Submitted:
15 March 2024
Posted:
15 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
0. Introduction
1. Materials and Methods
1.1. Measurement of the Physical Parameters of Tea Seeds
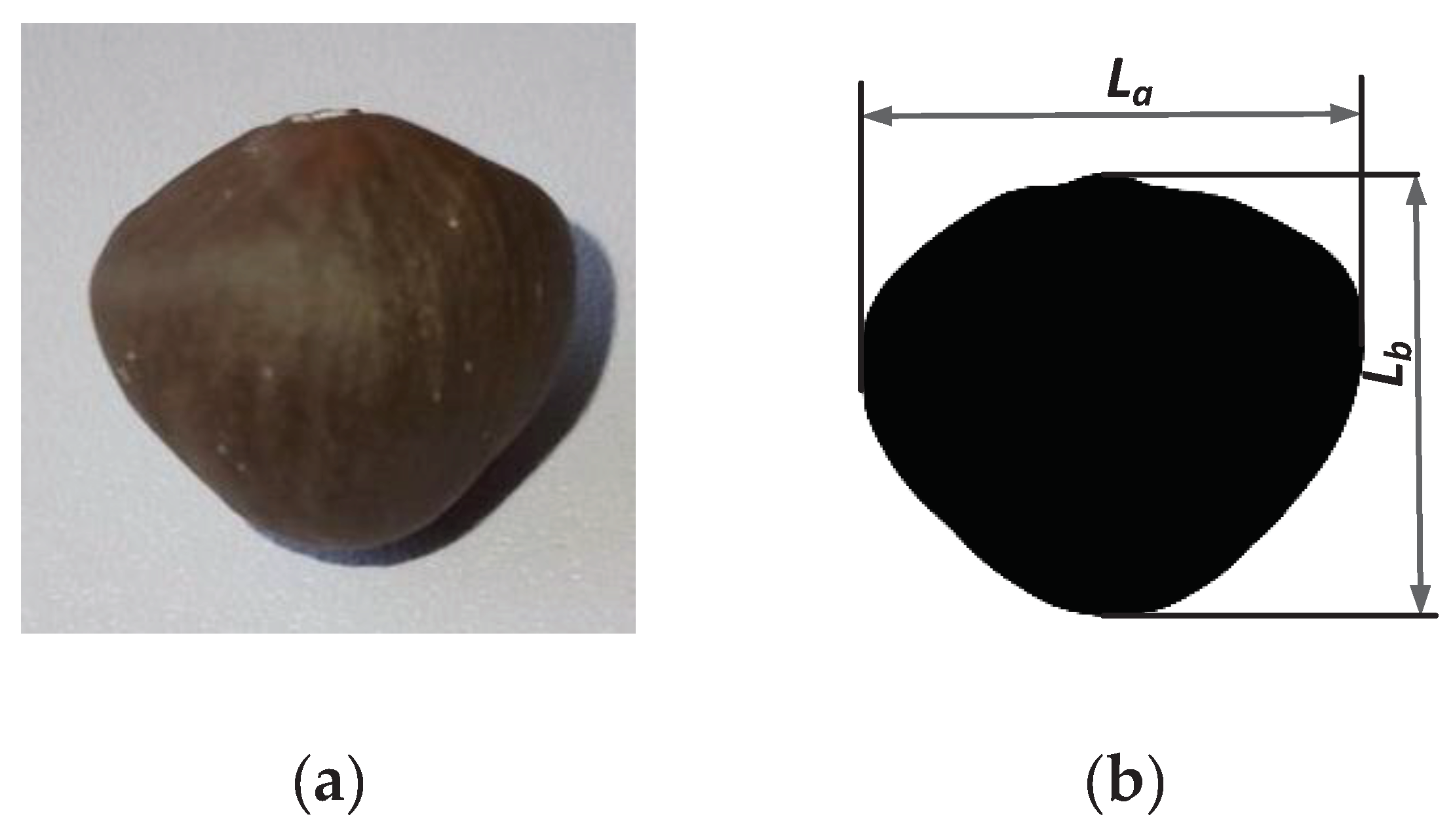
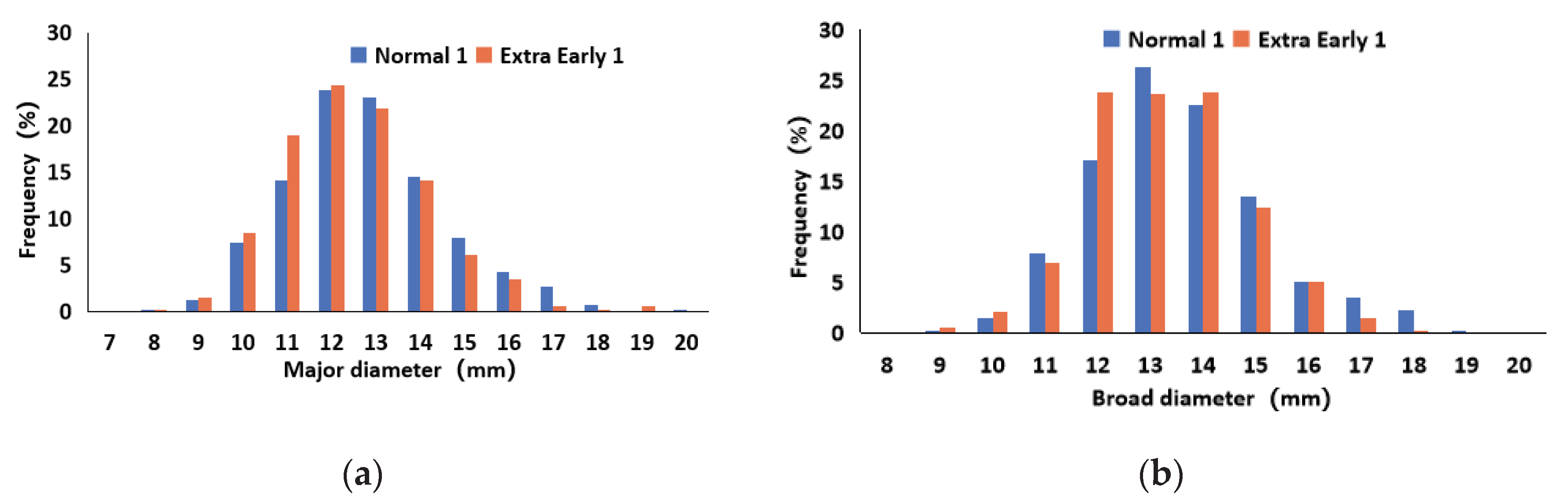
1.1.1. Size Measurement of Tea Seed
1.1.2. Hundred Grain Weight and Water Content Measurement
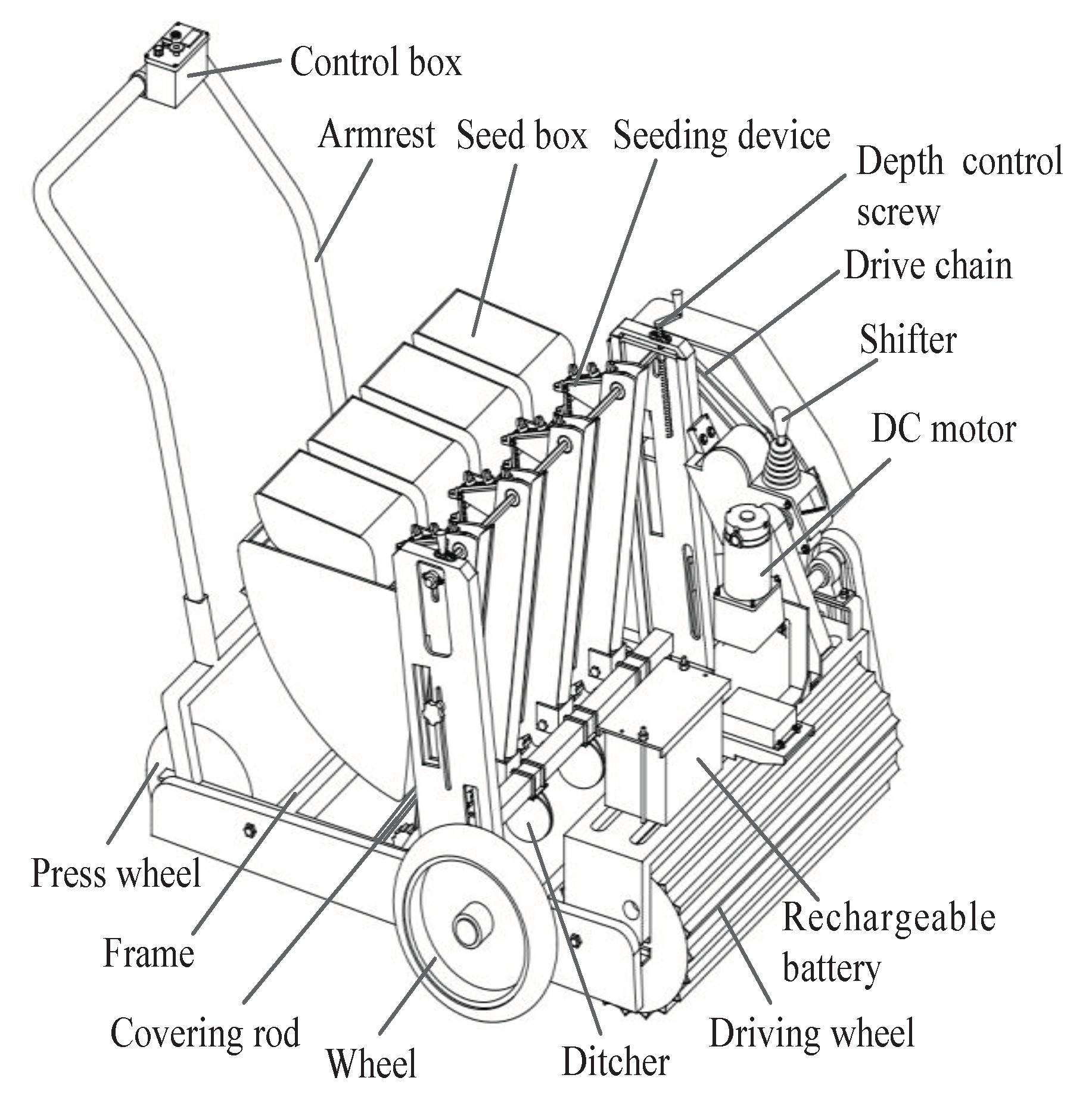
1.2. Structure and Key Components
1.2.1. Structure and Principle
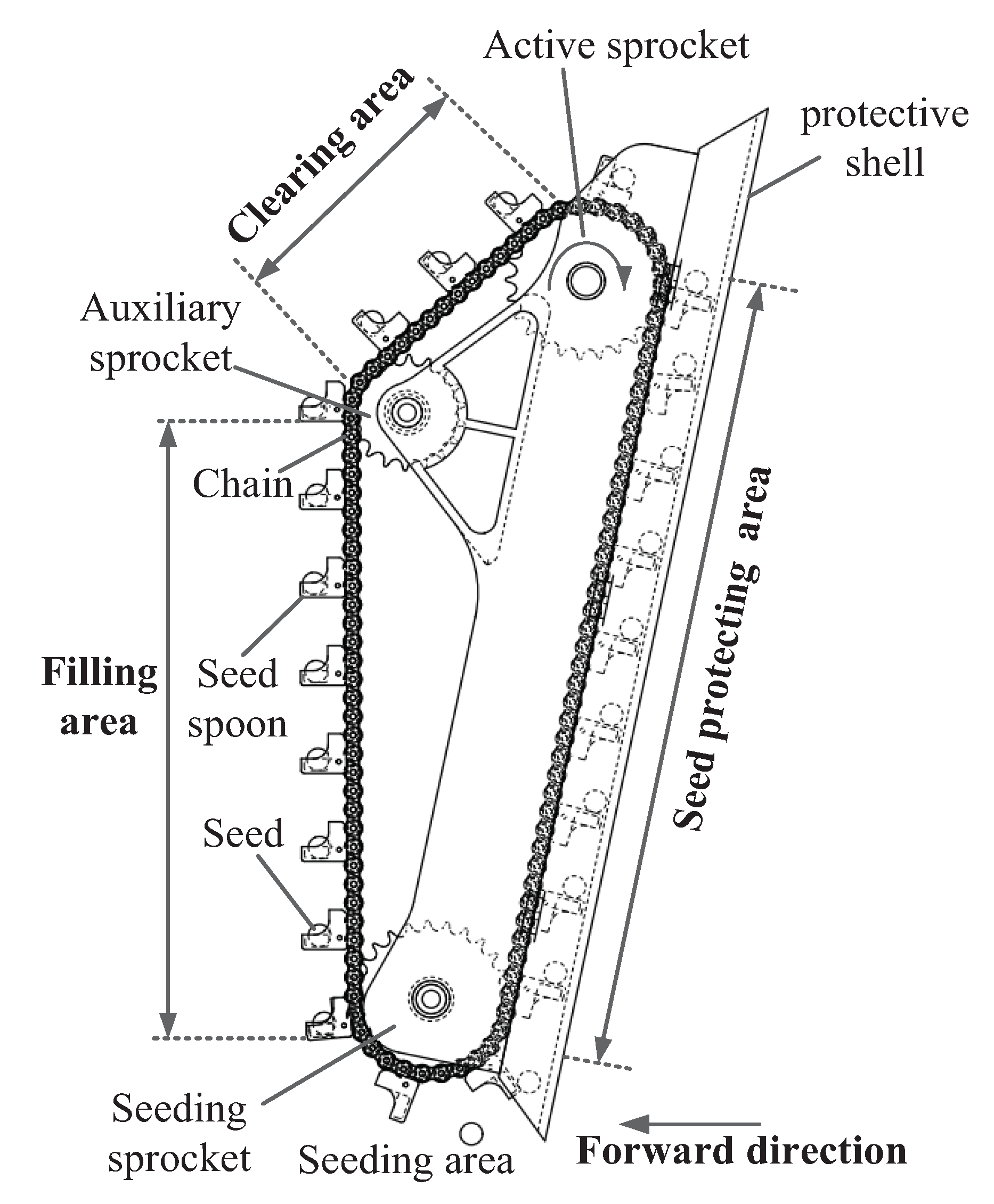
1.2.3. Structure of Seeding Device
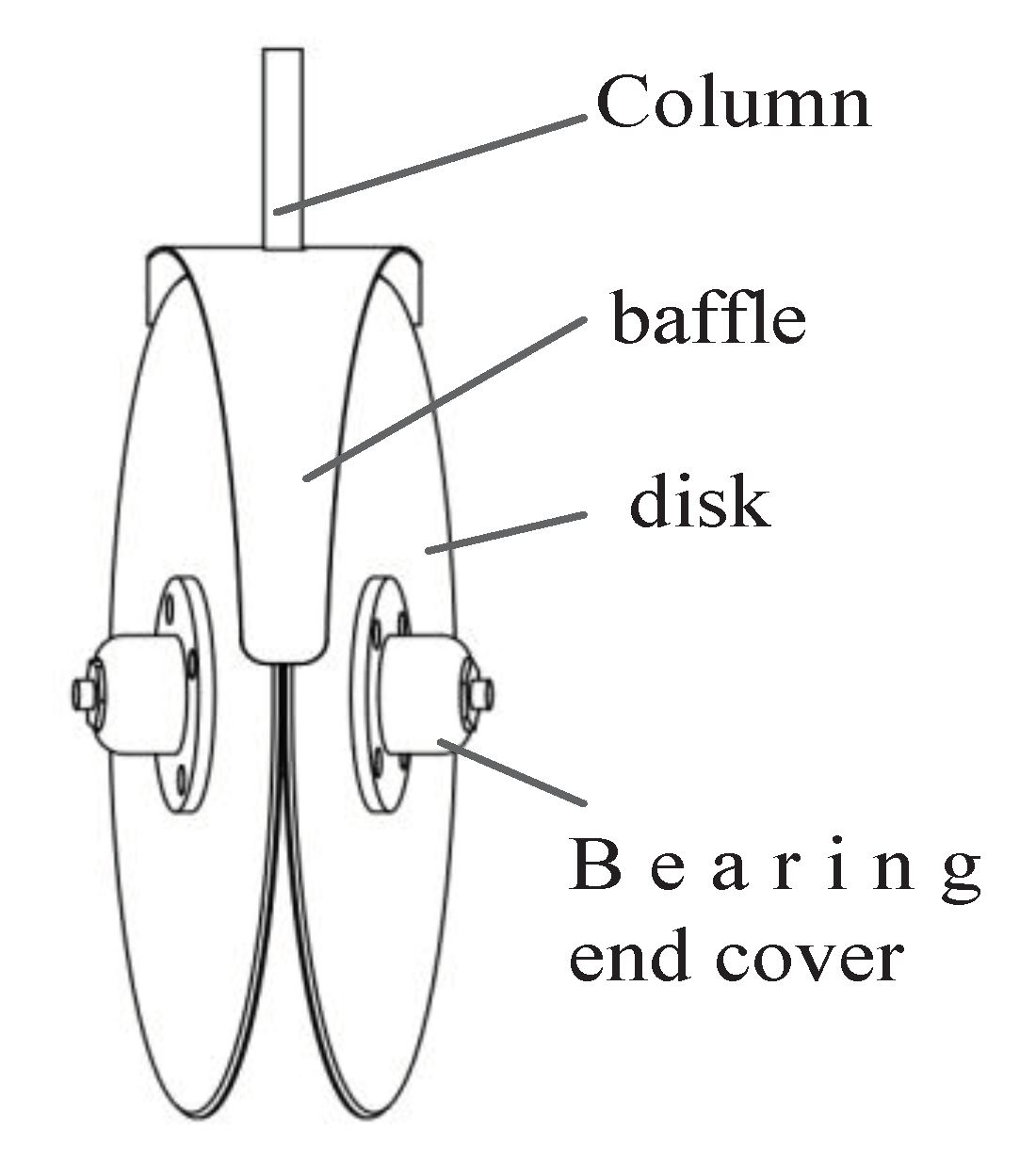
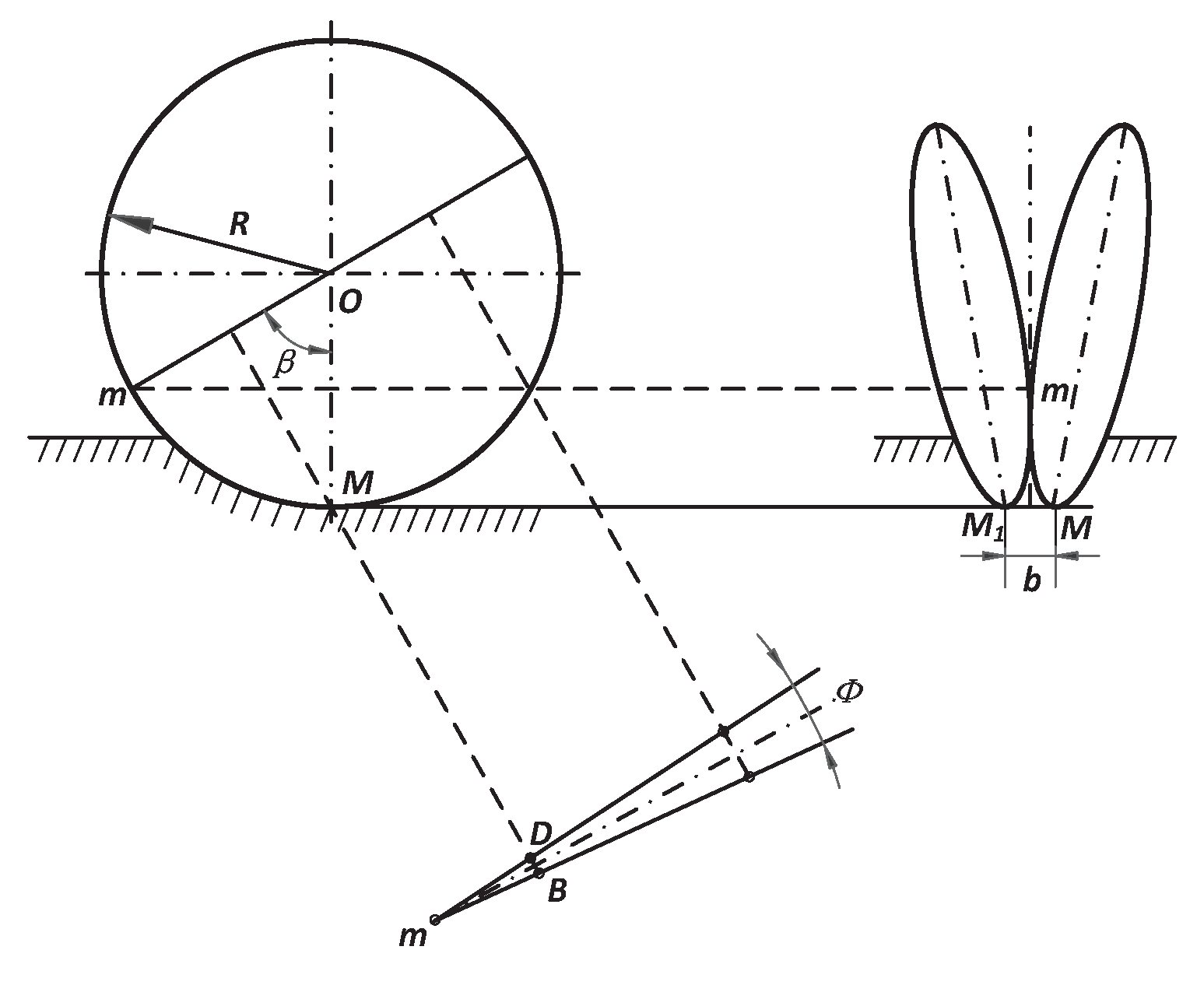
1.2.4. Structure of the Ditcher
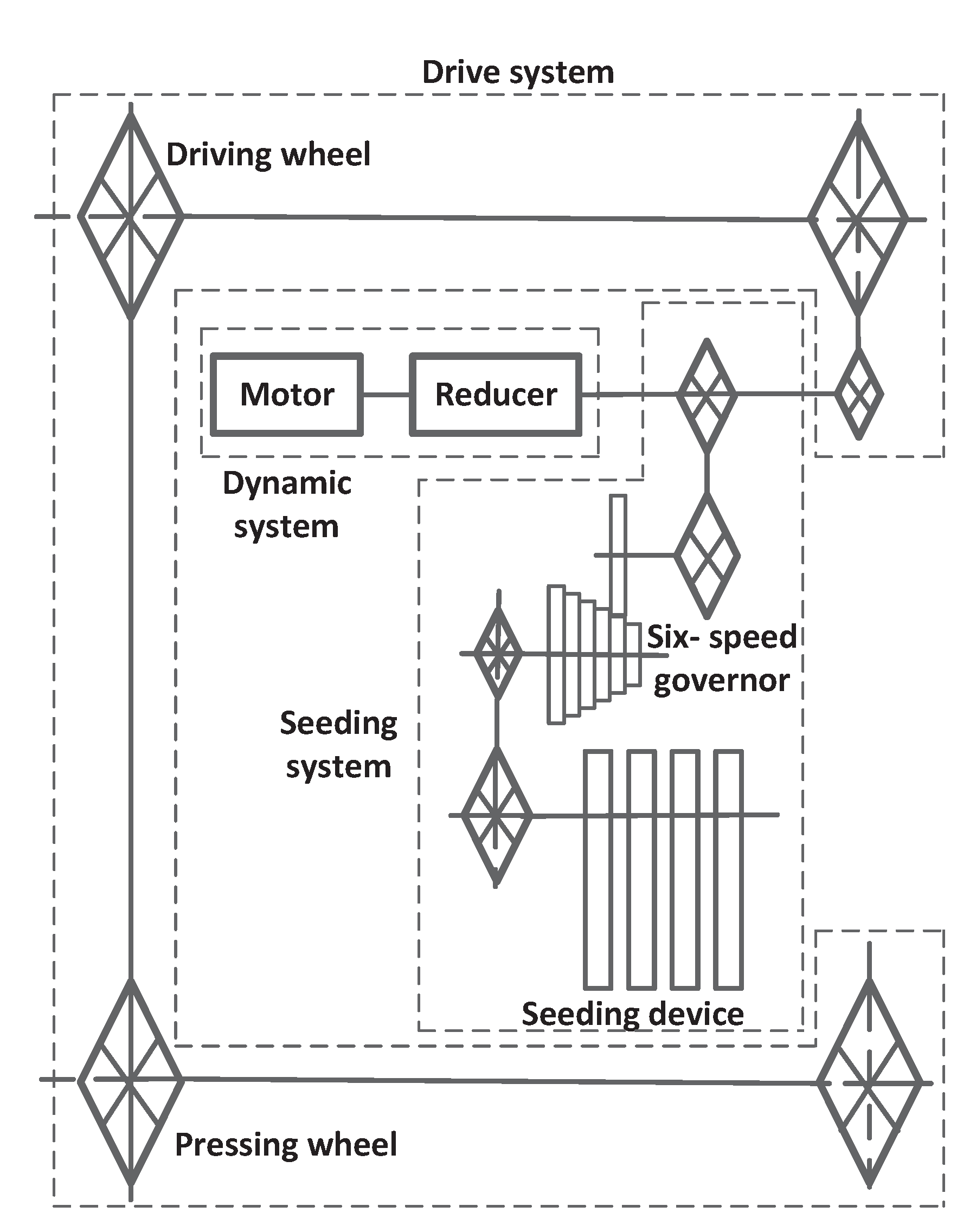
1.2.5. Design of Transmission System
1.2.6. Power Calculation and Battery Selection
- (1)
- Power calculation
- (2)
- Battery selection
1.3. Test Equipment and Materials
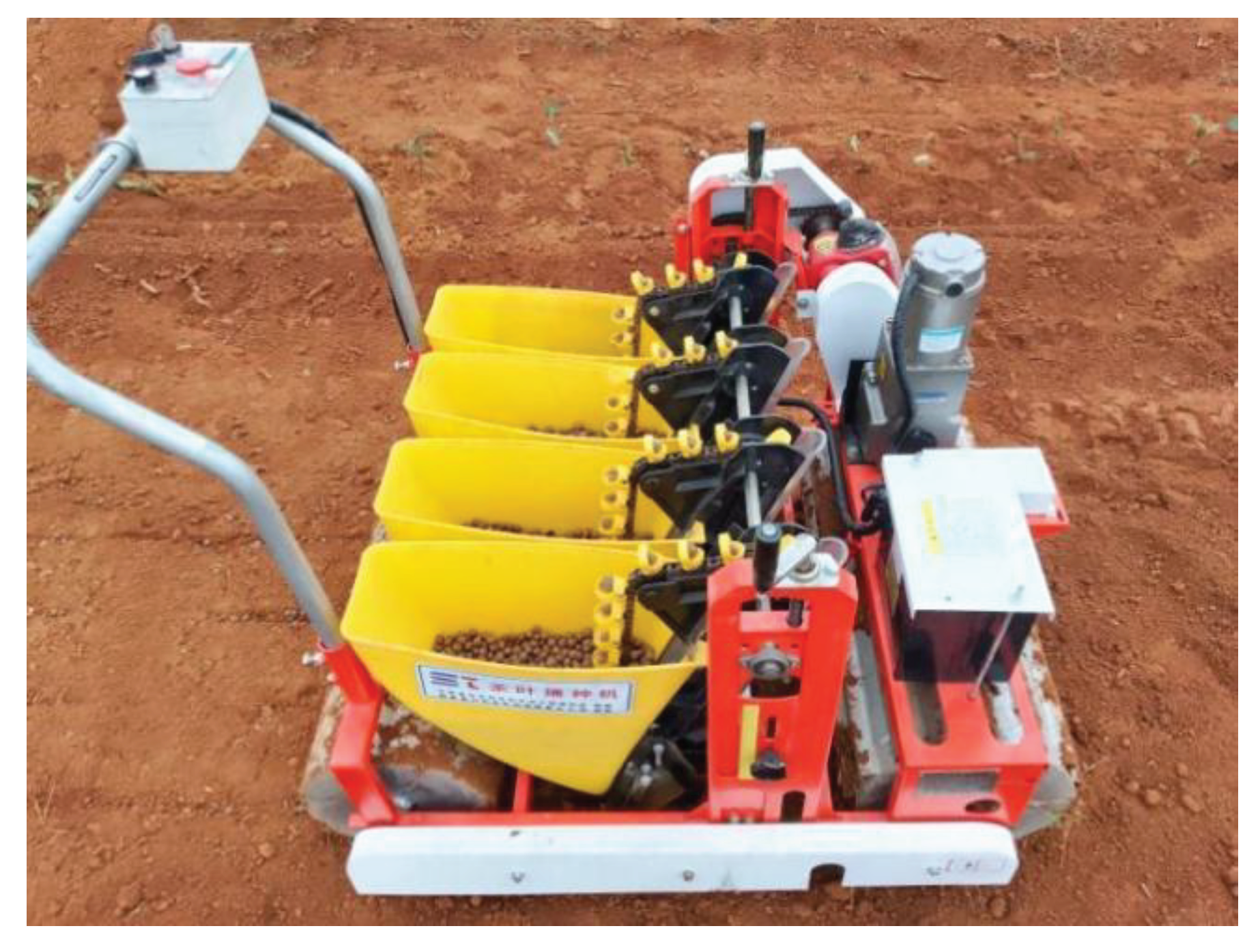

1.4. Evaluation Index and Experimental Design
1.4.1. Evaluation Index
1.4.2. Experimental Design
2. Results
2.1. Polar Difference Analysis
2.2. Significance Analysis
2.3. Validation Test
3. Discussion
- (1)
- From the test results, the replay index of the tea seed sowing of the test prototype was approximately 8%, and the leakage index was approximately 4%, which is somewhat high, meaning that the sowing effect can be further improved. The possible reasons are as follows. First, the test was carried out in an outdoor tea garden, and the changes in terrain and soil conditions may have increased the vibration of the whole machine and affected the sowing effect. Second, the prototype adopts different driving gears, and its optimal working state may not be the test combination recommended by the orthogonal test. Third, the prototype seed spoon was purchased from the market, considering only the size of the seed-spoon hole; we did not deeply study the impact of other factors.
- (2)
- As the key component of the seed planter, the material, dimensions, and shape characteristics of the seed scoop may influence seed-taking. In the future, the research team will conduct a theoretical analysis of the contact and friction between the tea seeds, seed spoon and arc of the shaped hole of the seed spoon to further explore the influence of the structure and material of the seed spoon on the seed-taking effect via numerical simulations.
- (3)
- The environment has an impact on the seeding effect of the seed planter. For example, under different soil types and humidity conditions, the seeding effect will be significantly different. Therefore, research on the appropriate environment for seeding is a problem that must be considered in the application and promotion of seed planters.
4. Conclusion
- (1)
- The physical and mechanical parameters of the tea seeds were determined, and two different types of tea seeds (Normal 1 and Extra Early 1) were selected for size measurement. The measurement results showed that the major and broad diameters of the tea seeds were normally distributed with a size distribution in which over 90% of the measurements fell between 10 and 16 mm. For Normal 1, the average hundred grain weight and water content were 105.52 g and 17.38%, respectively. For Extra Early 1, the average hundred grain weight and water content were 108.73 g and 15.47%, respectively.
- (2)
- A type of electric self-propelled tea seed precision seeder was designed to simultaneously perform ditching, seeding, soil covering, suppression, and other operations . Core components such as the seeding device, ditching device, and transmission system were designed and analyzed. After the analysis, a chain-spoon-type precision seed feeder was selected. The major diameter of the seed-spoon hole was 20 mm, the broad diameter was 16 mm, and the depth was 6 mm. A double-disc ditcher was used. By calculation, the diameter of the disc is 200 mm, the angle β of the convergence point of the disc is 68°, and the angle of the double disc is 15°. The transmission system of the entire machine was designed to achieve an adjustable range of 50 to 100 mm. The power of the whole machine was calculated, and the total power of the tea seed planter is 1.02 kW. The 1.5 kW DC motor and 24 V (50 Ah) battery are matched.
- (3)
- In the prototype test, the orthogonal test method was used to analyze the effects of the driving speed, ditching depth, and planting gear position on the working performance of the tea seed planter. The test results showed that the driving speed and planting gear position significantly affected the acceptance index, replay, and leakage index, whereas the ditching depth had little effect on the operational performance of the tea seed drill. The orthogonal test results showed that when the driving speed was moderate, the ditching depth was 30 mm, the planting gear position was 3, the corresponding acceptance index was 87.22%, the replay index was 8.89%, and the leakage index was 3.89%. The influence on the ditching depth was further verified in the case of the medium-speed gear and three planting gear positions, and the test results showed that the acceptance index exceeded 87%, whereas the replay and leakage indexes changed less.
References
- Wu, L.; Shu, S.; Xu, G.; Ye, C.; Wu, Y. Analysis on the technical gap and key problems of tea picker in china. Significances Bioeng Biosci 2023, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yi, B.; Zhang, J. Technology of tea seed rearing in Yunnan large leaf tea. Yunnan Agric Sci Technol 2010, 01, 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Z. Research progress of tea plant genetics and breeding. J Tea 1992, 02, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Lu, J.; Zheng, X.; Liang, Y. Advances in breeding and cultivar multiplication of tea since 2000. J Tea 2010, 36, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Shi, M. Advances in tea plant genetics and breeding. J Tea Sci 2015, 35, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Zhao, W.; Shi, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, F.; Yang, K.; Xin, S. Design and test of rolling spoon type flax combined seeder in the arid area of northwest china. J China Agric Univ 2022, 27, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Wang, X.; Xin, J.; Sun, L.; Wu, C. Design and test of arc duck-billed garlic seed planter. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach 2022, 53, 120–130. [Google Scholar]
- Panning, J.W.; Kocher, M.F.; Smith, J.A.; Kachman, S.D. Laboratory and field testing of seed spacing uniformity for sugar-beet planters. Appl Eng Agric 2000, 16, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W. Design and Experimental Study on Key Components of Garlic Seeder [Master’s Thesis],Northwest A & F University: Yangling; China, 2020.
- Barut, Z.B.; Özmerzİ, A. Effect of different operating parameters on seed holding in the single seed metering unit of a pneumatic planter. Turk J Agric For 2004, 28, 435–441. [Google Scholar]
- Ozherelyev, V.N.; Kotikov, F.N. Sprouted potato tuber dynamics and kinematics during mechanized planting. Procedia Eng 2017, 206, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Li, C.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, J.; Du, Z. Design and experiment of narrow-row-dense-planting precision planter for American ginseng. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach 2022, 53, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Han, D.; Han, Z.; Huang, J.; Chen, P.; He, B.; Zhang, L. Experiment on the influence of vibration on the seeding performance of the scoop-wheel seed meter. J Henan Agric Univ 2021, 55, 896–905. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M. Study on the Effect of Field Vibration on Sowing Quality of Potato Planter. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A & F University, Yangling; China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yazgi, A.; Degirmencioglu, A. Optimisation of the seed spacing uniformity performance of a vacuum-type precision seeder using response surface methodology. Biosyst Eng 2007, 97, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Cao, C.; Qin, K.; Ge, J. Design and experiment of wheel seed metering device with guide ring groove combining U-hole for Radix Peucedani. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach 2022, 53, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Dun, G.; Yu, C.; Yang, Y.; Ye, J.; Du, J.; Zhang, J. Parameter simulation optimization and experiment of seed plate type hole for soybean breeding. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 2019, 35, 62–73. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Liu, Z.; Shi, W.; Cheng, X. Design and experiment of chain casting corn precision seeder. J Agric Mech Res 2019, 41, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Zeng, Q. Study on storage characters of tea seed. J Tea Sci 1999, 01, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Q.; Bu, k.; Li, Y.; Jiao, W. Structure analysis of the large no-till seeder openers. J Agric Mech Res 2012, 34, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Agricultural Machinery Design Manual; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, K.; Li, B.; Wu, H. Practical techniques for off-site conservation and breeding of tea germplasm. Guangdong Tea 2021, 06, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.; Gao, N.; Meng, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y. Design and experiment of deep fertilizer applicator based on autonomous navigation for precise row-following. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach 2018, 49, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Song, W.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, H.; Zhu, L.; Yang, F. Design and experimental study on key components of garlic seeder. J Agric Mech Res 2022, 44, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, G. Design and Experiment of Chain-Spoon Type Ginseng Precision Seeder. Master’s Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. Structural Design and Experimental Research of a Double-Disc Trenching and Fertilizing and Mulching Machine for Tea Plantations [D] [Master’s Thesis]; Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2022.
- Meng, Z. Battery selection and data calculation. China Cable Telev 2002, 07, 70–71. [Google Scholar]
- GB_T 6973-2005;Agricultural Industry Standard of the P.R. China. Single-Grain (Precision) Planter Test Method; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2005.
- DGT007-2019;Agricultural Industry Standard of the P.R. China. Planter; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2019.

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Machine size (length × width × height)/mm | 1320 × 950 × 1140 |
| Weight / kg | 95 |
| Driving speed range / (m · s-1) | 0–1 |
| Operation width / mm | 800 |
| Number of working rows / rows | 4 |
| Line space /mm | 200 |
| Plant distance range / mm | 50–100 |
| Seeding depth range / mm | 30–50 |
| Block | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical plant spacing / mm | 48.3 | 58 | 67.7 | 77.3 | 87 | 96.7 |
| Designed plant spacing / mm | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 |
| Factors | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Driving gear (A) | low speed | medium speed | high speed |
| Ditching depth (B, mm) | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| Planting gear position (C) | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| Order Number |
Experimental factor | Evaluating indicator /% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B /(mm ) | C | AI | RI | LI | |
| 1 | low speed | 30 | 1 | 65.56 | 33.89 | 0.56 |
| 2 | low speed | 40 | 3 | 72.78 | 25.00 | 2.22 |
| 3 | low speed | 50 | 5 | 75.22 | 18.67 | 6.11 |
| 4 | medium speed | 30 | 3 | 87.22 | 8.89 | 3.89 |
| 5 | medium speed | 40 | 5 | 86.11 | 6.11 | 7.78 |
| 6 | medium speed | 50 | 1 | 77.22 | 21.11 | 1.67 |
| 7 | high speed | 30 | 5 | 82.78 | 3.89 | 13.33 |
| 8 | high speed | 40 | 1 | 76.67 | 18.89 | 4.44 |
| 9 | high speed | 50 | 3 | 85.00 | 6.11 | 8.89 |
| Evaluating indicator | Experimental factor | K1 | K2 | K3 | R | Optimal scheme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI | A | 71.187 | 83.517 | 81.483 | 12.330 | A2 |
| B | 78.520 | 78.520 | 79.147 | 0.627 | B3 | |
| C | 73.150 | 81.667 | 81.370 | 8.517 | C2 | |
| Order of influence | A >C >B | |||||
| RI | A | 25.853 | 12.073 | 9.630 | 16.223 | A3 |
| B | 15.557 | 16.667 | 15.297 | 1.370 | B3 | |
| C | 24.630 | 13.333 | 9.557 | 15.073 | C3 | |
| Order of influence | A >C >B | |||||
| LI | A | 2.963 | 4.447 | 8.887 | 5.924 | A1 |
| B | 5.927 | 4.813 | 5.55 | 1.114 | B2 | |
| C | 2.223 | 5.000 | 9.073 | 6.850 | C1 | |
| Order of influence | C >A >B | |||||
| Evaluating indicator | Parameter | Sum of squares | Degrees of freedom | Mean square | F | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI | A | 262.185 | 2 | 131.092 | 38.585 | * |
| B | 0.785 | 2 | 0.392 | 0.116 | ||
| C | 140.190 | 2 | 10.095 | 20.631 | * | |
| Error | 6.79 | 2 | ||||
| Sum | 409.96 | 8 | ||||
| RI | A | 459.889 | 2 | 229.945 | 148.639 | ** |
| B | 3.177 | 2 | 1.589 | 1.027 | ||
| C | 369.083 | 2 | 184.542 | 119.290 | ** | |
| Error | 3.09 | 2 | 1.55 | |||
| Sum | 835.24 | 8 | ||||
| LI | A | 57.000 | 2 | 28.500 | 33.063 | * |
| B | 1.929 | 2 | 0.964 | 1.119 | ||
| C | 71.224 | 2 | 35.612 | 41.313 | * | |
| Error | 1.72 | 2 | 0.86 | |||
| Sum | 131.87 | 8 |
| Order Number |
Experimental factor | Evaluating indicator /% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B /(mm ) | C | AI | RI | LI | |
| 1 | medium speed | 30 | 3 | 87.78 | 7.89 | 4.33 |
| 2 | medium speed | 40 | 3 | 87.22 | 7.67 | 5.11 |
| 3 | medium speed | 50 | 3 | 87.56 | 7.56 | 4.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





