B1 modulator H3B-8800 in myeloid neoplasms. Leukemia. 2021, 35, 3542–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaelin, W.G., Jr. The concept of synthetic lethality in the context of anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005, 5, 689–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Du, J.; Parsons, S.H.; Merzoug, F.F.; Webster, Y.; Iversen, P.W.; et al. Aurora A Kinase Inhibition Is Synthetic Lethal with Loss of the RB1 Tumor Suppressor Gene. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 248–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Jiang, X.X.; Zhao, X.Y.; Mao, P.A. Treatment of RB-deficient retinoblastoma with Aurora-A kinase inhibitor. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2022, 38, 244–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.; Yang, E.J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, C.; Pardeshi, L.; Shi, C.; et al. Synthetic lethality of RB1 and aurora A is driven by stathmin-mediated disruption of microtubule dynamics. Nat Commun. 2020, 11, 5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietanza, M.C.; Waqar, S.N.; Krug, L.M.; Dowlati, A.; Hann, C.L.; Chiappori, A.; et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase II Study of Temozolomide in Combination With Either Veliparib or Placebo in Patients With Relapsed-Sensitive or Refractory Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018, 36, 2386–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoumpoulidou, G.; Alvarez-Mendoza, C.; Mancusi, C.; Ahmed, R.M.; Denman, M.; Steele, C.D.; et al. Therapeutic vulnerability to PARP1,2 inhibition in RB1-mutant osteosarcoma. Nat Commun. 2021, 12, 7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Q.; Yu, T.; Chen, B.; Liu, M.; Sun, X.; Cao, H.; et al. Mutant RB1 enhances therapeutic efficacy of PARPis in lung adenocarcinoma by triggering the cGAS/STING pathway. JCI Insight. 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, G.; Armenia, J.; Mazzu, Y.Z.; Nandakumar, S.; Stopsack, K.H.; Atiq, M.O.; et al. Significance of BRCA2 and RB1 Co-loss in Aggressive Prostate Cancer Progression. Clin Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2047–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Tsujino, T.; Takai, T.; Gui, F.; Tsutsumi, T.; Sztupinszki, Z.; et al. RB1 loss overrides PARP inhibitor sensitivity driven by RNASEH2B loss in prostate cancer. Sci Adv. 2022, 8, eabl9794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G.; Zhuang, L.; Gan, B. Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022, 22, 381–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.E.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Bawcom, A.R.; Wu, J.; Ou, J.; et al. RB1-deficient prostate tumor growth and metastasis are vulnerable to ferroptosis induction via the E2F/ACSL4 axis. J Clin Invest. 2023, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaar, J.R.; Pagan, J.K.; Pagano, M. SCF ubiquitin ligase-targeted therapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Zhao, H.; Hoang, B.; Schwartz, E.L. Targeting the untargetable: RB1-deficient tumours are vulnerable to Skp2 ubiquitin ligase inhibition. Br J Cancer. 2022, 127, 969–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, H.; Bauzon, F.; Lu, Z.; Fu, H.; Cui, J.; et al. Deletions of Retinoblastoma 1 (Rb1) and Its Repressing Target S Phase Kinase-associated protein 2 (Skp2) Are Synthetic Lethal in Mouse Embryogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2016, 291, 10201–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Bauzon, F.; Ji, P.; Xu, X.; Sun, D.; Locker, J.; et al. Skp2 is required for survival of aberrantly proliferating Rb1-deficient cells and for tumorigenesis in Rb1+/- mice. Nat Genet. 2010, 42, 83–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, P.; Jiang, H.; Rekhtman, K.; Bloom, J.; Ichetovkin, M.; Pagano, M.; et al. An Rb-Skp2-p27 pathway mediates acute cell cycle inhibition by Rb and is retained in a partial-penetrance Rb mutant. Mol Cell. 2004, 16, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubry, A.; Yu, T.; Bremner, R. Preclinical studies reveal MLN4924 is a promising new retinoblastoma therapy. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Liu, M.; Han, D.; Li, M.; Toure, A.A.; Wang, Z.; et al. RB1 loss in castration-resistant prostate cancer confers vulnerability to LSD1 inhibition. Oncogene. 2022, 41, 852–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theriault, B.L.; Dimaras, H.; Gallie, B.L.; Corson, T.W. The genomic landscape of retinoblastoma: a review. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014, 42, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.; Malik, M.A.; Goswami, S.; Shukla, S.; Kaur, J. Epigenetic regulation of human retinoblastoma. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 14427–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, C.A.; Dyer, M.A. Genetics and epigenetics of human retinoblastoma. Annu Rev Pathol. 2015, 10, 547–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kim, J.K. Chromatin regulators in retinoblastoma: Biological roles and therapeutic applications. J Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 2318–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, J.; et al. Targeting of histone methyltransferase DOT1L plays a dual role in chemosensitization of retinoblastoma cells and enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Ge, S. Targeting the histone H3 lysine 79 methyltransferase DOT1L in MLL-rearranged leukemias. J Hematol Oncol. 2022, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimaras, H.; Corson, T.W.; Cobrinik, D.; White, A.; Zhao, J.; Munier, F.L.; et al. Retinoblastoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015, 1, 15021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.S.; Gallie, B.L.; Munier, F.L.; Beck Popovic, M. Chemotherapy for retinoblastoma. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2005, 18, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corson, T.W.; Gallie, B.L. One hit, two hits, three hits, more? Genomic changes in the development of retinoblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2007, 46, 617–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimaras, H.; Khetan, V.; Halliday, W.; Orlic, M.; Prigoda, N.L.; Piovesan, B.; et al. Loss of RB1 induces non-proliferative retinoma: increasing genomic instability correlates with progression to retinoblastoma. Hum Mol Genet. 2008, 17, 1363–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, M.G.; Kuznetsoff, J.N.; Zhang, M.G.; Dollar, J.J.; Durante, M.A.; Sayegh, Y.; et al. RB1 loss triggers dependence on ESRRG in retinoblastoma. Sci Adv. 2022, 8, eabm8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, A.; Wang, H.; Kamarajugadda, S.; Lu, J. Involvement of estrogen-related receptors in transcriptional response to hypoxia and growth of solid tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008, 105, 7821–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyal, J.S.; Gantner, M.L.; Smith, L.E.H. Retinal energy demands control vascular supply of the retina in development and disease: The role of neuronal lipid and glucose metabolism. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018, 64, 131–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangsa-Wirawan, N.D.; Linsenmeier, R.A. Retinal oxygen: fundamental and clinical aspects. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003, 121, 547–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Tripathy, A.; Yu, W.; Eberhart, C.G.; Asnaghi, L. Hypoxia inhibits growth, proliferation, and increases response to chemotherapy in retinoblastoma cells. Exp Eye Res. 2017, 162, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, J.; Venkatesan, N.; Lakshmanan, S.; Khetan, V.; Krishnakumar, S.; Biswas, J. Hypoxic tumor microenvironment in advanced retinoblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013, 60, 1598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).