Submitted:
15 March 2024
Posted:
15 March 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Interference Model of EPICA Stack Components
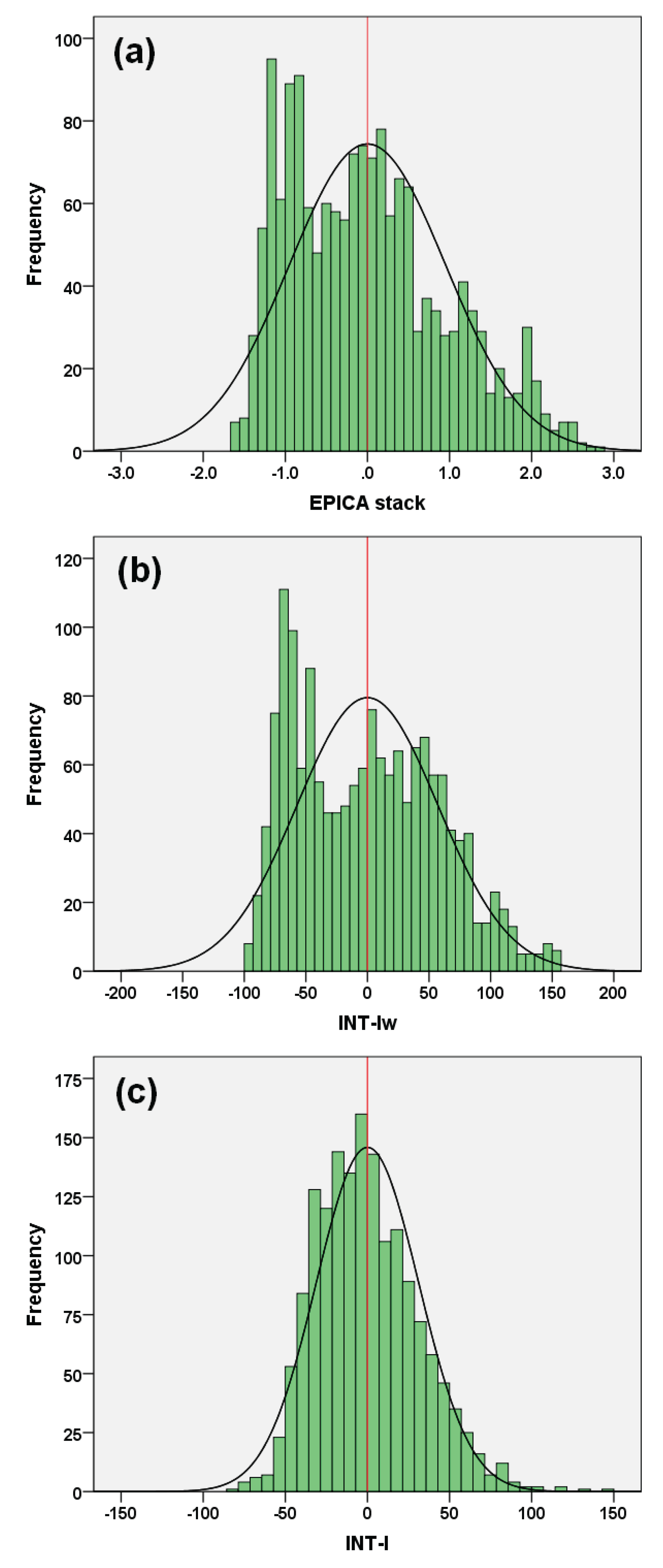
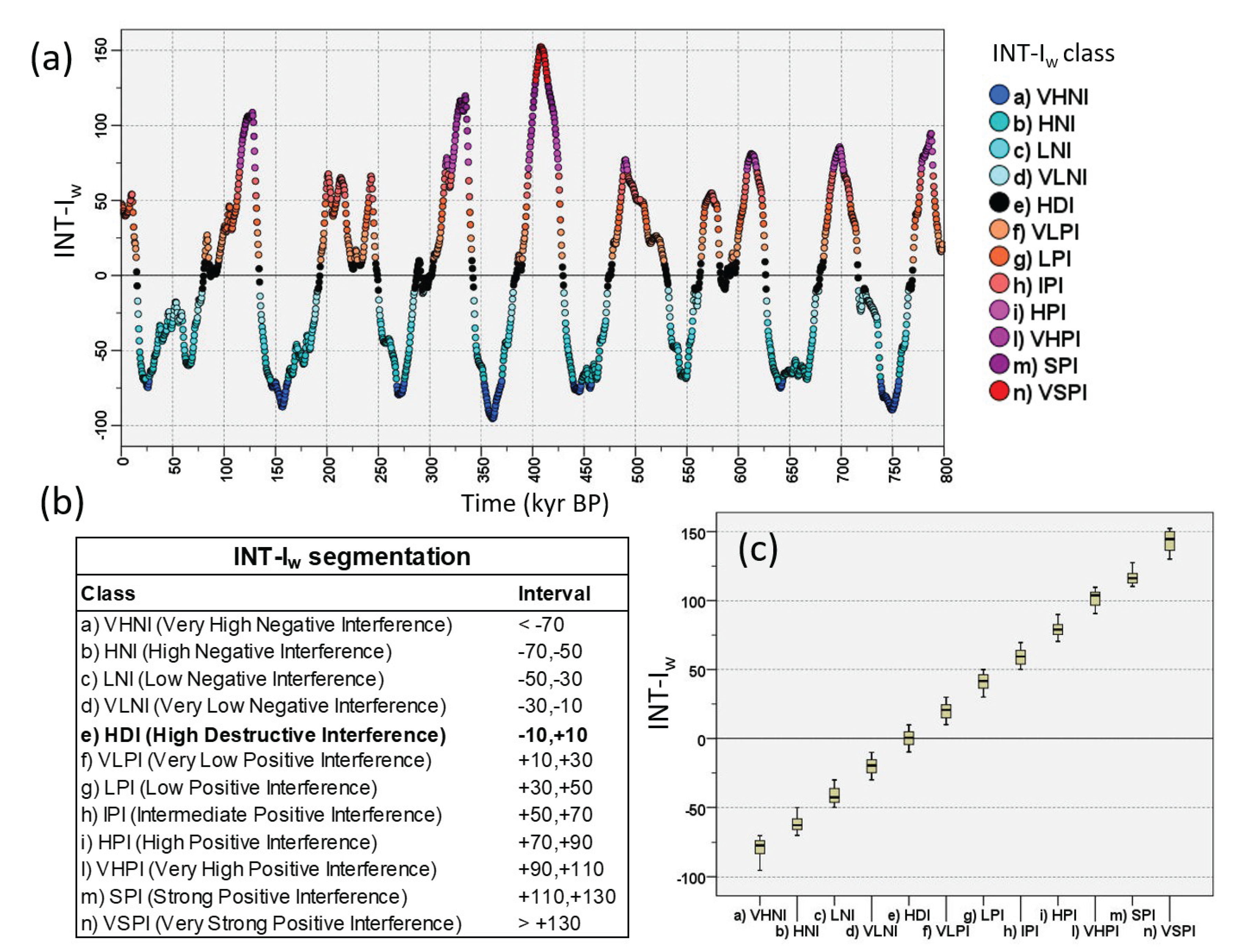
3.1.1. Interference Indices
- RMT: mid-term oscillation stack (4.4%);
- ROM: obliquity modulation cycle stack (4%);
- RSE: short eccentricity stack (51.6%);
- ROB: obliquity stack (19%);
- RPR: precession stack (8.4%);
- RHP: half-precession stack (3.8%);
- RS9.7: sun-9.7 kyr cycle stack (1.8%);
- RS6.0: sun-6.0 kyr cycle stack (2.6%);
- RUC3.7: ‘unclear’-3.7 kyr cycle stack (0.63%); and
- RS2.5: sun-2.5 kyr cycle stack (0.12%)
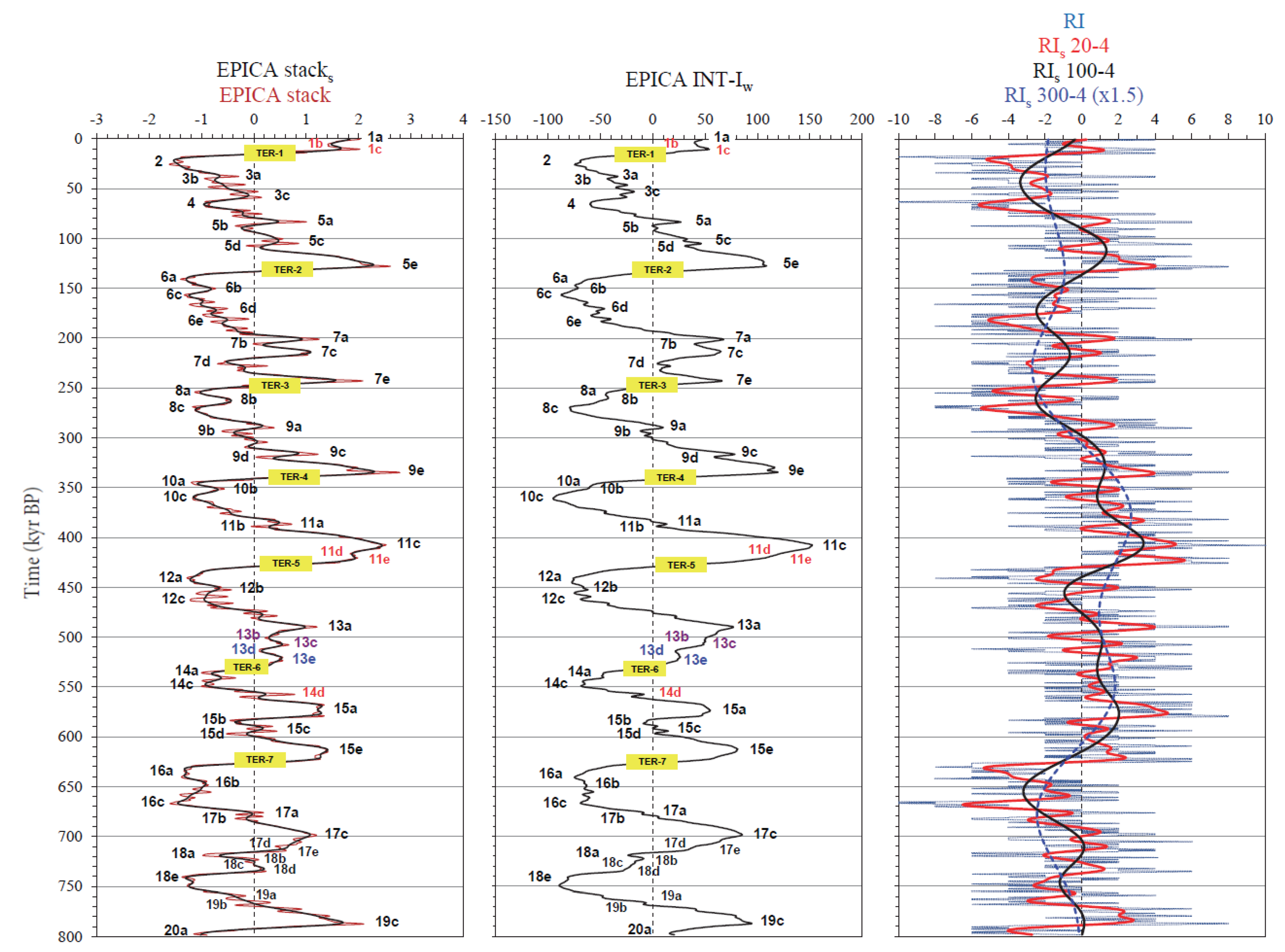
3.1.2. Polarity Alignment
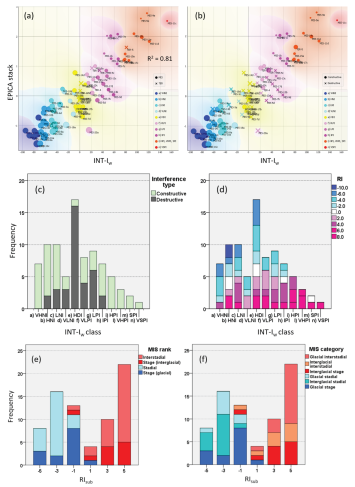
3.1.3. Constructive and Destructive Interference
3.1.4. Intensity Asymmetry
3.1.5. Time Asymmetry
3.2. Relationships among Orbital Forcings, EPICA Responses and Interference
4. Conclusions
- 1)
- The Antarctic stacked records during the last 800 kyr, which approximate global/NH atmospheric temperatures, are described by a variance-weighted interference model of independent thermal waves of different origins (midterm oscillation, orbitals, and suborbitals) that stochastically interfere at a given time according to their relative differences in frequency, intensity, and polarity.
- 2)
- Climate interference over a short-term timescale is a Gaussian stochastic process governed by chance. At the mid-/long-term scale, the stochastic interaction of the responses increasingly deviates from normality and exhibits a multi-modal distribution that reveals patterns of time alignments, suggesting a complex interaction among the components of the climate system.
- 3)
- Interglacial stages resulted from high to very strong (73%) and intermediate (27%) constructive interference of warming responses, and glacial stages derived by high/very high (64%) and low (36%) constructive interference of cooling responses, which are related to global δ18O depletion or enrichment, respectively.
- 4)
- MIS substages are the result of positive (interstadial) or negative (stadial) polarisation of millennial suborbital thermal waves.
- 5)
- Low-intensity MISs, including 90% of substages, fall in low-interference regions where dominant destructive interference minimises the thermal envelope.
- 6)
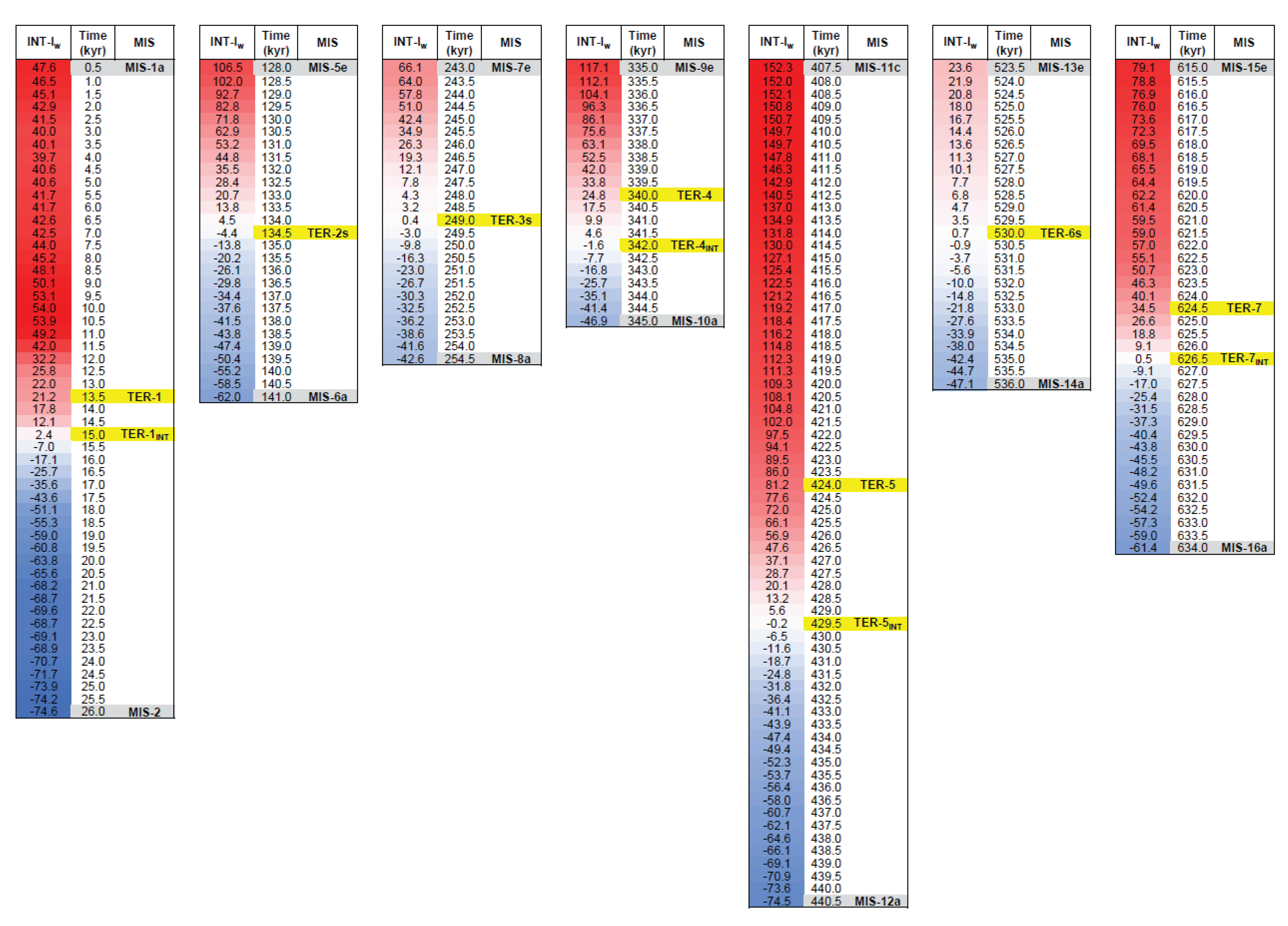
- The interference model allows the recalibration of the TER ages according to the structural notion of ‘cancellation interference’ of the thermal envelope. For TER-1/4/5/7 dated by the midpoint criterion, unexpected constructive interference leads significantly away from the neutrality region with a relevant positive bias, which is an artefact due to the asymmetry of glacial cycles. Therefore, terminations are most appropriately dated and described by the structural criterion of null interference which is associated with destructive patterns such as TER-2/3/6.
- 7)
- The intensity asymmetry of the EPICA stack record results from the interference process which, in turn, amplifies the bipolar envelope of the nonlinear thermal responses that interfere at a given time with a strong bias in the warming direction (interglacial, 539%), especially after the MBE (803%). This explains the key question of why the post-MBE interglacials appear warmer than the pre-MBE interglacials. However, even the post-MBE glacials appear slightly colder (89%) than the pre-MBE glacials (26%), albeit to a lesser magnitude.
- 8)
- The duration analysis of short eccentricity hemicycles exhibits an unexpected, intrinsic mean time asymmetry (prolonged cooling) in the nominal short eccentricity (5.8 kyr) and its EPICA response (8.6 kyr, 48% variation), as well as an interference-induced asymmetry (21.1 kyr) that amplifies the cooling duration of short eccentricity response by 145%. Thus, the overall effect of the increased temporal cooling resulting in the saw-tooth shape of glacial cycles (from 5.8 kyr to 21.1 kyr, i.e. 264%) is related to the joint action of phase-locked intermediate feedback mechanisms, and especially by the strong amplification of the physical interference process.
- 9)
- The nominal short eccentricity played a key role in pacing the feedback-amplified climate response and its central action in the interference process over the last 800 kyr.
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1 | The ‘mid-term’ component is the most recent portion of the Plio-Pleistocene long-term trend that cannot be documented in the EPICA record [19]. |
References
- Jouzel J. et al., 2007. Orbital and Millennial Antarctic Climate Variability over the Past 800,000 Years. Science Vol. 317, 10 August 2007, pp. 793-796. [CrossRef]
- Masson-Delmotte V., et al., 2010. EPICA Dome C record of glacial and interglacial intensities. Quat. Sci. Rev. 29 (2010) 113–128. [CrossRef]
- Lang N., Wolff E.W., 2011. Interglacial and glacial variability from the last 800 ka in marine, ice and terrestrial archives. Clim. Past, 7, 361–380, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Ellis R., Palmer M., 2016. Modulation of ice ages via precession and dust-albedo feedbacks. Geoscience Frontiers, v. 7 (2016), pp. 891-909. [CrossRef]
- Past interglacials working group of PAGES, 2016. Interglacials of the last 800,000 years. Rev. Geophys. 54:162–219. [CrossRef]
- Rapp D., 2019. Ice Ages and Interglacials. Measurements, Interpretation, and Models. Springer, Third Edition, pp. 362, ISBN 978-3-030-10465-8. [CrossRef]
- IPCC, 2013. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Stocker T.F., D. Qin, Plattner G.-K., Tignor M., Allen S.K., Boschung J., Nauels A., Xia Y., Bex V., Midgley P.M. (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 1535 pp.
- Viaggi P., 2018. δ18O and SST signal decomposition and dynamic of the Pliocene-Pleistocene climate system: new insights on orbital nonlinear behavior vs. long-term trend. Progress in Earth and Planetary Science, 2018, 5:81, 7 December 2018. 7 December. [CrossRef]
- Viaggi P., 2023. Global Evidence of Obliquity Damping in Climate Proxies and Sea-Level Record during the Last 1.2 Ma: A Missing Link for the Mid-Pleistocene Transition. Geosciences 2023, 13(12), 354. [CrossRef]
- Clark P.U., Archer D., Pollard D., Blum J.D., Rial J.A., Brovkin V., Mix A.C., Pisias N.G., Roy M., 2006. The middle Pleistocene transition: characteristics, mechanisms, and implications for long-term changes in atmospheric pCO2. Quat. Sci. Rev. [CrossRef]
- Lisiecki L.E., Raymo M.E., 2007. Plio–Pleistocene climate evolution; trends and transitions in glacial cycle dynamics. Quat. Sci. Rev. 26(2007):56–69. [CrossRef]
- Zachos J.C., Pagani M., Sloan L., Thomas E., Billups K., 2001. Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present. Science, Vol. 292, 27 April 2001. 27 April.
- Zachos J.C., Dickens G.R., Zeebe R.E., 2008. An early Cenozoic perspective on greenhouse warming and carbon-cycle dynamics. Nature, Vol. 451,17 January 2008. 17 January. [CrossRef]
- McClymont E.L., Sosdian S.M., Rosell-Melé A., Rosenthal Y., 2013. Pleistocene sea-surface temperature evolution: Early cooling, delayed glacial intensification, and implications for the mid-Pleistocene climate transition. Earth-Science Reviews, Volume 123, 173-193. [CrossRef]
- Kender S., Ravelo A.C., Worne S., Swann G.E.A., Leng M.J., Asahi H., Becker J., Detlef H., Aiello I.W., Andreasen D., Hall I.R., 2018. Closure of the Bering Strait caused Mid-Pleistocene Transition cooling. Nature Commun. (2018) 9:5386. 9. [CrossRef]
- Shoenfelt E.M., Winckler G., Lamy F., Anderson R.F., Bostick B.C., 2018. Highly bioavailable dust-borne iron delivered to the Southern Ocean during glacial periods. PNAS, 1-6.
- Farmer J.R., Hönisch B., Haynes L.L., Kroon D., Jung S., Ford H.L., Raymo M.E., Jaume-Seguí M., Bell D.B., Goldstein S.L., Pena L.D., Yehudai M., Kim J., 2019. Deep Atlantic Ocean carbon storage and the rise of 100,000-year glacial cycles. Nature Geosci. [CrossRef]
- Hasenfratz A.P., Jaccard S.L., Martínez-García A., Sigman D.M., Hodell D.A., Vance D., Bernasconi S.M., Kleiven H.F., Haumann F.A., Haug G.H., 2019. The residence time of Southern Ocean surface waters and the 100,000-year ice age cycle. Sci. 363, 1080-1084 (2019), 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Viaggi P., 2021a. Quantitative impact of astronomical and sun-related cycles on the Pleistocene climate system from Antarctica records. Quat. Sci. Adv., Volume 4, October 2021. 20 October. [CrossRef]
- Hönisch B., Hemming N.G., Archer D., Siddall M., McManus J.F., 2009. Atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration across the mid-Pleistocene transition. Science 324:1551. [CrossRef]
- Seki O., Foster G.L., Schmidt D.N., Mackensen A., Kawamura K., Pancost R.D., 2010. Alkenone and boron-based Pliocene pCO2 records. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 292 (2010), 201–211. [CrossRef]
- Bartoli G., Hönisch B., Zeebe R. E., 2011. Atmospheric CO2 decline during the Pliocene intensification of Northern Hemisphere glaciations, Paleoceanography, 26, PA4213. [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Boti M.A., Foster G.L., Chalk T.B., Rohling E.J., Sexton P.F., Lunt D.J., Pancost R.D., Badger M.P.S., Schmidt D.N., 2015. Plio-Pleistocene climate sensitivity evaluated using high-resolution CO2 records. Nature 518. [CrossRef]
- Hays J.D., Imbrie J., Shacklton N.J., 1976. Variation in the Earth’s orbit: pacemaker of the ice ages, Science, 194, 1121–1132, 1976.
- Imbrie J., Boyle E.A., Clemens S.C., Duffy A., Howard W.R., Kukla G., Kutzbach J., Martinson D.G., Mclntyre A., Mix A.C., Molfino B., Morley J.J., Peterson L.C., Pisias N.G., Prell W.L., Raymo M.E., Shackleton N.J., Toggweiler J.R., 1992. On the Structure and Origin of Major Glaciation Cycles 1. Linear Responses to Milankovitch Forcing. Paleoceanography. Vol. 7, No. 6, pp 701-738, December 1992. 19 December; 6.
- Imbrie J., Berger A., Boyle E.A., Clemens S.C., Duffy A., Howard W.R., Kukla G., Kutzbach J., Martinson D.G., Mcintyre A., Mix A.C., Molfino B., Morley J.J., Peterson L.C., Pisias N.G., Prell W.L., Raymo M.E., Shackleton N.J., Toggweile J.R., 1993. On the Structure and Origin of Major Glaciation Cycles 2. The 100,000-Year Cycle. Paleoceanography, Vol. 8, No. 6, pp. 699-735, December 1993. 19 December; 6.
- Head M.J., Gibbard P.L., 2005. Early–Middle Pleistocene transitions. An overview and recommendation for the defining boundary. From: Head M.J., Gibbard P.L. (eds). Early–middle Pleistocene transitions: the land–ocean evidence. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 247, 1–18. 0305–8719/05/$15© The Geological Society of London 2005.
- Head M.J., Pillans B., Farquhar S.A., 2008. The Early–Middle Pleistocene Transition: characterization and proposed guide for the defining boundary. Episodes, Vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 255-259, June 2008. 20 June.
- Loutre M.F., 2003. Clues from MIS 11 to predict the future climate. A modelling point of view. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 212 (2003) 213-224. [CrossRef]
- Berger A., Loutre M.F., 2010. Modeling the 100-kyr glacial–interglacial cycles. Global and Planetary Change 72 (2010) 275–281. [CrossRef]
- Berger A., Yin Q.Z., Herold N., 2012. MIS-11 and MIS-19, analogs of our Holocene interglacial. In: 3rd Int. Conf. on Earth Syst. Model., Hamburg. https://meetingorganizer.copernicus.org/3ICESM/3ICESM-11.pdf.
- Berger A., Yin Q., 2012. Modeling the lnterglacials of the last 1 Million Years. In: Berger et al. (eds.), Climate Change: Inferences From Paleoclimate and Regional Aspects. Springer-Verlag 2012.
- Yin Q.Z., Berger A., 2012. Individual contribution of insolation and CO2 to the interglacial climates of the past 800,000 years. Clim. Dyn. (2012) 38:709–724. [CrossRef]
- Verbitsky M.Y., Crucifix M., Volobuev D.M., 2018. A theory of Pleistocene glacial rhythmicity. Earth Syst. Dynam., 9, 1025–1043, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Laskar J., Robutel P., Joutel F., Gastineau M., Correia A.C.M., Levrard B., 2004. A long term numerical solution for the insolation quantities of the Earth. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 428, May 23 2004, manuscript no. La2004. 23 May.
- Laskar J., Fienga A., Gastineau M., Manche H., 2011. La2010: a new orbital solution for the long-term motion of the Earth. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 532, A89 (2011). [CrossRef]
- Broecker W.S., van Donk J., 1970. Insolation changes, ice volumes, and O18 record in deep-sea cores, Rev. Geophys. Space Phys., 8(1), 169–198. [CrossRef]
- Viaggi P., 2021b. Evidence of Climate Mitigation Feedbacks by Global Forest Cover Expansion during the Pliocene. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Res., 2021, 28(5), 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Berger A., Loutre M.F., 1997. Long-term variations in insolation and their effects on climate, the LLN experiments. Surveys in Geophysics, 18: 147–161, 1997.
- Shackleton N.J., 2000. The 100,000-Year Ice-Age Cycle Identified and Found to Lag Temperature, Carbon Dioxide, and Orbital Eccentricity. Science, Vol. 289, 15 September 2000. 15 September.
- Ruddiman W.F., 2003. Orbital insolation, ice volume, and greenhouse gases. Quat. Sci. Rev. 22, 1597–1629.
- Archer D., Martin P., Buffett B., Brovkin V., Rahmstorf S. & Ganopolski A., 2004. The importance of ocean temperature to global biogeochemistry. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 222 (2004), 333–348. [CrossRef]
- Rial J.A., Pielke R.A. Sr, Beniston M., Claussen M., Canadell J., Cox P., Held H., deNoblet-Ducoudré N., Prinn R., Reynolds J.F., Salas J.D., 2004. Nonlinearities, feedbacks and critical thresholds within the Earth’s climate system. Clim. Chang. 65(1–2):11–38, 2004.
- Brovkin V., Ganopolski A., Archer D., Rahmstorf S., 2007. Lowering of glacial atmospheric CO2 in response to changes in oceanic circulation and marine biogeochemistry. Paleoceanography, 22, PA4202. [CrossRef]
- Hansen J., Sato M., Kharecha P., Russell G., Lea D.W., Siddall M., 2007. Climate change and trace gases. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A (2007) 365, 1925–1954. [CrossRef]
- Bintanja R., van de Wal R.S.W., 2008. North American ice-sheet dynamics and the onset of 100,000-year glacial cycles. Nature, Vol 454, 14 August 2008, 869- 872. 14 August. [CrossRef]
- Herbert T.D., Peterson L.C., Lawrence K.T., Liu Z., 2010. Tropical ocean temperatures over the past 3.5 million years. Sci. 328:1530–1534. [CrossRef]
- Köhler P., Bintanja R., Fischer H., Joos F., Knutti R., Lohmann G., Masson-Delmotte V., 2010. What caused Earth’s temperature variations during the last 800,000 years? Data-based evidence on radiative forcing and constraints on climate sensitivity. Quat. Sci. Reviews 29 (2010) 129–145. [CrossRef]
- Lisiecki L.E., 2010. Links between eccentricity forcing and the 100,000-year glacial cycle. Nature Geoscience, vol 3, may 2010, 349-352. [CrossRef]
- Hansen J., Sato M., Kharecha P., von Schuckmann K., 2011. Earth’s energy imbalance and implications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 11:13421–13449. [CrossRef]
- Russon T., Elliot M., Sadekov A., Cabioch G., Corrège T., De Deckker P., 2011. The mid‐Pleistocene transition in the subtropical southwest Pacific, Paleoceanography, 26, PA1211. [CrossRef]
- Caccamo M.T., Magazù S., 2023. Exponential feedback effects in a parametric resonance climate model. Scientific Reports (2023), 13:22984. [CrossRef]
- Luthi D., Le Floch M., Bereiter B., Blunier T., Barnola J.M., Siegenthaler U., Raynaud D., Jouzel J., Fischer H., Kawamura K., Stocker T.F., 2008. High-resolution carbon dioxide concentration record 650,000–800,000 years before present. Nature, Vol 453, 15 May 2008. 15 May. [CrossRef]
- Loulergue L., Schilt A., Spahni R., Masson-Delmotte V., Blunier T., Lemieux B., Barnola J.M., Raynaud D., Stocker T.F., Chappellaz J., 2008. Orbital and millennial-scale features of atmospheric CH4 over the past 800,000 years. Nature, Vol 453, 15 May 2008. [CrossRef]
- Bereiter B., Eggleston S., Schmitt J., Nehrbass-Ahles C., Stocker TF., Fischer H., Kipfstuhl S., Chappellaz J., 2015. Revision of the EPICA Dome C CO2 record from 800 to 600 kyr before present. Geophys. Res. Lett., 42, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Skinner L.C., Shackleton N.J., 2005. An Atlantic lead over Pacific deep-water change across Termination I: Implications for the application of the marine isotope stage stratigraphy, Quat. Sci. Rev., 24, 571–580. [CrossRef]
- Lisiecki L.E., Raymo M.E., 2005. A Pliocene-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records. Paleoceanogr. 20:PA1003. [CrossRef]
- Bazin L., Landais A., Lemieux-Dudon B., Kele H.T.M., Veres D., Parrenin F., Martinerie P., Ritz C., Capron E., Lipenkov V., et al. An optimized multi-proxy, multi-site Antarctic ice and gas orbital chronology (AICC2012): 120–800 ka. Clim. Past 2013, 9, 1715–1731. [CrossRef]
- Bouchet, M., Landais, A., Grisart, A., Parrenin, F., Prié, F., Jacob, R., Fourré, E., Capron, E., Raynaud, D., Lipenkov, V. Y., Loutre, M.-F., Extier, T., Svensson, A., Legrain, E., Martinerie, P., Leuenberger, M., Jiang, W., Ritterbusch, F., Lu, Z.-T., and Yang, G.-M. The Antarctic Ice Core Chronology 2023 (AICC2023) chronological framework and associated timescale for the European Project for Ice Coring in Antarctica (EPICA) Dome C ice core, Clim. Past, 19, 2257–2286. [CrossRef]
- Waelbroeck C., Levi C., Duplessy J.-C., Labeyrie L., Michel E., Cortijo E., Bassinot F., Guichard F., 2006. Distant origin of circulation changes in the Indian Ocean during the last deglaciation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 243, 244–251.
- Lisiecki L.E., Raymo M.E., 2009. Diachronous benthic δ18O responses during late Pleistocene terminations, Paleoceanography, 24, PA3210. [CrossRef]
- Masson-Delmotte V., et al., 2006. Past and future polar amplification of climate change: climate model intercomparisons and ice-core constraints. Climate Dynamics (2006) 26: 513–529. [CrossRef]
- Railsback L.B., Gibbard P.L., Head M.J., Voarintsoa N.R.G., Toucanne S., 2015. An optimized scheme of lettered marine isotope substages for the last 1.0 million years, and the climatostratigraphic nature of isotope stages and substages. Quat. Sci. Rev. 111 (2015) 94-106. [CrossRef]
- American Commission on Stratigraphic Nomenclature, 1961. Code of stratigraphic nomenclature. Bull. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol., 5, 645–660.
- Shackleton N.J., Opdyke N.D., 1973. Oxygen isotope and palaeomagnetic stratigraphy of Equatorial Pacific core V28-238: Oxygen isotope temperatures and ice volumes on a 105 year and 106 year scale, Quat. Res., 3(1), 39–55. [CrossRef]
- Tzedakis P.C., Raynaud D., McManus J. F., Berger A., Brovkin V., Kiefer T., 2009. Interglacial diversity, Nat. Geosci., 2(11), 751–755. [CrossRef]
- Cohen K., Gibbard P. (2022). Global chronostratigraphical correlation table for the last 2.7 million years v.2019 (Poster version), Mendeley Data, V5. [CrossRef]
- Konijnendijk T.Y.M., Ziegler M., Lourens L.J., 2015. On the timing and forcing mechanisms of late Pleistocene glacial terminations: Insights from a new high- resolution benthic stable oxygen isotope record of the eastern Mediterranean. Quat. Sci. Rev., 129 (2015), 308-320. [CrossRef]
- Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopaedia, 2023. "Interference". Encyclopedia Britannica, Accessed 10 June 2023. https://www.britannica.com/science/interference-physics. 10 June.
- Tziperman E., Raymo M.E., Huybers P.J., Wunsch C., 2006. Consequences of pacing the Pleistocene 100 kyr ice ages by nonlinear phase locking to Milankovitch forcing. Paleoceanography, Vol. 21, (PA4206): 1-11. Paleoceanography. [CrossRef]
- Benzi R., Parisi G., Sutera A., Vulpiani A., 1982 Stochastic resonance in climatic change. Tellus 34, 10–16. [CrossRef]
- Wunsch C., 2004. Quantitative estimate of the Milankovitch-forced contribution to observed Quaternary climate change. Quaternary Science Reviews, 23, (2004), pp. 1001–1012. [CrossRef]
- Berger A., Mélice J. L., Loutre M. F., 2005. On the origin of the 100-kyr cycles in the astronomical forcing, Paleoceanography, 20, PA4019. [CrossRef]
- Rial J.A., 1999. Pacemaking the Ice Ages by frequency modulation of Earth's orbital eccentricity. Science 285, 564–568.
- Liu Z., Cleaveland L.C., Herbert T.D., 2008. Early onset and origin of 100-kyr cycles in Pleistocene tropical SST records. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 265 (2008), 703–715. [CrossRef]
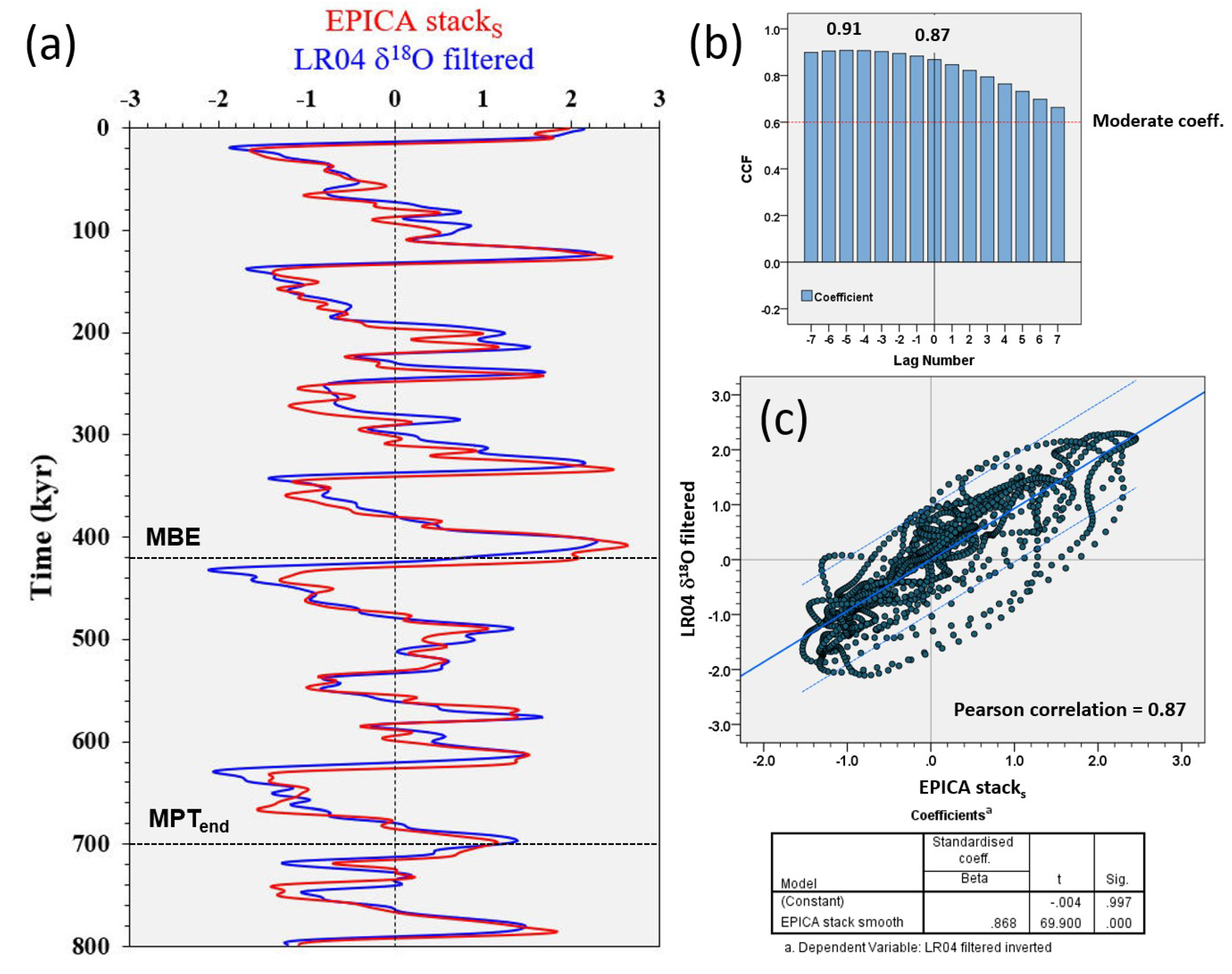
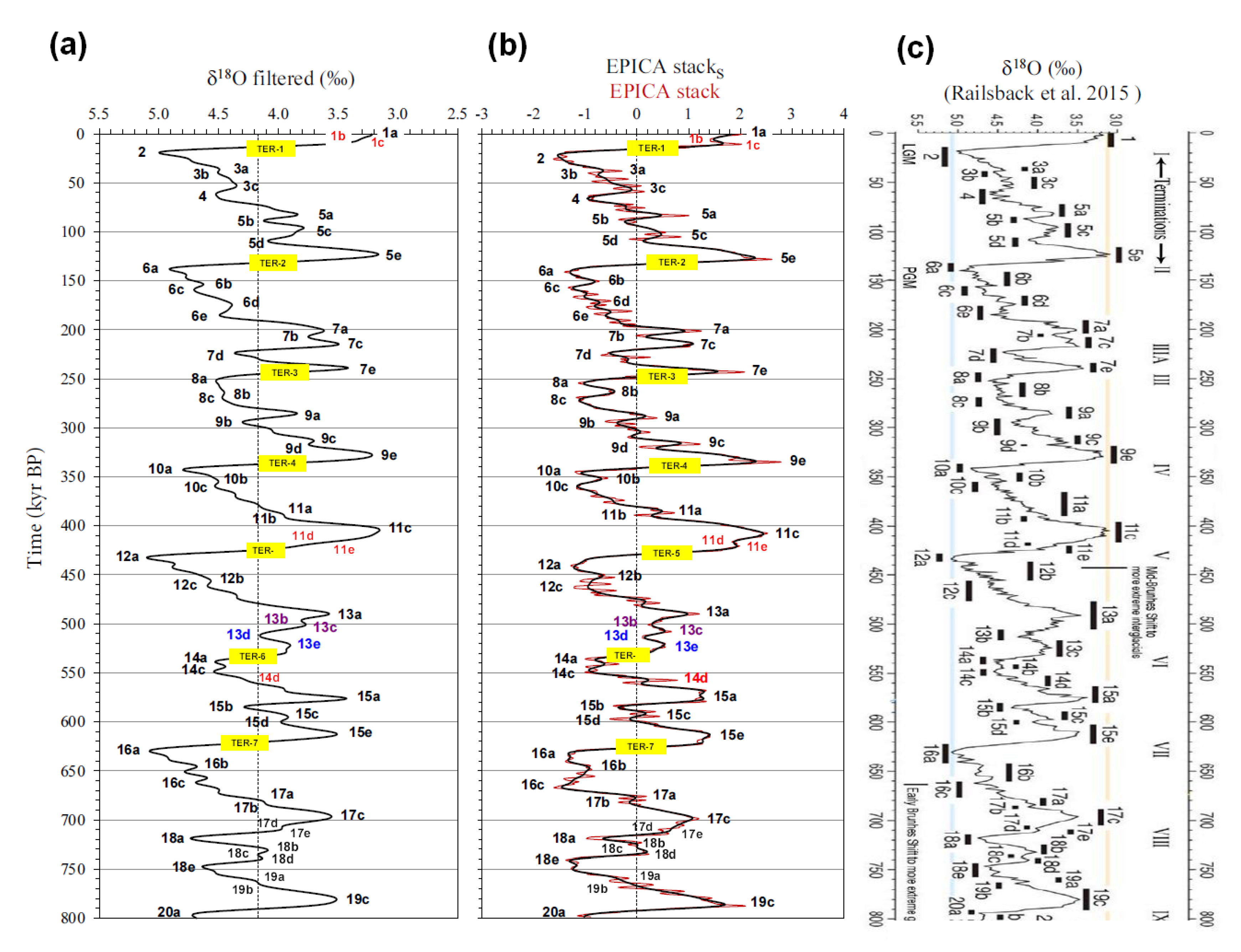
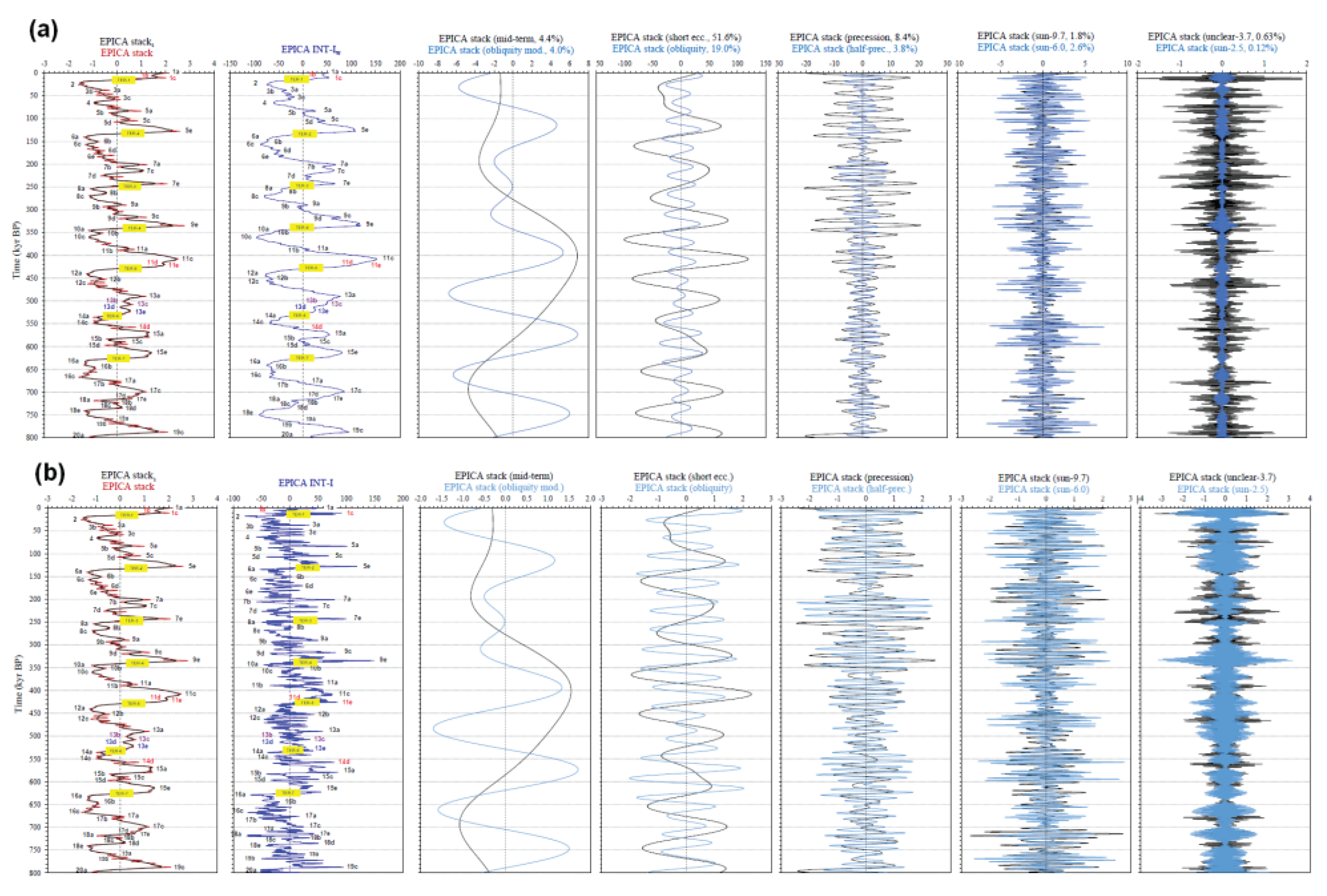
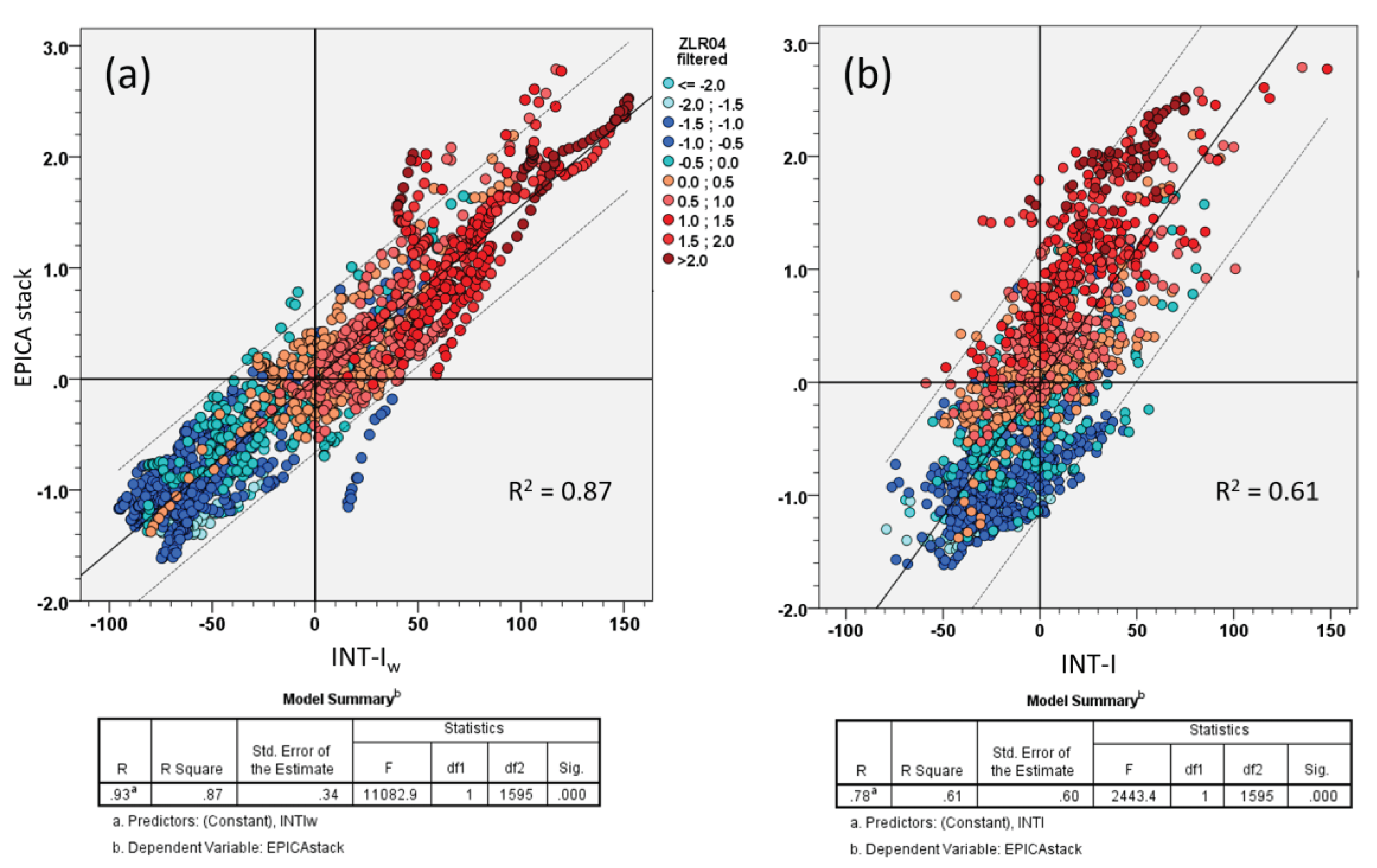
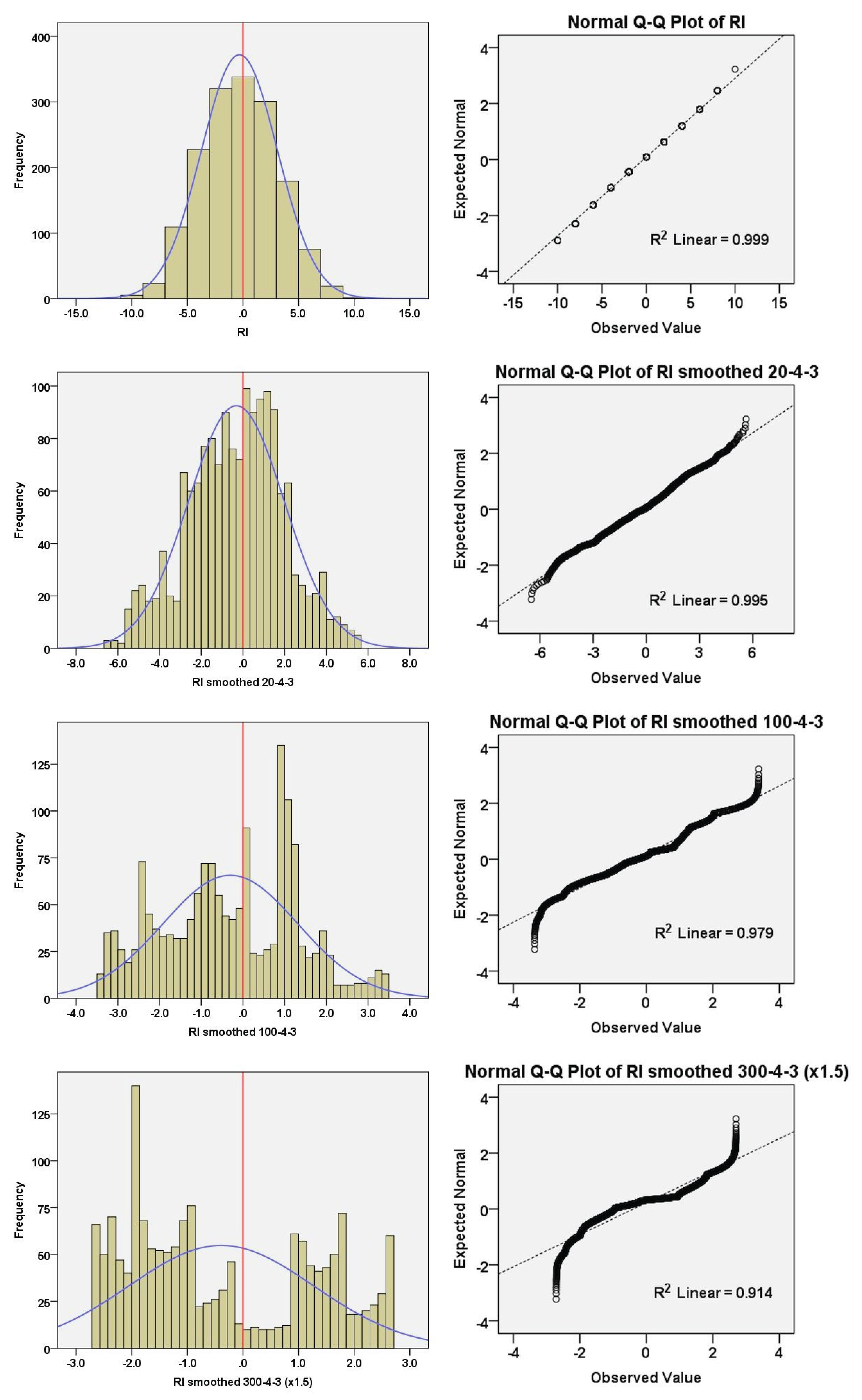
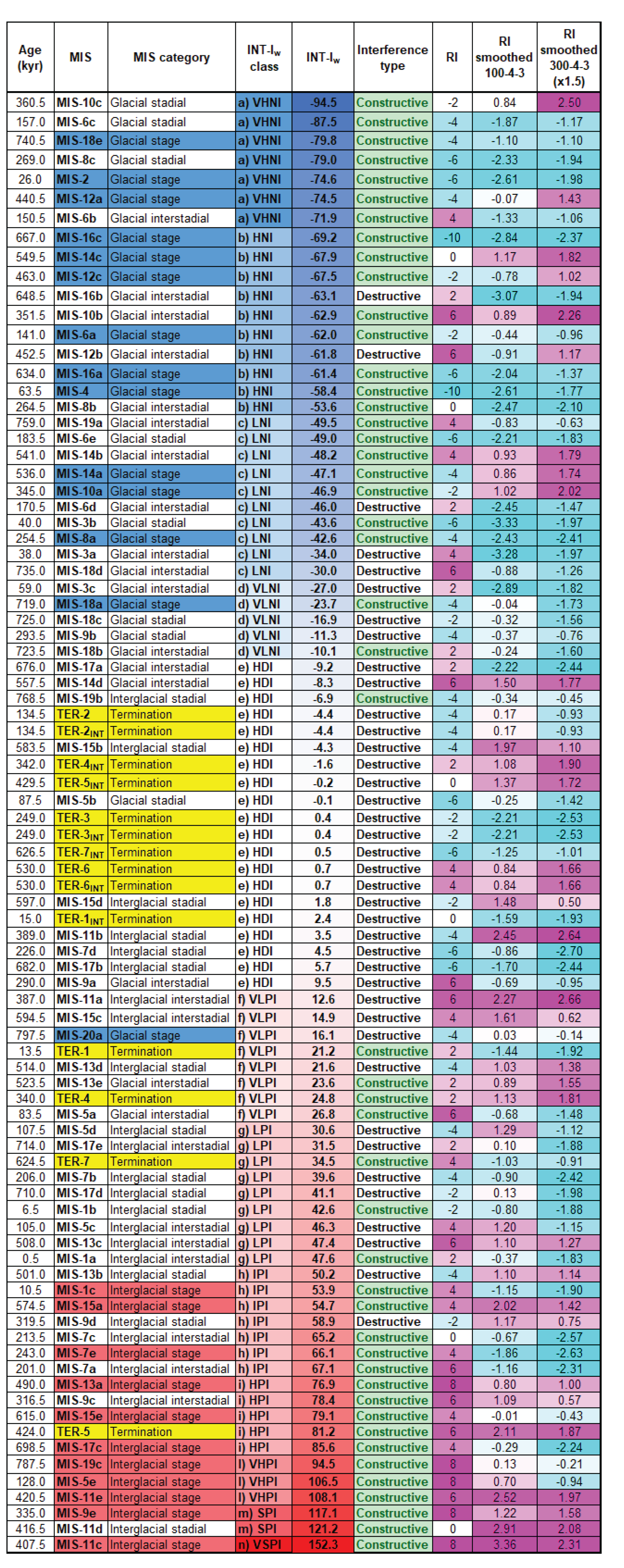
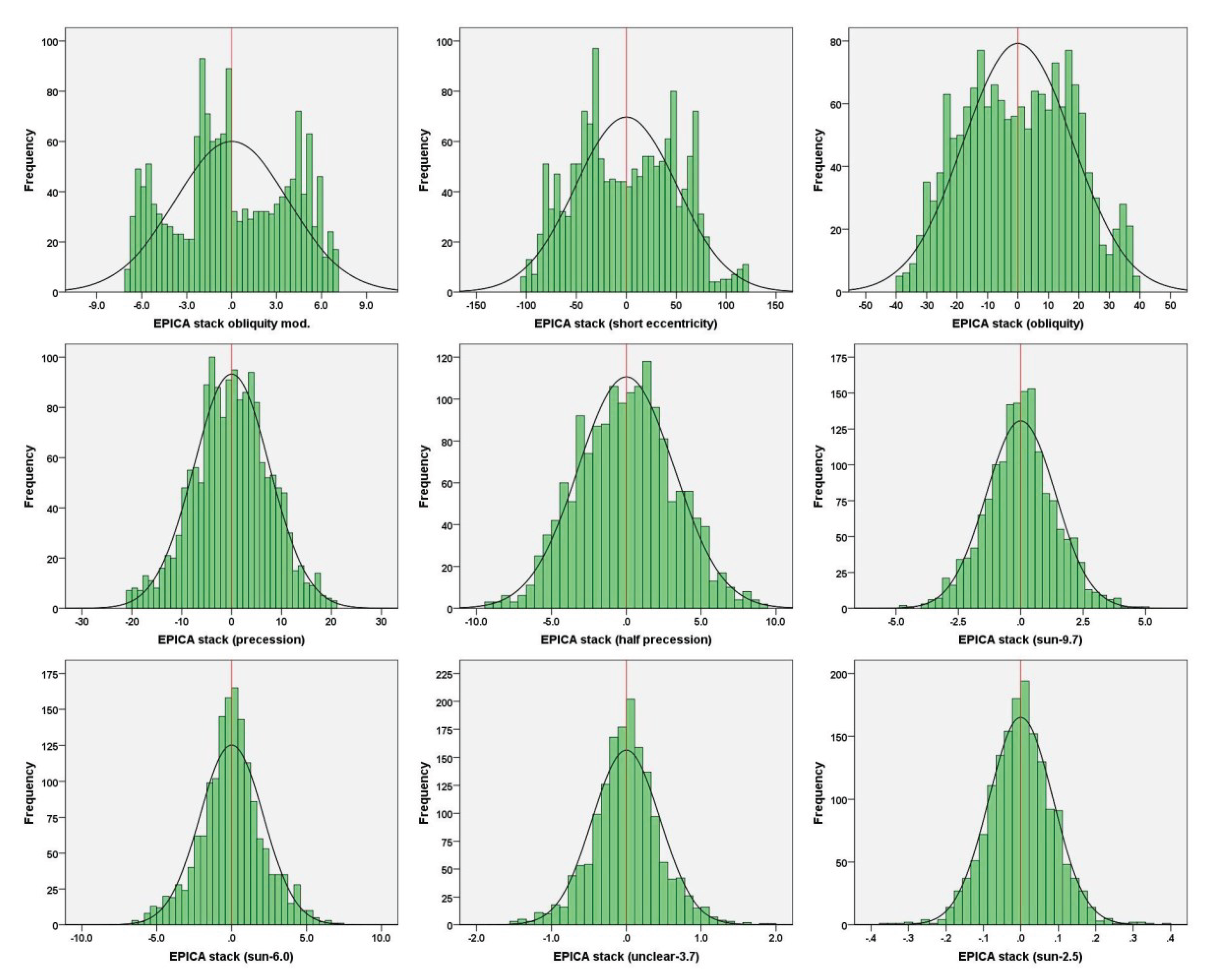
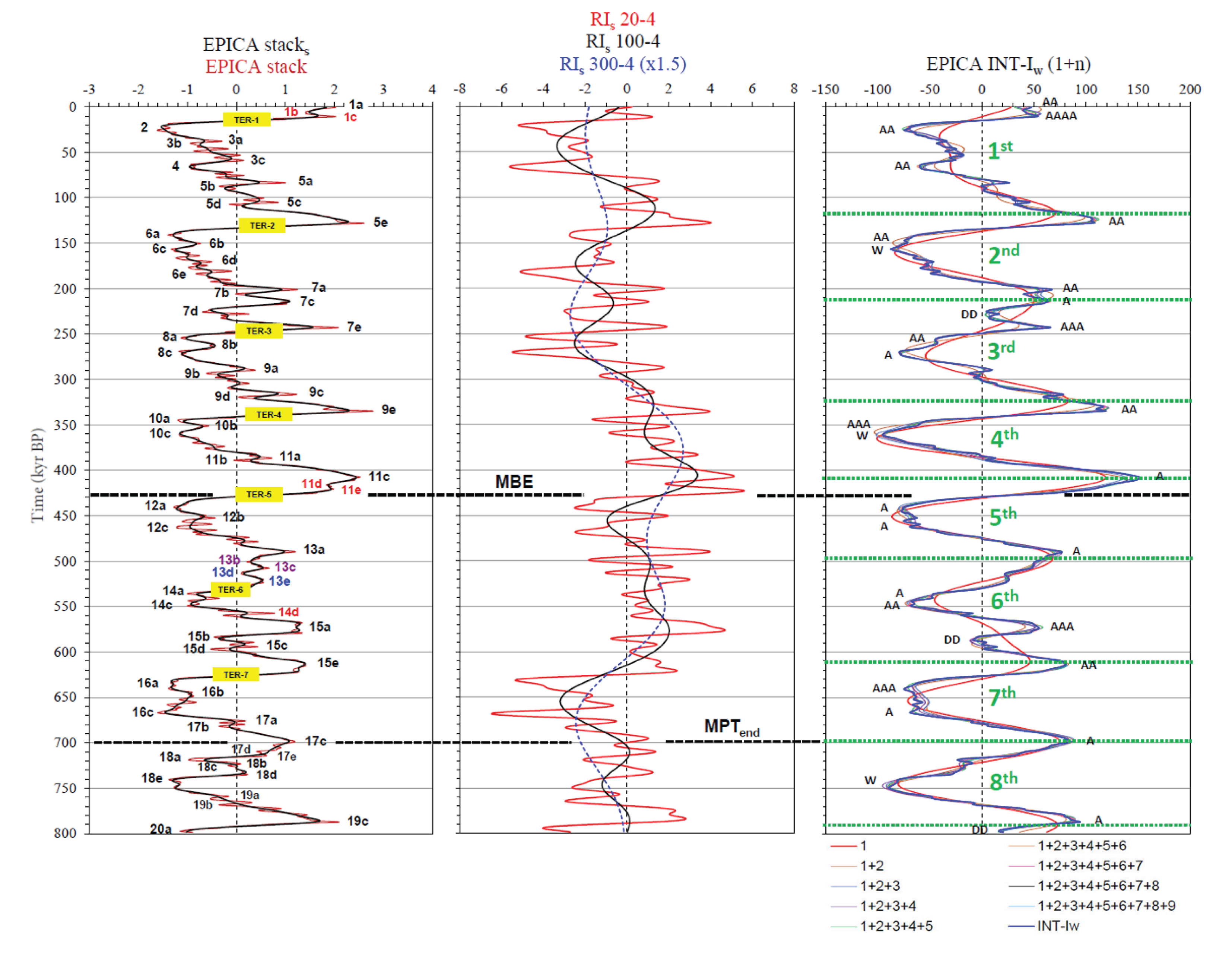
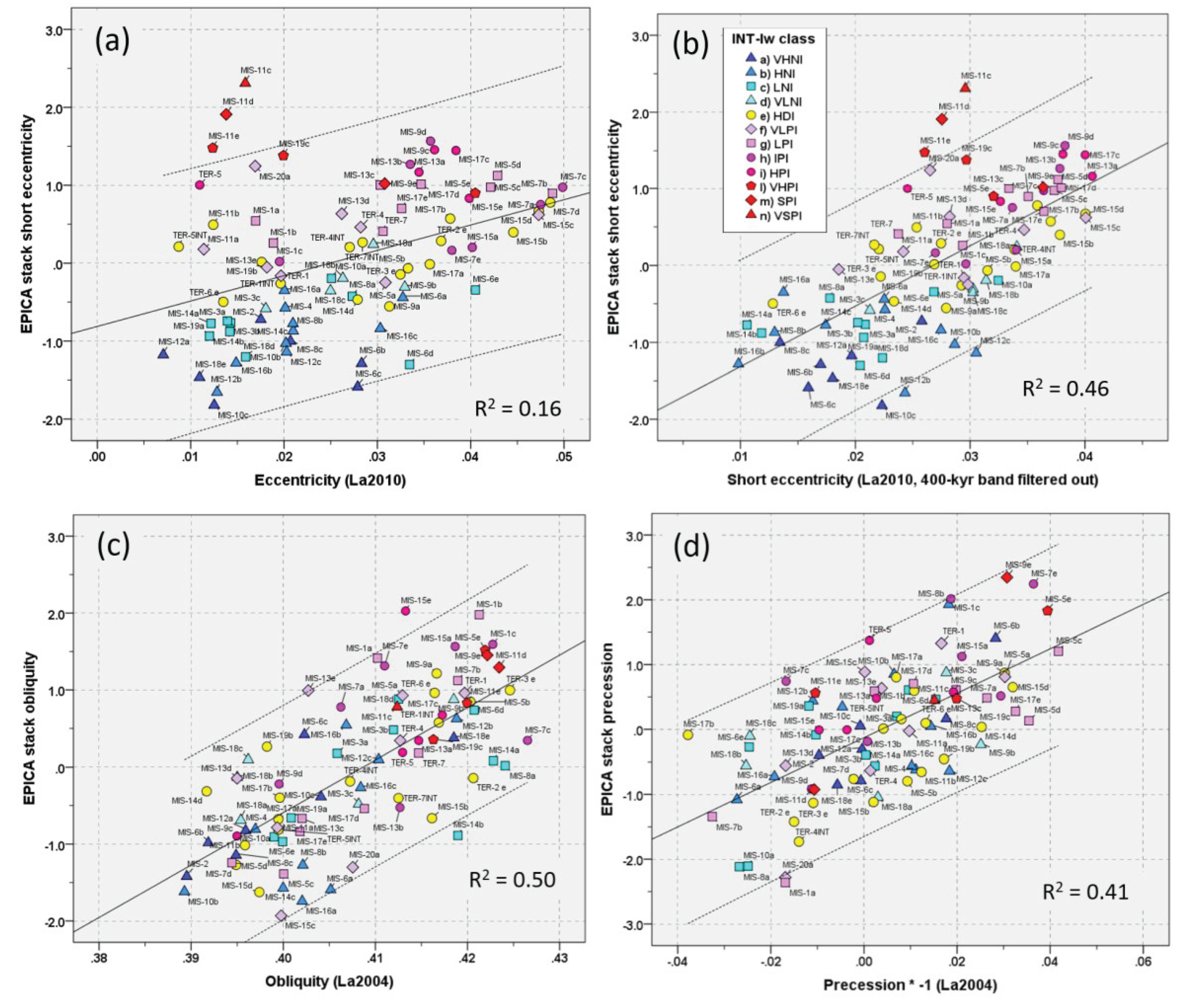
| Termination | Glacial MIS | Integlacial MIS | LR041 | LR042 | 𝛅18O eastern Mediterranean2 | EPICA stack (midpoint)3 |
| TER-1 | MIS-2 | MIS-1a | 14 | 16 | 17.3 | 13.3 (13.5) |
| TER-2 | MIS-6a | MIS-5e | 130 | 134 | 134.4 | 134.5 |
| TER-3 | MIS-8a | MIS-7e | 243 | 244 | 244.4 | 248.8 (249) |
| TER-4 | MIS-10a | MIS-9e | 337 | 336 | 338.4 | 340 |
| TER-5 | MIS-12a | MIS-11c | 424 | 429 | 427.1 | 424 |
| TER-6 | MIS-14a | MIS-13e | 533 | 534 | - | 529.8 (530) |
| TER-7 | MIS-16a | MIS-15e | 621 | 624 | 629.1 | 624.5 |
| Component | Variable | B | Std. error | t | Sig. |
| Constant | 6.263E-08 | 0.0044 | 0.00 | 1.000 | |
| EPICA stack mid-term | (4.4 × RMT) | 0.0289 | 0.0012 | 24.28 | 0.000 |
| EPICA stack obliquity mod. | (4 × ROM) | 0.0450 | 0.0012 | 38.64 | 0.000 |
| EPICA stack short ecc. | (51.6 × RSE) | 0.0133 | 0.0001 | 152.20 | 0.000 |
| EPICA stack obliquity | (19 × ROB) | 0.0220 | 0.0002 | 88.60 | 0.000 |
| EPICA stack prec. | (8.4 × RPR) | 0.0317 | 0.0006 | 53.42 | 0.000 |
| EPICA stack half prec. | (3.8 × RHP) | 0.0398 | 0.0015 | 26.84 | 0.000 |
| EPICA stack sun-9.7 | (1.8 × RS9.7) | 0.0546 | 0.0037 | 14.86 | 0.000 |
| EPICA stack sun-6.0 | (2.6 × RS6.0) | 0.0488 | 0.0023 | 21.15 | 0.000 |
| EPICA stack unclear-3.7 | (0.63 × RUC3.7) | 0.1056 | 0.0099 | 10.70 | 0.000 |
| EPICA stack sun-2.5 | (0.12 × RS2.5) | 0.1615 | 0.0518 | 3.12 | 0.002 |
| Termination | Glacial MIS | Integlacial MIS | LR041 (kyr) | LR042 (kyr) | 𝛅18O eastern Mediterranean2 (kyr) | EPICA (midpoint)3 (kyr) | INT-Iw (midpoint)3 (kyr) | EPICA (near-0)4 (kyr) | INT-Iw (near-0)4 |
| TER-1 | MIS-2 | MIS-1a | 14.0 | 16.0 | 17.3 | 13.3 (13.5) | 21.2 | 15 | 2.4 |
| TER-2 | MIS-6a | MIS-5e | 130.0 | 134.0 | 134.4 | 134.5 | ‒4.4 | 134.5 | ‒4.4 |
| TER-3 | MIS-8a | MIS-7e | 243.0 | 244.0 | 244.4 | 248.8 (249) | 0.4 | 249 | 0.4 |
| TER-4 | MIS-10a | MIS-9e | 337.0 | 336.0 | 338.4 | 340 | 24.8 | 342 | ‒1.6 |
| TER-5 | MIS-12a | MIS-11c | 424.0 | 429.0 | 427.1 | 424 | 81.2 | 429.5 | ‒0.2 |
| TER-6 | MIS-14a | MIS-13e | 533.0 | 534.0 | - | 529.8 (530) | 0.7 | 530 | 0.7 |
| TER-7 | MIS-16a | MIS-15e | 621.0 | 624.0 | 629.1 | 624.5 | 34.5 | 626.5 | 0.5 |
| Signal | Skewness | Minimum | Maximum |
| EPICA stack | 0.56 | ‒1.6 | 2.8 |
| EPICA INT-Iw | 0.35 | ‒95.4 | 152.3 |
| EPICA stack obliquity modulation | 0.01 | ‒6.8 | 6.9 |
| EPICA stack short eccentricity | 0.08 | ‒100.9 | 119.2 |
| EPICA stack obliquity | 0.05 | ‒38.3 | 38.6 |
| EPICA stack precession | ‒0.07 | ‒20.7 | 20.7 |
| EPICA stack half-precession | 0.03 | ‒9.3 | 9.4 |
| EPICA stack sun-9.7 | 0.05 | ‒4.8 | 4.9 |
| EPICA stack sun-6.0 | 0.02 | ‒6.6 | 7.2 |
| EPICA stack unclear-3.7 | 0.01 | ‒2.1 | 1.9 |
| EPICA stack sun-2.5 | 0.01 | ‒0.4 | 0.4 |
| Interference index | Skewness | Minimum | Maximum |
| INT-Iw (1) | 0.08 | ‒100.9 | 119.2 |
| INT-Iw Σ (m=1;n=2) | 0.23 | ‒103.7 | 139.7 |
| INT-Iw Σ (m=1;n=3) | 0.27 | ‒101.8 | 137.7 |
| INT-Iw Σ (m=1;n=4) | 0.32 | ‒95.8 | 144.5 |
| INT-Iw Σ (m=1;n=5) | 0.34 | ‒93.3 | 149.2 |
| INT-Iw Σ (m=1;n=6) | 0.35 | ‒94.5 | 152.4 |
| INT-Iw Σ (m=1;n=7) | 0.35 | ‒94.5 | 152.1 |
| INT-Iw Σ (m=1;n=8) | 0.35 | ‒95.4 | 152.3 |
| INT-Iw Σ (m=1;n=9) | 0.35 | ‒95.4 | 152.3 |
| INT-Iw | 0.35 | ‒95.4 | 152.3 |
| MIS | Age (kyr) | EPICA short ecc. stackw | EPICA INT-Iw | Variation (%)1 | Amplification/Damping1 | Polarity | Interference class | Interference type |
| MIS-1a | 0.5 | 28.0 | 47.6 | 70 | AA | Interglacial | LPI | Constructive |
| MIS-1c | 10.5 | 1.0 | 53.9 | 5290 | AAAA | Interglacial | IPI | Constructive |
| MIS-2 | 26.0 | ‒37.2 | ‒74.6 | 101 | AA | Glacial | VHNI | Constructive |
| MIS-4 | 63.5 | ‒29.7 | ‒58.4 | 97 | AA | Glacial | HNI | Constructive |
| MIS-5e | 128.0 | 46.4 | 106.5 | 130 | AA | Interglacial | VHPI | Constructive |
| MIS-6a | 141.0 | ‒22.8 | ‒62.0 | 172 | AA | Glacial | HNI | Constructive |
| MIS-6c | 157.0 | ‒82.0 | ‒87.5 | 7 | W | Glacial | VHNI | Constructive |
| MIS-7a | 201.0 | 38.8 | 67.1 | 73 | AA | Interglacial | IPI | Constructive |
| MIS-7c | 213.5 | 50.3 | 65.2 | 30 | A | Interglacial | IPI | Constructive |
| MIS-7d | 226.0 | 40.3 | 4.5 | ‒89 | DD | Glacial | HDI | Destructive |
| MIS-7e | 243.0 | 8.5 | 66.1 | 678 | AAA | Interglacial | IPI | Constructive |
| MIS-8a | 254.5 | ‒22.0 | ‒42.6 | 94 | AA | Glacial | LNI | Constructive |
| MIS-8c | 269.0 | ‒51.6 | ‒79.0 | 53 | A | Glacial | VHNI | Constructive |
| MIS-9e | 335.0 | 52.7 | 117.1 | 122 | AA | Interglacial | SPI | Constructive |
| MIS-10a | 345.0 | ‒10.0 | ‒46.9 | 369 | AAA | Glacial | LNI | Constructive |
| MIS-10c | 360.5 | ‒94.0 | ‒94.5 | 1 | W | Glacial | VHNI | Constructive |
| MIS-11c | 407.5 | 119.1 | 152.3 | 28 | A | Interglacial | VSPI | Constructive |
| MBE | 430.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| MIS-12a | 440.5 | ‒60.7 | ‒74.5 | 23 | A | Glacial | VHNI | Constructive |
| MIS-12c | 463.0 | ‒58.8 | ‒67.5 | 15 | A | Glacial | HNI | Constructive |
| MIS-13a | 490.0 | 60.3 | 76.9 | 28 | A | Interglacial | HPI | Constructive |
| MIS-14a | 536.0 | ‒39.9 | ‒47.1 | 18 | A | Glacial | LNI | Constructive |
| MIS-14c | 549.5 | ‒39.9 | ‒67.9 | 70 | AA | Glacial | HNI | Constructive |
| MIS-15a | 574.5 | 10.4 | 54.7 | 426 | AAA | Interglacial | IPI | Constructive |
| MIS-15b | 583.5 | 20.5 | ‒4.3 | ‒121 | DD | Glacial | HDI | Destructive |
| MIS-15e | 615.0 | 43.0 | 79.1 | 84 | AA | Interglacial | HPI | Constructive |
| MIS-16a | 634.0 | ‒18.0 | ‒61.4 | 241 | AAA | Glacial | HNI | Constructive |
| MIS-16c | 667.0 | ‒43.3 | ‒69.2 | 60 | A | Glacial | HNI | Constructive |
| MIS-17c | 698.5 | 74.6 | 85.6 | 15 | A | Interglacial | HPI | Constructive |
| MIS-18e | 740.5 | ‒75.7 | ‒79.8 | 5 | W | Glacial | VHNI | Constructive |
| MIS-19c | 787.5 | 71.2 | 94.5 | 33 | A | Interglacial | VHPI | Constructive |
| MIS-20a | 797.5 | 64.3 | 16.1 | ‒75 | DD | Glacial | VLPI | Destructive |
| Mean of variation (%): | ||||||||
| Glacials | 58 | |||||||
| Interglacials | 539 | |||||||
| Pre-MBE interglacials | 117 | |||||||
| Post-MBE interglacials | 803 | |||||||
| Pre-MBE glacials | 26 | |||||||
| Post-MBE glacials | 89 | |||||||
| 1 INT-Iw vs. EPICA short eccentricity stack weighted. | ||||||||
| Eccentricity (La2010) | EPICA stackw (short eccentricity) | EPICA INT-Iw | ||||||||||
| 100-kyr cycle | Max | Min | Cooling duration | Warming duration | Max | Min | Cooling duration | Warming duration | Max | Min | Cooling duration | Warming duration |
| 1st | 14.0 | 43.5 | 71.5 | 29.5 | ‒4.5 | 33.0 | 83.5 | 37.5 | 10.0 | 26.0 | 101.5 | 16.0 |
| 2nd | 115.0 | 154.5 | 61.5 | 39.5 | 116.5 | 160.0 | 52.5 | 43.5 | 127.5 | 157.0 | 56.5 | 29.5 |
| 3rd | 216.0 | 267.5 | 43.5 | 51.5 | 212.5 | 274.0 | 49.5 | 61.5 | 213.5 | 270.0 | 64.5 | 56.5 |
| 4th | 311.0 | 373.0 | 32.0 | 62.0 | 323.5 | 365.0 | 43.5 | 41.5 | 334.5 | 361.0 | 46.5 | 26.5 |
| 5th | 405.0 | 438.0 | 54.5 | 33.0 | 408.5 | 451.0 | 46.5 | 42.5 | 407.5 | 445.0 | 45.0 | 37.5 |
| 6th | 492.5 | 534.5 | 61.5 | 42.0 | 497.5 | 543.0 | 66.5 | 45.5 | 490.0 | 549.0 | 63.5 | 59.0 |
| 7th | 596.0 | 644.0 | 48.5 | 48.0 | 609.5 | 654.0 | 44.5 | 44.5 | 612.5 | 641.0 | 57.5 | 28.5 |
| 8th | 692.5 | 748.0 | 34.0 | 55.5 | 698.5 | 745.0 | 45.5 | 46.5 | 698.5 | 749.0 | 38.0 | 50.5 |
| 9th | 782.0 | - | - | - | 790.5 | - | - | - | 787.0 | - | - | - |
| Mean | 50.9 | 45.1 | 54.0 | 45.4 | 59.1 | 38.0 | ||||||
| SD | 14.0 | 11.2 | 14.0 | 7.1 | 19.5 | 15.7 | ||||||
| Time asymmetry (cool minus warm) | 5.8 | 8.6 | 21.1 | |||||||||
| Prolonged cooling: | 48%1 | 145%2 | ||||||||||
| 264%1 | ||||||||||||
| Forcing | EPICA signal | Cross-spectrum freq. (kyr-1) | Cross-spectrum period (kyr) | Coherency | Phase shift (Deg, kyr) | ||
| Eccentricity | Short ecc. stack | 0.01125 | 88.9 | 0.94 | 17.4 | 4.30 | EPICA signal leads |
| Short eccentricity1 | Short ecc. stack | 0.01125 | 88.9 | 0.94 | 18.3 | 4.52 | EPICA signal leads |
| Obliquity | Obliquity stack | 0.025 | 40.0 | 0.98 | ‒37.9 | ‒4.21 | EPICA signal lags |
| Precession | Precession stack | 0.0425 | 23.5 | 0.67 | ‒60.8 | ‒3.97 | EPICA signal lags |
| 1400-kyr band filtered out by wavelet analysis. | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





