Submitted:
07 March 2024
Posted:
08 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
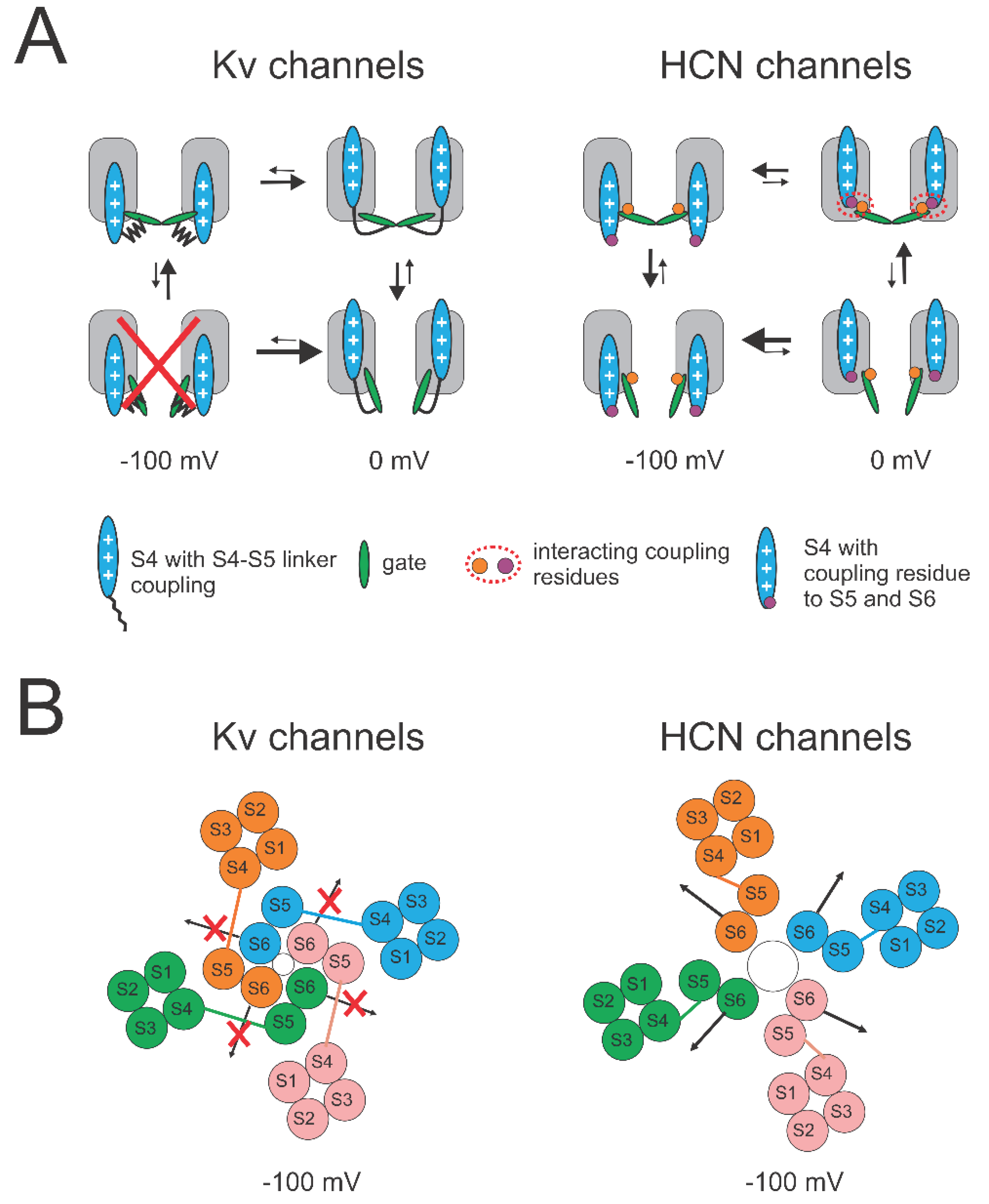
2. Results
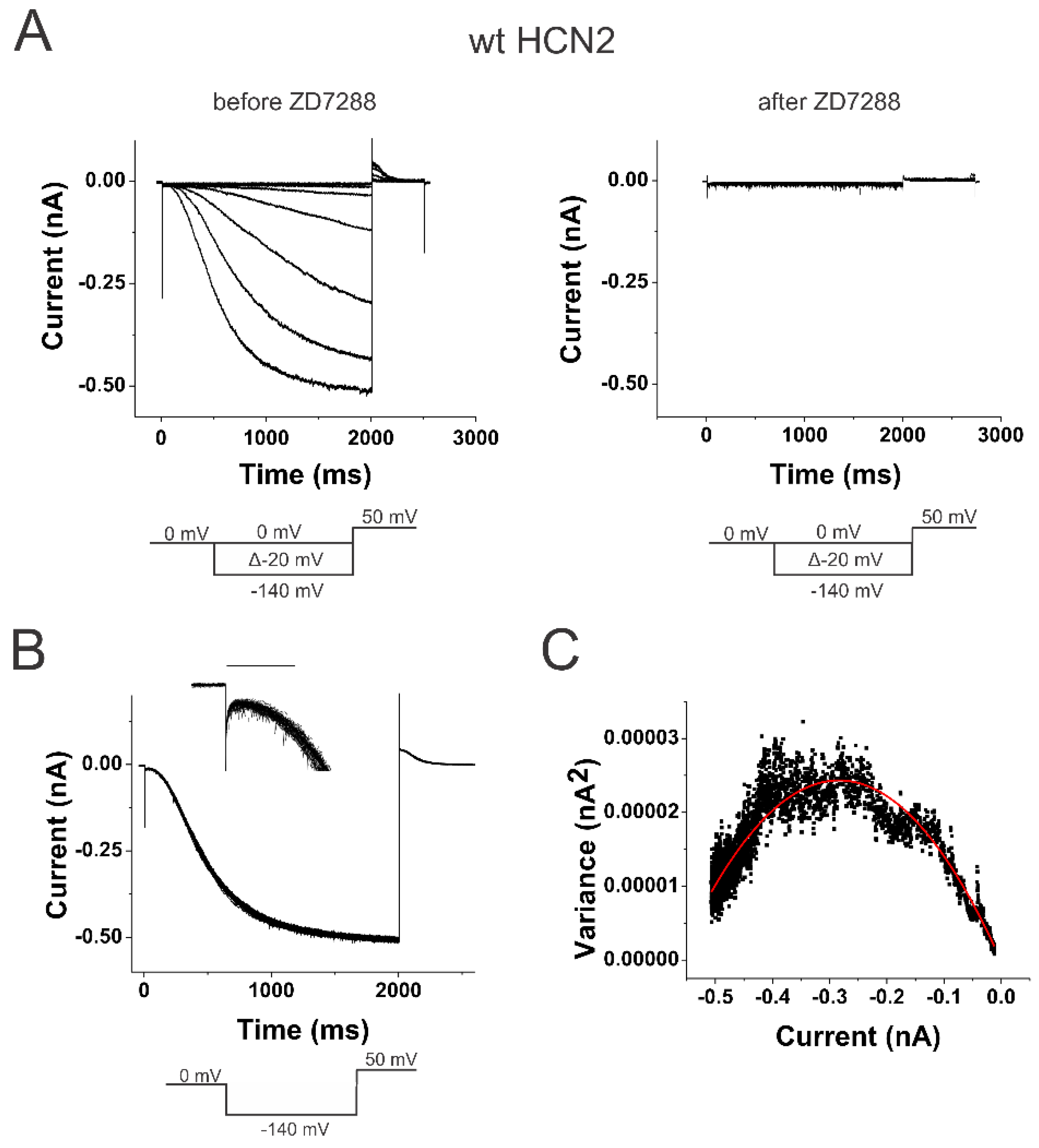
2.1. Weak Coupling in HCN Channels
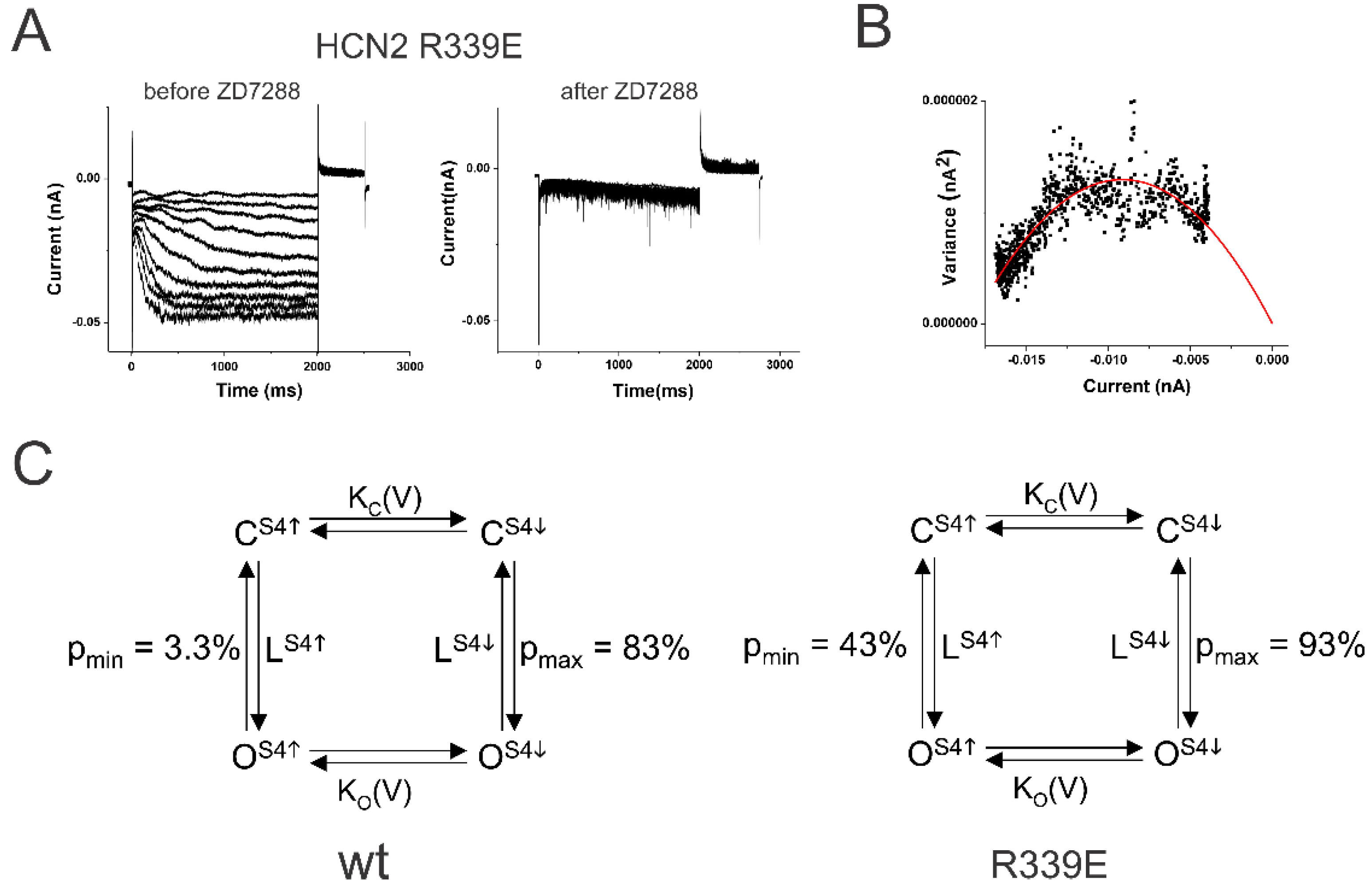
2.2. S4-S5 Mutation Further Weakens the Coupling
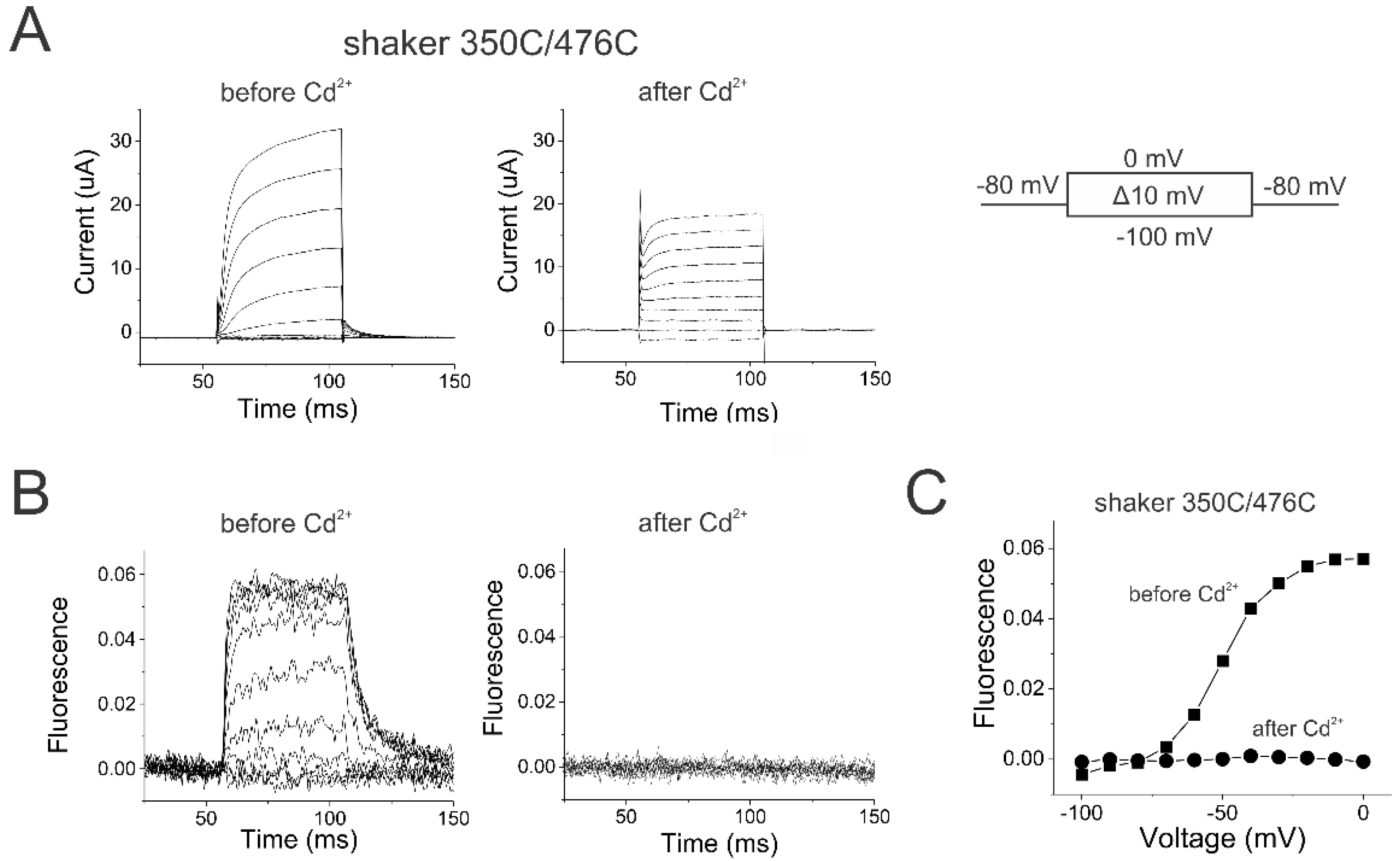
2.3. Reciprocal Effects of Gate and Voltage Sensor in Strongly-Coupled Ion Channels
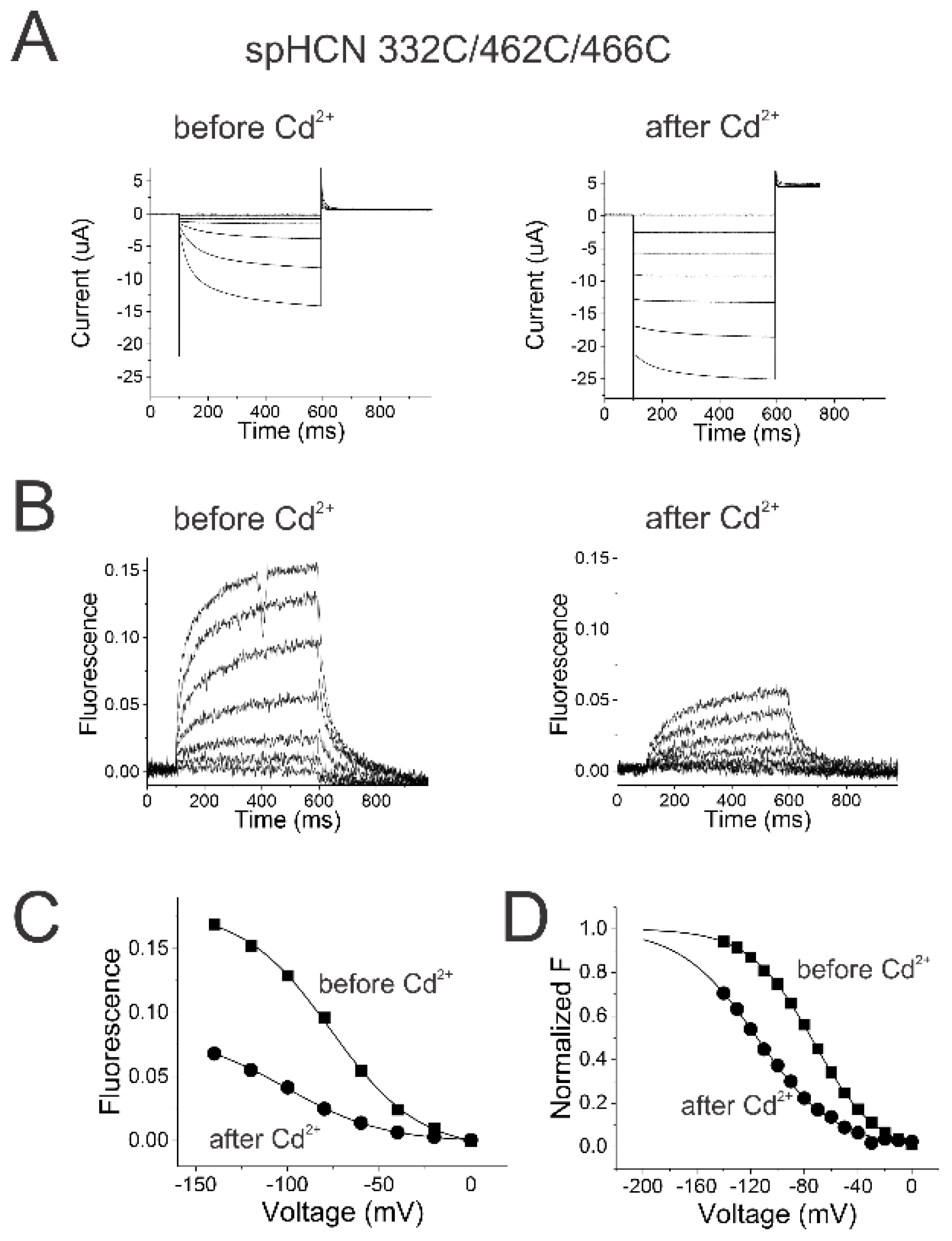
2.4. Reciprocal Effects of Gate and Voltage Sensor in Weakly-Coupled Ion Channels
2.5. Coupling Mutation Affects Both Open Probability and S4 Movement
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Expression System
4.2. Two-Electrode Voltage Clamp
4.3. Voltage Clamp Fluorometry
4.4. Noise Analysis
4.5. Coupling Constants
4.6. Molecular Modeling
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, H.F.; Difrancesco, D.; Noble, S.J. How does adrenaline accelerate the heart? Nature 1979, 280, 235–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldar, M.; Griffin, J.C.; Abbott, J.A.; Benditt, D.; Bhandari, A.; Herre, J.M.; Benson, D.W.; Scheinman, M.M. Permanent cardiac pacing in patients with the long QT syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 1987, 10, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biel, M.; Wahl-Schott, C.; Michalakis, S.; Zong, X. Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Channels: From Genes to Function. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 847–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivolta, I.; Binda, A.; Masi, A.; DiFrancesco, J.C. Cardiac and neuronal HCN channelopathies. Pflugers Arch 2020, 472, 931–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauss, R.; Seifert, R.; Kaupp, U.B. Molecular identification of a hyperpolarization-activated channel in sea urchin sperm. Nature 1998, 393, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, A.; Zong, X.; Jeglitsch, M.; Hofmann, F.; Biel, M. A family of hyperpolarization-activated mammalian cation channels. Nature 1998, 393, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, B.; Liu, D.T.; Yao, H.; Bartsch, D.; Kandel, E.R.; A Siegelbaum, S.; Tibbs, G.R. Identification of a Gene Encoding a Hyperpolarization-Activated Pacemaker Channel of Brain. Cell 1998, 93, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; MacKinnon, R. Structures of the Human HCN1 Hyperpolarization-Activated Channel. Cell 2017, 168, 111–120 e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.-F.; Bae, C.; Stix, R.; Fernández-Mariño, A.I.; Huffer, K.; Chang, T.-H.; Jiang, J.; Faraldo-Gómez, J.D.; Swartz, K.J. Structure of the Shaker Kv channel and mechanism of slow C-type inactivation. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whicher, J.R.; MacKinnon, R. Structure of the voltage-gated K + channel Eag1 reveals an alternative voltage sensing mechanism. Science 2016, 353, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, H.; Baker, O.S.; Dhillon, D.S.; Isacoff, E.Y. Transmembrane Movement of the Shaker K+ Channel S4. Neuron 1996, 16, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Männikkö, R.; Elinder, F.; Larsson, H.P. Voltage-sensing mechanism is conserved among ion channels gated by opposite voltages. Nature 2002, 419, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Ruta, V.; Chen, J.; Lee, A.; MacKinnon, R. The principle of gating charge movement in a voltage-dependent K+ channel. Nature 2003, 423, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.B.; Campbell, E.B.; MacKinnon, R. Voltage Sensor of Kv1.2: Structural Basis of Electromechanical Coupling. Science 2005, 309, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Klem, A.M.; Ramu, Y. Coupling between Voltage Sensors and Activation Gate in Voltage-gated K+ Channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2002, 120, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, G.; Aman, T.K.; DiMaio, F.; Zagotta, W.N. The HCN channel voltage sensor undergoes a large downward motion during hyperpolarization. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-H.; MacKinnon, R. Voltage Sensor Movements during Hyperpolarization in the HCN Channel. Cell 2019, 179, 1582–1589 e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Ramentol, R.; Perez, M.E.; Noskov, S.Y.; Larsson, H.P. A second S4 movement opens hyperpolarization-activated HCN channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.B.; Campbell, E.B.; Mackinnon, R. Crystal Structure of a Mammalian Voltage-Dependent Shaker Family K+ Channel. Science 2005, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Klem, A.M.; Ramu, Y. Ion conduction pore is conserved among potassium channels. Nature 2001, 413, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tristani-Firouzi, M.; Chen, J.; Sanguinetti, M.C. Interactions between S4-S5 Linker and S6 Transmembrane Domain Modulate Gating of HERG K+ Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 18994–19000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, G.E.; Zagotta, W.N. Insights into the molecular mechanism for hyperpolarization-dependent activation of HCN channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2018, 115, E8086–E8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; MacKinnon, R. Cryo-EM Structure of the Open Human Ether-à-go-go -Related K + Channel hERG. Cell 2017, 169, 422–430 e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whicher, J.R.; MacKinnon, R. Structure of the voltage-gated K + channel Eag1 reveals an alternative voltage sensing mechanism. Science 2016, 353, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islas, L.D.; Sigworth, F.J. Voltage Sensitivity and Gating Charge in Shaker and Shab Family Potassium Channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 1999, 114, 723–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezanilla, F.; Perozo, E.; Stefani, E. Gating of Shaker K+ channels: II. The components of gating currents and a model of channel activation. Biophys. J. 1994, 66, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezanilla, F.; White, M.M.; Taylor, R.E. Gating currents associated with potassium channel activation. Nature 1982, 296, 657–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Yellen, G. Charge movement in gating-locked HCN channels reveals weak coupling of voltage sensors and gate. J. Gen. Physiol. 2012, 140, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Mitcheson, J.S.; Tristani-Firouzi, M.; Lin, M.; Sanguinetti, M.C. The S4–S5 linker couples voltage sensing and activation of pacemaker channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2001, 98, 11277–11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruening-Wright, A.; Elinder, F.; Larsson, H.P. Kinetic Relationship between the Voltage Sensor and the Activation Gate in spHCN Channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2007, 130, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, C.S.; Loots, E.; Isacoff, E.Y. Reconstructing Voltage Sensor–Pore Interaction from a Fluorescence Scan of a Voltage-Gated K+ Channel. Neuron 2000, 27, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannuzzu, L.M.; Isacoff, E.Y. Independence and Cooperativity in Rearrangements of a Potassium Channel Voltage Sensor Revealed by Single Subunit Fluorescence. J. Gen. Physiol. 2000, 115, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, M.; Shin, K.S.; Yellen, G. The Activation Gate of a Voltage-Gated K+ Channel Can Be Trapped in the Open State by an Intersubunit Metal Bridge. Neuron 1998, 21, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, C.S.; Loots, E.; Isacoff, E.Y. Reconstructing Voltage Sensor–Pore Interaction from a Fluorescence Scan of a Voltage-Gated K+ Channel. Neuron 2000, 27, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothberg, B.S.; Shin, K.S.; Yellen, G. Movements near the Gate of a Hyperpolarization-activated Cation Channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 2003, 122, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saponaro, A.; Bauer, D.; Giese, M.H.; Swuec, P.; Porro, A.; Gasparri, F.; Sharifzadeh, A.S.; Chaves-Sanjuan, A.; Alberio, L.; Parisi, G. Gating movements and ion permeation in HCN4 pacemaker channels. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 2929–2943 e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomare, C.; Bucchi, A.; Camatini, E.; Baruscotti, M.; Viscomi, C.; Moroni, A.; DiFrancesco, D. Integrated Allosteric Model of Voltage Gating of Hcn Channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2001, 117, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, H.P. The Search Is on for the Voltage Sensor-to-gate Coupling. J. Gen. Physiol. 2002, 120, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, R.B.; Siegelbaum, S.A. Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Currents: From Molecules to Physiological Function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2003, 65, 453–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, T.; E Gordon, S. Quickening the Pace: Looking into the Heart of HCN Channels. Neuron 2004, 42, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Holmgren, M.; Jurman, M.E.; Yellen, G. Gated Access to the Pore of a Voltage-Dependent K+ Channel. Neuron 1997, 19, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothberg, B.S.; Shin, K.S.; Phale, P.S.; Yellen, G. Voltage-Controlled Gating at the Intracellular Entrance to a Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 2002, 119, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.S.; Rothberg, B.S.; Yellen, G. Blocker State Dependence and Trapping in Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2001, 117, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombola, F.; Pathak, M.M.; Isacoff, E.Y. How does voltage open an ion channel? Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2006, 22, 23–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decher, N.; Chen, J.; Sanguinetti, M.C. Voltage-dependent gating of hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated pacemaker channels: molecular coupling between the S4-S5 and C-linkers. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 13859–13865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramentol, R.; Perez, M.E.; Larsson, H.P. Gating mechanism of hyperpolarization-activated HCN pacemaker channels. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Cunningham, K.P.; Ramentol, R.; Perez, M.E.; Larsson, H.P. Similar voltage-sensor movement in spHCN channels can cause closing, opening, or inactivation. J. Gen. Physiol. 2023, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; George, M.S.; Siegelbaum, S.A. Voltage Sensor Movement and cAMP Binding Allosterically Regulate an Inherently Voltage-independent Closed−Open Transition in HCN Channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2007, 129, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Männikkö, R.; Pandey, S.; Larsson, H.P.; Elinder, F. Hysteresis in the voltage dependence of HCN channels: conversion between two modes affects pacemaker properties. J. Gen. Physiol. 2005, 125, 305–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiFrancesco, D. Characterization of the pace-maker current kinetics in calf Purkinje fibres. J. Physiol. 1984, 348, 341–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiFrancesco, D.; Ferroni, A. Delayed activation of the cardiac pacemaker current and its dependence on conditioning pre-hyperpolarizations. Pfl?gers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 1983, 396, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowgill, J.; Klenchin, V.A.; Alvarez-Baron, C.; Tewari, D.; Blair, A.; Chanda, B. Bipolar switching by HCN voltage sensor underlies hyperpolarization activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2018, 116, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruening-Wright, A.; Larsson, H.P. Slow Conformational Changes of the Voltage Sensor during the Mode Shift in Hyperpolarization-Activated Cyclic-Nucleotide-Gated Channels. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, A.; Bezanilla, F. Characterizing voltage-dependent conformational changes in the Shaker K+ channel with fluorescence. Neuron, 1997, 19, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannuzzu, L.M.; Moronne, M.M.; Isacoff, E.Y. Direct Physical Measure of Conformational Rearrangement Underlying Potassium Channel Gating. Science 1996, 271, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, O.; Gonzalez, C.; Latorre, R. Counting Channels: A Tutorial Guide on Ion Channel Fluctuation Analysis. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2002, 26, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, F.; Neumcke, B.; Nonner, W.; Stämpfli, R. Conductance fluctuations from the inactivation process of sodium channels in myelinated nerve fibres. J. Physiol. 1980, 308, 217–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, S.H.; Conti, F. Nonstationary noise analysis and application to patch clamp recordings. Methods Enzymol, 1992, 207, 131–148. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




