Submitted:
02 April 2024
Posted:
03 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
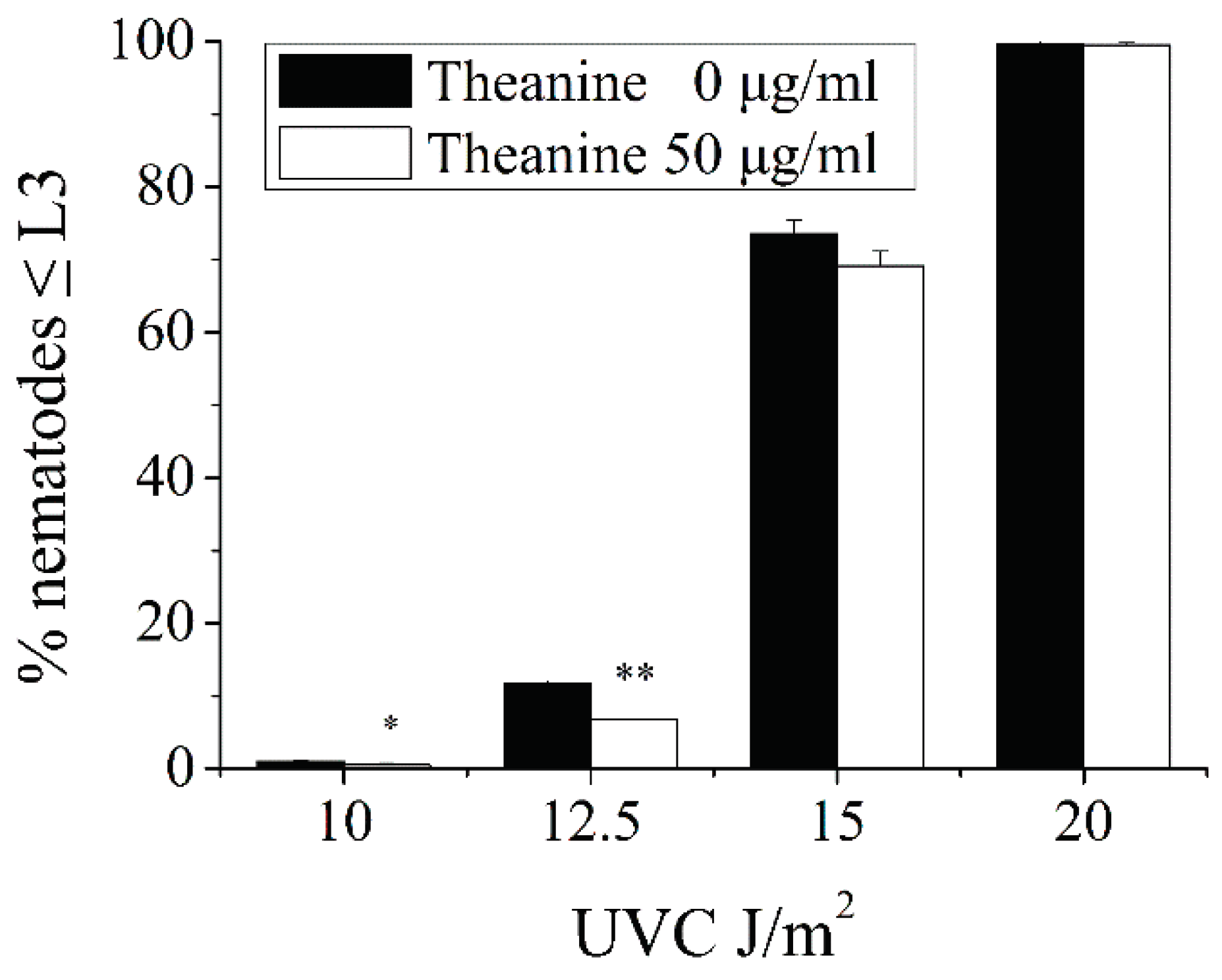
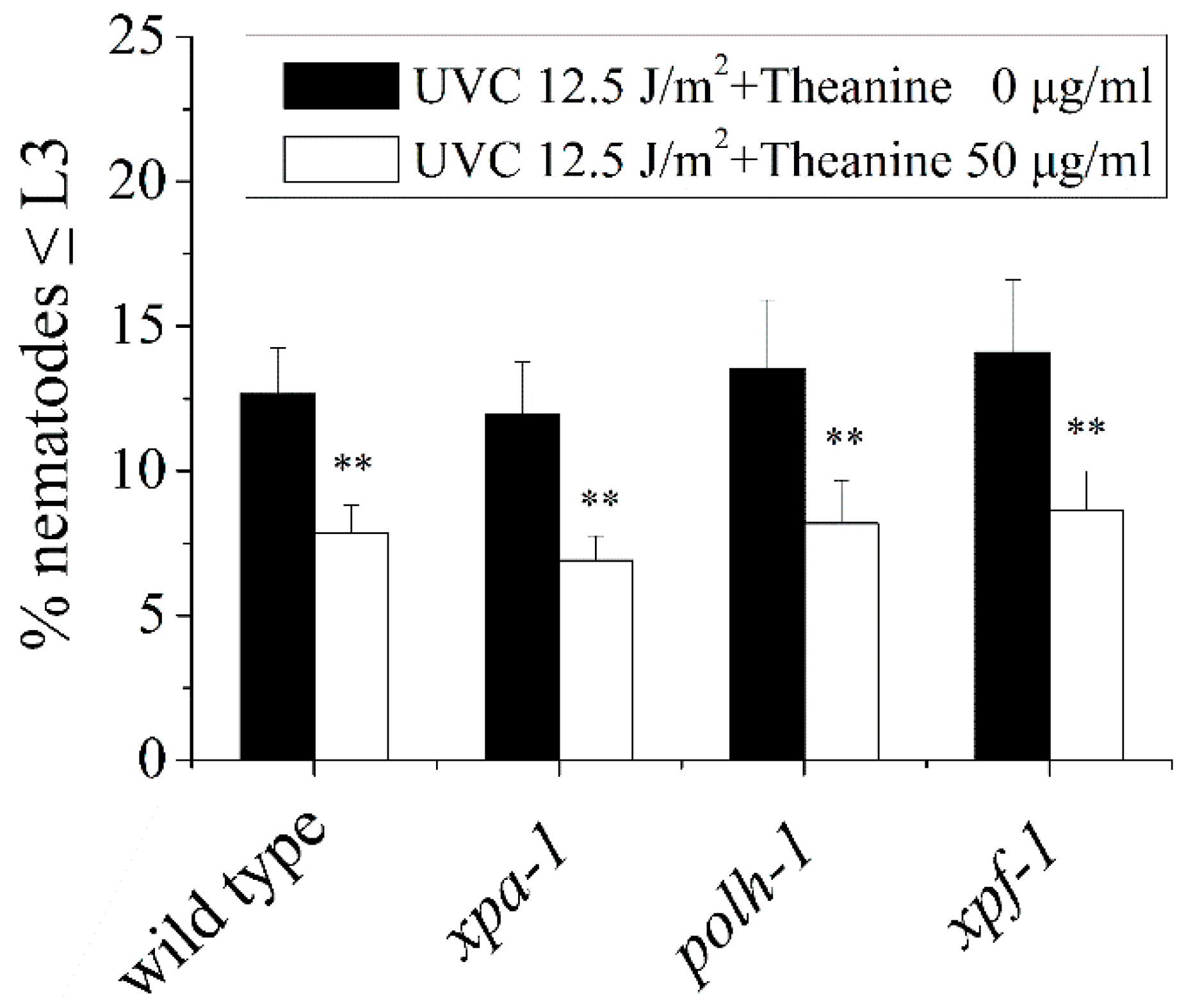
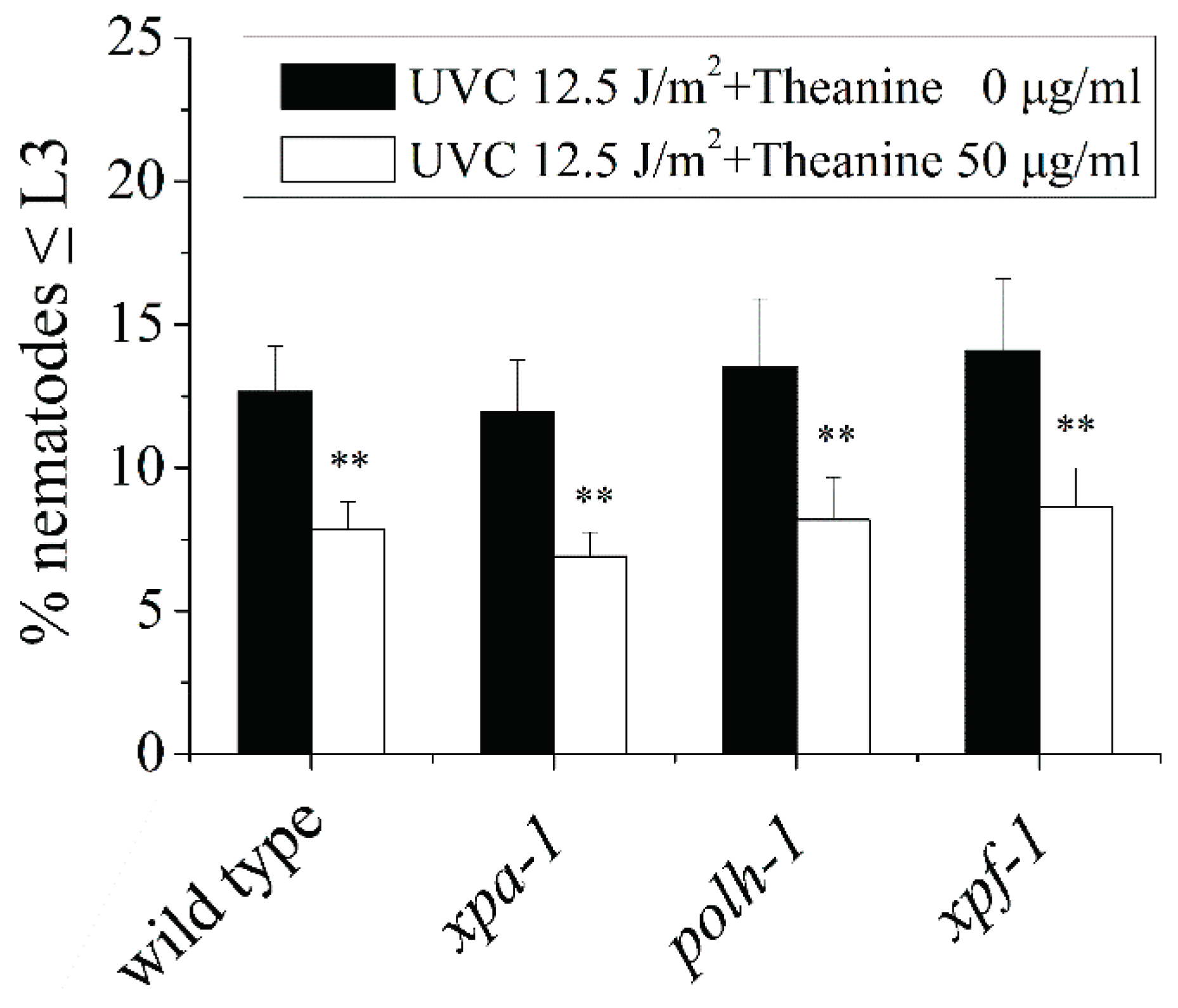
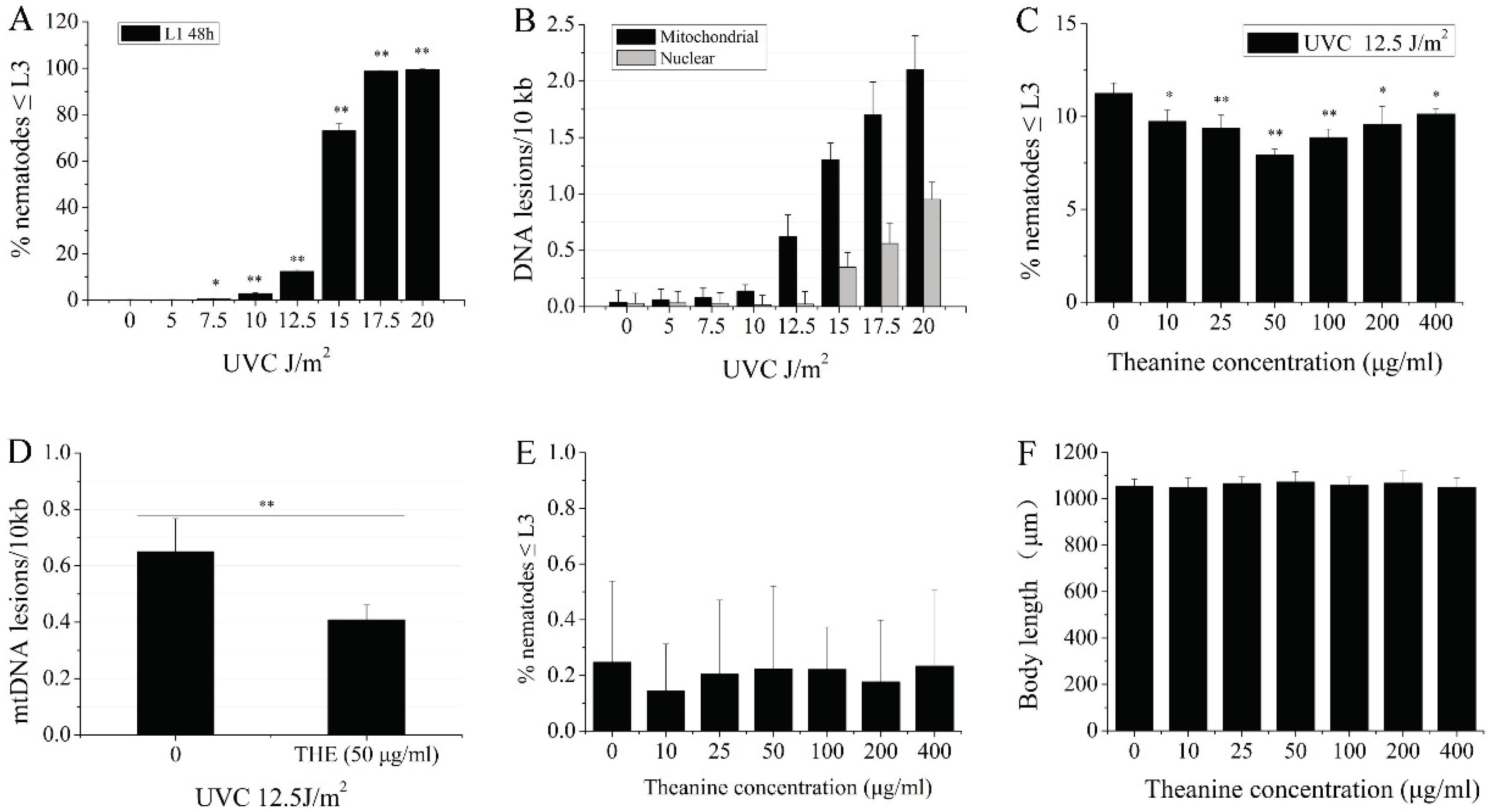
2.1. L-Theanine Enhanced the Removal of UVC-Induced mtDNA Damage
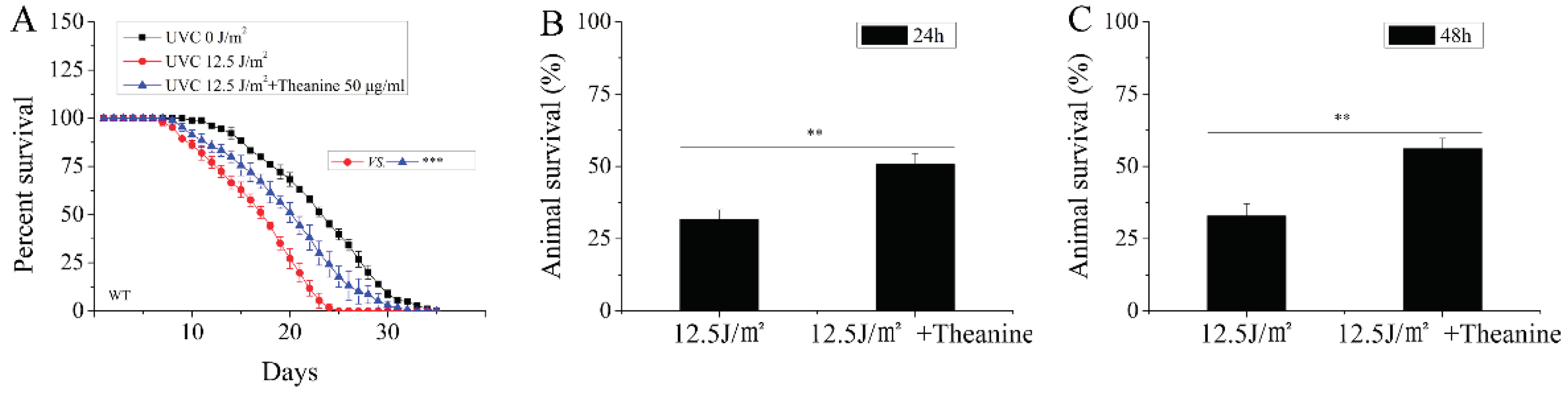
2.2. L-Theanine Extended the Lifespan and Enhanced the Heat-Stress Resistance of UVC-Exposed Nematodes
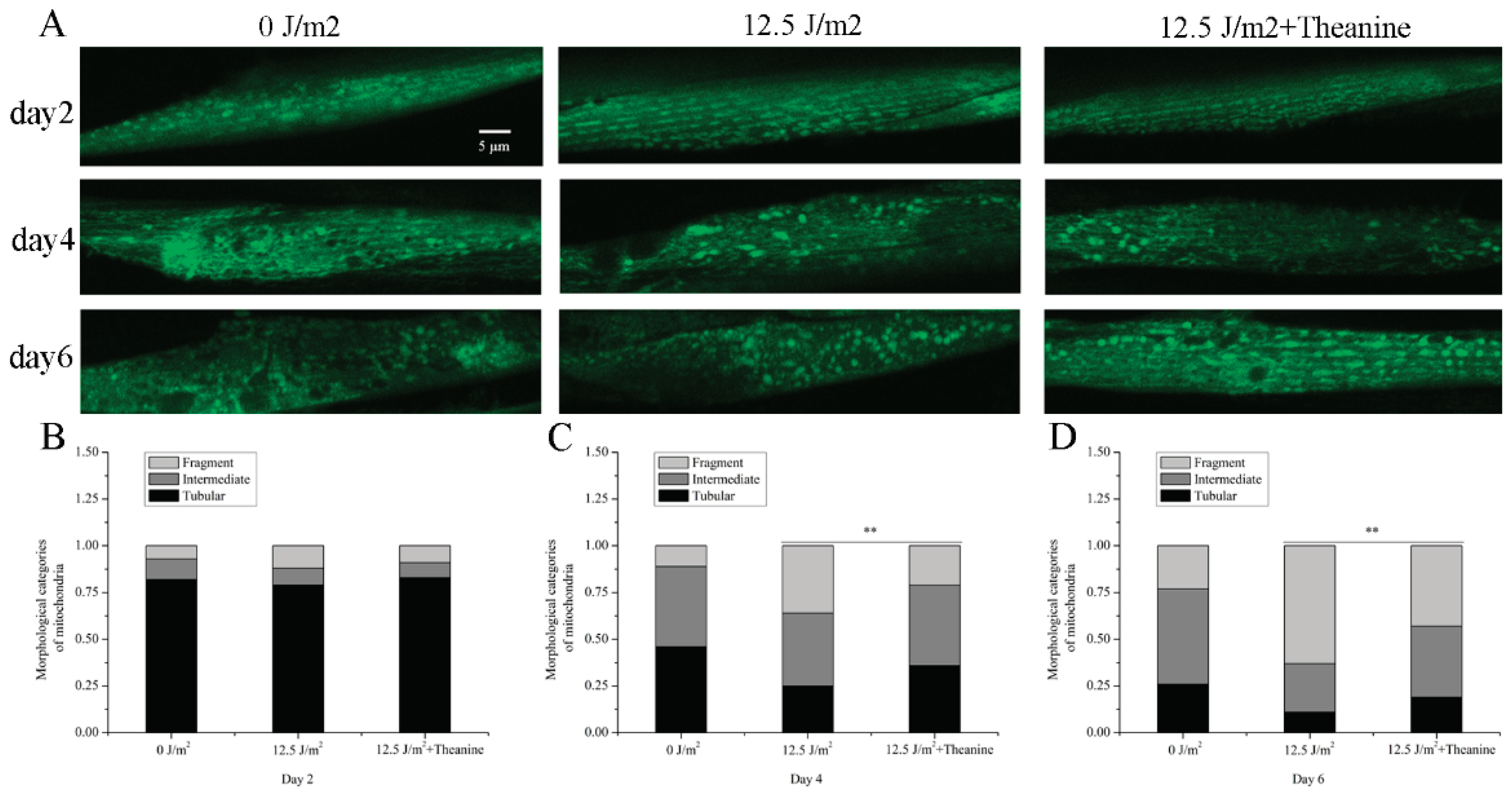
2.3. L-Theanine Improved Mitochondrial Morphology of UVC-Exposed Nematodes
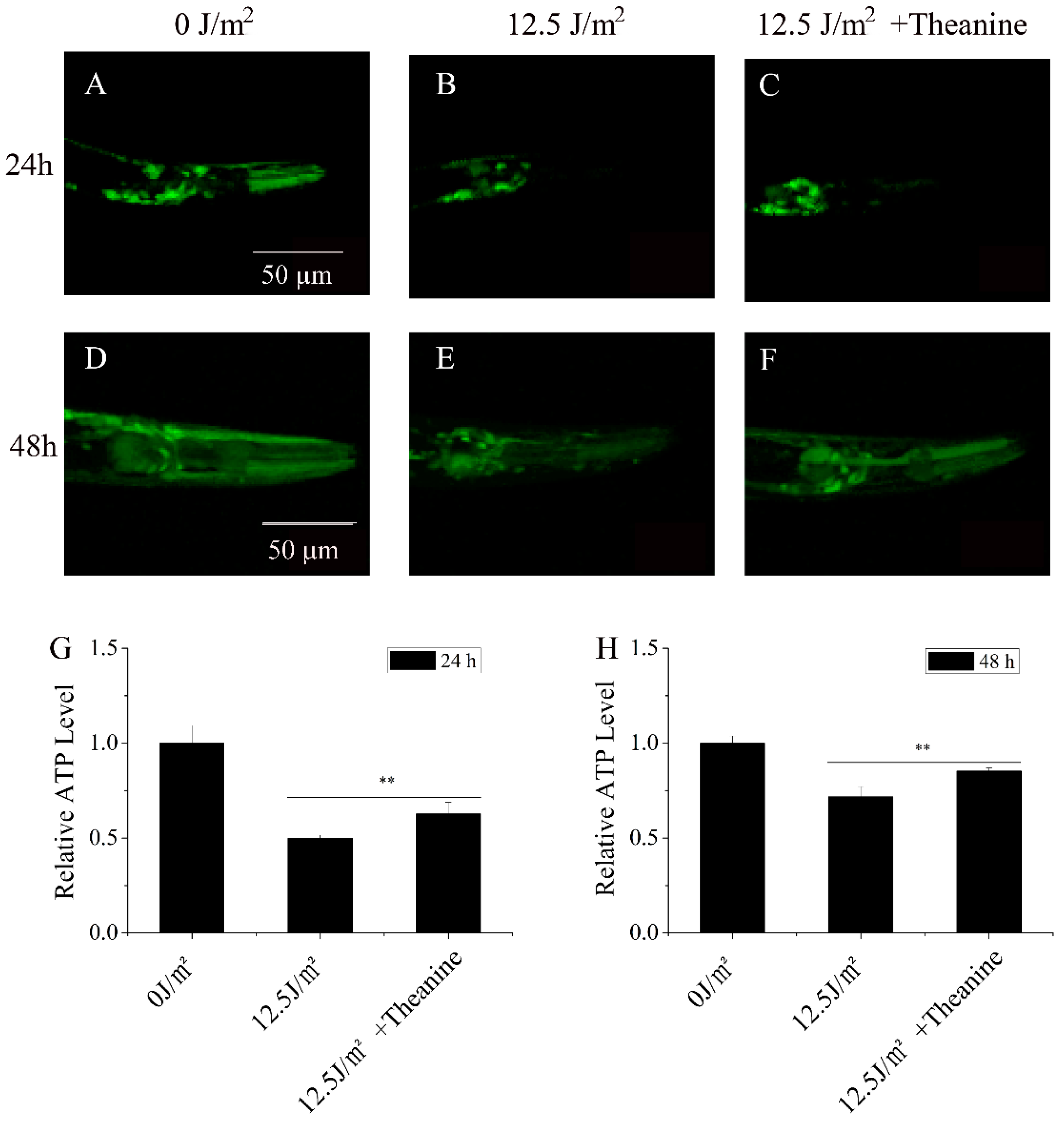
2.4. L-Theanine Elevated Steady-State ATP Level in UVC-Exposed Nematodes
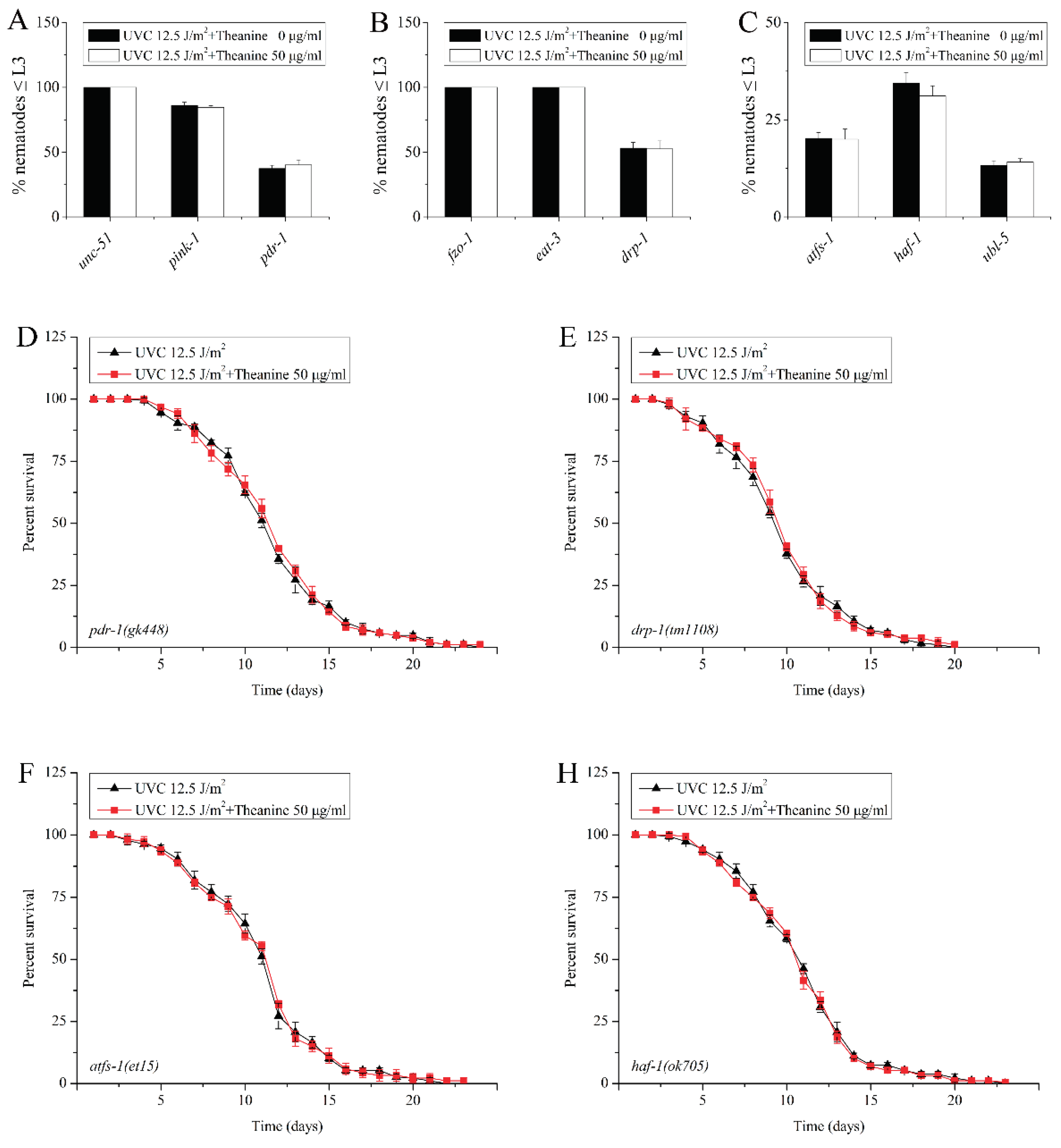
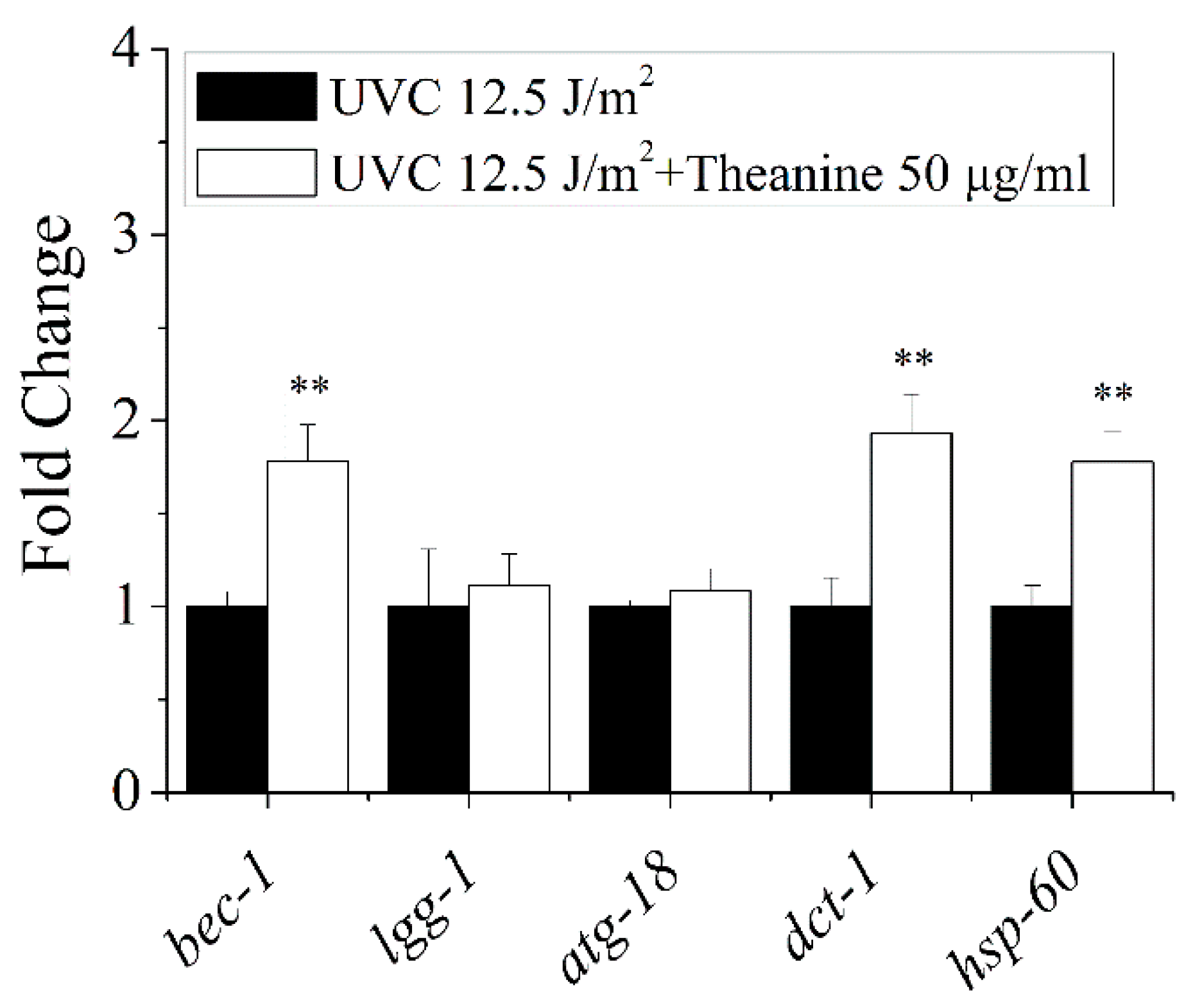
2.5. Autophagy, Mitochondrial Dynamics, and UPRmt Mediated the Reduction of mtDNA Damage and Extension of Lifespan in UVC-Exposed C. elegans Treated by L-Theanine
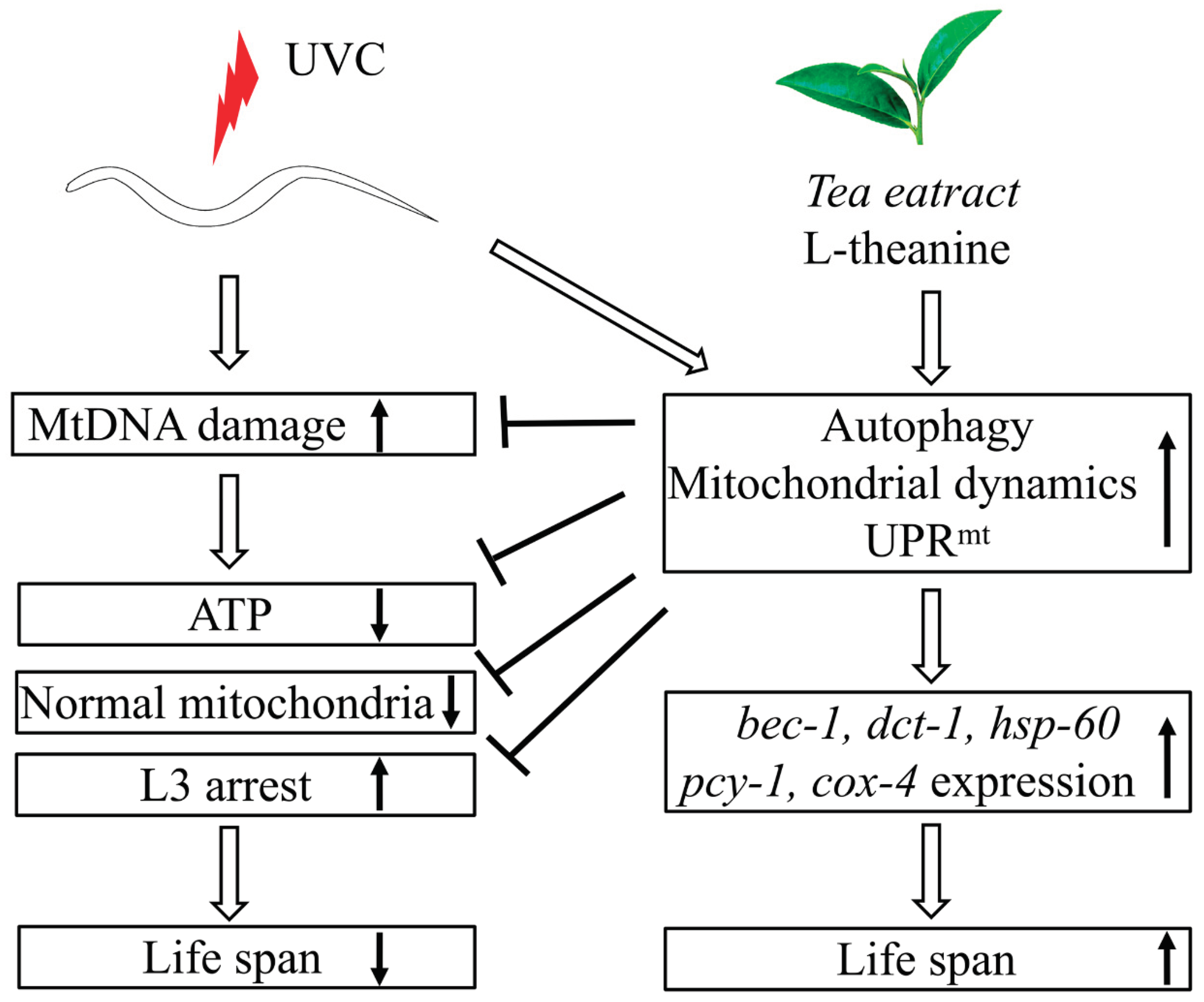
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. C. elegans Strains and Culture Conditions
4.3. UVC Exposure
4.4. Lifespan Experiments and Heat-Stress Resistance Assays
4.5. L3 Arrest Analysis
4.6. MtDNA and nDNA Damage Measurements
4.7. Body Length
4.8. Steady-State ATP Level Analysis
4.9. Quantitative Realtime-PCR
4.10. Confocal Microscopy and Image Processing
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Gene name | Primer sequence |
|---|---|
|
bec-1 lgg-1 atg-18 dct-1 hsp-60 cox-4 cts-1 pyc-1 hxk-1 tba-1 |
Fw (5΄TGATCTCTGCTGACAAGGCTT3΄) Rv (5΄CCGACCTTGAATCCAGTTGG3΄) Fw (5΄GCACCAAAGTCAAAGCTCCA3΄) Rv (5΄CCTCGTGATGGTCCTGGTAG3΄) Fw (5΄TGGGGCACAAAGATGGCTA3΄) Rv (5΄CCAAGATGTGTAAGATTTTCGCC3΄) Fw (5΄ATCGCACAATCTCCTCACGT3΄) Rv (5΄GGACAGTCTTTGGAGGTGTATT3΄) Fw (5΄GGGGAAGCCCAAAGATCACA3΄) Rv (5΄TCCAGCCTCCTCATTAGCCT3΄) Fw (5΄GCCCCAATTCGCGCCAAGGA3΄) Rv (5΄AGGTTGGCGGCAGTTCTGGG3΄) Fw (5΄CTCGACAACTTCCCAGATAACC3΄) Rv (5΄GGTACAGGTTGCGATAGATGATAGC3΄) Fw (5΄TCCAACTACTCCTCTTGCTACTGAC3΄) Rv (5΄GTGATCATACATCCTGGTCTACTGC3΄) Fw (5΄GTGCGACGAGTACTTTCTCAACTG3΄) Rv (5΄CTAGAGATGACGTCACACACTTCTC3΄) Fw (5΄TGATCTCTGCTGACAAGGCTT3΄) Rv (5΄CCGACCTTGAATCCAGTTGG3΄) |
References
- Cunha-Oliveira, T.; Montezinho, L.; Simões, R.F.; Carvalho, M.; Ferreiro, E.; Silva, F.S.G. Mitochondria: A Promising Convergent Target for the Treatment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Cells 2024, 13, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, S.N.; Lo Giudice, C.; Lavecchia, A.; Poeta, M.L.; Chiara, M.; Picardi, E.; Pesole, G. Mitochondrial and Nuclear DNA Variants in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Enrichment in the Mitochondrial Control Region and Sirtuin Pathway Genes in Spinal Cord Tissue. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bess, A.S.; Crocker, T.L.; Ryde, I.T.; Meyer, J.N. Mitochondrial dynamics and autophagy aid in removal of persistent mitochondrial dna damage in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nucleic acids research 2012, 40, 7916–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, N.L.; Kleeberger, S.R.; Burkholder, A.B.; Walters, D.M.; Gladwell, W.; Gerrish, K.; Vellers, H.L. Vanadium Pentoxide Exposure Causes Strain-Dependent Changes in Mitochondrial DNA Heteroplasmy, Copy Number, and Lesions, but Not Nuclear DNA Lesions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, D.A.; Gerrard, J.M.; Glover, S.M.; Ghr, R. Preferential attack of mitochondrial DNA by afiatoxin B1 during hepatocaricongenesis. Science 1982, 215, 73–75. [Google Scholar]
- Natarelli, N.; Gahoonia, N.; Aflatooni, S.; Bhatia, S.; Sivamani, R.K. Dermatologic Manifestations of Mitochondrial Dysfunction: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ma, J.; Lu, W. The significance of mitochondrial dysfunction in cancer. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute 2020, 21, 5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinti, M.V.; Fink, G.K.; Hathaway, Q.A.; Durr, A.J.; Kunovac, A.; Hollander, J.M. Mitochondrial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus: an organ-based analysis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019, 316, 268–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Sachdeva, P. Critical appraisal on mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Aging Med (Milton). 2022, 5, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, C.; An, P.; Luo, Y.; Jiao, L.; Luo, J.; Li, Y. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Therapeutic Perspectives in Cardiovascular Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 16053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Guan, T.; Shafiq, K.; Yu, Q.; Jiao, X.; Na, D.; Li, M.; Zhang, G.; Kong, J. Mitochondrial dysfunction in aging. Ageing Res Rev. 2023, 88, 101955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 1974, 77, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, F.; Eckert, G.P. Caenorhabditis elegans as a Model for the Effects of Phytochemicals on Mitochondria and Aging. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onraet, T.; Zuryn, S. C. elegans as a model to study mitochondrial biology and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024, 154 (Pt A), 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, C.S. Genome sequence of the nematode C. elegans: a platform for investigating biology. Science 1998, 282, 2012–2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Ma, Z. Anti-Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans of Polysaccharides from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Molecules 2024, 29, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somuah-Asante, S.; Sakamoto, K. Stress Buffering and Longevity Effects of Amber Extract on Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). Molecules 2022, 27, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, M.C.; Rooney, J.P.; Ryde, I.T.; Bernal, A.J.; Bess, A.S.; Crocker, T.L.; Ji, A.Q.; Meyer, J.N. Effects of early life exposure to ultraviolet C radiation on mitochondrial DNA content, transcription, ATP production, and oxygen consumption in developing Caenorhabditis elegans. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breton, S.; Stewart, D.T.; Hoeh, W.R. Characte.rization of a mitochondrial ORF from the gender-associated mtDNAs of Mytilus spp. (Bivalvia: Mytilidae): Identification of the “missing” ATPase 8 gene. Mar Genom. 2010, 3, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma. E.; Joshi, R.; Gulati, A. L-Theanine: An astounding sui generis integrant in tea. Food Chemistry 2018, 242, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Peng, Y.; Gong, Y. New Perspectives on Sleep Regulation by Tea: Harmonizing Pathological Sleep and Energy Balance under Stress. Foods 2022, 11, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.Y.; Meng, X.; Gan, R.Y.; Zhao, C.N.; Liu, Q.; Feng, Y.B. Li, S.; Wei, X.L.; Atanasov, A.G.; Corke, H.; Li, H.B. Health Functions and Related Molecular Mechanisms of Tea Components: An Update Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20, 6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Kang, J.; Zhu, H.; Wang, K.; Han, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; He, P.; Tu, Y.; et al. L-Theanine and Immunity: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Yang, S.; Xie, Z.; Wan, X. Synaptic modification by L-theanine, a natural constituent in green tea, rescues the impairment of hippocampal long-term potentiation and memory in AD mice. Neuropharmacology 2018, 138, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.; McKune, A.J.; Georgousopoulou, E.N.; Kellett, J.; D’Cunha, N.M.; Sergi, D.; Mellor, D.; Naumovski, N. The Effect of L-Theanine Incorporated in a Functional Food Product (Mango Sorbet) on Physiological Responses in Healthy Males: A Pilot Randomised Controlled Trial. Foods 2020, 9, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Wu, D.T.; Kenaan, A.; Geng, F.; Li, H.B.; Gunaratne, A.; Li, H.; Gan, R.Y. L-Theanine: A Unique Functional Amino Acid in Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) With Multiple Health Benefits and Food Applications. Front Nutr. 2022, 9, 853846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, S. Modulation of irinotecan-induced genomic DNA damage by theanine. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2012, 50, 1749–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romesberg, A.; Van Houten, B. Targeting Mitochondrial Function with Chemoptogenetics. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palikaras, K.; Lionaki, E.; Tavernarakis, N. Coordination of mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis during ageing in C. elegans. Nature 2015, 521, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, R.; Smith, R.L.; De Vos, W.H.; Manders, E.M.M.; van der Spek, H. In Vivo Visualization and Quantification of Mitochondrial Morphology in C. elegans. Methods Mol Biol. 2021, 2276, 397–407. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, M.C.; Rooney, J.P.; Ryde, I.T.; Bernal, A.J.; Bess, A.S.; Crocker, T.L.; Ji, A.Q.; Meyer, J.N. Effects of early life exposure to ultraviolet C radiation on mitochondrial DNA content, transcription, ATP production, and oxygen consumption in developing Caenorhabditis elegans. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, S.; Li, A.; Weinert, J.L.; Fritsch, C.; Ericson, N.G.; Alexander-Floyd, J.; Braeckman, B.P.; Haynes, C.M.; Bielas, J.H.; Gidalevitz, T.; Vermulst, M. Multiple Molecular Mechanisms Rescue mtDNA Disease in C. elegans. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 3115–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, M.; Qin, J.; Ye, B.; Wang, Q. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Chronic Liver Disease. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 3156–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dua, N.; Seshadri, A.; Badrinarayanan, A. DarT-mediated mtDNA damage induces dynamic reorganization and selective segregation of mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 2022, 221, e202205104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokolenko, I.N.; Wilson, G.L.; Alexeyev, M.F. Persistent damage induces mitochondrial DNA degradation. DNA Repair 2013, 12, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D. 3rd.; Yang, Q. Genetically Encoded ATP Biosensors for Direct Monitoring of Cellular ATP Dynamics. Cells 2022, 11, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Vizarra, E.; Zeviani, M. Mitochondrial disorders of the OXPHOS system. FEBS Lett. 2021, 595, 1062–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, C.; Feng, C.; Yan, C.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Guo, C.; Wang, X. Role of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in homeostasis regulation. Redox Rep. 2022, 27, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Bai, K.W.; He, J.; Niu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T. Curcumin attenuates hepatic mitochondrial dysfunction through the maintenance of thiol pool, inhibition of mtDNA damage, and stimulation of the mitochondrial thioredoxin system in heat-stressed broilers. J Anim Sci. 2018, 96, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Ye, F.; Dan, G.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Q.; Zou, Z.; Cao, J.; Sai, Y. Resveratrol Regulates Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Fission/Fusion to Attenuate Rotenone-Induced Neurotoxicity. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 6705621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Asunción, J.G.; Del Olmo, M.L.; Gómez-Cambronero, L.G.; Sastre, J.; Pallardó, F.V.; Viña, J. AZT induces oxidative damage to cardiac mitochondria: protective effect of vitamins C and E. Life Sci. 2004, 76, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Zhong, L.; Jiang, L.; Geng, C.; Yao, X.; Cao, J. Phellinus linteus mushroom protects against tacrine-induced mitochondrial impairment and oxidative stress in HepG2 cells. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddyvari, H.; Govatati, S.; Matha, S.K.; Korla, S.V.; Malempati, S.; Pasupuleti, S.R.; Bhanoori, M.; Nallanchakravarthula, V. Therapeutic effect of green tea extract on alcohol induced hepatic mitochondrial DNA damage in albino wistar rats. J Adv Res. 2017, 8, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, S.; Schurman, S.H.; Harboe, C.; de Souza-Pinto, N.C.; Bohr, V.A. Base excision repair of oxidative DNA damage and association with cancer and aging. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu W, Liu Y, Yin H. Mitochondrial Dynamics: Biogenesis, Fission, Fusion, and Mitophagy in the Regulation of Stem Cell Behaviors. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 9757201. [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge, D.G.; Kang, B.H.; Kokel, D.; Mitani, S.; Staehelin, L.A.; Xue, D. Caenorhabditis elegans drp-1 and fis-2 regulate distinct cell-death execution pathways downstream of ced-3 and independent of ced-9. Mol Cell 2008, 31, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, R.; Bo, H.; Zhang, Y. Exercise Improves the Coordination of the Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response and Mitophagy in Aging Skeletal Muscle. Life (Basel) 2023, 13, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Chai, R.; Luan, Y.; Du, Y.; Xue, W.; Shi, S.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y. Trends in mitochondrial unfolded protein response research from 2004 to 2022: A bibliometric analysis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023, 11, 1146963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, C.F.; Vander Wende, H.; Simko, M.; Klum, S.; Barfield, S.; Choi, H.; Pineda, V.V.; Kaeberlein, M. Activation of the mitochondrial unfolded protein response does not predict longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat Commun. 2014, 5, 3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto. M.; Moraes, C.T. Mechanisms linking mtDNA damage and aging. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015, 85, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, G.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Itaconate prolongs the healthy lifespan by activating UPRmt in Caenorhabditis elegans. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022, 923, 174951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.A.; Fleming, J.T. Basic Culture Methods. Methods in cell biology 1995, 48, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyd, W.A.; Crocker, T.L.; Rodriguez, A.M.; Leung, M.C.; Lehmann, D.W.; Freedman, J.H.; Van Houten, B.; Meyer, J.N. Nucleotide excision repair genes are expressed at low levels and are not detectably inducible in Caenorhabditis elegans somatic tissues, but their function is required for normal adult life after UVC exposure. Mutat Res. 2010, 683, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang. L.; Jie, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B. Significant longevity-extending effects of EGCG on Caenorhabditis elegans under stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009, 46, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermolaeva, M.A.; Segref, A.; Dakhovnik, A.; Ou, H.L.; Schneider, J.I.; Utermöhlen, O.; Hoppe, T.; Schumacher, B. DNA damage in germ cells induces an innate immune response that triggers systemic stress resistance. Nature 2013, 501, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Hunt, C.P.; Rooney, J.P.; Ryde, I.T.; Anbalagan, C.; Joglekar, R.; Meyer, J.N. PCR-Based Analysis of Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number, Mitochondrial DNA Damage, and Nuclear DNA Damage. Curr Protoc Toxicol. 2016, 67, 20.11.1–20.11.25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gai, T.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Ye, T.; Zhang, W. Neurotoxicity of bisphenol A exposure on Caenorhabditis elegans induced by disturbance of neurotransmitter and oxidative damage. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023, 252, 114617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





