Submitted:
01 March 2024
Posted:
04 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Regional Characteristics
2.2. Demographic, Clinical, and Laboratory Characteristics of the Participants
2.3. Immunoglobulin Replacement
2.4. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Study Approval
3. Results
3.1. Demographics, Clinical, and Laboratory Characteristics of the Participants at Baseline
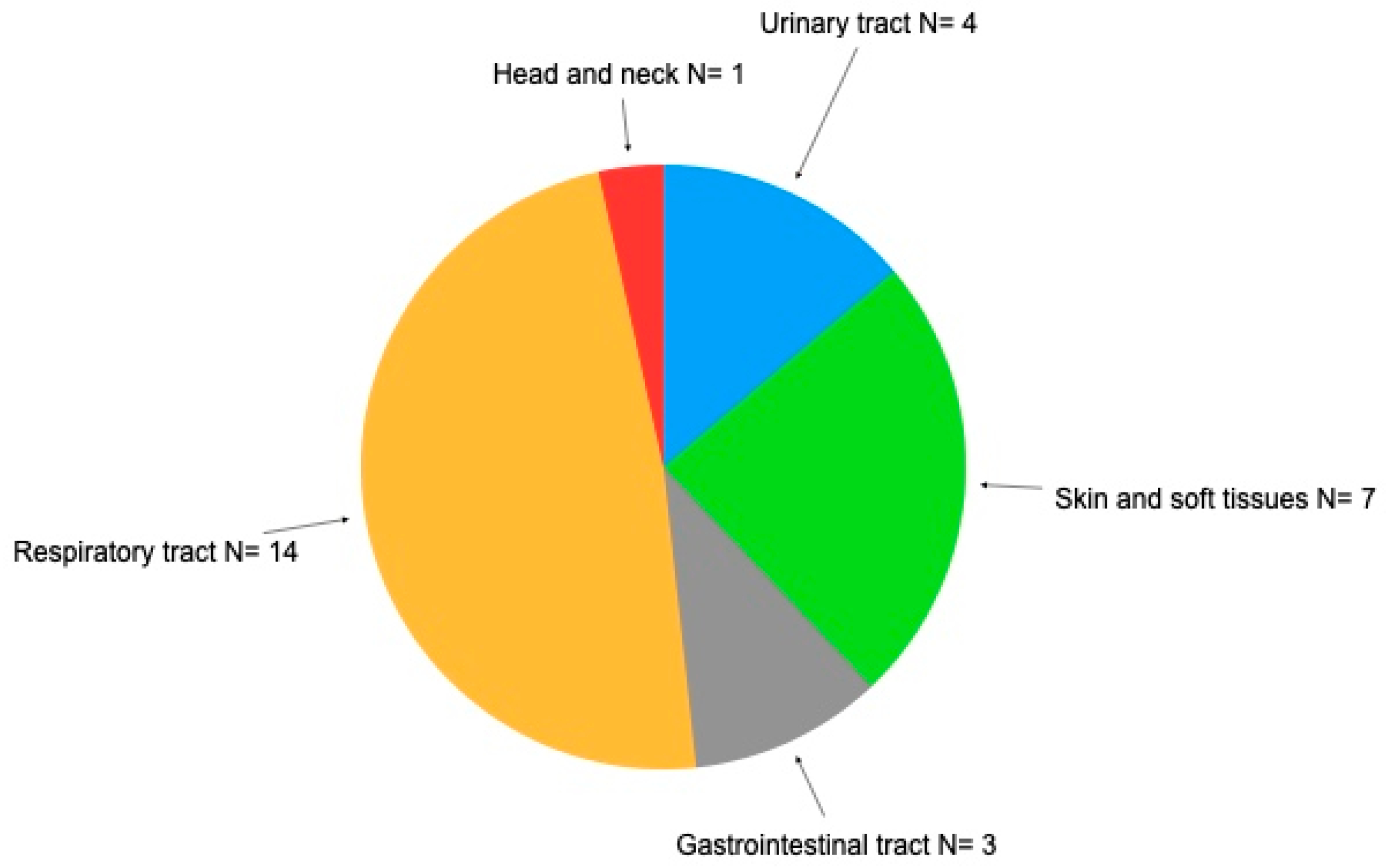
3.2. Impact of Infections on Patients with Secondary Antibody Deficiency after Treatment with Immunosuppressants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tuano KS, Seth N, Chinen J. Secondary immunodeficiencies: An overview. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021;127(6):617-626. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ramón S, Bermúdez A, González-Granado LI, Rodríguez-Gallego C, Sastre A, Soler-Palacín P; ID-Signal Onco-Haematology Group. Primary and Secondary Immunodeficiency Diseases in Oncohaematology: Warning Signs, Diagnosis, and Management. Front Immunol. 2019; 26;10:586. [CrossRef]
- Kaplan B, Bonagura VR. Secondary Hypogammaglobulinemia: An Increasingly Recognized Complication of Treatment with Immunomodulators and After Solid Organ Transplantation. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2019;39(1):31-47. [CrossRef]
- Axelrod H, Adams M. Biologic Agents and Secondary Immune Deficiency. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2021;41(4):639-652. [CrossRef]
- Crickx E, Weill JC, Reynaud CA, Mahévas M. Anti-CD20-mediated B-cell depletion in autoimmune diseases: successes, failures and future perspectives. Kidney Int. 2020;97(5):885-893. [CrossRef]
- de Souza KJ, Ferro RS, Prestes-Carneiro LE, Carrilho PAM, Vasconcelos DM. Infectious diseases and immunological markers associated with patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma treated with rituximab. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2018;40(1):13-17. [CrossRef]
- Stabler S, Giovannelli J, Launay D, Cotteau-Leroy A, Heusele M, Lefèvre G, Terriou L, Lambert M, Dubucquoi S, Hachulla E, Sobanski V. Serious Infectious Events and Immunoglobulin Replacement Therapy in Patients With Autoimmune Disease Receiving Rituximab: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;72(5):727-737. [CrossRef]
- Jolles S, Michallet M, Agostini C, Albert MH, Edgar D, Ria R, Trentin L, Lévy V. Treating secondary antibody deficiency in patients with haematological malignancy: European expert consensus. Eur J Haematol. 2021;106(4):439-449. [CrossRef]
- Boton Pereira DH, Primo LS, Pelizari G, Flores E, de Moraes-Vasconcelos D, Condino-Neto A, Prestes-Carneiro LE. Primary Immunodeficiencies in a Mesoregion of São Paulo, Brazil: Epidemiologic, Clinical, and Geospatial Approach. Front Immunol. 2020;11:862. [CrossRef]
- Han JW, Lee KY, Hwang JY, Koh DK, Lee JS. Antibody status in children with steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Yonsei Med J. 2010 Mar;51(2):239-43. Epub 2010 Feb 12. PMID: 20191016; PMCID: PMC2824870. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Batalla I, Vargas-Delgado ME, Meier L, Loges S. Sexual dimorphism in solid and hematological malignancies. Semin Immunopathol. 2019 Mar;41(2):251-263. Epub 2018 Oct 25. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, Global Cancer Observatory. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/en (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Houpert R, Almont T, Belahreche R, Faro M, Okouango J, Vestris M, Macni J, Pierre-Louis O, Montabord C, Beaubrun-Renard M, Soumah N, Boisseau M, Véronique-Baudin J, Joachim C. A population-based analysis of hematological malignancies from a French-West-Indies cancer registry's data (2009-2018). BMC Cancer. 2023;23(1):1197. [CrossRef]
- Ministério da Saúde, Instituto Nacional de Câncer Incidência de Câncer no asil. Available online: https://www.inca.gov.br/sites/ufu.sti.inca.local/files/media/document/estimativa-2023.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Thandra KC, Barsouk A, Saginala K, Padala SA, Barsouk A, Rawla P. Epidemiology of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma. Med Sci (Basel). 2021;9(1):5. [CrossRef]
- Roberts DM, Jones RB, Smith RM, Alberici F, Kumaratne DS, Burns S, Jayne DR. Rituximab-associated hypogammaglobulinemia: incidence, predictors and outcomes in patients with multi-system autoimmune disease. J Autoimmun. 2015 Feb;57:60-5. Epub 2014 Dec 31. PMID: 25556904. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barmettler S, Ong MS, Farmer JR, Choi H, Walter J. Association of Immunoglobulin Levels, Infectious Risk, and Mortality With Rituximab and Hypogammaglobulinemia. JAMA Netw Open. 2018 Nov 2;1(7):e184169. PMID: 30646343; PMCID: PMC6324375. [CrossRef]
- Ottaviano G, Sgrulletti M, Moschese V. Secondary rituximab-associated versus primary immunodeficiencies: The enigmatic border. Eur J Immunol. 2022;52(10):1572-1580. [CrossRef]
- Roberts DM, Jones RB, Smith RM, Alberici F, Kumaratne DS, Burns S, Jayne DR. Rituximab-associated hypogammaglobulinemia: incidence, predictors and outcomes in patients with multi-system autoimmune disease. J Autoimmun. 2015 Feb;57:60-5. Epub 2014 Dec 31. PMID: 25556904. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wudhikarn K, Palomba ML, Pennisi M, Garcia-Recio M, Flynn JR, Devlin SM, Afuye A, Silverberg ML, Maloy MA, Shah GL, Scordo M, Dahi PB, Sauter CS, Batlevi CL, Santomasso BD, Mead E, Seo SK, Perales MA. Infection during the first year in patients treated with CD19 CAR T cells for diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2020;10(8):79. [CrossRef]
- Cannon L, Pan A, Kovalick L, Sarkissian A, Wu EY. Secondary immunodeficiencies and infectious considerations of biologic immunomodulatory therapies. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023 Jun;130(6):718-726. Epub 2023 Feb 18. PMID: 36801438; PMCID: PMC10247415. [CrossRef]
- Han JW, Lee KY, Hwang JY, Koh DK, Lee JS. Antibody status in children with steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Yonsei Med J. 2010;51(2):239-43. [CrossRef]
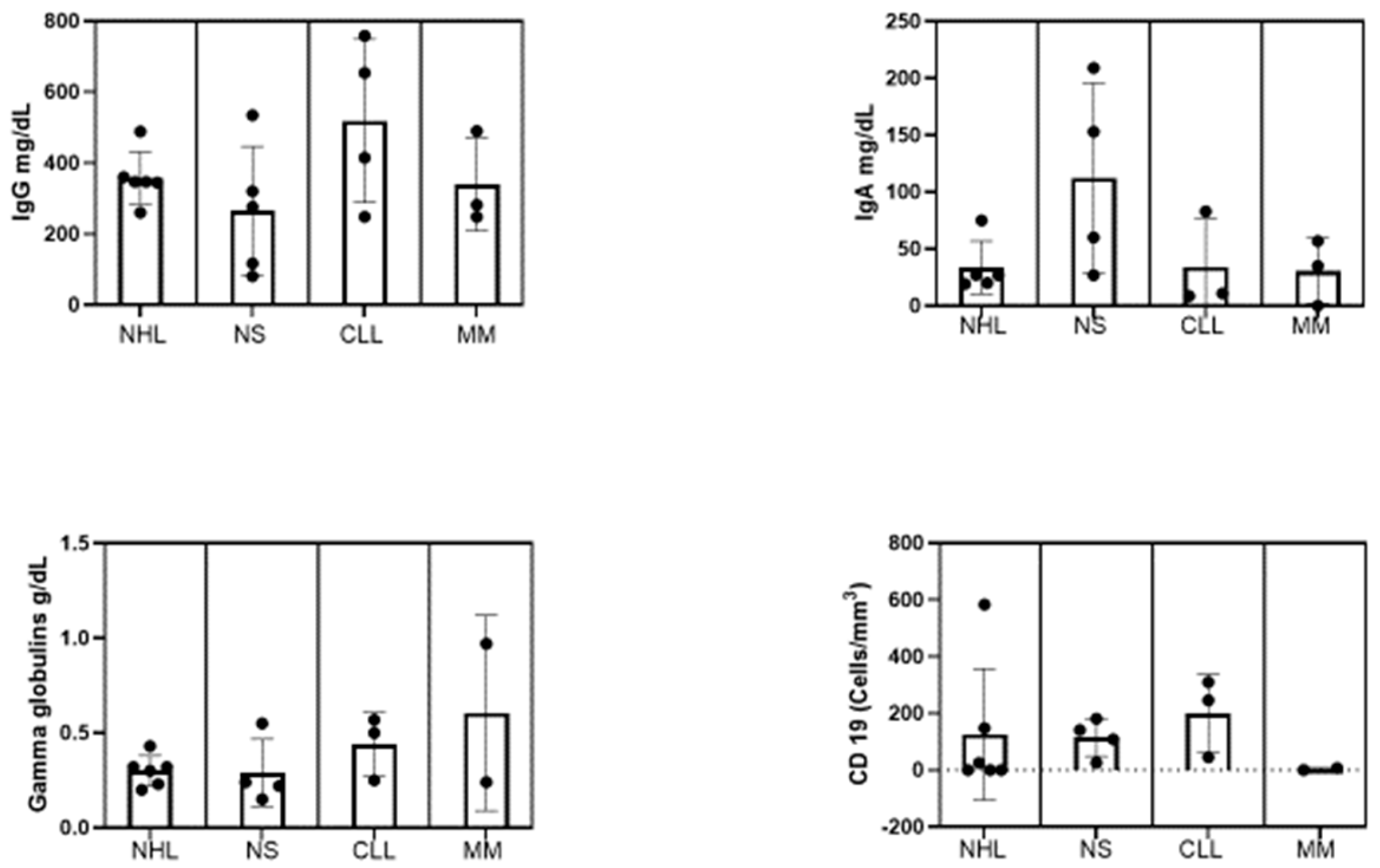
| No. | IgG (mg/dL) | IgA (mg/dL) | γ-Globulins (g/dL) | CD19 (cells/mm3) | Pathology | Target | Drug use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 360 | 27 | 0.30 | 0 | NHL | Anti-CD-20 | Rituximab |
| 2 | 489 | 75 | 0.43 | 584 | NHL | Anti-CD-20 | Rituximab |
| 3 | 260 | 27.2 | 0.23 | 25 | NHL | Anti-CD-20 | Rituximab |
| 4 | 345 | 19.2 | 0.32 | 0 | NHL | Anti-CD-20 | Rituximab |
| 5 | 347 | 20 | 0.32 | 148 | NHL | BTK | Ibrutinib |
| 6 | 347 | 2210 | 0.20 | 00 | NHL | BTK | Ibrutinib |
| 7 | 117 | 153 | 0.22 | 141 | NS | Anti-CD-20 | Prednisone |
| 8 | 320 | NA | NA | NA | NS | Anti-CD-20 | Prednisone |
| 9 | 535 | 209 | 0.55 | 26 | NS | IMPDH | Prednisone;/mycophenolate |
| 10 | 276 | 27 | 0.24 | 109 | NS | Anti-CD-20 | Prednisone |
| 11 | 81 | 60 | 0.15 | 181 | NS | Anti-CD-20 | Prednisone |
| 12 | 248 | 10.9 | 0.24 | 246 | CLL | Anti-CD-20 | Rituximab |
| 13 | 654 | 8.73 | 0.70 | 45 | CLL | Anti-CD-20 | Rituximab |
| 14 | 759 | 83 | 0.97 | 310 | CLL | Anti-CD-20 | Rituximab |
| 15 | 415 | NA | NA | NA | CLL | Anti-CD-20 | Rituximab; ibrutinib |
| 16 | 490 | 35 | 0.50 | NA | MM | DNA | Cyclophosphamide;talidomid |
| 17 | 248 | 57 | 0.57 | 7 | MM | Anti-CD-20 | Rituximab |
| 18 | 282 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 | MM | BCMA/CD3 | Teclistamab |
| 19 | 76 | 33 | 0.11 | 218 | PD | 0 | No imunossupressor |
| 20 | 460 | 39.7 | 0.35 | 0 | ITP | Anti-CD-20 | Rituximab |
| Participants (N=20) | n (%) | Mean±SD | 95% Confidence interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | <18 | 7 (35) | 10.80±7.29 | 4.05–17.54 |
| 18–60 | 7 (35) | 49.29±12.74 | 37.51–61.07 | |
| ≥60 | 6 (30) | 70.83±8.25 | 62.17–79.50 | |
| Gender | Female | 8 (40) | ||
| Male | 12 (60) | |||
| Race | European | 10 (50) | ||
| South American | 6 (30) | |||
| African | 2 (10) | |||
| Asian | 2 (10) | |||
| SID type | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | 6 (30) | ||
| Nephrotic Syndrome | 5 (25) | |||
| Chronic lymphocyte leukemia | 4 (25) | |||
| Multiple myeloma | 3 (15) | |||
| Protein-losing enteropathy | 1 (5) | |||
| Immune thrombocytopenia | 1 (5) | |||
| Baseline immunoglobulin (mg/dL) | IgG<400 | 12 (60) | 269.3±89.67 | 212.3–326.2 |
| IgG≥400 | 8 (40) | 570.1±135.7 | 456.7–683.5 | |
| IgA<6.0 | 1(5) | – | – | |
| IgA>6.1<40 | 10 (50) | 24.77±10.08 | 17.56–31.98 | |
| >41 | 7 (35) | 406.7±797.1 | -1474.5 | |
| γ-Globulins (g/dL) | <0.70 | 19 (95) | 0.31±0.12 | 0.25–0.38 |
| >0.70 | 1 (5) | 0.97 | ||
| CD19+ B cell count (cells/mm3) | >20 | 11 (55) | 1.16±2.85 | 1.83–4.06 |
| ≤20 | 6 (30) | 184.8±161.0 | 76.66–293 | |
| NA | 3 (15) | |||
| Origen of the service | Public | 10 (50) | ||
| Private | 10 (50) | |||
| IgG replacement | Endovenous | 12 (60) | ||
| Subcutaneous | 4 (25) | |||
| Not indicated | 4 (25) |
| Patient number | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | |
| Infection sites | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory | + | +++ | + | ++ | + | |||||||||||||||
| Amigdalitis | ++++ | + | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | |||||||||||||
| Sinusitis | ++ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Otitis | + | +++ | ++ | + | +++ | + | +++ | +++ | ||||||||||||
| Pneumonia | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| Skin diseases and soft tissues | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Herpes simplex | ++ | +++ | +++ | |||||||||||||||||
| Herpes zoster | ++ | + | + | +++ | ||||||||||||||||
| Skin mycosis | +++ | +++ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Head and neck | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Tongue lesion | ++ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Other | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Gastroenteritis | - | +++ | +++ | + | ||||||||||||||||
| Urinary tract infection | +++ | + | +++ | ++ | ||||||||||||||||
| Dengue infection (number) | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| Covid-19 infection (number) | ++ | + | + | + | ++ | |||||||||||||||
| Sepsis | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | +++ | ||||||||||||||
| Severity of infections | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mild | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||
| Moderate | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| Life-threatening | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||
| Fatal | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





