1. Introduction
Bioethanol is a promising clean liquid fuel that could significantly reduce CO
2 emissions if used instead of gasoline [
1]. However, the effective separation of ethanol from the fermentation broth is still a major obstacle to its industrial production. The traditional distillation process is energy-intensive, and the osmotic evaporation process is complex [
2,
3,
4,
5]. In contrast, adsorption separation is an energy-efficient, environmentally friendly, and economically competitive method [
6,
7]. It is particularly difficult to separate dilute ethanol/water mixtures when ethanol is a minor component of fermentation mixtures. To achieve the best performance, it is necessary to selectively capture the small amount of ethanol in the solution and reject the water molecules [
8]. Therefore, there is interest in developing an adsorbent that can selectively adsorb ethanol.
The separation of ethanol and water mixed solutions can be challenging due to their similar molecular size and dipole moments [
9]. To achieve separation, adsorbent materials are used to adjust their adsorption characteristics. Various materials such as silica molecular sieves [
10], metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) [
11], polymer resins [
12], and carbon nanotubes [
13] have been utilized as adsorbents for ethanol adsorption. It is important to note that while zeolite membranes can be effective for separating ethanol/water mixed solutions, they can also be expensive to produce [
14]. Additionally, the pore structure of silica zeolite-1 is not ideal for further modification, which can limit its practical use. Similarly, while MOFs can be effective for separation, they are known to be susceptible to hydrolysis in humid environments, which can also limit their large-scale use [
15]. Ultimately, to achieve selective adsorption of ethanol, it is important to consider London dispersion interactions. In a study conducted by G. F. de Lima et al., a water-stable MOF named Zn
2(BDC)
2(TED) was prepared and found to have the ability to adsorb ethanol/water mixtures selectively [
16]. The preferential adsorption of ethanol over water in the framework is attributed to the van der Waals forces between the ethanol alkyl group and the benzene ring present in Zn
2(BDC)
2(TED). This makes it a promising candidate for applications requiring the separation of ethanol from water. Research has demonstrated that a substance that can isolate ethanol from water must have water-resistant properties so it can provide hydrophobic sites while keeping hydrophilic sites apart. The most effective adsorption effect can be achieved when matching the length of the hydrophobic chain with that of the alcohol chain through dispersive interactions between the alkyl groups.
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is a copolymer containing both soft and hard segments [
17]. The soft segment consists of a long, low polymer chain that provides hydrophobic alkyl sites. The hard segments, on the other hand, consist of polar groups like urethane groups, which offer abundant hydrophilic hydrogen bonding sites. Due to these abundant hydrogen bonding sites, the target materials can be introduced into the TPU material through in-situ polymerization, template leaching, or thermally induced phase separation to obtain composites with specific properties [
18]. Poly(N-isoproplacrylamide) (PNIPAM) contains both hydrophilic amide groups (-CONH-) and hydrophobic isopropyl groups (-CH(CH3)2-), exhibiting both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties [
19,
20]. 1H MAS NMR quantitatively characterizes the preferential alignment of alcohol molecules near PNIPAM in ethanol/water mixtures, independent of temperature [
21]. Meanwhile, as the temperature increases, PNIPAM becomes more hydrophobic, making it more effective in adsorbing and separating alcohols. However, its poor mechanical properties limit its practical application. Composite polymers of PNIPAM with three-dimensional polymeric network structures can be made by incorporating cross-linking agents to enhance their mechanical properties. Ou R et al. have successfully prepared TPU-PNIPAM composite membranes that possess the ability to separate both oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions [
22]. Hydrogen bonds were formed between the poly-(ethyl carbamate) group and the acrylamide group, which made it possible for PNIPAM to be evenly coated on the surface of TPU. As the amount of PNIPAM increased, the number of hydrophilic sites in TPU and PNIPAM decreased, while the surface roughness increased. This leads to the hypothesis that PNIPAM can be used to flexibly modify TPU and act as a host-guest switch for ethanol/water adsorption separation.
The study aimed to transform the surface flexibility of TPU material by conducting the in-situ polymerization of PNIPAM on it. This process resulted in the preparation of TPU-PNIPAM composite material, which was then used to separate the ethanol and water mixture and to explore its selective adsorption and separation performance. The study also discussed the selective adsorption effect of TPU-PNIAPM on other alcohol/water mixtures.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization Analysis
2.1.1. Morphology Analysis
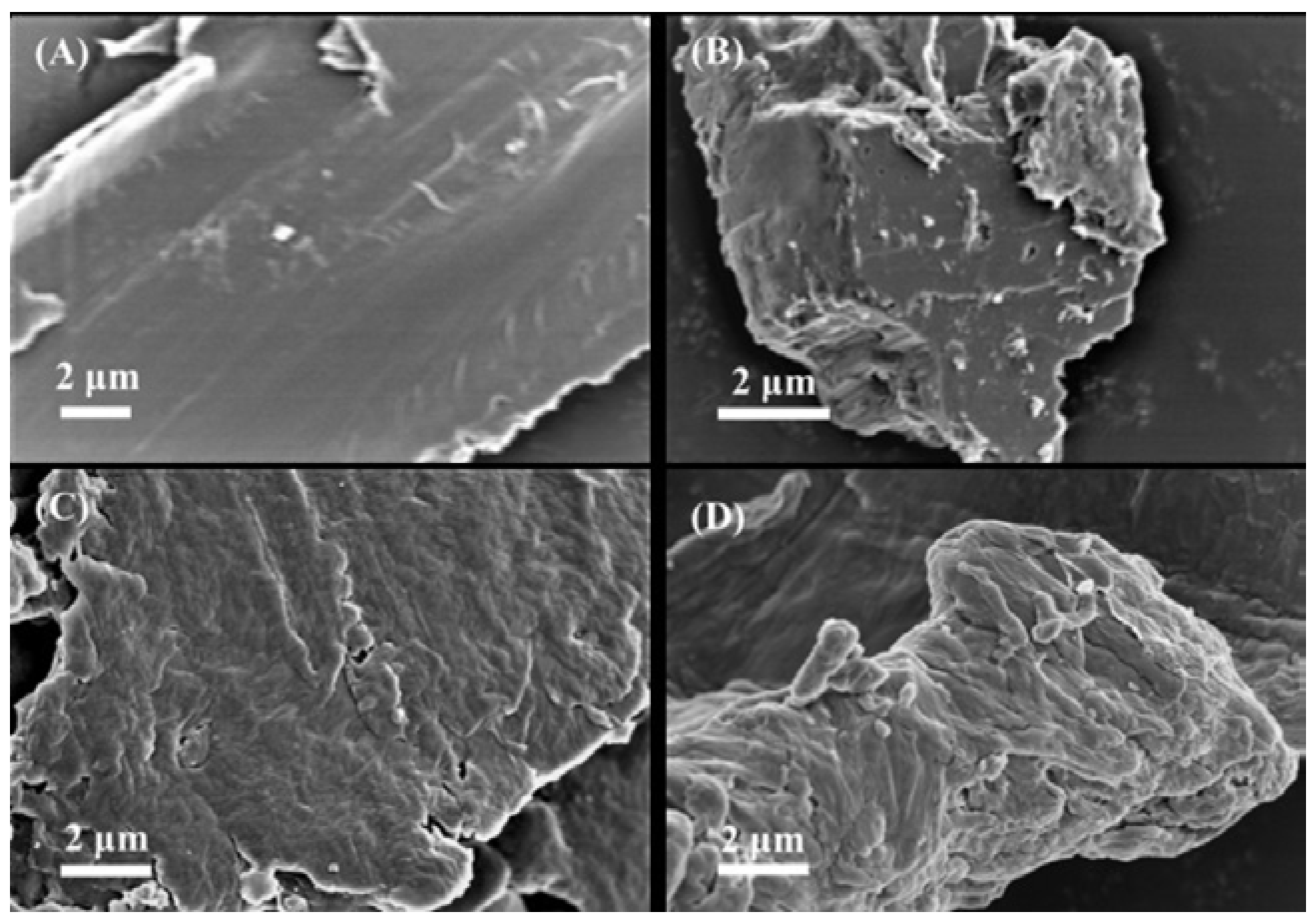
As per
Figure 1, it can be observed that the surface of TPU has a smooth layer-like structure. T-N
0.5, T-N
1.0 and T-N
1.5 exhibit the characteristics of stacked layers. As the mass of the polymerized monomers increases, the density of the stacks also increases, leading to a rougher surface. This demonstrates that PNIPAM was successfully loaded onto the surface of TPU through in situ polymerization.
2.1.2. FT-IR, Raman and TG
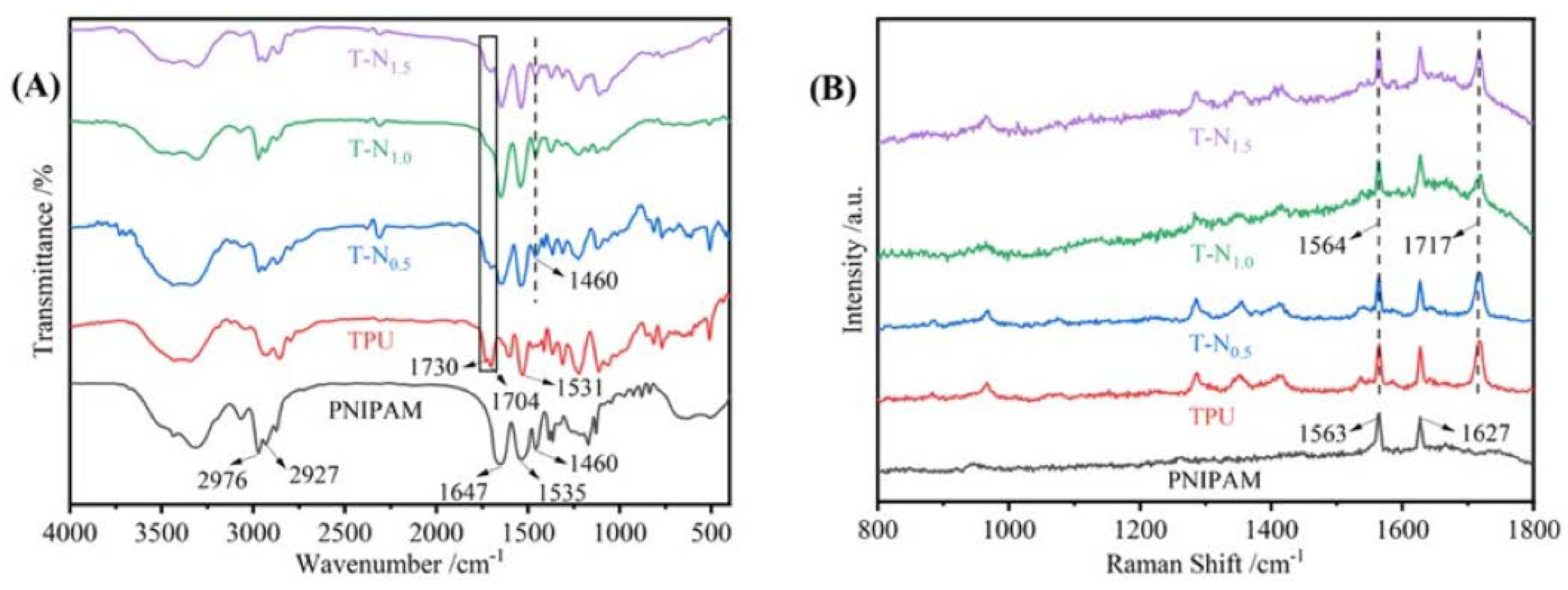
In
Figure 2(A), the vibrational peaks observed at 2976, 2927, and 1460 cm
-1 are ascribed to PNIPAM's methyl (-CH3), methylene (-CH2-), and isopropyl (-CH(CH3)2) stretching vibrations. Additionally, the vibrational peaks at 1647 and 1537 cm
-1 are attributed to the stretching vibrations of the carbonyl and amide groups, respectively. The TPU exhibits vibrational peaks at 1730 and 1704 cm
-1, which are attributed to the free carbonyl and hydrogen-bonded carbonyl stretching vibrations, respectively. The characteristic peaks in TPU and PNIPAM were observed simultaneously in T-N
0.5, T-N
1.0, and T-N
1.5. The stretching vibrational peak of the carbonyl group in TPU is attributed to the vibrational peaks at 1730 and 1704 cm
-1, while the isopropyl group in PNIPAM is responsible for the vibrational peak at 1460 cm
-1. In comparison to TPU, T-N
0.5 demonstrates a significant reduction in the free carbonyl peak at 1730 cm
-1. Furthermore, the peak is no longer observable in T-N
1.0 and T-N
1.5, indicating the formation of a hydrogen bond between the carbonyl group and PNIPAM. The free carbonyl group transforms into a hydrogen-bonded carbonyl group, and the bonding between PNIPAM and TPU is achieved through hydrogen bonding.
High-resolution laser Raman spectroscopy is used as a complementary method to FT-IR. In
Figure 2(B), the peaks observed at 1563 and 1627 cm
-1 in PNIPAM are attributed to the stretching vibration of amide and carbonyl groups, while the peaks seen at 1717 and 1564 cm
-1 in TPU are attributed to the stretching vibration of carbonyl and amide groups. For TPU-PNIPAM, the carbonyl vibrational peak at 1717 cm
-1 is slightly distorted and weakened. This can be explained by the formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonds between TPU and PNIPAM, which is consistent with the FT-IR spectral analysis.
According to the results presented in
Table 1, the isopropyl peaks of T-N
0.5, T-N1.0, and T-N
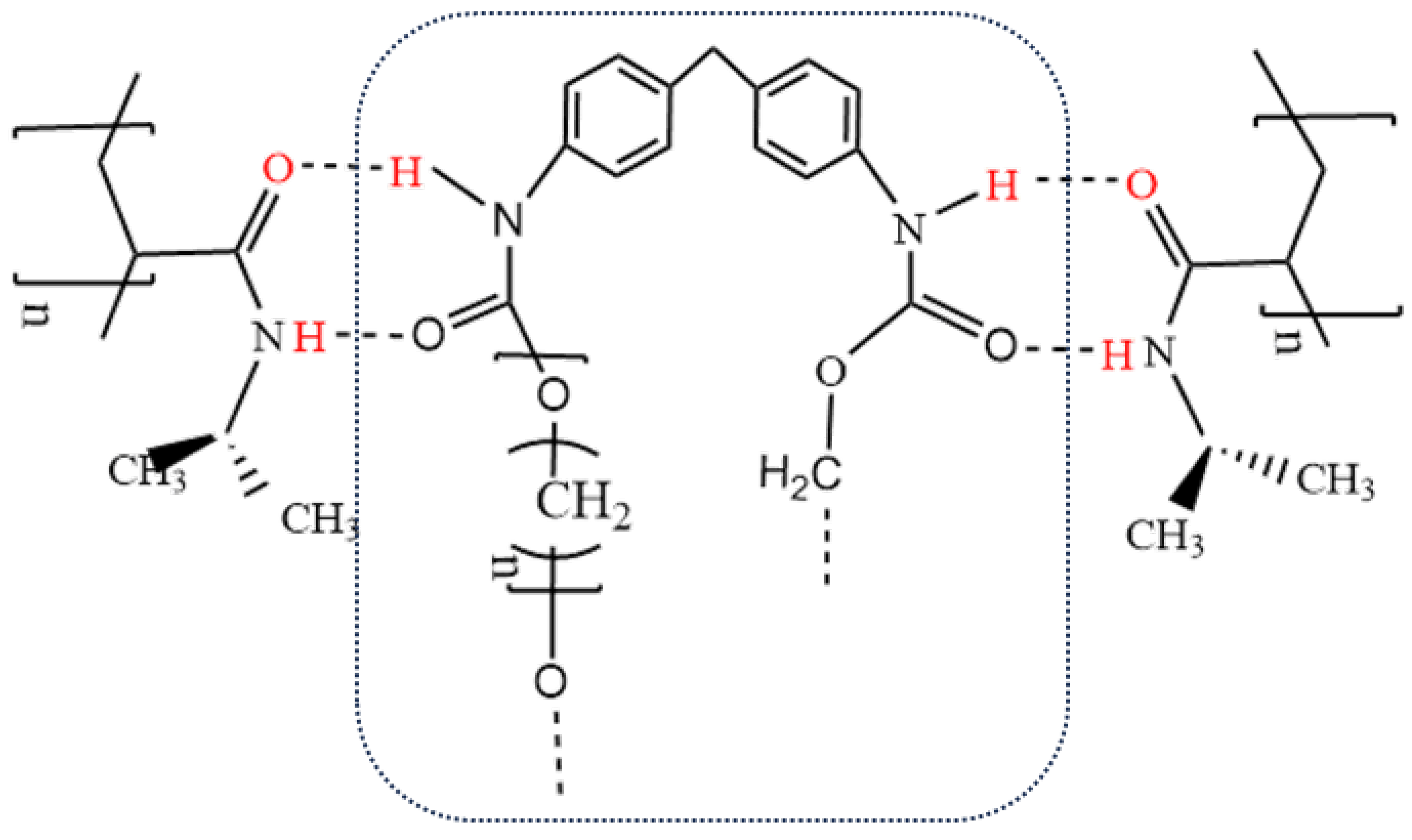
1.5 had relative areas of 2.16%, 2.93%, and 3.37% in FT-IR spectra, respectively. The relative areas of the amino peaks were 9.44%, 8.93%, and 7.24% in Raman spectra. The spectroscopic characterization results obtained from FT-IR and Raman analyses indicated that PNIPAM was successfully loaded on the TPU surface via in situ polymerization. The bonding between the two occurred through the formation of an O--H hydrogen bond between the carbonyl oxygen and amino hydrogen. Due to the formation of hydrogen bonds between TPU and PNIPAM, the carbonyl and amino groups on the surface of both were heavily masked. These groups can form hydrogen bonds with water but are now covered. On the other hand, the hydrophobic isopropyl groups are exposed. This outcome inevitably leads to an improvement in dispersive interactions between isopropyl and alcohol alkyl groups, this improvement favors the selective adsorption of alcohols. In other words, the hydrogen bonding between PNIPAM and TPU effectively enhances the hydrophobicity of the TPU-PNIPAM composites, which is beneficial for the selective adsorption and separation of the alcohol/aqueous solution, as shown in
Figure 3.
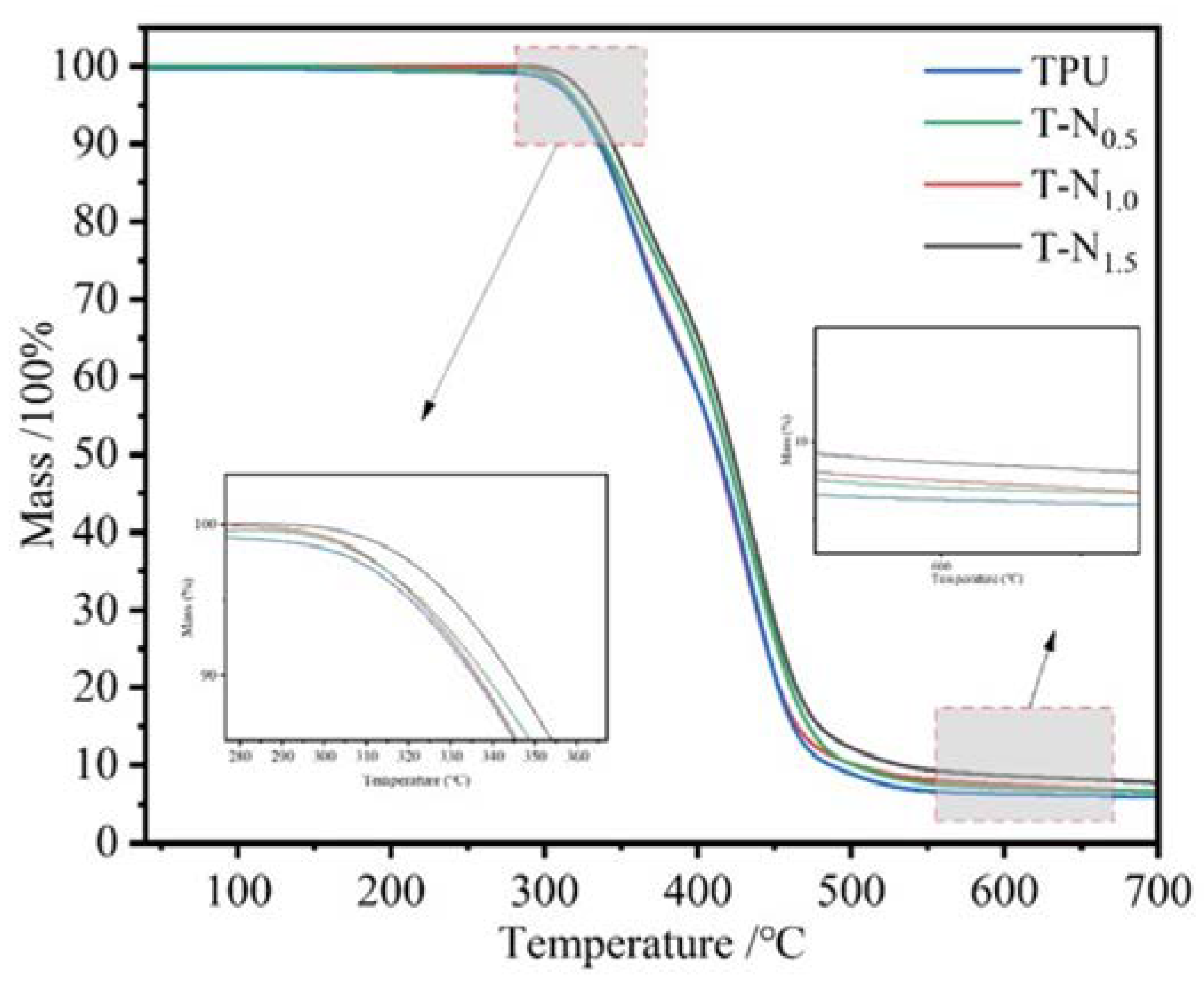
The temperature at which TPU and PNIPAM decompose is 310°C and 350°C, respectively.
Figure 4 displays the thermogravimetric curve of TPU-PNIPAM. The decrease in mass before decomposition is due to the evaporation of water that is adsorbed on the surface of the sample with the interstitial space. As the amount of PNIPAM on TPU increases, the loss of adsorbed water mass decreases progressively. As the number of hydrogen bonds between TPU-PNIPAM increases, there are fewer bonding sites left for water. This results in a decrease in the degree of adsorption of airborne water. In other words, loading PNIPAM can effectively improve the hydrophobicity of TPU. The thermogravimetric curves of TPU-PNIPAM show minimal changes compared to TPU due to the small mass loading of PNIPAM. At a thermal decomposition temperature of 650°C, the masses of TPU, T-N
0.5, T-N
1.0, and T-N
1.5 become 5.91%, 6.46%, 6.62%, and 7.74% of their original values, respectively.
2.2. Adsorption Property Analysis
2.2.1. Maximum Adsorption Capacity
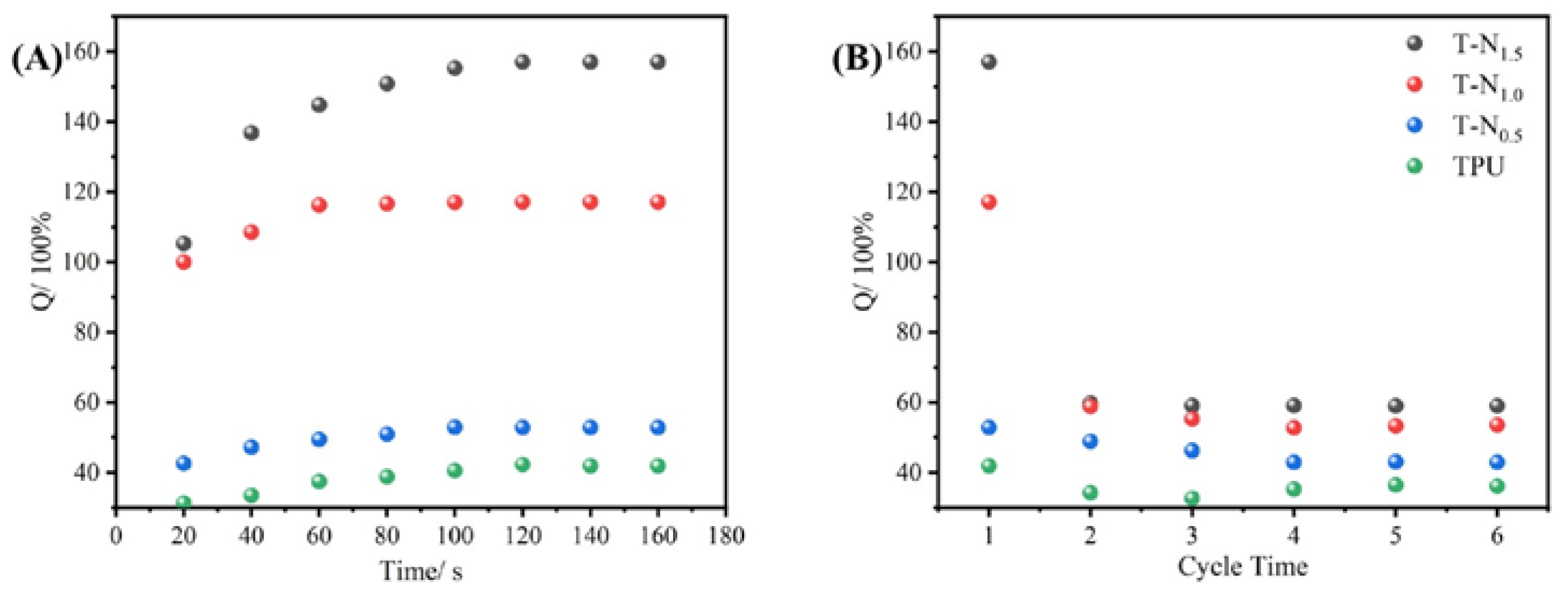
The TPU, T-N
0.5, T-N
1.0, and T-N
1.5 samples were immersed in ethanol for fixed time intervals, followed by removal and weighing to establish adsorption equilibrium curves. Upon reaching saturation adsorption, the ethanol absorbed by the material was extracted through simple extrusion before subjecting it to further rounds of ethanol adsorption for a total of six cycles. The equation of saturated absorption capacity (Q
m) was expressed as follows:
where m
0 and m
t are the mass of the monolith before and after the experiment, respectively.
As depicted in the
Figure 5, TPU, T-N
0.5, T-N
1.0, and T-N
1.5 exhibit ethanol adsorption capabilities and achieve equilibrium within approximately 1 minute. Moreover, an increase in PNIPAM loading on TPU leads to enhanced saturated adsorption capacity of the composite material for ethanol. Notably, the saturated adsorption capacity of T-N
1.5 for ethanol reaches 157.02%, which is approximately fourfold higher than that of pure TPU. After the initial adsorption, the foam exhibited a decrease in its saturated adsorption capacity, which eventually reached a stable state. Following six cycles of adsorption-desorption, the saturated adsorption capacities of T-N
1.5, T-N
1.0, T-N
0.5 and TPU decreased from 157.02%, 117.09%, 52.84% and 41.85% to 59.00%, 53.54%, 42.86% and 36.11%respectively. This is attributed to the presence of PNIPAM on the surface of TPU, which facilitates interaction between isopropyl groups and ethanol alkyl groups. The incorporation of more polymer enhances its ability to interact with ethanol. However, conventional extrusion methods are unable to eliminate adsorbed ethanol and may result in polymer elution, consequently reducing the saturated adsorption capacity in subsequent cycles.
2.2.2. The Impact of PNIPAM Loading on the Adsorption Performance
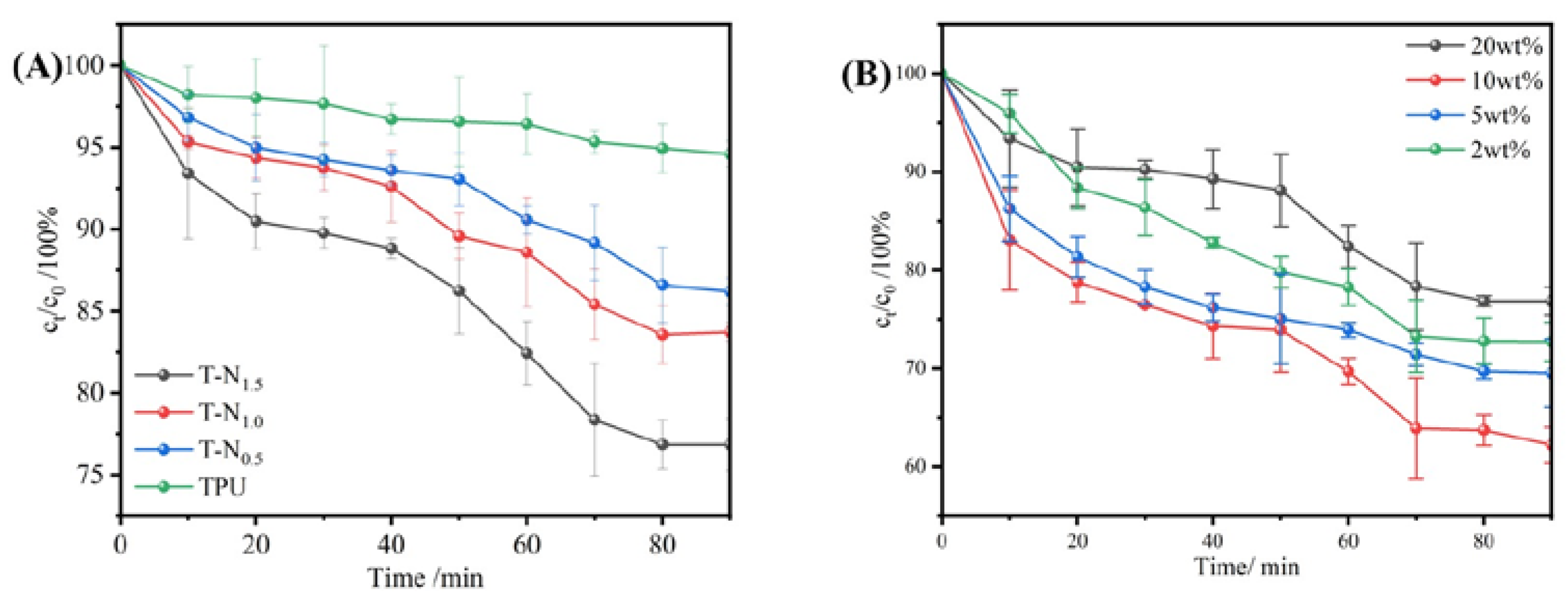
In
Figure 6(A), it is demonstrated that the adsorption of TPU resulted in a reduction of the concentration of the ethanol/water mixture solution by approximately 5%. This indicates that TPU material displays preferential adsorption properties for ethanol. Moreover, the selective adsorption of ethanol by TPU-PNIPAM was observed to increase with the input of polymerization monomers. After 90 minutes, T-N
0.5, T-N
1.0, and T-N
1.5 adsorption caused a decrease in the concentration of ethanol/water mixture solution by 13.8%, 16.3%, and 23.2%, respectively. This suggests that the selective adsorption of TPU-PNIPAM composite on the ethanol/water mixture solution is improved with an increase in the PNIPAM loading on the TPU surface. As the concentration of the polymerized monomer NIPAM increases, the number of hydrogen bonds between PNIPAM and TPU also increases. This is because the carbonyl and amino groups, which can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, are concealed, while a significant number of exposed isopropyl groups create London dispersion interactions with the ethyl group of ethanol. T-N
1.5 was found to have the strongest selective adsorption capacity for ethanol, its selective adsorption capacity for ethanol within 90 minutes is about five times that of TPU. T-N
1.5 was used as the adsorption material in all subsequent experiments.
2.2.3. Effect of Initial Ethanol Concentration on Adsorption Performance
Ethanol solutions with 20wt%, 10wt%, 5wt%, and 2wt% mass fractions were used to investigate the effect of initial ethanol/water concentration on the TPU-PNIPAM composite's selective adsorption performance.
Figure 6(B) presents the results. TPU-PNIPAM exhibited selective adsorption for varying concentrations of ethanol solutions. The best adsorption performance was observed for the 10wt% ethanol solution, which was reduced to 62.2% of its original concentration in 90 minutes, the concentration of 20wt%, 5wt%, and 2wt% ethanol solution decreased to 76.8%, 69.5%, and 72.7% respectively. The TPU-PNIPAM material exhibited consistent adsorption behavior for various concentrations of ethanol and water solutions. Moreover, the ethanol concentration in the solution decreased, indicating that TPU-PNIPAM has better adsorption capacity for ethanol/water mixed solutions than for water alone. This proves that it selectively adsorbs ethanol.
The ethanol/water adsorption curves were observed for various initial concentrations. The results showed that there was a rapid ethanol adsorption phase in the first 20 minutes, followed by a smooth adsorption phase between 20-50 minutes. Then there was another rapid adsorption phase from 50-70 minutes, and finally, the curve reached equilibrium with smooth adsorption from 70-90 minutes. TPU-PNIPAM possesses hydrophobic properties that enable it to adsorb ethanol selectively. During the first 20 minutes of the process, the adsorption behavior is governed by kinetic diffusion, allowing ethanol to be quickly absorbed and arranged on the surface of TPU-PNIPAM, leading to a rapid decrease in ethanol concentration in the ethanol/aqueous solution. When ethanol and water are mixed, they form a network of hydrogen bonds, which causes water molecules to be absorbed between ethanol molecules. This co-adsorption of water and alcohol occurs on the surface of TPU-PNIPAM. As a result, water molecules will be adsorbed within the first 20 minutes of rapid ethanol adsorption. This phenomenon has been observed in previous studies [
23]. According to a study by R. F. DeJaco et al., when the adsorption capacity of alcohol reaches a moderate level, the co-adsorption of water reaches its maximum level. However, the co-adsorption of water then decreases as the adsorption capacity of alcohol further increases. As a result, the concentration of ethanol decreases gradually during 20-50 minutes due to the co-adsorption of alcohol and water. [
24] Between 50-70 minutes, the process of adsorption is controlled by thermodynamics. At this stage, the ethanol molecules that have been adsorbed on the hydrophobic point of TPU-PNIPAM undergo rearrangement, which results in the discharge of co-adsorbed water molecules from the hydrogen bond network. This leads to a rapid reduction of ethanol concentration in the ethanol/water mixed solution. In the last 70-90 minutes, the adsorption curve became flat once again. This is because the hydroxyl group of the ethanol molecule provided the bonding adsorption site for the water molecule again after rearranging. As a result, the overall performance was that the selective adsorption capacity decreased, and the adsorption reached equilibrium.
It has been observed that a higher selectivity of ethanol can be achieved in low-concentration ethanol/water mixed solutions, particularly in 10wt% ethanol/water mixed solutions. However, when the concentration of the solution is increased to 20wt%, the more ethanol molecules adsorb on TPU-PNIPAM, which creates numerous bonding sites for water molecules, ultimately leading to a decrease in selectivity. The results of the experiment indicate that TPU-PNIPAM can selectively adsorb ethanol/water mixtures with varying concentrations. However, the intertwined hydrogen bond networks present in ethanol/water mixed solutions can be affected by the concentration of alcohol, which in turn can impact the hydrogen bond network within the solution and the bonding site of water on the surface of TPU-PNIPAM. As a result, the adsorption curve of TPU-PNIPAM for ethanol exhibits a characteristic trend of fast-slow-fast.
2.2.4. The Effect of Temperature on the Adsorption Performance of Composite Materials
Various experiments were conducted using mixed ethanol and water solutions with different mass fractions (20wt%, 10wt%, 5wt%, and 2wt%) to examine how temperature affects the selective adsorption performance of TPU-PNIPAM composite material on ethanol. PNIPAM is a polymer that is sensitive to temperature. It is deemed that as the temperature increases, the hydrophobic alcohol molecules are more likely to be adsorbed and retained in the polymer network than the polar water molecules. This implies that warming provides PNIPAM with the ability to adsorb ethanol selectively. The adsorption of alcohol molecules on PNIPAM promotes the dehydration of the polymer chain. This is because alcohol molecules preferentially adsorb onto PNIPAM, which hinders the hydrogen bonding between PNIPAM and water molecules. As a result, the hydrophobicity of the polymer chain is increased. This phenomenon has been observed in previous studies [
25,
26]. When the temperature was raised to 55℃, the selective adsorption performance of TPU-PNIPAM on mixed solutions of different concentrations of ethanol and water improved. This improvement was similar to the trends observed at room temperature, the best ethanol selective adsorption effect was observed at 10wt%. As a result, the concentration of ethanol in the 10wt% solution decreased to 55.0% of its initial concentration. These observations are shown in
Figure 7(A) and 7(B). The experimental results demonstrate that by increasing temperature, TPU-PNIPAM can achieve better selective adsorption capacity of ethanol in ethanol/water mixed solution.
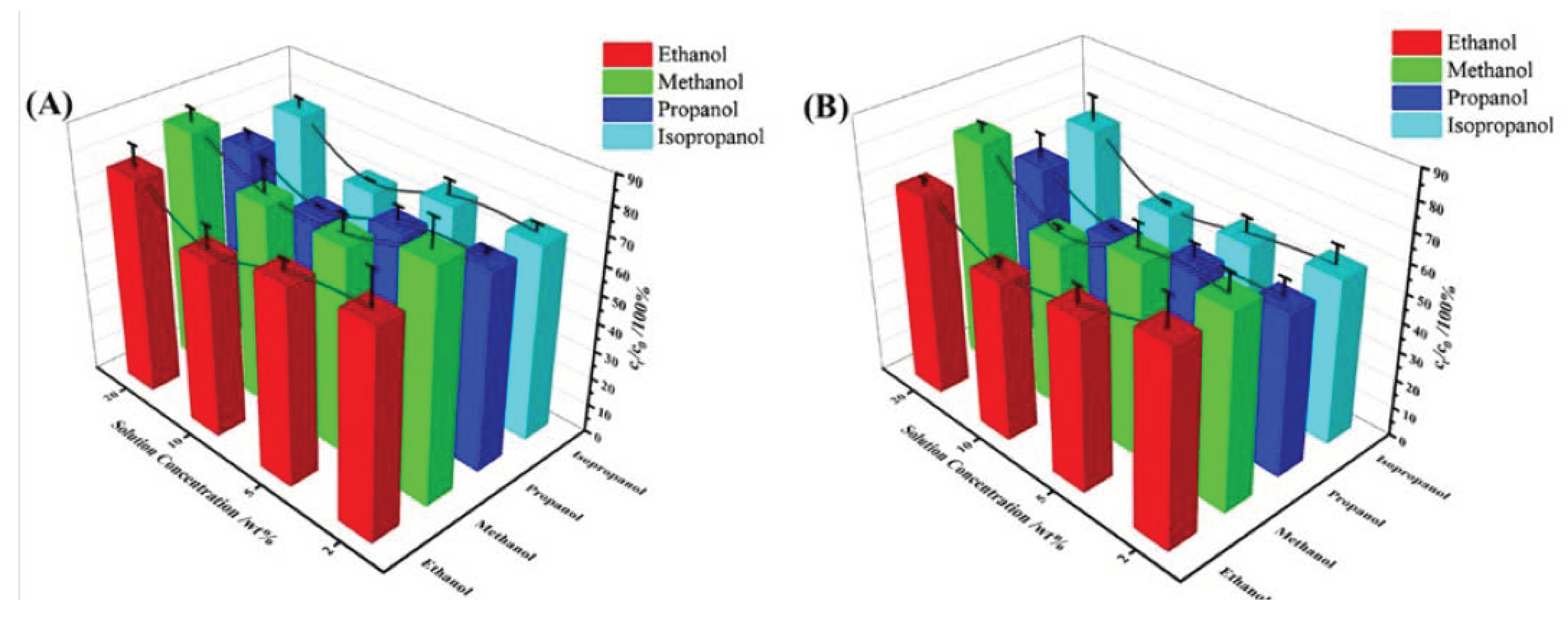
2.2.5. Effect of Different Alcohols on Selective Adsorption Performance
The study investigated the adsorption properties of methanol, n-propyl alcohol, and isopropyl alcohol with different concentrations (20wt%, 10wt%, 5wt%, and 2wt%). TPU-PNIPAM showed similar selective adsorption characteristics for all three alcohols, as indicated in
Figure 7. TPU-PNIPAM has demonstrated a selective capacity for adsorbing methanol/water, propanol/water, and isopropanol/water, similar to ethanol/water mixed solutions. TPU-PNIPAM exhibited the highest adsorption capacity in a mixed solution of 10wt% alcohol and water. Increasing the temperature to 55℃ further improved the selective adsorption capacity of TPU-PNIPAM for alcohol. According to
Figure 7, when subjected to the same conditions, different alcohols exhibit varying degrees of selective adsorption capacity. Methanol shows the least capacity, followed by ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, and propyl alcohol. For instance, after reaching an adsorption equilibrium for a mixed solution with an initial concentration of 10 wt%, the solution concentration drops to 72.7%, 62.2%, 68.6%, and 58.2% (at room temperature) for methanol, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, and propyl alcohol respectively. At 55℃, the solution concentration drops to 58.1%, 55.0%, 50.5%, and 48.7% respectively. In a mixed solution of alcohol and water with an initial concentration of 20wt%, the selective adsorption difference between isopropyl alcohol and propyl alcohol was high, at 76.1%, 68.4%, 71.3%, and 62.4% at room temperature and 55℃. This indicates that propanol was more preferentially adsorbed.
Short-chain alcohols like ethanol have properties similar to water, and can easily form uniform mixed solutions with water. Therefore, to separate alcohol from water, it is necessary to isolate or cover the hydrophilic point in the adsorption material that can form hydrogen bonds with water. This will allow selective adsorption of alcohol molecules using London dispersion. In this paper, TPU and PNIPAM are combined using hydrogen bonds. This bonding method not only separates the hydrophilic hydrogen bond site on the surface of TPU but also occupies the same site within the PNIPAM network structure. Additionally, the exposed isopropyl group on the surface of PNIPAM is utilized as a hydrophobic point to disperse the alkyl group of alcohol molecules. This selective adsorption allows for the separation of alcohol and water in mixed solutions. As the length of the alkyl chain in methanol, ethanol, and propanol increases, the strength of the London dispersion force between these alcohols and TPU-PNIPAM also increases. This means that longer alkyl chains enhance the selective adsorption ability of the alcohols and improve the adsorption and separation capacity of mixed solutions, such as methanol/water, ethanol/water, and propanol/water. Regarding the difference in adsorption properties of isopropyl alcohol and propyl alcohol in high concentration alcohol/water mixed solution, some researchers suggest that it is caused by the large steric hindrance of isopropyl alcohol [
26]. We believe that the concentration of the alcohol and water mixture has a significant impact on the selective adsorption performance, as mentioned earlier. Both factors work together to improve the adsorption selectivity of propyl alcohol over isopropyl alcohol.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Thermoplastic polyurethane pellets (Zhongcheng Plasticizing), tetrahydrofuran, sodium chloride, isopropanol (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.), N-isopropylacrylamide (Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.), N, N-methylenebisacrylamide (Anhui Zaisheng Technology Co., Ltd.), ammonium persulfate(Anhui Sunrise Technology Co., Ltd.), anhydrous ethanol (Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.), anhydrous methanol (Beijing Chemical Plant), propanol (Tianjin Yongda Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.), distilled water, the above reagents are analytically pure and are used directly without further purification.
3.2. Preparation of TPU-PNIPAM
Initially, 2 grams of TPU was dried in an oven for 12 hours and then weighed. Afterward, it was dissolved in 8 milliliters of tetrahydrofuran, heated, and stirred until it became homogeneous and transparent. Pre-ground sodium chloride particles were then added and mixed thoroughly. The mixture was swiftly poured into cylindrical molds that had a diameter of 30 mm and a depth of 10 mm. After being left in a fume hood for 24 hours, it was transferred to an oven where it was dried at a temperature of 55°C. After thoroughly drying and forming the product, remove it from the mold and sand it. Then, place it in distilled water and replace the water once every 8 hours until no sodium chloride precipitates. Once this is done, the reshaped TPU material can be dried and stored for future use.
0.50g, 1.00g, and 1.50g of N-isopropyl acrylamide were weighed to use as the polymerization monomer. Additionally, 1% of the monomer mass of N, N-methylenebisacrylamide was also weighed and added as a cross-linking agent. The mixture was stirred in 30 ml of distilled water to dissolve and create a colorless transparent solution. TPU material was added to a reaction solution, to which 100μL of 10wt% ammonium persulfate solution was added as the initiator. The reaction was carried out in an oxygen-free environment at 70℃ for 3 hours. After the reaction, the product was washed with distilled water at 25℃ and 45℃ to remove any unreacted monomer. The TPU-PNIPAM composite material was then dried to obtain T-N0.5, T-N1.0 and T-N1.5.
3.3. Characterization of Materials
The sample was characterized using a FEI scanning electron microscope. The sample was fixed onto the sample table with conductive adhesive and coated with a thin layer of gold to prevent electrostatic charging.
The sample was analyzed using a Nicolet IS5 Fourier infrared spectrometer. The product was first cut into a fine powder, then mixed thoroughly with potassium bromide at a ratio of 1:100. After that, the mixture was pressed into thin slices using a tablet press. Finally, it was scanned 32 times within the wavelength range of 4000-400cm-1.
Raman spectrum analysis was conducted using a LabRAM HR Evolution high-resolution laser Raman spectrometer with a laser wavelength of 514nm and scanning range of 800-1800cm-1.
QMS403D \ Bruker V70 thermogravimetric analyzer was used to perform thermogravimetric analysis of the experimental samples in N2 atmosphere. The temperature was increased from room temperature to 700℃ at a rate of 20℃/min.
3.4. Adsorption Performance Test
The effectiveness of TPU-PNIPAM in selectively adsorbing alcohol/water mixtures was tested using a SHIMADZU GC-8A gas chromatograph with a Q column. High-purity helium served as the carrier gas and was maintained at a pre-column pressure of 400 kPa, injection column pressure of 220 kPa, and a reference column pressure of 230 kPa. The helium flow rate was set at 37.5 mL/min. The current flowing through the bridge was measured at 140 mA. The injection and detection chambers were maintained at a temperature of 200°C, while the column box was heated to 180°C. A single injection volume of 0.2 μl was used for each test. In a closed bottle, 3 ml of an alcohol/water mixture was taken and a prepared TPU-PNIPAM material was placed inside for each test. Samples were collected and documented at 10-minute intervals to measure the alteration in the concentration of the solution within a 90-minute timeframe.
4. Conclusions
A TPU-PNIPAM composite material was prepared by in-situ polymerization to selectively adsorb alcohol from a mixed solution of alcohol and water for the first time. The molecular structure of TPU and PNIPAM both have hydrogen bond sites that can bind with water. By forming a hydrogen bond between the carbonyl oxygen and amino hydrogen, TPU and PNIPAM can expose the hydrophobic isopropyl group of PNIPAM to the greatest extent while covering the hydrophilic point. This resulted in the formation of a hydrophobic TPU-PNIPAM composite which allowed for selective adsorption of alcohols in the alcohol/water mixture through London dispersion force between alkyl groups. The performance of TPU-PNIPAM in selectively adsorbing alcohol/water mixed solutions was tested by comparing the concentration of alcohol/water before and after adsorption. As the amount of PNIPAM loaded on the surface of TPU increases, the number of hydrogen bonds between TPU and PNIPAM increases, the hydrophilic point is largely covered, and the dispersion between the exposed isopropyl group and the alcohol alkyl group is enhanced. This results in the TPU-PNIPAM having an enhanced selective adsorption ability for alcohol/water mixed solution. When mixing alcohol and water solutions with varying initial concentrations, the adsorption of alcohol molecules is accompanied by the co-adsorption of water. The adsorption curve of such mixtures shows a fast-slow-fast-equilibrium characteristic, with the two initial fast adsorptions driven by kinetics and thermodynamics, respectively. As the amount of alcohol adsorbed reaches a medium level, the co-adsorption of water reaches its maximum, leading to a gentle decrease in the adsorption curve. When the temperature was raised to 55℃, the TPU-PNIPAM exhibited better selective adsorption performance on alcohol/water mixtures of varying concentrations. With an increase in temperature, alcohol molecules were more favorably adsorbed and retained in the polymer network than water molecules. This was because the hydrophobic isopropyl group of PNIPAM was more exposed, leading to an enhanced van der Waals interaction with alcohol alkyl groups. In addition to the general adsorption law, different types of alcohol/water mixed solutions exhibit varying degrees of selective adsorption capacity under the same conditions. The selective adsorption capacity of different alcohols increases gradually in the order of methanol, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, and propyl alcohol. This is due to the increased dispersion of hydrophobic alkyl and alkyl alcohol. In the mixed solution of alcohol/water at 20wt%, the steric hindrance of the alkyl groups of isopropyl alcohol results in a less effective selective adsorption effect compared to propyl alcohol. The TPU-PNIPAM composite is suitable for the selective adsorption and separation of alcohol/water mixed solutions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.W. and G.Z.; methodology, F.W. and G.Z.; software, F.W.; validation, F.W. and Z.Z.; formal analysis, F.W.; investigation, F.W.; resources, F.W.; data curation, F.W.; writing—original draft preparation, F.W.; writing—review and editing, F.W. and T.C.; visualization, F.W.; supervision, G.Z. and T.C.; project administration, G.Z. and T.C.; funding acquisition, G.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Jilin Province Natural Science Foundation ,grant number, 20220101194JC.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We thank Baiyi Li, Jiaming Chen, Jiaqi Wang and Yaru Wei for their instruction.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- He X., P., Wang T.,Huang J. H.,Chen J.X.,Li J.D. Fabrication and characterization of superhydrophobic PDMS composite membranes for efficient ethanol recovery via pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalaparaju, A., Zhao X.S., Jiang J. W. Biofuel purification by pervaporation and vapor permeation in metal-organic frameworks: a computational study. ENERGY&ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE. 2011, 4, 2107–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R., van Baten J.M. Water/Alcohol Mixture Adsorption in Hydrophobic Materials: Enhanced Water Ingress Caused by Hydrogen Bonding. ACS Omega. 2020, 5, 28393–28402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovau, S., Gaykawad S.,Straathof A. J. J.,Van der Bruggen B. Influence of fermentation by-products on the purification of ethanol from water using pervaporation. Bioresource Technol. 2011, 102, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I., Pa N.F. C.,Nawawi M. G. M.,Rahman W. A. W. A. Modified Polydimethylsiloxane/Polystyrene Blended IPN Pervaporation Membrane for Ethanol/Water Separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 2666–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommu, A., Singh J.K. Separation of Ethanol and Water Using Graphene and Hexagonal Boron Nitride Slit Pores: A Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 7867–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PITT W. W., JR., HAAG G.L. Recovery of ethanol from fermentation broths using selective sorption-desorption. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1983, 25, 123–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lively R., P., Dose M.E.,Thompson J. A.,McCool B. A.,Chance R. R.,Koros W. J. Ethanol and water adsorption in methanol-derived ZIF-71. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 8667–8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., Huang H.,Chang Y.,Zhong C. Integrated High Water Affinity and Size Exclusion Effect on Robust Cu-Based Metal-Organic Framework for Efficient Ethanol-Water Separation. ACS SUSTAINABLE CHEMISTRY & ENGINEERING. 2021, 9, 3195–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeJaco R., F., Dorneles de Mello M.,Nguyen H. G. T.,Jeon M. Y.,van Zee R. D.,Tsapatsis M.,Siepmann J. I. Modeling and simulation of gas separations with spiral-wound membranes. AIChE Journal. 2020, 66, e16868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousin-Saint-Remi, J., Denayer J.F.M. Applying the wave theory to fixed-bed dynamics of Metal-Organic Frameworks exhibiting stepped adsorption isotherms: Water/ethanol separation on ZIF-8. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 324, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado J., A., Agueda V.I.,Uguina M. A.,Sotelo J. L.,Garcia A.,Brea P.,Garcia-Sanz A. Separation of ethanol-water liquid mixtures by on a polymeric resin Sepabeads 207®. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winarto, Yamamoto E., Yasuoka K. Integrated High Water Affinity and Size Exclusion Effect on Robust Cu-Based Metal–Organic Framework for Efficient Ethanol–Water Separation. ACS SUSTAINABLE CHEMISTRY & ENGINEERING. 2021, 9, 3195–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C., Lu X.,Wang Z. Effects of sodium ions on the separation performance of pure-silica MFI zeolite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalaparaju, A., Zhao X.S.,Jiang J. W. Molecular Understanding for the Adsorption of Water and Alcohols in Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Zeolitic Metal-Organic Frameworks. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2010, 114, 11542–11550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima G., F., Mavrandonakis A.,de Abreu H. A.,Duarte H. A.,Heine T. Mechanism of Alcohol-Water Separation in Metal-Organic Frameworks. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2013, 117, 4124–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic. Z S., Hong. D, Javni. I, Erina. N, Zhang. F, Ilavsky. J. Phase structure in segmented polyurethanes having fatty acid-based soft segments. POLYMER. 2013, 54, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T., Chen B. Facile Fabrication of Porous Conductive Thermoplastic Polyurethane Nanocomposite Films via Solution Casting. SCIENTIFIC REPORTS. 2017, 7, 17470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong H., P., Qiu J.H.,Yu S. H. Thermoresponsive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/Graphene/Au Nanocomposite Hydrogel for Water Treatment by a Laser-Assisted Approach. SMALL. 2015, 11, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, S., Krause P.,Tabaka W. Combined Cononsolvency and Temperature Effects on Adsorbed PNIPAM Microgels. Langmuir. 2017, 33, 14296–14277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N., Ru G.,Wang L.,Feng, J. 1H MAS NMR Studies of the Phase Separation of Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) Gel in Binary Solvents. Langmuir. 2009, 25, 5898–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, R., Wei J.,Jiang L., Simon G. P.,Wang H. Robust Thermoresponsive Polymer Composite Membrane with Switchable Superhydrophilicity and Superhydrophobicity for Efficient Oil-Water Separation. Environmental Science & Technology. 2016, 50, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang C., H., Bai P.,Siepmann I.,Clark A. E.,J. Deconstructing Hydrogen-Bond Networks in Confined Nanoporous Materials: Implications for Alcohol-Water Separation. Phys. Chem. C. 2014, 118, 19723–19732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeJaco R., F., Dorneles de Mello M.,Nguyen H. G. T.,Jeon M. Y.,van Zee R. D.,Tsapatsis M.,Siepmann J. I. Modeling and simulation of gas separations with spiral-wound membranes. AIChE Journal. 2020, 66, e16868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H., Tanaka F. Reentrant volume phase transition of cross-linked poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gels in mixed solvents of water/methanol. SOFT MATTER. 2012, 8, 3010–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu B., L., Wang J.,Ru G. Y.,Liu C. Y.,Feng J. W. Phase Transition and Preferential Alcohol Adsorption of Poly(N,N-diethylacrylamide) Gel in Water/Alcohol Mixtures. MACROMOLECULES. 2015, 48, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).