Submitted:
12 March 2024
Posted:
18 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Ethical Aspects
2.2. Design, Place and Period of Study
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Case Definition
2.5. Clinical and Demographic Data
2.6. Laboratory Procedures
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
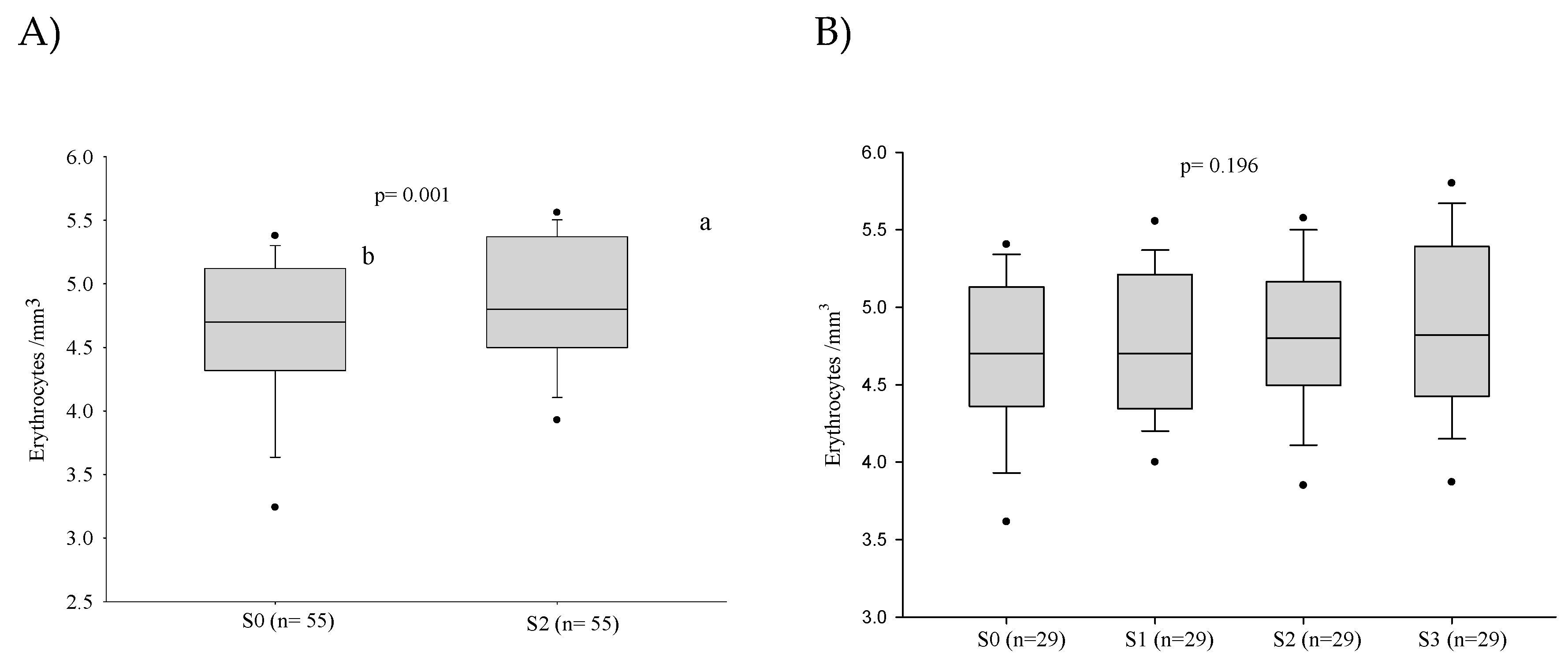
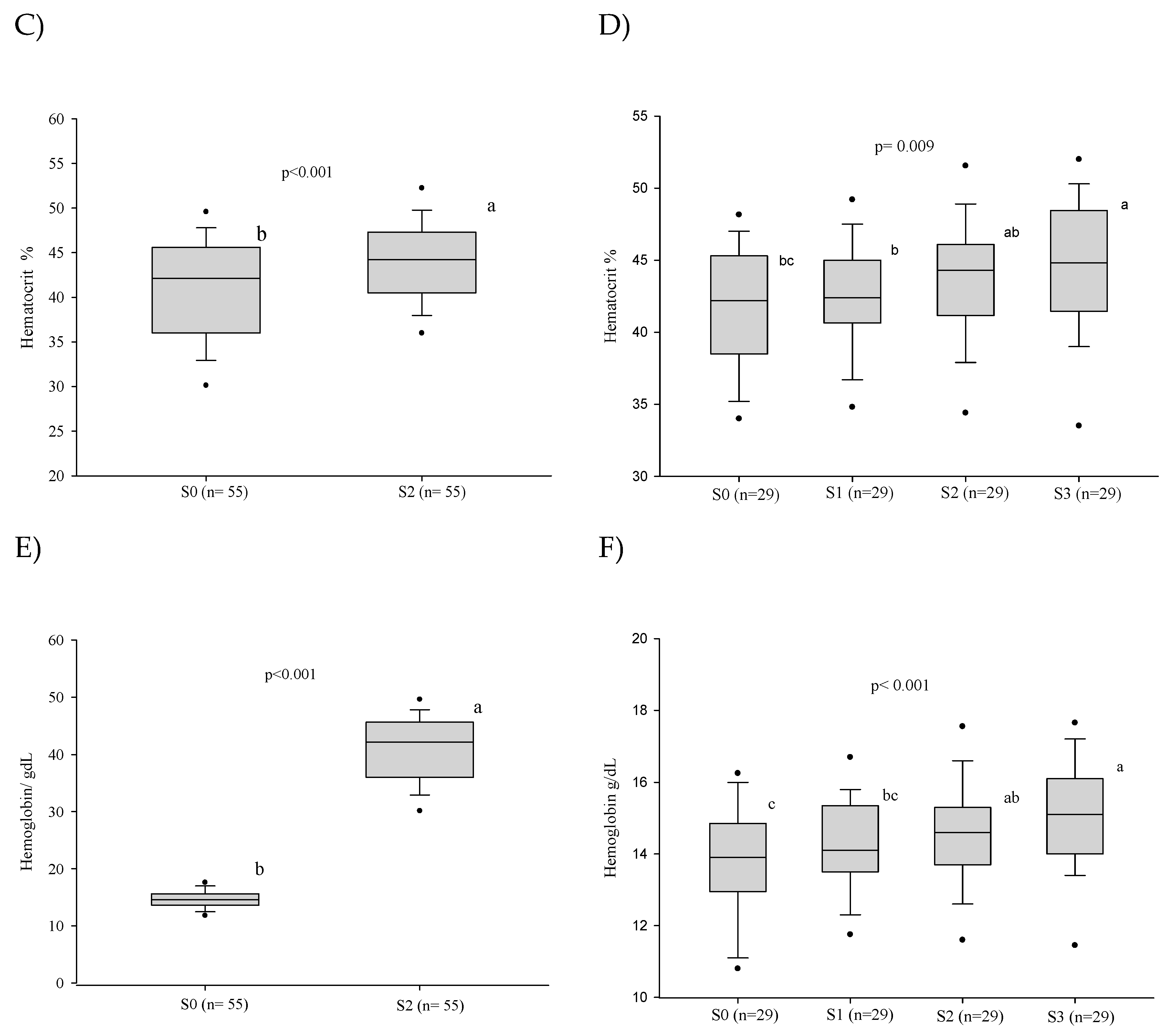
3.1. Red Blood Series
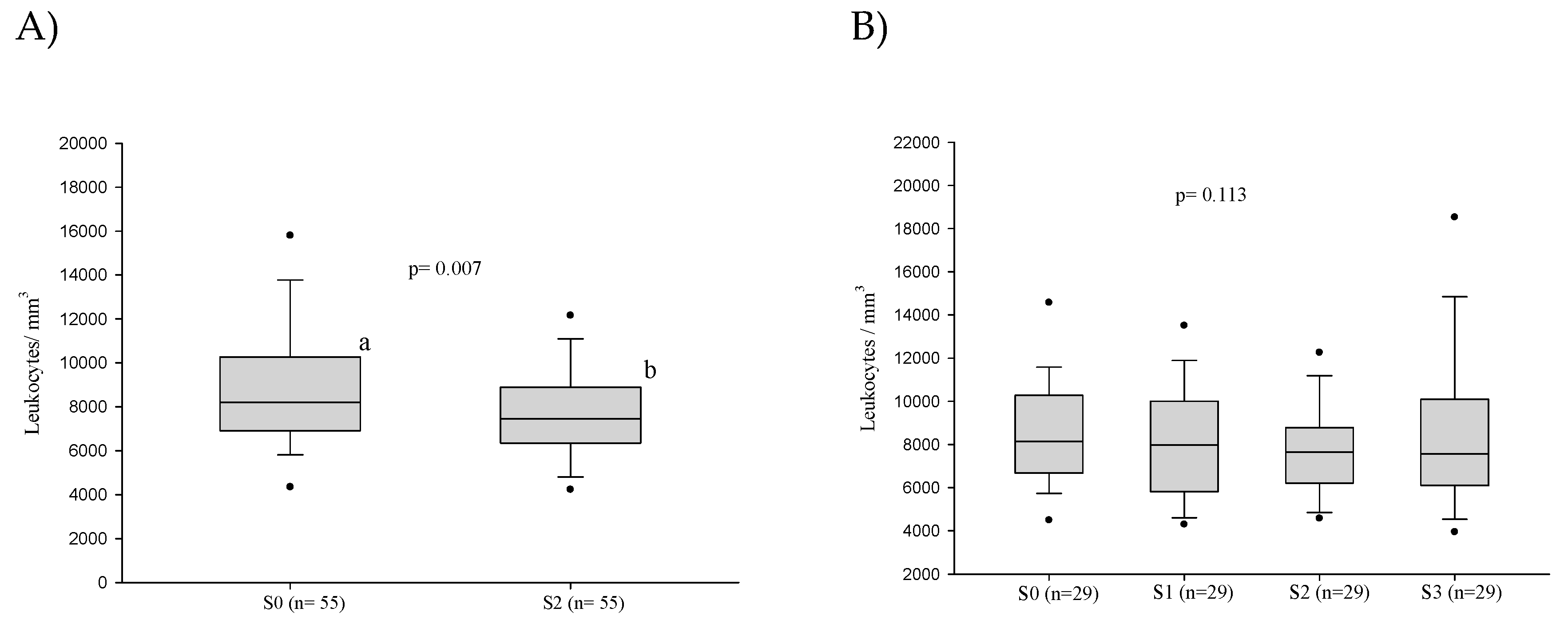
3.2. White Blood Series
3.2.1. Frequency of Alterations
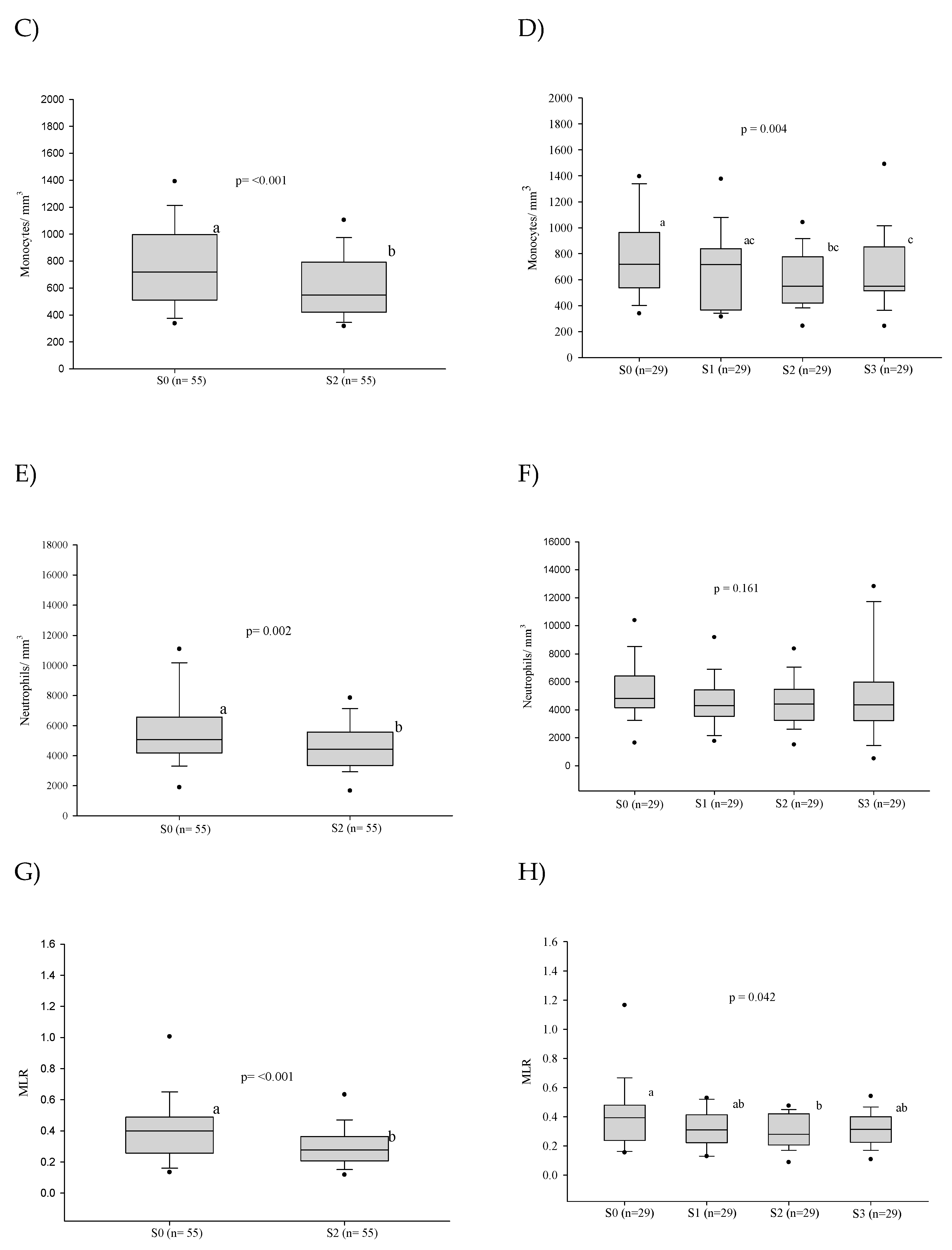
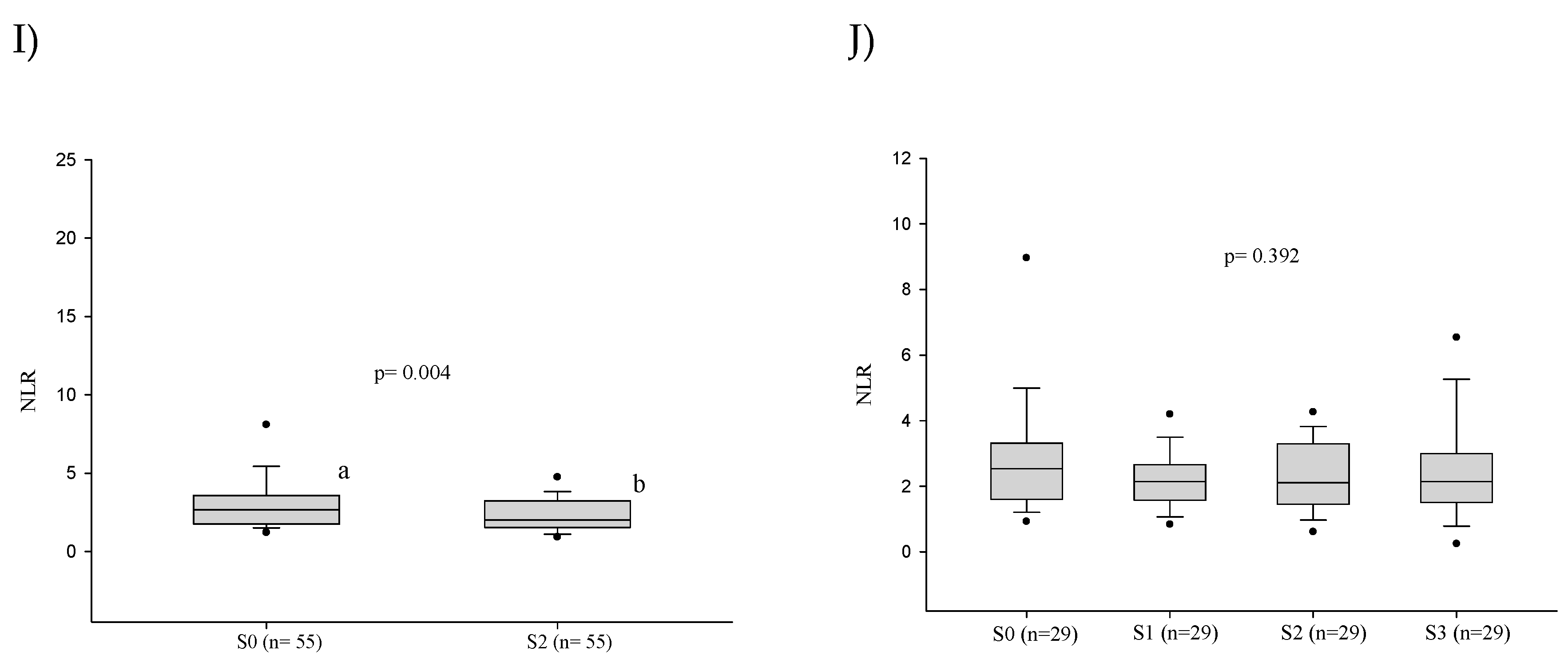
3.2.2. White Blood Cell Counts
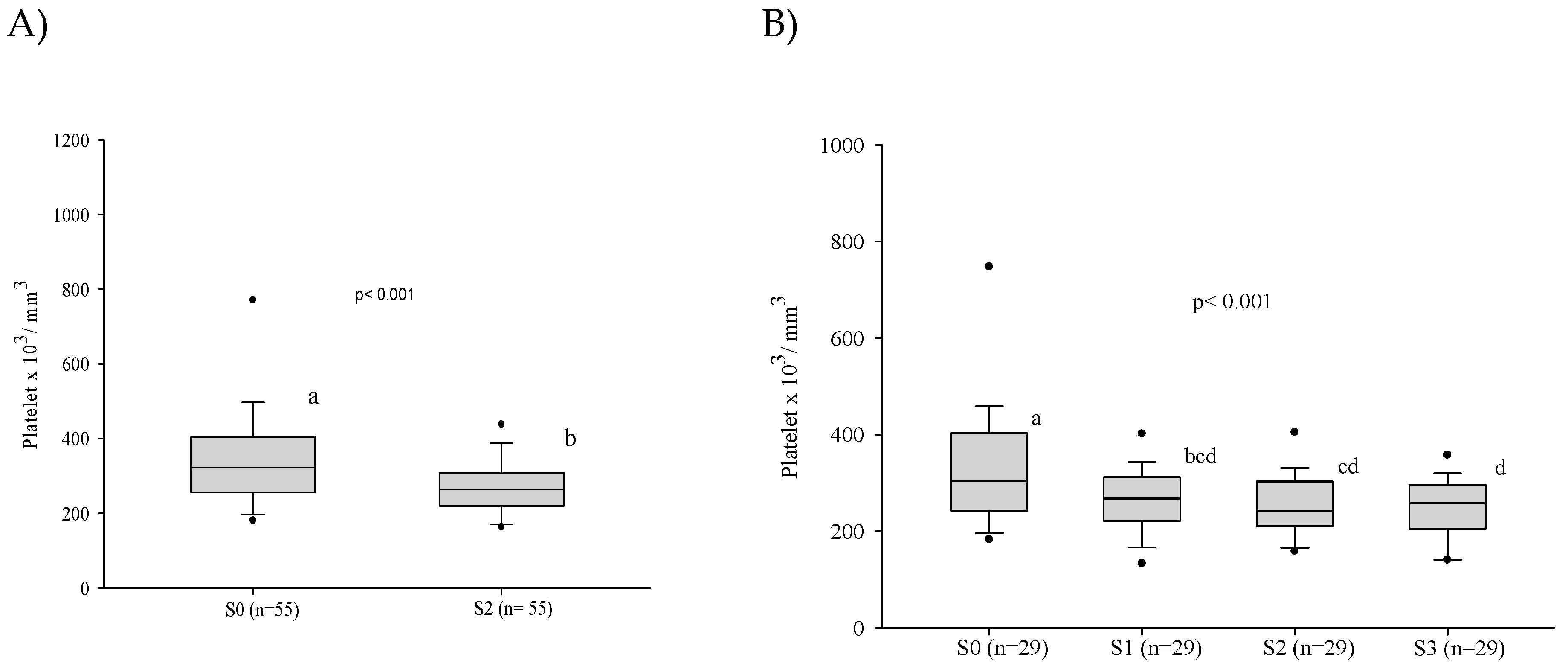
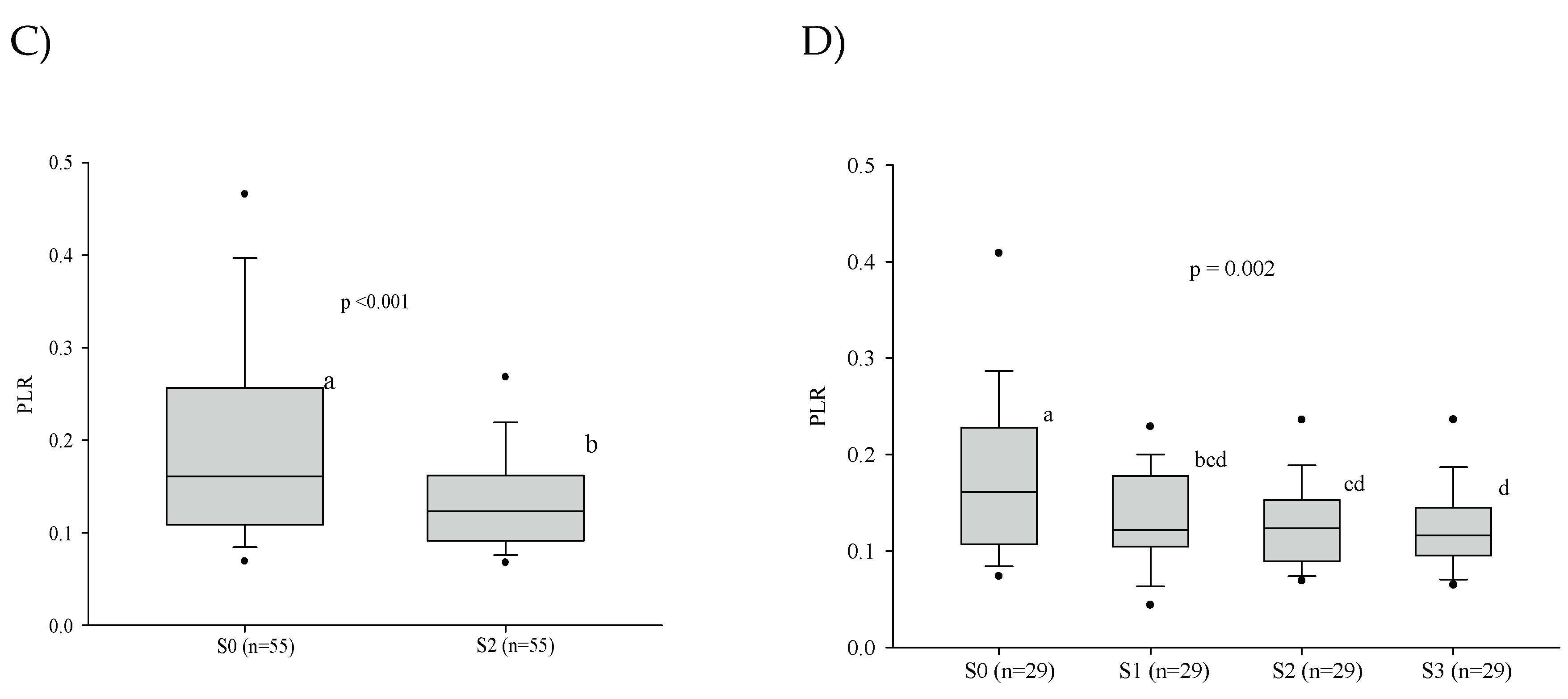
3.3. Platelet Series
3.4. Cellular Immaturity
3.5. Influence of the Severity of the Paracoccidioidomycosis Patients on the Hematologic Alterations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mendes, R.P.; Cavalcante, R. de S.; Marques, S.A.; Marques, M.E.A.; Venturini, J.; Sylvestre, T.F.; Paniago, A.M.M.; Pereira, A.C.; da Silva, J. de F.; Fabro, A.T.; et al. Paracoccidioidomycosis: Current Perspectives from Brazil. TOMICROJ 2017, 11, 224–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, Z.F.; Silva, D. da; Lazéra, M.; Petri, V.; Oliveira, R.M. de; Sabroza, P.C.; Wanke, B. Paracoccidioidomycosis Mortality in Brazil (1980-1995). Cad. Saúde Pública 2002, 18, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londero, A.T. Paracoccidioidomicose: Patogenia, Formas Clínicas, Manifestações Pulmonares e Diagnóstico. 1986, 2, 41–57.
- Bellissimo-Rodrigues, F.; Bollela, V.R.; Da Fonseca, B.A.L.; Martinez, R. Endemic Paracoccidioidomycosis: Relationship between Clinical Presentation and Patients’ Demographic Features. Med Mycol 2013, 51, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, W.B. de; Santos, G.M.C. dos; Silva, V.E.B. da; Gonçalves, E. da G. do R.; Silva, A.R. da Paracoccidioidomycosis in the State of Maranhão, Brazil: Geographical and Clinical Aspects. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2012, 45, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paniago, A.M.M.; Aguiar, J.I.A.; Aguiar, E.S.; Cunha, R.V. da; Pereira, G.R. de O.L.; Londero, A.T.; Wanke, B. Paracoccidioidomicose: Estudo Clínico e Epidemiológico de 422 Casos Observados No Estado de Mato Grosso Do Sul. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2003, 36, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.M.; Bucaretchi, F.; Barison, E. de M.; Hessel, G.; Tresoldi, A.T. Paracoccidioidomycosis in Children: Clinical Presentation, Follow-up and Outcome. Rev. Inst. Med. trop. S. Paulo 2004, 46, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Custódio, J.M.; Enokida, I.M.; Gonçalves, D.A.; Leone de Oliveira, S.M. do V.; Venturini, J.; Carvalho, L.R.; Mendes, R.P.; Paniago, A.M.M. Dynamics of Plasma Micronutrient Concentrations and Their Correlation with Serum Proteins and Thyroid Hormones in Patients with Paracoccidioidomycosis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doedens, A.L.; Phan, A.T.; Stradner, M.H.; Fujimoto, J.K.; Nguyen, J.V.; Yang, E.; Johnson, R.S.; Goldrath, A.W. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors Enhance the Effector Responses of CD8+ T Cells to Persistent Antigen. Nat Immunol 2013, 14, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, J.; Cavalcante, R.S.; de Assis Golim, M.; Marchetti, C.M.; de Azevedo, P.Z.; Amorim, B.C.; de Arruda, M.S.P.; Mendes, R.P. Phenotypic and Functional Evaluations of Peripheral Blood Monocytes from Chronic-Form Paracoccidioidomycosis Patients before and after Treatment. BMC Infect Dis 2014, 14, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chaudhury, A.; Zhang, M.; Savoldo, B.; Metelitsa, L.S.; Rodgers, J.; Yustein, J.T.; Neilson, J.R.; Dotti, G. Glycolysis Determines Dichotomous Regulation of T Cell Subsets in Hypoxia. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2016, 126, 2678–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffbrand, A.V.; Steensma, D.P. Hoffbrand’s Essential Haematology; Eighth edition.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, 2020; ISBN 978-1-119-49595-6. [Google Scholar]
- Pekelharing, J.M.; Hauss, O.; Jonge, R. de; Lokhof, J.; Sodikromo, J.; Spaans, M.; Brouwer, R.; Lathouder, S. de; Hinzmann, R. Haematology Reference Intervals for Established and Novel Parameters in Healthy Adults. Sysmex J Int. 2010, 20, 01–11. [Google Scholar]
- The jamovi project Jamovi; 2021.
- Cavalcante, R. de S.; Sylvestre, T.F.; Levorato, A.D.; de Carvalho, L.R.; Mendes, R.P. Comparison between Itraconazole and Cotrimoxazole in the Treatment of Paracoccidiodomycosis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2014, 8, e2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.; Ganz, T.; Goodnough, L.T. Anemia of Inflammation. Blood 2019, 133, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, G.E. The Anemia of Chronic Disorders. Semin Hematol 1966, 3, 351–375. [Google Scholar]
- Guralnik, J.M.; Eisenstaedt, R.S.; Ferrucci, L.; Klein, H.G.; Woodman, R.C. Prevalence of Anemia in Persons 65 Years and Older in the United States: Evidence for a High Rate of Unexplained Anemia. Blood 2004, 104, 2263–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Brito, E. da C.A.; Siqueira, I.V.; Venturini, J.; Félix, V.L.T.; dos Santos, A.O.G.M.; Mendes, R.P.; Weber, S.S.; Paniago, A.M.M. Iron Metabolism Disorders of Patients with Chronic Paracoccidioidomycosis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Iperen, C.E.; Gaillard, C.A.J.M.; Kraaijenhagen, R.J.; Braam, B.G.; Marx, J.J.M.; van de Wiel, A. Response of Erythropoiesis and Iron Metabolism to Recombinant Human Erythropoietin in Intensive Care Unit Patients. Critical Care Medicine 2000, 28, 2773–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, T.; Nemeth, E. Iron Sequestration and Anemia of Inflammation. Seminars in Hematology 2009, 46, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.; Kang, Y.A.; Yoon, Y.S.; Um, S.-W.; Lee, S.M.; Yoo, C.-G.; Kim, Y.W.; Han, S.K.; Shim, Y.-S.; Yim, J.-J. The Prevalence and Evolution of Anemia Associated with Tuberculosis. J Korean Med Sci 2006, 21, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchella, P.A.; Donkor, S.; Owolabi, O.; Sutherland, J.S.; McDermid, J.M. Complex Anemia in Tuberculosis: The Need to Consider Causes and Timing When Designing Interventions. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2015, 60, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailão, E.F.L.C.; Parente, J.A.; Pigosso, L.L.; Castro, K.P. de; Fonseca, F.L.; Silva-Bailão, M.G.; Báo, S.N.; Bailão, A.M.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Hernandez, O.; et al. Hemoglobin Uptake by Paracoccidioides Spp. Is Receptor-Mediated. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2014, 8, e2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinudomwong, P.; Binyasing, A.; Trongsakul, R.; Paisooksantivatana, K. Diagnostic Performance of Reticulocyte Hemoglobin Equivalent in Assessing the Iron Status. Clinical Laboratory Analysis 2020, 34, e23225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benard, G. An Overview of the Immunopathology of Human Paracoccidioidomycosis. Mycopathologia 2008, 165, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loures, F.V.; Pina, A.; Felonato, M.; Araújo, E.F.; Leite, K.R.M.; Calich, V.L.G. Toll-like Receptor 4 Signaling Leads to Severe Fungal Infection Associated with Enhanced Proinflammatory Immunity and Impaired Expansion of Regulatory T Cells. Infect Immun 2010, 78, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goihman-Yahr, M.; Rothenberg, A.; Bretaña, A.; Istúriz, G.; Rosquete, R.; Avila-Millán, E.; Viloria, N.; de Borges, N.S.; Carrasquero, M.; de Fernández, B.P.; et al. Digestion of Killed Paracoccidioides Brasiliensis by Neutrophils. Mycopathologia 1989, 106, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffner, A.; Davis, C.E.; Schaffner, T.; Markert, M.; Douglas, H.; Braude, A.I. In Vitro Susceptibility of Fungi to Killing by Neutrophil Granulocytes Discriminates between Primary Pathogenicity and Opportunism. J. Clin. Invest. 1986, 78, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xidieh, C.F.; Lenzi, H.L.; Calich, V.L.G.; Burger, E. Influence of the Genetic Background on the Pattern of Lesions Developed by Resistant and Susceptible Mice Infected with Paracoccidioides Brasiliensis. Medical Microbiology and Immunology 1999, 188, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.; Peracoli, M.T.; Soares, A.; Montenegro, R.; Mendes, R.P.; Meira, D.A. Host-Parasite Relationship in Paracoccidioidomycosis. Curr Top Med Mycol 1993, 5, 115–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, F.; Miyazaki, S. New Biodefense Strategies by Neutrophils. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 2005, 53, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moscardi-Bacchi, M.; Brummer, E.; Stevens, D.A. Support of Paracoccidioides Brasiliensis Multiplication by Human Monocytes or Macrophages: Inhibition by Activated Phagocytes. Journal of Medical Microbiology 1994, 40, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvi, S.A.; Soares, A.M.V.C.; Peraçoli, M.T.S.; Franco, M.; Ruiz, R.L.; Marcondes-Machado, J.; Fecchio, D.; Mattos, M.C.I.; Mendes, R.P. Study of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid in Paracoccidioidomycosis: Cytopathology and Alveolar Macrophage Function in Response to Gamma Interferon; Comparison with Blood Monocytes. Microbes and Infection 2003, 5, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bava, A.J.; Mistchenko, A.S.; Palacios, M.F.; Estevez, M.E.; Tiraboschi, N.I.; Sen, L.; Negroni, R.; Diez, R.A. Lymphocyte Subpopulations and Cytokine Production in Paracoccidioidomycosis Patients. Microbiology and Immunology 1991, 35, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, F.G.; Ruas, L.P.; Pereira, R.M.; Lima, X.T.; Antunes, E.; Mamoni, R.L.; Blotta, M.H.S.L. Functional and Phenotypic Evaluation of Eosinophils from Patients with the Acute Form of Paracoccidioidomycosis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2017, 11, e0005601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikanai-Yasuda, M.A.; Higaki, Y.; Uip, D.E.; Mori, N.S.; Del Negro, G.; Melo, N.T.; Hutzler, R.U.; Amato Neto, V. Comprometimento Da Medula Óssea e Eosinofilia Na Paracoccidioidomicose. Rev. Inst. Med. trop. S. Paulo 1992, 34, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorelik, O.; Izhakian, S.; Barchel, D.; Almoznino-Sarafian, D.; Tzur, I.; Swarka, M.; Beberashvili, I.; Feldman, L.; Cohen, N.; Shteinshnaider, M. Prognostic Significance of Platelet Count Changes during Hospitalization for Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Platelets 2017, 28, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semple, J.W.; Freedman, J. Platelets and Innate Immunity. Cell Mol Life Sci 2010, 67, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, D.; Kerrigan, S.W.; Watson, S.P. Platelets and the Innate Immune System: Mechanisms of Bacterial-Induced Platelet Activation. J Thromb Haemost 2011, 9, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitchford, S.; Pan, D.; Welch, H.C.E. Platelets in Neutrophil Recruitment to Sites of Inflammation. Curr Opin Hematol 2017, 24, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.; Xue, X. Targeting Iron Metabolism in Cancer Therapy. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8412–8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abakay, O.; Abakay, A.; Sen, H.S.; Tanrikulu, A.C. The Relationship Between Inflammatory Marker Levels and Pulmonary Tuberculosis Severity. Inflammation 2015, 38, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, A.F.; de Camargo, Z.P.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Portela, T.F.; Hoffmann-Santos, H.D.; Pinheiro, B.G.; Possa, A.P.; Cavalcante, L.R. da S.; Hagen, F.; Hahn, R.C. Puzzling Paracoccidioidomycosis: Factors Associated with the Severity of Paracoccidioides Lutzii Infections. Int J Infect Dis 2021, 107, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, Z.F.; Wanke, B.; Travassos, C.; Oliveira, R.M.; Xavier, D.R.; Coimbra, C.E.A. Hospital Morbidity Due to Paracoccidioidomycosis in Brazil (1998-2006). Trop Med Int Health 2015, 20, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | n (%) | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 60 (96.8) | 88.8 | 99.6 |
| Female | 02 (3.2) | 0.4 | 11.2 |
| Rural activity | |||
| Yes ǂ | 55 (88.7) | 78.1 | 95.3 |
| Never | 06 (9.7) | 3.6 | 19.8 |
| Ignored | 01 (1.6) | 0.0 | 8.6 |
| Use of Tobacco | |||
| Regularly | 51 (82.3) | 70.5 | 90.8 |
| Former smoker | 07 (11.3) | 4.6 | 21.9 |
| Never | 04 (6.5) | 1.8 | 15.7 |
| Degree of severity of PCM | |||
| Moderate | 37 (59.7) | 46.5 | 72.0 |
| Severe | 17 (27.4) | 16.8 | 40.2 |
| Mild | 08 (12.9) | 5.7 | 23.8 |
| Antifungal treatment | |||
| Itraconazole | 39 (62.9) | 49.7 | 74.8 |
| Cotrimoxazole | 23 (37.1) | 25.2 | 50.3 |
| Variable | Patients | S0 | S1 | S2 | S3 | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (number) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Anemia | 62 | 28 (45.2) | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 55* | 21 (39.3) | ... | 11(20.0) | ... | 0.008 | |
| 29** | 08 (27.6) | 06 (20.7) | 06 (20.7) | 03 (10.3) | 0.063 |
| Variable | Patients | S0 | S1 | S2 | S3 | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (number) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Leukopenia* | 55 | 02 (3.6) | ... | 02 (3.6) | ... | 0.564 |
| Leukopenia† | 29 | 01 (3.4) | - | - | 02 (6.9) | 0.317 |
| Leukocytosis* | 55 | 11 (20.0) | ... | 08 (14.5) | ... | 0.366 |
| Leukocytosis† | 29 | 06 (20.7) | 05 (17.2) | 06 (20.7) | 05 (17.2) | 0.940 |
| Neutropenia* | 55 | 01 (1.8) | ... | 03 (5.5) | ... | 0.157 |
| Neutropenia† | 29 | 01 (3.4) | 01 (3.4) | 02 (6.9) | 03 (10.3) | 0.194 |
| Neutrophilia* | 55 | 08 (14.5) | ... | 04 (7.3) | ... | 0.206 |
| Neutrophilia† | 29 | 03 (10.3) | 02 (6.9) | 02 (6.9) | 05 (17.2) | 0.429 |
| Eosinophilia* | 55 | 14 (25.4) | ... | 14 (25.4) | ... | 1.000 |
| Eosinophilia† | 29 | 09 (31.0) | 12 (41.4) | 10 (34.5) | 08 (27.6) | 0.274 |
| Monocytosis* | 55 | 22 (40.0) | ... | 09 (16.4) | ... | 0.003 |
| Monocytosis† | 29 | 11 (37.9) | 06 (20.7) | 04 (13.8) | 07 (24.1) | 0.059 |
| Lymphopenia* | 55 | 14 (25.5) | ... | 11 (20.0) | ... | 0.366 |
| Lymphopenia† | 29 | 06 (20.7) | 06 (20.7) | 06 (20.7) | 07 (24.1) | 0.954 |
| Lymphocytosis* | 55 | 03 (5.5) | ... | 03 (5.5) | ... | 1.000 |
| Lymphocytosis† | 29 | 03 (10.3) | 03 (10.3) | 02 (6.9) | 03 (10.3) | 0.801 |
| Variables | S0 | S2 | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean±SD | Mean±SD | ||
| median [Q1; Q3] | median [Q1; Q3] | ||
| IGs† | 0.0 [0.0; 0.1] | 0.0 [0.0; 0.1] | 0.756 |
| IGs (%)† | 0.5 [0.3; 0.7] | 0.2 [0.0; 0.3] | 0.037 |
| Ret (%)* | 1.3±0.6 | 3.3±8.1 | 0.942 |
| IRF* | 6.8±2.8 | 7.0±4.0 | 0.441 |
| Ret-He* | 31.4±3.0 | 33.5±1.7 | 0.016 |
| IPF† | 31.6 [29.5; 33.9] | 33.7 [32.8; 34.3] | 0.056 |
| Variables | Severe (n = 17) | Mild+Moderate (n = 45) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Anemia | 12 (70.6) | 16 (35.6) | 0.013 |
| Leukopenia* | 0 (0.0) | 03 (6.7) | 0.555 |
| Leukocytosis | 02 (11.8) | 09 (20.0) | 0.712 |
| Neutropenia* | 0 (0.0) | 02 (4.4) | 1.000 |
| Neutrophilia* | 02 (11.8) | 06 (13.3) | 1.000 |
| Monocytosis | 07 (41.2) | 17 (37.8) | 0.806 |
| Eosinophilia | 02 (11.8) | 04 (8.9) | 0.662 |
| Lymphopenia | 02 (11.8) | 04 (8.9) | 0.662 |
| Lymphocytosis | 02 (11.8) | 09 (20.0) | 0.712 |
| Thrombocytosis* | 03 (17.6) | 03 (6.7) | 0.333 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





