Submitted:
13 March 2024
Posted:
15 March 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Autophagy: an overview
Cell-autonomous autophagy
Non-autonomously regulated autophagy:
- Non-autonomously regulated autophagy in Aging
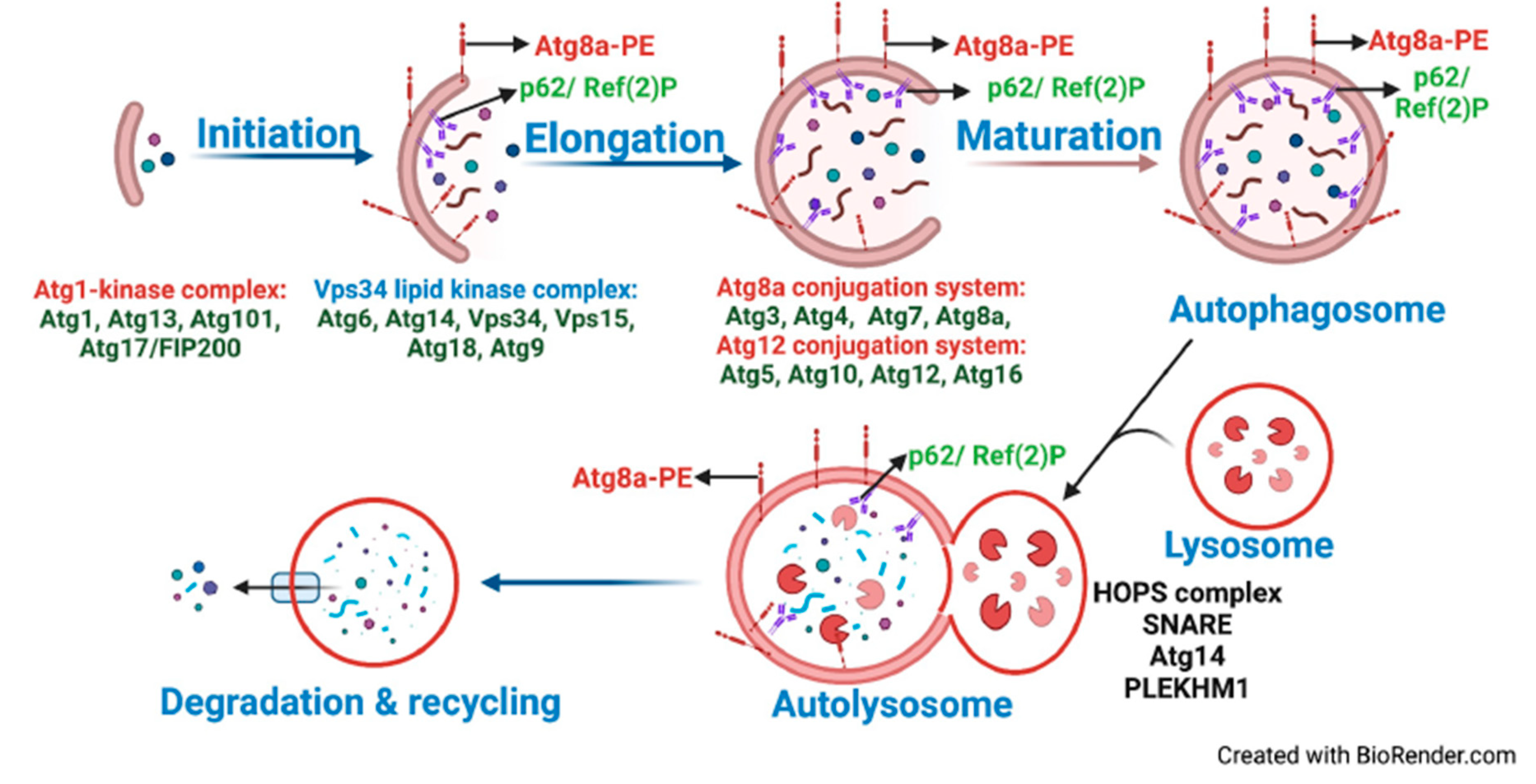
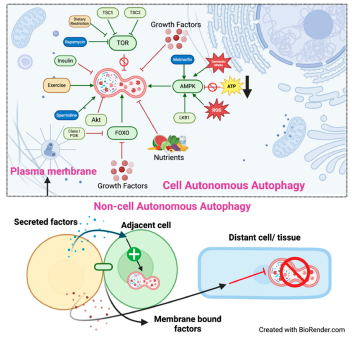
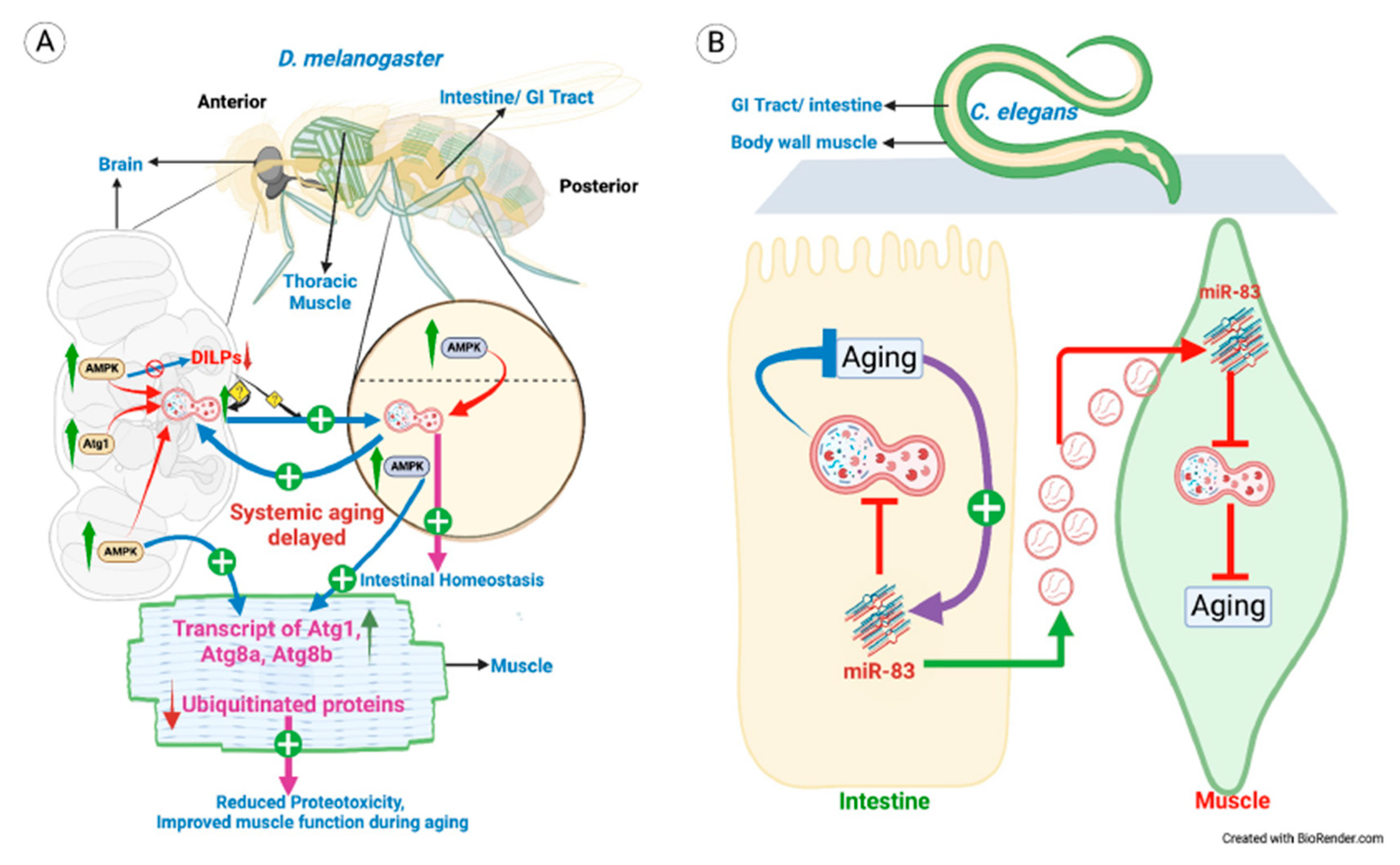
- 2.
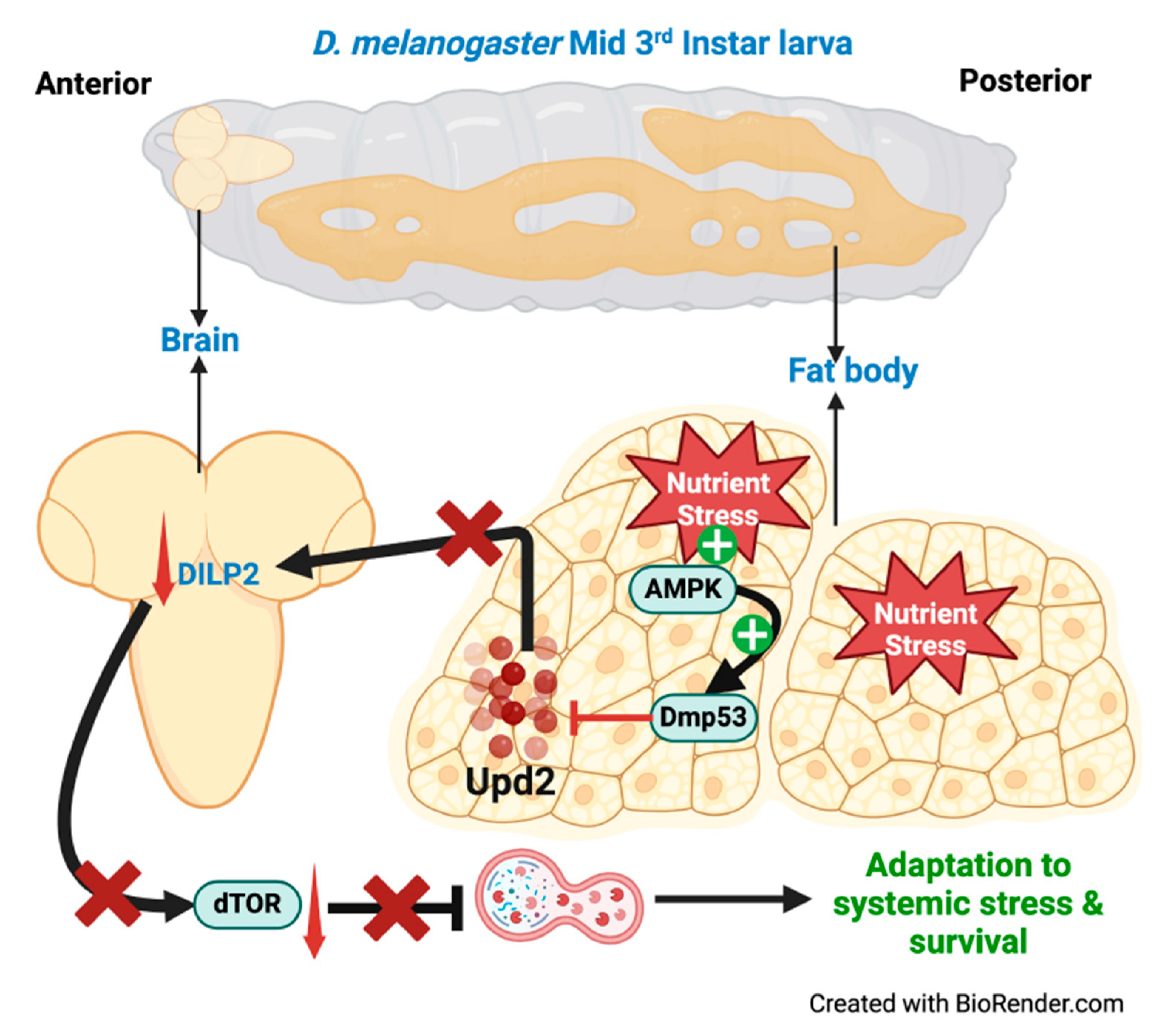
- Cell non-autonomous autophagy in systemic body response
- 3.
- Non-autonomously regulated autophagy in Development
- 4.
- Cell non-autonomous autophagy in Neurodegeneration and protein aggregation pathologies
- 5.
- Cell non-autonomous autophagy in Cancer and supercompetition
- 6.
- Cell non-autonomous autophagy in ECM-mediated regulation and Stem cell maintenance
- 7.
- Cell non-autonomous autophagy in mitochondrial degradation
Concluding Remarks
| Model organism | Source cell/tissue | Target cell/tissue | Molecule | Process affecting | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D. melanogaster | Adult brain | Intestine, muscles | DILPs | Aging | [4] |
| C. elegans | Intestine | BWM | miR-83 | Aging | [86] |
| D. melanogaster | Fat body | Brain | Dmp53, Upd2 | Survival during stress | [88] |
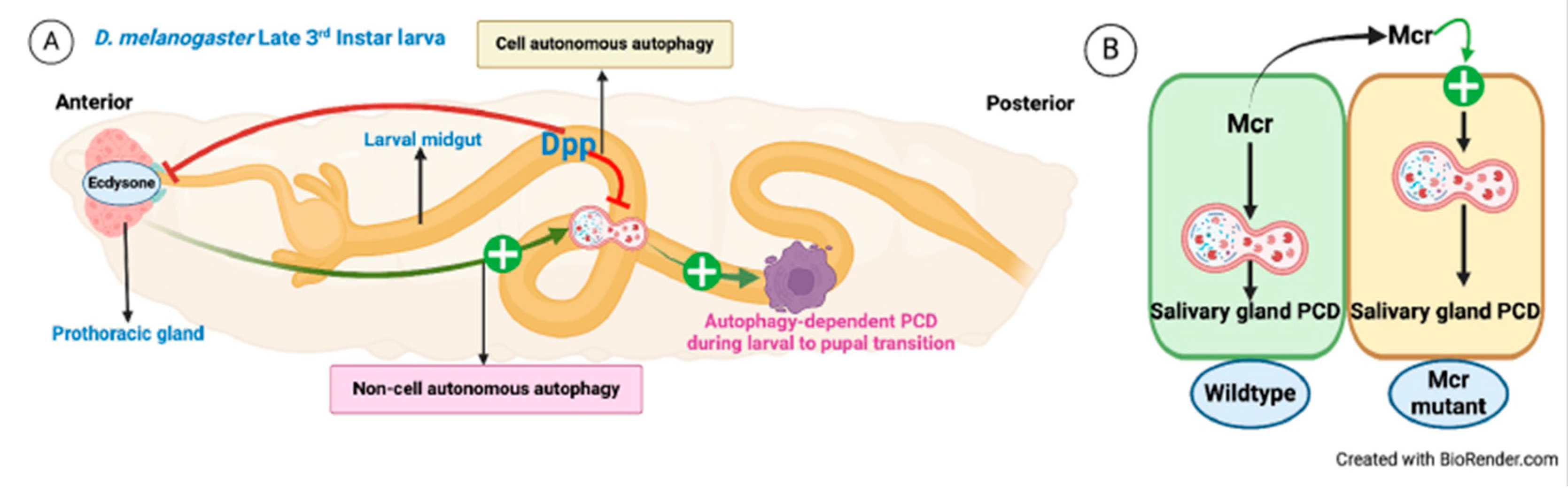
| D. melanogaster | Midgut | Prothoracic gland | Dpp, 20E | PCD | [99] |
| D. melanogaster | Salivary gland Mcr+/+ | Salivary gland Mcr-/- | Mcr | PCD | [103] |
| HEK293T cells | ALS-ACM | HEK293T healthy cell | Secreted factors in ACM | Neuronal degradation | [108] |
| C. elegans | BWM | Coelomocyte | NA | Neuronal degradation | [114] |
| D. melanogaster | Hel25EWT cell | Hel25E-/- cell | Relative protein levels | Supercompetition | [137] |
| D. melanogaster | Fat-/- cell | Fat+/+ cell | Relative protein levels | Cancer | [136] |
| U2OS cells | Nutrient-replete cell | Nutrient-deplete cell | Ammonia | Cancer | [123,124] |
| D. melanogaster | Tumor niche | RafGOFScrib-/- | JNK | Cancer | [131] |
| D. melanogaster | Tumor niche | RasV12Scrib-/- | JNK, ROS | Cancer | [125] |
| D. melanogaster | ttv+/+ cell | ttv-/- cell | ECM component | ECM regulation | [145] |
| D. melanogaster | GSCs | CySCs | EGF | GSC maintenance | [87] |
| D. melanogaster | CySCs, Hub cells | GSCs | BMP ligands | GSC maintenance | [155] |
Conflict of Interest Statement
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- S. Alers, A.S. Löffler, S. Wesselborg, B. Stork, Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the Regulation of Autophagy: Cross Talk, Shortcuts, and Feedbacks, Mol Cell Biol 32 (2012) 2–11. [CrossRef]
- D.M. Gwinn, D.B. Shackelford, D.F. Egan, M.M. Mihaylova, A. Mery, D.S. Vasquez, B.E. Turk, R.J. Shaw, AMPK Phosphorylation of Raptor Mediates a Metabolic Checkpoint, Mol Cell 30 (2008) 214–226. [CrossRef]
- J. Kim, M. Kundu, B. Viollet, K.L. Guan, AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1, Nat Cell Biol 13 (2011) 132–141. [CrossRef]
- M. Ulgherait, A. Rana, M. Rera, J. Graniel, D.W. Walker, AMPK modulates tissue and organismal aging in a non-cell-autonomous manner, Cell Rep 8 (2014) 1767–1780. [CrossRef]
- T. Noda, Y. Ohsumi, Tor, a phosphatidylinositol kinase homologue, controls autophagy in yeast, Journal of Biological Chemistry 273 (1998). [CrossRef]
- D. Meley, C. Bauvy, J.H.P.M. Houben-Weerts, P.F. Dubbelhuis, M.T.J. Helmond, P. Codogno, A.J. Meijer, AMP-activated protein kinase and the regulation of autophagic proteolysis, Journal of Biological Chemistry 281 (2006) 34870–34879. [CrossRef]
- N. Hosokawa, T. Hara, T. Kaizuka, C. Kishi, A. Takamura, Y. Miura, S.I. Iemura, T. Natsume, K. Takehana, N. Yamada, J.L. Guan, N. Oshiro, N. Mizushima, Nutrient-dependent mTORCl association with the ULK1-Atg13-FIP200 complex required for autophagy, Mol Biol Cell 20 (2009). [CrossRef]
- D. Mijaljica, M. Prescott, R.J. Devenish, Microautophagy in mammalian cells: Revisiting a 40-year-old conundrum, Autophagy 7 (2011) 673–682. [CrossRef]
- S. Kaushik, A.M. Cuervo, Chaperone-mediated autophagy: A unique way to enter the lysosome world, Trends Cell Biol 22 (2012) 407–417. [CrossRef]
- N.C. Mulakkal, P. Nagy, S. Takats, R. Tusco, G. Juhász, I.P. Nezis, Autophagy in drosophila: From historical studies to current knowledge, Biomed Res Int 2014 (2014). [CrossRef]
- W. Cao, J. Li, K. Yang, D. Cao, An overview of autophagy: Mechanism, regulation and research progress, Bull Cancer 108 (2021) 304–322. [CrossRef]
- C. de Duve, R. Wattiaux, Functions of Lysosomes, Annu Rev Physiol 28 (1966) 435–492. [CrossRef]
- M. Tsukada, Y. Ohsumi, Isolation and characterization of autophagy-defective mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, FEBS Lett 333 (1993) 169–174. [CrossRef]
- T.M. Harding, K.A. Morano, S. V. Scott, D.J. Klionsky, Isolation and characterization of yeast mutants in the cytoplasm to vacuole protein targeting pathway, Journal of Cell Biology 131 (1995). [CrossRef]
- M. Thumm, R. Egner, B. Koch, M. Schlumpberger, M. Straub, M. Veenhuis, D.H. Wolf, Isolation of autophagocytosis mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, FEBS Lett 349 (1994). [CrossRef]
- N. Mizushima, T. Yoshimori, Y. Ohsumi, The role of atg proteins in autophagosome formation, Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27 (2011). [CrossRef]
- J. Yan, H. Kuroyanagi, A. Kuroiwa, Y.I. Matsuda, H. Tokumitsu, T. Tomoda, T. Shirasawa, M.A. Muramatsu, Identification of mouse ULK1, a novel protein kinase structurally related to C. elegans UNC-51, Biochem Biophys Res Commun 246 (1998). [CrossRef]
- C.A. Mercer, A. Kaliappan, P.B. Dennis, A novel, human Atg13 binding protein, Atg101, interacts with ULK1 and is essential for macroautophagy, Autophagy 5 (2009). [CrossRef]
- N. Hosokawa, T. Sasaki, S.I. Iemura, T. Natsume, T. Hara, N. Mizushima, Atg101, a novel mammalian autophagy protein interacting with Atg13, Autophagy 5 (2009). [CrossRef]
- E.Y.W. Chan, A. Longatti, N.C. McKnight, S.A. Tooze, Kinase-Inactivated ULK Proteins Inhibit Autophagy via Their Conserved C-Terminal Domains Using an Atg13-Independent Mechanism, Mol Cell Biol 29 (2009). [CrossRef]
- T. Hara, A. Takamura, C. Kishi, S.I. Iemura, T. Natsume, J.L. Guan, N. Mizushima, FIP200, a ULK-interacting protein, is required for autophagosome formation in mammalian cells, Journal of Cell Biology 181 (2008). [CrossRef]
- Y.C. Kim, K.L. Guan, MTOR: A pharmacologic target for autophagy regulation, Journal of Clinical Investigation 125 (2015) 25–32. [CrossRef]
- I.G. Ganley, D.H. Lam, J. Wang, X. Ding, S. Chen, X. Jiang, ULK1·ATG13·FIP200 Complex Mediates mTOR Signaling and Is Essential for Autophagy, Journal of Biological Chemistry 284 (2009) 12297–12305. [CrossRef]
- R.C. Scott, O. Schuldiner, T.P. Neufeld, Role and regulation of starvation-induced autophagy in the Drosophila fat body, Dev Cell 7 (2004). [CrossRef]
- P.M. Wong, C. Puente, I.G. Ganley, X. Jiang, The ULK1 complex sensing nutrient signals for autophagy activation, Autophagy 9 (2013) 124–137. [CrossRef]
- F.C. Dorsey, K.L. Rose, S. Coenen, S.M. Prater, V. Cavett, J.L. Cleveland, J. Caldwell-Busby, Mapping the phosphorylation sites of Ulk1., J Proteome Res 8 (2009) 5253–63. [CrossRef]
- H.X. Yuan, R.C. Russell, K.L. Guan, Regulation of PIK3C3/VPS34 complexes by MTOR in nutrient stress-induced autophagy, Autophagy 9 (2013) 1983–1995. [CrossRef]
- J.M. Park, C.H. Jung, M. Seo, N.M. Otto, D. Grunwald, K.H. Kim, B. Moriarity, Y.M. Kim, C. Starker, R.S. Nho, D. Voytas, D.H. Kim, The ULK1 complex mediates MTORC1 signaling to the autophagy initiation machinery via binding and phosphorylating ATG14, Autophagy 12 (2016) 547–564. [CrossRef]
- J.M. Park, M. Seo, C.H. Jung, D. Grunwald, M. Stone, N.M. Otto, E. Toso, Y. Ahn, M. Kyba, T.J. Griffin, L.A. Higgins, D.H. Kim, ULK1 phosphorylates Ser30 of BECN1 in association with ATG14 to stimulate autophagy induction, Autophagy 14 (2018) 584–597. [CrossRef]
- R.C. Russell, Y. Tian, H. Yuan, H.W. Park, Y.-Y. Chang, J. Kim, H. Kim, T.P. Neufeld, A. Dillin, K.-L. Guan, ULK1 induces autophagy by phosphorylating Beclin-1 and activating VPS34 lipid kinase, Nat Cell Biol 15 (2013) 741–750. [CrossRef]
- Z. Yue, S. Jin, C. Yang, A.J. Levine, N. Heintz, Beclin 1, an autophagy gene essential for early embryonic development, is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100 (2003). [CrossRef]
- E. Itakura, N. Mizushima, Atg14 and UVRAG: Mutually exclusive subunits of mammalian Beclin 1-PI3K complexes, Autophagy 5 (2009). [CrossRef]
- E. Itakura, C. Kishi, K. Inoue, N. Mizushima, Beclin 1 forms two distinct phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complexes with mammalian Atg14 and UVRAG, Mol Biol Cell 19 (2008). [CrossRef]
- Ogier-Denis, E.F.C. Blommaart, A.J. Meijer, P. Codogno, Distinct classes of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinases are involved in signaling pa7thways that control macroautophagy in HT-29 cells, Journal of Biological Chemistry 275 (2000). [CrossRef]
- K. Lindmo, A. Brech, K.D. Finley, S. Gaumer, D. Contamine, T.E. Rusten, H. Stenmark, The PI 3-kinase regulator Vps15 is required for autophagic clearance of protein aggregates, Autophagy 4 (2008). [CrossRef]
- K. Devereaux, C. Dall’Armi, A. Alcazar-Roman, Y. Ogasawara, X. Zhou, F. Wang, A. Yamamoto, P. de Camilli, G. Di Paolo, Regulation of Mammalian Autophagy by Class II and III PI 3-Kinases through PI3P Synthesis, PLoS One 8 (2013). [CrossRef]
- H.C. Dooley, M. Razi, H.E.J. Polson, S.E. Girardin, M.I. Wilson, S.A. Tooze, WIPI2 Links LC3 Conjugation with PI3P, Autophagosome Formation, and Pathogen Clearance by Recruiting Atg12-5-16L1, Mol Cell 55 (2014). [CrossRef]
- T. Proikas-Cezanne, S. Waddell, A. Gaugel, T. Frickey, A. Lupas, A. Nordheim, WIPI-1α (WIPI49), a member of the novel 7-bladed WIPI protein family, is aberrantly expressed in human cancer and is linked to starvation-induced autophagy, Oncogene 23 (2004). [CrossRef]
- Q. Lu, P. Yang, X. Huang, W. Hu, B. Guo, F. Wu, L. Lin, A.L. Kovács, L. Yu, H. Zhang, The WD40 Repeat PtdIns(3)P-Binding Protein EPG-6 Regulates Progression of Omegasomes to Autophagosomes, Dev Cell 21 (2011) 343–357. [CrossRef]
- Y. Ohashi, Activation mechanisms of the vps34 complexes, Cells 10 (2021). [CrossRef]
- S. Chowdhury, C. Otomo, A. Leitner, K. Ohashi, R. Aebersold, G.C. Lander, T. Otomo, Insights into autophagosome biogenesis from structural and biochemical analyses of the ATG2A-WIPI4 complex, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115 (2018) E9792–E9801. [CrossRef]
- T. Osawa, Y. Ishii, N.N. Noda, Human ATG2B possesses a lipid transfer activity which is accelerated by negatively charged lipids and WIPI4, Genes to Cells 25 (2020) 65–70. [CrossRef]
- A.R.J. Young, E.Y.W. Chan, X.W. Hu, R. Köchl, S.G. Crawshaw, S. High, D.W. Halley, J. Lippincott-Schwartz, S.A. Tooze, Starvation and ULK1-dependent cycling of mammalian Atg9 between the TGN and endosomes, J Cell Sci 119 (2006) 3888–3900. [CrossRef]
- H. Yamamoto, S. Kakuta, T.M. Watanabe, A. Kitamura, T. Sekito, C. Kondo-Kakuta, R. Ichikawa, M. Kinjo, Y. Ohsumi, Atg9 vesicles are an important membrane source during early steps of autophagosome formation, Journal of Cell Biology 198 (2012) 219–233. [CrossRef]
- R. Gómez-Sánchez, J. Rose, R. Guimarães, M. Mari, D. Papinski, E. Rieter, W.J. Geerts, R. Hardenberg, C. Kraft, C. Ungermann, F. Reggiori, Atg9 establishes Atg2-dependent contact sites between the endoplasmic reticulum and phagophores, Journal of Cell Biology 217 (2018) 2743–2763. [CrossRef]
- K. Matoba, T. Kotani, A. Tsutsumi, T. Tsuji, T. Mori, D. Noshiro, Y. Sugita, N. Nomura, S. Iwata, Y. Ohsumi, T. Fujimoto, H. Nakatogawa, M. Kikkawa, N.N. Noda, Atg9 is a lipid scramblase that mediates autophagosomal membrane expansion, Nat Struct Mol Biol 27 (2020) 1185–1193. [CrossRef]
- S. Maeda, C. Otomo, T. Otomo, The autophagic membrane tether ATG2A transfers lipids between membranes, Elife 8 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Y. Ohsumi, N. Mizushima, Two ubiquitin-like conjugation systems essential for autophagy, Semin Cell Dev Biol 15 (2004). [CrossRef]
- N. Mizushima, T. Noda, T. Yoshimori, Y. Tanaka, T. Ishii, M.D. George, D.J. Klionsky, M. Ohsumi, Y. Ohsumi, A protein conjugation system essential for autophagy, Nature 395 (1998). [CrossRef]
- N. Mizushima, T. Noda, Y. Ohsumi, Apg16p is required for the function of the Apg12p-Apg5p conjugate in the yeast autophagy pathway, EMBO Journal 18 (1999). [CrossRef]
- N. Fujita, T. Itoh, H. Omori, M. Fukuda, T. Noda, T. Yoshimori, The Atg16L complex specifies the site of LC3 lipidation for membrane biogenesis in autophagy, Mol Biol Cell 19 (2008). [CrossRef]
- E. Hirata, Y. Ohya, K. Suzuki, Atg4 plays an important role in efficient expansion of autophagic isolation membranes by cleaving lipidated Atg8 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, PLoS One 12 (2017). [CrossRef]
- G. Juhász, B. Érdi, M. Sass, T.P. Neufeld, Atg7-dependent autophagy promotes neuronal health, stress tolerance, and longevity but is dispensable for metamorphosis in Drosophila, Genes Dev 21 (2007) 3061–3066. [CrossRef]
- Y. Ichimura, T. Kirisako, T. Takao, Y. Satomi, Y. Shimonishi, N. Ishihara, N. Mizushima, I. Tanida, E. Kominami, M. Ohsumi, T. Noda, Y. Ohsumi, A ubiquitin-like system mediates protein lipidation, Nature 408 (2000) 488–492. [CrossRef]
- M. Komatsu, S. Waguri, T. Chiba, S. Murata, J.I. Iwata, I. Tanida, T. Ueno, M. Koike, Y. Uchiyama, E. Kominami, K. Tanaka, Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice, Nature 441 (2006). [CrossRef]
- M. Komatsu, S. Waguri, T. Ueno, J. Iwata, S. Murata, I. Tanida, J. Ezaki, N. Mizushima, Y. Ohsumi, Y. Uchiyama, E. Kominami, K. Tanaka, T. Chiba, Impairment of starvation-induced and constitutive autophagy in Atg7-deficient mice, Journal of Cell Biology 169 (2005). [CrossRef]
- M. Li, Y. Hou, J. Wang, X. Chen, Z.M. Shao, X.M. Yin, Kinetics comparisons of mammalian Atg4 homologues indicate selective preferences toward diverse Atg8 substrates, Journal of Biological Chemistry 286 (2011). [CrossRef]
- Y. Yamada, N.N. Suzuki, Y. Fujioka, Y. Ohsumi, Y. Ichimura, F. Inagaki, Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of Atg3, Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 62 (2006). [CrossRef]
- Y. Yamada, N.N. Suzuki, T. Hanada, Y. Ichimura, H. Kumeta, Y. Fujioka, Y. Ohsumi, F. Inagaki, The crystal structure of Atg3, an autophagy-related ubiquitin carrier protein (E2) enzyme that mediates Atg8 lipidation, Journal of Biological Chemistry 282 (2007). [CrossRef]
- T. Shintani, N. Mizushima, Y. Ogawa, A. Matsuura, T. Noda, Y. Ohsumi, Apg10p, a novel protein-conjugating enzyme essential for autophagy in yeast, EMBO Journal 18 (1999). [CrossRef]
- T. Nemoto, I. Tanida, E. Tanida-Miyake, N. Minematsu-Ikeguchi, M. Yokota, M. Ohsumi, T. Ueno, E. Kominami, The mouse APG10 homologue, an E2-like enzyme for Apg12p conjugation, facilitates MAP-LC3 modification, Journal of Biological Chemistry 278 (2003). [CrossRef]
- Y. Ichimura, T. Kumanomidou, Y.S. Sou, T. Mizushima, J. Ezaki, T. Ueno, E. Kominami, T. Yamane, K. Tanaka, M. Komatsu, Structural basis for sorting mechanism of p62 in selective autophagy, Journal of Biological Chemistry 283 (2008). [CrossRef]
- S. Jäger, C. Bucci, I. Tanida, T. Ueno, E. Kominami, P. Saftig, E.L. Eskelinen, Role for Rab7 in maturation of late autophagic vacuoles, J Cell Sci 117 (2004). [CrossRef]
- M.G. Gutierrez, D.B. Munafó, W. Berón, M.I. Colombo, Rab7 is required for the normal progression of the autophagic pathway in mammalian cells, J Cell Sci 117 (2004). [CrossRef]
- P. Jiang, T. Nishimura, Y. Sakamaki, E. Itakura, T. Hatta, T. Natsume, N. Mizushima, The HOPS complex mediates autophagosome-lysosome fusion through interaction with syntaxin 17, Mol Biol Cell 25 (2014). [CrossRef]
- U. Nair, A. Jotwani, J. Geng, N. Gammoh, D. Richerson, W.L. Yen, J. Griffith, S. Nag, K. Wang, T. Moss, M. Baba, J.A. McNew, X. Jiang, F. Reggiori, T.J. Melia, D.J. Klionsky, SNARE proteins are required for macroautophagy, Cell 146 (2011). [CrossRef]
- Hatano, M. Matsui, A. Yamamoto, H. Nakaya, T. Yoshimori, Y. Ohsumi, T. Tokuhisa, N. Mizushima, The role of autophagy during the early neonatal starvation period, Nature 432 (2004) 1032–1036. [CrossRef]
- M. Rangel, J. Kong, V. Bhatt, K. Khayati, J.Y. Guo, Autophagy and tumorigenesis, FEBS Journal 289 (2022) 7177–7198. [CrossRef]
- D.R. Miller, A. Thorburn, Autophagy and organelle homeostasis in cancer, Dev Cell 56 (2021) 906–918. [CrossRef]
- N. Mizushima, A brief history of autophagy from cell biology to physiology and disease, Nat Cell Biol 20 (2018). [CrossRef]
- A.P.K. Wodrich, A.W. Scott, E. Giniger, What do we mean by “aging”? Questions and perspectives revealed by studies in Drosophila, Mech Ageing Dev 213 (2023). [CrossRef]
- C. López-Otín, M.A. Blasco, L. Partridge, M. Serrano, G. Kroemer, The hallmarks of aging, Cell 153 (2013). [CrossRef]
- H. Koga, S. Kaushik, A.M. Cuervo, Protein homeostasis and aging: The importance of exquisite quality control, Ageing Res Rev 10 (2011) 205–215. [CrossRef]
- M.C. Barbosa, R.A. Grosso, C.M. Fader, Hallmarks of aging: An autophagic perspective, Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 10 (2019). [CrossRef]
- K.M. Berendzen, J. Durieux, L.W. Shao, Y. Tian, H. eui Kim, S. Wolff, Y. Liu, A. Dillin, Neuroendocrine Coordination of Mitochondrial Stress Signaling and Proteostasis, Cell 166 (2016) 1553-1563.e10. [CrossRef]
- D. O’Brien, L.M. Jones, S. Good, J. Miles, M.S. Vijayabaskar, R. Aston, C.E. Smith, D.R. Westhead, P. van Oosten-Hawle, A PQM-1-Mediated Response Triggers Transcellular Chaperone Signaling and Regulates Organismal Proteostasis, Cell Rep 23 (2018) 3905–3919. [CrossRef]
- R.C. Taylor, A. Dillin, XXBP-1 Is a cell-nonautonomous regulator of stress resistance and longevity, Cell 153 (2013) 1435. [CrossRef]
- P. Van Oosten-Hawle, R.S. Porter, R.I. Morimoto, Regulation of organismal proteostasis by transcellular chaperone signaling, Cell 153 (2013) 1366. [CrossRef]
- J.T. Chang, C. Kumsta, A.B. Hellman, L.M. Adams, M. Hansen, Spatiotemporal regulation of autophagy during Caenorhabditis elegans aging, Elife 6 (2017). [CrossRef]
- D.F. Egan, D.B. Shackelford, M.M. Mihaylova, S. Gelino, R.A. Kohnz, W. Mair, D.S. Vasquez, A. Joshi, D.M. Gwinn, R. Taylor, J.M. Asara, J. Fitzpatrick, A. Dillin, B. Viollet, M. Kundu, M. Hansen, R.J. Shaw, Phosphorylation of ULK1 (hATG1) by AMP-activated protein kinase connects energy sensing to mitophagy, Science (1979) 331 (2011) 456–461. [CrossRef]
- R.C. Scott, G. Juhász, T.P. Neufeld, Direct Induction of Autophagy by Atg1 Inhibits Cell Growth and Induces Apoptotic Cell Death, Current Biology 17 (2007) 1–11. [CrossRef]
- L.R. Lapierre, C. Kumsta, M. Sandri, A. Ballabio, M. Hansen, Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of autophagy in aging, Autophagy 11 (2015) 867–880. [CrossRef]
- S.V. Thalyana, F.J. Slack, MicroRNAs and their roles in aging, J Cell Sci 125 (2012) 7–17. [CrossRef]
- X. Chen, H. Liang, J. Zhang, K. Zen, C.Y. Zhang, Secreted microRNAs: A new form of intercellular communication, Trends Cell Biol 22 (2012) 125–132. [CrossRef]
- D. Gerlach, E. V. Kriventseva, N. Rahman, C.E. Vejnar, E.M. Zdobnov, miROrtho: Computational survey of microRNA genes, Nucleic Acids Res 37 (2009). [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhou, X. Wang, M. Song, Z. He, G. Cui, G. Peng, C. Dieterich, A. Antebi, N. Jing, Y. Shen, A secreted microRNA disrupts autophagy in distinct tissues of Caenorhabditis elegans upon ageing, Nat Commun 10 (2019). [CrossRef]
- R. Sênos Demarco, B.S. Uyemura, D.L. Jones, EGFR Signaling Stimulates Autophagy to Regulate Stem Cell Maintenance and Lipid Homeostasis in the Drosophila Testis, Cell Rep 30 (2020) 1101-1116.e5. [CrossRef]
- M.C. Ingaramo, J.A. Sánchez, N. Perrimon, A. Dekanty, Fat Body p53 Regulates Systemic Insulin Signaling and Autophagy under Nutrient Stress via Drosophila Upd2 Repression, Cell Rep 33 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Y. Fuchs, H. Steller, Live to die another way: Modes of programmed cell death and the signals emanating from dying cells, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16 (2015) 329–344. [CrossRef]
- S. Arakawa, M. Tsujioka, T. Yoshida, H. Tajima-Sakurai, Y. Nishida, Y. Matsuoka, I. Yoshino, Y. Tsujimoto, S. Shimizu, Role of Atg5-dependent cell death in the embryonic development of Bax/Bak double-knockout mice, Cell Death Differ 24 (2017) 1598–1608. [CrossRef]
- D. Denton, T. Xu, S. Kumar, Autophagy as a pro-death pathway, Immunol Cell Biol 93 (2015) 35–42. [CrossRef]
- L. Galluzzi, I. Vitale, J.M. Abrams, E.S. Alnemri, E.H. Baehrecke, M. V. Blagosklonny, T.M. Dawson, V.L. Dawson, W.S. El-Deiry, S. Fulda, E. Gottlieb, D.R. Green, M.O. Hengartner, O. Kepp, R.A. Knight, S. Kumar, S.A. Lipton, X. Lu, F. Madeo, W. Malorni, P. Mehlen, G. Nũez, M.E. Peter, M. Piacentini, D.C. Rubinsztein, Y. Shi, H.U. Simon, P. Vandenabeele, E. White, J. Yuan, B. Zhivotovsky, G. Melino, G. Kroemer, Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012, Cell Death Differ 19 (2012) 107–120. [CrossRef]
- J. Yuan, G. Kroemer, Alternative cell death mechanisms in development and beyond, Genes Dev 24 (2010) 2592–2602. [CrossRef]
- K. King-Jones, C.S. Thummel, Nuclear receptors - A perspective from Drosophila, Nat Rev Genet 6 (2005) 311–323. [CrossRef]
- D. Denton, M.T. Aung-Htut, S. Kumar, Developmentally programmed cell death in Drosophila, Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1833 (2013) 3499–3506. [CrossRef]
- S. Kumar, D. Cakouros, Transcriptional control of the core cell-death machinery, Trends Biochem Sci 29 (2004) 193–199. [CrossRef]
- S. Nicolson, D. Denton, S. Kumar, Ecdysone-mediated programmed cell death in Drosophila, International Journal of Developmental Biology 59 (2015) 23–32. [CrossRef]
- E.H. Baechrecke, Steroid regulation of programmed cell death during Drosophila development, Cell Death Differ 7 (2000). [CrossRef]
- D. Denton, T. Xu, S. Dayan, S. Nicolson, S. Kumar, Dpp regulates autophagy-dependent midgut removal and signals to block ecdysone production, Cell Death Differ 26 (2019) 763–778. [CrossRef]
- D.L. Berry, E.H. Baehrecke, Growth Arrest and Autophagy Are Required for Salivary Gland Cell Degradation in Drosophila, Cell 131 (2007) 1137–1148. [CrossRef]
- P.E. Joubert, G. Meiffren, I.P. Grégoire, G. Pontini, C. Richetta, M. Flacher, O. Azocar, P.O. Vidalain, M. Vidal, V. Lotteau, P. Codogno, C. Rabourdin-Combe, M. Faure, Autophagy Induction by the Pathogen Receptor CD46, Cell Host Microbe 6 (2009) 354–366. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Sanjuan, C.P. Dillon, S.W.G. Tait, S. Moshiach, F. Dorsey, S. Connell, M. Komatsu, K. Tanaka, J.L. Cleveland, S. Withoff, D.R. Green, Toll-like receptor signalling in macrophages links the autophagy pathway to phagocytosis, Nature 450 (2007) 1253–1257. [CrossRef]
- L. Lin, F.S.L.M. Rodrigues, C. Kary, A. Contet, M. Logan, R.H.G. Baxter, W. Wood, E.H. Baehrecke, Complement-Related Regulates Autophagy in Neighboring Cells, Cell 170 (2017) 158-171.e8. [CrossRef]
- T.K. Chang, B. V. Shravage, S.D. Hayes, C.M. Powers, R.T. Simin, J. Wade Harper, E.H. Baehrecke, Uba1 functions in Atg7- and Atg3-independent autophagy, Nat Cell Biol 15 (2013) 1067–1078. [CrossRef]
- A.M. Blokhuis, E.J.N. Groen, M. Koppers, L.H. Van Den Berg, R.J. Pasterkamp, Protein aggregation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Acta Neuropathol 125 (2013) 777–794. [CrossRef]
- Kim, L. Tempest, A. Velagapudi, R. Libby, J. Ravits, TDP-43 and ubiquitinated cytoplasmic aggregates in sporadic ALS are low frequency and widely distributed in the lower motor neuron columns independent of disease spread, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis 11 (2010) 321–327. [CrossRef]
- M. Yang, L. Chen, K. Swaminathan, S. Herrlinger, F. Lai, R. Shiekhattar, J.F. Chen, A C9ORF72/SMCR8-containing complex regulates ULK1 and plays a dual role in autophagy, Sci Adv 2 (2016). [CrossRef]
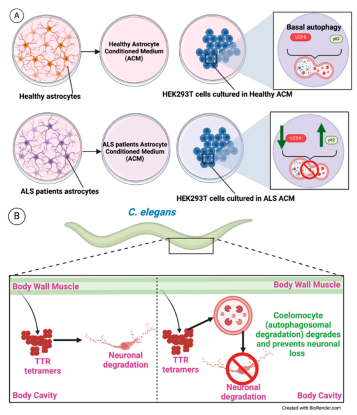
- M. Madill, K. McDonagh, J. Ma, A. Vajda, P. McLoughlin, T. O’Brien, O. Hardiman, S. Shen, Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patient iPSC-derived astrocytes impair autophagy via non-cell autonomous mechanisms, Mol Brain 10 (2017). [CrossRef]
- M. Goedert, B. Falcon, F. Clavaguera, M. Tolnay, Prion-like mechanisms in the pathogenesis of tauopathies and synucleinopathies, Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 14 (2014) 1–11. [CrossRef]
- C.I. Nussbaum-Krammer, R.I. Morimoto, Caenorhabditis elegans as a model system for studying non-cellautonomous mechanisms in protein-misfolding diseases, DMM Disease Models and Mechanisms 7 (2014) 31–39. [CrossRef]
- T. Coelho, M.S. Maurer, O.B. Suhr, THAOS-The Transthyretin Amyloidosis Outcomes Survey: Initial report on clinical manifestations in patients with hereditary and wild-type transthyretin amyloidosis, Curr Med Res Opin 29 (2013) 63–76. [CrossRef]
- S.M. Johnson, S. Connelly, C. Fearns, E.T. Powers, J.W. Kelly, The transthyretin amyloidoses: From delineating the molecular mechanism of aggregation linked to pathology to a regulatory-agency-approved drug, J Mol Biol 421 (2012) 185–203. [CrossRef]
- J.D. Schonhoft, C. Monteiro, L. Plate, Y.S. Eisele, J.M. Kelly, D. Boland, C.G. Parker, B.F. Cravatt, S. Teruya, S. Helmke, M. Maurer, J. Berk, Y. Sekijima, M. Novais, T. Coelho, E.T. Powers, J.W. Kelly, Peptide probes detect misfolded transthyretin oligomers in plasma of hereditary amyloidosis patients, Sci Transl Med 9 (2017). [CrossRef]
- K. Madhivanan, E.R. Greiner, M. Alves-Ferreira, D. Soriano-Castell, N. Rouzbeh, C.A. Aguirre, J.F. Paulsson, J. Chapman, X. Jiang, F.K. Ooi, C. Lemos, A. Dillin, V. Prahlad, J.W. Kelly, S.E. Encalada, Cellular clearance of circulating transthyretin decreases cell-nonautonomous proteotoxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115 (2018) E7710–E7719. [CrossRef]
- M.G.V. Heiden, L.C. Cantley, C.B. Thompson, Understanding the warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation, Science (1979) 324 (2009) 1029–1033. [CrossRef]
- Warburg 1956, (n.d.).
- R.J. DeBerardinis, J.J. Lum, G. Hatzivassiliou, C.B. Thompson, The Biology of Cancer: Metabolic Reprogramming Fuels Cell Growth and Proliferation, Cell Metab 7 (2008) 11–20. [CrossRef]
- R.J. DeBerardinis, A. Mancuso, E. Daikhin, I. Nissim, M. Yudkoff, S. Wehrli, C.B. Thompson, Beyond aerobic glycolysis: Transformed cells can engage in glutamine metabolism that exceeds the requirement for protein and nucleotide synthesis, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104 (2007). [CrossRef]
- P. Gao, I. Tchernyshyov, T.C. Chang, Y.S. Lee, K. Kita, T. Ochi, K.I. Zeller, A.M. De Marzo, J.E. Van Eyk, J.T. Mendell, C. V. Dang, C-Myc suppression of miR-23a/b enhances mitochondrial glutaminase expression and glutamine metabolism, Nature 458 (2009) 762–765. [CrossRef]
- M. Szeliga, M. Obara-Michlewska, Glutamine in neoplastic cells: Focus on the expression and roles of glutaminases, Neurochem Int 55 (2009) 71–75. [CrossRef]
- B.P. Bode, B.C. Fuchs, B.P. Hurley, J.L. Conroy, J.E. Suetterlin, K.K. Tanabe, D.B. Rhoads, S.F. Abcouwer, W.W. Souba, Molecular and functional analysis of glutamine uptake in human hepatoma and liver-derived cells, Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 283 (2002). [CrossRef]
- R.J. Deberardinis, T. Cheng, Q’s next: The diverse functions of glutamine in metabolism, cell biology and cancer, Oncogene 29 (2010) 313–324. [CrossRef]
- C.H. Eng, K. Yu, J. Lucas, E. White, R.T. Abraham, Ammonia derived from glutaminolysis is a diffusible regulator of autophagy, Sci Signal 3 (2010). [CrossRef]
- C.H. Eng, R.T. Abraham, Glutaminolysis yields a metabolic by-product that stimulates autophagy, Autophagy 6 (2010). [CrossRef]
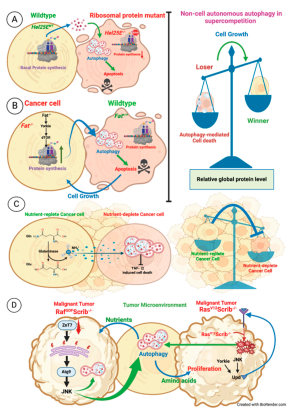
- N.S. Katheder, R. Khezri, F. O’Farrell, S.W. Schultz, A. Jain, M.K.O. Schink, T.A. Theodossiou, T. Johansen, G. Juhász, D. Bilder, A. Brech, H. Stenmark, T.E. Rusten, Microenvironmental autophagy promotes tumour growth, Nature 541 (2017) 417–420. [CrossRef]
- M. Hershfinkel, W.F. Silverman, I. Sekler, The zinc sensing receptor, a link between zinc and cell signaling, in: Molecular Medicine, 2007: pp. 331–336. [CrossRef]
- R.S. Macdonald, Zinc and Health: Current Status and Future Directions The Role of Zinc in Growth and Cell Proliferation 1,2, 2000. https://academic.oup.com/jn/article-abstract/130/5/1500S/4686427.
- M. Yan, Y. Song, C.P. Wong, K. Hardin, E. Ho, Zinc Deficiency Alters DNA Damage Response Genes in Normal Human Prostate Epithelial Cells 1,2,3, 2008.
- T. Kambe, T. Tsuji, A. Hashimoto, N. Itsumura, The physiological, biochemical, and molecular roles of zinc transporters in zinc homeostasis and metabolism, Physiol Rev 95 (2015). [CrossRef]
- K.A. Mccall, C.-C. Huang, C.A. Fierke, Zinc and Health: Current Status and Future Directions Function and Mechanism of Zinc Metalloenzymes 1, J. Nutr 130 (2000).
- T. Wei, X. Ji, Y. Gao, X. Zhu, G. Xiao, ZnT7 RNAi favors RafGOFscrib−/−-induced tumor growth and invasion in Drosophila through JNK signaling pathway, Oncogene 40 (2021) 2217–2229. [CrossRef]
- K. Doggett, F.A. Grusche, H.E. Richardson, A.M. Brumby, Loss of the Drosophila cell polarity regulator Scribbled promotes epithelial tissue overgrowth and cooperation with oncogenic Ras-Raf through impaired Hippo pathway signaling, BMC Dev Biol 11 (2011). [CrossRef]
- J.A. McCubrey, L.S. Steelman, W.H. Chappell, S.L. Abrams, E.W.T. Wong, F. Chang, B. Lehmann, D.M. Terrian, M. Milella, A. Tafuri, F. Stivala, M. Libra, J. Basecke, C. Evangelisti, A.M. Martelli, R.A. Franklin, Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance, Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1773 (2007) 1263–1284. [CrossRef]
- M. Uhlirova, H. Jasper, D. Bohmann, Non-cell-autonomous induction of tissue overgrowth by JNK/Ras cooperation in a Drosophila tumor model, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102 (2005). [CrossRef]
- L. Poillet-Perez, E. White, Role of tumor and host autophagy in cancer metabolism, Genes Dev 33 (2019). [CrossRef]
- R. Nagata, N. Akai, S. Kondo, K. Saito, S. Ohsawa, T. Igaki, Yorkie drives supercompetition by non-autonomous induction of autophagy via bantam microRNA in Drosophila, Current Biology 32 (2022) 1064-1076.e4. [CrossRef]
- R. Nagata, M. Nakamura, Y. Sanaki, T. Igaki, Cell Competition Is Driven by Autophagy, Dev Cell 51 (2019) 99-112.e4. [CrossRef]
- J.R. Bishop, M. Schuksz, J.D. Esko, Heparan sulphate proteoglycans fine-tune mammalian physiology, Nature 446 (2007) 1030–1037. [CrossRef]
- U. Häcker, K. Nybakken, N. Perrimon, Heparan sulphate proteoglycans: The sweet side of development, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6 (2005) 530–541. [CrossRef]
- C.A. Kirkpatrick, S.B. Selleck, Heparan sulfate proteoglycans at a glance, J Cell Sci 120 (2007) 1829–1832. [CrossRef]
- X. Lin, Functions of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in cell signaling during development, Development 131 (2004) 6009–6021. [CrossRef]
- A.D. Lander, S.B. Selleck, The elusive functions of proteoglycans: In vivo veritas, Journal of Cell Biology 148 (2000). [CrossRef]
- K.G. Johnson, A.P. Tenney, A. Ghose, A.M. Duckworth, M.E. Higashi, K. Parfitt, O. Marcu, T.R. Heslip, J.L. Marsh, T.L. Schwarz, J.G. Flanagan, D. Van Vactor, The HSPGs Syndecan and dallylike bind the receptor phosphatase LAR and exert distinct effects on synaptic development, Neuron 49 (2006) 517–531. [CrossRef]
- E. Stryker, K.G. Johnson, LAR, liprin α and the regulation of active zone morphogenesis, J Cell Sci 120 (2007) 3723–3728. [CrossRef]
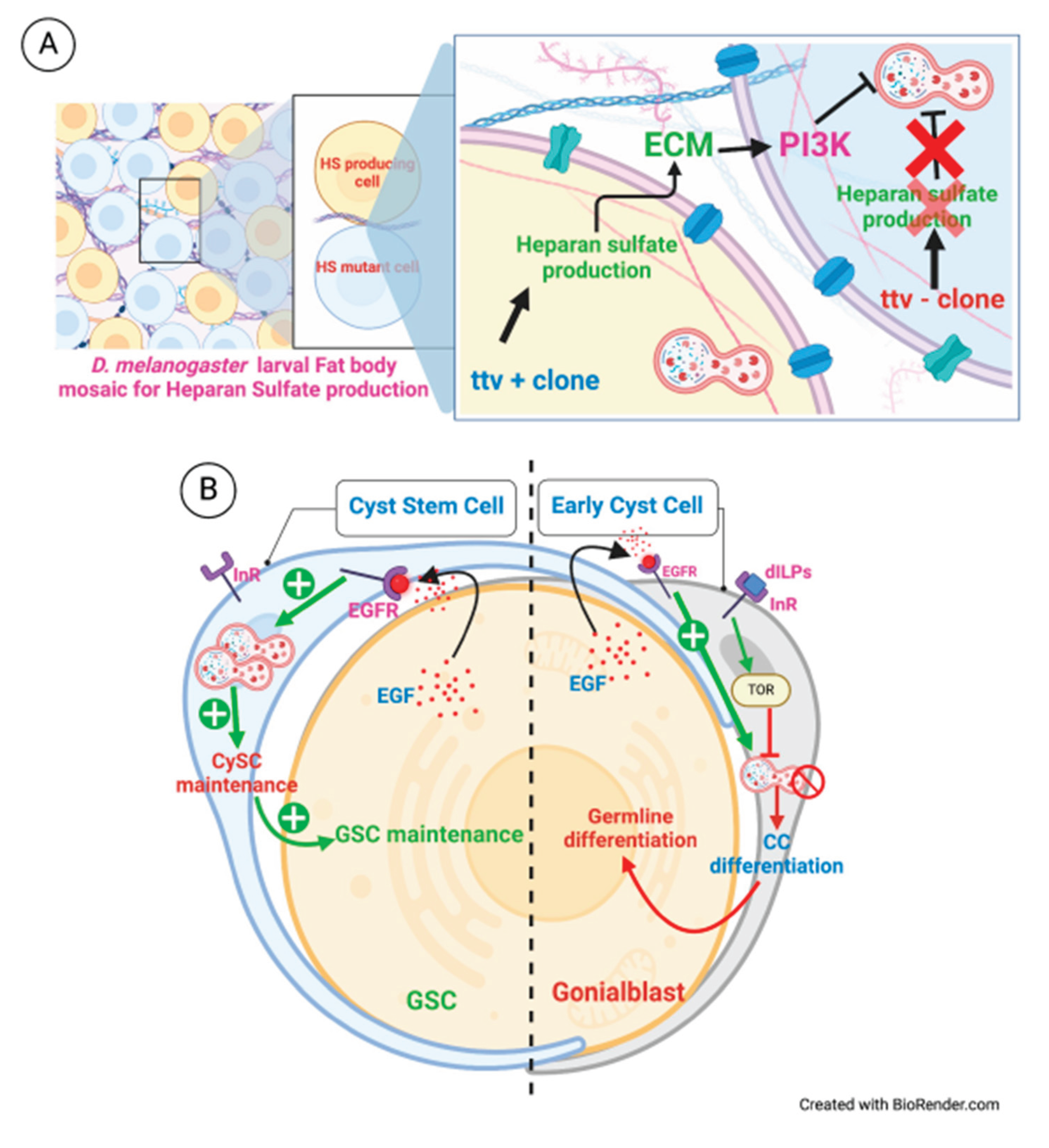
- C.E. Reynolds-Peterson, N. Zhao, J. Xu, T.M. Serman, J. Xu, S.B. Selleck, Heparan sulfate proteoglycans regulate autophagy in Drosophila, Autophagy 13 (2017) 1262–1279. [CrossRef]
- Y. Ren, C.A. Kirkpatrick, J.M. Rawson, M. Sun, S.B. Selleck, Cell type-specific requirements for heparan sulfate biosynthesis at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction: Effects on synapse function, membrane trafficking, and mitochondrial localization, Journal of Neuroscience 29 (2009) 8539–8550. [CrossRef]
- D. Drummond-Barbosa, Stem cells, their niches and the systemic environment: An aging network, Genetics 180 (2008) 1787–1797. [CrossRef]
- B. Levine, D.J. Klionsky, Development by self-digestion: Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy, Dev Cell 6 (2004). [CrossRef]
- A.G. Hudson, B.B. Parrott, Y. Qian, C. Schulz, A Temporal Signature of Epidermal Growth Factor Signaling Regulates the Differentiation of Germline Cells in Testes of Drosophila melanogaster, PLoS One 8 (2013). [CrossRef]
- L.A. Perkins, M.R. Johnson, M.B. Melnick, N. Perrimon, The nonreceptor protein tyrosine phosphatase Corkscrew functions in multiple receptor tyrosine kinase pathways in Drosophila, Dev Biol 180 (1996). [CrossRef]
- Y. Yung, Y. Dolginov, Z. Yao, H. Rubinfeld, D. Michael, T. Hanoch, E. Roubini, Z. Lando, D. Zharhary, R. Seger, Detection of ERK activation by a novel monoclonal antibody, FEBS Lett 408 (1997). [CrossRef]
- M. de Cuevas, E.L. Matunis, The stem cell niche: Lessons from the Drosophila testis, Development 138 (2011) 2861–2869. [CrossRef]
- A.A. Shivdasani, P.W. Ingham, Regulation of Stem Cell Maintenance and Transit Amplifying Cell Proliferation by TGF-β Signaling in Drosophila Spermatogenesis, Current Biology 13 (2003) 2065–2072. [CrossRef]
- E. Kawase, M.D. Wong, B.C. Ding, T. Xie, Gbb/Bmp signaling is essential for maintaining germline stem cells and for repressing bam transcription in the Drosophila testis, Development 131 (2004) 1365–1375. [CrossRef]
- V.B. Varga, D. Schuller, F. Szikszai, J. Szinyákovics, G. Puska, T. Vellai, T. Kovács, Autophagy is required for spermatogonial differentiation in the Drosophila testis, Biol Futur 73 (2022) 187–204. [CrossRef]
- G. Ashrafi, T.L. Schwarz, The pathways of mitophagy for quality control and clearance of mitochondria, Cell Death Differ 20 (2013) 31–42. [CrossRef]
- R.C. Scarpulla, R.B. Vega, D.P. Kelly, Transcriptional integration of mitochondrial biogenesis, Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism 23 (2012) 459–466. [CrossRef]
- R.J. Youle, A.M. Van Der Bliek, Mitochondrial fission, fusion, and stress, Science (1979) 337 (2012) 1062–1065. [CrossRef]
- C.H.O. Davis, K.Y. Kim, E.A. Bushong, E.A. Mills, D. Boassa, T. Shih, M. Kinebuchi, S. Phan, Y. Zhou, N.A. Bihlmeyer, J. V. Nguyen, Y. Jin, M.H. Ellisman, N. Marsh-Armstrong, Transcellular degradation of axonal mitochondria, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111 (2014) 9633–9638. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





