1. Introduction
Extracellular vesicle (EVs) are membranous particles enclosed by lipid bilayers with diameter ranging from 50 nm to 1 μm derived from almost all cells [
1]. By inheriting abundant signaling molecules from donor cells, such as nucleic acids and proteins, EVs play a role in intercellular communication and associate with disease progression [
2,
3,
4]. EVs can be classified into several subgroups based on size and generation mechanism, including microvesicles, microparticles and exosomes [
3,
5]. Among these subgroups, exosomes are microvesicles ranging in size from 50 to 150 nm with an average of ~100 nm [
3]. Multivesicular bodies (MVBs) contain multiple intraluminal vesicles (ILVs), which fuse with the plasma membrane to release ILVs as exosomes [
6]. Therefore, exosomes contain proteins of cell surface and soluble proteins linked to the extracellular environment [
7,
8]. Efficient isolation and reliable analysis of EVs are important prerequisites for the clinical application of EVs. Conventional techniques for isolating EVs, such as ultracentrifugation, ultrafiltration, particle size exclusion chromatography, and polymer precipitation, are time-consuming and inefficient [
9]. Microfluidic technology achieves efficient EV isolation and detection with only a very small amount (10
-9 to 10
-18 liters) of liquid specimens and reagents, and has the advantages of integration, high throughput [
10]. With the support of microfluidic technology, the successful establishment of clinical EV detection platforms is expected soon. In this review, we will explore the latest developments in microfluidic-based EV isolation and analysis, as well as discuss the challenges and future directions of this rapidly evolving field.
2. Microfluidic-based EV isolation strategies
2.1. Label-free microfluidic isolation
Label-free isolation strategies depend on the physical characteristics of EVs, such as their size, density, and deformability, to separate them from other components present in bodily fluids. Conventional label-free methods, such as ultrafiltration (UF), ultracentrifugation (UC) and size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) usually require large sample volumes. UC differentiates EVs and other components based on size and density, and has been recognized as one of the most commonly used EV isolation methods [
11,
12]. However, the long UC period might result in coprecipitation of protein aggregates. In addition, the quality of EVs cannot be guaranteed due to repeated centrifugation processes and excessive centrifugal force [
13]. UF adopts membrane filters with suitable pore sizes to purify EVs from other particles [
14]. Regrettably, the accumulation of debris on the filter membranes will decrease the efficiency of EV isolation and shorten the lifespan of the membranes. [
15]. SEC isolates particles with different sizes based on their different flow rates on the column filled with porous beads. As a mild EV isolation method, SEC can obtain EVs with relatively complete structure and function [
16,
17]. However, the tedious procedure, low-throughput and recovery of SEC limit its wide application.
Holding the properties of easy-integration, high-throughput and low sample consumption, microfluidics technology provides a variety of strategies for efficienct label-free EV isolation[
18,
19,
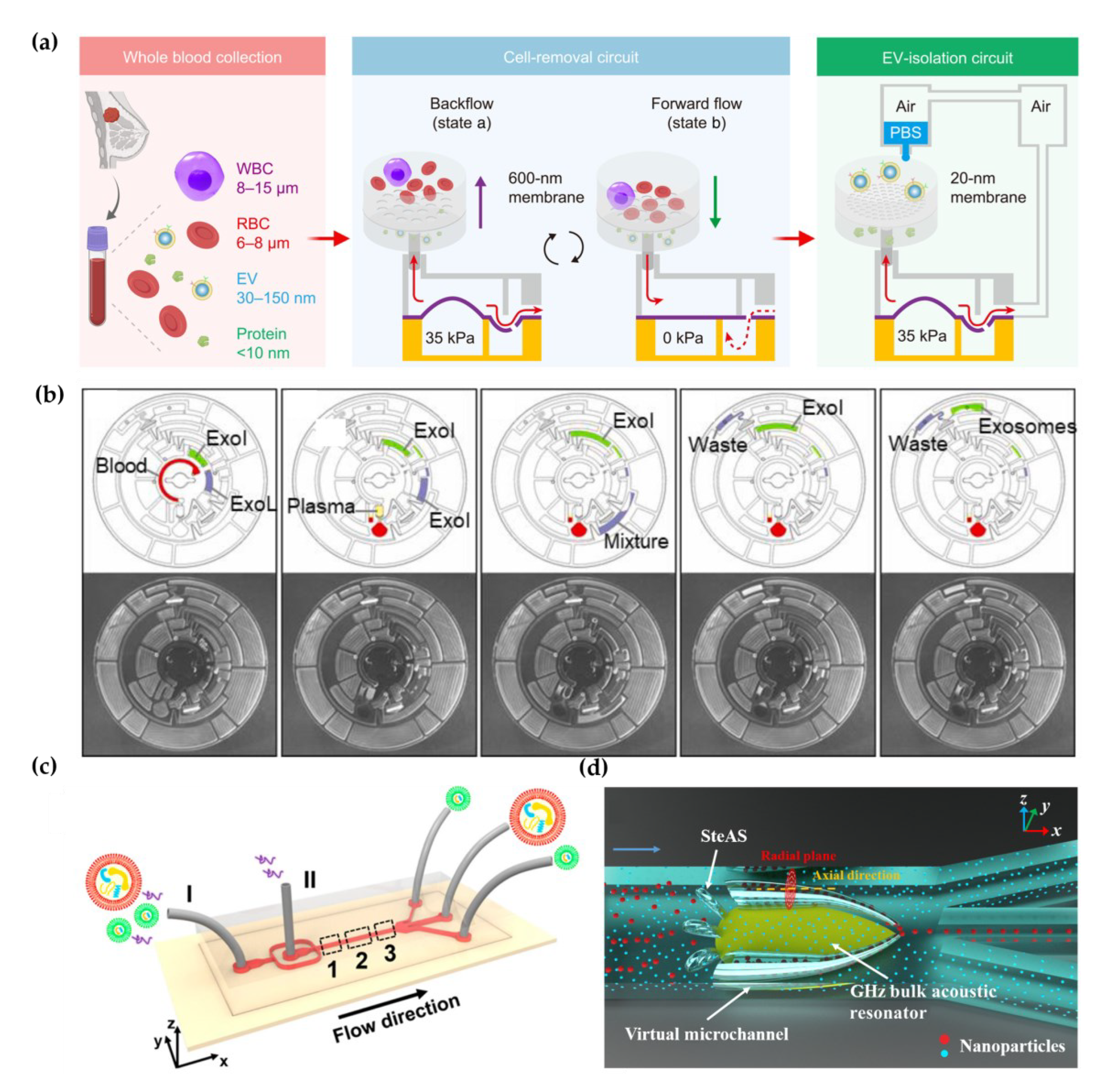
20]. For example, Li et al. integrated filtration and microfluidics technology to design cascaded microfluidic circuits for preprogrammed, clog-free and gentle isolation of EVs directly from blood within 30 min (
Figure 1a) [
21]. The problems of filter fouling and particle aggregations were solved by the pulsatile flows generated by the porous membrane, which lifting particles away from the menbrane. Researchers engineered an automated centrifugal microfluidic disc featuring membranes with specific functionalities (Exo-CMDS) for exosome isolation (
Figure 1b) [
22]. As a one-step method, Exo-CMDS enriched exosomes with optimal exosomal concentration of 5.1×10
9 particles/mL from small amount of blood samples (<300 μL) in 8 min. The above methods require tedious fabrication of microfluidic chips, which increased the uncertainty of trials. Liu et al. proposed a viscoelastic-based microfluidic system for direct label-free isolation of exosomes (
Figure 1c) [
23]. A simple microfluidic device with two inlets, three outlets and a straight microchannel was designed for viscoelastic separation of exosomes. The presence of oxyethylene (PEO) causes elastic lift forces which drives EVs toward the microchannel centerline according to their sizes. Under the size cutoff of 200 nm, exosomes were separated from large EVs. In addition, Yang et al. demonstrated a self-adaptive virtual microchannel for nanoparticle enrichment and separation in a continuous manner (
Figure 1d) [
24]. A gigahertz bulk acoustic resonator and microfluidics triggered and stabilized acoustic waves and streams to form a virtual channel with a self-adjusted diameter from dozens to a few micrometers. By a customized arc-shaped resonator, exosomes from patient plasma were purified. The system is stable and has high automation potential because of the self-adaptive and contactless continuous speration mode. Although label-free microfluidic isolation has the advantages of high throughput, rapidity and cheapness. The low purity and inability to isolate EV subtypes limit its downstream applicaiotion.
2.2. Affinity-based EV isolation
Affinity-based isolation methods exploit the interaction between affinity ligands (antibodies, peptides or aptamers) and receptors on EV membranes to isolate EVs specifically [
25,
26]. These ligands are typically modified on the surface of materials or interfaces, such as magnetic beads [
27,
28,
29], carbon cloth [
30], graphene [
31], or Ti2CTx MXene membranes [
32].The strength and duration of the interaction between affinity ligands and receptors on surfaces determine the capture efficiency of EVs. However, the compromised interaction between EVs and traditional interfaces limits their capture efficiency. The micro/nano-scale channels in microfluidic chips can enhance the contact frequency between recognition ligands on the chips and molecules on EV membranes, thus increasing EV capture efficiency. For example, the herringbone microfluidic chip, comprising patterned microgrooves, enhances fluid mixing efficiency by manipulating flow states and forming helical motions [
33]. Therefore, collision between biological targets and affinity trapping substrates is improved, resulting in improved EV capture efficiency [
34].
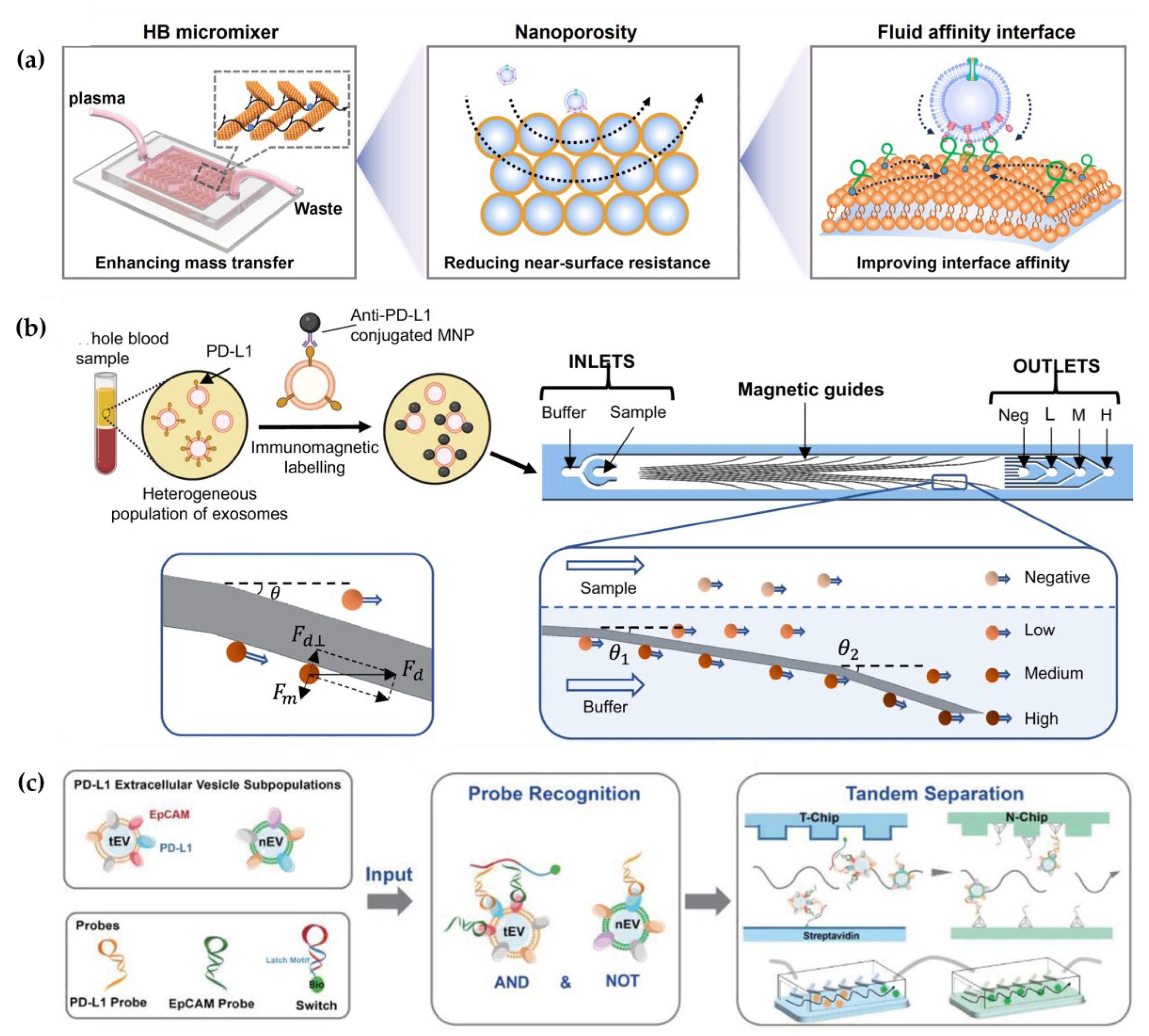
However, the near-surface hydrodynamic resistance decreases mass transfer in the microchannel [
35]. To overcome this near-surface hydrodynamic resistance, Li et al. developed a 3D porous sponge microfluidic chip made by salt-crystallization, which provided a high surface-to-volume ratio [
8]. Otherwise, researchers also developed a fluid nanoporous microinterface (FluidporeFace) in a herringbone microfluidic chip for efficienct capture of tumor-derived EVs (
Figure 2a) [
34]. Supported lipid bilayers (SLBs) were encapsulated on the nanoporous herringbone microstructures, which not only improved the mass transfer, but also enabled multivalent recognication of aptamers, thus achieving multi-scale enhanced affinity reaction. As a result, the affinity increased by ~83-fold compared with the nonfluid interface. In addition, they designed a microfluidic chip to create a dynamic multivalent magnetic interface, enhancing the kinetics and thermodynamics of biomolecular recognition for the efficient isolation of EVs derived from tumors (T-EVs) [
36]. Utilizing magnetic and flow fields, this engineered interface achieved a harmonious balance of affinity, selectivity, reversibility, and extendibility. As a result, they achieved a high-throughput recovery of T-EVs, facilitating comprehensive protein profiling. However, when utilizing a single ligand for EV capture and another ligand for EV detection, it is challenging to eliminate the interference of free proteins and obtain the requisite subtypes of EVs, thereby rendering it inadequate for clinical applications. To eliminate interference from free proteins, Zhang et al. designed a microfluidic differentiation method that accurately captured PD-L1
+ EVs [
37]. PD-L1
+ EVs were labeled with biotin using DNA computation, incorporating dual input of lipid probes and PD-L1 aptamer. Subsequently, these labeled EVs were captured with streptavidin-modified microfluidic chips selectively.
Different subtypes of EVs represent distinct sources and diverse biological functions. Therefore, analysis of EV subtypes is crucial for studying the biological mechanism of EVs. On the contrary, all antibody-based enrichment systems are limited to highly specific isolation protocols, which result in partial EV loss due to differences in the expression of EV membrane surface proteins. Chen et al. proposed a novel herringbone microfluidics device, which not only possessed the advantages of herringbone microfluidics, but also incorporated aptamer-functionalized core-shell bar code (AFCSBs) [
33]. Because their antiopal hydrogel shells have abundant interconnecting pores, barcodes can provide a rich surface area for anchoring of multiple DNA aptamers, enabling specific capture of multiple tumor-derived exosomes. However, its essence lies in using one type of aptamer for molecular capture and another type for molecular discrimination, making it still unable to distinguish different EVs. In order to isolate subtypes of EVs, MUN et al. developed a microfluidic chip-based magnetically labeled exosome isolation system (MEIS-chip) that involved magnetic nanoclusters (MNCs) conjugated with CD63 and HER2 with different degrees of magnetization (CD63 conjugated with low-saturation magnetized MNCs, CD63-LMC, and HER2 conjugated with high-saturation magnetized MNCs, HER2-HMC) [
38]. Common exosomes were captured by CD63-LMC, while exosomes with HER-overexpression bound to both CD63-LMC and HER2-HMC simultaneously. This allows for the acquisition of varying degrees of magnetic particles and magnetic separation in the MEIS-chip via a magnetic field, ultimately resulting in the separation of different EV populations. Moreover, Chen et al. designed a nanoscale cytometry platform called NanoEPIC to enable the collection of small EVs (sEVs) bearing four different expression levels of PD-L1 by labeling them with antibody-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) (
Figure 2b) [
39]. EVs with higher PD-L1 expression levels had greater lateral deflection towards the edge of the device in the microfluidic flow channel due to their increased magnetic susceptibility resulting from binding to more MNPs. This facilitated the separation of sEVs based on four levels of PD-L1 expression: negative, low (exoL), medium (exo-M), and high (exo-H). Lu et al. achieved the isolation of tumor PD-L1
+ EVs and non-tumor PD-L1
+ EVs through DNA logic-mediated double aptamer recognition and tandem chip for the first time (
Figure 2c) [
40]. Tumor-derived EVs were identified by EpCAM and PD-L1 nucleic acid ligands, inducing the "AND" logic operation, whereas non-tumor-derived PD-L1
+ EVs only express PD-L1, thus invoking the "NOT" logic operation. These two independent outputs facilitated the separation of tumor and non-tumor origin PD-L1
+ EVs through tandem microfluidics, respectively. Consequently, utilizing a streptavidin-functionalized microfluidic chip (T-Chip), only tumor-derived PD-L1+ EV populations can be isolated. After excluding tumor-derived PD-L1
+ EVs, the remaining PD-L1
+ EVs from normal cells can be captured through hybridization between the extension sequence on the PD-L1 probe and the corresponding cDNA modified on the second microfluidic chip (N-Chip).
Currently, the microfluidic technology based on affinity separation has made tremendous advancements. There have been significant improvements in purification, capture efficiency, and subpopulation separation. Despite some progress in various studies, there are still certain limitations. To effectively apply these technologies to clinical diagnosis and precision treatment, further innovation and improvement are still needed. In short, the efficient isolation of EVs is the premise for researching their biological function research and clinical application. It is still necessary to develop new methods for the high-efficiency and high-purity isolation of EV subtypes.
3. Microfluidic-based fluorescent detection.
3.1. Fluorescent detection
Fluorescence technology combined with microfluidic platform has been widely used in EV detection, which has the characteristics of fast response, good precision and high sensitivity. After capturing EVs in microfluidic chips, membrane stains or fluorescent labeled antibodies are usually used to identify EVs [
41]. For example, Kanwar et al. used a fluorescent carbanine dye (DiO) to stain exosome membrane, and counted the total number of exosomes captured on a microfluidic device (ExoChip) [
42]. Antibodies against EV specific biomarkers, such as CD63, CD9 and CD81 are used for EV identification and quantification [
43]. Besides, fluorescent labeled antibodies against disease related biomarkers on EV membrane are usually used for quantitative and qualitative analysis of EV biomarkers, thus reflecting the progression of diseases. For example, Hisey et al. captured ovarian cancer exosomes in a herringbone groove microfluidic device and quantified EpCAM
+ exosomes [
44]. The quantitative results showed that EpCAM
+ exosomes were related with HGSOC disease progression. After utilizing the integrated microfluidic Exosome Separation and Detection System (EXID System), Lu et al. examined the abundance of exosomal PD-L1. [
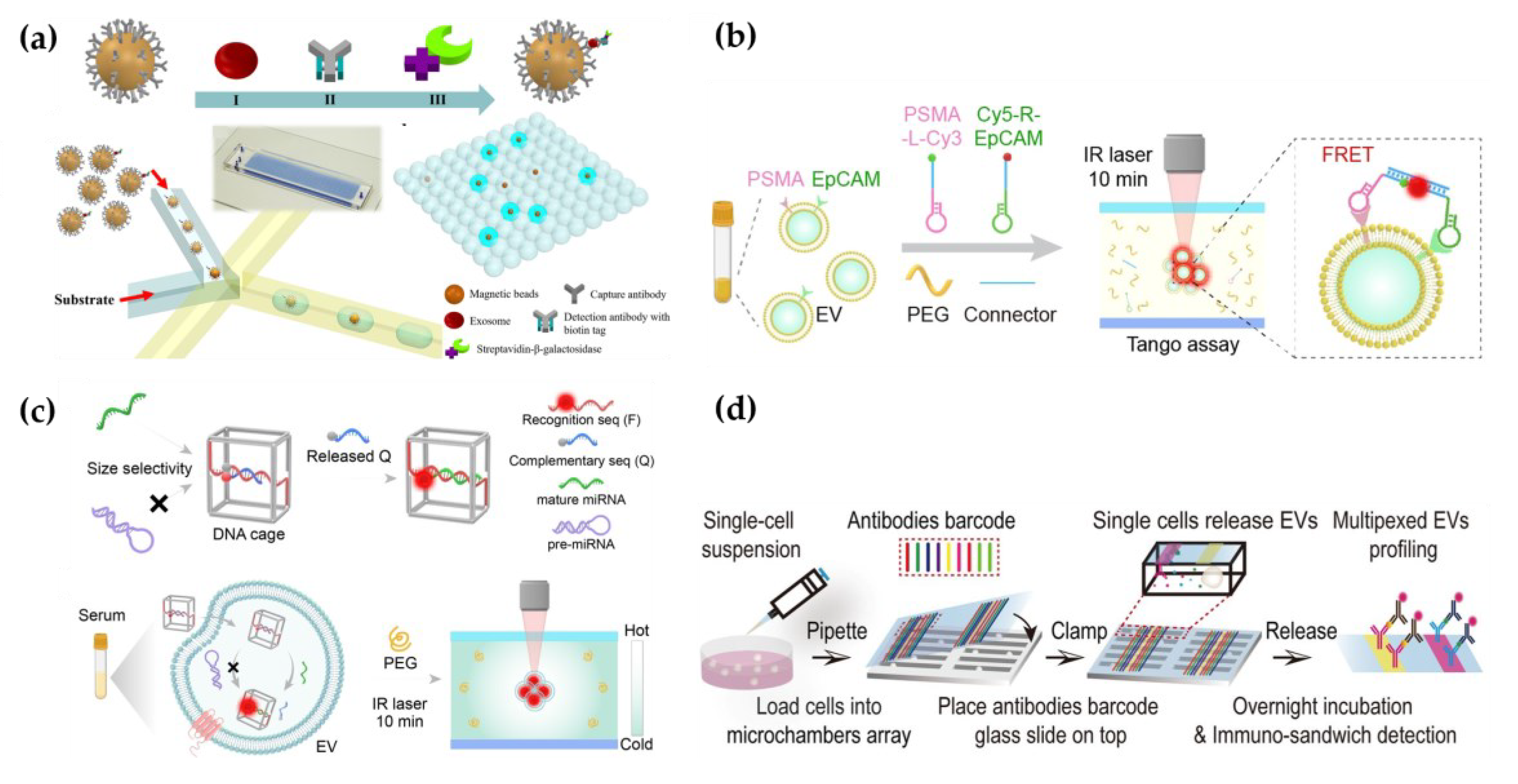
45]. Using the EXID system, a significant difference in fluorescence intensity was observed. The strategy had a limit of detection (LOD) of 10.76 /µL and exosomal PD-L1 level reflected the sensibility for immune response. The conventional methods offer bulk information of proteins on EVs, which hardly enables absolute quantification. Liu et al. constructed “exosome-magnetic microbead-enzymatic reporter” complexes and encapsulated the complexes into droplets which ensured a single complex was encapsulated in a droplet. As a result, cancer-specific exosomes were absolute counted with a low limit of detection of 10 exosomes µL
-1 (
Figure 3a) [
46].
The heterogeneity of EVs challanges the acknowledgement of their biological significance and clinical application. To explore the heterogeneity of EVs, Zhang’s group developed a microfluidic chip featuring self-assembled 3D herringbone nanopatterns, enabling highly sensitive fluorescent detection of EV surface proteins [
47]. The device was used to detect exosome subtypes expressing CD24, EpCAM, and FRalpha proteins in 2 μL plasma samples from 20 ovarian cancer patients, and to suggest exosomal FRalpha as a promising biomarker in the early detection and monitoring of ovarian cancer progression. Furthermore, MMP14 on EVs holds potential for early detection and prognosis assessment in breast cancer metastasis [
48]. The above microfluidic devices need cumbersome fabrication processes. Besides, the interaction between proteins and antibodies may be limited due to the steric hindrance caused by the posttranslational modification of proteins [
49,
50]. Sun’s group developed a microfluidic thermophoresis device, which accumulated particles in a size-dependent manner and amplified fluorescence signals based on the different diffusion rates of particles in nonuniform temperature field [
51]. Seven fluorescently labeled aptamers targeting different epitopes were employed for subtyping analysis of EVs. This method demonstrated a sensitivity and specificity of 95% and 100%, respectively, in cancer detection, and it can also be utilized for cancer classification. Furthermore, the method is applicable for the proteomic analysis of EVs in breast cancer, enabling the identification of metastatic breast cancer, monitoring treatment responses, and predicting patients' progression-free survival rates [
52].
In addition to phenotypic heterogeneity, the tracing of EV origins is also particularly important. It can accurately detect and monitor the progression of diseases. Sun's group utilized microfluidic thermophoresis devices for the specific detection of tumor-derived EVs, achieving an accuracy of 97% [
53]. Similarly, a rapid and non-invasive diagnostic assay, named the one-step thermophoretic AND gate operation (Tango), has been developed for precise identification of prostate cancer (PCa)-derived EVs directly in serum samples within 15 minutes. This method demonstrated an impressive overall accuracy of 91% in discerning PCa from benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) using a streamlined single-step format. This innovative technique holds tremendous potential for the swift and non-invasive diagnosis of cancers (
Figure 3b) [
54].
Besides proteins on EV surface, miRNAs are also important biomarkers and therapeutic targets for diseases [
55]. Sun’s group demonstrated a thermal swim sensor (TSN) employing nanoflares for the in situ detection of exosomal miRNA, eliminating the need for RNA extraction or target amplification. Through the thermophoretic accumulation of nanoflare-treated exosomes, a heightened fluorescent signal was produced upon binding with exosome miRNA, facilitating the direct quantitative assessment of exosome miRNA. [
56]. Afterwards, they devised a DNA tetrahedron-based thermophoretic analysis (DTTA) for the on-situ detection of mRNA in EVs, achieving remarkable sensitivity and specificity [
57]. Recently, they developed a DTTA for high sensitive and selective in situ detection of mature miRNA in EVs. This assay achieved a detection limit of 2.05 fM for mature miRNA in EVs without interference from pre-miRNA, and distinguishes between breast cancer patients and healthy donors with an overall accuracy of 90% (
Figure 3c) [
58].
Moreover, cell culture supernatant or EVs in body fluids lose the interaction information with other symbiotic cells in tissues, making it unable to accurately represent the role of EVs in intercellular communication [
59]. Ji et al. employed spatially patterned antibody barcodes, achieved the multiplexed profiling of single-cell EV secretion from over 1,000 individual cells concurrently. This innovative approach enabled the comprehensive characterization of human oral squamous cell carcinoma, unraveling previously obscured single-cell heterogeneity in EV secretion dynamics (
Figure 3d) [
60]. This technology facilitates a thorough assessment of EV secretion diversity at the single-cell level, offering an invaluable tool to supplement existing single-cell analysis and EV research. Afterwards, they applied this platform to analyze the characteristic spectra of paired neuronal-microglial and neuronal-astrocyte single cells in the human cell lineage. These results provides a basis for exploring how neurons and immune cells interact through complex secretion networks [
61].
While fluorescence technology utilizing microfluidic techniques has been successfully employed in EV detection, offering commendable accuracy and high sensitivity, it is not without its drawbacks. Some ons include the intricate preparation of fluorescence labels and the occurrence of spectral interference. This interference encompasses background interference and spectral overlap issues, along with the phenomenon of photobleaching in fluorescent molecules. The resolution of these issues will contribute to enhancing the accuracy of fluorescence detection of EVs.
3.2. Visualization detection.
In recent years, the method of detecting EVs through microfluidic technology using the colorimetric method has undergone significant development and has simplified the equipment [
26,
62,
63]. Visualization detection relies on the change that can be observed by naked eyes, such as color changes within the detection system, which occur as a result of chemical or biochemical interactions between specific target analytes and colorimetric probes. One significant advantage of visualization assays is their independence from bulky off-chip detection systems. Consequently, visualization detection has garnered growing interest in biomedical research, particularly for disease diagnosis, owing to its distinct advantages in EVs detection [
59].
For instance, Chen et al. introduced a traditional colorimetric technique to detect EVs whin a 3D scaffold chip [
64]. They proposed a ZnO nanowire coated 3D scaffold chip device for effective immune capture and classical visual and colorimetric detection of EVs. In the work by Di et al., a rapid analysis method was introduced, utilizing nano-enzyme-assisted immunosorbent assay, eliminating the need for antibody detection [
65]. The approach involved the immobilization of nanoparticles on the phospholipid membrane of exosomes, followed by the addition of chromogenic agents. For another, Jiang’s group developed a sensor platform, which can be visually analyzed EV surface proteins in minutes. The sensor consists of a gold nanoparticle (AuNP) and a set of aptamers [
66]. In addition, Ko et al. engineered a photofluidic platform powered by smartphones to quantify brain-derived exosomes. This innovative chip enables rapid processing, delivering results within one hour, which is ten-fold quicker than conventional methods. The device boasts a detection limit of approximately 10
7 exosomes/mL [
67]. Utilizing enzyme amplification, it can detect exosome biomarkers, with results easily read through a smartphone camera.
Although many researchers have made incredible progress in the field of visualization detection methods, which can rapidly detect a wide range of biomolecules, from infectious diseases-related protein biomarkers to glucose and nucleic acids, the extensive application of visualization detection is limited. It is mainly used in underdeveloped regions, and low sensitivity is its major drawback.
3.3. Electrochemical detection
Electrochemical methods tranfer the signals of EV recognition to electrochemical signals, such as voltage, current, and resistance [
68]. Microfluidic-based electrochemical techniques have attracted great attention in EV detection due to their broad detection range, high sensitivity and specificity.
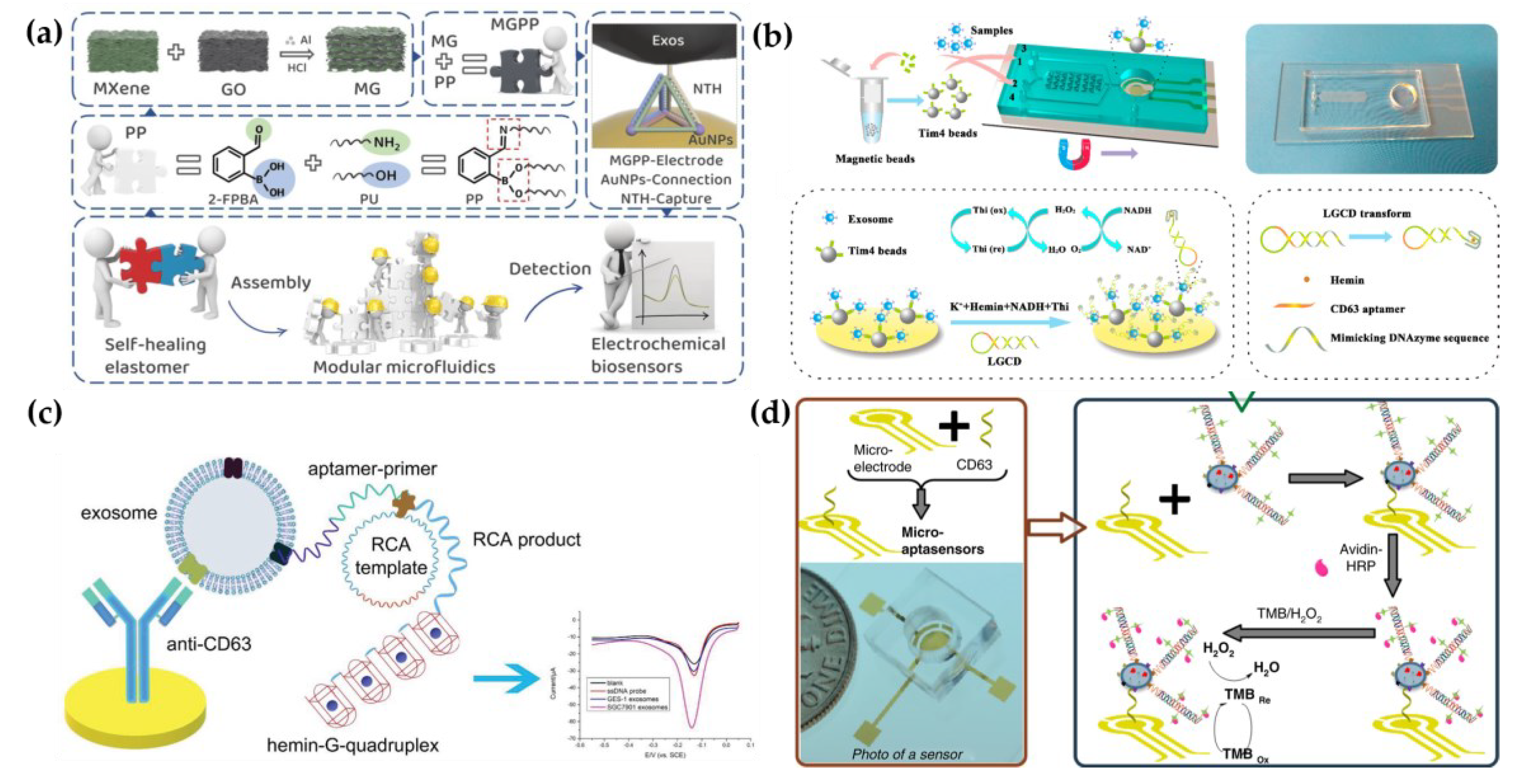
Affinity ligands are usually modified in microfluidic chips for EV capture. Then, the electrochemically responsive molecules were triggered to cause change of electrochemical signals. To date, great efforts have been devoted to introduce various signal production and amplification strategies, such as metal nanoparticles, tetrahedral DNA nanostructures (TDN), and nucleic acid-based amplification analysis to electrochemical biosensors for EV detection. For example, Wang et al. have developed a new filter-electrochemical microfluidic chip (FEMC) that integrated on-chip separation and in situ surface protein electrochemical analysis of exosomes in whole blood of breast cancer patients (
Figure 4a) [
69]. In this system, Zirconium-based metal-organic frameworks (Zr-MOFs) loaded with numerous electroactive methylene blue molecules (Zr-MOFMB@UiO-66) were attached to exosomes collected on electrode surfaces, leading to the amplification of electrical signals. The entire FEMC assay took 1 hour to complete, enabling timely and more informed opportunities for the diagnosis of breast cancer. To highly sensitively detect colorectal cancer exosomes, a microfluidic electrochemical biosensing platform based on TDN-based signal amplification was constructed [
70]. TDN including EpCAM aptamer was immobilized on Au nanoparticles (AuNPs) as a recognition element to harvest the exosomes. Then, the AuNPs had an obvious catalytic effect on the redox reaction of ferricyanide, enabling electrochemical detection [Microfluidic Technology for the Isolation and Analysis of Exosomes]. The platform had a broad measurement range (50–10
5 particles/µL) and a low limit of detection (42 particles/µL).
Besides, an increasing number of nucleic acid amplification methods have been employed in electrochemical biosensors. Xu et al. proposed a two-stage microfluidic platform (ExoPCD-chip) for the electrochemical analysis of hepatocellular exosomes in serum (
Figure 4b) [
71]. Particularly, exosomes captured by electrochemical aptasensors with a CD63 aptamer led to the accumulation of the hemin/G-quadruplex. This complex could function as a NADH oxidase and horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-mimicking DNAzyme simultaneously. Thus, the freshly formed H
2O
2 by NADH oxidation could be continuously catalyzed, accompanied by significant signal enhancement [
72]. Moreover, a staggered Y-shaped micropillar mixing pattern was introduced to create an anisotropic flow without any surface modification to improve exosome enrichment efficiency. Due to the flexible programmability, aptamers are easily engineered for signal amplification, to improve EV detection sensitivity. For example, a hemin/G-quadruplex system and rolling circle amplification (RCA) were combined in an aptasensor for the selective and sensitive detection of gastric cancer exosomes(Figure4c) [
73]. RCA is recognized as a nucleic acid amplification analysis that can be performed at room temperature to preserve the integrity of exosomes. In addition, Zhang et al. designed a remarkably selective electrochemical micro-aptasensor with a detection limit of 5×10
2 exosomes/mL by integrating a micropatterned electrochemical aptasensor and a signal amplification strategy of hybridization chain reaction (HCR) (
Figure 4d) [
74]. Biotin-labeled HCR products were used to bind specifically to enriched exosomes utilizing EpCAM aptamers as a bridge. This was followed by the attachment of multiple avidin-HRPs, producing a current signal through the enzyme reaction. Moreover, the proposed aptasensor was effective in discriminating serum samples from early-stage lung cancer patients and late-stage patients, indicating significant promise for early cancer diagnosis.
To sum up, electrochemistry proves highly suitable for EV analysis within an integrated microfluidic chip, offering a multitude of advantages. Furthermore, no requirements for optical transparency expand the choice of materials in electrochemical response. However, contamination and changes in pH, temperature, and ionic concentration often influence the lifetimes of electrodes, which needs to be addressed [
75]. So far, only a limited number of microfluidic devices incorporated with electrochemical techniques have been developed for EV detection. We believe that there will be a growing number of microfluidic devices combined with electrochemical detection as a promising means for point-of-care diagnostics.
3.4. Surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)
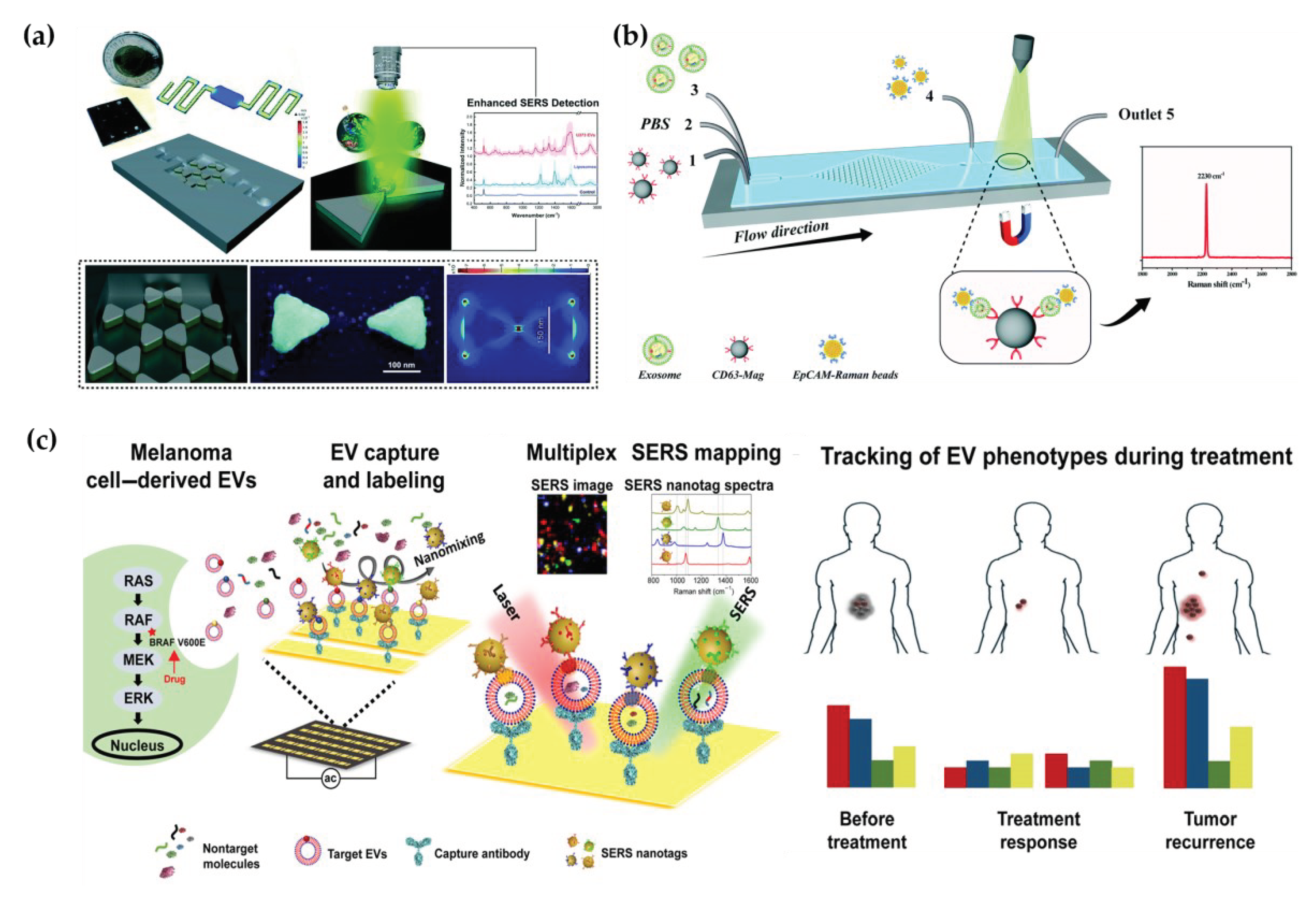
Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) effectively generates spectra on certain metal surfaces, providing vibrational and rotational energy information of molecules, which is reflected in spectral peaks used to specifically identify molecules [
75,
76]. However, SERS measurements present significant challenges in reproducibility and sensitivity [
76]. In this aspect, microfluidic surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (MF-SERS) is making progress in resolving some significant and previously insurmountable issues and limitations of SERS detection to some extent, thus improving detection capability and extending its application [
78]. Through the utilization of high-throughput nanosurface microfluidics control technology and unique fingerprint identification, precise testing of ultra-small populations of biochemical particles, such as cancer EVs.
In efforts to amplify Raman signals from cancer-derived EVs, Mahsa et al. developed a nanosurface fluidic device for label-free, non-immunological SERS detection of EVs. This device effectively distinguished the SERS fingerprint of EVs from noncancerous glial cells (NHA) and two sub-populations of the GBM EVs (i.e. U87 and U373). The sample solution flowed from the input ports to the serpentine analysis channels (50×250 μm
2) to achieve a single-layer distribution of EVs on the nanosurface. At the same time, metal nanomaterials with SERS activity formed a hexagonal nanoscale triangular array, with each two triangles forming a bowtie structure with a suspended gap region area to amplify the EM-field enhancement, electromagnetic field enhancement factor of 9×10
5 (
Figure 5a) [
79]. In addition to the above-mentioned label-free microfluidic Raman chip, Wang et al. developed a new one with immunoassay for quickly and sensitively detecting the exosomes (
Figure 3b) [
80]. Hybrid channels of triangular column arrays were used to enrich CD63-positive exosomes and fixed them in the Raman detection region. EpCAM-labeled Raman beads with high densities of nitrile were used as probes for detection, and the detection limit was 1.6×10
2 particles per mL with 20 μL samples.
Various biomarkers can indicate diverse biological functions, making it significant to detect multiple exogenous biomarkers. Han et al. proposed a microfluidic-SERS technique for profiling numerous exosomal biomarkers to diagnose osteosarcoma. Gold nanoparticles labeled with SERS tags can selectively bind to exosomes using specific antibodies in samples, forming exosome immunocomplexes. A microfluidic chip, comprising two symmetrical polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) layers and a nanoporous polycarbonate track-etched (PCTE) membrane, was employed for exosome purification [
81]. Microfluidic tangential flow filtration effectively eliminated plasma biomolecules and free SERS tags, while enriching exosome immunocomplexes on the membrane for in situ SERS analysis [
82]. Herein, Wang et al. also showcased a multiplex EV phenotype analyzer chip (EPAC). EPAC integrates a nanomixing enhanced microchip and a multiplex surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) nanotag system for direct EV phenotyping. [
62,
81]. They observed the EV phenotypic heterogeneity and longitudinally monitored the EV phenotypic evolution, finding specific EV profiles involved in the development of drug resistance and the potential of EV phenotyping for monitoring treatment responses [
83]. (
Figure 5c) Thus, the microfluidic-SERS method offers great potential for the detection of external vesicles and cancer diagnosis.
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
EVs are intricately linked to numerous physiological processes as well as the onset and progression of diseases. Efficient EV isolation methods and sensitive EV detection methods will help to improve the understanding of the physiological and pathological effects of EVs, and provide important support for the precision medicine of related diseases. At present, the conventional EV isolation and detection technologies still have limitations. Microfluidic-based methods for isolation and detection of EVs have obvious advantages of high integration, low consumption, fast speed, high separation efficient and high detection sensitivity, which opens up new ideas and directions for the research of EVs. With the help of microfluidic chips, the efficient isolation, enrichment and multi-marker detection of EVs with different sizes can be integrated into a single chip, and a more diversified clinical detection instrument can be built.
The field of microfluidic-based EV isolation and detection is still in its infancy, and there are still a lot of theoretical and technical problems to be solved. Therefore, the means to achieve highly selective and accurate isolation of EVs in actual biological samples, achieve sensitive and selective detection of these EVs and even the biological information carried in them will be important topics in the study of EVs based on microfluidic chips. With the development of technology and in-depth research, the isolation and analysis of individual EVs can be realized by microfluidic method, and commercial EV chips are also expected to be applied in clinical practice.
In this article, the existing methods of microfluidic-based EV isolation and analysis are reviewed. Compared with traditional ultracentrifugation, ultrafiltration, immunocapture and co-precipitation, microfluidic chips are smaller and more flexible, and microfluidic immunoaffinity methods can isolate high-purity EVs with strong specificity. The isolation methods based on the physical characteristics of EVs do not need to add expensive reagents such as antigens and antibodies. Therefore, the cost is low, and the isolation process will not cause contamination, which is conducive to downstream analysis. Microfluidic-based EV analysis methods have the advantages of fast analysis speed, high throughput and low reagent consumption, which can meet the needs of rapid detection of EVs in a large number of clinical samples. Therefore, microfluidic technology has significant advantages in the isolation of EVs in a small amount of clinical samples and the rapid estimation of diseases.
Although microfluidic technology has made remarkable progress in the field of EV isolation and analysis. It usually needs to be combined with some instruments such as injection pumps and fluorescence detectors, which limits its application scenarios to a certain extent. In addition, EVs are small in size and similar in density to body fluids, a single separation method is inadequate. How to balance the relationship between EV purity and recovery on microfluidic chips is also a great challenge.
In recent years, with the rapid development of micro/nano manufacture, new materials and information technology, the design of microfluidic chips and the performance of supporting devices will be further improved. It is mainly reflected in: (1) The development of precision manufacture technology makes it possible to integrate multiple EV isolation methods and realize the integration of EV isolation and detection on one chip; (2) By combining the chips and portable detection equipments, a miniaturized EV microfluidic isolation and analysis platform is constructed to realize the rapid detection of EVs and greatly expand its application space. With the miniaturization, integration and automation of microfluidic EV isolation and analysis devices, microfluidic technology will play an increasingly important role in EV isolation, biochemical detection and mechanism research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Z. and M.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Z., J.C., Q.X., D.L.; writing—review and editing, L.Z., X.Y., L.J., J.C.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Xiamen Medical College Transverse Project (HX202302), National Natural Science Foundation of China (22304145), Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, China (2023J05285), the Medical and Health Guidance Project of Xiamen Science and Technology Bureau (3502Z20224ZD1299), Project of Xiamen Medical College (K2023-12, K2023-45), College Students' Innovative Entrepreneurial Training Plan Program of Fujian Province (202312631009). the Education and Research Project of Young and Middle-aged Teachers of Fujian Province, China. (JAT220406).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhu, L.; Tian, W.; Yuan, L.; Chi, C.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Zheng, M.; Yang, C.; Song, Y. Aptamer-based extracellular vesicle isolation, analysis and therapeutics. IMed. 2023, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, P.; Morelli, A. Regulation of immune responses by extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V. The biology function and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2020, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, A.; Lobb, R. The evolving translational potential of small extracellular vesicles in cancer. Nat. Rev. Can. 2020, 20, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Théry, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niel, G.; D'Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Peng, C.; Yi, J.; Zhang, D.; Xiang, X.; Peng, X.; Su, B.; Liu, B.; Shen, Y.; Qiao, L. Highly efficient exosome purification from human plasma by tangential flow filtration based microfluidic chip. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 333, 129563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Song, S.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tong, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Construction of Exosome SORL1 Detection Platform Based on 3D Porous Microfluidic Chip and its Application in Early Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer. Small 2023, 19, e2207381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coumans, F.; Brisson, A.; Buzas, E.; Dignat-George, F.; Drees, E.; El-Andaloussi, S.; Emanueli, C.; Gasecka, A.; Hendrix, A.; Hill, A.; et al. Methodological Guidelines to Study Extracellular Vesicles. Circulation research 2017, 120, 1632–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royo, F.; Théry, C.; Falcón-Pérez, J.M.; Nieuwland, R.; Witwer, K.W. Methods for Separation and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles: Results of a Worldwide Survey Performed by the ISEV Rigor and Standardization Subcommittee. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzás, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lässer, C.; Lötvall, J.; Nolte-'t Hoen, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J.; et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, H.; Adda, C.G.; Liem, M.; Ang, C.S.; Mechler, A.; Simpson, R.J.; Hulett, M.D.; Mathivanan, S. Comparative proteomics evaluation of plasma exosome isolation techniques and assessment of the stability of exosomes in normal human blood plasma. Proteomics 2013, 13, 3354–3364. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Kaslan, M.; Lee, S.H.; Yao, J.; Gao, Z. Progress in Exosome Isolation Techniques. Theranostics 2017, 7, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, M.; Khosroheidari, M.; Kanchi Ravi, R.; DiStefano, J. Comparison of protein, microRNA, and mRNA yields using different methods of urinary exosome isolation for the discovery of kidney disease biomarkers. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, J.Z.; Lee, Y.; Vader, P.; Mäger, I.; Johansson, H.J.; Heusermann, W.; Wiklander, O.P.; Hällbrink, M.; Seow, Y.; Bultema, J.J.; et al. Ultrafiltration with size-exclusion liquid chromatography for high yield isolation of extracellular vesicles preserving intact biophysical and functional properties. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhom, K.; Obi, P.O.; Saleem, A. A Review of Exosomal Isolation Methods: Is Size Exclusion Chromatography the Best Option? Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudineh, M.; Aldridge, P.; Ahmed, S.; Green, B.; Kermanshah, L.; Nguyen, V.; Tu, C.; Mohamadi, R.; Nam, R.; Hansen, A.; et al. Tracking the dynamics of circulating tumour cell phenotypes using nanoparticle-mediated magnetic ranking. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibsen, S.; Wright, J.; Lewis, J.; Kim, S.; Ko, S.; Ong, J.; Manouchehri, S.; Vyas, A.; Akers, J.; Chen, C.; et al. Rapid Isolation and Detection of Exosomes and Associated Biomarkers from Plasma. ACS nano. 2017, 11, 6641–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaltis, D.; Quake, S.; Yang, C. Developing optofluidic technology through the fusion of microfluidics and optics. Nature 2006, 442, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Deng, J.; Bai, L.; Qin, L.; Mei, H.; Zeng, M.; Tian, F.; et al. Cascaded microfluidic circuits for pulsatile filtration of extracellular vesicles from whole blood for early cancer diagnosis. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Fu, J.; Wu, X.; Liang, X.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Wu, X.; Cao, L.L.; Xu, Z.Y.; Dong, M. Microfluidic-based exosome isolation and highly sensitive aptamer exosome membrane protein detection for lung cancer diagnosis. Biosens Bioelectron 2022, 214, 114487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Guo, J.; Tian, F.; Yang, N.; Yan, F.; Ding, Y.; Wei, J.; Hu, G.; Nie, G.; Sun, J. Field-Free Isolation of Exosomes from Extracellular Vesicles by Microfluidic Viscoelastic Flows. ACS Nano. 2017, 11, 6968–6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jin, K.; He, M.; Wei, W.; Chen, X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Pang, W.; Ren, X.; et al. Self-adaptive virtual microchannel for continuous enrichment and separation of nanoparticles. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn8440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Im, H.; Castro, C.; Breakefield, X.; Weissleder, R.; Lee, H. New Technologies for Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1917–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boriachek, K.; Masud, M.; Palma, C.; Phan, H.; Yamauchi, Y.; Hossain, M.; Nguyen, N.; Salomon, C.; Shiddiky, M. Avoiding Pre-Isolation Step in Exosome Analysis: Direct Isolation and Sensitive Detection of Exosomes Using Gold-Loaded Nanoporous Ferric Oxide Nanozymes. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3827–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.K.; Whiteside, T.L. Immunoaffinity-Based Isolation of Melanoma Cell-Derived and T Cell-Derived Exosomes from Plasma of Melanoma Patients. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2265, 305–321. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Yu, Z.; Liu, X.; Xie, Q.; Wu, M.; Chen, G. Aptamer-Assisted Traceless Isolation of PD-L1-Positive Small Extracellular Vesicles for Dissecting Their Subpopulation Signature and Function. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnappan, R.; Ramadan, Q.; Zourob, M. An integrated lab-on-a-chip platform for pre-concentration and detection of colorectal cancer exosomes using anti-CD63 aptamer as a recognition element. Biosens Bioelectron 2023, 220, 114856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, J.; Lau, S.; Akbarinejad, A.; Bryant, D.T.; Chamley, L.W.; Pilkington, L.I.; Barker, D.; Williams, D.E.; Evans, C.W.; Travas-Sejdic, J. Electrochemical Approach for Specific Capture and Rapid Release of Nanoscale Placental Extracellular Vesicles Using Aptamer-Modified Conducting Terpolymer-Coated Carbon Cloth. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 3981–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yu, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Shang, L.; Zu, Y.; Shi, K. Aptamer decorated magnetic graphene oxide nanoparticles for effective capture of exosomes. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Zhuang, L.; Chang, Z.; Ge, M.; Mei, Q.; Yang, L.; Dong, W.-F. Hierarchical Au nanoarrays functionalized 2D Ti2CTx MXene membranes for the detection of exosomes isolated from human lung carcinoma cells. Biosens Bioelectron 2022, 216, 114647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Bian, F.; Guo, J.; Zhao, Y. Aptamer-Functionalized Barcodes in Herringbone Microfluidics for Multiple Detection of Exosomes. Small Methods 2022, 6, e2200236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Gao, J.; Zhao, K.; Chen, X.; Lin, X.; Huang, C.; An, Y.; Xiao, X.; Wu, Q.; Cui, L.; et al. Fluid nanoporous microinterface enables multiscale-enhanced affinity interaction for tumor-derived extracellular vesicle detection. PNAS. 2022, 119, e2213236119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Hurley, J.; Roberts, D.; Chakrabortty, S.; Enderle, D.; Noerholm, M.; Breakefield, X.; Skog, J. Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: opportunities and challenges. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Shu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Chen, X.; Lin, F.; Feng, J.; Huang, C.; Wang, H.; et al. A Fluid Multivalent Magnetic Interface for High-Performance Isolation and Proteomic Profiling of Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2023, 62, e202215337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Lu, Y.; Kang, S.; Yang, C.; Song, Y. Reliable Detection of Extracellular PD-L1 by DNA Computation-Mediated Microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 9373–9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, B.; Kim, R.; Jeong, H.; Kang, B.; Kim, J.; Son, H.Y.; Lim, J.; Rho, H.W.; Lim, E.K.; Haam, S. An immuno-magnetophoresis-based microfluidic chip to isolate and detect HER2-Positive cancer-derived exosomes via multiple separation. Biosens Bioelectron 2023, 239, 115592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Duong, B.; Ahmed, S.; Dhavarasa, P.; Wang, Z.; Labib, M.; Flynn, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. A magneto-activated nanoscale cytometry platform for molecular profiling of small extracellular vesicles. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Lin, B.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Yang, C.; Song, Y. Isolation of PD-L1 Extracellular Vesicle Subpopulations Using DNA Computation Mediated Microfluidic Tandem Separation. Small methods 2023, 7, e2300516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, N.; Du, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Xu, W.; Luo, Y.; Lin, Y. Recent Advances in Biosensors for Detecting Cancer-Derived Exosomes. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1236–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwar, S.; Dunlay, C.; Simeone, D.; Nagrath, S. Microfluidic device (ExoChip) for on-chip isolation, quantification and characterization of circulating exosomes. Lab Chip. 2014, 14, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudani, J.; Gossett, D.; Tse, H.; Lamm, R.; Kulkarni, R.; Carlo, D. Rapid inertial solution exchange for enrichment and flow cytometric detection of microvesicles. Biomicrofluidics 2015, 9, 014112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisey, C.; Dorayappan, K.; Cohn, D.; Selvendiran, K.; Hansford, D. Microfluidic affinity separation chip for selective capture and release of label-free ovarian cancer exosomes. Lab Chip. 2018, 18, 3144–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Ye, L.; Jian, X.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Tong, Z.; Wu, Z.; Shi, N.; Han, Y.; Mao, H. Integrated microfluidic system for isolating exosome and analyzing protein marker PD-L1. Biosens Bioelectron 2022, 204, 113879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Xu, X.; Li, B.; Situ, B.; Pan, W.; Hu, Y.; An, T.; Yao, S.; Zheng, L. Single-Exosome-Counting Immunoassays for Cancer Diagnostics. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 4226–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhou, X.; He, M.; Shang, Y.; Tetlow, A.; Godwin, A.; Zeng, Y. Ultrasensitive detection of circulating exosomes with a 3D-nanopatterned microfluidic chip. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, X.; Gardashova, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Zeng, Y. Molecular and functional extracellular vesicle analysis using nanopatterned microchips monitors tumor progression and metastasis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xu, Y.; Wei, X.; Lin, H.; Huang, M.; Lin, B.; Song, Y.; Yang, C. Coupling Aptamer-based Protein Tagging with Metabolic Glycan Labeling for In Situ Visualization and Biological Function Study of Exosomal Protein-Specific Glycosylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 18111–18115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xu, Y.; Kang, S.; Lin, B.; Zhang, C.; You, Z.; Lin, H.; Yang, C.; Song, Y. Quantification-Promoted Discovery of Glycosylated Exosomal PD-L1 as a Potential Tumor Biomarker. Small Methods 2022, 6, e2200549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Tian, F.; Cai, L.; Zhang, W.; Feng, Q.; Chang, J.; Wan, F.; Yang, Y.; Dai, B.; et al. Low-cost thermophoretic profiling of extracellular-vesicle surface proteins for the early detection and classification of cancers. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Zhang, S.H.; Liu, C.; Han, Z.W.; Liu, Y.; Deng, J.Q.; Li, Y.K.; Wu, X.; Cai, L.L.; Qin, L.L.; et al. Protein analysis of extracellular vesicles to monitor and predict therapeutic response in metastatic breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Deng, J.; Han, Z.; Liu, C.; Tian, F.; Xu, R.; Han, D.; Zhang, S.; Sun, J. Molecular Identification of Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Using Thermophoresis-Mediated DNA Computation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.Q.; Zhao, S.; Li, J.H.; Cheng, Y.C.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.L.; Tian, F.; Dai, B.; Sun, J.S. One-Step Thermophoretic AND Gate Operation on Extracellular Vesicles Improves Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2022, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thind, A.; Wilson, C. Exosomal miRNAs as cancer biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2016, 5, 31292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Deng, J.; Li, L.; Sun, J. Thermophoretic Detection of Exosomal microRNAs by NanoFlares. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.W.; Wan, F.N.; Deng, J.Q.; Zhao, J.X.; Li, Y.K.; Yang, Y.J.; Jiang, Q.; Ding, B.Q.; Liu, C.; Dai, B.; et al. Ultrasensitive detection of mRNA in extracellular vesicles using DNA tetrahedron-based thermophoretic assay. Nano Today 2021, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, S.H.; Hu, H.J.; Cheng, Y.C.; Zou, K.X.; Song, J.; Deng, J.Q.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, X.B.; Ke, G.L.; et al. Selective In Situ Analysis of Mature microRNAs in Extracellular Vesicles Using a DNA Cage-Based Thermophoretic Assay. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2023, 62. [Google Scholar]
- Crescitelli, R.; Lässer, C.; Lötvall, J. Isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicle subpopulations from tissues. Nat. Protoc. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.H.; Qi, D.Y.; Li, L.M.; Su, H.R.; Li, X.J.; Luo, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhang, F.Y.; Lin, B.C.; Liu, T.J.; et al. Multiplexed profiling of single-cell extracellular vesicles secretion. PNAS. 2019, 116, 5979–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Ji, Y.; Zhu, F.; Liu, L.; Li, L.; Bai, X.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Luo, Y.; Lin, B.; et al. Mapping secretome-mediated interaction between paired neuron–macrophage single cells. PNAS. 2022, 119, e2200944119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidyanathan, R.; Naghibosadat, M.; Rauf, S.; Korbie, D.; Carrascosa, L.; Shiddiky, M.; Trau, M. Detecting exosomes specifically: a multiplexed device based on alternating current electrohydrodynamic induced nanoshearing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11125–11132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, S.; Shehata Draz, M.; Zarghooni, M.; Sanati-Nezhad, A.; Ghavami, S.; Shafiee, H.; Akbari, M. Microfluidic approaches for isolation, detection, and characterization of extracellular vesicles: Current status and future directions. Biosens Bioelectron 2017, 91, 588–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Cheng, S.; Cao, P.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xie, M.; Xu, Y.; Huang, W. Detection of exosomes by ZnO nanowires coated three-dimensional scaffold chip device. Biosens Bioelectron 2018, 122, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, H.; Mi, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Li, A.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, H.; Rong, P.; Liu, D. Nanozyme-assisted sensitive profiling of exosomal proteins for rapid cancer diagnosis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9303–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Shi, M.; Liu, Y.; Wan, S.; Cui, C.; Zhang, L.; Tan, W. Aptamer/AuNP Biosensor for Colorimetric Profiling of Exosomal Proteins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 11916–11920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.; Hemphill, M.; Gabrieli, D.; Wu, L.; Yelleswarapu, V.; Lawrence, G.; Pennycooke, W.; Singh, A.; Meaney, D.; Issadore, D. Smartphone-enabled optofluidic exosome diagnostic for concussion recovery. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Park, J.S.; Huang, C.-H.; Jo, A.; Cook, K.; Wang, R.; Lin, H.-Y.; Van Deun, J.; Li, H.; Min, J.; et al. An integrated magneto-electrochemical device for the rapid profiling of tumour extracellular vesicles from blood plasma. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Sun, M.; Feng, B.; Shen, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Yu, S. A filter-electrochemical microfluidic chip for multiple surface protein analysis of exosomes to detect and classify breast cancer. Biosens Bioelectron 2023, 239, 115590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Jing, A. Room-Temperature Self-Healing Conductive Elastomers for Modular Assembly as a Microfluidic Electrochemical Biosensing Platform for the Detection of Colorectal Cancer Exosomes. Micromachines 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liao, C.; Zuo, P.; Liu, Z.; Ye, B. Magnetic-Based Microfluidic Device for On-Chip Isolation and Detection of Tumor-Derived Exosomes. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13451–13458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Luo, X.; Huang, Y.; Xie, T.; Pilarsky, C.; Dang, Y.; Zhang, J. Microfluidic Technology for the Isolation and Analysis of Exosomes. Micromachines 2022, 13.1571.
- Huang, R.; He, L.; Xia, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.; Xie, H.; Wang, S.; Peng, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. A Sensitive Aptasensor Based on a Hemin/G-Quadruplex-Assisted Signal Amplification Strategy for Electrochemical Detection of Gastric Cancer Exosomes. Small 2019, 15, e1900735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tian, Z.; Yang, S.; Rich, J.; Zhao, S.; Klingeborn, M.; Huang, P.; Li, Z.; Stout, A.; Murphy, Q.; et al. Electrochemical micro-aptasensors for exosome detection based on hybridization chain reaction amplification. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2021, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lin, S.; Zhou, C.; Cui, D.; Haick, H.; Tang, N. From Conventional to Microfluidic: Progress in Extracellular Vesicle Separation and Individual Characterization. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2202437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panneerselvam, R.; Sadat, H.; Höhn, E.; Das, A.; Noothalapati, H.; Belder, D. Microfluidics and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, a win-win combination? Lab Chip. 2022, 22, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.; Jeong, H.; Park, J.; Hong, S.; Choi, Y. Correlation between Cancerous Exosomes and Protein Markers Based on Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) and Principal Component Analysis (PCA). ACS sensors 2018, 3, 2637–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Fang, J.; Xu, Z. Advances in droplet microfluidics for SERS and Raman analysis. Biosens Bioelectron 2022, 198, 113822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.; Isaac Hosseini, I.; AbdelFatah, T.; Montermini, L.; Wachsmann Hogiu, S.; Rak, J.; Mahshid, S. Plasmonic nanobowtiefluidic device for sensitive detection of glioma extracellular vesicles by Raman spectrometry. Lab Chip. 2021, 21, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Shi, H.; Tang, K.; Qiao, L.; Yu, G.; Ding, C.; Yu, S. Microfluidic Raman biochip detection of exosomes: a promising tool for prostate cancer diagnosis. Lab Chip. 2020, 20, 4632–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Shiddiky, M.; Trau, M. Enabling Rapid and Specific Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Immunoassay Using Nanoscaled Surface Shear Forces. ACS nano 2015, 9, 6354–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Peng, X.; Yang, Y.; Yi, J.; Zhao, D.; Bao, Q.; Long, S.; Yu, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, B.; et al. Integrated microfluidic-SERS for exosome biomarker profiling and osteosarcoma diagnosis. Biosens Bioelectron 2022, 217, 114709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wuethrich, A.; Sina, A.; Lane, R.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Cebon, J.; Behren, A.; Trau, M. Tracking extracellular vesicle phenotypic changes enables treatment monitoring in melanoma. Sci. adv. 2020, 6, eaax3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).