Submitted:
05 March 2024
Posted:
06 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Participants
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Metabolic Syndrome Defining Condition
2.4. DNA Extraction
2.5. Genotyping
2.6. Laboratory Analysis and Cytokine Dosage
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. IL-10 and IL-1β Serum Concentrations’ Associations with Hematological, Biochemical, and Anthropometric Measurements
3.2. Participants’ Serum IL-10 and IL-1β Levels and Other Clinical Signs and Symptoms
3.3. IL-10 and IL-1β Gene Polymorphisms’ Genotype Frequency Distribution and Their Relationship with Their Serum Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística Projeções Da População | IBGE Censo 2022: Número de Pessoas Com 65 Anos Ou Mais de Idade Cresceu 57,4% Em 12 Anos.
- Vasconcelos, A.M.N.; Gomes, M.M.F. Transição Demográfica: A Experiência Brasileira. Epidemiologia e Serviços de Saúde 2012, 21, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, R.E. The Epidemiologic Transition: Changing Patterns of Mortality and Population Dynamics. Am J Lifestyle Med 2009, 3, 19S–26S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, A.M.N.; Gomes, M.M.F. Transição Demográfica: A Experiência Brasileira. Epidemiologia e Serviços de Saúde 2012, 21, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires Brandão, A.; Araújo Brandão, A.; da Rocha Nogueira, A.; Suplicy, H.; Ilha Guimarães, J.; de Oliveira, J.E.P. I Diretriz Brasileira de Diagnóstico e Tratamento Da Síndrome Metabólica. Arq Bras Cardiol 2005, 84, 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, R.; Santos, A.J.; Kislaya, I.; Nunes, B.; Freire, A.C. Síndrome Metabólica Em Portugal: Prevalência e Fatores Associados. Acta Med Port 2022, 35, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahed, G.; Aoun, L.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Allam, S.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Bouferraa, Y.; Assi, H.I. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simão, A.; Precoma, D.; Andrade, J.; Correa Filho, H.; Saraiva, J.; Oliveira, G.; Murro, A.; Campos, A.; Alessi, A.; Avezum Junior, A.; et al. I Diretriz Brasileira de Prevenção Cardiovascular. Arq Bras Cardiol 2013, 101, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J. A Comprehensive Review on Metabolic Syndrome. Cardiol Res Pract 2014, 2014, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuolo, J.; Gliozzi, M.; Musolino, V.; Carresi, C.; Scarano, F.; Nucera, S.; Scicchitano, M.; Bosco, F.; Ruga, S.; Zito, M.C.; et al. From Metabolic Syndrome to Neurological Diseases: Role of Autophagy. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandl, G.; Wolfrum, C. Hemostasis, Endothelial Stress, Inflammation, and the Metabolic Syndrome. Semin Immunopathol 2018, 40, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Aggarwal, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Inflammation, a Double-Edge Sword for Cancer and Other Age-Related Diseases. Front Immunol 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppack, S.W. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Adipose Tissue. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 2001, 60, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maintinguer Norde, M.; Oki, E.; Ferreira Carioca, A.A.; Teixeira Damasceno, N.R.; Fisberg, R.M.; Lobo Marchioni, D.M.; Rogero, M.M. Influence of IL1B, IL6 and IL10 Gene Variants and Plasma Fatty Acid Interaction on Metabolic Syndrome Risk in a Cross-Sectional Population-Based Study. Clinical Nutrition 2018, 37, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Higashimori, T.; Park, S.-Y.; Choi, H.; Dong, J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Noh, H.-L.; Cho, Y.-R.; Cline, G.; Kim, Y.-B.; et al. Differential Effects of Interleukin-6 and -10 on Skeletal Muscle and Liver Insulin Action In Vivo. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Y.; Bu, L.; Yan, L.; Liu, D. Hydrodynamic Delivery of MIL10 Gene Protects Mice From High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Glucose Intolerance. Molecular Therapy 2013, 21, 1852–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, K.; Pontillo, A.; Giugliano, F.; Giugliano, G.; Marfella, R.; Nicoletti, G.; Giugliano, D. Association of Low Interleukin-10 Levels with the Metabolic Syndrome in Obese Women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Yin, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Xiao, Y. IL-10/STAT3 Is Reduced in Childhood Obesity with Hypertriglyceridemia and Is Related to Triglyceride Level in Diet-Induced Obese Rats. BMC Endocr Disord 2018, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.-L.; Zhao, S.-J.; Lin, X.-X.; Liao, A.-H. IL-10: A Bridge between Immune Cells and Metabolism during Pregnancy. J Reprod Immunol 2022, 154, 103750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, A.G.; Skadow, M.H.; Qu, R.; Oh, J.; Mowel, W.K.; Brewer, J.R.; Kaffe, E.; Williams, K.J.; Kluger, Y.; Crawford, J.M.; et al. IL-10 Constrains Sphingolipid Metabolism via Fatty Acid Desaturation to Limit Inflammation. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, A.L.V.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Haute, G.V.; Costa, B.P.; Pedrazza, L.; Donadio, M.V.F.; de Oliveira, J.R.; Bodanese, L.C. Association of IL-10 to Coronary Disease Severity in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Clinica Chimica Acta 2019, 495, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaMarche, N.M.; Kane, H.; Kohlgruber, A.C.; Dong, H.; Lynch, L.; Brenner, M.B. Distinct INKT Cell Populations Use IFNγ or ER Stress-Induced IL-10 to Control Adipose Tissue Homeostasis. Cell Metab 2020, 32, 243–258.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfadul, H.; Sabico, S.; Al-Daghri, N.M. The Role of Interleukin-1β in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuki, T.; Horai, R.; Sudo, K.; Iwakura, Y. IL-1 Plays an Important Role in Lipid Metabolism by Regulating Insulin Levels under Physiological Conditions. J Exp Med 2003, 198, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maedler, K.; Dharmadhikari, G.; Schumann, D.M.; Størling, J. Interleukin-Targeted Therapy for Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes. 2011; pp. 257–278. [Google Scholar]
- Netea, M.G.; Dinarello, C.A. More than Inflammation: Interleukin-1β Polymorphisms and the Lipid Metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011, 96, 1279–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedemann, S.J.; Trimigliozzi, K.; Dror, E.; Meier, D.T.; Molina-Tijeras, J.A.; Rachid, L.; Le Foll, C.; Magnan, C.; Schulze, F.; Stawiski, M.; et al. The Cephalic Phase of Insulin Release Is Modulated by IL-1β. Cell Metab 2022, 34, 991–1003.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballak, D.B.; Stienstra, R.; Tack, C.J.; Dinarello, C.A.; van Diepen, J.A. IL-1 Family Members in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Metabolic Disease: Focus on Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Insulin Resistance. Cytokine 2015, 75, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yin, Z.; Cao, S.; Gao, W.; Liu, L.; Yin, Y.; Liu, P.; Shu, Y. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Association between IL-1B Polymorphisms and Cancer Risk. PLoS One 2013, 8, e63654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.-M.; Liu, J.; Cao, X.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, X.-H.; Li, C.-J.; Dai, Z.-J.; Zhang, W.-G. Association Between Interleukin-10-3575T>A (Rs1800890) Polymorphism and Cancer Risk. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 2015, 19, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.; Vieira, P.; O’Garra, A. Biology and Therapeutic Potential of Interleukin-10. Journal of Experimental Medicine 2020, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, H.L.P. da A Reforma Da Saúde de Brasília, Brasil. Cien Saude Colet 2019, 24, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, N.; Tavira, B.; Hofwimmer, K.; Gutsmann, B.; Massier, L.; Abildgaard, J.; Juul, A.; Rydén, M.; Arner, P.; Laurencikiene, J. Sex-Specific Regulation of IL-10 Production in Human Adipose Tissue in Obesity. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.K. The Relationship Between IL-10 and Dislipidemia in Type 2 Diabetics. Al-Mustansiriyah Journal of Science 2011, 22, 202–213. [Google Scholar]
- Moraitis, A.G.; Freeman, L.A.; Shamburek, R.D.; Wesley, R.; Wilson, W.; Grant, C.M.; Price, S.; Demosky, S.; Thacker, S.G.; Zarzour, A.; et al. Elevated Interleukin-10: A New Cause of Dyslipidemia Leading to Severe HDL Deficiency. J Clin Lipidol 2015, 9, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, I.S.; Pereira, Í.S.; Santos, D.P.; Lopes, D.N.; Prado, A.O.; Calado, S.P.M.; Gonçalves, C. V.; Galantini, M.P.L.; Muniz, I.P.R.; Santos, G.S.; et al. Association between Body Composition and Inflammation: A Central Role of IL-17 and IL-10 in Diabetic and Hypertensive Elderly Women. Exp Gerontol 2019, 127, 110734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, J.R.; Tavira, B.; Douagi, I.; Kulyté, A.; Arner, P.; Rydén, M.; Laurencikiene, J. Human-Specific Function of IL-10 in Adipose Tissue Linked to Insulin Resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2019, 104, 4552–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M.; Fasshauer, M.; Tönjes, A.; Kratzsch, J.; Schön, M.; Paschke, R. Association of Interleukin-6, C-Reactive Protein, Interleukin-10 and Adiponectin Plasma Concentrations with Measures of Obesity, Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Metabolism. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes 2005, 113, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, A.S.; Daneshpour, M.S.; Akbarzadeh, M.; Hedayati, M.; Azizi, F.; Zarkesh, M. Association of Baseline and Changes in Adiponectin, Homocysteine, High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein, Interleukin-6, and Interleukin-10 Levels and Metabolic Syndrome Incidence: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, T.W.; Arnesen, H.; Seljeflot, I. Components of the Interleukin-6 Transsignalling System Are Associated with the Metabolic Syndrome, Endothelial Dysfunction and Arterial Stiffness. Metabolism 2013, 62, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira Rossi, J.L.; Barbalho, S.M.; Reverete de Araujo, R.; Bechara, M.D.; Sloan, K.P.; Sloan, L.A. Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Diseases: Going beyond Traditional Risk Factors. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2022, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francischetti, I.; Moreno, J.B.; Scholz, M.; Yoshida, W.B. Os Leucócitos e a Resposta Inflamatória Na Lesão de Isquemia-Reperfusão. Revista Brasileira de Cirurgia Cardiovascular 2010, 25, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruvinel, W. de M.; Mesquita Júnior, D.; Araújo, J.A.P.; Catelan, T.T.T.; Souza, A.W.S. de; Silva, N.P. da; Andrade, L.E.C. Sistema Imunitário: Parte I. Fundamentos Da Imunidade Inata Com Ênfase Nos Mecanismos Moleculares e Celulares Da Resposta Inflamatória. Rev Bras Reumatol 2010, 50, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwood, P.; Krakowiak, P.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Hansen, R.; Pessah, I.; Van de Water, J. Elevated Plasma Cytokines in Autism Spectrum Disorders Provide Evidence of Immune Dysfunction and Are Associated with Impaired Behavioral Outcome. Brain Behav Immun 2011, 25, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.S.; Guo, Y.; Ramos, R.I.; Hebroni, F.; Plaisier, S.B.; Xuan, C.; Granick, J.L.; Matsushima, H.; Takashima, A.; Iwakura, Y.; et al. Neutrophil-Derived IL-1β Is Sufficient for Abscess Formation in Immunity against Staphylococcus Aureus in Mice. PLoS Pathog 2012, 8, e1003047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.P.; Sanchez, Z.M. Consumo de Álcool Durante a Pandemia Da COVID-19: Uma Reflexão Necessária Para o Enfrentamento Da Situação. Cad Saude Publica 2020, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAIO, R.; DICHI, J.B.; BURINI, R.C. Implicações Do Alcoolismo e Da Doença Hepática Crônica Sobre o Metabolismo de Micronutrientes. Arq Gastroenterol 2000, 37, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achur, R.N.; Freeman, W.M.; Vrana, K.E. Circulating Cytokines as Biomarkers of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology 2010, 5, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameters | [IL-10] pg/mL | [IL-1 β] pg/mL | |
| [IL-10] pg/mL | ρ | 1.000 | 0.016 |
| P-value | - | 0.825 | |
| [IL-1 β] pg/mL | ρ | 0.016 | 1.000 |
| P-value | 0.825 | - | |
| Total leukocytes | ρ | -0.06 | 0.213** |
| P-value | 0.406 | 0.003 | |
| Rod neutrophils | ρ | 0.011 | 0.093 |
| P-value | 0.878 | 0.201 | |
| Segmented neutrophils | ρ | -0.02 | 0.163* |
| P-value | 0.781 | 0.024 | |
| Eosinophils | ρ | -0.096 | 0.046 |
| P-value | 0.187 | 0.530 | |
| Basophils | ρ | -0.104 | 0.028 |
| P-value | 0.154 | 0.703 | |
| Lymphocytes | ρ | 0.053 | -0.131 |
| P-value | 0.467 | 0.070 | |
| Monocytes | ρ | -0.068 | -0.104 |
| P-value | 0.350 | 0.153 | |
| Total cholesterol | ρ | 0.008 | 0.050 |
| P-value | 0.910 | 0.492 | |
| Triglycerides | ρ | -0.268** | 0.079 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.272 | |
| HDL | ρ | 0.365** | 0.038 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.598 | |
| LDL | ρ | 0.003 | 0.034 |
| P-value | 0.972 | 0.648 | |
| Total lipids | ρ | -0.023 | 0.106 |
| P-value | 0.830 | 0.311 | |
| Glucose | ρ | -0.370** | 0.017 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.817 | |
| HbA1c | ρ | -0.379** | 0.052 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.476 | |
| Estimated average blood glucose | ρ | -0.377** | 0.056 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.442 | |
| Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase | ρ | 0.115 | -0.010 |
| P-value | 0.111 | 0.894 | |
| Pyruvic glutamic transaminase | ρ | 0.016 | -0.113 |
| P-value | 0.821 | 0.116 | |
| Time with T2DM | ρ | -0.264** | -0.031 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.677 | |
| Time with SAH | ρ | -0.071 | -0.053 |
| P-value | 0.332 | 0.471 | |
| BMI | ρ | 0.109 | 0.038 |
| P-value | 0.146 | 0.608 | |
| Waist Circumference | ρ | -0.150 | 0.073 |
| P-value | 0.062 | 0.366 | |
| Fat mass | ρ | 0.293** | 0.011 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.896 | |
| Lean Mass | ρ | -0.263** | -0.03 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.707 | |
| Bone mineral content | ρ | -0.328** | -0.012 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.879 | |
| [IL-10] pg/mL | [IL-1β] pg/mL | |||||||||||||
| N | P25 | Median | P75 | P value | N | P25 | Median | P75 | P value | |||||
| MetS | Yes | 127 | 4.28 | 4.59 | 4.84 | <0.001* | 127 | 3.53 | 6.23 | 8.66 | 0.482 | |||
| No | 66 | 5.24 | 5.35 | 5.57 | 66 | 4.74 | 7.47 | 8.75 | ||||||
| Sarcopenia (DEXA) | Yes | 23 | 4.25 | 4.84 | 5.28 | 0.722 | 23 | 4.83 | 7.44 | 8.75 | 0.537 | |||
| No | 170 | 4.51 | 4.85 | 5.23 | 170 | 3.53 | 7.30 | 8.75 | ||||||
| SAH | Yes | 147 | 4.35 | 4.84 | 5.22 | 0.266 | 147 | 3.53 | 6.23 | 8.75 | 0.231 | |||
| No | 46 | 4.37 | 5.09 | 5.34 | 46 | 4.77 | 7.48 | 8.78 | ||||||
| T2DM | Yes | 108 | 4.34 | 4.83 | 5.12 | 0.007* | 108 | 3.53 | 7.30 | 8.68 | 0.821 | |||
| No | 85 | 4.51 | 5.02 | 5.38 | 85 | 3.54 | 7.40 | 8.76 | ||||||
| Age | 60 to 65 | 81 | 4.51 | 4.84a | 5.29 | 0.042* | 81 | 3.54 | 6.25 | 7.53 | 0.691 | |||
| 66 to 69 | 43 | 4.51 | 4.83a | 5.06 | 43 | 3.53 | 7.47 | 8.84 | ||||||
| 70 to 75 | 40 | 4.35 | 5.045a | 5.31 | 40 | 3.52 | 6.02 | 8.76 | ||||||
| 76 to 79 | 16 | 4.67 | 5.035a | 5.27 | 16 | 4.86 | 7.51 | 8.81 | ||||||
| ≥80 | 13 | 4.11 | 4.48b | 4.84 | 13 | 3.65 | 7.53 | 8.66 | ||||||
| Smoking | Yes | 14 | 4.31 | 4.94 | 5.24 | 0.808 | 14 | 3.50 | 6.85 | 8.75 | 0.644 | |||
| No | 179 | 4.37 | 4.84 | 5.24 | 179 | 3.54 | 7.40 | 8.75 | ||||||
| Use of alcoholic beverages | Yes | 9 | 4.48 | 5.01 | 5.24 | 0.709 | 9 | 3.51 | 3.53 | 5.94 | 0.037* | |||
| No | 184 | 4.37 | 4.84 | 5.24 | 184 | 3.55 | 7.42 | 8.75 | ||||||
| Perform physical exercises | Yes | 135 | 4.37 | 4.86 | 5.27 | 0.573 | 135 | 3.54 | 7.30 | 8.75 | 0.853 | |||
| No | 58 | 4.48 | 4.84 | 5.22 | 58 | 3.53 | 7.40 | 8.76 | ||||||
| Altered PA | Yes | 80 | 4.35 | 4.84 | 5.22 | 0.358 | 80 | 3.52 | 7.41 | 8.77 | 0.596 | |||
| No | 95 | 4.51 | 4.86 | 5.24 | 95 | 4.74 | 7.48 | 8.76 | ||||||
| Altered PAS | Yes | 56 | 4.33 | 4.79 | 5.16 | 0.241 | 56 | 3.52 | 6.24 | 8.73 | 0.288 | |||
| No | 116 | 4.51 | 4.86 | 5.24 | 116 | 4.71 | 7.48 | 8.77 | ||||||
| Altered PAD | No | 116 | 4.37 | 4.86 | 5.23 | 0.954 | 116 | 4.71 | 7.48 | 8.75 | 0.301 | |||
| Yes | 53 | 4.48 | 4.83 | 5.22 | 53 | 3.52 | 6.25 | 8.79 | ||||||
| HDL | Altered | 40 | 4.24 | 4.51 | 4.93 | <0.001* | 40 | 3.53 | 7.46 | 8.81 | 0.709 | |||
| Normal | 152 | 4.59 | 5.01 | 5.28 | 152 | 3.54 | 7.30 | 8.75 | ||||||
| Glucose | Altered | 98 | 4.29 | 4.76 | 5.01 | <0.001* | 98 | 3.53 | 6.27 | 7.65 | 0.567 | |||
| Normal | 95 | 4.79 | 5.22 | 5.40 | 95 | 4.68 | 7.41 | 8.76 | ||||||
| HbA1c | Altered | 110 | 4.29 | 4.77 | 5.02 | <0.001* | 110 | 3.54 | 7.46 | 8.75 | 0.341 | |||
| Normal | 82 | 4.79 | 5.19 | 5.38 | 82 | 3.52 | 6.19 | 8.69 | ||||||
| Total cholesterol | Altered | 102 | 4.48 | 4.86 | 5.24 | 0.806 | 102 | 3.54 | 7.41 | 8.76 | 0.911 | |||
| Normal | 91 | 4.35 | 4.84 | 5.22 | 91 | 3.53 | 6.29 | 8.75 | ||||||
| LDL | Altered | 100 | 4.37 | 4.84 | 5.24 | 0.945 | 100 | 3.54 | 7.46 | 8.79 | 0.891 | |||
| Normal | 87 | 4.35 | 4.84 | 5.22 | 87 | 3.53 | 6.29 | 8.75 | ||||||
| Waist Circumference | Altered | 123 | 4.51 | 4.84 | 5.07 | 0.851 | 123 | 3.53 | 7.30 | 8.75 | 0.343 | |||
| Normal | 32 | 4.28 | 4.82 | 5.30 | 32 | 3.52 | 6.23 | 7.50 | ||||||
| Biological sex | Female | 154 | 4.74 | 5.01 | 5.28 | <0.001* | 154 | 3.54 | 7.41 | 8.75 | 0.588 | |||
| Male | 39 | 4.25 | 4.31 | 5.18 | 39 | 3.53 | 6.09 | 8.79 | ||||||
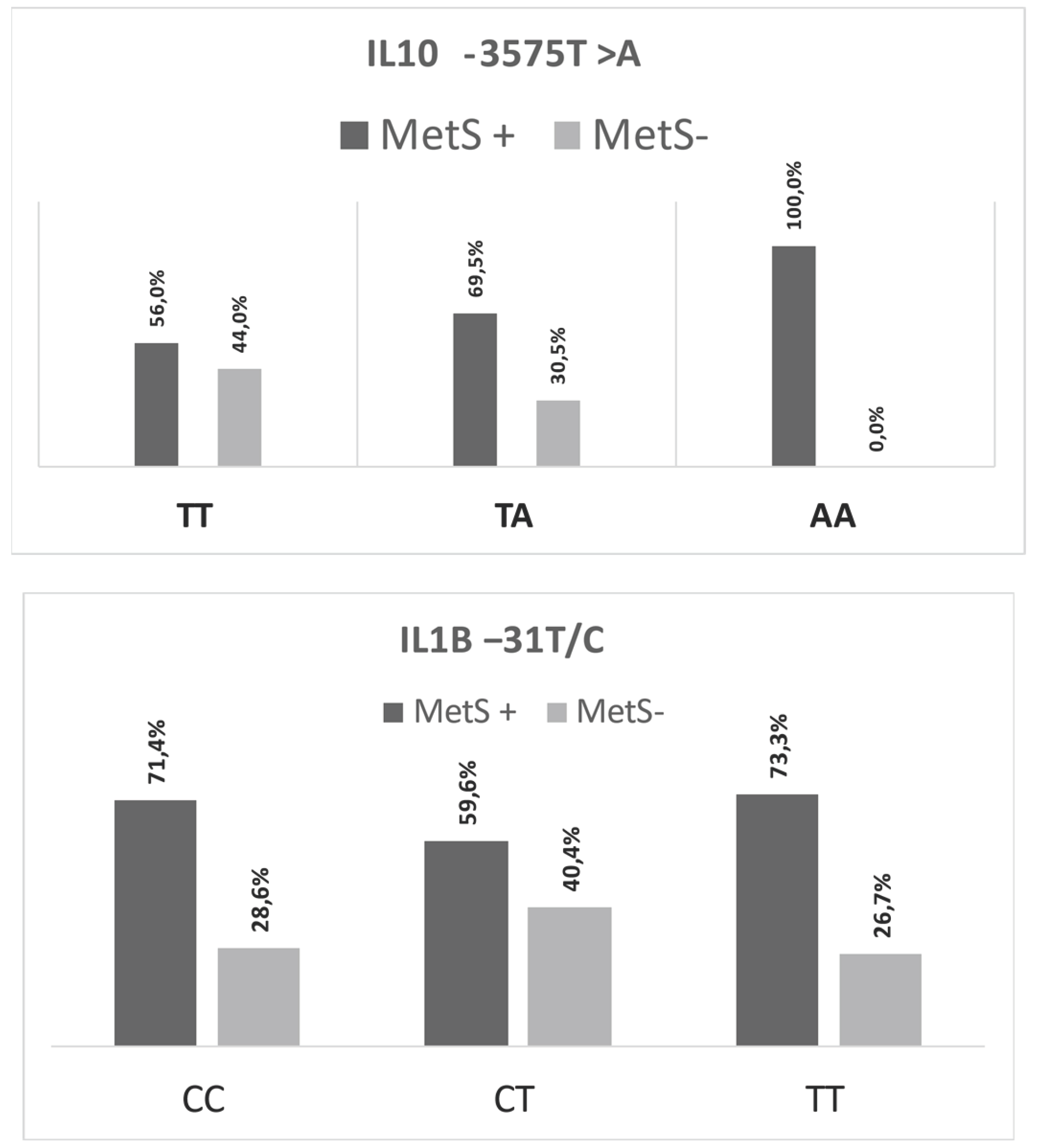
| IL10 -3575T >A | IL1Β −31T>C | |||||
| TT | TA | AA | CC | CT | TT | |
| [IL-10] pg/mL | [IL-10] pg/mL | [IL-10] pg/mL | [IL-1Β] pg/mL | [IL-1Β] pg/mL | [IL-1Β] pg/mL | |
| N | 109 | 59 | 25 | 84 | 94 | 15 |
| % | 56.5 | 30.6 | 12.9 | 43.5 | 48.7 | 7.8 |
| P25 | 4.76 | 4.28 | 4.02 | 3.49 | 7.48 | 17.46 |
| Median | 5.02a | 4.84b | 4.23c | 3.52a | 7.53b | 17.52c |
| P75 | 5.34 | 5.23 | 4.29 | 4.76 | 8.82 | 18.66 |
| P–value | <0.001* | <0.001* | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





