1. Introduction
Oral cancer is defined as a cancer occurring in the oral cavity including the buccal mucosa, maxillary and mandibular gingiva, hard palate, tongue, mouth floor and lips by the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Approximately 370,000 people per year worldwide are treated with oral cancer and more than 17,000 of these patients die of oral cancer [
1,
2,
3]. The oral mucosa is covered by stratified squamous epithelia and is divided into keratinized epithelium and non-keratinized epithelium [
5]. More than 90% of oral cancer are histopathologically diagnosed as squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) [
6], but malignant diseases in the oral area include oral SCC (OSCC), salivary gland cancer, malignant melanoma, malignant lymphoma, sarcoma and metastatic cancer [
7].
Surgery is the first choice for patients with resectable OSCC [
7]. Postoperative radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy is recommended for patients with adverse features found in a histological examination after surgery [
7]. We routinely conduct postoperative treatment based on the evaluation of the risk of recurrence and metastasis of the tumor, and biological malignancy of cancer cells in patients with complete surgical resection [
8,
9]. We also perform appropriate surveillance after initial treatment, resulting in markedly higher survival rates in patients with OSCC [
10]. However, some patients cannot undergo surgery due to locoregional tumor progression, distant metastasis, and tolerance of the patients for surgery. Moreover, locoregional recurrence and distant metastasis in patients who received the initial treatment may have difficulty with salvage treatment. These patients are to be treated by chemoradiation, while such patients with a history of radiotherapy and chemotherapy are to receive anti-programmed death 1 (PD-1) antibodies, nivolumab and pembrolizumab according to the latest guidelines [
7].
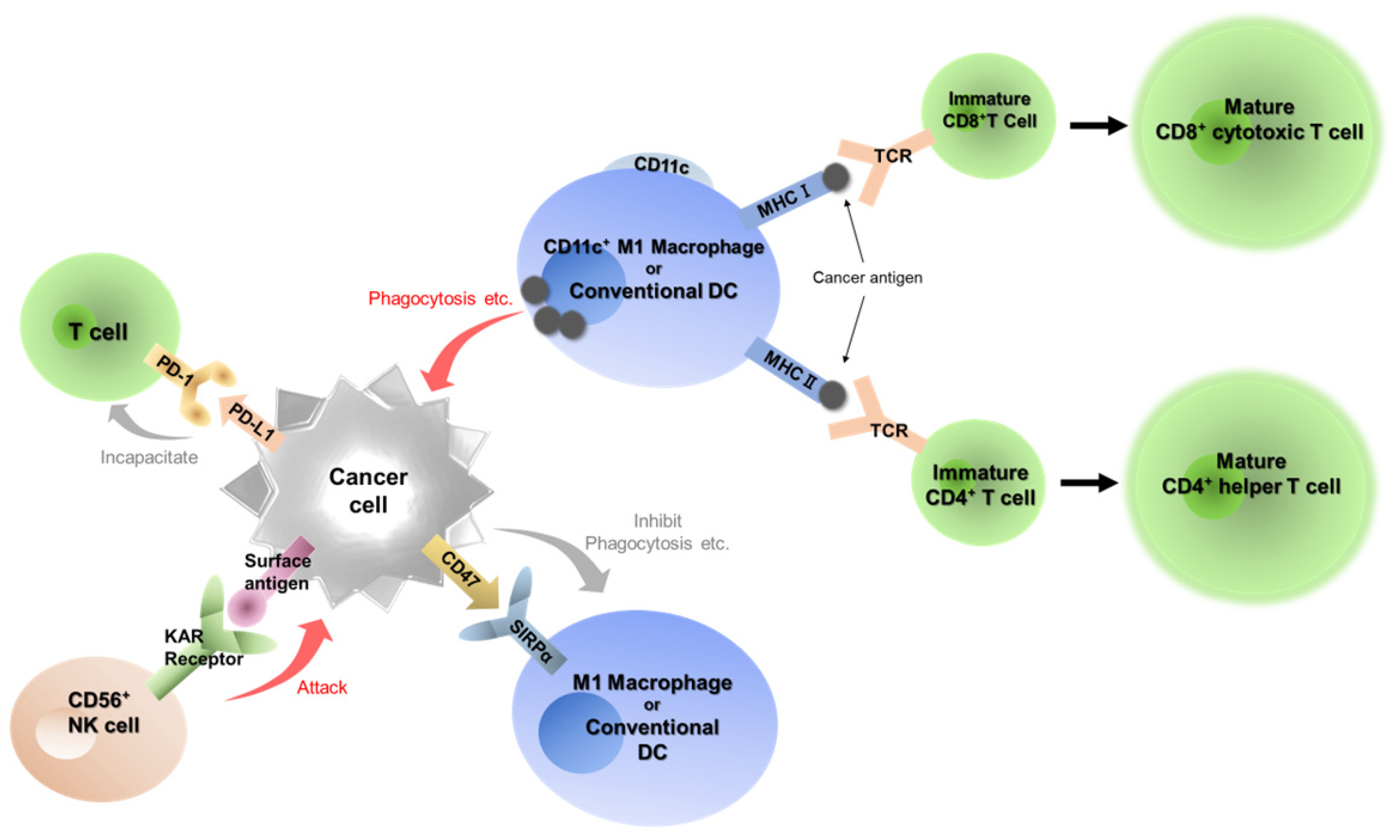
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), including anti-PD-1 antibodies, are significantly changing treatment strategies for human malignant diseases including oral cancer [
11,
12]. Cancer cells usually escape from immune system and acquire proliferative capacity and invasive/metastatic potential (
Figure 1). In the cancer immunoediting system, the PD-1/programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) plays a central role [
13]. PD-1 is the major receptor in immune cells as an activated checkpoint in the immune system and is expressed in T cells, B cells and natural killer cells activated in the tumor microenvironment [
14,
15,
16]. PD-L1 is a PD-1 ligand that induces phosphorylation of two motifs in PD-1. This interaction inhibits proliferation and response of T cells, then PD-L1 and PD-1 signaling is called the “Do not kill me signal” [
16]. At present, seven ICIs involved in the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway are approved in clinical use [
17], including the anti-PD-1 antibodies, nivolumab [
11,
18] and pembrolizumab [
12] which can be used for head and neck cancer in Japan. These antibody drugs have markedly changed the therapeutic strategy for unresectable head and neck cancer, and the expression level of PD-L1 in tumor cells and surrounding cells has been linked to the therapeutic effect of pembrolizumab [
12].
CD47/signal-regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) has been a recent focus as an immune checkpoint in macrophage/dendritic cells (DCs) [
19,
20,
21]. SIRPα is an immunosuppressive receptor expressed in myeloid cells, including macrophages, DCs and neutrophils [
20]. SIRPα is frequently overexpressed in cancer cells and binds to CD47 which is known to express on all normal cells [
20,
21]. Binding of CD47 and SIRPα causes SIRPα to activate multiple phosphatases, which results in inhibition of the functions of SIRPα-expressing cells [
20,
21]. This signaling between CD47 and SIRPα is called as “Do not eat me signal”. An anti-CD47 antibody is now trying to use against hematopoietic malignancies [
22,
23,
24].
We have focused on the two immune checkpoints, PD-1/PD-L1, the “Do not kill me signal”, and CD47/SIRPα, the “Do not eat me signal”, to examine the kinetics of tumor immunity in the tumor microenvironment of OSCC (
Figure 1). In this study, we performed a retrospective analysis of the expression of seven immune-related factors, including PD-L1, PD-1, CD47, CD4, CD8, CD56 and CD11c, and examined their correlation with clinicopathological status.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Clinical Data
Twenty-one patients with OSCC who were treated in the section of oral and maxillofacial surgery at Dokkyo Medical University Hospital in 2014 and could be followed up for 5 years or more were included in this study. The patients who were treated with chemotherapeutic agents before taking biopsy or surgical materials were excluded. Clinicopathological data were obtained from electronic medical records. Age, gender, primary site, disease stage and prognosis were extracted as clinical information. Cancer staging was determined using the UICC TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 8th edition [
4].
2.2. Immunohistochemical Staining
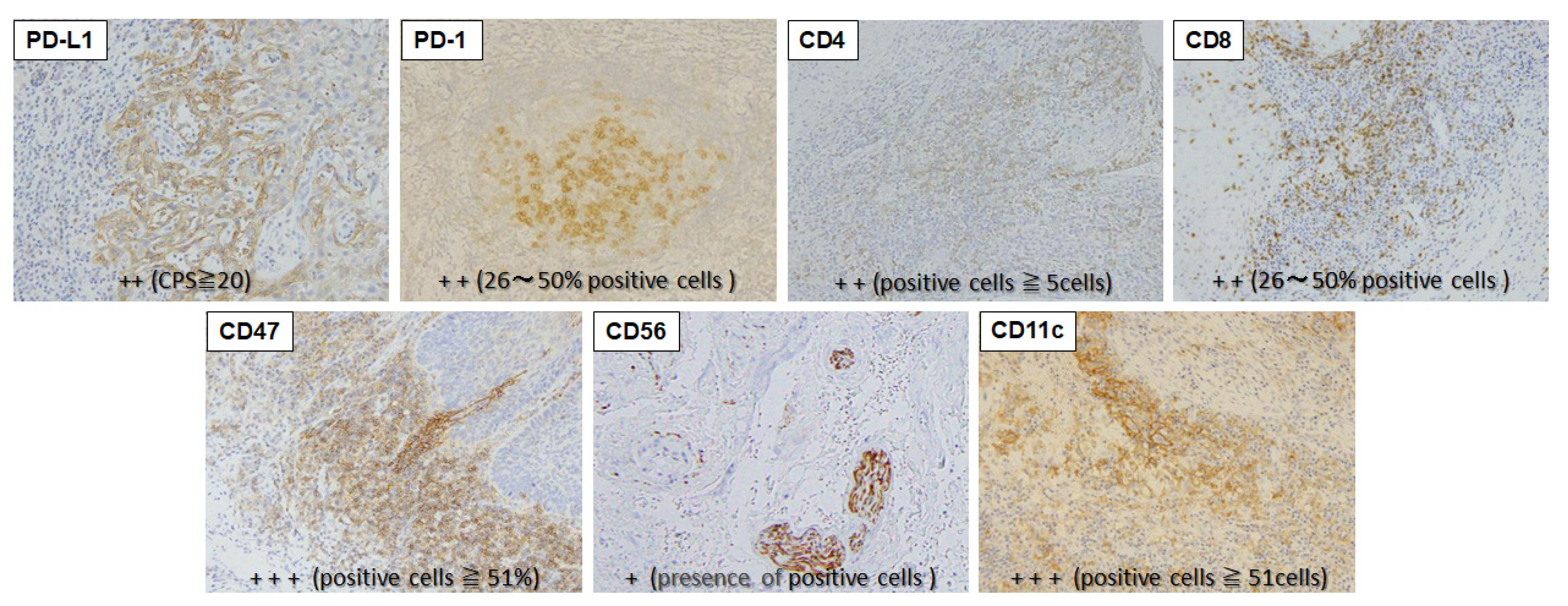
Immunohistochemical staining of specimens resected in biopsy or surgery was performed for PD-L1, PD-1, CD47, CD4, CD8, CD56 and CD11c (
Table 1). Resected tissue was immediately fixed with 10% neutral-buffered formalin solution and paraffin-embedded to prepare 4-µm sections.
PD-1, CD4 and CD8 were stained with mouse anti-PD1 monoclonal antibody (clone. NAT105 ab52587, 1:50 dilution, Abcam, Cambridge, UK), mouse anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody (clone. 1F6 NCL-L-CD4-1F6, 1:40 dilution, Leica Biosystems, Wetzlar, Germany), and mouse anti-CD8 monoclonal antibody (clone. 4B11, R-T-U, PA0183, Leica Biosystems) using a BOND-III Fully Automated IHC and ISH Staining System (Leica Biosystems).
Other factors were stained as follows. The sections were deparaffinized with xylene and serially rehydrated with ethanol. Antigen was activated by microwave at 95ºC for 10 min (pH 6.0 citrate buffer solution), washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and then treated with 0.3% hydrogen peroxide in methanol for 20 min for inhibition of endogenous peroxidase; a 30-minute total blocking time. X0909 Protein Block Serum-Free (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) was used for blocking. Incubations with rabbit anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody (clone. 28-8 ab205921, 1:100 dilution, Abcam), rabbit anti-CD47 monoclonal antibody (clone. EPR21794 ab218810, 1:1000 dilution, Abcam), rabbit anti-CD11c monoclonal antibody (clone. D3V1E #45581, 1:400 dilution, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA) and mouse anti-CD56 monoclonal antibody (clone. CD564 NCL-L-CD56-504, 1:100 dilution, Leica Biosystems) as primary antibodies were performed for 60 min. Thereafter, the procedure followed the polymer-immune complex method using EnVision (K4001, Dako) and EnVision FLEX (K8004, Dako). Staining intensity was graded using 2 to 4 stages per immune-related factor based on previous reports (
Table 1). Examples of positively stained cells are shown in
Figure 2.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The staining status of immune-related factors was compared by clinical stage and characteristics of the primary sites of the tumors. Primary sites of the tumors were divided into those with keratinized squamous epithelium (maxillary and mandibular gingiva) and non-keratinized squamous epithelium (ventral surface of tongue, floor of mouth, and buccal mucosa). Data were evaluated by chi-square test or Fisher exact test (expected value ≤ 5) (two-sided 95% CI, p<0.05) using IBM SPSS ver. 27. 0 (IBM SPSS, Inc., Tokyo, Japan).
2.4. Ethical Standards
The study was approved by Dokkyo Medical University Hospital Ethics Committee (R-59-5-J). This was an opt-out study and no patient or their representatives requested exclusion from the study.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Patients with OSCC
The study included 21 patients (13 male (61.9%), 8 female (38.1%)) with primary OSCC (
Table 2). The mean age of the patients was 64.9 years and the median age was 66.5 years. The primary tumor sites were the tongue (n=6, 28.6%), buccal mucosa (n=3, 14.3%), mandibular gingiva (n=8, 38.1%), and maxillary gingiva (n=4, 19.0%). The T stage was classified as T1 (n=2, 9.5%), T2 (n=4, 19.0%), T4a (n=14, 66.7%), and T4b (n=1, 4.8%); and the N stage as N0 (n=9, 42.9%), N1 (n=5, 23.8%), N2a (n=1, 4.8%), N2b (n=4, 19.0%), and N2c (n=2, 9.5%); resulting in a N-positive status in 12 patients (47.1%). Cancer stage was classified as Stage1(n=2, 9.5%), 2 (n=3, 14.3%), 3 (n=1, 4.8%), and 4a (n=15, 71.4%). Five patients (23.8%) died within 5 years after the first visit and 3 (14.3%) had recurrence or metastasis within 5 years.
3.2. Immunohistochemical Staining of Seven Immune-Related Factors
Results for the seven immune-related factors in the patients are shown in
Table 3. The staining levels for PD-L1 were 0, +, ++ and +++ in 4, 12, 5 and 0 patients; 8, 4, 7 and 2 patients for PD-1; 4, 6, 4 and 7 patients for CD4; 3, 5, 7, and 6 patients for CD8; 0, 3, 6, and 12 patients for CD47; 16, 5, 0 and 0 patients for CD56; and 16, 5, 0 and 0 patients for CD11c. Based on these results, we separated the expression levels of the 6 factors into (+) and (-) for statistical comparison (
Table 1).
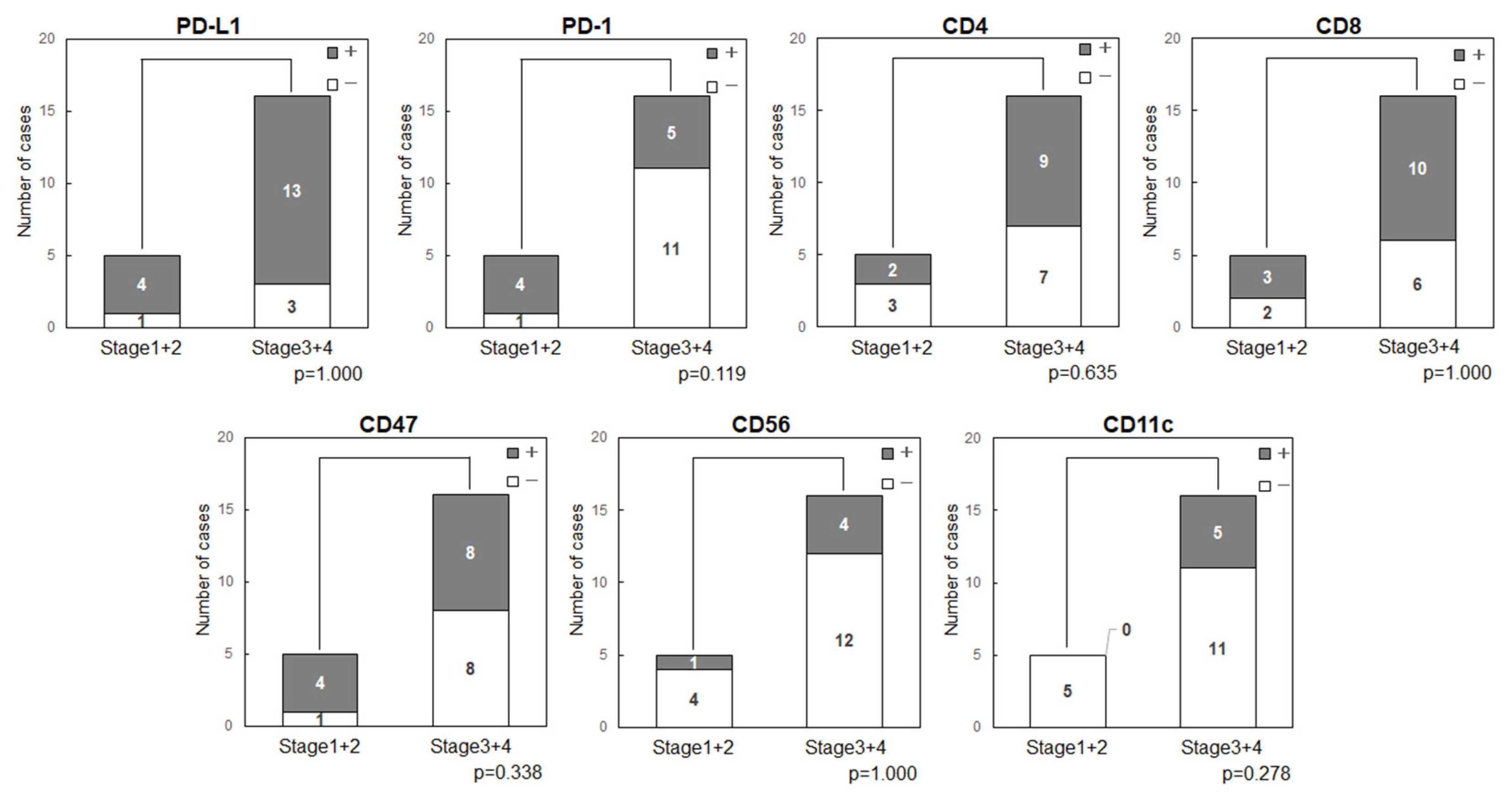
3.3. Cancer Stage
3.3.3. Cancer Stage and Expression of Immune-Related Factors in OSCC
Expression status of the immune-related factors was compared with cancer stage (
Figure 3). The stage showed no relationship with expression of PD-L1 (p=1.000), PD-1 (p=0.119), CD47 (p=0.338), CD11c (p=0.278) or other factors.
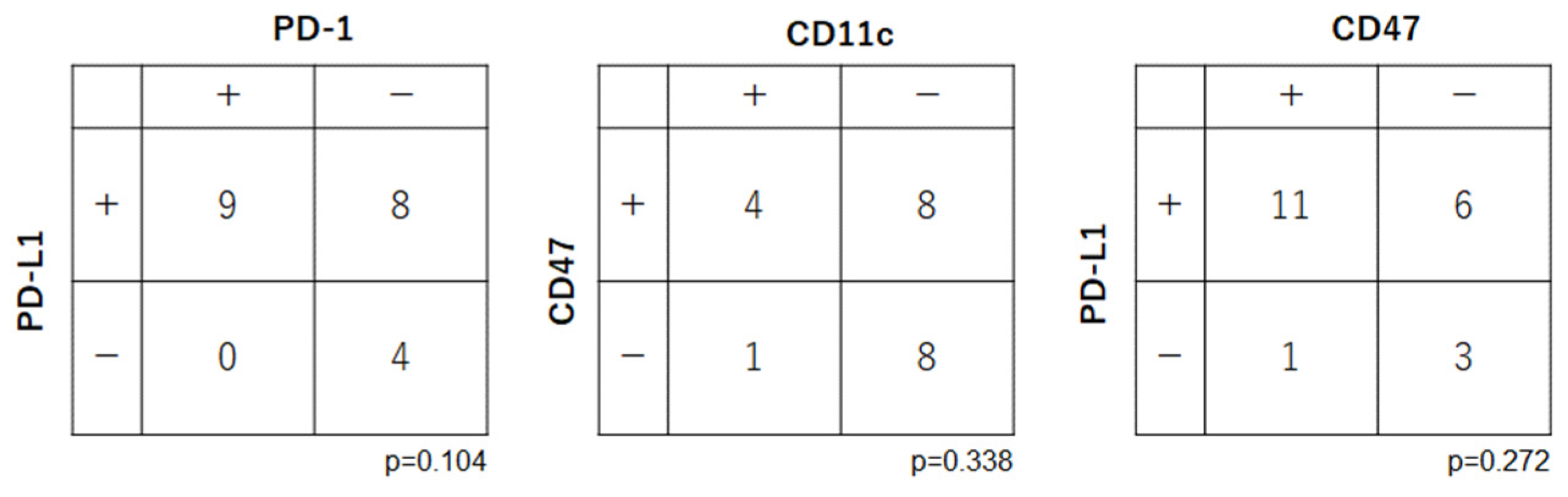
3.4. Relationships among Expression Levels of Immune Checkpoint-Related Factors in OSCC
Correlations were examined among the immune checkpoint-related factors (PD-1, PD-L1, CD47 and CD11c) (
Figure 4). There were no significant relationships between the expression levels of PD-1 and PD-L1 (p=0.104), CD47 and CD11c (p=0.338), and PD-L1 and CD11c (p=0.272).
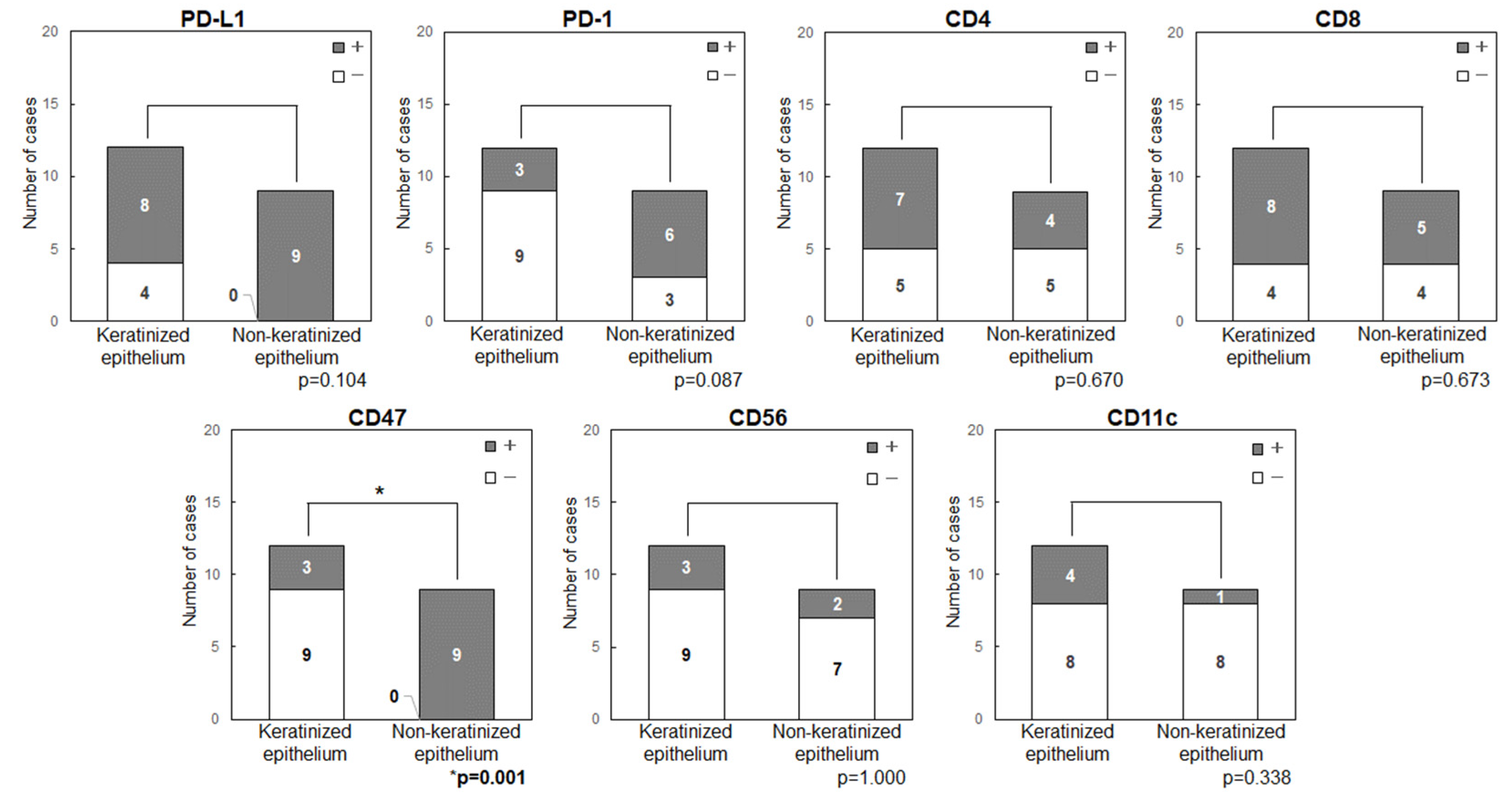
3.5. Comparison of the Expression Levels of Immune Checkpoint-Related Factors in Primary Tumor Sites (Keratinized or Non-Keratinized Epithelium)
Anatomical features and expression of immune checkpoint-related factors were compared by classifying primary sites into those with keratinized (maxillary and mandibular gingiva) and non-keratinized (tongue and buccal mucosa) epithelium (
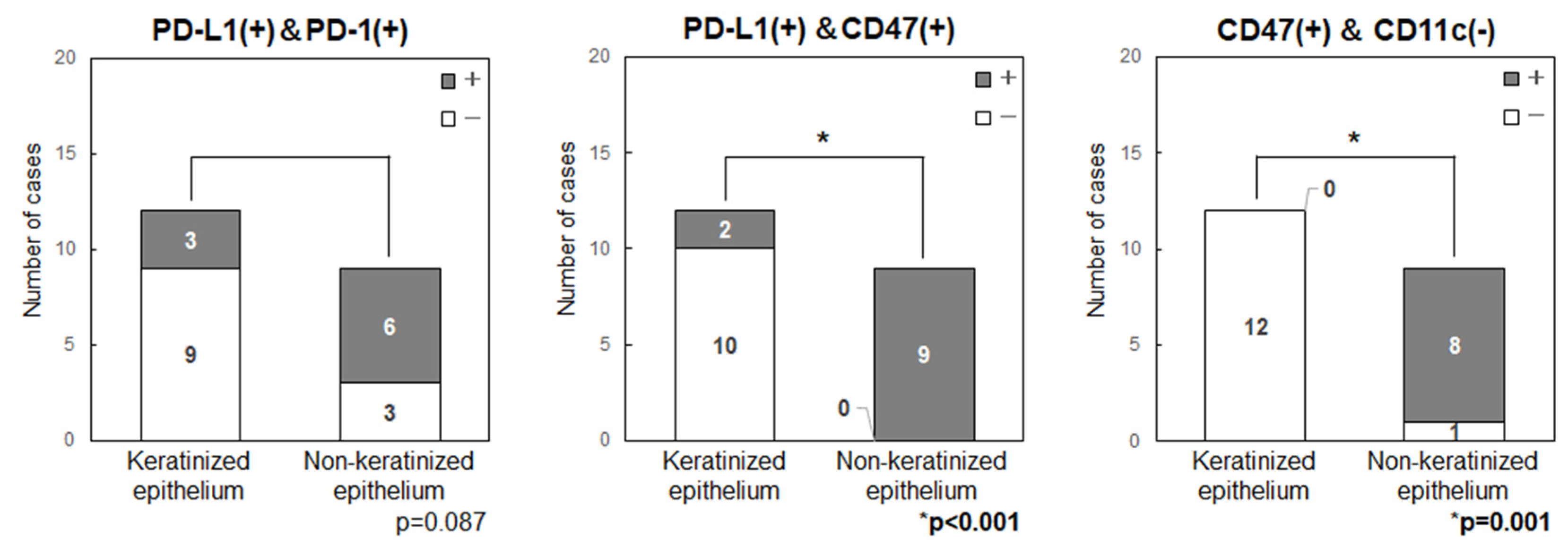
Figure 5). In all patients with tongue cancer, the tumor developed from non-keratinized mucosa in the ventral surface, rather than keratinized mucosa in the dorsal surface, then these were classified as non-keratinized site origin. The primary sites in non-keratinized epithelium had significantly higher expression levels of CD47 (p=0.001) and showed a tendency for higher levels of PD-L1 (p=0.104) and PD-1 (p=0.087). Double positive cases for PD-L1/CD47 were significantly higher in the non-keratinized sites than those in keratinized sites (p<0.001) (
Figure 6). CD47(+)/CD11c(-) cases were also significantly higher in the non-keratinized sites (p=0.001), and PD-L1(+)/PD-1(+) cases were tend to be high in non-keratinized sites (p=0.087) (
Figure 6). There was no significance difference in the expression levels of PD-L1 (p=0.676) and CD47 (p=0.647) in normal epithelia at keratinized and non-keratinized sites on the same slides (
Supplementary Figure S1), indicating that the findings were tumor-specific.
4. Discussion
We examined the immune status of OSCC tumor microenvironment by focusing on two immune checkpoints, PD-1/PD-L1, the “Do not kill me signal”, and CD47/CD11c, the “Do not eat me signal”. There were no significant findings relating immune-related factors (PD-L1, PD-1, CD47, CD4, CD8, CD56 and CD11c) and several clinicopathological statuses. However, the immune-checkpoint related factors (PD-L1, PD-1, CD47) were highly expressed in non-keratinized epithelium-originated tumors when compared to those in keratinized epithelium-originated tumors.
In the oral mucosa, the attached gingiva, palatal mucosa and dorsal tongue are covered by keratinized squamous epithelium. In contrast, floor of mouth, ventral surface of tongue, oral lip mucosa, buccal mucosa and soft palate are covered by non-keratinized squamous epithelium [
5]. Keratinization in the epithelia is important for protecting the body from biological pathogens and extrinsic stress, i.e., mechanical (physical) and chemical stress [
5]. It is unclear if both innate and adaptive immune mechanisms are activated, in addition to physical protection, in keratinized mucosa or conversely if these immune mechanisms are more activated in non-keratinized mucosa than keratinized mucosa. Immune cells may work differently in keratinized and non-keratinized sites. The buccal mucosa and ventral surface of tongue, which are non-keratinized epithelia, are common sites of oral lichen planus (OLP), a disease of T cell disorders [
19]. It is of interest that immunoediting via immune checkpoint-related factors was facilitated in non-keratinized sites. Several researchers reported that keratinization of oral mucosal epithelia affected the immune response [
19,
20,
21,
22]. However, our present finding is the first study to show a difference of the tumor immunity in the originating-epithelium of OSCC, keratinized or non-keratinized.
Blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 axis is already used in clinical practice using several antibody drugs [
11,
12,
16], and more than 100 clinical studies are ongoing [
23]. Current clinical studies show a strong relationship between the PD-L1 expression level and clinical efficacy [
12]. However, the response rate to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition alone is not so high and antitumor activity of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition alone hardly to be shown in a “cold tumor” [
23,
24]. CD47, a cell surface molecule of the immunoglobulin superfamily, is another established target that is overexpressed in malignant cells [
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30]. CD47 binds to SIRPα, a receptor in various bone marrow derived cells, and functions as an innate inhibitory checkpoint that inhibits phagocytosis against tumor cells and activation of downstream responses [
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30]. When inhibiting activation of innate immunity, tumor antigen presentation and priming of the T cell response, CD47 may enable tumor cells to evade both innate and adaptive immune surveillance [
23,
24,
31]. Overexpression of CD47 has also been shown to function as a tolerance mechanism against PD-1/PD-L1 therapy [
23,
24,
32]. Based on these mechanisms, dual blockade of PD-1/PD-L1 and CD47/SIRPα immune checkpoint inhibitory signals has been examined [
23,
24].
This study has some limitation, such as somewhat small sample scale, lack of the information for responses of tumors to ICIs, and the lack of the examination for another major negative immune regulator, regulatory T cells (Treg). It was reported that Treg highly infiltrated in OSCC [
33,
34]. Treg and other factors that suppress tumor immunity, resulting in changes from hot to cold tumors, is a critical issue in immunotherapy. At present, it is difficult to show activated Treg by immunohistochemical staining alone. The examination of existence of activated Tregs in OSCC might be necessary using fresh tissue. Furthermore, based on the current results, we are planning to examine the effects of blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 axis and/or CD47/SIRPα axis at keratinized and non-keratinized primary sites, and to evaluate the likely efficacy of dual blockade of immune checkpoint inhibitory signals in non-keratinized mucosa.
5. Conclusions
Tumor immunity, an immune escape status of OSCC might be different in the originating-epithelium, keratinized or non-keratinized.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Supplementary Figure: PD-L1 and CD47 expression in non-tumor regions close to the primary site. Neither PD-L1 (p=0.676) nor CD47 (p=0.647) expression differed significantly between keratinized and non-keratinized areas in normal epithelium. These results show that the findings in
Figure 5 and
Figure 6 are tumor-specific.
Author Contributions
All authors (YKi, CF, THy, YKo, RS, AK, SY, YKu, THa, WK, KI, TW, HK) contributed to the study conception and design. Data collection was performed by YKi. IHC samples were evaluated by YKi, CF and HK. Analysis was performed by YKi and CF. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YKi, CF and HK. All authors read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by a Research Grant from Dokkyo Medical University (grant no. 2372) and JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP22K10179 and JP22K17214
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki using residual OSCC samples obtained in biopsy or surgery. The study was approved by the Dokkyo Medical University Hospital Ethics Committee (R-59-5-J).
Informed Consent Statement
This was an opt-out study and no patient or their representatives requested exclusion from the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Ms. Chiaki Matsuyama and Ms. Ayako Shimizu (Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Dokkyo Medical University School of Medicine) for their excellent technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/oral-health.
- Bishop, J.A.; Sciubba, J.J.; Westra, W.H. Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity and oropharynx. Surg Pathol Clin 2011, 4, 1127–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLO-BOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brierley, J.D.; Gospodarowicz, M.K.; Wittenkind, C. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours 8e; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: HobLoken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Komori, T.; Ono, M.; Hara, E.S.; Ueda, J.; Nguyen, H.T.T; Nguyen, H.T.; Yonezawa, T.; Maeba, T.; Kimura-Ono, A.; Takarada, T.; Momota, R.; Maekawa, K.; Kuboki, T.; Oohashi, T. Type IV collagen α6 chain is a regulator of keratin 10 in keratinization of oral mucosal epithelium. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnakulasuriya, S. Global epidemiology of oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol 2009, 45, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCCN Guidelines for Head and Neck Cancers (Version 1.2022). Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/head-and-neck.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Fukumoto, C.; Ogisawa, S.; Tani, M.; Hyodo, T.; Kamimura, R.; Sawatani, Y.; et al. Clinical characteristics, treatment methods and prognoses of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma in Japanese population: a single institution retrospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr 2020, 20, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, C.; Sawatani, Y.; Shiraishi, R.; Zama, M.; Shimura, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Komiyama, Y.; Fujita, A.; Wakui, T.; Kawamata, H. Effectiveness of cetuximab as preemptive postsurgical therapy for oral squamous cell carcinoma patients with major risk: A single-center retrospective cohort study. Investig New Drugs 2021, 39, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumoto, C.; Oshima, R.; Sawatani, Y.; Shiraishi, R.; Hyodo, T.; Kamimura, R.; Hasegawa, T.; Komiyama, Y.; Izumi, S.; Fujita, A.; et al. Surveillance for patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma after complete surgical resection as primary treatment: A single-center retrospective cohort study. Cancers 2021, 13, 5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Nivolumab for recurrent squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 2016, 375, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtness, B.; Harrington, K.J.; Greil, R.; Soulieres, D.; Tahara, M.; de Castro, G., Jr.; Psyrri, A.; Baste, N.; Neupane, P.; Bratland, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2019, 394, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoto, K.; Al-Habsi, M.; Honjo, T. Role of PD-1 in immunity and diseases. Emerging concepts targeting immune checkpoints in cancer and autoimmunity. Journal Name Year, Volume, 75–97.
- Topalian, S.L.; Taube, J.M.; Pardoll, D.M. Neoadjuvant checkpoint blockade for cancer immunotherapy. Science 2020, 367, 6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abril-Rodriguez, G.; Ribas, A. SnapShot: Immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 848–848.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, Q.; Pan, Y.; Fang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhao, T.; Zhu, G.; Jiang, T.; Li, S.; Cao, H. Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors versus anti-PD-1/PD-L1 combined with other therapies for tumors: A systematic review. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korman, A.J.; Garrett-Thomson, S.C.; Lonberg, N. The foundations of immune checkpoint blockade and the ipilimumab approval decennial. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2021, 21, 509–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskovitz, J.; Moy, J.; Ferris, R.L. Immunotherapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Curr Oncol Rep 2018, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, K.; Ochiai, T.; Shen, F.C.; Hasegawa, H. Phenotypic alteration of basal cells in oral lichen planus; switching keratin 19 and desmoglein 1 expression. J Oral Sci 2018, 60, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, I.; Neves.; J.F.; Carrero.; D. et al. Immunomodulatory role of keratin 76 in oral and gastric cancer. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 3437. [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, I.; Watt, F.M. The role of keratins in modulating carcinogenesis via communication with cells of the immune system. Cell Stress 2019, 3, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Hu, Q.; Yang, L.; Zeng, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, D.; Dai, W.; Lu, H.; Fang, J.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Z. The niche-specialist and age-related oral microbial ecosystem: crosstalk with host immune cells in homeostasis. Microb Genom. 2022, 8, mgen000811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiao, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Tang, P.; Ouyang, Z.; Liang, W.; Mao, Y.; Wang, A.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Gui, X. Blockade of dual immune checkpoint inhibitory signals with a CD47/PD-L1 bispecific antibody for cancer treatment. Theranostics 2023, 13, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Dominik, P.K.; Stanfield, J.; Ding, S.; Yang, W.; Kurd, N.; Llewellyn, R.; Heyen, J.; Wang, C.; Melton, Z.; Van Blarcom, T.; Lindquist, K.C.; Chaparro-Riggers, J.; Salek-Ardakani, S. Dual checkpoint blockade of CD47 and PD-L1 using an affinity-tuned bispecific antibody maximizes antitumor immunity. J Immunother Cancer 2021, 9, e003464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Hsieh, R.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Krause, K.J.; Yuan, Y.; Biter, A.B.; Welsh, J.; Curran, M.A.; Hong, D.S. Inhibition of the CD47-SIRPα axis for cancer therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of emerging clinical data. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 1027235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veillette, A.; Chen, J. SIRPα-CD47 immune checkpoint blockade in anticancer therapy. Trends Immunol 2018, 39, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiskopf, K. Cancer immunotherapy targeting the CD47/SIRPα axis. Eur J Cancer 2017, 76, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Xun, Y.; You, H. The landscape overview of CD47-based immunotherapy for hematological malignancies. Biomarker Res 2023, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Zhong, T.; Pang, X.; Huang, Z.; Jin, C.; Wang, Z. M.; Li, B.; Xia, Y. Ligufalimab.; a novel anti-CD47 antibody with no hemagglutination demonstrates both monotherapy and combo antitumor activity. J Immunother Cancer 2022, 10, e005517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Yang, F.; Liu, X.; Sheng, Y.; Du, K.; He, M.; Lyu, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Wei, Z.; Wang, F.; Zheng, S.; Sui, J. A pH-dependent anti-CD47 antibody that selectively targets solid tumors and improves therapeutic efficacy and safety. J Hematol Oncol 2023, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matlung, H.L.; Szilagyi, K.; Barclay, NA.; et al. The CD47-SIRPα signaling axis as an innate immune checkpoint in cancer. Immunol Rev 2017, 276, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhani, N.J.; Patnaik, A.; Liao. J, B.; et al. A phase Ib study of the anti-CD47 antibody magrolimab with the PD-L1 inhibitor avelumab (a) in solid tumor (ST) and ovarian cancer (OC) patients. J Clin Oncol 2020, 38, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoba, T.; Imai, M.; Ohkura, N.; Kawakita, D.; Ijichi, K.; Toyama, T.; Morita, A.; Murakami, S.; Sakaguchi, S.; Yamazaki, S. Regulatory T cells expressing abundant CTLA-4 on the cell surface with a proliferative gene profile are key features of human head and neck cancer. Int J Cancer 2019, 144, 2811–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minohara, K.; Imai, M.; Matoba, T.; Wing, J.B.; Shime, H.; Odanaka, M.; Uraki, R.; Kawakita, D.; Toyama, T.; Takahashi, S.; Morita, A.; Murakami, S.; Ohkura, N.; Sakaguchi, S.; Iwasaki, S.; Yamazaki, S. Mature dendritic cells enriched in regulatory molecules may control regulatory T cells and the prognosis of head and neck cancer. Cancer Sci 2023, 114, 1256–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).