Submitted:
14 March 2024
Posted:
15 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
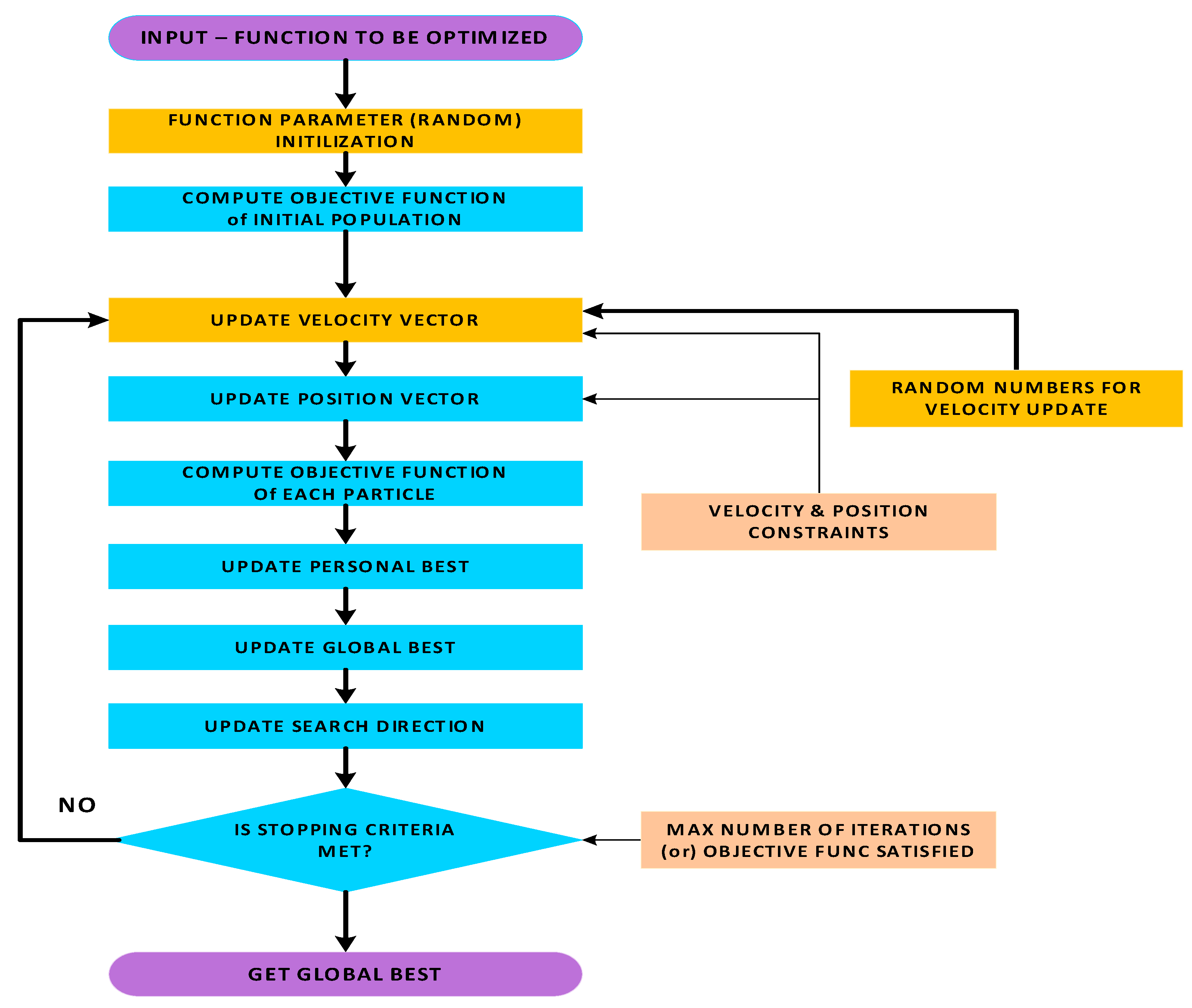
2.1. Particle Swarm Optimization
- Initialize Parameters:
- Define the population size (number of particles),
- Define the number of decision variables (dimension),
- Define the maximum number of iterations, .
- Define the inertia weight,
- Define acceleration constants: cognitive and social, .
- Initialize the position and velocity of each particle randomly within the search space.
- Set the best-known position for each particle n, to its initial position.
- Evaluate Fitness:
- Update the personal best position for each particle if its current fitness is better than its previous best fitness.
- Update Global Best:
- g.
- Determine the particle with the best fitness among all particles in the swarm, .
- h.
- Update the global best position with the position of the particle with the best fitness, .
- i.
- Update Velocities and Positions:
- Check Stopping Criteria:
- j.
- If the maximum number of iterations is reached or a satisfactory solution is found, stop the algorithm.
- k.
- Otherwise, go back to step 2 and repeat the process.
-
Output:Return the global best position as the solution to the optimization problem..
2.2. Quasi-Random Sequence Enhancements
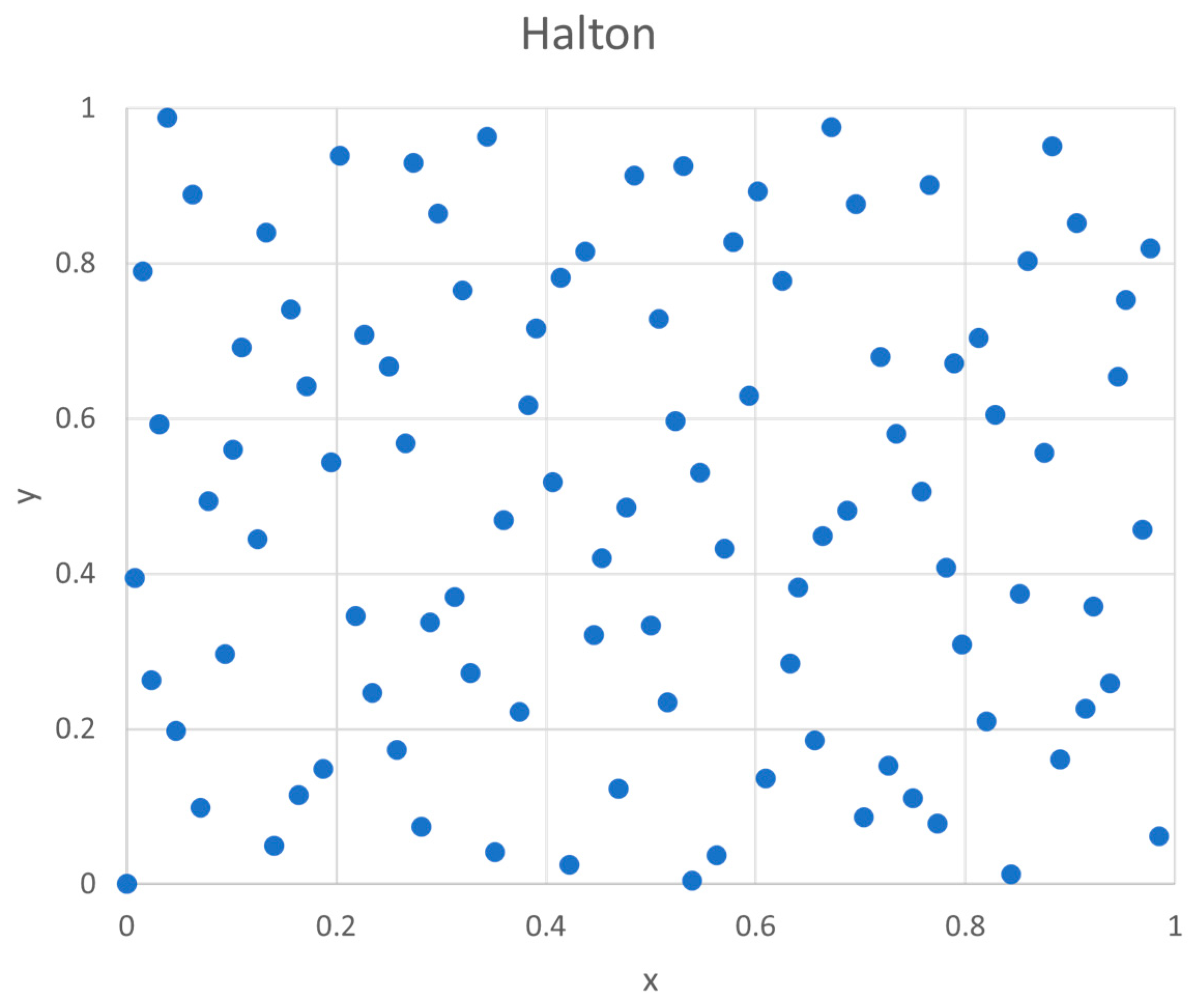
2.3. Halton Sequence Points
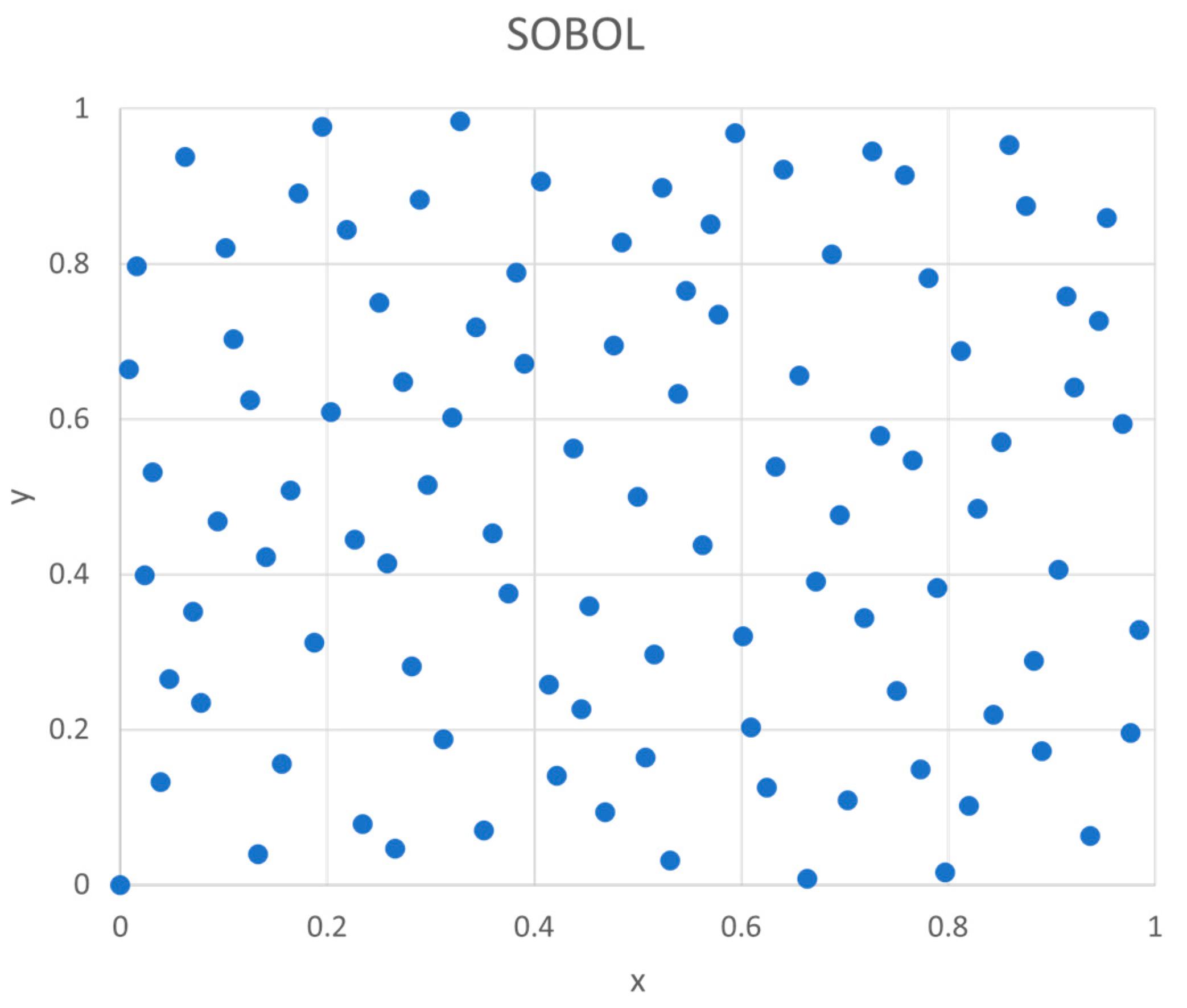
2.4. SOBOL Sequence Points
3. Results
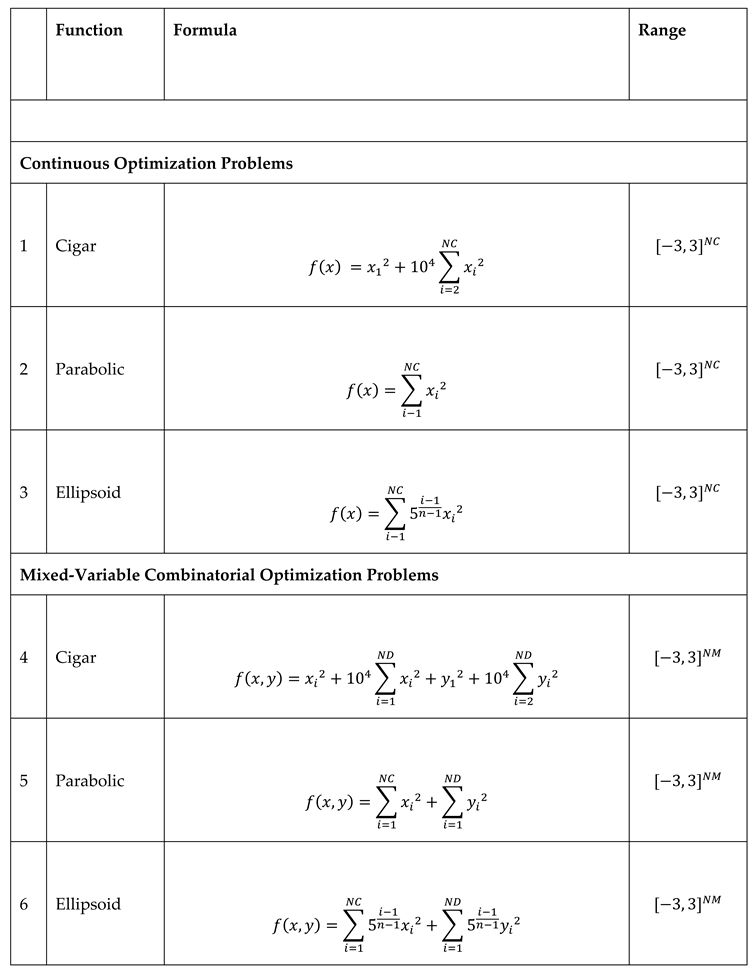
3.1. Test Cases
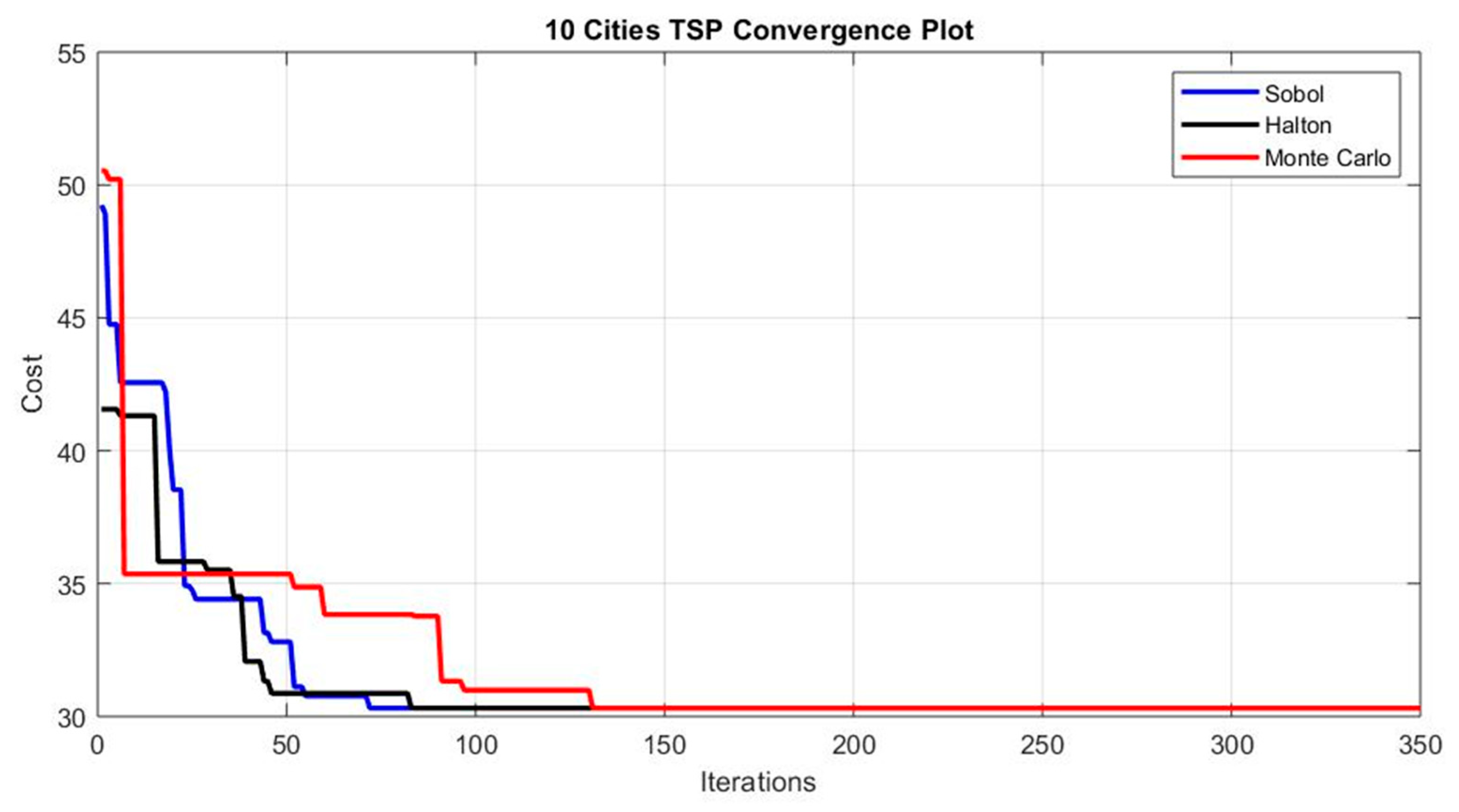
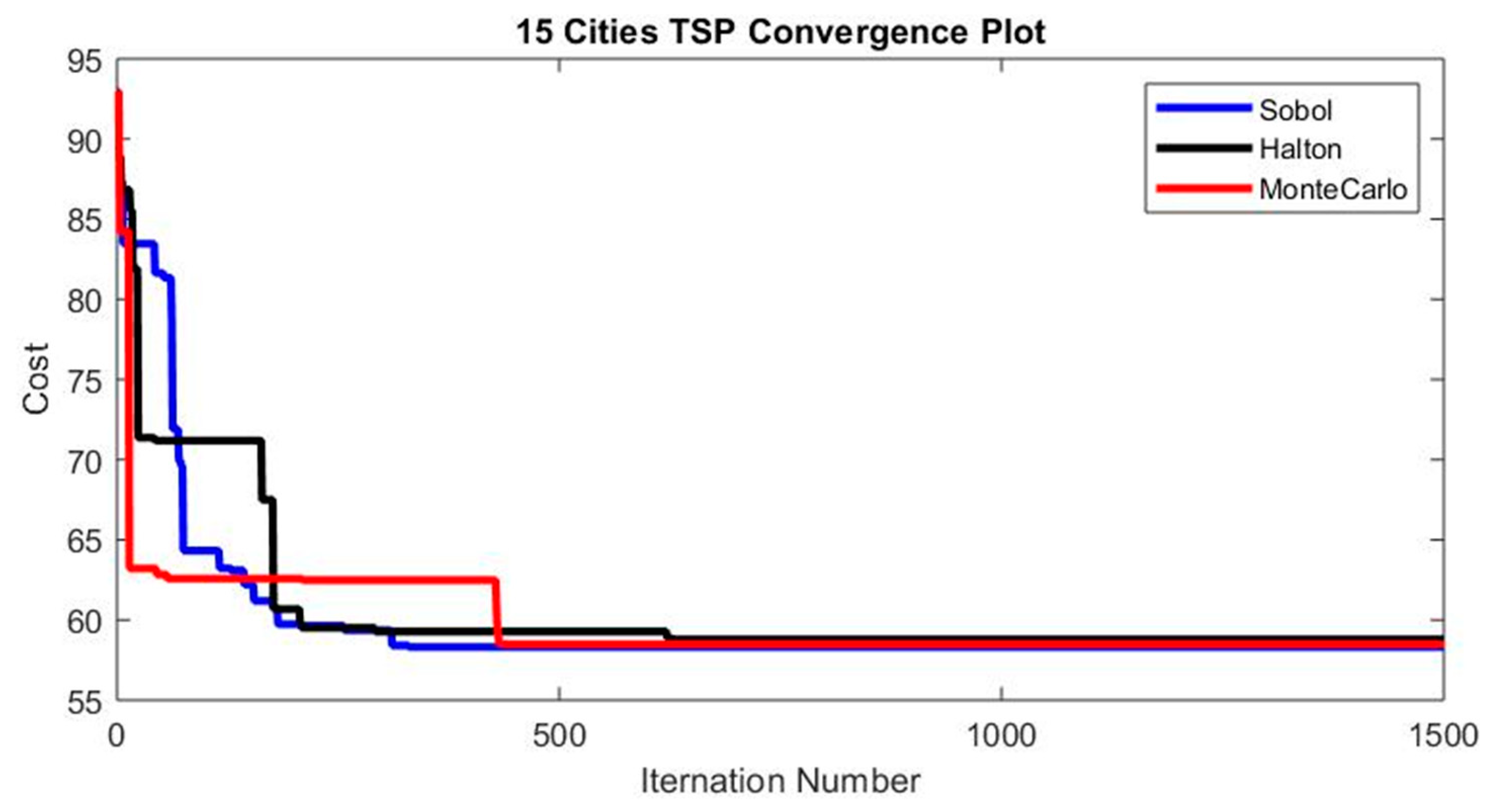
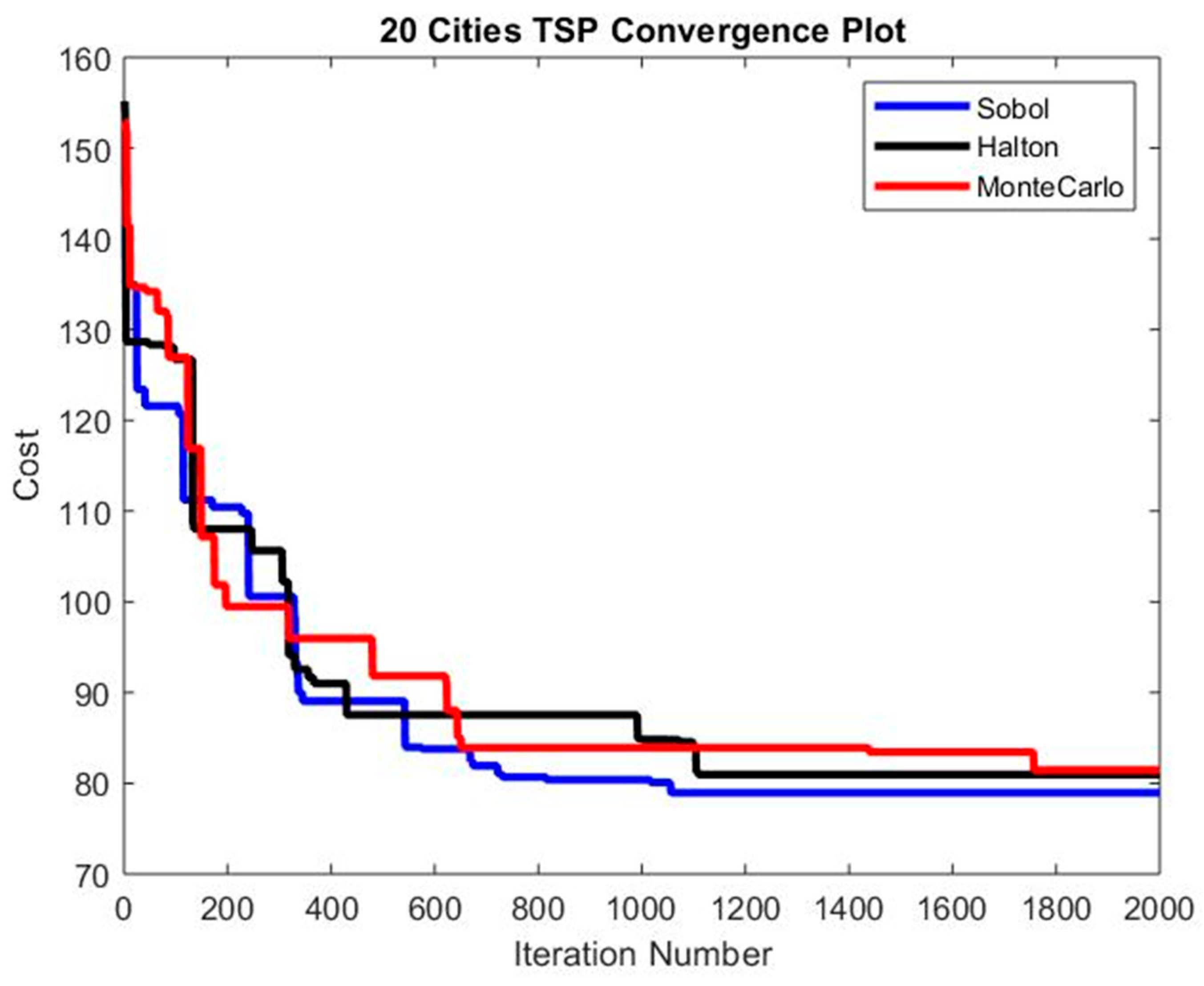
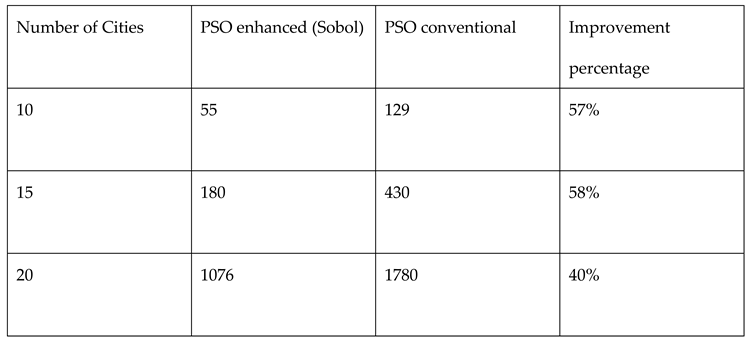
3.2. Traveling Salesman Problem Optimization Procedure
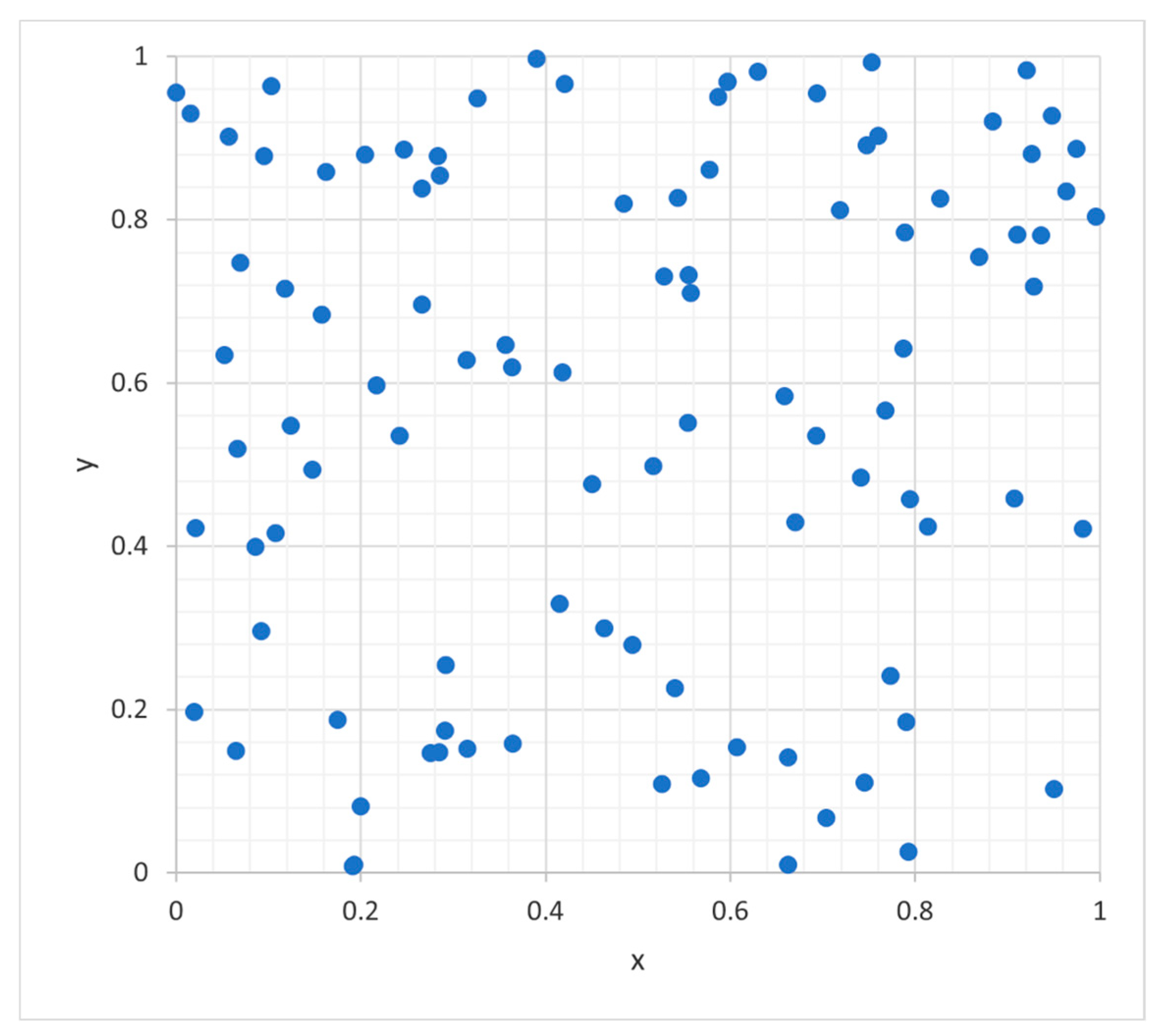
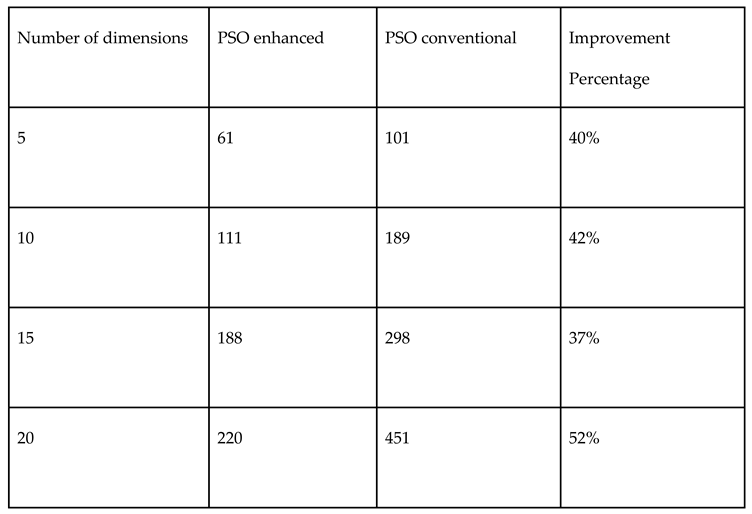
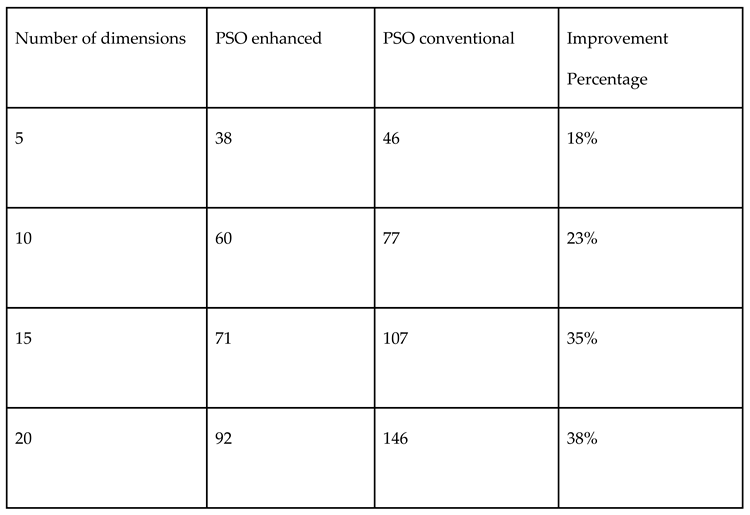
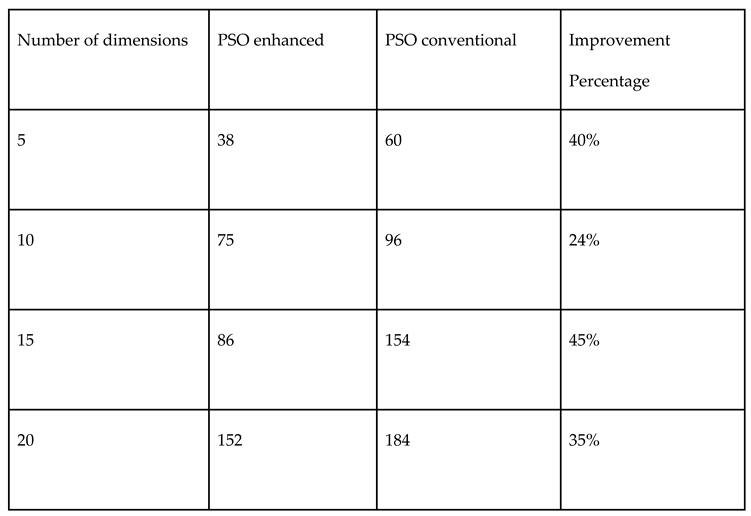
3.3. Sobol vs. Monte Carlo Random Numbers
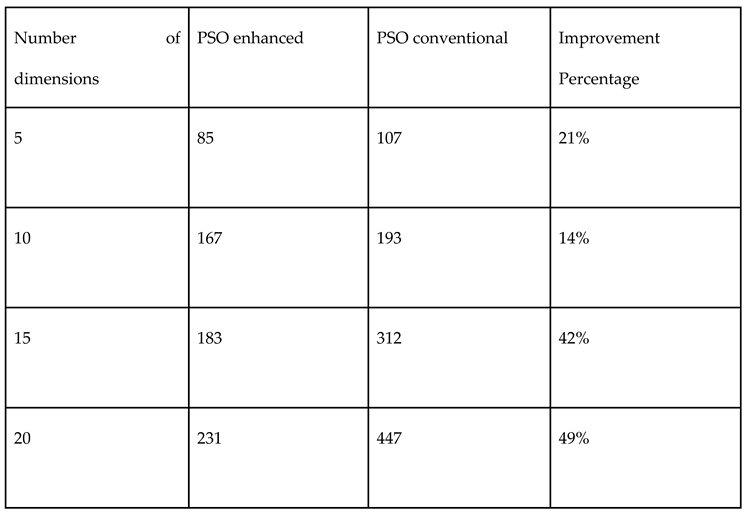
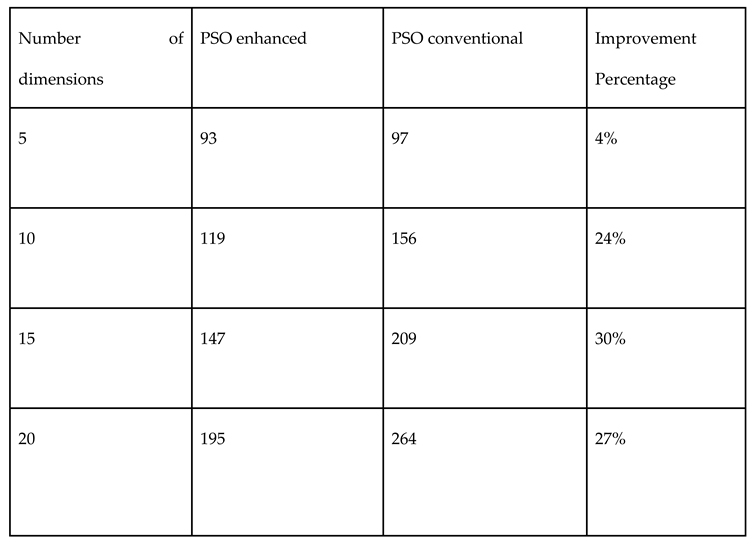
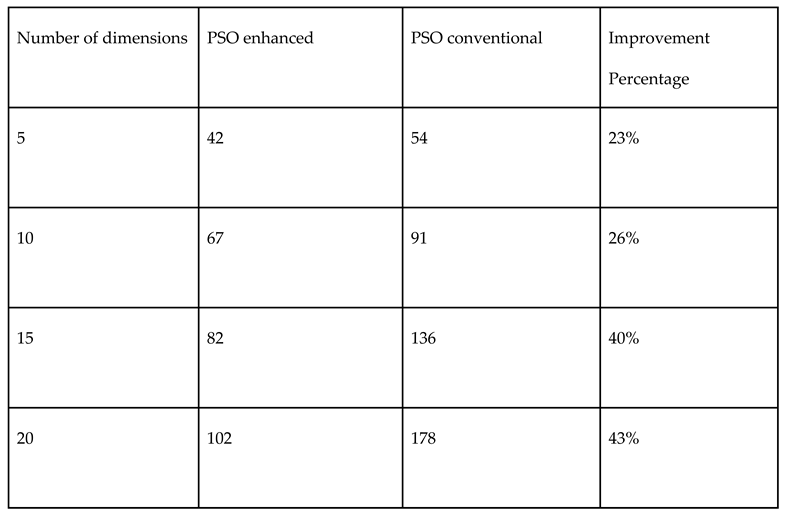
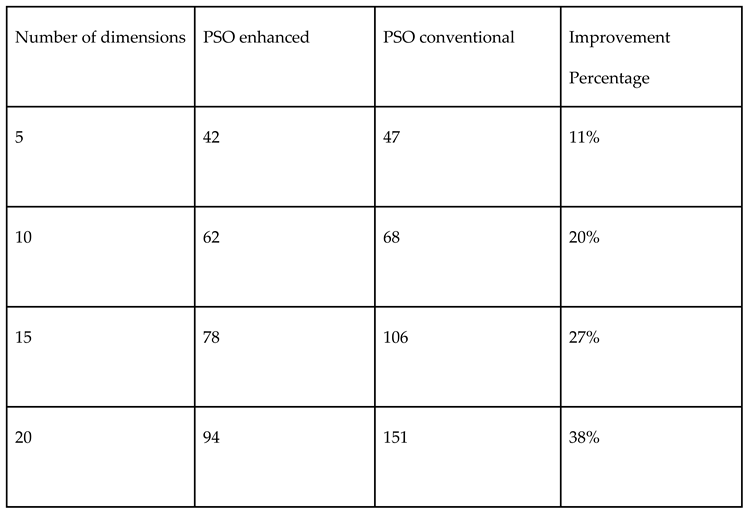
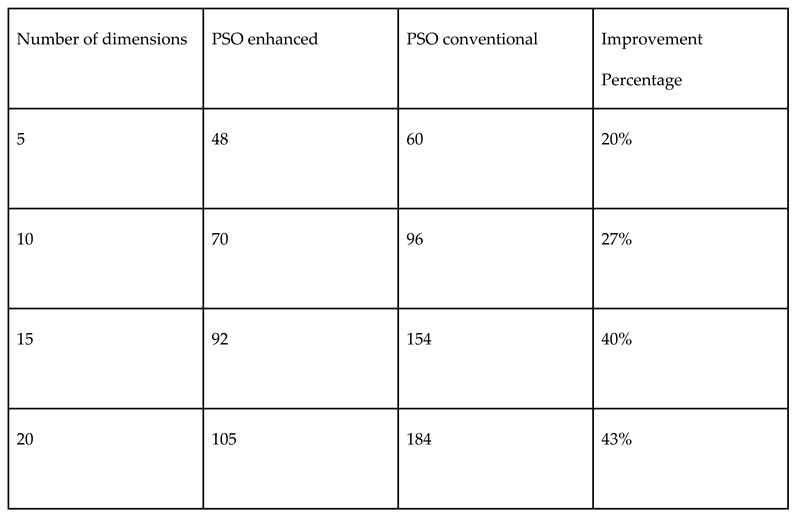
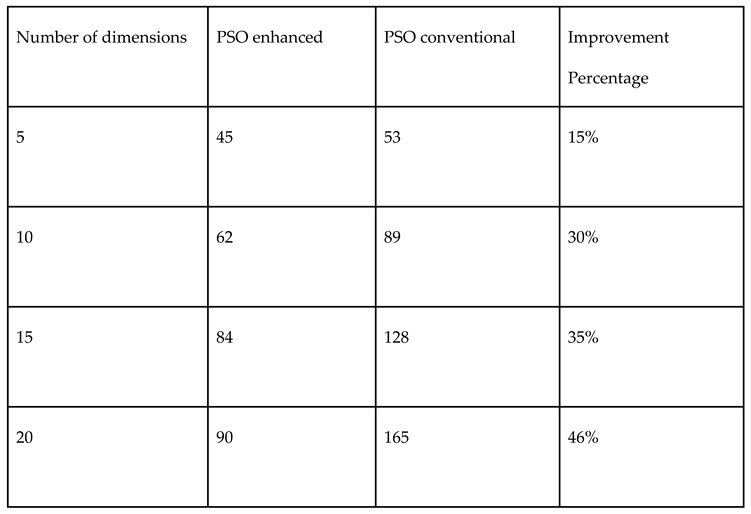
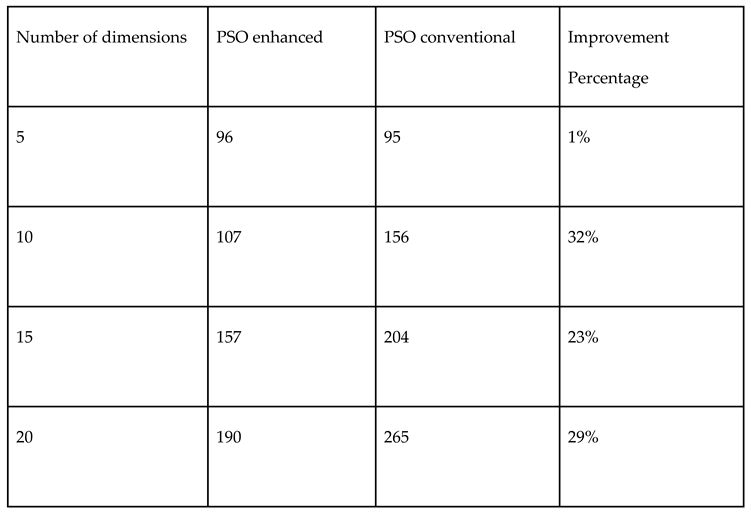
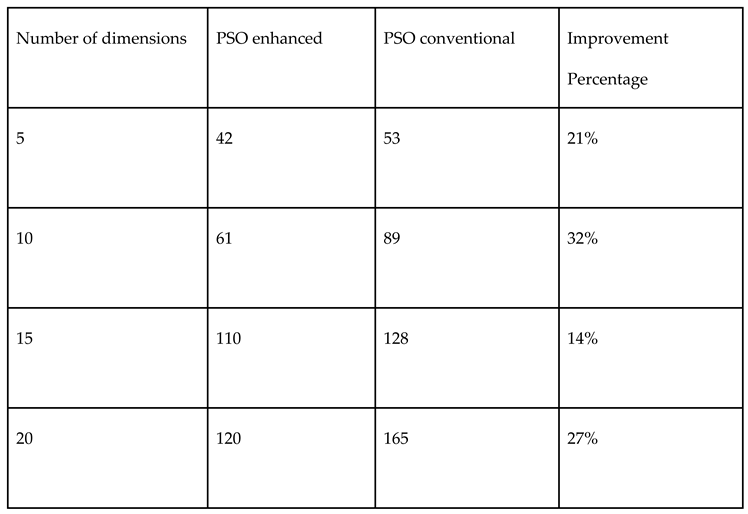
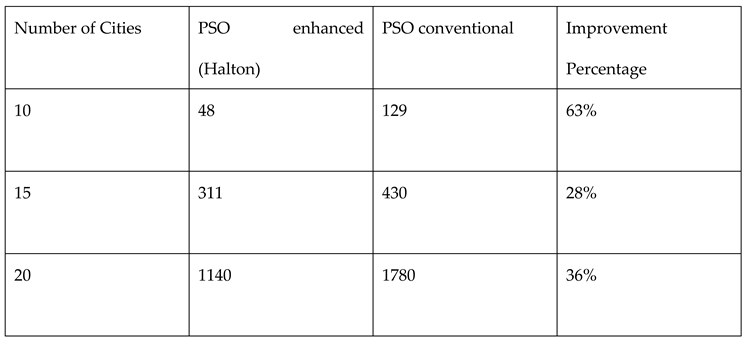
3.4. Halton vs. Monte Carlo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- T.M. Shami, A. A. T.M. Shami, A. A. El-Saleh, M. Alswaitti, Q. Al-Tashi, M. A. Summakieh and S. Mirjalili, “Particle Swarm Optimization: A Comprehensive Survey,” in IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 100131-10061, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Kennedy and R. Eberhart, "Particle swarm optimization," Proceedings of ICNN'95 - International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 1995, pp. 1942-1948 vol.4. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Bansal, P. K. J. C. Bansal, P. K. Singh, M. Saraswat, A. Verma, S. S. Jadon and A. Abraham, "Inertia Weight strategies in Particle Swarm Optimization," 2011 Third World Congress on Nature and Biologically Inspired Computing, Salamanca, Spain, 2011, pp. 633-640. [CrossRef]
- Ning Li, Yuan-Qing Qin, De-Bao Sun and Tong Zou, "Particle swarm optimization with mutation operator," Proceedings of 2004 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (IEEE Cat. No.04EX826), Shanghai, China, 2004, pp. 2251-2256 vol.4. [CrossRef]
- Z. Zhou, F. Z. Zhou, F. Li, J. H. Abawajy and C. Gao, "Improved PSO Algorithm Integrated With Opposition-Based Learning and Tentative Perception in Networked Data Centers," in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 55872-55880, 2020. [CrossRef]
- B. Mandal, P. K. B. Mandal, P. K. Roy and S. Mandal, "Hybridization of Particle Swarm Optimization with Biogeography-Based Optimization for Reactive Power and Voltage Control," 2014 Fourth International Conference of Emerging Applications of Information Technology, Kolkata, India, 2014, pp. 34-39. [CrossRef]
- Y. Cai and S. X. Yang, "An improved PSO-based approach with dynamic parameter tuning for cooperative target searching of multi-robots," 2014 World Automation Congress (WAC), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2014, pp. 616-621. [CrossRef]
- Morokoff, William J., and Russel E. Caflisch. “Quasi-Random Sequences and Their Discrepancies.”. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 1994, 15, 1251–1279. [CrossRef]
- Niederreiter, Harald. 1992. Random Number Generation and Quasi-Monte Carlo Methods. CBMS-NSF Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics 63. Philadelphia, Pa: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics.
- Sobol, I.M. Uniformly distributed sequences with an additional uniform property. USSR Journal of Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Physics (English translation) 1976, 16, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwekar UM, Gebreslassie BH (2016) Efficient Ant Colony Optimization (EACO) Algorithm for Deterministic Optimization. Int J Swarm Intel Evol Comput 5: 131. [CrossRef]
- Sarman, K. Hadia, Arjun H. Joshi, Chaitalee K. Patel, Yogesh P. Kosta, “Solving City Routing Issue with Particle Swarm Optimization”. International Journal of Computer Applications 2012, 47. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





