Submitted:
29 February 2024
Posted:
13 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- 1.
- Characterization of the physicochemical properties of CFs.
- 2.
- Establishment of the adsorption efficiency of five MPPs of different plastic materials (e.g., PVC, PP, LDPE, HDPE, and Nylon 6) on the hydrophobic surface of CFs via batch adsorption tests at ambient temperature.
- 3.
- Determination of the effect of the adsorption environment on the adsorption rate of MPPs onto the surface of CFs.
- 4.
- Establishment of the dominant mechanism driving the adsorption of microplastic MPPs onto CFs.
2. Experimental Methodology
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Adsorbents: Cattail Fibers (CFs) and Activated Carbon
2.1.2. Microplastic Particles (MPPs)
2.1.3. Adsorption Environment
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Cattail Fiber Characterization
2.2.2. Batch Adsorption Tests
2.2.3. Experimental Design
2.2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
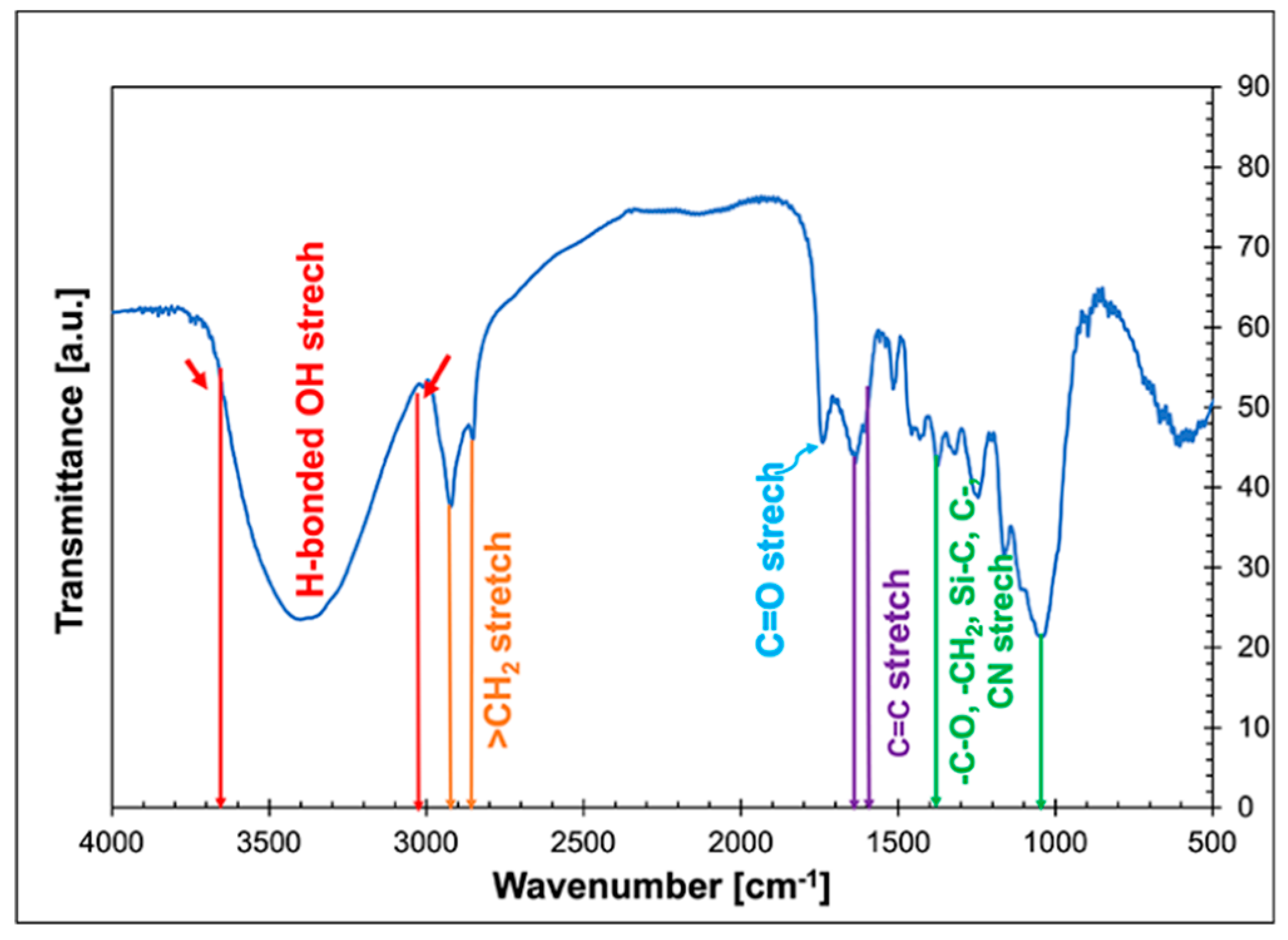
3.1. Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis of Cattail Fibres
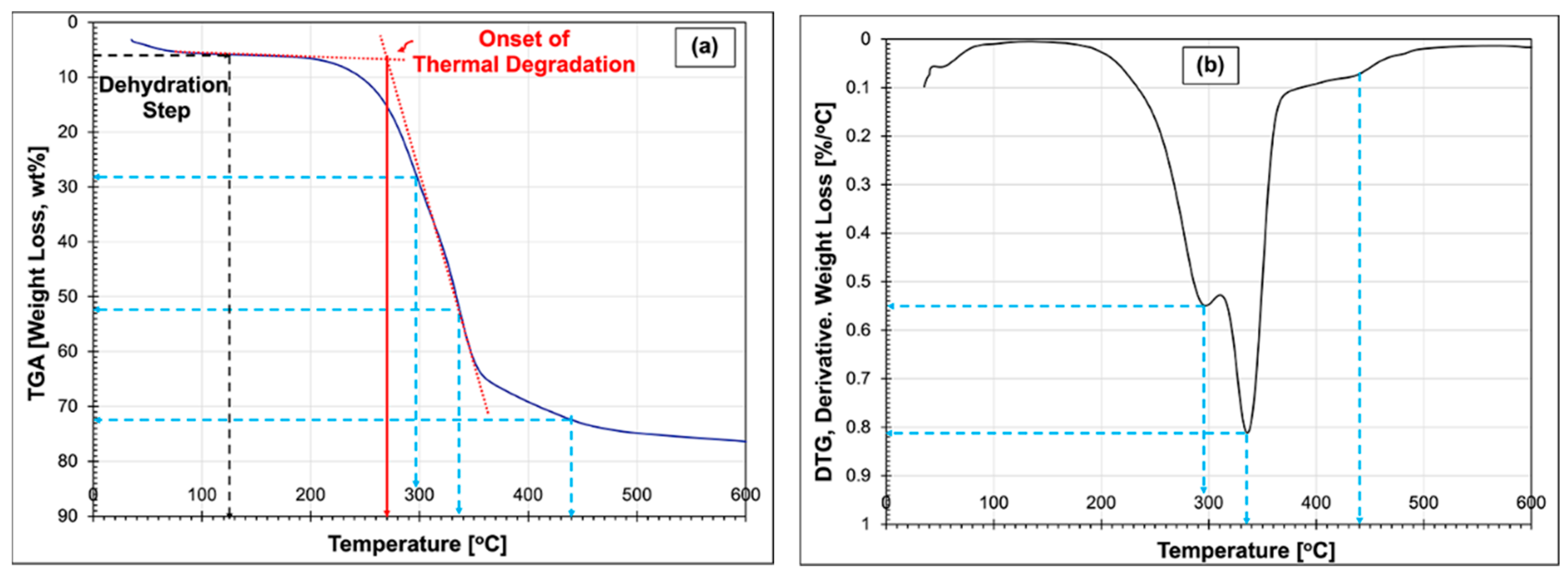
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) of Cattail Fibres
3.3. Contac Angle of Cattail Fibres and MPPs
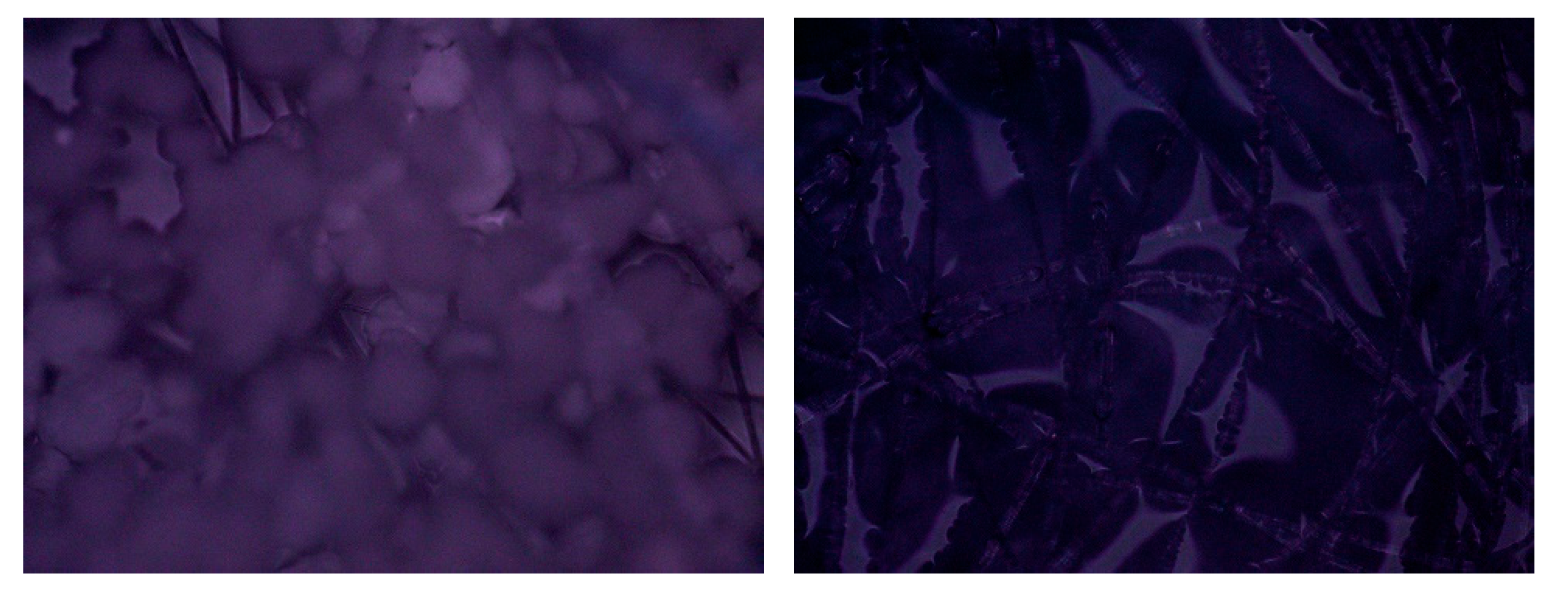
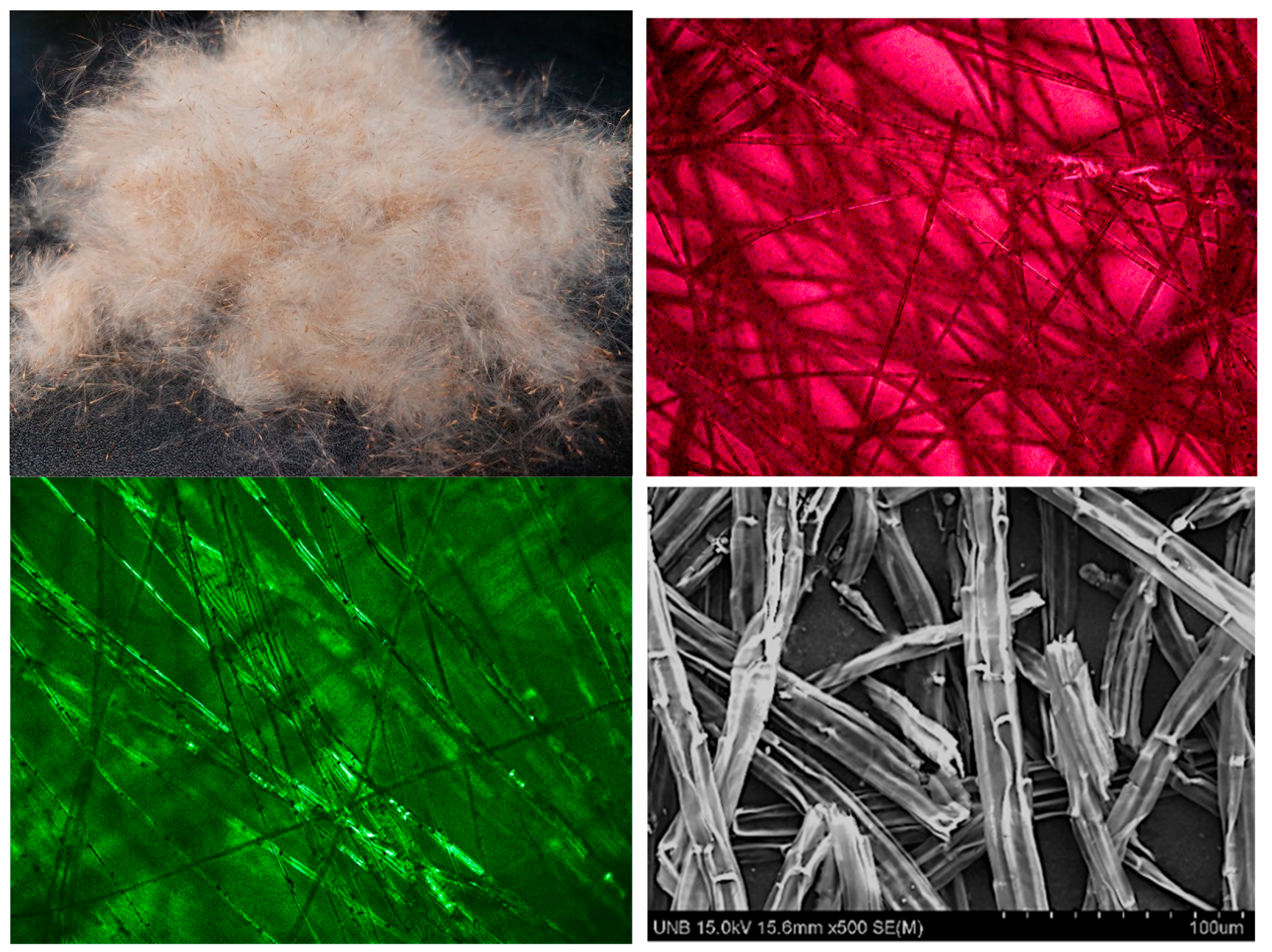
3.4. Optical and Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.5. Surface Area of CFs and Activated Carbon
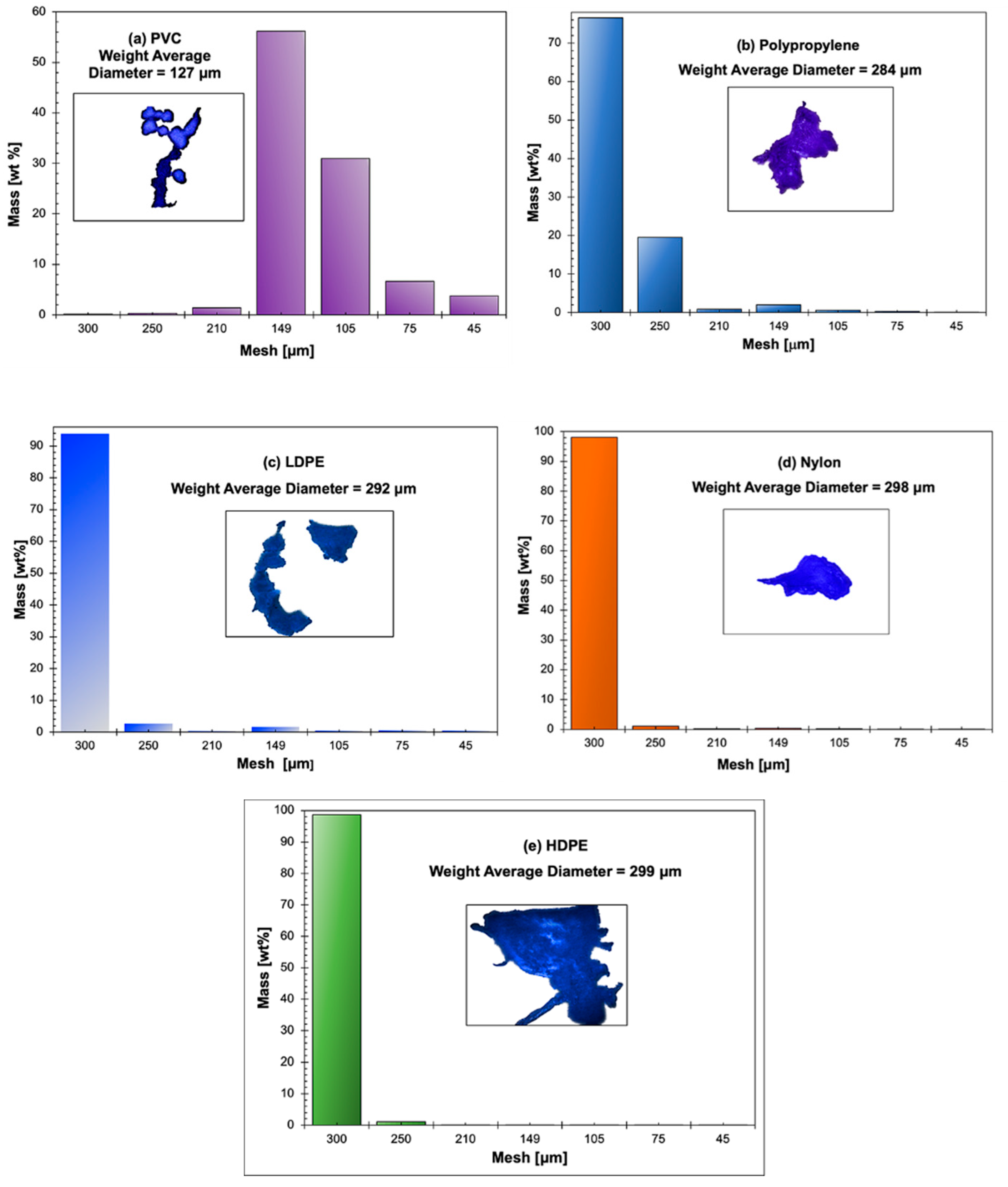
3.6. Sieve Analysis of Microplastic Particles
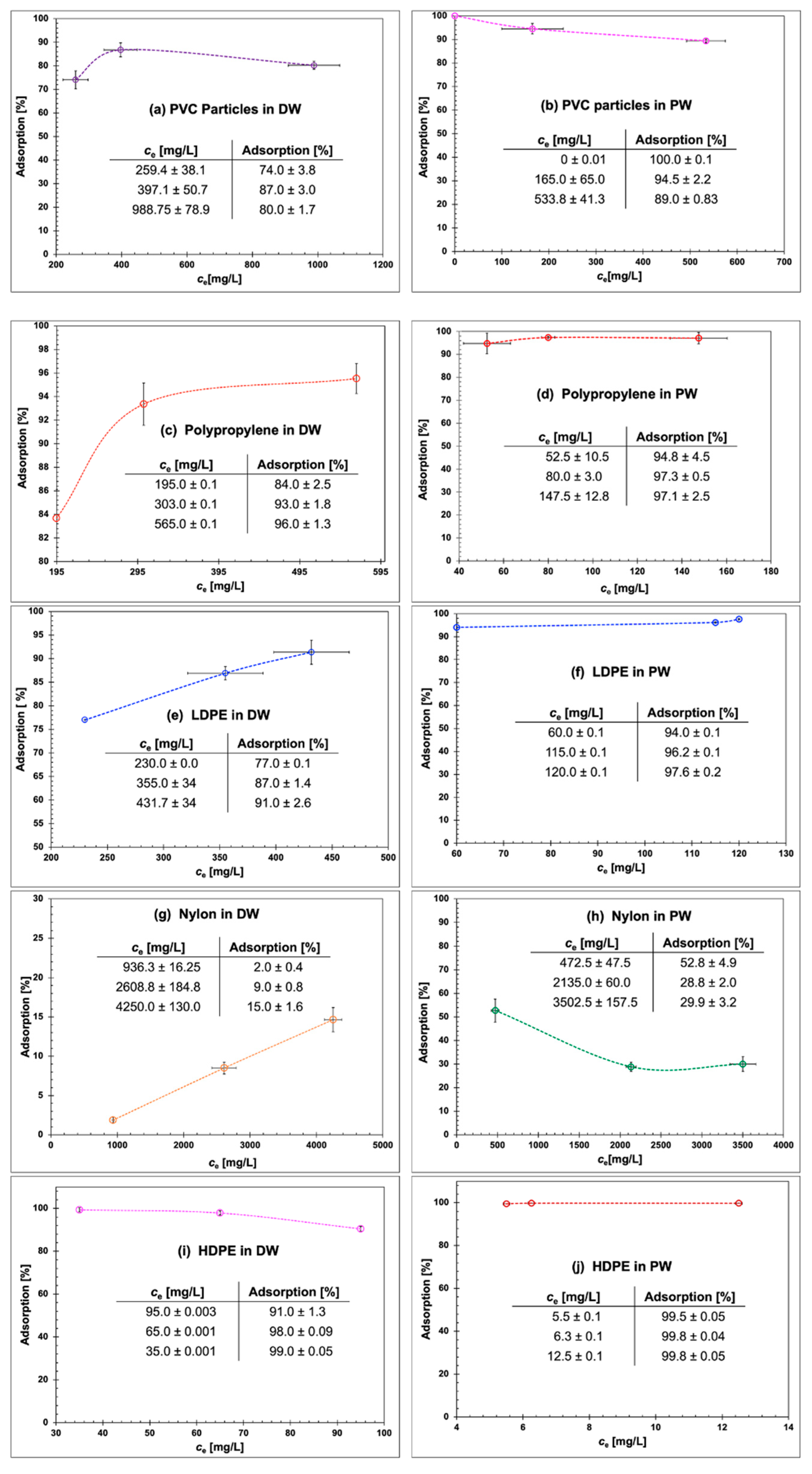
3.7. Batch Adsorption Tests of MMPs onto CFs
3.8. Adsorption Mechanism of MPPs onto the CFs Surface
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgement
References
- Our Planet is choking on plastic. UN Environment Programme. Available online: https://www.unep.org/interactives/beat-plastic-pollution/?gad_source=1&gclid=EAIaIQobChMI-Yf4r5ehhAMVf2lHAR0ldQeREAAYASAAEgIN3_D_BwE. (accessed on February 10 2024).
- Kang, H.; Washington, A.; Capobianco, MD.; Yan, X.; Cruz, VV.; Weed, M.; Johnson, J.; Johns III, G.; Brudvig, GW.; Pan, X.; Gu, J. Concentration-Dependent Photocatalytic Upcycling of Poly (ethylene terephthalate) Plastic Waste. ACS Mater. Lett. 2023, 5, 3032–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Kong, XY.; Lyu, M.; Tay, XT.; Đokić, M.; Chin, KF.; Yang, CT.; Lee, EK.; Zhang, J.; Tham, CY.; Chan, WX. Upcycling of non-biodegradable plastics by base metal photocatalysis. Chem. 2023, 9, 2683–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Ding, T.; Peng, C.; Naz, I.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Micro-and nanoplastics in wastewater treatment plants: occurrence, removal, fate, impacts and remediation technologies–a critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 130205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohana, AA.; Farhad, SM.; Haque, N.; Pramanik, BK. Understanding the fate of nano-plastics in wastewater treatment plants and their removal using membrane processes. Chemosphere. 2021, 284, 31430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Xiao, D.; Wang, M.; Gao, Y.; Ma, D. Solar-driven photocatalysis for recycling and upcycling plastics. Appl. Catal. B. 2024, 341, 123357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briassoulis, D. Agricultural plastics as a potential threat to food security, health, and environment through soil pollution by microplastics: Problem definition. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164533, (1-31). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, BK.; Pramanik, SK.; Monira, S. Understanding the fragmentation of microplastics into nano-plastics and removal of nano/microplastics from wastewater using membrane, air flotation and nano-ferrofluid processes. Chemosphere. 2021, 282, 131053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Wei, W.; Chen, H; Ni, BJ. Removal of microplastics and nanoplastics from urban waters: separation and degradation. Water Research 2022, 221, 118820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, JC.; et., al. Microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; et. al., Ecotoxicological effects of microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 15, 122273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; et., al. Defense responses in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to low-density polyethylene microplastics in soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf 2020, 187, 109–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; et. al. Toxicological effects of polystyrene microplastics on earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, MN.; et., al. al. Effects of microplasti. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 157, 111280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, I.; et. al. Identification of microplastics in wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7409–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Seijo, A.; et., al. Low-density polyethylene microplastics. Environ. Chem. 2019, 2019. 16, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, F.; et., al. The contribution of washing processes of synthetic clothes to microplastic pollution. Sci. Rep., 2019, 9, 1–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; et., al. Negligible effects of microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 776–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, T.; et., al. A rapid-screening approach to detect and quantify microplastics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, A.; et., al. A first assessment of microplastics and other anthropogenic. FACETS. 2020, 5, 615–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintenig, SM. ; Low numbers of microplastics detected in drinking water from ground water sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 631–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.; et., al. Microplastic contamination. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 230–5. [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson, K.; Norén, F. Screening of microplastic particles; Swedish Environmental Research Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rout, PR.; Mohanty, A.; Sharma, A.; Miglani, M.; Liu, D.; Varjani, S. Micro-and nanoplastics removal mechanisms in wastewater treatment plants: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 6, p100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.; Örmeci, B. Removal effectiveness of nanoplastics (< 400 nm) with separation processes used for water and wastewater treatment. Water. 2020, 12, 635. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hong, L.; Shao, J.; Zhang, B.; Yu, J.; Chu, S. An integrated plasma-photocatalytic system for upcycling of polyolefin plastic. ChemSusChem. 2023, 28, e202300106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziajahromi, S.; et., al. Wastewater treatment plants as a pathway for microplastics. Water Res. 2017, 112, 93–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. et. al. A type of thiophene-bridged silica aerogel with a high adsorption capacity. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 1894–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, SA.; et., al. Pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and endocrine disruptors in water. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2003, 20, 449–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; et., al. The occurrence of pharmaceuticals in South Wales. UK. Water Res 2008, 42, 3498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NilsNilsen, E.; et., al. Grand challenges in assessing the adverse effects of contaminants. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim., SD.; et., al. Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1013–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, SR.; Razzak, SA.; Hassan, I.; Hossain, MM. Microplastics in Freshwater and Drinking Water: Sources, Impacts, Detection, and Removal Strategies. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, SA.; et., al. Cauliflower leave, an agricultural waste biomass adsorbent, and its application for the removal of MB dye. Int. J. Anal. Chem 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedia, J.; et., al. A review on the synthesis and characterization of biomass-derived carbons. C 2018, 4, 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, N.; Yang, Y. Properties and potential applications of natural cellulose fibers from cornhusks. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 190–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, JE. Natural fibres and the environment: environmental benefits of natural fibre production and use. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Natural Fibres, Rome, Italy; 2008; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, V.; Khayet, M. Evaluation of the surface free energy of plant surfaces: toward standardizing the procedure. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, J.; Talebian-Kiakalaieh, A.; Zhang, S.; Hashem, E.; Guo, M.; Qiao, S. Recent advancement on photocatalytic plastic upcycling. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 1611–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, S.; Gui, W.; Li, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, J. Photocatalytic Upcycling of Plastic Waste: Mechanism, Integrating Modus, and Selectivity. vSmall Struct. 2023, 4, 2300142, (1 of 12). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, H. Selected properties of cattail fibre for biomedical applications. MScE Thesis, . Department of Biosystems Engineering University of Manitoba. Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chakma, K.; Cicek, N.; Rahman, M. Characterization of cattail fibre chemical groups by Fourier-Transform infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR). Manitoba Institute of Materials (MIM) Annual Conference. University of Manitoba Winnipeg, Canada, 2018.
- Barragán, EU.; Guerrero, CF.; Zamudio, AM.; Cepeda, AB.; Heinze, T.; Koschella, A. Isolation of cellulose nanocrystals from Typha domingensis named southern cattail using a batch reactor. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 1136–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiyanto, AB.; Oktiani, R; Ragadhita, R. How to read and interpret FTIR spectroscope of organic material. Indonesian Journal of Science and Technology. 2019, 7, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Dong, T.; Xu, G.; Wang, F. Study on structure and wetting characteristic of cattail fibers as natural materials for oil sorption. Environ. Technol. 2016, 16, 37, Paper No. UM-BIOE 4240-18/19-163193-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, Z. The effect of scouring on cattail fibre properties for biomedical applications; Biosystems Engineering, University of Manitoba.: Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, T.; X, G.; Wang, F. Oil spill cleanup by structured natural sorbents made from cattail fibers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Jiang, G.; Cheng, T.; Bai, R.; Song, L. Cattail fibers as source of cellulose to prepare a novel type of composite aerogel adsorbent for the removal of enrofloxacin in wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 171–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zhang. J.; Li, C.; Wang, F.; Shi, L.; Tao, M.; Weng, B.; Yan, B.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y. Characterization of potential cellulose fiber from cattail fiber: A study on micro/nano structure and other properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamali Moghaddam, M. Typha leaves fiber and its composites: A review. J. Nat. Fibers. 2022, 19, 4993–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- —. Structural and thermal properties of cellulose microfiber isolated from Typha australis by sequential alkali-oxidative treatment. J. Nat. Fibers. 2022, 19, 10526–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guechi, E.; Benabdesselam, S. Removal of cadmium and copper from aqueous media by biosorption on cattail (Typha angustifolia) leaves: Kinetic and isotherm studies. Water Treat. Desalin. 2020, 173, 367–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, DR.; Kar, M.; Pringle, JM. Fundamentals of ionic liquids: from chemistry to applications; John Wiley & Sons, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hakkak, JS.; Barbooti, MM. Thermogravimetric study on typha (Typha angustifolia L.). J. Therm. Anal. 1989, 35, 815–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebio-Punal, T.; Naya, S.; López-Beceiro, J.; Tarrío-Saavedra, J.; Artiaga, R. Thermogravimetric analysis of wood, holocellulose, and lignin from five wood species. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 109, 1163–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakma, K.; Cicek, N.; Rahman, M. Fiber extraction efficiency, quality and characterization of cattail fibres for textile applications; Canadian Society for Bioengineering Conference (CSBE): Winnipeg, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ifelebuegu, AO.; Johnson, A. Nonconventional low-cost cellulose-and keratin-based biopolymeric sorbents for oil/water separation and spill cleanup: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 964–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellbach, SL.; Monteiro, SN.; Drelich, JW. A novel method for contact angle measurements on natural fibers. Mater. Lett. 2016, 164, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accu Dyne Test ™. Critical Surface Tension and Contact Angle with Water for Various Polymers. Available online: https://www.accudynetest.com/polytable_03.html?sortby=contact_angle (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- De Luna, MS.; Galizia, M.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Rosa, R.; Lojkowski, W.; Leonelli, C.; Ancierno, D.; Filippone, G. Dispersing hydrophilic nanoparticles in hydrophobic polymers: HDPE/ZnO nanocomposites by a novel template-based apprach. eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 362–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqa, AJ.; Chaudhury, K.; Adhikari, B. Hydrophilic low density polyethylene (LDPE) films for cell adhesion and proliferation. Res. Rev. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 1, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, DR.; Santese, F.; Toth, R.; Posocco, P.; Pricl, S.; Fermeglia, M. Simple, fast, and accurate in silico estimations of contact angle, surface tension, and work of adhesion of water and oil nanodroplets on amorphous polypropylene surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2012, 6, 2855–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sant’Ana, PL.; Bortoleto, JR.; Drrant, SF. Contact Angle and Wettability of Commercial Polymers after Plasma Treatment. LJP. 2022, 22, 13–33. [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen-Leinonen, E. ; Determination of Cleanability of Plastic Surfaces. Academic Dissertation, . Faculty of Agriculture and Forestry, University of Helsinki, 2005; pp. 1–67.
- Biolin Scientific. Attension. Technology Note 7. Influence of surface roughness on contact angle and wettability. Available online: https://www.biolinscientific.com (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Rahman, M.; Cicek, N.; Chakma, K. The optimum parameters for fibre yield (%) and characterization of Typha latifolia L. fibres for textile applications. Fibers Polym. 2021, 22, 1543–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, YB.; Lee, MW. Use of non-wood fibres (from cattails and red algae) and their effects on paper opacity. Appita. 2011, 64, 5–445. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.; McGowan, T.; Bajwa, SG.; Bajwa, DS. Impact of fiber treatment on the oil absorption characteristics of plant fibers. BioResources. 2016, 11, 6452–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Shen, R.; Gao, J.; Li, J. An efficient approach to prepare water-redispersible starch nanocrystals from waxy potato starch. Polymers. 2021, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthamaraikannan, P.; Kathiresan, M. Characterization of raw and alkali treated new natural cellulosic fiber from Coccinia grandis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 332–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, TJ. A new classification of pore sizes. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2007, 160, (Characterization of Porous Solids VII), 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Vinayagam, V.; Murugan, S.; Kumaresan, R.; Narayanan, M.; Sillanpää, M.; Dai Viet, NV.; Kushwaha, OS.; Jenis, P.; Potdar, P.; Gadiya, S. Sustainable adsorbents for the removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewater: A review. Chemosphere. 2022, 134597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampman, S.; Bonnie Sanders, B.; Hrivnak, N.; Kinson, J.; Polakowski, C. Characterization and failure analysis of plastics: ASM International; ASM International,: 2003.
- Kent, R. Energy management in plastics processing: strategies, targets, techniques, and tools; Elsevier: 2018.
- Chackalamannil, S.; Rotella, D.; Ward, S. Comprehensive medicinal chemistry III; Elsevier, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Letcher, TM. Storing energy: with special reference to renewable energy sources; Elsevier, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Godwin, AD.; Kutz, M. Applied plastics engineering handbook; William Andrew Applied Science Publishers, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tilton, RD.; Robertson, CR.; Gast, AP. Manipulation of hydrophobic interactions in protein adsorption. Langmuir. 1991, 7, 2710–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puddu, V.; Perry, CC. Peptide adsorption on silica nanoparticles: evidence of hydrophobic interactions. ACS nano, 2012, 6, 6356–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, LD.; Lamazaki, ET.; Atvars, TD. Evaluation of the polarity of polyamide surfaces using the fluorescence emission of pyrene. Dyes Pigm. 2008, 76, 669–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Long, X.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tan, J.; Chen, R. Synergistic effect of hydrogen bonding and π-π interaction for enhanced adsorption of rhodamine B from water using corn straw biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 121060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, JD.; Langhus, BG.; Patel, C. Technical summary of oil & gas produced water treatment technologies. All Consulting, LLC: Tulsa, OK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Garde, S. Hydrophobic interactions in context. Nature. 2015, 517, 277–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Pashalidis, I.; Kayan, B.; Kalderis, D. Microplastics as carriers of hydrophilic pollutants in an aqueous environment. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 350, 118182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafa, N.; Ahmed, B.; Zohora, F.; Bakya, J.; Ahmed, S.; Ahmed, SF.; Mofijur, M.; Chowdhury, AA.; Almomani, F. Microplastics as carriers of toxic pollutants: Source, transport, and toxicological effects. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 123190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
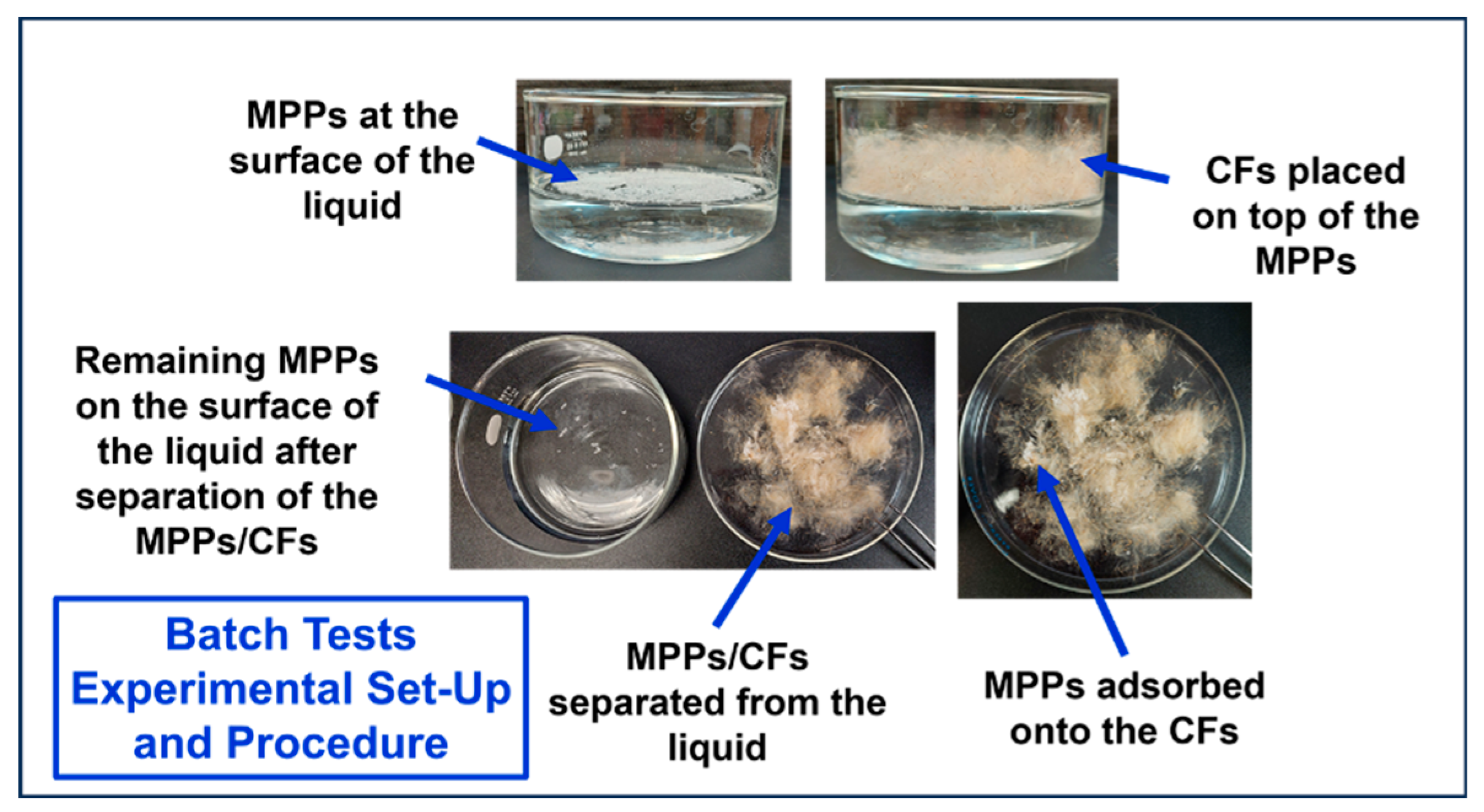



| Adsorbent Material | Microplastic Particles | Distilled Water, DW Solution Concentration [wt%] Volume: 200 ml |
Produced Water, PW Solution Concentration [wt%] Volume: 200 ml |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| PVC | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 0.5 | 0.5 | ||
| 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| PP | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 0.5 | 0.5 | ||
| 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Cattail Fibers | LDPE | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| 0.3 grams | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| T = 24°C | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| Nylon 6 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 0.5 | 0.5 | ||
| 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| HDPE | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 0.5 | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





