Submitted:
10 March 2024
Posted:
11 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Radiopharmaceutical
Recombinant α1-Microglobulin (A1M)
Animal Experiments
Radioactivity Measurements
Absorbed Dose Calculation
Bone Marrow
Kidneys
Proteomics
Sample Preparation and Digestion
Tryptic Digestion and Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) Labelling
LC-MS/MS Analysis
Proteomic Data Analysis
Analysis of Protein Regulation
Results
Absorbed Dose to Kidneys and Bone Marrow
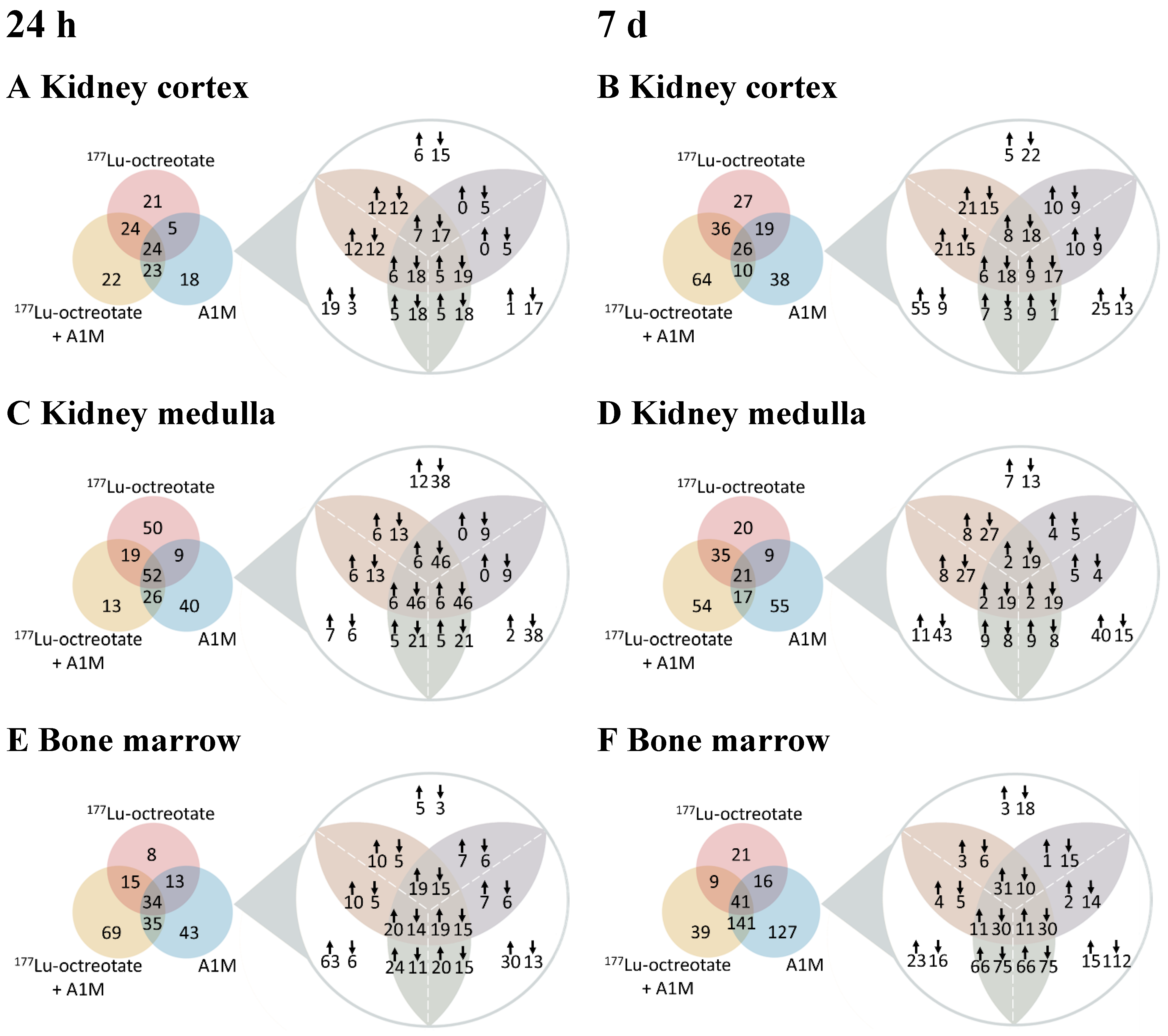
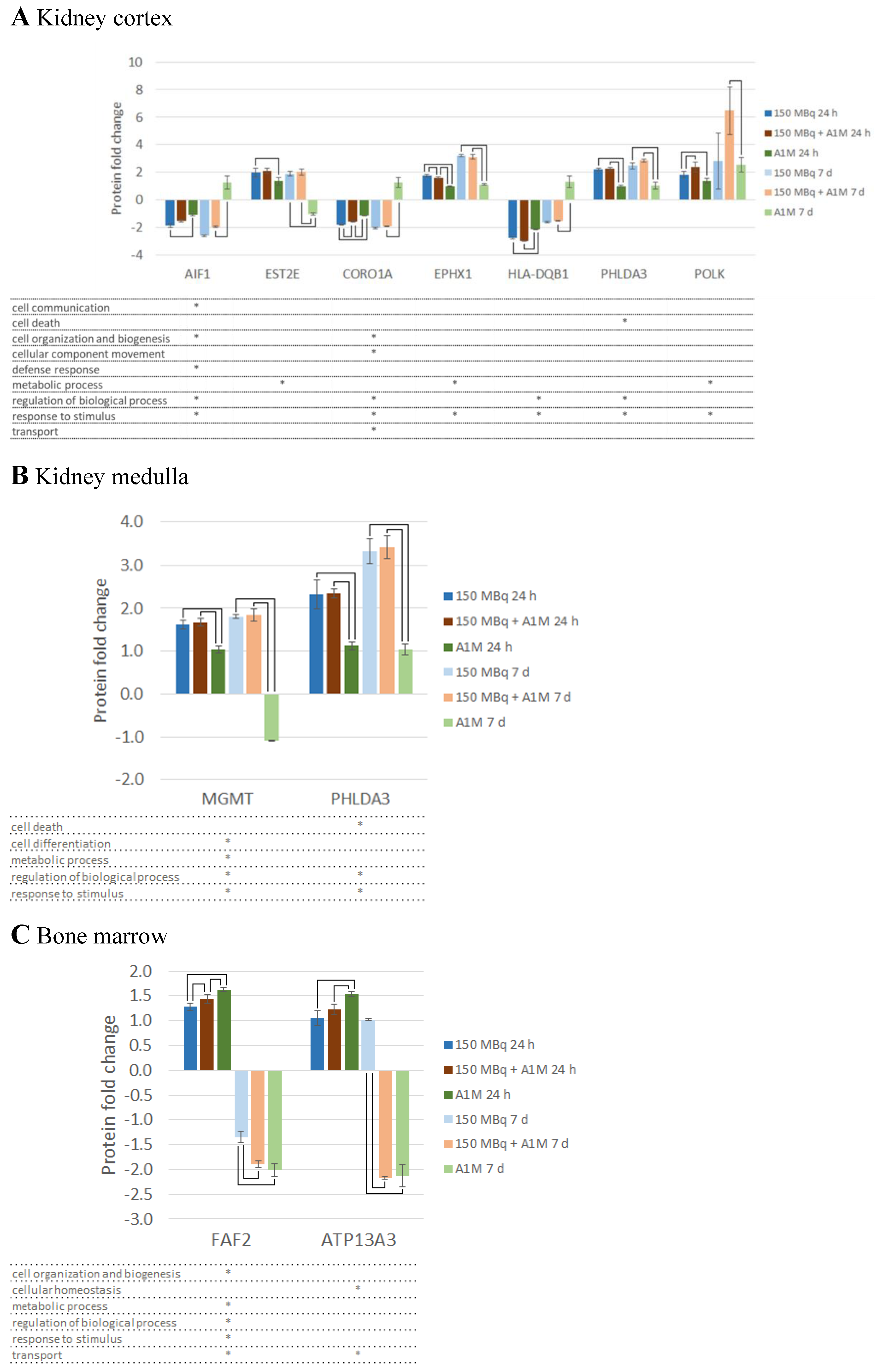
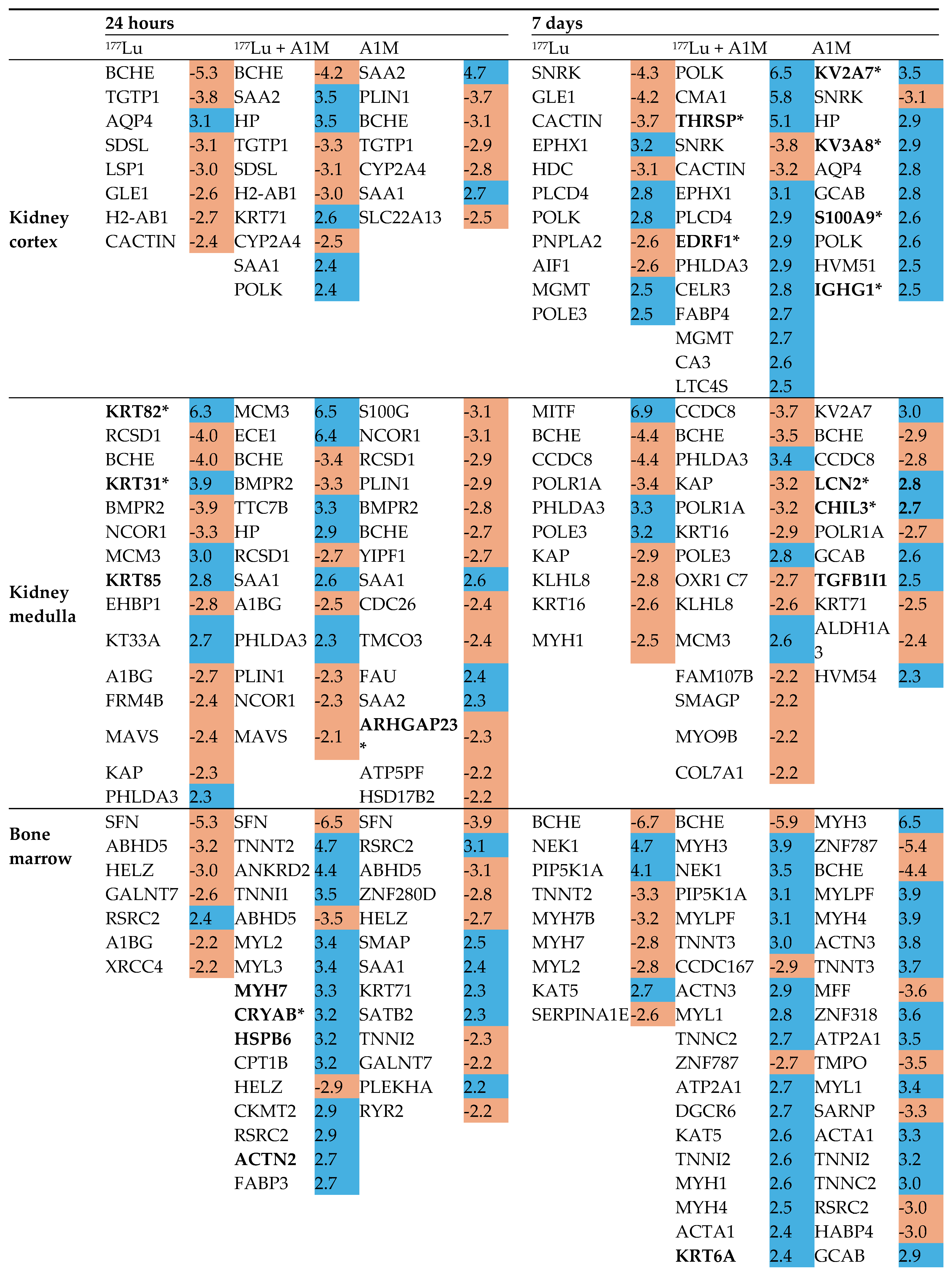
Differentially Regulated Proteins, DRPs
Canonical Pathway Analysis
Upstream Regulators
Toxicity Functions
Discussion
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
References
- Olsson, M.G.; Olofsson, T.; Tapper, H.; Akerstrom, B. The lipocalin alpha1-microglobulin protects erythroid K562 cells against oxidative damage induced by heme and reactive oxygen species. Free radical research 2008, 42, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garske-Román, U.; Sandström, M.; Fröss Baron, K.; Lundin, L.; Hellman, P.; Welin, S.; Johansson, S.; Khan, T.; Lundqvist, H.; Eriksson, B.; et al. Prospective observational study of (177)Lu-DOTA-octreotate therapy in 200 patients with advanced metastasized neuroendocrine tumours (NETs): feasibility and impact of a dosimetry-guided study protocol on outcome and toxicity. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging 2018, 45, 970–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, M.; Bernhardt, P.; Svensson, J.B.; Wängberg, B.; Ahlman, H.; Forssell-Aronsson, E. Estimation of absorbed dose to the kidneys in patients after treatment with 177Lu-octreotate: comparison between methods based on planar scintigraphy. EJNMMI research 2012, 2, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twardella, D.; Chang-Claude, J. Studies on radiosensitivity from an epidemiological point of view - overview of methods and results. Radiotherapy and oncology : journal of the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology 2002, 62, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geenen, L.; Nonnekens, J.; Konijnenberg, M.; Baatout, S.; De Jong, M.; Aerts, A. Overcoming nephrotoxicity in peptide receptor radionuclide therapy using [(177)Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE for the treatment of neuroendocrine tumours. Nuclear medicine and biology 2021, 102-103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolleman, E.J.; Valkema, R.; de Jong, M.; Kooij, P.P.; Krenning, E.P. Safe and effective inhibition of renal uptake of radiolabelled octreotide by a combination of lysine and arginine. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging 2003, 30, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolleman, E.J.; Bernard, B.F.; Breeman, W.A.; Forrer, F.; de Blois, E.; Hoppin, J.; Gotthardt, M.; Boerman, O.C.; Krenning, E.P.; de Jong, M. Molecular imaging of reduced renal uptake of radiolabelled [DOTA0,Tyr3]octreotate by the combination of lysine and Gelofusine in rats. Nuklearmedizin. Nuclear medicine 2008, 47, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okunieff, P.; Swarts, S.; Keng, P.; Sun, W.; Wang, W.; Kim, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Williams, J.P.; et al. Antioxidants reduce consequences of radiation exposure. Advances in experimental medicine and biology 2008, 614, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansson A; Örbom A; Vilhelmsson Timmermand O; Ahlstedt J; Strand SE; B, Å. Kidney protection with the radical scavenger α1-microglobulin (A1M) during peptide receptor radionuclide and radioligand therapy. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerstrom, B.; Gram, M. A1M, an extravascular tissue cleaning and housekeeping protein. Free radical biology & medicine 2014, 74, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlstedt, J.; Tran, T.A.; Strand, F.; Holmqvist, B.; Strand, S.E.; Gram, M.; Akerstrom, B. Biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of recombinant alpha1-microglobulin and its potential use in radioprotection of kidneys. American journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging 2015, 5, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alattar AG; Kristiansson A; Karlsson H; Vallius S; Ahlstedt J; Forssell-Aronsson E; Åkerström B; Strand SE; Flygare J; M, G. Recombinant α1-microglobulin (rA1M) protects against hematopoietic and renal toxicity, alone and in combination with amino acids, in a 177Lu-DOTATATE mouse radiation mode. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 928. [Google Scholar]
- Kristiansson, A.; Ahlstedt, J.; Holmqvist, B.; Brinte, A.; Tran, T.A.; Forssell-Aronsson, E.; Strand, S.E.; Gram, M.; Åkerström, B. Protection of Kidney Function with Human Antioxidation Protein α(1)-Microglobulin in a Mouse (177)Lu-DOTATATE Radiation Therapy Model. Antioxid Redox Signal 2019, 30, 1746–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, C.K.; Shubbar, E.; Schüler, E.; Åkerström, B.; Gram, M.; Forssell-Aronsson, E.B. Recombinant α(1)-Microglobulin Is a Potential Kidney Protector in (177)Lu-Octreotate Treatment of Neuroendocrine Tumors. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine 2019, 60, 1600–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, F.A.; Nonnekens, J.; Konijnenberg, M.W.; de Jong, M. To go where no one has gone before: the necessity of radiobiology studies for exploration beyond the limits of the "Holy Gray" in radionuclide therapy. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging 2021, 48, 2680–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, A.; Eberlein, U.; Holm, S.; Hustinx, R.; Konijnenberg, M.; Strigari, L.; van Leeuwen, F.W.B.; Glatting, G.; Lassmann, M. EANM position paper on the role of radiobiology in nuclear medicine. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreassen, C.N.; Schack, L.M.; Laursen, L.V.; Alsner, J. Radiogenomics - current status, challenges and future directions. Cancer letters 2016, 382, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczynski, D. Radiation proteomics: a brief overview. Proteomics 2014, 14, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüler, E.; Rudqvist, N.; Parris, T.Z.; Langen, B.; Helou, K.; Forssell-Aronsson, E. Transcriptional response of kidney tissue after 177Lu-octreotate administration in mice. Nuclear medicine and biology 2014, 41, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüler, E.; Rudqvist, N.; Parris, T.Z.; Langen, B.; Spetz, J.; Helou, K.; Forssell-Aronsson, E. Time- and dose rate-related effects of internal (177)Lu exposure on gene expression in mouse kidney tissue. Nuclear medicine and biology 2014, 41, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüler, E.; Larsson, M.; Parris, T.Z.; Johansson, M.E.; Helou, K.; Forssell-Aronsson, E. Potential Biomarkers for Radiation-Induced Renal Toxicity following 177Lu-Octreotate Administration in Mice. PloS one 2015, 10, e0136204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüler, E.; Parris, T.Z.; Helou, K.; Forssell-Aronsson, E. Distinct microRNA expression profiles in mouse renal cortical tissue after 177Lu-octreotate administration. PloS one 2014, 9, e112645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler E, J.D. , Larsson M, Parris TZ, Helou K, Forssell-Aronsson E. Proteomics and functional analysis for the assessment of radiation induced response after 177Lu-octreotate administration in mice. 2014.
- Andersson, M. Apoptotic effects in renal cortex after treatment with 177Lu-octreotate. University of Gothenburg, 2019.
- Andersson, C.; Shubbar, E.; Schuler, E.; Akersson, B.; Gram, M.; Forssell-Aronsson, E. rA1M is a potential kidney protector in (177)Lu-octreotate treatment of neuroendocrine tumors. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerström, B.; Rosenlöf, L.; Hägerwall, A.; Rutardottir, S.; Ahlstedt, J.; Johansson, M.E.; Erlandsson, L.; Allhorn, M.; Gram, M. rA1M-035, a Physicochemically Improved Human Recombinant α(1)-Microglobulin, Has Therapeutic Effects in Rhabdomyolysis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Antioxidants & redox signaling 2019, 30, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolch, W.E.; Eckerman, K.F.; Sgouros, G.; Thomas, S.R. MIRD pamphlet No. 21: a generalized schema for radiopharmaceutical dosimetry--standardization of nomenclature. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine 2009, 50, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckerman K, E.A. ICRP Publication 107. Nuclear decay data for dosimetric calculations; 2008; pp. 7-96.
- Miller, W.H.; Hartmann-Siantar, C.; Fisher, D.; Descalle, M.A.; Daly, T.; Lehmann, J.; Lewis, M.R.; Hoffman, T.; Smith, J.; Situ, P.D.; et al. Evaluation of beta-absorbed fractions in a mouse model for 90Y, 188Re, 166Ho, 149Pm, 64Cu, and 177Lu radionuclides. Cancer biotherapy & radiopharmaceuticals 2005, 20, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüler, E.; Österlund, A.; Forssell-Aronsson, E. The amount of injected 177Lu-octreotate strongly influences biodistribution and dosimetry in C57BL/6N mice. Acta oncologica (Stockholm, Sweden) 2016, 55, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, J.; Mölne, J.; Forssell-Aronsson, E.; Konijnenberg, M.; Bernhardt, P. Nephrotoxicity profiles and threshold dose values for [177Lu]-DOTATATE in nude mice. Nuclear medicine and biology 2012, 39, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Zougman, A.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nature methods 2009, 6, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, N.S.; Grunenwald, A.; Figueres, M.-L.; Chauvet, S.; Daugan, M.; Knockaert, S.; Robe-Rybkine, T.; Noe, R.; May, O.; Frimat, M.; et al. Characterization of Renal Injury and Inflammation in an Experimental Model of Intravascular Hemolysis. Frontiers in Immunology 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djudjaj, S.; Papasotiriou, M.; Bülow, R.D.; Wagnerova, A.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Cohen, C.D.; Strnad, P.; Goumenos, D.S.; Floege, J.; Boor, P. Keratins are novel markers of renal epithelial cell injury. Kidney international 2016, 89, 792–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.; Watson, N.; Long, E.; Sharpe, S.; Zhong, W.; Xu, S.Z.; Atkin, S.L. Expression of somatostatin and somatostatin receptor subtypes 1-5 in human normal and diseased kidney. The journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry : official journal of the Histochemistry Society 2008, 56, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, V.S.; Ferguson, M.A.; Bonventre, J.V. Biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology 2008, 48, 463–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansson, A.; Ahlstedt, J.; Holmqvist, B.; Brinte, A.; Tran, T.A.; Forssell-Aronsson, E.; Strand, S.E.; Gram, M.; Akerstrom, B. Protection of Kidney Function with Human Antioxidation Protein alpha1-Microglobulin in a Mouse (177)Lu-DOTATATE Radiation Therapy Model. Antioxidants & redox signaling 2019, 30, 1746–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lu, X.; Feng, J.B.; Tian, M.; Liu, Q.J. Identification and Validation of Candidate Radiation-responsive Genes for Human Biodosimetr. Biomedical and environmental sciences : BES 2017, 30, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kultova, G.; Tichy, A.; Rehulkova, H.; Myslivcova-Fucikova, A. The hunt for radiation biomarkers: current situation. International journal of radiation biology 2020, 96, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, F.; Coleman, M.A.; Jones, I.M.; Wyrobek, A.J. Candidate protein biodosimeters of human exposure to ionizing radiation. International journal of radiation biology 2006, 82, 605–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipuk, J.E.; Moldoveanu, T.; Llambi, F.; Parsons, M.J.; Green, D.R. The BCL-2 family reunion. Molecular cell 2010, 37, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Qi, Z.; Chen, M.; Xiao, T.; Guan, J.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Q.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Z. Serum amyloid A1 as a biomarker for radiation dose estimation and lethality prediction in irradiated mouse. Annals of translational medicine 2019, 7, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åkerstrom, B.; Logdberg, L.; Berggard, T.; Osmark, P.; Lindqvist, A. alpha(1)-Microglobulin: a yellow-brown lipocalin. Biochimica et biophysica acta 2000, 1482, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Lorimore, S.A.; Evans, C.A.; Whetton, A.D.; Wright, E.G. A proteomic analysis of murine bone marrow and its response to ionizing radiation. Proteomics 2005, 5, 4254–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magić, Z.; Matić-Ivanović, S.; Savić, J.; Poznanović, G. Ionizing radiation-induced expression of the genes associated with the acute response to injury in the rat. Radiation research 1995, 143, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergwik, J.; Kristiansson, A.; Allhorn, M.; Gram, M.; Åkerström, B. Structure, Functions, and Physiological Roles of the Lipocalin α(1)-Microglobulin (A1M). Frontiers in physiology 2021, 12, 645650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.B.F.; Stødkilde, K.; Sæderup, K.L.; Kuhlee, A.; Raunser, S.; Graversen, J.H.; Moestrup, S.K. Haptoglobin. Antioxid Redox Signal 2017, 26, 814–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansson, A.; Bergwik, J.; Alattar, A.G.; Flygare, J.; Gram, M.; Hansson, S.R.; Olsson, M.L.; Storry, J.R.; Allhorn, M.; Åkerström, B. Human radical scavenger α(1)-microglobulin protects against hemolysis in vitro and α(1)-microglobulin knockout mice exhibit a macrocytic anemia phenotype. Free radical biology & medicine 2021, 162, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wester, L.; Michaëlsson, E.; Holmdahl, R.; Olofsson, T.; Akerström, B. Receptor for alpha1-microglobulin on T lymphocytes: inhibition of antigen-induced interleukin-2 production. Scandinavian journal of immunology 1998, 48, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Luna, J.L.; Leyva-Cobian, F.; Mollinedo, F. Identification of the protein HC receptor. FEBS letters 1988, 236, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmos, G.; López-Ongil, S.; Ruiz Torres, M.P. Integrin-linked kinase: A new actor in the ageing process? Experimental gerontology 2017, 100, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Hao, C.M. SIRT1 and Kidney Function. Kidney diseases (Basel, Switzerland) 2016, 1, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najjar, I.; Fagard, R. STAT1 and pathogens, not a friendly relationship. Biochimie 2010, 92, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhayana, S.; Song, F.; Jacob, J.; Fadda, P.; Denko, N.C.; Xu-Welliver, M.; Chakravarti, A.; Jacob, N.K. Urinary miRNAs as Biomarkers for Noninvasive Evaluation of Radiation-Induced Renal Tubular Injury. Radiation research 2017, 188, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Kidney cortex | |||||
| Time | Group | Ingenuity Canonical Pathways | p-value | z-score | Involved proteins |
| 24 h | 177Lu + A1M | Estrogen Receptor Signaling* | 4.37E-02 | -2.00 | ARG2, BAD, NCOR1, RAP2A |
| 7 d | 177Lu | Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling | 3.24E-04 | -2.00 | BAX, MCM7, NCOA3, NCOR2, NQO1 |
| Kidney medulla | |||||
| Time | Group | Ingenuity Canonical Pathways | p-value | z-score | Involved proteins |
| 24 h | 177Lu + A1M | 3-phosphoinositide Biosynthesis | 7.94E-03 | -2.00 | PAWR, PIP5K1A, PPP1R1A,PPP1R1B |
| Superpathway of Inositol Phosphate Compounds | 1.45E-02 | -2.00 | |||
| A1M | 3-phosphoinositide Biosynthesis | 1.35E-02 | -2.00 | ||
| Superpathway of Inositol Phosphate Compounds | 2.45E-02 | -2.00 | |||
| Bone marrow | |||||
| Time | Group | Ingenuity Canonical Pathways | p-value | z-score | Involved proteins |
| 24 h | 177Lu + A1M | Actin Cytoskeleton Signaling | 7.24E-10 | 2.53 | ACTA1, ACTN2, CFL2, MYH1, MYH7, MYH8, MYL2, MYL3, MYL6B, MYLK2 ,MYLK3, MYLPF, TTN |
| ILK Signaling | 2.19E-08 | 2.11 | ACTA1, ACTN2, CFL2, CREBBP, FLNC, MYH1, MYH7, MYH8, MYL2, MYL3, MYL6B | ||
| Hepatic Fibrosis Signaling Pathway | 8.13E-05 | 2.53 | AXIN1, CREBBP, MYL2, MYL3, MYL6B, MYLK2, MYLK3, MYLPF, TRADD, TTN | ||
| Regulation of Actin-based Motility by Rho | 2.34E-04 | 2.24 | ACTA1, MYL2, MYL3, MYL6B, MYLPF | ||
| PAK Signaling | 3.02E-04 | 2.00 | CFL2, MYL2, MYL3, YL6B, MYLPF | ||
| Apelin Cardiomyocyte Signaling Pathway | 3.47E-04 | 2.24 | ATP2A1, MYL2, MYL3, MYL6B, MYLPF | ||
| Signaling by Rho Family GTPases | 7.08E-04 | 2.45 | ACTA1, CFL2, DES, MYL2, MYL3, MYL6B, MYLPF | ||
| Cdc42 Signaling | 2.34E-03 | 2.24 | CFL2, MYL2, MYL3, MYL6B, MYLPF | ||
| Cardiac Hypertrophy Signaling | 3.39E-03 | 2.24 | CREBBP, HSPB1, MYL2, MYL3, MYL6B, MYLPF | ||
| Gα12/13 Signaling | 8.13E-03 | 2.00 | MYL2, MYL3, MYL6B, MYLPF | ||
| CXCR4 Signaling | 1.82E-02 | 2.00 | |||
| A1M | Actin Cytoskeleton Signaling | 5.13E-03 | -2.00 | Actn3, MYH3, MYH4, MYLK3, MYLPF | |
| ILK Signaling | 1.62E-02 | -2.00 | Actn3, CREBBP, MYH3, MYH4 | ||
| 7d | 177Lu | ILK Signaling | 3.55E-05 | -2.45 | ACTN2, MYH7, MYH7B, MYL2, MYL3, MYL6B |
| Phospholipase C Signaling | 1.45E-03 | -2.00 | ARHGEF18, GNB4, MYL2, MYL3, MYL6B | ||
| 177Lu + A1M | Calcium Signaling | 5.01E-12 | 2.24 | ACTA1, ACTC1, ATP2A1, CACNA2D1, MYH1, MYH3, MYH4, MYH8, MYL1,RYR1, RYR2, TNNC2, TNNI2, TNNT2, TNNT3, Tpm1, Tpm2 | |
| Actin Cytoskeleton Signaling | 4.90E-06 | 3.16 | ACTA1, ACTC1, Actn3, MYH1, MYH3, MYH4, MYH8, MYL1, MYLPF, PIP5K1A, TTN | ||
| ILK Signaling | 6.03E-05 | 2.33 | ACTA1, ACTC1, Actn3, FLNC, MYH1, MYH3, MYH4, MYH8, MYL1 | ||
| Regulation of Actin-based Motility by Rho | 1.48E-03 | 2.24 | ACTA1, ACTC1, MYL1, MYLPF, PIP5K1A | ||
| Signaling by Rho Family GTPases | 1.74E-03 | 2.12 | ACTA1, ACTC1, ARHGEF18, DES, GFAP, MYL1, MYLPF, PIP5K1A | ||
| Integrin Signaling* | 4.37E-02 | 2.23 | ACTA1, ACTC1, Actn3, CAPN7, TTN | ||
| A1M | Calcium Signaling | 1.62E-09 | 2.00 | ACTA1, ACTC1, ATP2A1, MYH1, MYH3, MYH4, MYH8, MYL1, MYL2, RYR1, RYR2, TNNC2, TNNI2, TNNT2, TNNT3, Tpm1, Tpm2 | |
| Actin Cytoskeleton Signaling | 5.89E-06 | 2.71 | ACTA1, ACTC1, Actn3, MYH1, MYH3, MYH4, MYH8, MYL1, MYL2, MYLK3, MYLPF, PIP5K1A, TTN | ||
| *Not significant when considering only molecules and/or relationships in mouse | |||||
| Upstream regulator | Tissue | Time | Group | Predicted state | Target proteins in dataset |
| Bvht | Bone marrow | 24 h | 177Lu + A1M | Activated | MYH7, MYL2, MYL3, MYOM1, SMYD1, TNNI1, TNNT2, TTN |
| 7 d | 177Lu | Inhibited | MYH7, MYL2, MYL3, TNNI1, TNNT2 | ||
| DNMT3B | Bone marrow | 24 h | A1M | Activated | CASQ1, RYR2, TNNT2, TNNT3 |
| 7 d | 177Lu | Activated | MYH7, MYH7B, MYL2, MYL3, TNNI1, TNNT2 | ||
| ETV6-RUNX1 | Cortex | 24 h | 177Lu | Activated | CORO1A, GBP2, PSMB9, PTPRC |
| Medulla | 24 h | 177Lu | Activated | CORO1A, CYBB, GBP2, ITGB2, MGMT, PSMB9, PTPRC, STMN1 | |
| Ifnar | Cortex | 24 h | 177Lu | Inhibited | GBP2, IFIT1B, PSMB8, PSMB9, TAPBP, VCAM1 |
| A1M | Inhibited | GBP2, PSMB8, PSMB9, TAP1, TAPBP | |||
| IFNG | Cortex | 24 h | 177Lu + A1M | Inhibited | ACE, AIF1, ARG2, BBC3, C1QB, GBP2, HLA-DQB1, Iigp1, PSMB10, PSMB8, PSMB9, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 |
| A1M | Inhibited | ACE, ARG2, GBP2, HLA-DQB1, Iigp1, PSMB8, PSMB9, SLC2A4, TAP1, TAPBP, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 | |||
| Medulla | 24 h | 177Lu | Inhibited | AIF1, ALDH1A3, CD74, CYBB, ECE1, GBP2, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, PARVG, PPP1R1B, PSMB9, SDC4, SMAGP, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 | |
| IL10RA | Cortex | 24 h | 177Lu + A1M | Activated | ARG2, GBP2, Iigp1, LUM, MEP1A, PSMB8, PSMB9, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 |
| 7 d | 177Lu | Activated | CLIC6, IFI16, LTC4S, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 | ||
| KDM5A | Bone marrow | 24 h | 177Lu + A1M | Inhibited | ACTN2, FXYD1, MYH7, MYH8, MYL6B, PGAM2, TNNC2, TNNT2, Tpm2, TRIM72 |
| A1M | Activated | Actn3, FXYD1, MYH4, TNNC2, TNNI2, TNNT2 | |||
| 7 d | 177Lu | Activated | ACTN2, MYH7, MYL6B, TNNT2 | ||
| 177Lu + A1M | Inhibited | ACTC1, Actn3, MFN2, MYH4, MYH8, MYL1, PGAM2, RYR1, TNNC2, TNNI2, TNNT2, Tpm1, Tpm2, TRIM72 | |||
| A1M | Inhibited | ACTC1, Actn3, MFN2, MYH4, MYH8, MYL1, PGAM2, RYR1, TNNC2, TNNI2, TNNT2, Tpm1, Tpm2, TRIM72 | |||
| LHX1 | Cortex | 24 h | 177Lu + A1M | Inhibited | AADAT, Kap, MEP1A, MEP1B, SLC22A24 |
| A1M | Inhibited | AADAT, Kap, MEP1A, MEP1B, SLC22A24 | |||
| mir-21 | Cortex | 24 h | A1M | Activated | GBP2, Iigp1, TAP1, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 |
| 7 d | 177Lu + A1M | Activated | AIF1, COL1A1, COL3A1, IGHM, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 | ||
| Medulla | 24 h | 177Lu | Activated | AIF1, BMPR2, GBP2, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 | |
| MRTFA | Cortex | 7 d | A1M | Inhibited | CMA1, LCN2, LTF, Ngp, S100A9 |
| Medulla | 7 d | A1M | Inhibited | CAMP, LCN2, Ngp, S100A9 | |
| MRTFB | Cortex | 7 d | 177Lu + A1M | Inhibited | CMA1, LCN2, LTF, Ngp, S100A9 |
| Medulla | 7 d | A1M | Inhibited | CAMP, LCN2, Ngp, S100A9 | |
| MYOCD | Bone marrow | 24 h | 177Lu + A1M | Activated | ACTA1, ACTN2, DES, MYH7, MYL2, TNNI1, TNNT2, TTN |
| 7 d | 177Lu | Inhibited | ACTN2, MYH7, MYL2, TNNI1, TNNT2 | ||
| MYOD1 | Bone marrow | 24 h | 177Lu + A1M | Activated | ACTA1, ANKRD2, ATP2A1, CKM, DES, MYLPF, TNNC2, TNNT2 |
| A1M | Inhibited | ANKRD2, MYH3, MYH4, MYLPF, TNNC2, TNNI2, TNNT2, TNNT3 | |||
| 7 d | 177Lu + A1M | Activated | ACTA1, ATP2A1, DES, DMD, ENO3, INPP5K, MYH3, MYH4, MYL1, MYLPF, TNNC2, TNNI2, TNNT2, TNNT3 | ||
| A1M | Activated | ACTA1, ATP2A1, DES, ENO3, MYH3, MYH4, MYL1, MYLPF, TNNC2, TNNI2, TNNT2, TNNT3 | |||
| NOS2 | Cortex | 7 d | 177Lu + A1M | Inhibited | BAX, FABP4, FASN, KRT13, MB, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 |
| Bone marrow | 24 h | 177Lu + A1M | Inhibited | ACTA1, COX6A2, COX7A1, MB, MYH7, MYL2, MYL3, TNNT2 | |
| 7d | A1M | Inhibited | ACTA1, ACTC1, CD3E, COX6A2, IGHG1, KRT13, MB, MYL2, TNNT2, TNNT3 | ||
| NRAS | Cortex | 24 h | A1M | Activated | GBP2, Iigp1, PSMB8, TAP1, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 |
| Medulla | 7 d | 177Lu | Inhibited | BAX, EPHX1, KCTD12, PHLDA3 | |
| RB1 | Bone marrow | 24 h | 177Lu + A1M | Activated | ACTN2, CKM, COL5A1, FXYD1, MECR, MYH7, MYH8, MYL6B, PGAM2, TNNC2, TNNT2, Tpm2, TRIM72 |
| 7 d | 177Lu + A1M | Activated | ACTC1, Actn3, BAK1, BCL2L11, Esrra, Krt10, KRT5, LOXL2, MFN2, MYH4, MYH8, MYL1, PGAM2, RYR1, TNNC2, TNNI2, TNNT2, Tpm1, Tpm2, TRIM72, TUBG1, ZNF638 | ||
| A1M | Activated | ACTC1, Actn3, BAK1, Krt10, LOXL2, MFN2, MYH4, MYH8, MYL1, PGAM2, RYR1, SAFB, TNNC2, TNNI2, TNNT2, Tpm1, Tpm2, TRIM72, ZNF638 | |||
| SIRT1 | Cortex | 24 h | 177Lu | Activated | BBC3, CORO1A, HLA-DQB1, IFIT1B, Iigp1, PSMB9, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 |
| 177Lu + A1M | Activated | BBC3, CORO1A, HLA-DQB1, HMGCR, IFIT1B, Iigp1, PSMB9, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 | |||
| A1M | Activated | HLA-DQB1, HMGCR, Iigp1, PSMB9, TAP1, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 | |||
| SMTNL1 | Bone marrow | 24 h | 177Lu + A1M | Inhibited | ACTA1, FLNC, MYOM1, TNNC2, Tpm2 |
| A1M | Activated | MYH4, TNNC2, TNNI2, TNNT3 | |||
| 7 d | 177Lu + A1M | Inhibited | ACTA1, FLNC, MYH4, MYL1, MYOM1, PYGM, TNNC2, TNNI2, TNNT3, Tpm1, Tpm2 | ||
| A1M | Inhibited | ACTA1, FLNC, MYH4, MYL1, MYOM1, PYGM, TNNC2, TNNI2, TNNT3, Tpm1, Tpm2 | |||
| SRF | Bone marrow | 24 h | 177Lu + A1M | Activated | ACTA1, CKM, DES, FHL1, LDB3, MYH1, MYH7, MYL3, MYOM1, Nebl, Tpm2, TTN |
| 7 d | 177Lu + A1M | Activated | ACTA1, ACTC1, BCL2L11, DES, DMD, LDB3, MYH1, MYH4, MYL1, MYOM1, Nebl, Tpm1, Tpm2, TTN, TUBB4B | ||
| A1M | Activated | ACTA1, ACTC1, AKAP12, DES, Igkv1-117, LDB3, MYH1, MYH4, MYL1, MYOM1, Nebl, Tpm1, Tpm2, TTN, TUBB4B | |||
| STAT1 | Cortex | 24 h | 177Lu | Inhibited | CEACAM1, GBP2, IFIT1B, Iigp1, PSMB10, PSMB8, PSMB9, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 |
| 177Lu + A1M | Inhibited | BAD, Cyp2d9 (includes others), GBP2, IFIT1B, Iigp1, PSMB10, PSMB8, PSMB9, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 | |||
| A1M | Inhibited | BAD, Cyp2d9 (includes others), GBP2, Iigp1, PSMB8, PSMB9, TAP1, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 | |||
| Medulla | 24 h | 177Lu | Inhibited | ALDH1A3, BAD, CAND2, GBP2, HLA-DQA1, PSMB9, SMAGP, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 | |
| TRIM24 | Cortex | 24 h | 177Lu | Activated | GBP2, IFIT1B, Iigp1, PSMB10, PSMB8, PSMB9, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 |
| 177Lu + A1M | Activated | GBP2, IFIT1B, Iigp1, PSMB10, PSMB8, PSMB9, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 | |||
| A1M | Activated | GBP2, Iigp1, PSMB8, PSMB9, TAP1, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 | |||
| Medulla | 24 h | 177Lu | Activated | GBP2, MGMT, PSMB9, Tgtp1/Tgtp2 |
| Kidney cortex | ||||||
| Time | Treatment | Category | Function | p-value | z-score | Target proteins in dataset |
| 7 d | 177Lu + A1M | Renal Inflammation, Renal Nephritis | Nephritis | 1.73E-02 | -1.88 | FABP1, HLA-DQB1, DCN, IGHM, BAX, SIRT1, Uox |
| Kidney medulla | ||||||
| Time | Treatment | Category | Function | p-value | z-score | Target proteins in dataset |
| 24 h | 177Lu | Glomerular Injury | Glomerulosclerosis | 3.45E-03 | -1.19* | Kap, CDKN1B, REN, HMOX1, STMN1 |
| 24 h | 177Lu | Renal Necrosis/Cell Death | Cell death | 3.17E-02 | -0.81 | MAVS, CDKN1B, SOD1, CYBB, BAD, STMN1 |
| 7 d | 177Lu + A1M | Renal Necrosis/Cell Death** | Cell viability | 8.66E-04 | 1.45 | CAV1, BAX, ABCC10, MAPT |
| 7 d | A1M | Renal Necrosis/Cell Death** | Cell death | 2.69E-02 | 0.14 | PTGDS, TGFB1I1, SOD1, CALB1, LCN2 |
| *No bias correction of the z-score was made**Not found when considering molecules and/or relationships in mouse only | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





