Submitted:
14 March 2024
Posted:
15 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
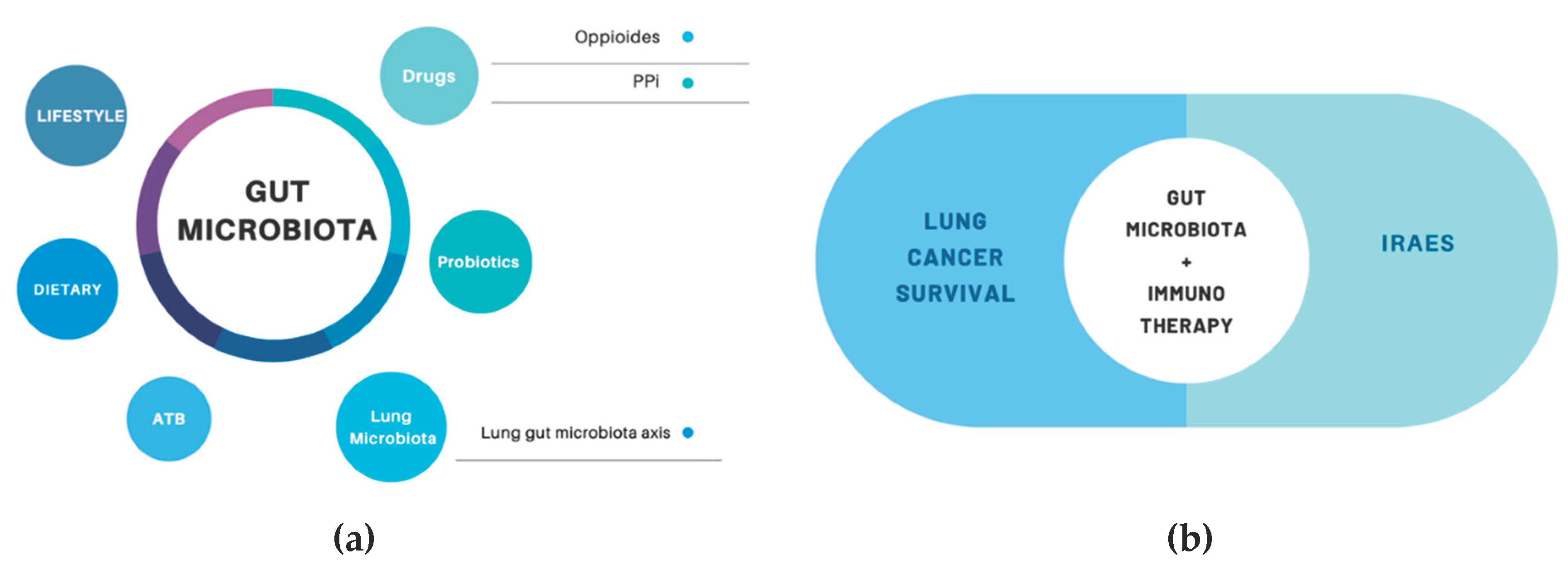
1. Introduction
2. Gut Microbiota and NSCLC
2.1. Gut – Lung – Microbiota Axis
2.2. Gut Microbiota Composition, Anti-Tumor Activity and Antibiotics
2.3. Gut Microbiota and Probiotics Use
2.4. Gut Microbiota and iRAes
2.5. Other Conditions Modifying Gut Microbiota
3. Future Directions
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rocco, D.; Della Gravara, L.; Ragone, A.; Sapio, L.; Naviglio, S.; Gridelli, C. Prognostic Factors in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15, 4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.; Ng, T.L. A Narrative Review from Gut to Lungs: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and the Gastrointestinal Microbiome. Transl Lung Cancer Res 2023, 12, 909–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzo, F.; Maroccia, Z.; Hammarberg Ferri, I.; Fiorentini, C. Role of the Microbiota in Lung Cancer: Insights on Prevention and Treatment. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botticelli, A.; Vernocchi, P.; Marini, F.; Quagliariello, A.; Cerbelli, B.; Reddel, S.; Del Chierico, F.; Di Pietro, F.; Giusti, R.; Tomassini, A.; et al. Gut Metabolomics Profiling of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients under Immunotherapy Treatment. J Transl Med 2020, 18, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, T. Gut Microbiota: A Promising Milestone in Enhancing the Efficacy of PD1/PD-L1 Blockade Therapy. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 847350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.Y.; Wu, C.-Y.; Yu, J. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Cancer Treatment: Friend or Foe? Gut 2020, 69, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; Shohag, S.; Ahasan, M.T.; Sarkar, N.; Khan, H.; Hasan, A.M.; Cavalu, S.; Rauf, A. Microbiome in Cancer: Role in Carcinogenesis and Impact in Therapeutic Strategies. Biomed Pharmacother 2022, 149, 112898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredin, P.; Naidoo, J. Correction to: The Gut Microbiome, Immune Check Point Inhibition and Immune-related Adverse Events in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Z. Gut-Lung Axis: Role of the Gut Microbiota in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Immunotherapy. Front Oncol 2023, 13, 1257515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, K.; Marinov, B.; Farooqi, A.A.; Gazouli, M. Gut Microbiota in Lung Cancer: Where Do We Stand? Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 10429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, V.G.P.; Forder, A.; Pewarchuk, M.E.; Telkar, N.; de Araujo, R.P.; Stewart, G.L.; Vieira, J.; Reis, P.P.; Lam, W.L. The Complex Role of the Microbiome in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Development and Progression. Cells 2023, 12, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernocchi, P.; Gili, T.; Conte, F.; Del Chierico, F.; Conta, G.; Miccheli, A.; Botticelli, A.; Paci, P.; Caldarelli, G.; Nuti, M.; et al. Network Analysis of Gut Microbiome and Metabolome to Discover Microbiota-Linked Biomarkers in Patients Affected by Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, 8730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Dong, H.; Xia, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, H.; Yao, C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S. The Diversity of Gut Microbiome Is Associated With Favorable Responses to Anti–Programmed Death 1 Immunotherapy in Chinese Patients With NSCLC. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2019, 14, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.; Liu, C.-G.; Zang, D.; Chen, J. Gut Microbiota and Dietary Intervention: Affecting Immunotherapy Efficacy in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front Immunol 2024, 15, 1343450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Deng, Y.; Shao, T.; Cui, Y.; Shen, Y. Causal Effects of Gut Microbiota in the Development of Lung Cancer and Its Histological Subtypes: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Thorac Cancer 2024, 15, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francino, M.P. Antibiotics and the Human Gut Microbiome: Dysbioses and Accumulation of Resistances. Front Microbiol 2016, 6, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, C.M.-M.; Lletí, A.C.C.; Sánchez, R.P.; Román, C.D.; Alonso, P.T.; González, B.F. Impact of the Use of Antibiotics on the Clinical Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Rev Esp Quimioter 2022, 35, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakozaki, T.; Okuma, Y.; Omori, M.; Hosomi, Y. Impact of Prior Antibiotic Use on the Efficacy of Nivolumab for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncol Lett 2019, 17, 2946–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J.E.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, M.Ah.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, I.-H. The Effect of Antibiotics on the Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Solid Cancers Undergoing Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment: A Retrospective Study. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Geng, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shi, N.; Dong, M. Effects of Concomitant Antibiotics Use on Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Efficacy in Cancer Patients. Frontiers in Oncology 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaderbhai, C.; Richard, C.; Fumet, J.D.; Aarnink, A.; Foucher, P.; Coudert, B.; Favier, L.; Lagrange, A.; Limagne, E.; Boidot, R.; et al. Antibiotic Use Does Not Appear to Influence Response to Nivolumab. Anticancer Research 2017, 37, 3195–3200. [Google Scholar]
- Derosa, L.; Hellmann, M.D.; Spaziano, M.; Halpenny, D.; Fidelle, M.; Rizvi, H.; Long, N.; Plodkowski, A.J.; Arbour, K.C.; Chaft, J.E.; et al. Negative Association of Antibiotics on Clinical Activity of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Advanced Renal Cell and Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Ann Oncol 2018, 29, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huemer, F.; Rinnerthaler, G.; Westphal, T.; Hackl, H.; Hutarew, G.; Gampenrieder, S.P.; Weiss, L.; Greil, R. Impact of Antibiotic Treatment on Immune-Checkpoint Blockade Efficacy in Advanced Non-Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 16512–16520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Gao, G.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, T.; Jia, Y.; He, Y.; Li, A.; Su, C.; et al. Antibiotics Are Associated with Attenuated Efficacy of Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Therapies in Chinese Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2019, 130, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, G.; Triulzi, T.; Proto, C.; Signorelli, D.; Imbimbo, M.; Poggi, M.; Fucà, G.; Ganzinelli, M.; Vitali, M.; Palmieri, D.; et al. Association between Antibiotic-Immunotherapy Exposure Ratio and Outcome in Metastatic Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2019, 132, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.-H.; Tsai, T.-C.; Chang, J.W.-C.; Deng, S.-T.; Cheng, C.-Y. Association of Prior Fluoroquinolone Treatment with Survival Outcomes of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Asia. J Clin Pharm Ther 2021, 46, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Ruiz, E.; Jiménez-Castro, J.; Berciano-Guerrero, M.-A.; Valdivia, J.; Estalella-Mendoza, S.; Toscano, F.; Rodriguez de la Borbolla Artacho, M.; Garrido-Siles, M.; Martínez-Bautista, M.J.; Villatoro Roldan, R.; et al. Impact of Intestinal Dysbiosis-Related Drugs on the Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Clinical Practice. Clin Transl Oncol 2020, 22, 1778–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svaton, M.; Zemanova, M.; Zemanova, P.; Kultan, J.; Fischer, O.; Skrickova, J.; Jakubikova, L.; Cernovska, M.; Hrnciarik, M.; Jirousek, M.; et al. Impact of Concomitant Medication Administered at the Time of Initiation of Nivolumab Therapy on Outcome in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Anticancer Res 2020, 40, 2209–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalabi, M.; Cardona, A.; Nagarkar, D.R.; Dhawahir Scala, A.; Gandara, D.R.; Rittmeyer, A.; Albert, M.L.; Powles, T.; Kok, M.; Herrera, F.G.; et al. Efficacy of Chemotherapy and Atezolizumab in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Receiving Antibiotics and Proton Pump Inhibitors: Pooled Post Hoc Analyses of the OAK and POPLAR Trials. Ann Oncol 2020, 31, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinsley, N.; Zhou, C.; Tan, G.; Rack, S.; Lorigan, P.; Blackhall, F.; Krebs, M.; Carter, L.; Thistlethwaite, F.; Graham, D.; et al. Cumulative Antibiotic Use Significantly Decreases Efficacy of Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Oncologist 2020, 25, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.A.; Ebadi, M.; Zhang, S.; Meybodi, M.A.; Ali, A.M.; DeFor, T.; Shanley, R.; Weisdorf, D.; Ryan, C.; Vasu, S.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Antibiotic Exposure Association with Clinical Outcomes of Chemotherapy versus Immunotherapy across Three Tumour Types. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e000803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geum, M.J.; Kim, C.; Kang, J.E.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Son, E.S.; Lim, S.M.; Rhie, S.J. Broad-Spectrum Antibiotic Regimen Affects Survival in Patients Receiving Nivolumab for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2021, 14, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortellini, A.; Ricciuti, B.; Facchinetti, F.; Alessi, J.V.M.; Venkatraman, D.; Dall’Olio, F.G.; Cravero, P.; Vaz, V.R.; Ottaviani, D.; Majem, M.; et al. Antibiotic-Exposed Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Preserve Efficacy Outcomes Following First-Line Chemo-Immunotherapy. Ann Oncol 2021, 32, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impact of Antibiotics and Proton Pump Inhibitors on Efficacy and Tolerance of Anti-PD-1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors - PubMed Available online:. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34777340/ (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Cortellini, A.; Di Maio, M.; Nigro, O.; Leonetti, A.; Cortinovis, D.L.; Aerts, J.G.; Guaitoli, G.; Barbieri, F.; Giusti, R.; Ferrara, M.G.; et al. Differential Influence of Antibiotic Therapy and Other Medications on Oncological Outcomes of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with First-Line Pembrolizumab versus Cytotoxic Chemotherapy. J Immunother Cancer 2021, 9, e002421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Hirasawa, Y.; Hosonuma, M.; Murayama, M.; Narikawa, Y.; Ariizumi, H.; Ohkuma, R.; Shida, M.; Kubota, Y.; et al. Antibiotic Usage Reduced Overall Survival by over 70% in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients on Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy. Anticancer Research 2021, 41, 4985–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, A.M.; Badaoui, S.; Kichenadasse, G.; Karapetis, C.S.; McKinnon, R.A.; Rowland, A.; Sorich, M.J. Efficacy of Atezolizumab in Patients With Advanced NSCLC Receiving Concomitant Antibiotic or Proton Pump Inhibitor Treatment: Pooled Analysis of Five Randomized Control Trials. J Thorac Oncol 2022, 17, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyein, A.F.; Bari, S.; Hogue, S.; Zhao, Y.; Maller, B.; Sha, S.; Gomez, M.F.; Rollison, D.E.; Robinson, L.A. Effect of Prior Antibiotic or Chemotherapy Treatment on Immunotherapy Response in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Ma, Q.-G.; Chen, X.-T.; Wen, X.; Zhang, N.; Liu, W.-M.; Wang, T.-T.; Zhang, L.-Z. Different Classes of Antibiotics Exhibit Disparate Negative Impacts on the Therapeutic Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Am J Cancer Res 2022, 12, 3175–3184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manning-Bennett, A.T.; Cervesi, J.; Bandinelli, P.-A.; Sorich, M.J.; Hopkins, A.M. Prognostic Associations of Concomitant Antibiotic Use in Patients with Advanced NSCLC Treated with Atezolizumab: Sensitivity Analysis of a Pooled Investigation of Five Randomised Control Trials. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihinen, H.; Jokinen, A.; Laajala, T.D.; Wahid, N.; Peltola, L.; Kettunen, T.; Rönkä, A.; Tiainen, L.; Skyttä, T.; Kohtamäki, L.; et al. Antibiotic Treatment Is an Independent Poor Risk Factor in NSCLC But Not in Melanoma Patients Who Had Received Anti-PD-1/L1 Monotherapy. Clin Lung Cancer 2023, 24, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakozaki, T.; Richard, C.; Elkrief, A.; Hosomi, Y.; Benlaïfaoui, M.; Mimpen, I.; Terrisse, S.; Derosa, L.; Zitvogel, L.; Routy, B.; et al. The Gut Microbiome Associates with Immune Checkpoint Inhibition Outcomes in Patients with Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Immunology Research 2020, 8, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenda, A.; Iwan, E.; Krawczyk, P.; Frąk, M.; Chmielewska, I.; Bomba, A.; Giza, A.; Rolska-Kopińska, A.; Szczyrek, M.; Kieszko, R.; et al. Attempting to Identify Bacterial Allies in Immunotherapy of NSCLC Patients. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14, 6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Yang, D.; Wang, H.; Cui, X.; Si, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. Relationship between Intestinal Flora Structure and Metabolite Analysis and Immunotherapy Efficacy in Chinese NSCLC Patients. Thorac Cancer 2020, 11, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, K.; Shimokawa, M.; Takamori, S.; Shimamatsu, S.; Hirai, F.; Tagawa, T.; Okamoto, T.; Hamatake, M.; Tsuchiya-Kawano, Y.; Otsubo, K.; et al. Clinical Impact of Probiotics on the Efficacy of Anti-PD-1 Monotherapy in Patients with Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer: A Multicenter Retrospective Survival Analysis Study with Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting. International Journal of Cancer 2021, 149, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Wu, C.; Wu, Q.; Luo, S.; Liu, J.; Xie, X. Impact of Probiotics Use on Clinical Outcomes of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Therapy in Cancer Patients. Cancer Med 2022, 12, 1841–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Sakata, S.; Imamura, K.; Iyama, S.; Jodai, T.; Saruwatari, K.; Hamada, S.; Akaike, K.; Anai, M.; Fukusima, K.; et al. Association of Clostridium Butyricum Therapy Using the Live Bacterial Product CBM588 with the Survival of Patients with Lung Cancer Receiving Chemoimmunotherapy Combinations. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamura, K. Roles of Microbiota in Response to Cancer Immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol 2020, 65, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, L.; Song, B. Impact of Opioid Analgesics on the Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in a Lung Cancer Population. BMC Pulm Med 2022, 22, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, Y.-H.; Kang, E.J.; Hong, S.; Park, S.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, J.-Y. Survival Outcomes of Patients with Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Concomitantly Receiving Proton Pump Inhibitors and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. International Journal of Cancer 2022, 150, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, S.; Pabst, L.; Dory, A.; Klotz, M.; Gourieux, B.; Michel, B.; Mascaux, C. Do Proton Pump Inhibitors Alter the Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Patients? A Meta-Analysis. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1070076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duttagupta, S.; Hakozaki, T.; Routy, B.; Messaoudene, M. The Gut Microbiome from a Biomarker to a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Immunotherapy Response in Patients with Lung Cancer. Curr Oncol 2023, 30, 9406–9427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippenszky, L.; Mittendorf, K.F.; Kiss, Z.; LeNoue-Newton, M.L.; Napan-Molina, P.; Rahman, P.; Ye, C.; Laczi, B.; Csernai, E.; Jain, N.M.; et al. Prediction of Effectiveness and Toxicities of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Using Real-World Patient Data. JCO Clin Cancer Inform 2024, 8, e2300207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuffrè, M.; Moretti, R.; Tiribelli, C. Gut Microbes Meet Machine Learning: The Next Step towards Advancing Our Understanding of the Gut Microbiome in Health and Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Jo, J.-H.; Zhang, Z.; MacGibeny, M.A.; Han, J.; Proctor, D.M.; Taylor, M.E.; Che, Y.; Juneau, P.; Apolo, A.B.; et al. Predicting Cancer Immunotherapy Response from Gut Microbiomes Using Machine Learning Models. Oncotarget 2022, 13, 876–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | Study | Patients | Treatment | ANTIBIOTICS typologies | ANTIBIOTICS exposistion timing | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | Antibiotic Use Does Not Appear to Influence Response to Nivolumab | 74 | Anti PD1, Nivolumab |
Fluoroquinolones |
3 Months Before ICIs starting | [21] |
| 2018 | Negative association of antibiotics on clinical activity of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced renal cell and non-small-cell lung cancer | 239 | Anti PD1, Anti CTLA4 Monotherapy or Combination |
Fluoroquinolones Betalactams |
30 days before immunotherapy starting | [22] |
| 2018 | Impact of prior antibiotic use on the efficacy of nivolumab for non-small cell lung cancer | 90 | Anti PD1, Nivolumab |
Not specified | 30 days before immunotherapy starting | [18] |
| 2018 | Impact of antibiotic treatment on immune-checkpoint blockade efficacy in advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer | 30 | Anti PD1, Nivolumab, Pembrolizumab |
Not specified | 30 days before and after immunotherapy starting | [23] |
| 2019 | Antibiotics are associated with attenuated efficacy of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapies in Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer | 109 | Anti PD1, Anti PDL1 |
Not specified | Not Specified | [24] |
| 2019 | The effect of antibiotics on the clinical outcomes of patients with solid cancers undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment: a retrospective study | 131 | Anti PD1, Anti PDL1, Anti CTLA4 Monotherapy or Combination |
Fluoroquinolones, Betalactms Cephalosporins |
60 days before immunotgerapy starting | [19] |
| 2019 | Association between Antibiotic-Immunotherapy Exposure Ratio and outcome in metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | 157 | Anti PD1, Anti PDL1, Anti CTLA4 Monotherapy or Combination |
Not Specified | Before and During Immunotherapy | [25] |
| 2020 | Association of prior fluoroquinolone treatment with survival outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitors in Asia | 340 | Anti PD1, Anti PD1, Anti CTLA4 Monotherapy or Combination |
Fluoroquinolones | 30 days before immunotherapy starting | [26] |
| 2020 | Impact of intestinal dysbiosis-related drugs on the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in clinical practice | 120 | Anti PD1, Anti CTLA4 Monotherapy or Combination |
Not Specified | Not Specified | [27] |
| 2020 | Impact of Concomitant Medication Administered at the Time of Initiation of Nivolumab Therapy on Outcome in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer | 224 | Anti PD1, Nivolumab |
Not Specified | Not Specified | [28] |
| 2020 | Efficacy of chemotherapy and atezolizumab in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer receiving antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors: pooled post hoc analyses of the OAK and POPLAR trials | 757 | Anti PDL1, Atezolizumab |
Fluoroquinolones, Carbapanems, Macrolides, Glycopeptides |
30 days before and after immunotherapy starting | [29] |
| 2020 | Cumulative Antibiotic Use Significantly Decreases Efficacy of Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Advanced Cancer | 64 | Anti PD1 | Not Specified | 15 days before and 45 after starting immunotherapy | [30] |
| 2020 | Comparative analysis of antibiotic exposure association with clinical outcomes of chemotherapy versus immunotherapy across three tumour types | 140 | Anti PD1 | Vancomicyn, Nitrofurantoin, Rifampin, Rifaximin, Tobramicyn, |
30 days befor and after immunotherapy stating | [31] |
| 2021 | Broad-Spectrum Antibiotic Regimen Affects Survival in Patients Receiving Nivolumab for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | 140 | Anti PD1, Nivolumab |
Not Specified | Not Specified | [32] |
| 2021 | Antibiotic-exposed patients with non-small-cell lung cancer preserve efficacy outcomes following first-line chemo-immunotherapy | 302 | Chemotherapy Immunotherapy |
Not Specified | 7 days before and after immunotherapy starting | [33] |
| 2021 | Impact of Antibiotics and Proton Pump Inhibitors on Efficacy and Tolerance of Anti-PD-1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors | 65 | Anti PD1, Anti CTLA4 Monotherapy or Combination |
Not Specified | 60 days before immunotherapy starting | [34] |
| 2021 | Differential influence of antibiotic therapy and other medications on oncological outcomes of patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with first-line pembrolizumab versus cytotoxic chemotherapy | 950 | Anti PD1, Pembrolizumab |
Piperacillin-Tazobactam, Clindamycin, Metronidazole, Meropenem | 30 days before immunotherapy starting | [35] |
| 2021 | Antibiotic Usage Reduced Overall Survival by over 70% in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients | 69 | Anti PD1 | Not Specified | 21 days before immunotherapy starting | [36] |
| 2022 | Efficacy of Atezolizumab in Patients With Advanced NSCLC Receiving Concomitant Antibiotic or Proton Pump Inhibitor Treatment: Pooled Analysis of Five Randomized Control Trials | 2723 | Anti PDL1, Atezolizumab |
Not Specified | 30 days before immunotherapy starting | [37] |
| 2022 | Impact of the use of antibiotics on the clinical response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer | 140 | Anti PD1, Anti PD1, Anti CTLA4 Monotherapy or Combination |
Fluoroquinolones, Betalactms |
2 months before and after immunotherapy starting | [17] |
| 2022 | Effect of prior antibiotic or chemotherapy treatment on immunotherapy response in non-small cell lung cancer | 256 | Anti PD1, Anti PDL1, Anti CTLA4 Monotherapy or Combination |
Fluoroquinolones, Cefazolin, Azithromicin |
60 days before and after immunotherapy starting | [38] |
| 2022 | Different classes of antibiotics exhibit disparate negative impacts on the therapeutic efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients | 148 | Anti PD1, Anti PDL1, Chemotherapy |
Fluoroquinolones, Betalactms |
60 days before and after immunotherapy starting | [39] |
| 2023 | Prognostic Associations of Concomitant Antibiotic Use in Patients with Advanced NSCLC Treated with Atezolizumab: Sensitivity Analysis of a Pooled Investigation of Five Randomised Control Trials | 2724 | Anti PDL1, Atezolizumab, Alone or in combination with chemotherapy |
Not Specified | Not Specified | [40] |
| 2023 | Antibiotic Treatment is an Independent Poor Risk Factor in NSCLC But Not in Melanoma Patients Who had Received Anti-PD-1/L1 Monotherapy | 199 | Anti PD1, Anti PDL1 |
Not Specified | 3 months before and 1 months after immunotherapy starting | [41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





