Submitted:
05 March 2024
Posted:
06 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
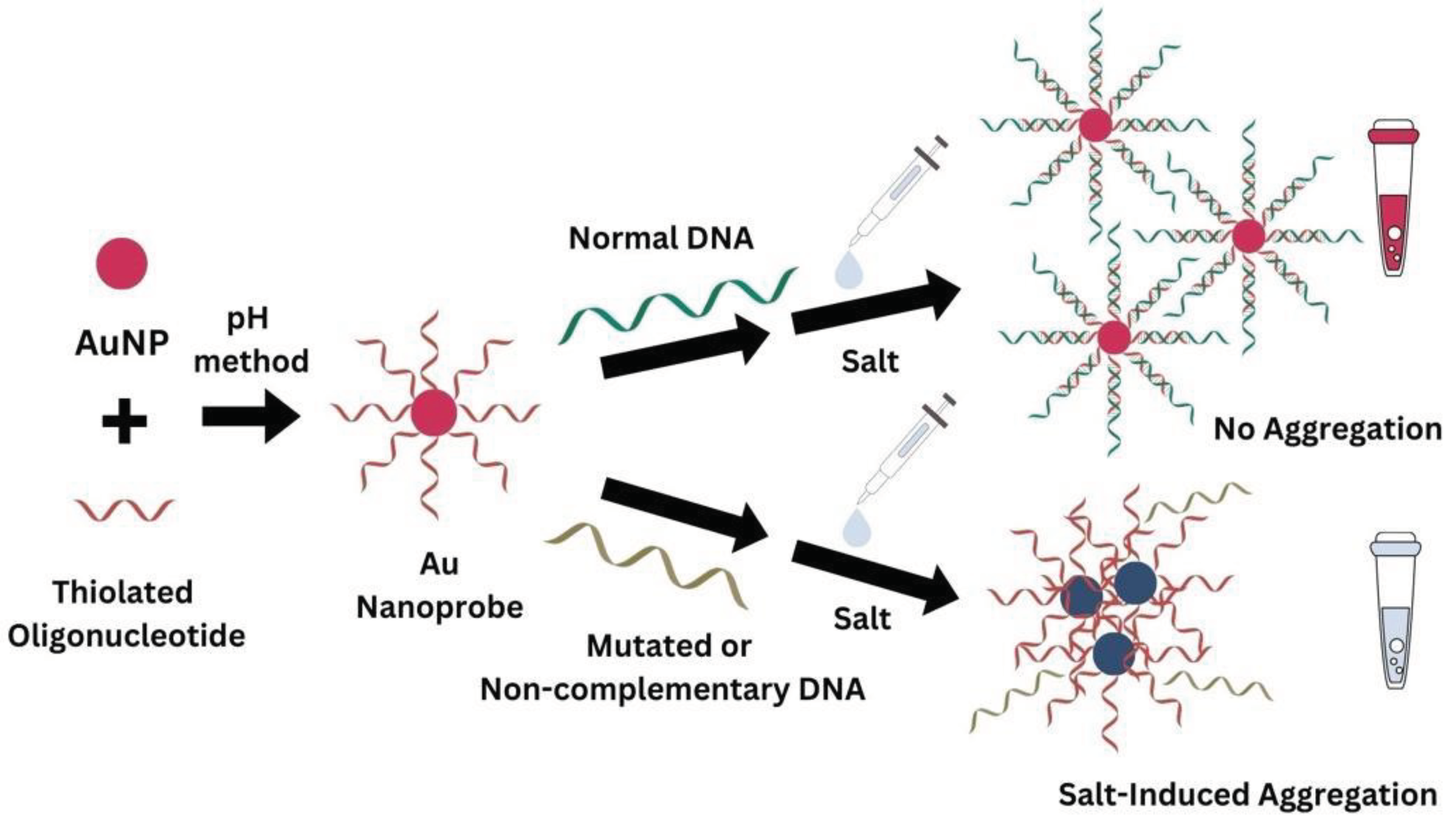
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Au Nanoprobe Synthesis
2.1.1. Au Nanoparticles Synthesis and Characterization
2.1.2. Functionalization
2.2. Au Nanoprobe Characterization
2.2.1. Gel Electrophoresis
2.2.2. UV–Vis Analysis
2.2.3. Dynamic Light Scattering and Electrophoretic Light Scattering:
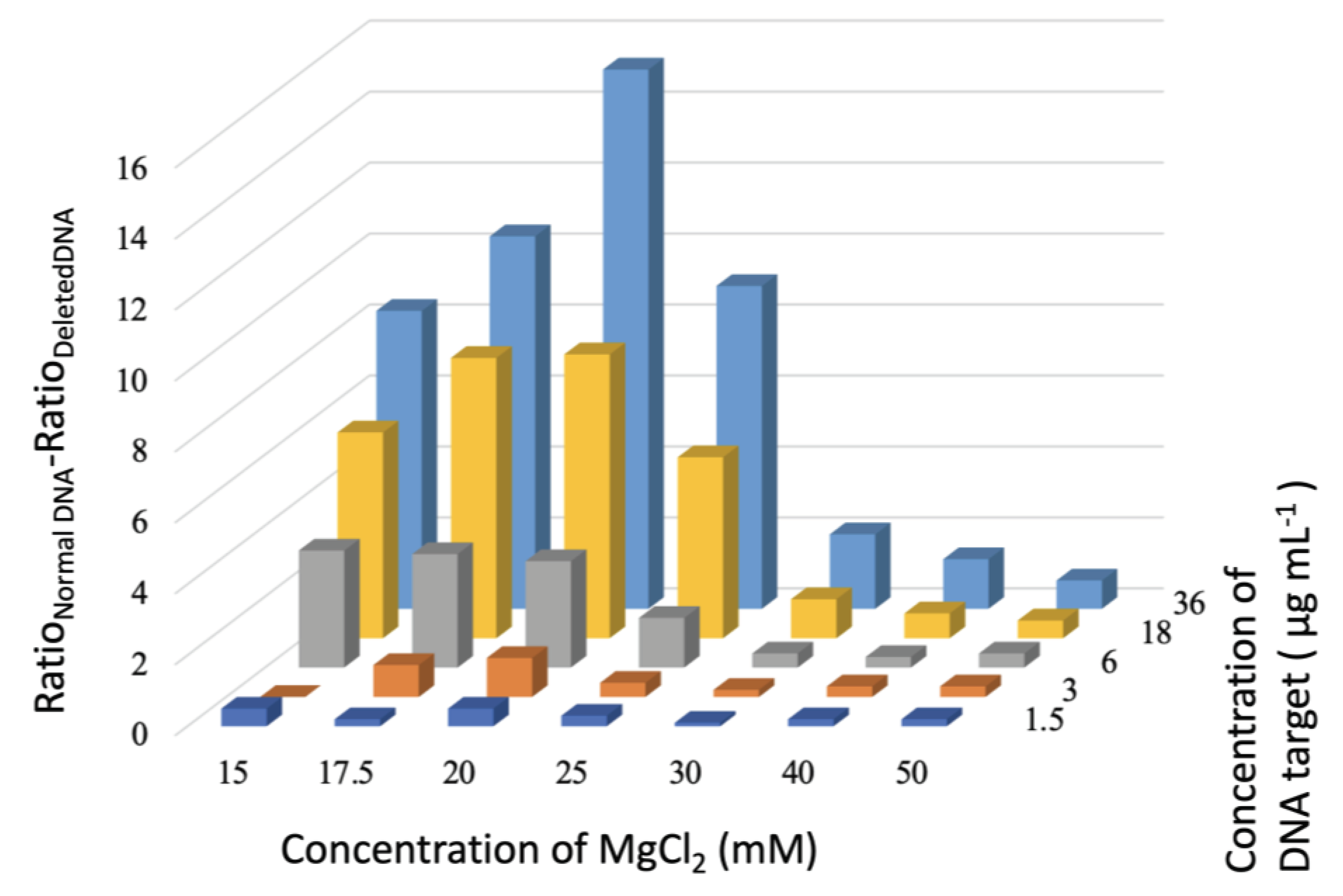
2.2.4. Non-Cross-Linking Detection Assay
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Au Nanoprobe Functionalization
3.1.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the 35nm AuNPs Stock
| Batch | Diameter (nm) | Zeta Potential | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UV-Vis1 | DLS2 | |||
| Hydrodinamic diameter2 | Polydispersity (Đ) | |||
| 1 | 37 | 38 | 0.19 | -34.7 ± 1.3 |
| 2 | 36 | 41 | 0.21 | -32.7 ± 1.0 |
| 3 | 35 | 36 | 0.17 | -34.2 ± 1.5 |
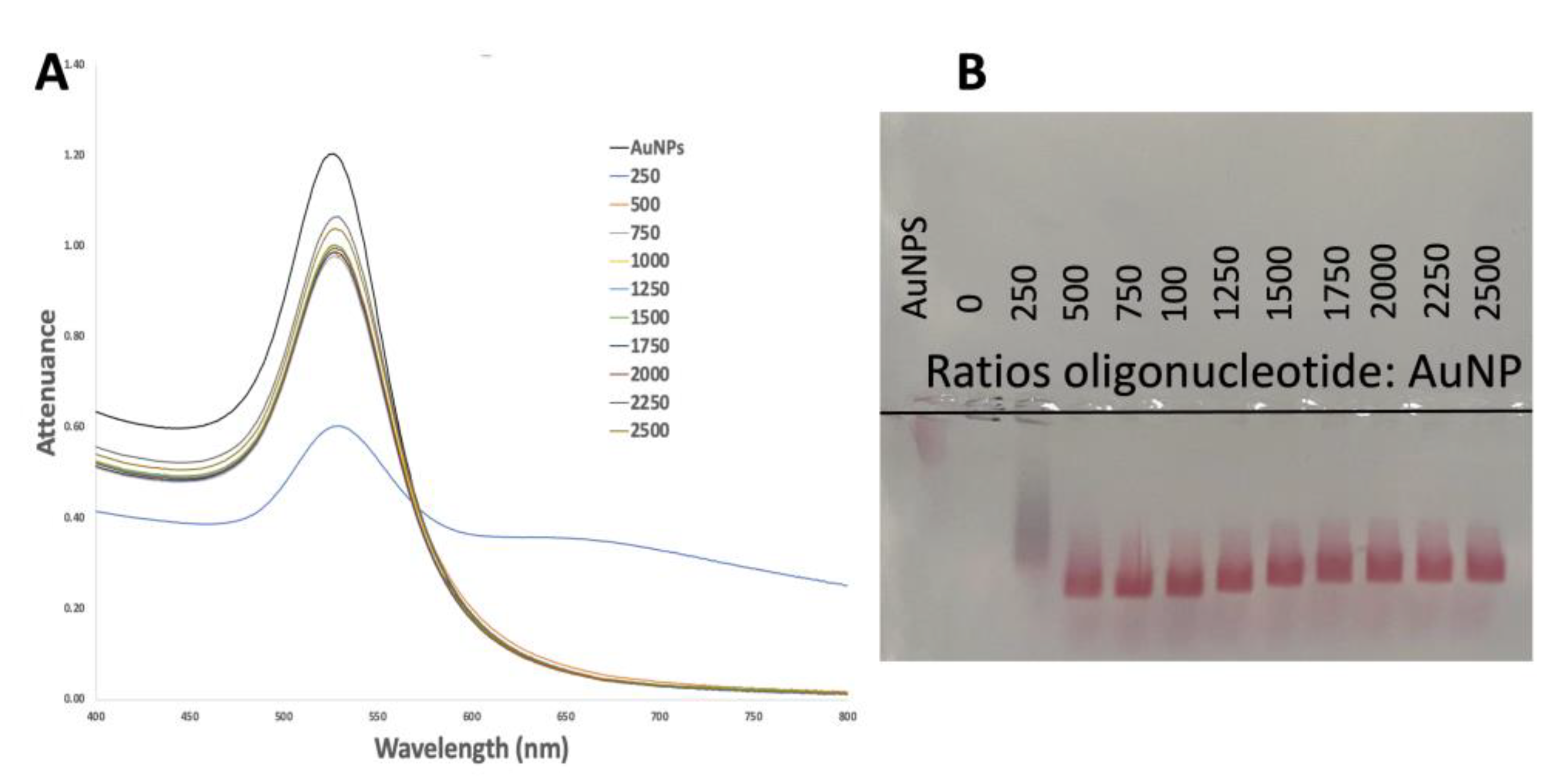
3.1.2. Successful Functionalization of AuNPs
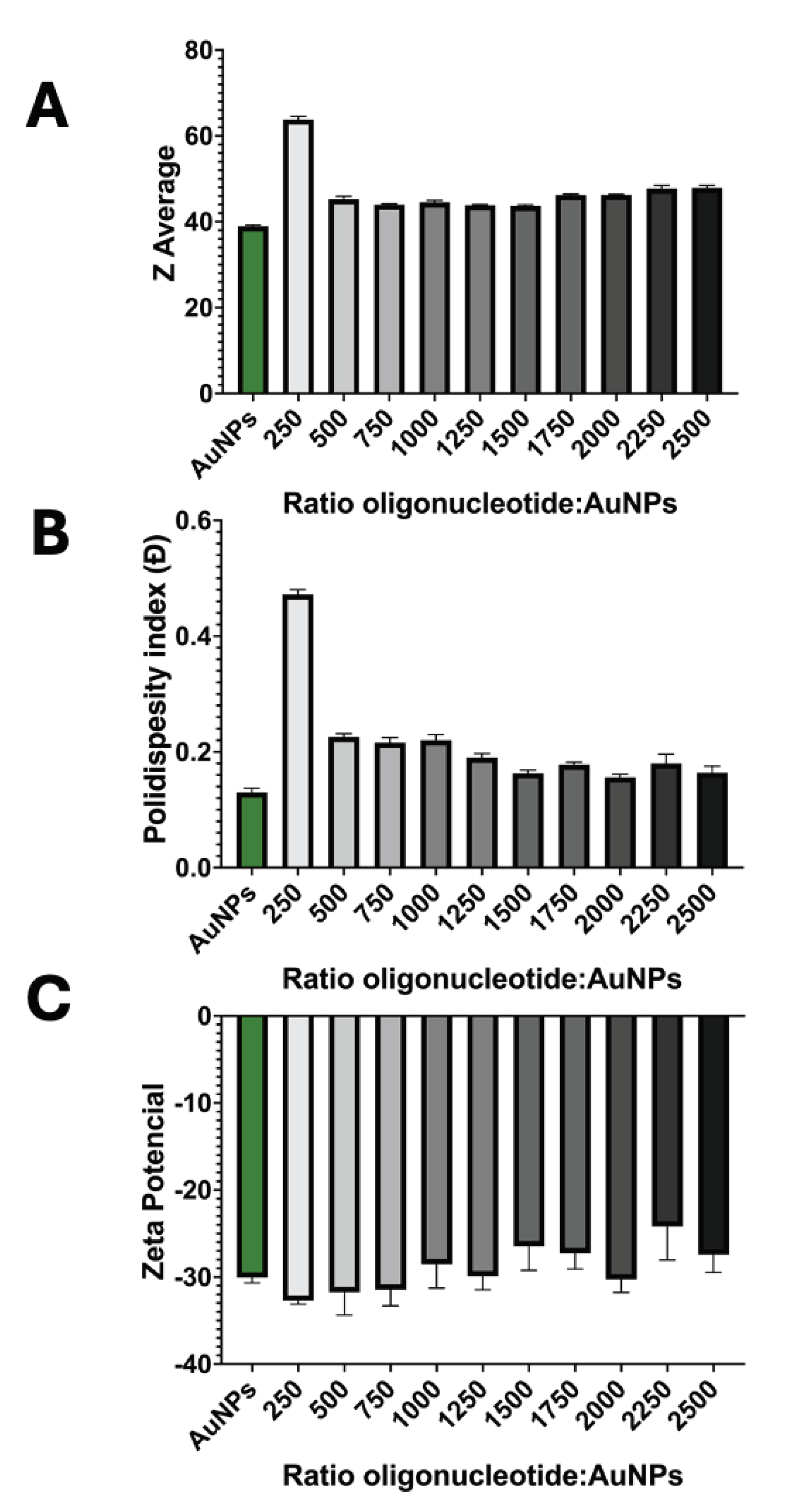
3.2. Detection Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Almeida, M.P.; Pereira, E.; Baptista, P.; Gomes, I.; Figueiredo, S.; Soares, L.; Franco, R. Gold nanoparticles as (bio) chemical sensors. In Comprehensive analytical chemistry; Elsevier: 2014; Volume 66, pp. 529-567.
- Franco, R.; Pedrosa, P.; Carlos, F.F.; Veigas, B.; Baptista, P.V. Gold nanoparticles for DNA/RNA-based diagnostics. Handbook of nanoparticles 2015, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enea, M.; Araújo, A.M.; Almeida, M.P.; Soares, M.E.; Gonçalves-Monteiro, S.; Pinho, P.G.; Pereira, E.; Bastos, M.L.; Carmo, H. A Metabolomic Approach for the In Vivo Study of Gold Nanospheres and Nanostars after a Single-Dose Intravenous Administration to Wistar Rats. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enea, M.; Pereira, E.; Costa, J.; Soares, M.E.; Dias da Silva, D.; Bastos, M.L.; Carmo, H.F. Cellular uptake and toxicity of gold nanoparticles on two distinct hepatic cell models. Toxicol In Vitro 2021, 70, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enea, M.; Pereira, E.; Silva, D.D.; Costa, J.; Soares, M.E.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; Carmo, H. Study of the intestinal uptake and permeability of gold nanoparticles using both in vitro and in vivo approaches. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 195102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, P.; Pereira, E.; Eaton, P.; Doria, G.; Miranda, A.; Gomes, I.; Quaresma, P.; Franco, R. Gold nanoparticles for the development of clinical diagnosis methods. Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry 2008, 391, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, A.L.; de Almeida, M.P.; Cardoso, F.; Pinto, M.; Pereira, E.; Franco, R.; Matos, O. Development of a Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral-Flow Immunoassay for Pneumocystis Pneumonia Serological Diagnosis at Point-of-Care. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.J.; Caetano, S.; Dalot, A.; Sabino, F.; Calmeiro, T.R.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Pereira, E.; Prudêncio, M.; Byrne, H.J.; et al. A simple polystyrene microfluidic device for sensitive and accurate SERS-based detection of infection by malaria parasites. Analyst 2023, 148, 4053–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enea, M.; Peixoto de Almeida, M.; Dias, A.; Ferreira, B.; Bernardes, C.; Flores, O.; Pereira, E.; Franco, R. Improved Gold Nanoprobes for Detection of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms: The Influence of Size. Particle & Particle Systems Characterization 2022, 39, 2200137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, P.; Doria, G.; Henriques, D.; Pereira, E.; Franco, R. Colorimetric detection of eukaryotic gene expression with DNA-derivatized gold nanoparticles. Journal of biotechnology 2005, 119, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlos, F.F.; Flores, O.; Doria, G.; Baptista, P.V. Characterization of genomic single nucleotide polymorphism via colorimetric detection using a single gold nanoprobe. Anal Biochem 2014, 465, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria, G.; Larguinho, M.; Dias, J.T.; Pereira, E.; Franco, R.; Baptista, P.V. Gold-silver-alloy nanoprobes for one-pot multiplex DNA detection. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 255101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, P.; Doria, G.; Pereira, E.; Baptista, P.V.; Franco, R. Imaging gold nanoparticles for DNA sequence recognition in biomedical applications. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience 2007, 6, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Kazerooni, E.A. Lung Cancer Screening. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2022, 43, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, A.A.; Solomon, B.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Gainor, J.F.; Heist, R.S. Lung cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Z.; Kuo, P.L.; Huang, Y.L.; Tang, E.K.; Chen, C.S.; Wu, M.T.; Lin, Y.P. Differences in lung cancer characteristics and mortality rate between screened and non-screened cohorts. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 19386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Ohe, Y.; Tsuta, K.; Fukui, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Yoshida, T.; Tateishi, U.; Nokihara, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Sekine, I.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation detection using high-resolution melting analysis predicts outcomes in patients with advanced non small cell lung cancer treated with gefitinib. Clin Cancer Res 2007, 13, 5385–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, T.J.; Bell, D.W.; Sordella, R.; Gurubhagavatula, S.; Okimoto, R.A.; Brannigan, B.W.; Harris, P.L.; Haserlat, S.M.; Supko, J.G.; Haluska, F.G.; et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 2004, 350, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paez, J.G.; Jänne, P.A.; Lee, J.C.; Tracy, S.; Greulich, H.; Gabriel, S.; Herman, P.; Kaye, F.J.; Lindeman, N.; Boggon, T.J.; et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004, 304, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riely, G.J.; Pao, W.; Pham, D.; Li, A.R.; Rizvi, N.; Venkatraman, E.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M.; Miller, V.A. Clinical course of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and epidermal growth factor receptor exon 19 and exon 21 mutations treated with gefitinib or erlotinib. Clin Cancer Res 2006, 12, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigematsu, H.; Gazdar, A.F. Somatic mutations of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway in lung cancers. Int J Cancer 2006, 118, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Chandra, K.; Dam, D.H.; Wiederrecht, G.P.; Odom, T.W. Shape-Dependent Nonlinear Optical Properties of Anisotropic Gold Nanoparticles. J Phys Chem Lett 2015, 6, 4904–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiss, W.; Thanh, N.T.; Aveyard, J.; Fernig, D.G. Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV-vis spectra. Anal Chem 2007, 79, 4215–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, S.; Castro, A.; Correia da Costa, J.M.; Pereira, E. Biosensor based immunoassay: A new approach for serotyping of Toxoplasma gondii. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, M.R.; Pallem, V.L.; Stretz, H.A.; Wells, M.J. Extinction, emission, and scattering spectroscopy of 5-50 nm citrate-coated gold nanoparticles: An argument for curvature effects on aggregation. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 2017, 175, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastús, N.G.; Comenge, J.; Puntes, V. Kinetically controlled seeded growth synthesis of citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: size focusing versus Ostwald ripening. Langmuir 2011, 27, 11098–11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gouriye, T.; Goeken, K.; Servos, M.R.; Gill, R.; Liu, J. Toward fast and quantitative modification of large gold nanoparticles by thiolated DNA: scaling of nanoscale forces, kinetics, and the need for thiol reduction. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2013, 117, 15677–15684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Servos, M.R.; Liu, J. Instantaneous and quantitative functionalization of gold nanoparticles with thiolated DNA using a pH-assisted and surfactant-free route. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2012, 134, 7266–7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, S.J.; Lytton-Jean, A.K.; Mirkin, C.A. Maximizing DNA loading on a range of gold nanoparticle sizes. Anal Chem 2006, 78, 8313–8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirkin, C.A.; Letsinger, R.L.; Mucic, R.C.; Storhoff, J.J. A DNA-based method for rationally assembling nanoparticles into macroscopic materials. Nature 1996, 382, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, J. Freezing-Driven DNA Adsorption on Gold Nanoparticles: Tolerating Extremely Low Salt Concentration but Requiring High DNA Concentration. Langmuir 2019, 35, 6476–6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, L.; Csáki, A.; Jatschka, J.; Fritzsche, W.; Flores, O.; Franco, R.; Pereira, E. Localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) biosensing using gold nanotriangles: detection of DNA hybridization events at room temperature. Analyst 2014, 139, 4964–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Kang, T.; Yoon, K.-A.; Lee, S.Y.; Joo, S.-W.; Lee, K. Colorimetric detection of mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor using gold nanoparticle aggregation. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2010, 25, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Oligonycleotide | Length (bp) | Sequence 5´to 3´ |
|---|---|---|
| Thiol-modified oligonucleotide |
16 | SH-C6-CCTTAATTCTCTTCGT |
| Normal DNA | 100 | GAG TGT AGC TCC TAA AGG AAC AAC CGA AAA GCC TCT ACAACGAAGAGAATTAAGG AAC TAT CGC TGC CCT TAA AAT TGA AAG AGT GGA AGA CCT AGG TCT |
| Deleted DNA | 84 | GAG TGT AGC TCC TAA AGG AAC AAC CGA AAA GCC TCT ACA () AAC TAT CGC TGC CCT TAA AAT TGA AAG AGT GGA AGA CCT AGG TCT |
| Noncomplementary random DNA | 84 | CTTAGACCCTACAATGTACTAGTAGGCCTCTGCGCTGGCAATACAGATAAGATAATGTAGTCCCTGGCCTCAAAGGAACTCTCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





