Submitted:
13 March 2024
Posted:
14 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
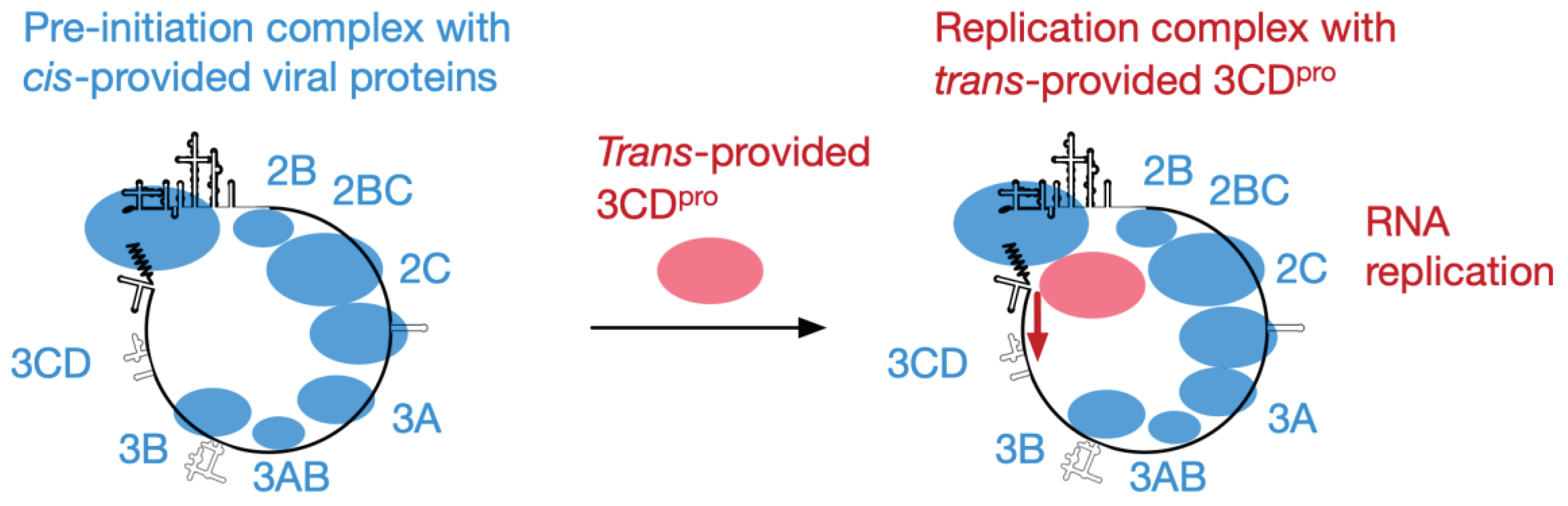
Importance
1. Introduction
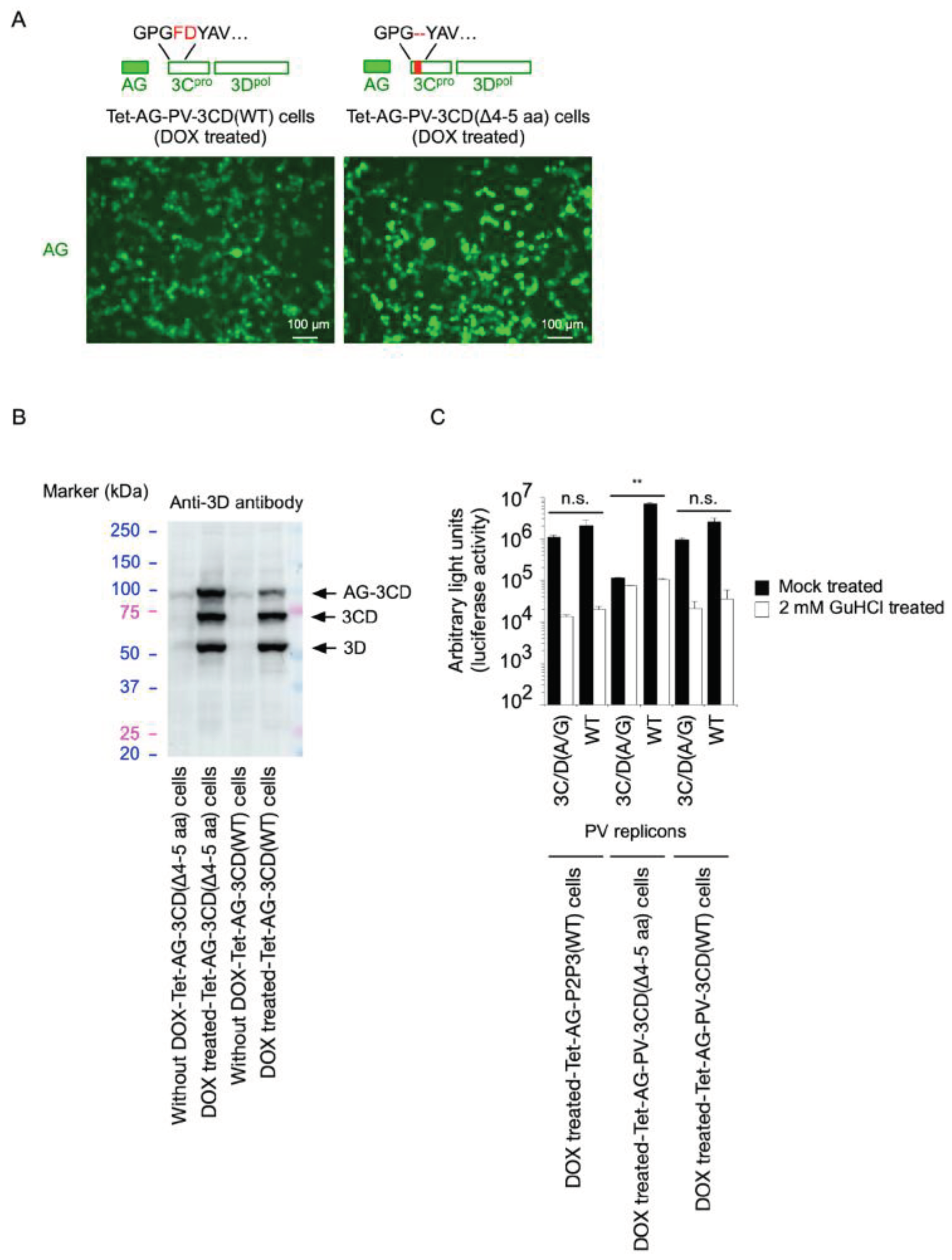
2. Results
3. Discussions
4. Materials and Methods
5. Plasmids
5.1. Lentivirus Expression Vectors for PV Non-Structural Proteins
5.2. PV Replicon Mutants
5.3. EV-A71 Replicon Mutants
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Disclosure
List of Abbreviations
References
- Kitamura, N.; Semler, B.L.; Rothberg, P.G.; Larsen, G.R.; Adler, C.J.; Dorner, A.J.; Emini, E.A.; Hanecak, R.; Lee, J.J.; van der Werf, S.; et al. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature 1981, 291, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lulla, V.; Dinan, A.M.; Hosmillo, M.; Chaudhry, Y.; Sherry, L.; Irigoyen, N.; Nayak, K.M.; Stonehouse, N.J.; Zilbauer, M.; Goodfellow, I.; et al. An upstream protein-coding region in enteroviruses modulates virus infection in gut epithelial cells. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 4, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, H.; Nicklin, M.J.; Murray, M.G.; Anderson, C.W.; Dunn, J.J.; Studier, F.; Wimmer, E. A second virus-encoded proteinase involved in proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein. Cell 1986, 45, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ypma-Wong, M.F.; Dewalt, P.G.; Johnson, V.H.; Lamb, J.G.; Semler, B.L. Protein 3CD is the major poliovirus proteinase responsible for cleavage of the p1 capsid precursor. Virology 1988, 166, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagnola, G.; Peersen, O. Co-folding and RNA activation of poliovirus 3Cpro polyprotein precursors. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Wang, P.; Qin, C.-F.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, G.-C.; Yang, J.; Sun, X.; Wu, W.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Human Enterovirus Nonstructural Protein 2CATPase Functions as Both an RNA Helicase and ATP-Independent RNA Chaperone. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieva, J.L.; Madan, V.; Carrasco, L. Viroporins: Structure and biological functions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeager, C.; Carter, G.; Gohara, D.W.; Yennawar, N.H.; Enemark, E.J.; Arnold, J.J.; E Cameron, C. Enteroviral 2C protein is an RNA-stimulated ATPase and uses a two-step mechanism for binding to RNA and ATP. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 11775–11798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Mueller, S.; Paul, A.V.; Wimmer, E.; Jiang, P. Direct Interaction between Two Viral Proteins, the Nonstructural Protein 2CATPase and the Capsid Protein VP3, Is Required for Enterovirus Morphogenesis. PLOS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Smeets, R.L.; Willems, P.H.; Dijkman, H.B.; Galama, J.M.; Melchers, W.J. Coxsackievirus protein 2B modifies endoplasmic reticulum membrane and plasma membrane permeability and facilitates virus release. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 3519–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, A.; Detjen, B.; Pozzatti, R.; Wimmer, E. The location of the polio genome protein in viral RNAs and its implication for RNA synthesis. Nature 1977, 268, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, J.; Ishikawa, K.; Arita, M.; Taniguchi, K. ACBD3-mediated recruitment of PI4KB to picornavirus RNA replication sites. EMBO J. 2011, 31, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greninger, A.L.; Knudsen, G.M.; Betegon, M.; Burlingame, A.L.; DeRisi, J.L. The 3A Protein from Multiple Picornaviruses Utilizes the Golgi Adaptor Protein ACBD3 To Recruit PI4KIIIβ. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3605–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessels, E.; Duijsings, D.; Niu, T.-K.; Neumann, S.; Oorschot, V.M.; de Lange, F.; Lanke, K.H.; Klumperman, J.; Henke, A.; Jackson, C.L.; et al. A Viral Protein that Blocks Arf1-Mediated COP-I Assembly by Inhibiting the Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor GBF1. Dev. Cell 2006, 11, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belov, G.A.; Feng, Q.; Nikovics, K.; Jackson, C.L.; Ehrenfeld, E. A Critical Role of a Cellular Membrane Traffic Protein in Poliovirus RNA Replication. PLOS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.-Y.; Ilnytska, O.; Belov, G.; Santiana, M.; Chen, Y.-H.; Takvorian, P.M.; Pau, C.; van der Schaar, H.; Kaushik-Basu, N.; Balla, T.; et al. Viral Reorganization of the Secretory Pathway Generates Distinct Organelles for RNA Replication. Cell 2010, 141, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorobantu, C.M.; van der Schaar, H.M.; Ford, L.A.; Strating, J.R.P.M.; Ulferts, R.; Fang, Y.; Belov, G.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M. Recruitment of PI4KIIIβ to Coxsackievirus B3 Replication Organelles Is Independent of ACBD3, GBF1, and Arf1. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2725–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Pallansch, M.; Kew, O.M.; Semler, B.L.; Omilianowski, D.R.; Anderson, C.W.; Wimmer, E.; Rueckert, R.R. Protein processing map of poliovirus. J. Virol. 1984, 49, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takegami, T.; Semler, B.L.; Anderson, C.W.; Wimmer, E. Membrane fractions active in poliovirus RNA replication contain VPg precursor polypeptides. Virology 1983, 128, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhy, D.A.; Giddings, T.H.; Kirkegaard, K. Remodeling the Endoplasmic Reticulum by Poliovirus Infection and by Individual Viral Proteins: An Autophagy-Like Origin for Virus-Induced Vesicles. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8953–8965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.V.; Cao, X.; Harris, K.S.; Lama, J.; Wimmer, E. Studies with poliovirus polymerase 3Dpol. Stimulation of poly(U) synthesis in vitro by purified poliovirus protein 3AB. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 29173–29181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama, J.; Paul, A.; Harris, K.; Wimmer, E. Properties of purified recombinant poliovirus protein 3aB as substrate for viral proteinases and as co-factor for RNA polymerase 3Dpol. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, O.C.; Ehrenfeld, E. Effects of Poliovirus 3AB Protein on 3D Polymerase-catalyzed Reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 12832–12840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andino, R.; Rieckhof, G.; Achacoso, P.; Baltimore, D. Poliovirus RNA synthesis utilizes an RNP complex formed around the 5′-end of viral RNA. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3587–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamarnik, A.V.; Andino, R. Switch from translation to RNA replication in a positive-stranded RNA virus. Minerva Anestesiol. 1998, 12, 2293–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.V.; Rieder, E.; Kim, D.W.; van Boom, J.H.; Wimmer, E. Identification of an RNA Hairpin in Poliovirus RNA That Serves as the Primary Template in the In Vitro Uridylylation of VPg. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10359–10370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.V.; Mugavero, J.; Molla, A.; Wimmer, E. Internal Ribosomal Entry Site Scanning of the Poliovirus Polyprotein: Implications for Proteolytic Processing. Virology 1998, 250, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, C.N.; Smoler, D.; Wimmer, E.; Baltimore, D. Defective Interfering Particles of Poliovirus I. Isolation and Physical Properties. J. Virol. 1971, 7, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuge, S.; Saito, I.; Nomoto, A. Primary structure of poliovirus defective-interfering particle genomes and possible generation mechanisms of the particles. J. Mol. Biol. 1986, 192, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Novak, J.; Kirkegaard, K. Coupling between genome translation and replication in an RNA virus. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 1726–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, R.J.; Tada, H.; Ypma-Wong, M.F.; Semler, B.L.; Wimmer, E. Mutational analysis of the genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 4207–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.V.; Molla, A.; Wimmer, E. Studies of a Putative Amphipathic Helix in the N-Terminus of Poliovirus Protein 2C. Virology 1994, 199, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lu, H.H.; Mueller, S.; Wimmer, E. The C-terminal residues of poliovirus proteinase 2A(pro) are critical for viral RNA replication but not for cis- or trans-proteolytic cleavage. J Gen Virol. 2001, 82 (Pt 2) Pt 2, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herod, M.R.; Gold, S.; Lasecka-Dykes, L.; Wright, C.; Ward, J.C.; McLean, T.C.; Forrest, S.; Jackson, T.; Tuthill, T.J.; Rowlands, D.J.; et al. Genetic economy in picornaviruses: Foot-and-mouth disease virus replication exploits alternative precursor cleavage pathways. PLOS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, D.M.; Hayward, C.; Rowlands, D.J.; Stonehouse, N.J.; Herod, M.R. Insights into Polyprotein Processing and RNA-Protein Interactions in Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Genome Replication. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0017123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, M.; Kojima, H.; Nagano, T.; Okabe, T.; Wakita, T.; Shimizu, H. Oxysterol-Binding Protein Family I Is the Target of Minor Enviroxime-Like Compounds. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4252–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, M. Mechanism of Poliovirus Resistance to Host Phosphatidylinositol-4 Kinase III β Inhibitor. ACS Infect. Dis. 2015, 2, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyoo, H.; Dorobantu, C.M.; van der Schaar, H.M.; van Kuppeveld, F.J. Modulation of proteolytic polyprotein processing by coxsackievirus mutants resistant to inhibitors targeting phosphatidylinositol-4-kinase IIIβ or oxysterol binding protein. Antivir. Res. 2017, 147, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melia, C.E.; van der Schaar, H.M.; Lyoo, H.; Limpens, R.W.; Feng, Q.; Wahedi, M.; Overheul, G.J.; van Rij, R.P.; Snijder, E.J.; Koster, A.J.; et al. Escaping Host Factor PI4KB Inhibition: Enterovirus Genomic RNA Replication in the Absence of Replication Organelles. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, M.; Bigay, J. Poliovirus Evolution toward Independence from the Phosphatidylinositol-4 Kinase III β/Oxysterol-Binding Protein Family I Pathway. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitsuka, H.; Ohsawa, C.; Ohiwa, T.; Umeda, I.; Suhara, Y. Antipicornavirus flavone Ro 09-0179. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1982, 22, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Heinz, B.; Vance, L.M. The antiviral compound enviroxime targets the 3A coding region of rhinovirus and poliovirus. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 4189–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, M. Phosphatidylinositol-4 kinase III beta and oxysterol-binding protein accumulate unesterified cholesterol on poliovirus-induced membrane structure. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 58, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, M. High-Order Epistasis and Functional Coupling of Infection Steps Drive Virus Evolution toward Independence from a Host Pathway. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0080021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikel, J.H.; Paget, C.J.; DeLong, D.C.; Nelson, J.D.; Wu, C.Y.E.; Paschal, J.W.; Dinner, A.; Templeton, R.J.; Chaney, M.O. Synthesis of syn and anti isomers of 6-[[(hydroxyimino)phenyl]methyl]-1-[(1-methylethyl)sulfonyl]-1H-benzimidazol-2-amine. Inhibitors of rhinovirus multiplication. J. Med. Chem. 1980, 23, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, M.; Kojima, H.; Nagano, T.; Okabe, T.; Wakita, T.; Shimizu, H. Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase III Beta Is a Target of Enviroxime-Like Compounds for Antipoliovirus Activity. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2364–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delang, L.; Paeshuyse, J.; Neyts, J. The role of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases and phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate during viral replication. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLeod, A.M.; Mitchell, D.R.; Palmer, N.J.; Van de Poël, H.; Conrath, K.; Andrews, M.; Leyssen, P.; Neyts, J. Identification of a Series of Compounds with Potent Antiviral Activity for the Treatment of Enterovirus Infections. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strating, J.R.; van der Linden, L.; Albulescu, L.; Bigay, J.; Arita, M.; Delang, L.; Leyssen, P.; van der Schaar, H.M.; Lanke, K.H.; Thibaut, H.J.; et al. Itraconazole Inhibits Enterovirus Replication by Targeting the Oxysterol-Binding Protein. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 600–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T.; Fujita, M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Nomanbhoy, T.; Rosenblum, J.S.; Nagasawa, M. 134. KRP-A218, an Orally Active and Selective PI4KB Inhibitor with Broad-Spectrum Anti-Rhinovirus Activity, Has Potent Therapeutic Antiviral Activity In vivo. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, S82–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semler, B.L.; Anderson, C.W.; Hanecak, R.; Dorner, L.F.; Wimmer, E. A membrane-associated precursor to poliovirus VPg identified by immunoprecipitation with antibodies directed against a synthetic heptapeptide. Cell 1982, 28, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Arita, M.; Sakai, S.; Kojima, H.; Senda, M.; Senda, T.; Hanada, K.; Kato, R. Ligand Recognition by the Lipid Transfer Domain of Human OSBP Is Important for Enterovirus Replication. ACS Infect. Dis. 2022, 8, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lovell, S.; Tiew, K.-C.; Mandadapu, S.R.; Alliston, K.R.; Battaile, K.P.; Groutas, W.C.; Chang, K.-O. Broad-Spectrum Antivirals against 3C or 3C-Like Proteases of Picornaviruses, Noroviruses, and Coronaviruses. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11754–11762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.A.; Dragovich, P.S.; Webber, S.E.; Fuhrman, S.A.; Patick, A.K.; Zalman, L.S.; Hendrickson, T.F.; Love, R.A.; Prins, T.J.; Marakovits, J.T.; et al. Structure-assisted design of mechanism-based irreversible inhibitors of human rhinovirus 3C protease with potent antiviral activity against multiple rhinovirus serotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1999, 96, 11000–11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kräusslich, H.-G.; Nicklin, M.J.; Lee, C.-K.; Wimmer, E. Polyprotein processing in picornavirus replication. Biochimie 1988, 70, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, O.H.; Svedin, E.; Kapell, S.; Nurminen, A.; Hytönen, V.P.; Flodström-Tullberg, M. Enteroviral proteases: Structure, host interactions and pathogenicity. Rev. Med Virol. 2016, 26, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, H.; Yoshino, Y.; Miyazawa, M.; Horie, H.; Ohka, S.; Nomoto, A. 2A Protease Is Not a Prerequisite for Poliovirus Replication. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5947–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuer, Q.; Kuhn, R.J.; Wimmer, E. Characterization of poliovirus clones containing lethal and nonlethal mutations in the genome-linked protein VPg. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 2967–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hämmerle, T.; Hellen, C.U.; Wimmer, E. Site-directed mutagenesis of the putative catalytic triad of poliovirus 3C proteinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 5412–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Jablonski, S.; Morrow, C.D. Mutation of the aspartic acid residues of the GDD sequence motif of poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase results in enzymes with altered metal ion requirements for activity. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Thompson, A.; Peersen, O.B. Structural basis for proteolysis-dependent activation of the poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3462–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shengjuler, D.; Chan, Y.M.; Sun, S.; Moustafa, I.M.; Li, Z.-L.; Gohara, D.W.; Buck, M.; Cremer, P.S.; Boehr, D.D.; Cameron, C.E. The RNA-Binding Site of Poliovirus 3C Protein Doubles as a Phosphoinositide-Binding Domain. Structure 2017, 25, 1875–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, W.S.; Parsley, T.B.; Bogerd, H.P.; Towner, J.S.; Semler, B.L.; Cullen, B.R. Utilization of a mammalian cell-based RNA binding assay to characterize the RNA binding properties of picornavirus 3C proteinases. RNA 1998, 4, 215–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amero, C.D.; Arnold, J.J.; Moustafa, I.M.; Cameron, C.E.; Foster, M.P. Identification of the oriI-Binding Site of Poliovirus 3C Protein by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 4363–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, M.; Nagata, N.; Sata, T.; Miyamura, T.; Shimizu, H. Quantitative analysis of poliomyelitis-like paralysis in mice induced by a poliovirus replicon. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3317–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, M.; Iwai-Itamochi, M. Evaluation of antigenic differences between wild and Sabin vaccine strains of poliovirus using the pseudovirus neutralization test. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, M.; Iwai, M.; Wakita, T.; Shimizu, H. Development of a Poliovirus Neutralization Test with Poliovirus Pseudovirus for Measurement of Neutralizing Antibody Titer in Human Serum. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Charini, W.; Burns, C.C.; Ehrenfeld, E.; Semler, B.L. trans rescue of a mutant poliovirus RNA polymerase function. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 2655–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teterina, N.L.; Zhou, W.D.; Cho, M.W.; Ehrenfeld, E. Inefficient complementation activity of poliovirus 2C and 3D proteins for rescue of lethal mutations. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 4245–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wimmer, E. Intragenomic Complementation of a 3AB Mutant in Dicistronic Polioviruses. Virology 1995, 209, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towner, J.S.; Mazanet, M.M.; Semler, B.L. Rescue of defective poliovirus RNA replication by 3AB-containing precursor polyproteins [In Process Citation]. Journal of virology. 1998, 72, 7191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Franco, D.; Paul, A.V.; Wimmer, E. Tyrosine 3 of Poliovirus Terminal Peptide VPg(3B) Has an Essential Function in RNA Replication in the Context of Its Precursor Protein, 3AB. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5669–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.H.; Li, X.; Cuconati, A.; Wimmer, E. Analysis of picornavirus 2A(pro) proteins: Separation of proteinase from translation and replication functions. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 7445–7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, I.; Chaudhry, Y.; Richardson, A.; Meredith, J.; Almond, J.W.; Barclay, W.; Evans, D.J. Identification of a cis-Acting Replication Element within the Poliovirus Coding Region. J. Virol. 2000, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.-Q.; Townsend, H.L.; Jha, B.K.; Paranjape, J.M.; Silverman, R.H.; Barton, D.J. A Phylogenetically Conserved RNA Structure in the Poliovirus Open Reading Frame Inhibits the Antiviral Endoribonuclease RNase L. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5561–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, H.L.; Jha, B.K.; Han, J.-Q.; Maluf, N.K.; Silverman, R.H.; Barton, D.J. A viral RNA competitively inhibits the antiviral endoribonuclease domain of RNase L. RNA 2008, 14, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ward, C.B.; Mueller, S.; Futcher, B.; Skiena, S.; Paul, A.V.; Wimmer, E. Identification of two functionally redundant RNA elements in the coding sequence of poliovirus using computer-generated design. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2012, 109, 14301–14307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrill, C.P.; Westesson, O.; Schulte, M.B.; Strings, V.R.; Segal, M.; Andino, R. Global RNA Structure Analysis of Poliovirus Identifies a Conserved RNA Structure Involved in Viral Replication and Infectivity. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 11670–11683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.V.; Yin, J.; Mugavero, J.; Rieder, E.; Liu, Y.; Wimmer, E. A “Slide-back” Mechanism for the Initiation of Protein-primed RNA Synthesis by the RNA Polymerase of Poliovirus. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 43951–43960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, Y.C.; Semler, B.L.; Ehrenfeld, E. Requirements for RNA Replication of a Poliovirus Replicon by Coxsackievirus B3 RNA Polymerase. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9413–9421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Hurk, P.J.J.C.v.D.; Schrama, I.W.J.; Galama, J.M.D.; Melchers, W.J.G. Trans-complementation of a genetic defect in the coxsackie B3 virus 2B protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ooij, M.J.M.; Vogt, D.A.; Paul, A.; Castro, C.; Kuijpers, J.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Cameron, C.E.; Wimmer, E.; Andino, R.; Melchers, W.J.G. Structural and functional characterization of the coxsackievirus B3 CRE(2C): Role of CRE(2C) in negative- and positive-strand RNA synthesis. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Lin, Q.; Wang, C.; Xing, J.; Yan, K.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Cardona, C.J.; Xing, Z. Enterovirus A71 2B Inhibits Interferon-Activated JAK/STAT Signaling by Inducing Caspase-3-Dependent Karyopherin-α1 Degradation. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 762869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalzampuia, H.; Ganji, V.K.; Elango, S.; Krishnaswamy, N.; Umapathi, V.; Reddy, G.R.; Sanyal, A.; Hj, D. Expression of foot-and-mouth disease virus non-structural protein 3A upregulates the expression of autophagy and immune response genes in vitro. Virus Res. 2020, 292, 198247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barco, A.; Feduchi, E.; Carrasco, L. Poliovirus Protease 3Cpro Kills Cells by Apoptosis. Virology 2000, 266, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuyumcu-Martinez, N.M.; Van Eden, M.E.; Younan, P.; Lloyd, R.E. Cleavage of Poly(A)-Binding Protein by Poliovirus 3C Protease Inhibits Host Cell Translation: A Novel Mechanism for Host Translation Shutoff. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothstein, M.A.; Richards, O.C.; Amin, C.; Ehrenfeld, E. Enzymatic activity of poliovirus RNA polymerase synthesized in Escherichia coli from viral cDNA. Virology 1988, 164, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.S.; Reddigari, S.R.; Nicklin, M.J.; Hämmerle, T.; Wimmer, E. Purification and characterization of poliovirus polypeptide 3CD, a proteinase and a precursor for RNA polymerase. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 7481–7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.S.; Pathak, H.B.; Goodfellow, I.G.; Arnold, J.J.; Cameron, C.E. Insight into Poliovirus Genome Replication and Encapsidation Obtained from Studies of 3B-3C Cleavage Site Mutants. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9370–9387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.; Rowlands, D.; Clarke, B. The complete nucleotide sequence of the RNA coding for the primary translation product of foot and mouth disease virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 2461–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forss, S.; Strebel, K.; Beck, E.; Schaller, H. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 6587–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.G.; Kapusinszky, B.; Wang, C.; Rose, R.K.; Lipton, H.L.; Delwart, E.L. The Fecal Viral Flora of Wild Rodents. PLOS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Kuhn, R.J.; Wimmer, E. Replication of poliovirus RNA containing two VPg coding sequences leads to a specific deletion event. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 5572–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berryman, S.; Moffat, K.; Harak, C.; Lohmann, V.; Jackson, T. Foot-and-mouth disease virus replicates independently of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and type III phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 1841–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.; Pathak, H.B.; Cameron, C.E.; Rombaut, B.; Wimmer, E.; Paul, A.V. Stimulation of poliovirus RNA synthesis and virus maturation in a HeLa cell-free in vitro translation-RNA replication system by viral protein 3CDpro. Virol. J. 2005, 2, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, A.; Ogram, S.A.; Morasco, B.J.; Smerage, L.E.; Flanegan, J.B. Viral precursor protein P3 and its processed products perform discrete and essential functions in the poliovirus RNA replication complex. Virology 2015, 485, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percy, N.; Barclay, W.S.; Sullivan, M.; Almond, J.W. A poliovirus replicon containing the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene can be used to study the replication and encapsidation of poliovirus RNA. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 5040–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagino-Yamagishi, K.; Nomoto, A. In vitro construction of poliovirus defective interfering particles. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 5386–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barclay, W.; Percy, N.; Almond, J.W.; Moon, D.; Richardson, A.; Evans, D.J.; Li, Q.; Hutchinson, G. Encapsidation studies of poliovirus subgenomic replicons. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansardi, D.C.; Porter, D.C.; Morrow, C.D. Complementation of a poliovirus defective genome by a recombinant vaccinia virus which provides poliovirus P1 capsid precursor in trans. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.-Y.; Van Eden, M.; Busch, M.G.; Ehrenfeld, E.; Summers, D.F. trans -Encapsidation of a Poliovirus Replicon by Different Picornavirus Capsid Proteins. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 7972–7977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, M.; Iwai-Itamochi, M. High-throughput analysis of anti-poliovirus neutralization antibody titre in human serum by the pseudovirus neutralization test. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugent, C.I.; Johnson, K.L.; Sarnow, P.; Kirkegaard, K. Functional Coupling between Replication and Packaging of Poliovirus Replicon RNA. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, J.; Ooi, Y.S.; Wilkinson, A.W.; Peters, C.E.; Foy, E.; Johnson, J.R.; Zengel, J.; Ding, S.; Weng, K.-F.; Laufman, O.; et al. Enterovirus pathogenesis requires the host methyltransferase SETD3. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2523–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.E.; Schulze-Gahmen, U.; Eckhardt, M.; Jang, G.M.; Xu, J.; Pulido, E.H.; Bardine, C.; Craik, C.S.; Ott, M.; Gozani, O.; et al. Structure-function analysis of enterovirus protease 2A in complex with its essential host factor SETD3. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, M.T.; Smith, M.; Carlyle, S.; Konopka-Anstadt, J.L.; Burns, C.C.; Konz, J.; Andino, R.; Macadam, A. Genetic stabilization of attenuated oral vaccines against poliovirus types 1 and 3. Nature 2023, 619, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Two years since rollout of novel oral polio vaccine type 2 (nOPV2): How’s it all working out? 2023. Available online: https://polioeradicationorg/news-post/two-years-since-rollout-of-novel-oral-polio-vaccine-type-2-nopv2-hows-it-all-working-out/.
- Arita, M.; Wakita, T.; Shimizu, H. Characterization of pharmacologically active compounds that inhibit poliovirus and enterovirus 71 infectivity. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2518–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, J.; Andino, R. Poliovirus Requires a Precise 5′ End for Efficient Positive-Strand RNA Synthesis. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6394–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, M. Essential Domains of Oxysterol-Binding Protein Required for Poliovirus Replication. Viruses 2022, 14, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, M.; Ami, Y.; Wakita, T.; Shimizu, H. Cooperative Effect of the Attenuation Determinants Derived from Poliovirus Sabin 1 Strain Is Essential for Attenuation of Enterovirus 71 in the NOD/SCID Mouse Infection Model. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamentsky, L.; Jones, T.R.; Fraser, A.; Bray, M.-A.; Logan, D.J.; Madden, K.L.; Ljosa, V.; Rueden, C.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Carpen-ter, A.E. Improved structure, function and compatibility for CellProfiler: Modular high-throughput image analysis software. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1179–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




