Submitted:
05 March 2024
Posted:
06 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction - Motivation for This Review
2. Autoinflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases
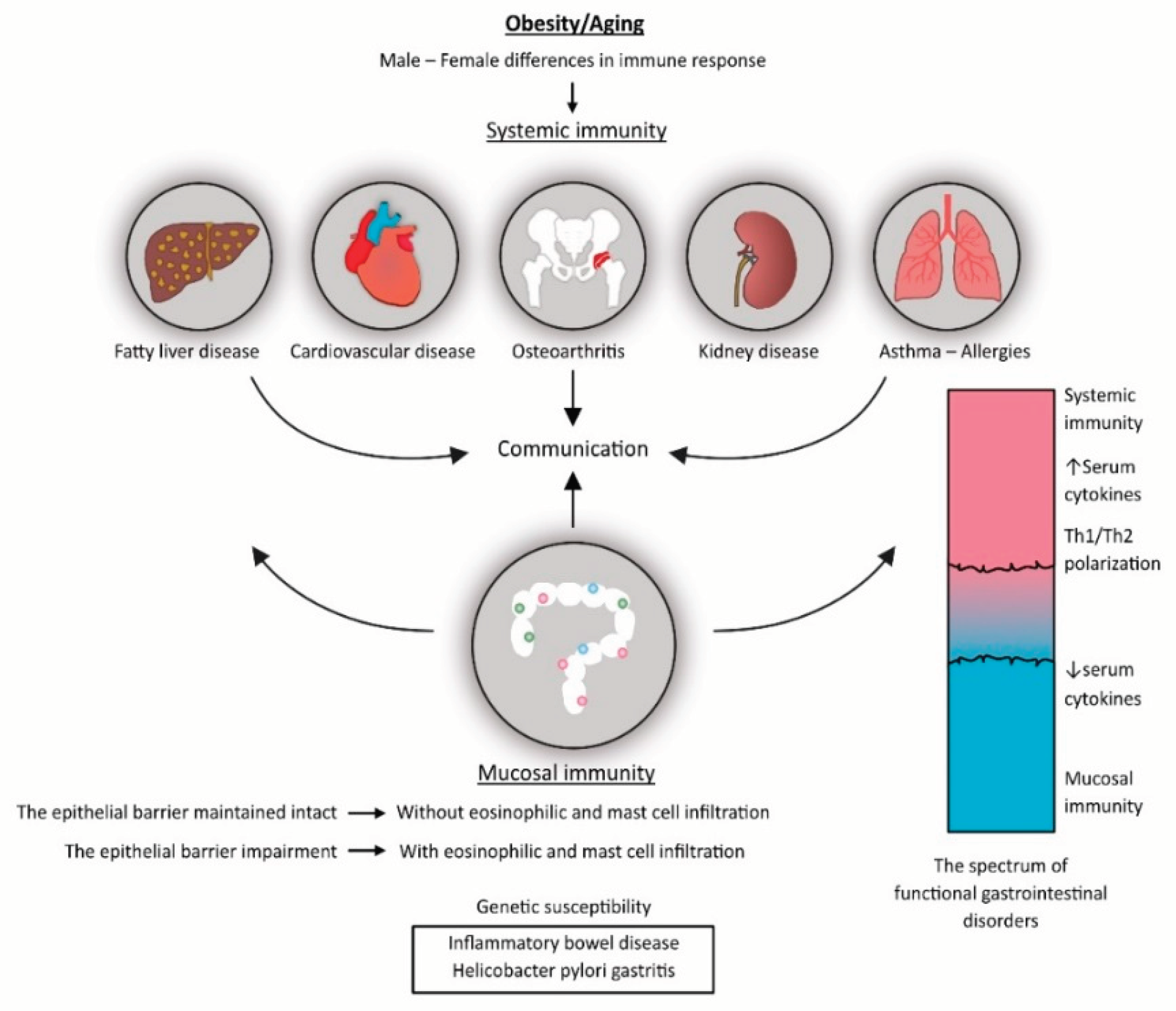
3. The Role of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Other Chronic Diseases
4. Inflammation Is the Vital Tissue and the Whole Body`s Reaction
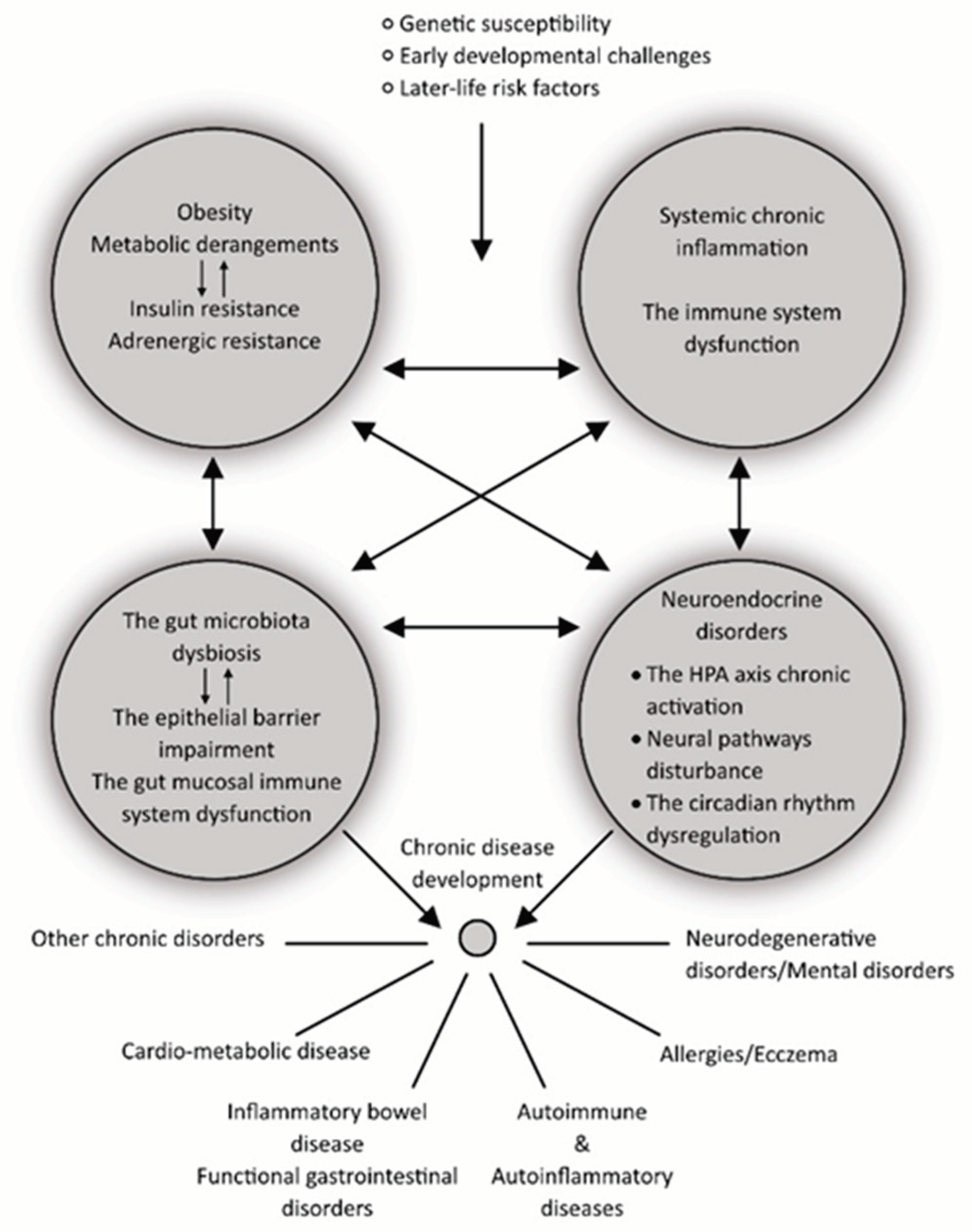
5. An Interplay between the Neuroendocrine, Immune, and Metabolic Pathways in Aging and Obesity, as a Driver of Chronic Disease Development
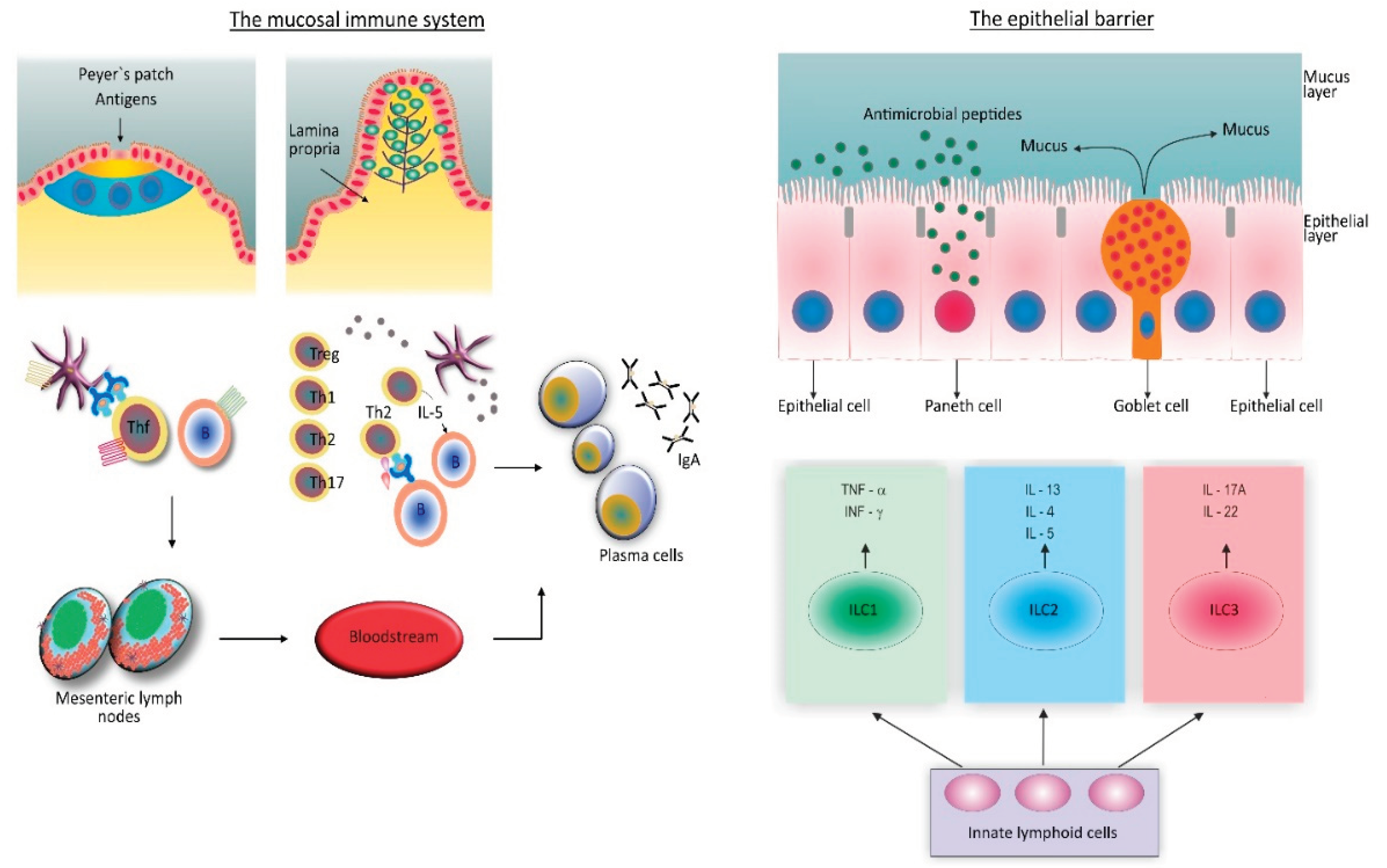
6. The Role of the Gut Microbiome and the Gut Mucosal Immune System in Chronic Disease Development
7. Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
8. Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders with Inflammation in the Background (PI-IBS and EoE)
9. Proofs That Inflammation Is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Functional Dyspepsia
10. Proofs That Inflammation Is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
11. Discussion
12. Future Perspectives
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IBD | inflammatory bowel diseases |
| UC | ulcerative colitis |
| CD | Chron's disease |
| HP | Helicobacter pylori |
| FGID's | functional gastrointestinal disorders |
| IBS | irritable bowel syndrome |
| FD | functional dyspepsia |
| Treg cells | regulatory T cells |
| Teff cells | effector T cells |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| DCs | dendritic cells |
| NK cells | natural killer cells |
| Th1 cells | T helper cells type 1 |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor-β |
| T2D | type 2 diabetes |
| CVD | cardiovascular diseases |
| HPA | hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal |
| ILC1 | innate lymphoid cells type 1 |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharides |
| SCFA | short-chain fatty acids |
| BCFA | branched-chain amino acids |
| IgA | immunolobulin A |
| FDCs | follicular dendritic cells |
| Thf cells | follicular Th cells |
| PDS | postprandial distress syndrome |
| EPS | epigastric pain syndrome |
| PI-IBS | post-infection irritable bowel syndrome |
| 5-HT | 5-hydroxytryptamine |
| Th17 | T-helper 17 |
| EoE | eosinophilic esophagitis |
| ILC3 | innate lymphoid type 3 cells |
| CRH | corticotropin-releasing hormone |
| HIF | hypoxia-inducible factor |
| CRF | corticotropin-releasing factor |
| TSLP | thymic stromal lymphoprotein |
| iNKT cells | invariant natural killer T cells |
| Th2 | T-helper 2 |
| ILC2 | innate lymphoid type 2 cells |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| LBP | lipopolysaccharide binding protein |
| IFABP | intestinal fatty acid binding protein |
References
- Lu, Q.; Yang, M.F.; Liang, Y.J.; Xu, J.; Xu, H.M.; Nie, Y.Q.; Wang, L.S.; Yao, J.; Li, D.F. Immunology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutics. J Inflamm Res. 2022, 15, 1825–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusters, J.G.; van Vliet, A.H.; Kuipers, E.J. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006, 19(3), 449–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drossman, D.A. Functional gastrointestinal disorders: history, pathophysiology, clinical features and Rome IV. Gastroenterol. 2016, 150, 1262–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drossman, D.A.; Tack, J. Rome Foundation Clinical Diagnostic Criteria for Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction. Gastroenterol. 2022, 162(3), 675–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Singh, R.; Ro, S.; Ghoshal, U.C. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in functional gastrointestinal disorders: Underpinning the symptoms and pathophysiology. JGH Open. 2021, 5, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann Gastroenterol. 2015, 28(2), 203–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foster, J.A.; McVey Neufeld, K.A. Gut-brain axis: How the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 305–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oudenhove, L.; Crowell, M.D.; Drossman, D.A.; Halpert, A.D.; Keefer, L.; Lackner, J.M.; Murphy, T.B.; Naliboff, B.D.; Levy, RL. Biopsychosocial Aspects of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Gastroenterol. 2016:S0016-5085(16)00218-3. [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, D.; Su, Q.; Shi, J. The role of inflammation in autoimmune disease: a therapeutic target. Front Immunol. 2023, 14, 1267091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szekanecz, Z.; McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G.; Szamosi, S.; Benkő, S.; Szűcs, G. Autoinflammation and autoimmunity across rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021, 17(10), 585–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Bourla, A.B.; Kastner, D.L.; Colbert, R.A.; Siegel, R.M. Lighting the fires within: the cell biology of autoinflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012, 12(8), 570–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, M.D.; Remedios, K.A.; Abbas, A.K. Mechanisms of human autoimmunity. J Clin Invest 2015, 125(6), 2228–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jörg, S.; Grohme, D.A.; Erzler, M.; Binsfeld, M.; Haghikia, A.; Müller, D.N.; Linker, R.A.; Kleinewietfeld, M. Environmental factors in autoimmune diseases and their role in multiple sclerosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4611–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Villar, M.; Hafler, D.A. Regulatory T cells in autoimmune disease. Nat Immunol. 2018, 19(7), 665–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, G.; Vera-Lastra, O.; Peralta-Amaro, A.L.; Jiménez-Arellano, M.P.; Saavedra, M.A.; Cruz-Domínguez, M.P.; Jara, LJ. Metabolic syndrome, autoimmunity and rheumatic diseases. Pharmacol Res. 2018, 133, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrich, C.M. Shaping the spectrum - From autoinflammation to autoimmunity. Clin Immunol. 2016, 165, 21–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 17. Greuter, T, Vavricka, S.R. Extraintestinal manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease – epidemiology, genetics, and pathogenesis. Exp Rev of Gastroenterol & Hepatol 2019, 13(4), 307–17. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Antony, V.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Liang, G. Pattern recognition receptor-mediated inflammation in diabetic vascular complications. Med Res Rev. 2020, 40(6), 2466–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderrazak, A.; Syrovets, T.; Couchie, D.; El Hadri, K.; Friguet, B.; Simmet, T.; Rouis, M. NLRP3 inflammasome: From a danger signal sensor to a regulatory node of oxidative stress and inflammatory diseases. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghilardi, N.; Ouyang, W. Targeting the development and effector functions of TH17 cells. Semin Immunol. 2007, 19(6), 383–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Neutrophils in tissue injury and repair. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 371(3), 531–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trtica Majnarić, L.; Guljaš, S.; Bosnić, Z.; Šerić, V.; Wittlinger, T. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Cardiovascular Risk Marker May Be Less Efficient in Women Than in Men. Biomol. 2021, 11(4), 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinewietfeld, M.; Hafler, D.A. The plasticity of human Treg and Th17 cells and its role in autoimmunity. Semin Immunol. 2013, 25(4), 305–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, C.D. Anatomy of a discovery: M1 and M2 macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzhitov, R. The spectrum of inflammatory responses. Science. 2021, 374(6571), 1070–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, L.C.; Artis, D. Beyond Host Defense: Emerging Functions of the Immune System in Regulating Complex Tissue Physiology. Cell. 2018, 173(3), 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.M.; Reeves, G.; Billman, G.E.; Sturmberg, J.P. Inflammation-Nature's Way to Efficiently Respond to All Types of Challenges: Implications for Understanding and Managing "the Epidemic" of Chronic Diseases. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018, 5, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat Med. 2019, 25(12), 1822–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R.; Schneider, D.S.; Soares, M.P. Disease tolerance as a defense strategy. Science. 2012, 335(6071), 936–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fava, G.A.; McEwen, B.S.; Guidi, J.; Gostoli, S.; Offidani, E.; Sonino, N. Clinical characterization of allostatic overload. Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2019, 108, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Bonafè, M.; Valensin, S.; Olivieri, F.; De Luca, M.; Ottaviani, E.; De Benedictis, G. Inflamm-aging: An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 908, 244–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Salvioli, S.; Garagnani, P.; de Eguileor, M.; Monti, D.; Capri, M. Immunobiography and the Heterogeneity of Immune Responses in the Elderly: A Focus on Inflammaging and Trained Immunity. Front Immunol. 2017, 8, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Morsiani, C.; Conte, M.; Santoro, A.; Grignolio, A.; Monti, D.; Capri, M.; Salvioli, S. The Continuum of Aging and Age-Related Diseases: Common Mechanisms but Different Rates. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straub, R.H.; Cutolo, M.; Buttgereit, F.; Pongratz, G. Energy regulation and neuroendocrine-immune control in chronic inflammatory diseases. J Intern Med. 2010, 267(6), 543–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, S.M.; Saltiel, A.R. Adapting to obesity with adipose tissue inflammation. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017, 13(11), 633–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andolfi, C.; Fisichella, P.M. Epidemiology of obesity and associated comorbidities. J Laparoendoscopic Adv Surg Techniq A. 2018, 28, 919–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedunchezhiyan, U.; Varughese, I.; Sun, A.R.; Wu, X.; Crawford, R.; Prasadam, I. Obesity, Inflammation, and Immune System in Osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 2022, 13, 907750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsatsoulis, A.; Paschou, S.A. Metabolically Healthy Obesity: Criteria, Epidemiology, Controversies, and Consequences. Curr Obes Rep. 2020, 9(2), 109–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, S.A., Pasquarelli-do-Nascimento, G., da Silva, D. Farias, G.R.; de Oliveira Santos, I.; Baptista, L.B.; Magalhães, K.G. Browning of the white adipose tissue regulation: new insights into nutritional and metabolic relevance in health and diseases. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2022, 19(1), 61. [CrossRef]
- Razeghian-Jahromi, I.; Karimi Akhormeh, A.; Razmkhah, M.; Zibaeenezhad, M.J. Immune system and atherosclerosis: Hostile or friendly relationship. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2022, 36, 3946320221092188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.; Mulvagh, S.L.; Merz, C.N.; Buring, J.E.; Manson, J.E. Cardiovascular Disease in Women: Clinical Perspectives. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1273–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, A.; Valdes, A.M. Role of the gut microbiome in chronic diseases: a narrative review. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2022, 76(4), 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.Z.; Zhu, L.B.; Li, Z.R.; Lin, J. Bacterial colonization and intestinal mucosal barrier development. World J Clin Pediatr. 2013, 2(4), 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Are we really vastly outnumbered? revisiting the ratio of bacterial to host cells in humans. Cell 2016, 164, 337–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, M.E.; Shi, H.N.; Walker, W.A. The long-term health effects of neonatal microbial flora. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009, 9, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res. 2020, 30(6), 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrncir, T. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis: Triggers, Consequences, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Options. Microorganisms. 2022, 10(3), 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlechte, J.; Skalosky, I.; Geuking, M.B.; McDonald, B. Long-distance relationships - regulation of systemic host defense against infections by the gut microbiota. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 809–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cong, Y. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites in the regulation of host immune responses and immune-related inflammatory diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021, 18(4), 866–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, M.J.; Ganta, C.K. Autonomic nervous system and immune system interactions. Compr Physiol. 2014, 4(3), 1177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, N.; Lécuyer, E.; Chassaing, B. Host/microbiota interactions in health and diseases—Time for mucosal microbiology! Mucosal Immunol. 2021, 14, 1006–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGhee, J.R.; Fujihashi, K. Inside the mucosal immune system. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10(9), e1001397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, D.B.; Fagarasan, S. IgA synthesis: a form of functional immune adaptation extending beyond gut. Curr Opin Immunol. 2012, 24(3), 261–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stebegg, M.; Kumar, S.D.; Silva-Cayetano, A.; Fonseca, V.R.; Linterman, M.A.; Graca, L. Regulation of the Germinal Center Response. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, G.; Pryor, J.; Holtmann, G.; Walker, M.M.; Talley, N.J.; Keely, S. Immune Activation in Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Gastroenterol Hepatol (NY). 2019, 15(10), 539–48. [Google Scholar]
- Sperber, A.D.; Bangdiwala, S.I.; Drossman, D.A.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Simren, M.; Tack, J.; Whitehead, W.E.; Dumitrascu, D.L.; Fang, X.; Fukudo, S.; et al. Worldwide Prevalence and Burden of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders, Results of Rome Foundation Global Study. Gastroenterology 2021, 160(1), 99–114.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hari, S.; Burns, G.L.; Hoedt, E.C.; Keely, S.; Talley, N.J. Eosinophils, Hypoxia-Inducible Factors, and Barrier Dysfunction in Functional Dyspepsia. Front Allergy. 2022, 3, 851482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouters, M.M.; Vicario, M.; Santos, J. The role of mast cells in functional GI disorders. Gut. 2016, 65(1), 155–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, C.J.; Drossman, D.A.; Talley, N.J.; Ruddy, J.; Ford, A.C. Functional gastrointestinal disorders: advances in understanding and management. Lancet. 2020, 396, 1664–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, T. Functional Dyspepsia: Current Understanding and Future Perspective. Digestion. 2024, 105(1), 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanghellini, V.; Chan, F.K.; Hasler, W.L.; Malagelada, J.R.; Suzuki, H.; Tack, J.; Talley, N.J. Gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016, 150(6), 1380–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Houte, K.; Carbone, F.; Goelen, N.; Schol, J.; Masuy, I.; Arts, J.; Caenepeel, P.; Staessen, D.; Vergauwe, P.; Van Roey, G.; et al. Effects of Rome IV Definitions of Functional Dyspepsia Subgroups in Secondary Care. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021, 19(8), 1620–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, R.D.; Johnson, A.C.; O'Mahony, S.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Cryan, J.F. Stress and the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Visceral Pain: Relevance to Irritable Bowel Syndrome. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016, 22(2), 102–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, G.; Carroll, G.; Mathe, A.; Horvat, J.; Foster, P.; Walker, M.M.; Talley, N.J.; Keely, S. Evidence for Local and Systemic Immune Activation in Functional Dyspepsia and the Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019, 114(3), 429–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Q.X.; Soh, A.Y.S.; Loke, W.; Lim, D.Y.; Yeo, W.S. The role of inflammation in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). J Inflamm Res. 2018, 11, 345–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazaridis, N.; Germanidis, G. Current insights into the innate immune system dysfunction in irritable bowel syndrome. Ann Gastroenterol. 2018, 31(2), 171–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berumen, A.; Edwinson, A.L.; Grover, M. Post-infection Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2021, 50(2), 445–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klem, F.; Wadhwa, A.; Prokop, L.J.; Sundt, W.J.; Farrugia, G.; Camilleri, M.; Singh, S.; Grover, M. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Irritable Bowel Syndrome After Infectious Enteritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterol 2017, 152(5), 1042–54.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carco, C.; Young, W.; Gearry, R.B.; Talley, N.J.; McNabb, W.C.; Roy, N.C. Increasing Evidence That Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Have a Microbial Pathogenesis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020, 10, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barman, M.; Unold, D.; Shifley, K.; Amir, E.; Hung, K.; Bos, N.; Salzman, N. Enteric salmonellosis disrupts the microbial ecology of the murine gastrointestinal tract. Infect Immun. 2008, 76(3), 907–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalanka, J.; Salonen, A.; Fuentes, S.; de Vos, W.M. Microbial signatures in post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome--toward patient stratification for improved diagnostics and treatment. Gut Microbes. 2015, 6(6), 364–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fang, X. Inflammation and Overlap of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Functional Dyspepsia. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021, 27(2), 153–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, V.V.; Ghiciuc, C.M.; Stefanescu, G.; Mihai, C.M.; Popp, A.; Sasaran, M.O.; Bozomitu, L.; Starcea, I.M.; Adam Raileanu, A.; Lupu, A. Emerging role of the gut microbiome in post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome: A literature review. World J Gastroenterol. 2023, 29(21), 3241–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.; Biglari, M.; Nasseri Moghaddam, S. Post-infectious Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Middle East J Dig Dis. 2019, 11(2), 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Z. Imbalanced shift of cytokine expression between T helper 1 and T helper 2 (Th1/Th2) in intestinal mucosa of patients with post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Winter, B.Y.; van den Wijngaard, R.M.; de Jonge, WJ. Intestinal mast cells in gut inflammation and motility disturbances. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012, 1822(1), 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.W.; Ma, Z.C.; Fu, J.; Huang, B.L.; Liu, F.J.; Sun, D.; Lan, C. Upregulated adenosine 2A receptor accelerates post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome by promoting CD4+ T cells' T helper 17 polarization. World J Gastroenterol. 2022, 28(25), 2955–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Kim, H.P.; Sperry, S.L.; Rybnicek, D.A.; Woosley, J.T.; Shaheen, N.J. A phenotypic analysis shows that eosinophilic esophagitis is a progressive fibrostenotic disease. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 79, 577–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racca, F.; Pellegatta, G.; Cataldo, G.; Vespa, E.; Carlani, E.; Pelaia, C.; Paoletti, G.; Messina, M.R.; Nappi, E.; Canonica, G.W.; et al. Type 2 Inflammation in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Targets. Front Physiol. 2022, 12, 815842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, D.; Marella, S.; Idelman, G.; Chang, J.W.; Chehade, M.; Hogan, S.P. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Immune mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Clin Exp Allergy. 2022, 52(10), 1142–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, Á.; Lucendo, A.J. Molecular basis and cellular mechanisms of eosinophilic esophagitis for the clinical practice. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019, 13(2), 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wąsik, J.; Małecka-Wojciesko, E. Eosinophilic Esophagitis—What Do We Know So Far? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023, 12(6), 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Shea, K.M.; Aceves, S.S.; Dellon, E.S.; Gupta, S.K.; Spergel, J.M.; Furuta, G.T.; Rothenberg, M.E. Pathophysiology of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterol. 2018, 154(2), 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, M.A.M.; Akhter, S.; Khan, M.R.; Saha, M.; Roy, P.K. Association of duodenal eosinophilia with Helicobacter pylori-negative functional dyspepsia. Arab J Gastroenterol. 2020, 21(1), 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.P.; Holck, S.; Janulaityte-Günther, D.; Kupcinskas, L.; Kiudelis, G.; Jonaitis, L.; Janciauskas, D.; Holck, P.; Bennedsen, M.; Permin, H.; et al. Gastric inflammatory markers and interleukins in patients with functional dyspepsia, with and without Helicobacter pylori infection. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2005, 44(2), 233–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Fairlie, T.; Brown, G.; Jones, M.P.; Eslick, G.D.; Duncanson, K.; Thapar, N.; Keely, S.; Koloski, N.; Shahi, M.; et al. Duodenal Eosinophils and Mast Cells in Functional Dyspepsia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022, 20(10), 2229–42.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eladham, M.W.; Selvakumar, B.; Saheb Sharif-Askari, N.; Saheb Sharif-Askari, F.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Halwani, R. Unraveling the gut-Lung axis: Exploring complex mechanisms in disease interplay. Heliyon. 2024, 10(1), e24032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuruvilla, M.E.; Lee, F.E.; Lee, G.B. Understanding Asthma Phenotypes, Endotypes, and Mechanisms of Disease. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019, 56(2), 219–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceulemans, M.; Jacobs, I.; Wauters, L.; Vanuytsel, T. Immune Activation in Functional Dyspepsia: Bystander Becoming the Suspect. Front Neurosci. 2022, 16, 831761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennet, S.M.; Polster, A.; Törnblom, H.; Isaksson, S.; Capronnier, S.; Tessier, A.; Le Nevé, B.; Simrén, M.; Öhman, L. Global Cytokine Profiles and Association With Clinical Characteristics in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016, 111(8), 1165–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goral, V.; Kucukoner, M.; Buyukbayram, H. Mast cells count and serum cytokine levels in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Hepatogastroenterol. 2010, 57(101), 751–4. [Google Scholar]
- Seyedmirzaee, S.; Hayatbakhsh, M.M.; Ahmadi, B.; Baniasadi, N.; Bagheri Rafsanjani, A.M.; Nikpoor, A.R.; Mohammadi, M. Serum immune biomarkers in irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2016, 40(5), 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, P.; Shoaie, S.; Nielsen, L.K. Irritable bowel syndrome and microbiome; Switching from conventional diagnosis and therapies to personalized interventions. J Transl Med. 2022, 20(1), 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkin, V.; Poluektov, Y.; Kogan, E.; Shifrin, O.; Sheptulin, A.; Kovaleva, A.; Kurbatova, A.; Krasnov, G.; Poluektova, E. Disruption of the pro-inflammatory, anti-inflammatory cytokines and tight junction proteins expression, associated with changes of the composition of the gut microbiota in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. PLoS One. 2021, 16(6), e0252930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, S.R.; Skvarc, D.; Ford, A.C.; Palsson, O.S.; Bangdiwala, S.I.; Sperber, A.D.; Mikocka-Walus, A. Negative Impact of Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction on Health-Related Quality of Life: Results From the Rome Foundation Global Epidemiology Survey. Gastroenterol. 2023, 164(4), 655–8.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, L.M.; Rosmalen, J.G. Dysfunction of stress responsive systems as a risk factor for functional somatic syndromes. J Psychosom Res. 2010, 68(5), 461–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Skoluda, N.; Ali, N.; Nater, U.M.; Mewes, R. Hair cortisol levels in women with medically unexplained symptoms. J Psychiatr Res. 2022, 146, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawbridge, R.; Sartor, M.L.; Scott, F.; Cleare, A.J. Inflammatory proteins are altered in chronic fatigue syndrome-A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019, 107, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashashati, M.; Moradi, M.; Sarosiek, I. Interleukin-6 in irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of IL-6 (-G174C) and circulating IL-6 levels. Cytokine. 2017, 99, 132–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamp, K.J.; Han, C.; Shulman, R.J.; Cain, K.C.; Barney, P.; Opp, M.R.; Chang, L.; Burr, R.L.; Heitkemper, M.M. Cytokine Levels and Symptoms Among Women with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Considering the Role of Hormonal Contraceptive Use. Biological Research For Nursing. 2021, 23(2), 171–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finlay, S.; Rudd, D.; McDermott, B.; Sarnyai, Z. Allostatic load and systemic comorbidities in psychiatric disorders. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2022, 140, 105726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafaei, S.; Kabir, K.; Kazemnejad, A.; Feizi, A.; Mansourian, M.; Hassanzadeh Keshteli, A.; Afshar, H.; Arzaghi, S.M.; Rasekhi Dehkordi, S.; Adibi, P.; et al. Explanation of somatic symptoms by mental health and personality traits: application of Bayesian regularized quantile regression in a large population study. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19(1), 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouillet, J.Z.; Boltri, M.; Lengvenyte, A.; Lajnef, M.; Richard, J.R.; Barrau, C.; Strumila, R.; Coyac, M.; Wu, C.L.; Boukouaci, W.; et al. Association of markers of inflammation and intestinal permeability in suicidal patients with major mood disorders. Journal of Affective Disorders Reports. 2023, 14, 100624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volarić, M.; Šojat, D.; Majnarić, L.T.; Vučić, D. The Association between Functional Dyspepsia and Metabolic Syndrome—The State of the Art. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2024, 21, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murni, A.W.; Darwin, E.; Zubir, N.; Nurdin, A.E. Analyzing Determinant Factors for Pathophysiology of Functional Dyspepsia Based on Plasma Cortisol Levels, IL-6 and IL-8 Expressions and H. pylori Activity. Acta Med Indones. 2018, 50(1), 38–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Konturek, P.C.; Brzozowski, T.; Konturek, S.J. Stress and the gut: pathophysiology, clinical consequences, diagnostic approach, and treatment options. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011, 62(6), 591–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, I.; Ceulemans, M.; Wauters, L.; Breynaert, C.; Vermeire, S.; Verstockt, B.; Vanuytsel, T. Role of Eosinophils in Intestinal Inflammation and Fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Overlooked Villain? Front Immunol. 2021, 12, 754413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wauters, L.; Burns, G.; Ceulemans, M.; Walker, M.M.; Vanuytsel, T.; Keely, S.; Talley, NJ. Duodenal inflammation: an emerging target for functional dyspepsia? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020, 24(6), 511–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robida, P.A.; Puzzovio, P.G.; Pahima, H.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Bochner, B.S. Human eosinophils and mast cells: Birds of a feather flock together. Immunol Rev. 2018, 282(1), 151–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, N.; Walker, M.M.; Talley, N.J. Gastrointestinal eosinophils in health, disease and functional disorders. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010, 7(3), 146–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinicola, B.L.; Pulvirenti, F.; Capponi, M.; Bonetti, M.; Brindisi, G.; Gori, A.; De Castro, G.; Anania, C.; Duse, M.; Zicari, A.M. Selective IgA Deficiency and Allergy: A Fresh Look to an Old Story. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022, 58(1), 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odineal, D.D.; Gershwin, M.E. The epidemiology and clinical manifestations of autoimmunity in selective IgA deficiency. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2020, 58, 107–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, C.A.; Neilan, N.A.; Schurman, J.V.; Taylor, D.L.; Kearns, G.L.; Abdel-Rahman, S.M. Montelukast in the treatment of duodenal eosinophilia in children with dyspepsia: effect on eosinophil density and activation in relation to pharmacokinetics. BMC Gastroenterol. 2009, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartuzi, Z.; Zbikowska-Gotz, M.; Romański, B.; Sinkiewicz, W. Evaluating the profile of selected cytokines in patients with food allergy and chronic gastritis. Med Sci Monit. 2000, 6(6), 1128–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Camargo, M.C.; El-Omar, E.; Liou, J.M.; Peek, R.; Schulz, C.; Smith, S.I.; Suerbaum, S. Helicobacter pylori infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2023, 9(1), 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andoh, A.; Nishida, A- Alteration of the Gut Microbiome in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Digestion. 2023, 104(1), 16–23. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittayanon, R.; Lau, J.T.; Yuan, Y.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Tse, F.; Surette, M.; Moayyedi, P. Gut Microbiota in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome-A Systematic Review. Gastroenterol. 2019, 157(1), 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermes, G.D.A.; Reijnders, D.; Kootte, R.S.; Goossens, G.H.; Smidt, H.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Blaak, E.E.; Zoetendal, E.G. Individual and cohort-specific gut microbiota patterns associated with tissue-specific insulin sensitivity in overweight and obese males. Sci Rep. 2020, 10(1), 7523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Rijnaarts, I.; Hermes, G.D.A.; de Roos, N.M.; Witteman, B.J.M.; de Wit, N.J.W.; Govers, C.; Smidt, H.; Zoetendal, E.G. Fecal Microbiota Signatures Are Not Consistently Related to Symptom Severity in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 2022, 67(11), 5137–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matenchuk, B.A.; Mandhane, P.J.; Kozyrskyj, A.L. Sleep, circadian rhythm, and gut microbiota. Sleep Med Rev. 2020, 53, 101340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanuytsel, T.; Bercik, P.; Boeckxstaens, G. Understanding neuroimmune interactions in disorders of gut-brain interaction: from functional to immune-mediated disorders. Gut. 2023, 72(4), 787–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatino, A.; Regolisti, G.; Brusasco, I.; Cabassi, A.; Morabito, S.; Fiaccadori, E. Alterations of intestinal barrier and microbiota in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015, 30(6), 924–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




