Submitted:
09 March 2024
Posted:
11 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
Results
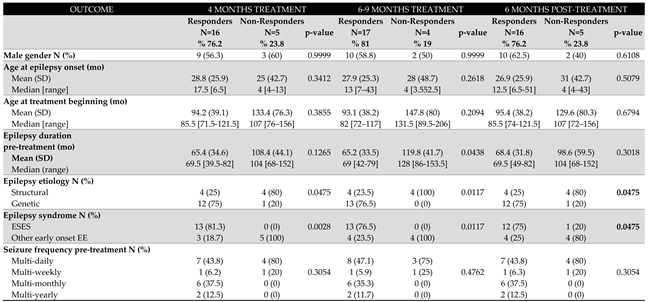
Patients
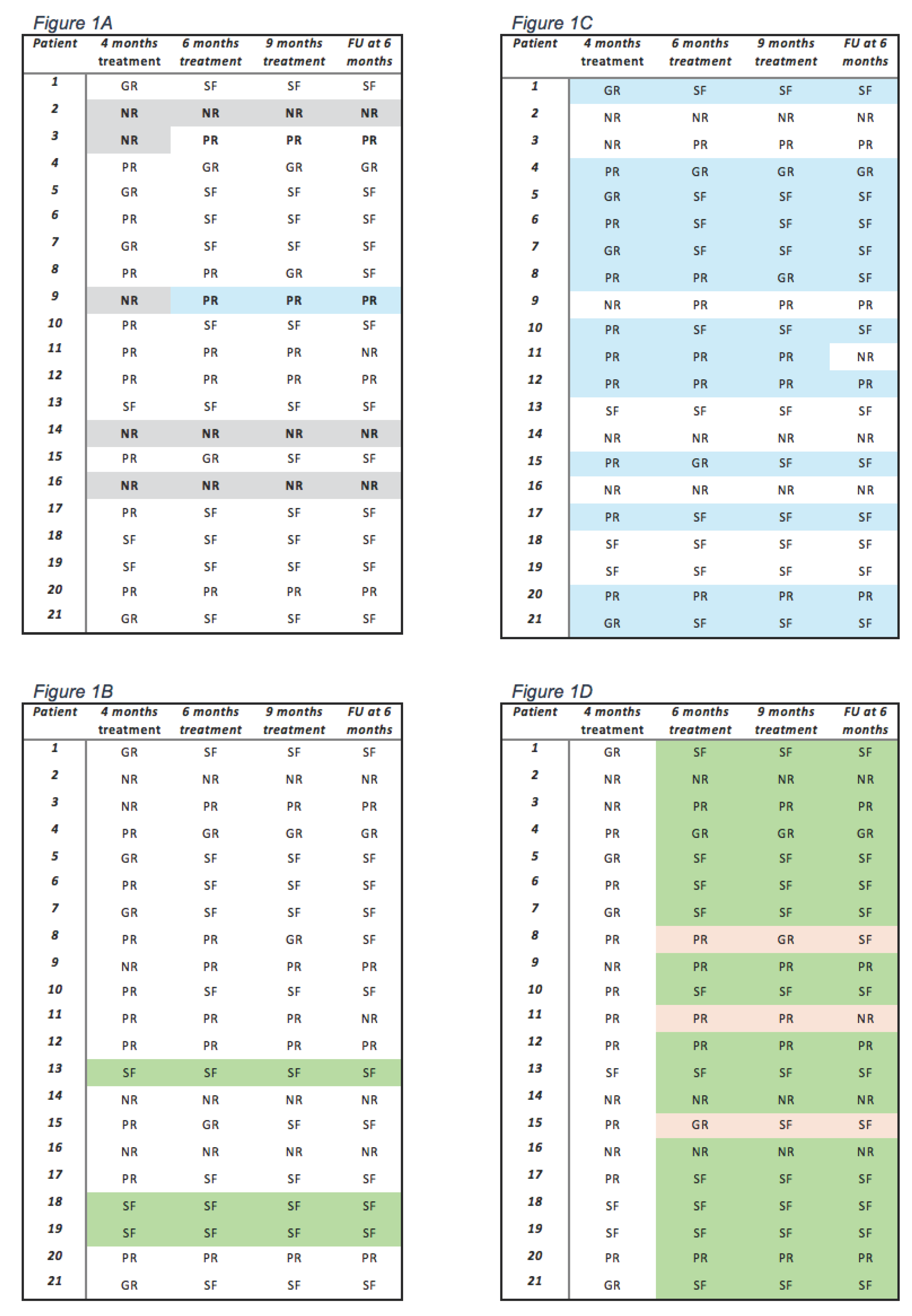
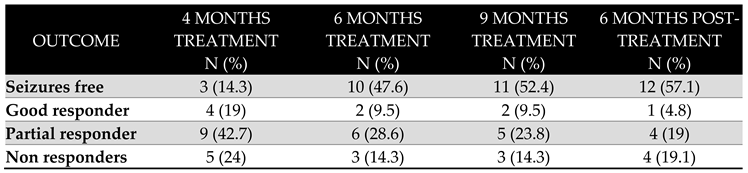
Seizure Outcome
QOL and Postural-Motor Outcome
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waaler, P.E.; Blom, B.H.; Skeidsvoll, H.; Mykletum, A. Prevalence, Classification, and Severity of Epilepsy in Children in Western Norway. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.T.; Berkovic, S.F.; Brodie, M.J.; Buchhalter, J.; Cross, J.H.; van Emde Boas, W.; Engel, J.; French, J.; Glauser, T.A.; Mathern, G.W.; et al. Revised terminology and concepts for organization of seizures and epilepsies: Report of the ILAE Commission on Classification and Terminology, 2005-2009. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A. , Gobbi G. A reflection on the role of genetics in the concept of "epileptic encephalopathy", as emerged from the most recent ILEA classification of epilepsy. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2020, 46, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z, Brodie MJ, Liew D, Kwan P. Treatment outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy treated with established and new antiepileptic drugs: a 30-year longitudinal cohort study. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 279–86.
- Parisi, P.; Spalice, A.; Nicita, F.; Papetti, L.; Ursitti, F.; Verrotti, A.; Iannetti, P.; Villa, M.P. “Epileptic Encephalopathy” of Infancy and Childhood: Electro-Clinical Pictures and Recent Understandings. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 8, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspall-Chaure, M.; Neville, B.G.; Scott, R.C. The medical management of the epilepsies in children: conceptual and practical considerations. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Hyslop, A.; Gentile, V.; Boni, A.; Miller, I.; Chiarello, D.; Pellino, G.; Zenesini, C.; Martinoni, M.; Lima, M.; et al. Early vagus nerve stimulator implantation as a main predictor of positive outcome in pediatric patients with epileptic encephalopathy. Epileptic Disord. 2021, 23, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Louw, E.; Van Den Hurk, D.; Neal, E.; Leiendecker, B.; Fitzsimmon, G.; Dority, L.; Thompson, L.; Marchió, M.; Dudzińska, M.; Dressler, A.; et al. Ketogenic diet guidelines for infants with refractory epilepsy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2016, 20, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Appleton, R. Corticosteroids in the management of the paediatric epilepsies. Arch. Dis. Child. 2005, 90, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhelst, H.; Boon, P.; Buyse, G.; Ceulemans, B.; D’hooghe, M.; De Meirleir, L.; Hasaerts, D.; Jansen, A.; Lagae, L.; Meurs, A.; et al. Steroids in intractable childhood epilepsy: Clinical experience and review of the literature. Seizure 2005, 14, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watemberg, N.; Zelnik, N.; Shahar, E.; Lerman-Sagie, T.; Goldberg-Stern, H.; Ben-Zeev, B.; Kramer, U. Efficacy of corticosteroid therapy in treating epileptic encephalopathies and refractory epilepsies other than West syndrome. J. Pediatr. Neurol. 2006, 04, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotagal, P. ; Md Current Status of Treatments for Children with Electrical Status in Slow-Wave Sleep (ESES/CSWS). Epilepsy Curr. 2017, 17, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munckhof, Bart van den, Alexis Arzimanoglou, Emilio Perucca, Heleen C. van Teeseling, Frans S. S. Leijten, Kees P. J. Braun, e Floor E. Jansen. «Corticosteroids versus Clobazam in 14. Epileptic Encephalopathy with ESES: A European Multicentre Randomised Controlled Clinical Trial (RESCUE ESES*)». Trials 2020, 21, 957.
- Prpić, I.; Blažeković, I.; Nišević, J.R.; Kolić, I. Corticosteroids in the management of pediatric epilepsies. Acta Clin. Croat. 2022, 60., 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.; Livingston, S. The effect of adrenocorticotropic hormone in epilepsy. J. Pediatr. 1950, 37, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorel, L.; Dusaucy-Bauloye, A. [Findings in 21 cases of Gibbs' hypsarrhythmia; spectacular effectiveness of ACTH]. . 1958, 58, 130–41. [Google Scholar]
- Okumura, A.; Tsuji, T.; Kato, T.; Natsume, J.; Negoro, T.; Watanabe, K. ACTH therapy for generalized seizures other than spasms. Seizure 2006, 15, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, D. Prednisone therapy in pediatric epilepsy. Pediatr. Neurol. 2003, 28, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanigasinghe, J.; Arambepola, C.; Ranganathan, S.S.; Sumanasena, S. Randomized, Single-Blind, Parallel Clinical Trial on Efficacy of Oral Prednisolone Versus Intramuscular Corticotropin: A 12-Month Assessment of Spasm Control in West Syndrome. Pediatr. Neurol. 2017, 76, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla-Castillo, R.A.; Palacios, G.C.; Ramirez-Campos, J.; Mora-Puga, M.; Diaz-Bustos, R. Methylprednisolone for the Treatment of Children with Refractory Epilepsy. Neuropediatrics 2009, 40, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mytinger, J. R, Quigg M. , Taft W.C., Buck ML, Rust R.S. Outcomes in treatment of infantile spasms with pulse methylprednisolone. J. Child Neurol. 2010, 25, 948–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ebinger, F.; Rating, D.; Wiemer-Kruel, A.; Schubert-Bast, S.; Bast, T.; Richter, S. Efficacy and Tolerability of Methylprednisolone Pulse Therapy in Childhood Epilepsies Other Than Infantile Spasms. Neuropediatrics 2014, 45, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaabdi, K.H.; Alshehri, R.O.; Althubiti, A.A.; Alsharef, Z.H.; Mulla, S.N.; Alshaer, D.S.; Alfaidi, N.S.; Jan, M.M. Intravenous Methylprednisolone for Intractable Childhood Epilepsy. Pediatr. Neurol. 2014, 50, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera MC, Randazzo G, Masnada S, Dontin SD, De Giorgis V, Balottin U, et al. Intravenous methylprednisolone pulse therapy for children with epileptic encephalopathy. Funct. Neurol. 2015, 30, 173–9.
- Yeh, H.-R.; Kim, M.-J.; Ko, T.-S.; Yum, M.-S.; You, S.-J. Short-Term Outcome of Intravenous Methylprednisolone Pulse Therapy in Patients With Infantile Spasms. Pediatr. Neurol. 2017, 71, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimizu, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Oboshi, T.; Horino, A.; Omatsu, H.; Koike, T.; Yoshitomi, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Otani, H.; Ikeda, H.; et al. Methylprednisolone pulse therapy in 31 patients with refractory epilepsy: A single-center retrospective analysis. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 109, 107116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Mundlamuri, R.C.; Kenchaiah, R.; Asranna, A.; Nagappa, M.; Bindu, P.; Seshagiri, D.; Viswanathan, L.G.; Shreedhar, A.; Duble, S.; et al. Role of pulse methylprednisolone in epileptic encephalopathy: A retrospective observational analysis. Epilepsy Res. 2021, 173, 106611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpurohit, M.; Gupta, A.; Madaan, P.; Sahu, J.K.; Singhi, P. Safety, Feasibility and Effectiveness of Pulse Methylprednisolone Therapy in Comparison with Intramuscular Adrenocorticotropic Hormone in Children with West Syndrome. Indian J. Pediatr. 2020, 88, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangarajan, A.; Mundlamuri, R.C.; Kenchaiah, R.; Prathyusha, P.V.; Viswanathan, L.G.; Asranna, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Nagappa, M.; Seshagiri, D.V.; Kulanthaivelu, K.; et al. Efficacy of pulse intravenous methylprednisolone in epileptic encephalopathy: a randomised controlled trial. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller AL, Chaptal C, McEwen BS, Peck Jr EJ. Modulation of high affinity GABA uptake into hippocampal synaptosomes by glucocorticoids. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1978, 3, 155–64.
- Jacobson, L.; Sapolsky, R. The Role of the Hippocampus in Feedback Regulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenocortical Axis*. Endocr. Rev. 1991, 12, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baram, TZ. Pathophysiology of massive infantile spasms: perspective on the putative role of the brain adrenal axis. Ann. Neurol. 1993, 33, 231–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, C.; Jordan, W.; Zieglga¨nsberger, W. Corticosterone reduces the excitability of hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. Brain Res. 1986, 383, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joëls, M. Steroid Hormones and Excitability in the Mammalian Brain. Front. Neuroendocr. 1997, 18, 2–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baram, T.Z.; Hatalski, C.G. Neuropeptide-mediated excitability: a key triggering mechanism for seizure generation in the developing brain. Trends Neurosci. 1998, 21, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watzka, M.; Bidlingmaier, F.; Beyenburg, S.; Henke, R.T.; Clusmann, H.; E Elger, C.; Schramm, J.; Klingmüller, D.; Stoffel-Wagner, B. Corticosteroid receptor mRNA expression in the brains of patients with epilepsy. Steroids 2000, 65, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joëls, M. Corticosteroid Actions in the Hippocampus. J. Neuroendocr. 2001, 13, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; Granata, T. Brain Inflammation in Epilepsy: Experimental and Clinical Evidence. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1724–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, N.; Granata, T.; Freri, E.; Ciusani, E.; Ragona, F.; Puvenna, V.; Teng, Q.; Alexopolous, A.; Janigro, D. Efficacy of Anti-Inflammatory Therapy in a Model of Acute Seizures and in a Population of Pediatric Drug Resistant Epileptics. PLOS ONE 2011, 6, e18200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.S. Role of Anticonvulsant and Antiepileptogenic Neurosteroids in the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Epilepsy. Front. Endocrinol. 2011, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Miller, S.D.; Koh, S. Immune mechanisms in epileptogenesis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frauman, A.G. An overview of the adverse reactions to adrenal corticosteroids. . 1996, 15, 203–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wanigasinghe, J.; Arambepola, C.; Ranganathan, S.S.; Jayasundara, K.; Weerasinghe, A.; Wickramarachchi, P. Epilepsy Outcome at Four Years in a Randomized Clinical Trial Comparing Oral Prednisolone and Intramuscular ACTH in West Syndrome. Pediatr. Neurol. 2021, 119, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Callaghan, F.J.K.; Edwards, S.W.; Alber, F.D.; Hancock, E.; Johnson, A.L.; Kennedy, C.R.; Likeman, M.; Lux, A.L.; Mackay, M.; A Mallick, A.; et al. Safety and effectiveness of hormonal treatment versus hormonal treatment with vigabatrin for infantile spasms (ICISS): a randomised, multicentre, open-label trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 16, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, V.K.; Narayanaswamy, V.; Shivappa, S.K.; Benakappa, N.; Benakappa, A. Corticotrophin-ACTH in Comparison to Prednisolone in West Syndrome – A Randomized Study. Indian J. Pediatr. 2018, 86, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, A.L.; Edwards, S.W.; Hancock, E.; Johnson, A.L.; Kennedy, C.R.; Newton, R.W.; O'Callaghan, F.J.; Verity, C.M.; Osborne, J.P. The United Kingdom Infantile Spasms Study comparing vigabatrin with prednisolone or tetracosactide at 14 days: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004, 364, 1773–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan FJK, Edwards SW, Alber FD, Cortina Borja M, Hancock E, Johnson AL, et al. Vigabatrin with hormonal treatment versus hormonal treatment alone (ICISS) for infantile spasms: 18-month outcomes of an open- label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2018, 2, 715–25.
- Darke, K.; Edwards, S.W.; Hancock, E.; Johnson, A.L.; Kennedy, C.R.; Lux, A.L.; Newton, R.W.; O'Callaghan, F.J.K.; Verity, C.M.; Osborne, J.P.; et al. Developmental and epilepsy outcomes at age 4 years in the UKISS trial comparing hormonal treatments to vigabatrin for infantile spasms: a multi-centre randomised trial. Arch. Dis. Child. 2010, 95, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzatu, M.; Bulteau, C.; Altuzarra, C.; Dulac, O.; Van Bogaert, P. Corticosteroids as treatment of epileptic syndromes with continuous spike-waves during slow-wave sleep. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, D.B.; Snyder, T.J. Corticosteroids for the Treatment of Landau-Kleffner Syndrome and Continuous Spike-Wave Discharge During Sleep. Pediatr. Neurol. 2005, 32, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Cai, F.; Jiang, L.; Hu, Y.; Feng, C. A prospective study of dexamethasone therapy in refractory epileptic encephalopathy with continuous spike-and-wave during sleep. Epilepsy Behav. 2016, 55, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatema, K.; Rahman, M.M.; Begum, S. Characteristics and Management of Children with Continuous Spikes and Waves during Slow Sleep. . 2015, 24, 806–12. [Google Scholar]
- Munckhof, B.v.D.; van Dee, V.; Sagi, L.; Caraballo, R.H.; Veggiotti, P.; Liukkonen, E.; Loddenkemper, T.; Fernández, I.S.; Buzatu, M.; Bulteau, C.; et al. Treatment of electrical status epilepticus in sleep: A pooled analysis of 575 cases. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1738–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamatogi, Y.; Ohtsuka, Y.; Ishida, T.; Ichiba, N.; Ishida, S.; Miyake, S.; Oka, E.; Ohtahara, S. Treatment of the lennox syndrome with ACTH: A clinical and electroencephalographic study. Brain Dev. 1979, 1, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gofshteyn, J.S.; Gurcharran, K.; Marquis, B.O.; Lamothe, J.; Gourley, D.; Grinspan, Z.; Nangia, S. Measurable outcomes for pediatric epileptic encephalopathy: a single-center experience with corticosteroid therapy. Epileptic Disord. 2021, 23, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Mundlamuri, R.C.; Kenchaiah, R.; Asranna, A.; Nagappa, M.; Bindu, P.; Seshagiri, D.; Viswanathan, L.G.; Shreedhar, A.; Duble, S.; et al. Role of pulse methylprednisolone in epileptic encephalopathy: A retrospective observational analysis. Epilepsy Res. 2021, 173, 106611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charuvanij, A.; A Ouvrier, R.; Procopis, P.G.; Antony, J.H.; Fagan, E.R. ACTH treatment in intractable seizures of childhood. Brain Dev. 1992, 14, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, J.; Sarajan, A.; Salari, M.; Sedghi, M. Therapeutic Effects of Adrenocorticotropic Hormone ACTH in Children with Severely Intractable Seizure. . 2017, 11, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bakker, D.P.; Catsman-Berrevoets, C.E.; Neuteboom, R.F. Effectiveness of a hybrid corticosteroid treatment regimen on refractory childhood seizures and a review of other corticosteroid treatments. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2015, 19, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, V.; Sharma, S.; Arya, R. ACTH therapy in refractory generalized epilepsy. Indian J. Pediatr. 2009, 76, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inui, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Sato, R.; Endo, W.; Kikuchi, A.; Nakayama, T.; Uematsu, M.; Takayanagi, M.; Kato, M.; et al. Efficacy of long term weekly ACTH therapy for intractable epilepsy. Brain Dev. 2015, 37, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossler, D.G.; Bainbridge, J.L.; Boggs, J.G.; Novotny, E.J.; Loddenkemper, T.; Faught, E.; Amengual-Gual, M.; Fischer, S.N.; Gloss, D.S.; Olson, D.M.; et al. Treatment of Refractory Convulsive Status Epilepticus: A Comprehensive Review by the American Epilepsy Society Treatments Committee. Epilepsy Curr. 2020, 20, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch LJ, Gaspard N, van Baalen A, Nabbout R, Demeret S, Loddenkemper T, et al. Proposed consensus definitions for new-onset refractory status epilepticus (NORSE), febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome (FIRES), and related conditions. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 739–44.
- Vezzani A, Ruegg S. The pivotal role of immunity and inflammatory processes in epilepsy is increasingly recognized: introduction. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 1–4.
- Shorvon, S.; Ferlisi, M. The treatment of super-refractory status epilepticus: a critical review of available therapies and a clinical treatment protocol. Brain 2011, 134, 2802–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A.; Balosso, S.; Aronica, E.; Ravizza, T. Basic mechanisms of status epilepticus due to infection and inflammation. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 56–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A. Epilepsy and Inflammation in the Brain: Overview and Pathophysiology. Epilepsy Curr. 2014, 14, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neugebauer, R.; Paik, M.; Hauser, W.A.; Nadel, E.; Leppik, I.; Susser, M. Stressful Life Events and with Seizure Frequency in Patients Epilepsy. Epilepsia 1994, 35, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, H.R.; Privitera, M.D. Stress as a seizure precipitant: Identification, associated factors, and treatment options. Seizure 2017, 44, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privitera, M.; Walters, M.; Lee, I.; Polak, E.; Fleck, A.; Schwieterman, D.; Haut, S.R. Characteristics of people with self-reported stress-precipitated seizures. Epilepsy Behav. 2014, 41, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, N.T.; Escayg, A. Stress and Epilepsy: Multiple Models, Multiple Outcomes. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 27, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, T.; Maguire, J.; Salpekar, J.A. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis targets for the treatment of epilepsy. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 746, 135618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie G, Maguire J. Chronic stress compromises GABAergic inhibition in the hippocampus and increases seizure susceptibility. Epilepsy Res. 2015, 109, 13–27.
- Castro, O.W.; Santos, V.R.; Pun, R.Y.K.; McKlveen, J.M.; Batie, M.; Holland, K.D.; Gardner, M.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Herman, J.P.; Danzer, S.C. Impact of Corticosterone Treatment on Spontaneous Seizure Frequency and Epileptiform Activity in Mice with Chronic Epilepsy. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e46044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culebras, A.; Miller, M.; Bertram, L.; Koch, J. Differential Response of Growth Hormone, Cortisol, and Prolactin to Seizures and to Stress. Epilepsia 1987, 28, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, R.J.; Browning, M.C.; Davidson, D.L. Serum prolactin and cortisol concentrations after grand mal seizures. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1980, 43, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, P.B.; Wannamaker, B.B.; Sagel, J.; Daniel, C.M. Serum prolactin and cortisol levels in evaluation of pseudoepileptic seizures. Ann. Neurol. 1985, 18, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulsin, A.C.; Solomon, M.B.; Privitera, M.D.; Danzer, S.C.; Herman, J.P. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis dysfunction in epilepsy. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 166, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao TC, Huang YW, Chang SM, Tsai SY, Wu AC, Tsai HJ. Association between oral corticosteroid bursts and severe adverse events: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2020, 173, 325–30.
- Stuart FA, Segal TY, Keady S. Adverse psychological effects of corticosteroids in children and adolescents. Arch. Dis. Child. 2005, 90, 500–6.
- Yasir M, Goyal A, Sonthalia S. Corticosteroid Adverse Effects. Tampa, FL: StatPearls. 2022.
- Rice, J.B.; White, A.G.; Scarpati, L.M.; Wan, G.; Nelson, W.W. Long-term Systemic Corticosteroid Exposure: A Systematic Literature Review. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, 2216–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljebab, F.; Choonara, I.; Conroy, S. Systematic review of the toxicity of short-course oral corticosteroids in children. Arch. Dis. Child. 2016, 101, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, D.S.; Bullmore, E. Small-World Brain Networks Revisited. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Meunier, D.; Lambiotte, R.; Bullmore, E.T. Modular and Hierarchically Modular Organization of Brain Networks. Front. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, C.J.; Reijneveld, J.C. Graph theoretical analysis of complex networks in the brain. Nonlinear Biomed. Phys. 2007, 1, 3–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, B.; Puskás, S.; Bessenyei, M.; Emri, M.; Spisák, T.; Koselák, M.; Hollódy, K.; Fogarasi, A.; Kondákor, I.; Füle, K.; et al. EEG functional connectivity of the intrahemispheric cortico-cortical network of idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2011, 96, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittau, F.; Grova, C.; Moeller, F.; Dubeau, F.; Gotman, J. Patterns of altered functional connectivity in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otte WM, Dijkhuizen RM, van Meer MPA, van der Hel WS, Verlinde SAMW, van Nieuwenhuizen O, et al. Characterization of functional and structural integrity in experimental focal epilepsy: reduced network efficiency coincides with white matter changes. PLoS One 2012, 7, 39078 .
- Vollmar C, O’Muircheartaigh, Symms MR, G. J. Barker GJ, P. Thompson P, V. Kumari V, et al. Altered microstructural connectivity in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy: the missing link. Neurology 2012, 78, 1555–9.
- Chavez, M.; Valencia, M.; Navarro, V.; Latora, V.; Martinerie, J. Functional Modularity of Background Activities in Normal and Epileptic Brain Networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 118701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douw, L.; van Dellen, E.; de Groot, M.; Heimans, J.J.; Klein, M.; Stam, C.J.; Reijneveld, J.C. Epilepsy is related to theta band brain connectivity and network topology in brain tumor patients. BMC Neurosci. 2010, 11, 103–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponten, S.; Bartolomei, F.; Stam, C. Small-world networks and epilepsy: Graph theoretical analysis of intracerebrally recorded mesial temporal lobe seizures. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry JR, Benjamin O, Richardson MP. Seizure generation: the role of nodes and networks. Epilepsia 2012, 53, e166–9 .
- Bartolomei F, Bettus G, Stam CJ, Guye M. Interictal network proper- ties in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: a graph theoretical study from intracerebral recordings. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 124, 2345–53.
- Bernhardt, B.C.; Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Evans, A.C.; Bernasconi, N. Graph-Theoretical Analysis Reveals Disrupted Small-World Organization of Cortical Thickness Correlation Networks in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horstmann, M.-T.; Bialonski, S.; Noennig, N.; Mai, H.; Prusseit, J.; Wellmer, J.; Hinrichs, H.; Lehnertz, K. State dependent properties of epileptic brain networks: Comparative graph–theoretical analyses of simultaneously recorded EEG and MEG. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J., Jr.; Thompson, P.M.; Stern, J.M.; Staba, R.J.; Bragin, A.; Mody, I. Connectomics and epilepsy. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.A.; Kolaczyk, E.D.; Kirsch, H.E. Emergent network topology at seizure onset in humans. Epilepsy Res. 2008, 79, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Diessen E, Diederen SJH, Braun KPJ, Jansen FE, Stam CJ. Functional and structural brain networks in epilepsy: what have we learned? Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1855–65.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





