Submitted:
13 March 2024
Posted:
14 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. 11-cis Retinal, Vitamin A Metabolism, and Vitamin A Membrane Receptors

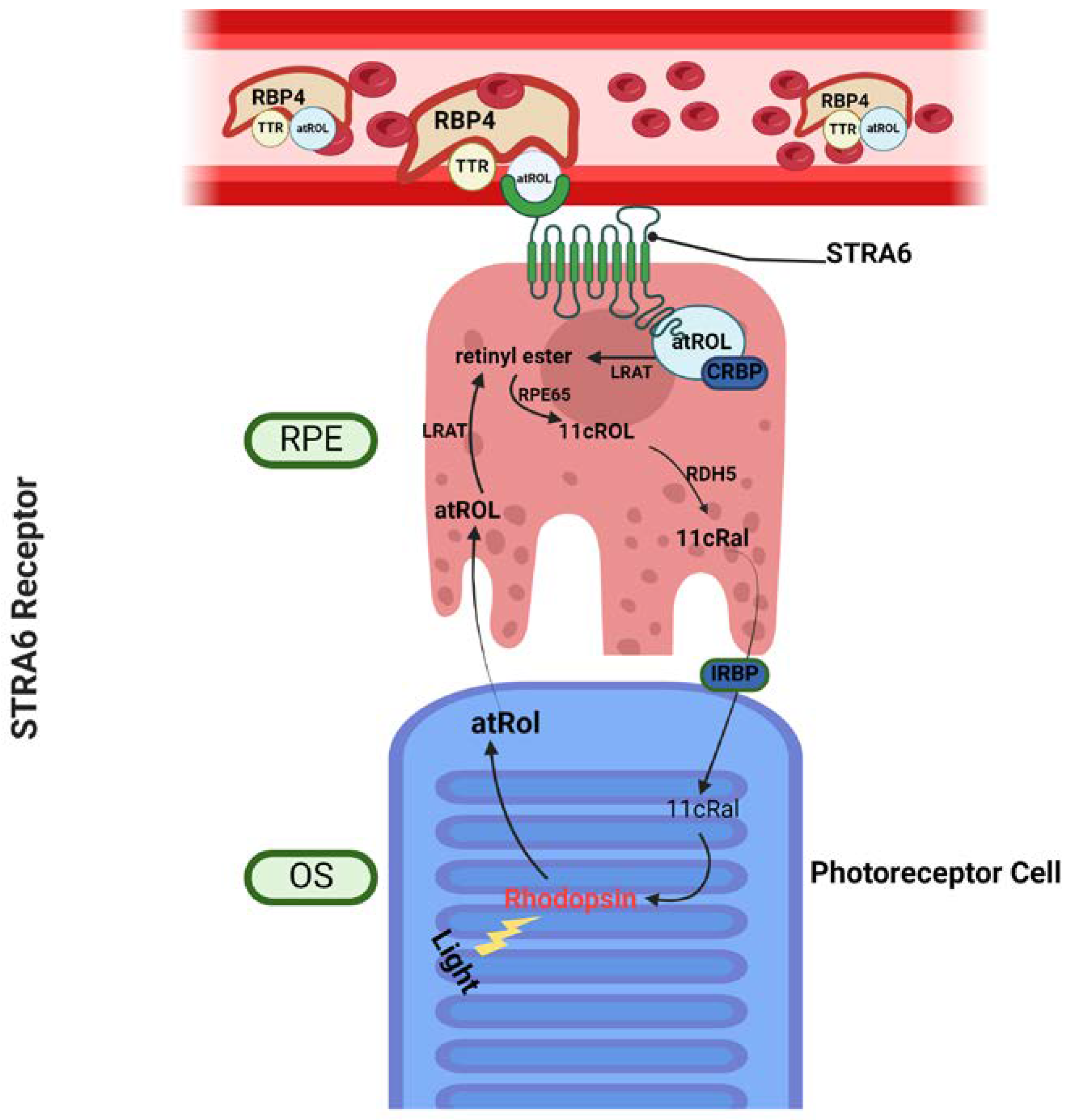
3. The Role of Vitamin A Membrane Receptors in Sustaining Visual Function
3.1. Stimulated by Retinoic Acid 6 – STRA6
3.2. Retinol Binding Protein 4 Receptor 2 – RBPR2
4. Opsin, Photoreceptor Morphology, Dynein and Kinesin Motor Proteins, and Unconventional Myosin Motor Proteins
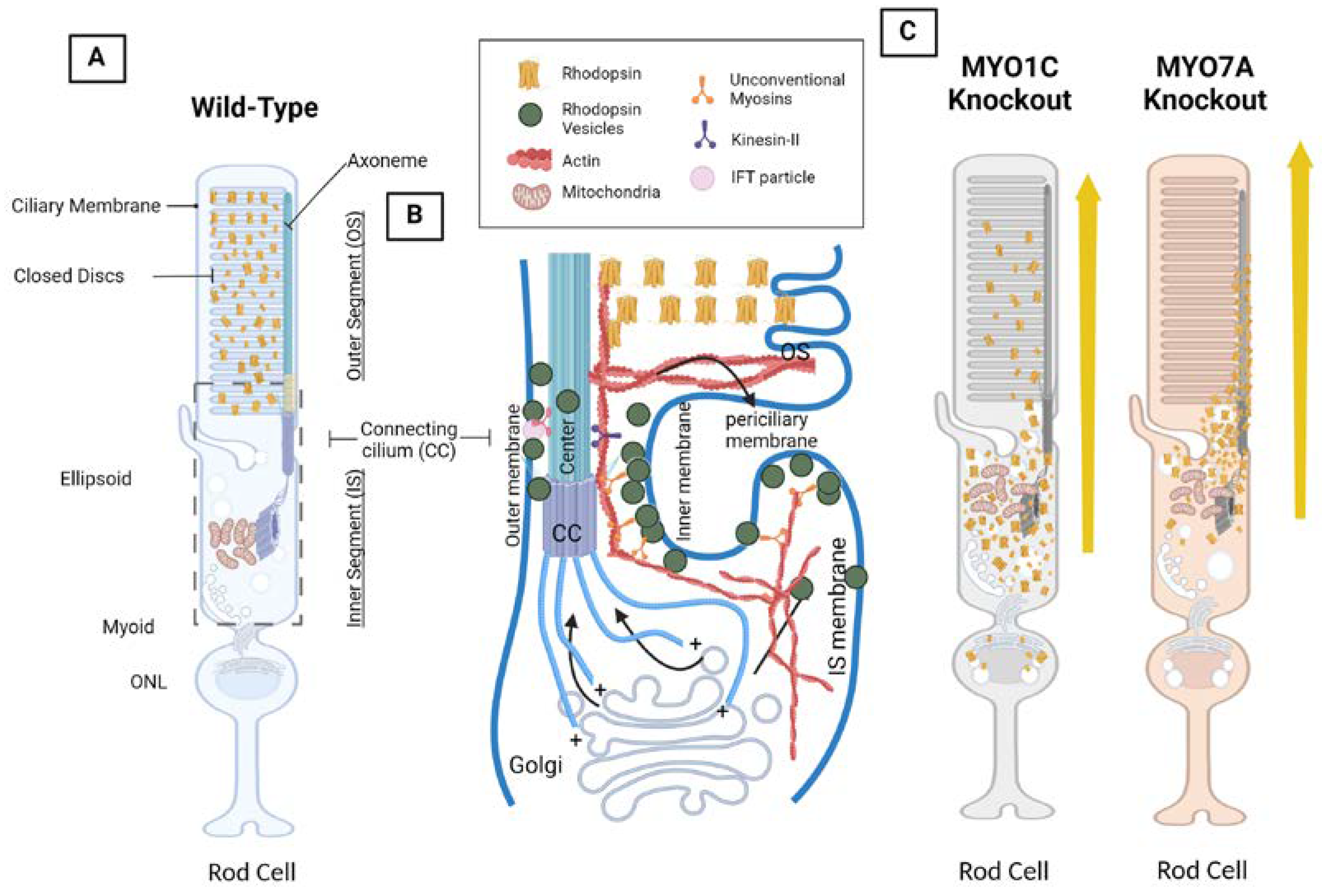
4.1. The VxPx Domain and the Arf4 Complex: Post-Golgi Rhodopsin Transport through a Ciliary Targeting Complex
4.2. Cytoplasmic Dynein Motor Proteins and Tctex-1: Post-Golgi Rhodopsin Transport through Retrograde Microtubule Transport
4.3. Kinesin Motor Proteins and IFT: Through the Connecting Cilium to the Outer Segment
4.4. Myosin Motor Protein 7A: MYO7A
4.5. Unconventional Myosin Motor Protein 1C, MYO1C: A New Player in Understanding Rod Opsin Transport in Visual Function
5. The Visual Cycle and Phototransduction Cascade – Actions of Vitamin A Receptors and Myosin Motor Proteins Converge and Form the Retinylidene Protein
6. Concluding Remarks and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shichida, Y.; Matsuyama, T. Evolution of Opsins and Phototransduction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2881–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, R.; Dronamraju, V.R.; Leung, M.; Gruesen, A.; Solanki, A.K.; Walterhouse, S.; Roehrich, H.; Song, G.; da Costa Monsanto, R.; Cureoglu, S.; et al. The Role of Motor Proteins in Photoreceptor Protein Transport and Visual Function. Ophthalmic Genet. 2022, 43, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, R.; Yu, J.; Honda, J.; Hu, J.; Whitelegge, J.; Ping, P.; Wiita, P.; Bok, D.; Sun, H. A Membrane Receptor for Retinol Binding Protein Mediates Cellular Uptake of Vitamin A. Science 2007, 315, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, M.; Goletz, P.W.; Crouch, R.K. 11-Cis and All-Trans Retinols Can Activate Rod Opsin: Rational Design of the Visual Cycle. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 7567–7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, J.E.; Wald, G. Vitamin A deficiency and night blindness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1958, 44, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, J.E.; Wald, G. The biological function of vitamin A acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1960, 46, 587–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiser, P.D.; Palczewski, K. Retinoids and Retinal Diseases. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 2016, 2, 197–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.R.; Cohen, G.B.; Zhukovsky, E.A.; Oprian, D.D. Constitutively Active Mutants of Rhodopsin. Neuron 1992, 9, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, G.P.; Amengual, J.; Palczewski, G.; Babino, D.; von Lintig, J. Carotenoid-Oxygenases: Key Players for Carotenoid Function and Homeostasis in Mammalian Biology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amengual, J.; Widjaja-Adhi, M.A.K.; Rodriguez-Santiago, S.; Hessel, S.; Golczak, M.; Palczewski, K.; von Lintig, J. Two Ca-rotenoid Oxygenases Contribute to Mammalian Provitamin A Metabolism ♦. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 34081–34096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.H. Mechanisms Involved in the Intestinal Absorption of Dietary Vitamin A and Provitamin A Carotenoids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.H. Carotenoids, β-Apocarotenoids, and Retinoids: The Long and the Short of It. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wongsiriroj, N.; Blaner, W.S. The Multifaceted Nature of Retinoid Transport and Metabolism. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2014, 3, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Byrne, S.M.; Blaner, W.S. Retinol and Retinyl Esters: Biochemistry and Physiology. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1731–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bok, D.; Heller, J. Transport of Retinol from the Blood to the Retina: An Autoradiographic Study of the Pigment Epithelial Cell Surface Receptor for Plasma Retinol-Binding Protein. Exp. Eye Res. 1976, 22, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, P.; Desmarchelier, C. Genetic Variations Associated with Vitamin A Status and Vitamin A Bioavailability. Nutrients 2017, 9, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Heller, J. Uptake of Retinol and Retinoic Acid from Serum Retinol-Binding Protein by Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 5216–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjøen, T.; Bjerkelund, T.; Blomhoff, H.K.; Norum, K.R.; Berg, T.; Blomhoff, R. Liver Takes up Retinol-Binding Protein from Plasma. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 10926–10930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomhoff, R.; Norum, K.R.; Berg, T. Hepatic Uptake of [3H]Retinol Bound to the Serum Retinol Binding Protein Involves Both Parenchymal and Perisinusoidal Stellate Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 13571–13575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, M.; Raz, A.; Goodman, D.S. Retinol-Binding Protein: The Transport Protein for Vitamin A in Human Plasma. J. Clin. Invest. 1968, 47, 2025–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, M.; von Lintig, J. STRA6: Role in Cellular Retinol Uptake and Efflux. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2015, 4, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadro, L.; Blaner, W.S.; Hamberger, L.; Novikoff, P.M.; Vogel, S.; Piantedosi, R.; Gottesman, M.E.; Colantuoni, V. The Role of Extrahepatic Retinol Binding Protein in the Mobilization of Retinoid Stores. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaner, W.S. STRA6, a Cell-Surface Receptor for Retinol-Binding Protein: The Plot Thickens. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillet, P.; Sapin, V.; Chazaud, C.; Messaddeq, N.; Décimo, D.; Dollé, P.; Chambon, P. Developmental Expression Pattern of Stra6, a Retinoic Acid-Responsive Gene Encoding a New Type of Membrane Protein. Mech. Dev. 1997, 63, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, J.; Kawaguchi, R.; Morrissey, M.; Sun, H.; McGettigan, P.; Nielsen, J.E.; Conroy, J.; Regan, R.; Kenny, E.; Cormican, P.; et al. First Implication of STRA6 Mutations in Isolated Anophthalmia, Microphthalmia, and Coloboma: A New Dimension to the STRA6 Phenotype. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golzio, C.; Martinovic-Bouriel, J.; Thomas, S.; Mougou-Zrelli, S.; Grattagliano-Bessieres, B.; Bonniere, M.; Delahaye, S.; Munnich, A.; Encha-Razavi, F.; Lyonnet, S.; et al. Matthew-Wood Syndrome Is Caused by Truncating Mutations in the Retinol-Binding Protein Receptor Gene STRA6. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 80, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, J.; Bok, D. A Specific Receptor for Retinol Binding Protein as Detected by the Binding of Human and Bovine Retinol Binding Protein to Pigment Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1976, 81, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.; Ramkumar, S.; von Lintig, J. Genetic Tuning of β-Carotene Oxygenase-1 Activity Rescues Cone Photoreceptor Function in STRA6-Deficient Mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2023, 32, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasutto, F.; Sticht, H.; Hammersen, G.; Gillessen-Kaesbach, G.; Fitzpatrick, D.R.; Nürnberg, G.; Brasch, F.; Schirm-er-Zimmermann, H.; Tolmie, J.L.; Chitayat, D.; et al. Mutations in STRA6 Cause a Broad Spectrum of Malformations Including Anophthalmia, Congenital Heart Defects, Diaphragmatic Hernia, Alveolar Capillary Dysplasia, Lung Hypoplasia, and Mental Retardation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 80, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alapatt, P.; Guo, F.; Komanetsky, S.M.; Wang, S.; Cai, J.; Sargsyan, A.; Rodríguez Díaz, E.; Bacon, B.T.; Aryal, P.; Graham, T.E. Liver Retinol Transporter and Receptor for Serum Retinol-Binding Protein (RBP4). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 1250–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, R.; Leung, M.; Roehrich, H.; Walterhouse, S.; Kondkar, A.A.; Fitzgibbon, W.; Biswal, M.R.; Lobo, G.P. Mice Lacking the Systemic Vitamin A Receptor RBPR2 Show Decreased Ocular Retinoids and Loss of Visual Function. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, O. The Retinal Pigment Epithelium in Visual Function. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 845–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin Ask, N.; Leung, M.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Lobo, G.P. Vitamin A Transporters in Visual Function: A Mini Review on Membrane Receptors for Dietary Vitamin A Uptake, Storage, and Transport to the Eye. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Yoshizawa, T.; Kamio, S.; Aoki, O.; Kawamata, Y.; Masushige, S.; Kato, S. Interactions of Transthyretin (TTR) and Retinol-Binding Protein (RBP) in the Uptake of Retinol by Primary Rat Hepatocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 1997, 234, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, R.; Leung, M.; Solanki, A.K.; Lobo, G.P. Mapping of the Extracellular RBP4 Ligand Binding Domain on the RBPR2 Receptor for Vitamin A Transport. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solanki, A.K.; Kondkar, A.A.; Fogerty, J.; Su, Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Lipschutz, J.H.; Nihalani, D.; Perkins, B.D.; Lobo, G.P. A Func-tional Binding Domain in the Rbpr2 Receptor Is Required for Vitamin A Transport, Ocular Retinoid Homeostasis, and Pho-toreceptor Cell Survival in Zebrafish. Cells 2020, 9, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Obert, E.; Rahman, B.; Rohrer, B.; Lobo, G.P. The Retinol Binding Protein Receptor 2 (Rbpr2) Is Required for Photo-receptor Outer Segment Morphogenesis and Visual Function in Zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, G.P.; Pauer, G.; Lipschutz, J.H.; Hagstrom, S.A. The Retinol-Binding Protein Receptor 2 (Rbpr2) Is Required for Pho-toreceptor Survival and Visual Function in the Zebrafish. In Proceedings of the Retinal Degenerative Diseases; Ash, J.D., Anderson, R.E., LaVail, M.M., Bowes Rickman, C., Hollyfield, J.G., Grimm, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2018; pp. 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molday, R.S.; Moritz, O.L. Photoreceptors at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 4039–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, N.; Lai, W.; Wang, F.; Zhu, X.; Wang, T. ER Complex Proteins Are Required for Rhodopsin Biosynthesis and Photoreceptor Survival in Drosophila and Mice. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 646–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimeno, D.; Feiner, L.; Lillo, C.; Teofilo, K.; Goldstein, L.S.B.; Pierce, E.A.; Williams, D.S. Analysis of Kinesin-2 Function in Photoreceptor Cells Using Synchronous Cre-loxP Knockout of Kif3a with RHO-Cre. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 5039–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marszalek, J.R.; Liu, X.; Roberts, E.A.; Chui, D.; Marth, J.D.; Williams, D.S.; Goldstein, L.S.B. Genetic Evidence for Selective Transport of Opsin and Arrestin by Kinesin-II in Mammalian Photoreceptors. Cell 2000, 102, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.H.; Makino, C.; Baylor, D.; Nathans, J. A Rhodopsin Gene Mutation Responsible for Autosomal Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa Results in a Protein That Is Defective in Localization to the Photoreceptor Outer Segment. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 5818–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concepcion, F.; Chen, J. Q344ter Mutation Causes Mislocalization of Rhodopsin Molecules That Are Catalytically Active: A Mouse Model of Q344ter-Induced Retinal Degeneration. PloS One 2010, 5, e10904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concepcion, F.; Mendez, A.; Chen, J. The Carboxyl-Terminal Domain Is Essential for Rhodopsin Transport in Rod Photore-ceptors. Vision Res. 2002, 42, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deretic, D.; Schmerl, S.; Hargrave, P.A.; Arendt, A.; McDowell, J.H. Regulation of Sorting and Post-Golgi Trafficking of Rhodopsin by Its C-Terminal Sequence QVS(A)PA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 10620–10625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deretic, D.; Williams, A.H.; Ransom, N.; Morel, V.; Hargrave, P.A.; Arendt, A. Rhodopsin C Terminus, the Site of Mutations Causing Retinal Disease, Regulates Trafficking by Binding to ADP-Ribosylation Factor 4 (ARF4). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2005, 102, 3301–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Morita, Y.; Mazelova, J.; Deretic, D. The Arf GAP ASAP1 Provides a Platform to Regulate Arf4- and Rab11–Rab8-mediated Ciliary Receptor Targeting. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 4057–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgan, C.P.; Hanscom, S.R.; Jolly, R.S.; Futter, C.E.; McCaffrey, M.W. Rab11-FIP3 Links the Rab11 GTPase and Cytoplasmic Dynein to Mediate Transport to the Endosomal-Recycling Compartment. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, C.P.; Hanscom, S.R.; Jolly, R.S.; Futter, C.E.; McCaffrey, M.W. Rab11-FIP3 Binds Dynein Light Intermediate Chain 2 and Its Overexpression Fragments the Golgi Complex. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 394, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Du, X.; Peng, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Jin, X.; Hou, L.; Deng, K.; Xu, T.; Tao, W. Dlic1 Deficiency Impairs Ciliogenesis of Photoreceptors by Destabilizing Dynein. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, A.W.; Chuang, J.-Z.; Bode, C.; Wolfrum, U.; Sung, C.-H. Rhodopsin’s Carboxy-Terminal Cytoplasmic Tail Acts as a Membrane Receptor for Cytoplasmic Dynein by Binding to the Dynein Light Chain Tctex-1. Cell 1999, 97, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearring, J.N.; San Agustin, J.T.; Lobanova, E.S.; Gabriel, C.J.; Lieu, E.C.; Monis, W.J.; Stuck, M.W.; Strittmatter, L.; Jaber, S.M.; Arshavsky, V.Y.; et al. Loss of Arf4 Causes Severe Degeneration of the Exocrine Pancreas but Not Cystic Kidney Disease or Retinal Degeneration. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, G.; Gerstner, C.D.; Frederick, J.M.; Boye, S.L.; Hauswirth, W.W.; Baehr, W. Small GTPases Rab8a and Rab11a Are Dispensable for Rhodopsin Transport in Mouse Photoreceptors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Fresquez, T.; Kandachar, V.; Deretic, D. The Arf GEF GBF1 and Arf4 Synergize with the Sensory Receptor Cargo, Rhodopsin, to Regulate Ciliary Membrane Trafficking. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 3975–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deretic, D.; Lorentzen, E.; Fresquez, T. The Ins and Outs of the Arf4-Based Ciliary Membrane-Targeting Complex. Small GTPases 2021, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baehr, W.; Hanke-Gogokhia, C.; Sharif, A.; Reed, M.; Dahl, T.; Frederick, J.M.; Ying, G. Insights into Photoreceptor Ciliogenesis Revealed by Animal Models. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2019, 71, 26–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troutt, L.L.; Burnside, B. Microtubule Polarity and Distribution in Teleost Photoreceptors. J. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krock, B.L.; Mills-Henry, I.; Perkins, B.D. Retrograde Intraflagellar Transport by Cytoplasmic Dynein-2 Is Required for Outer Segment Extension in Vertebrate Photoreceptors but Not Arrestin Translocation. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 5463–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insinna, C.; Baye, L.M.; Amsterdam, A.; Besharse, J.C.; Link, B.A. Analysis of a Zebrafish Dync1h1 Mutant Reveals Multiple Functions for Cytoplasmic Dynein 1 during Retinal Photoreceptor Development. Neural Develop. 2010, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, T.M.; Reed, M.; Gerstner, C.D.; Ying, G.; Baehr, W. Effect of Conditional Deletion of Cytoplasmic Dynein Heavy Chain DYNC1H1 on Postnatal Photoreceptors. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringo, D.L. Flagellar motion and fine structure of the flagellar apparatus in Chlamydomonas. J. Cell Biol. 1967, 33, 543–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, T.M. Cytoplasmic and Ciliary Connections between the Inner and Outer Segments of Mammalian Visual Re-ceptors. Vision Res. 1969, 9, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogaraju, S.; Cajanek, L.; Fort, C.; Blisnick, T.; Weber, K.; Taschner, M.; Mizuno, N.; Lamla, S.; Bastin, P.; Nigg, E.A.; et al. Molecular Basis of Tubulin Transport Within the Cilium by IFT74 and IFT81. Science 2013, 341, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Thein, M.; Brust-Mascher, I.; Civelekoglu-Scholey, G.; Lu, Y.; Acar, S.; Prevo, B.; Shaham, S.; Scholey, J.M. Intrafla-gellar Transport Delivers Tubulin Isotypes to Sensory Cilium Middle and Distal Segments. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, W.F.; Rosenbaum, J.L. Intraflagellar Transport Balances Continuous Turnover of Outer Doublet Microtubules. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craft, J.M.; Harris, J.A.; Hyman, S.; Kner, P.; Lechtreck, K.F. Tubulin Transport by IFT Is Upregulated during Ciliary Growth by a Cilium-Autonomous Mechanism. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocaoglu, O.P.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Kurokawa, K.; Jonnal, R.S.; Miller, D.T. Photoreceptor Disc Shedding in the Living Human Eye. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 4554–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillaud, L.; Wong, R.; Hirokawa, N. Disruption of KIF17–Mint1 Interaction by CaMKII-Dependent Phosphorylation: A Molecular Model of Kinesin–Cargo Release. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Pang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Han, X.; Xu, Y.; Deng, H.; Pan, J. FLA8/KIF3B Phosphorylation Regulates Kinesin-II Interaction with IFT-B to Control IFT Entry and Turnaround. Dev. Cell 2014, 30, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholey, J.M. Kinesin-2: A Family of Heterotrimeric and Homodimeric Motors with Diverse Intracellular Transport Functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2013, 29, 443–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funabashi, T.; Katoh, Y.; Okazaki, M.; Sugawa, M.; Nakayama, K. Interaction of Heterotrimeric Kinesin-II with IFT-B–Connecting Tetramer Is Crucial for Ciliogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 2867–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, L.B.; Rosenbaum, J.L. Chapter Two Intraflagellar Transport (IFT): Role in Ciliary Assembly, Resorption and Signalling. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Ciliary Function in Mammalian Development; Academic Press, 2008; Volume 85, pp. 23–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, L.B.; Geimer, S.; Rosenbaum, J.L. Dissecting the Molecular Mechanisms of Intraflagellar Transport in Chlamydo-monas. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grissom, P.M.; Vaisberg, E.A.; McIntosh, J.R. Identification of a Novel Light Intermediate Chain (D2LIC) for Mammalian Cytoplasmic Dynein 2. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, C.A.; Tritschler, D.; Taulman, P.; Bower, R.; Yoder, B.K.; Porter, M.E. A Novel Dynein Light Intermediate Chain Colocalizes with the Retrograde Motor for Intraflagellar Transport at Sites of Axoneme Assembly in Chlamydomonas and Mammalian Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 2041–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, J.C.; Haycraft, C.J.; Thomas, J.H.; Yoder, B.K.; Swoboda, P. XBX-1 Encodes a Dynein Light Intermediate Chain Re-quired for Retrograde Intraflagellar Transport and Cilia Assembly in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 2057–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, J.L.; Witman, G.B. Intraflagellar Transport. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Wei, Y.; Ronquillo, C.C.; Marc, R.E.; Yoder, B.K.; Frederick, J.M.; Baehr, W. Heterotrimeric Kinesin-2 (KIF3) Mediates Transition Zone and Axoneme Formation of Mouse Photoreceptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 12765–12778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Tam, B.M.; Ying, G.; Wu, S.; Hauswirth, W.W.; Frederick, J.M.; Moritz, O.L.; Baehr, W. Kinesin Family 17 (Osmotic Avoidance Abnormal-3) Is Dispensable for Photoreceptor Morphology and Function. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2015, 29, 4866–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenekoop, R.K.; Arriaga, M.A.; Trzupek, K.M.; Lentz, J.J. Usher Syndrome Type I. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, S.; Umeki, N.; Ikebe, R.; Ikebe, M. Impacts of Usher Syndrome Type IB Mutations on Human Myosin VIIa Motor Function. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 9505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Vansant, G.; Udovichenko, I.P.; Wolfrum, U.; Williams, D.S. Myosin VIIa, the Product of the Usher 1B Syndrome Gene, Is Concentrated in the Connecting Cilia of Photoreceptor Cells. Cell Motil. 1997, 37, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasson, T.; Heintzelman, M.B.; Santos-Sacchi, J.; Corey, D.P.; Mooseker, M.S. Expression in Cochlea and Retina of Myosin VIIa, the Gene Product Defective in Usher Syndrome Type 1B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9815–9819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Udovichenko, I.P.; Brown, S.D.M.; Steel, K.P.; Williams, D.S. Myosin VIIa Participates in Opsin Transport through The Photoreceptor Cilium. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 6267–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, V.S.; Gibbs, D.; Libby, R.T.; Aleman, T.S.; Welch, D.L.; Lillo, C.; Jacobson, S.G.; Radu, R.A.; Steel, K.P.; Williams, D.S. The Usher 1B Protein, MYO7A, Is Required for Normal Localization and Function of the Visual Retinoid Cycle Enzyme, RPE65. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 2560–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, D.; Azarian, S.M.; Lillo, C.; Kitamoto, J.; Klomp, A.E.; Steel, K.P.; Libby, R.T.; Williams, D.S. Role of Myosin VIIa and Rab27a in the Motility and Localization of RPE Melanosomes. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 6473–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różanowski, B.; Burke, J.M.; Boulton, M.E.; Sarna, T.; Różanowska, M. Human RPE Melanosomes Protect from Photosensi-tized and Iron-Mediated Oxidation but Become Pro-Oxidant in the Presence of Iron upon Photodegradation. Invest. Ophthalmol Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 2838–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, A.K.; Biswal, M.R.; Walterhouse, S.; Martin, R.; Kondkar, A.A.; Knölker, H.-J.; Rahman, B.; Arif, E.; Husain, S.; Montezuma, S.R.; et al. Loss of Motor Protein MYO1C Causes Rhodopsin Mislocalization and Results in Impaired Visual Function. Cells 2021, 10, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollingsworth, T.J.; Gross, A.K. Chapter One - Defective Trafficking of Rhodopsin and Its Role in Retinal Degenerations. In International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology; Jeon, K.W., Ed.; Academic Press, 2012; Volume 293, pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazelova, J.; Astuto-Gribble, L.; Inoue, H.; Tam, B.M.; Schonteich, E.; Prekeris, R.; Moritz, O.L.; Randazzo, P.A.; Deretic, D. Ciliary Targeting Motif VxPx Directs Assembly of a Trafficking Module through Arf4. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiser, P.D.; Golczak, M.; Maeda, A.; Palczewski, K. Key Enzymes of the Retinoid (Visual) Cycle in Vertebrate Retina. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripps, H.; Peachey, N.S.; Xu, X.; Nozell, S.E.; Smith, S.B.; Liou, G.I. The Rhodopsin Cycle Is Preserved in IRBP “Knockout” Mice despite Abnormalities in Retinal Structure and Function. Vis. Neurosci. 2000, 17, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichida, Y.; Morizumi, T. Mechanism of G-Protein Activation by Rhodopsin†. Photochem. Photobiol. 2007, 83, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinberg, F.; Wang, T.; De Maria, A.; Zhao, H.; Bassnett, S.; Chen, J.; Kefalov, V.J. The Na+/Ca2+, K+ Exchanger NCKX4 Is Required for Efficient Cone-Mediated Vision. eLife 2017, 6, e24550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, K.; Vinberg, F.; Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Kefalov, V.J. The Na+/Ca2+, K+ Exchanger 2 Modulates Mammalian Cone Phototransduction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiländer, H.; Achilles, A.; Friedel, U.; Maul, G.; Lottspeich, F.; Cook, N.J. Primary Structure and Functional Expression of the Na/Ca,K-Exchanger from Bovine Rod Photoreceptors. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.K. The Vertebrate Phototransduction Cascade: Amplification and Termination Mechanisms. In Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005; pp. 101–121. ISBN 978-3-540-32431-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Clarke, O.B.; Kim, J.; Stowe, S.; Kim, Y.-K.; Assur, Z.; Cavalier, M.; Godoy-Ruiz, R.; von Alpen, D.C.; Manzini, C.; et al. Structure of the STRA6 Receptor for Retinol Uptake. Science 2016, 353, aad8266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabile, B.K.; Kim, Y.-K.; Chen, Y.; Clarke, O.B.; Quadro, L.; Mancia, F. Sample Preparation for Structural and Functional Analyses of the STRA6 Receptor for Retinol-Binding Protein. Methods Enzymol. 2020, 637, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, A.; Volland, S.; Baliaouri, N.V.; Tran, E.M.; Williams, D.S. The Route of the Visual Receptor Rhodopsin along the Cilium. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 132, jcs229526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




