Submitted:
04 March 2024
Posted:
05 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Review of the Robertson-Walker Metric
2.1. Isotropic and Homogeneous space
2.2. Fundamental Observers
2.3. Synchronous Coordinates
2.4. Curved Spatial Hypersurface
2.5. Robertson Walker Metric
2.6. Rescale Time
3. The Possibility of Varying Speed of Light Theory in the Robertson-Walker Metric
4. The Consequences of the Varying Speed of Light
4.1. Stress Energy Tensor
4.2. Cosmological Redshift in the RW Metric
4.3. Hilbert-Einstein Action
4.4. Adiabatic Expansion and Cosmological Evolution of the Planck Constant
4.5. Einstein Tensors
4.6. Bianchi Identity and Cosmological Evolution of Rest Mass
5. Friedmann Equation and Huuble Tension
5.1. Hubble Radius
5.2. Local Physics Laws
6. Discussion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- M. J. Duff, L. B. Okun and G. Veneziano, JHEP 03, 023 (2002) [arXiv:physics/0110060 [physics]]. [CrossRef]
- J. P. Uzan, Rev. Mod. Phys. 75, 403 (2003) [arXiv:hep-ph/0205340 [hep-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- G. F. R. Ellis and J. P. Uzan, Am. J. Phys. 73, 240-247 (2005) [arXiv:gr-qc/0305099 [gr-qc]]. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Duff, Contemp. Phys. 56, no.1, 35-47 (2015) [arXiv:1412.2040 [hep-th]]. [CrossRef]
- S. Lee, JCAP 08, 054 (2021) [arXiv:2011.09274 [astro-ph.CO]]. [CrossRef]
- S. Lee, Foun. of Phys 53, 40 (2023) [arXiv:2303.13772 [physics.gen-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- G. Hinshaw et al., Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 208, 20 (2013) [arXiv:1212.5226 [astro-ph.CO]]. [CrossRef]
- N. Aghanim et al. [Planck], Astron. Astrophys. 641, A1 (2020) [arXiv:1807.06205 [astro-ph.CO]]. [CrossRef]
- L. Guzzo, J. Bel, D. Bianchi, C. Carbone, B. R. Granett, A. J. Hawken, F. G. Mohammad, A. Pezzotta, S. Rota and M. Zennaro, [arXiv:1803.10814 [astro-ph.CO]]. [CrossRef]
- R. Cawthon et al. [DES], Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 513, 5517 (2022) [arXiv:2012.12826 [astro-ph.CO]]. [CrossRef]
- D. Morin Introduction to Classical Mechanics (Cambridge University Press, 2007).
- J. N. Islam, An Introduction to Mathematical Cosmology (Cambridge University Press, 2001).
- J. V. Narlikar,An Introduction to Cosmology (Cambridge University Press, 3rd Ed 2002).
- M. P. Hobson, G. P. Efstathiou, and A. N. Lasenby, General Relativity: An Introduction for Physicists (Cambridge University Press, 2006).
- M. Roos, Introduction to Cosmology (John Wiley and Sons, 2015).
- J. D. Barrow, Phy. Rev. D. 59, 043515 (1988) [arXiv:astro-ph/9811022 [astro-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- Robertson, H. P. (1929). "On the Foundations of Relativistic Cosmology". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 15 (11): 822–829. Bibcode:1929PNAS...15..822R. [CrossRef]
- Walker, A. G. (1937), "On Milne’s theory of world-structure", Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society, Series 2, 42 (1): 90–127, Bibcode:1937PLMS...42...90W. [CrossRef]
- S. Lee, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 522, no.3, 3248-3255 (2023) [arXiv:2301.06947 [astro-ph.CO]]. [CrossRef]
- S. Lee, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 524, no.3, 4019-4023 (2023) [arXiv:2302.09735 [astro-ph.CO]]. [CrossRef]
- S. Lee, submitted.
- B. Leibundgut, Astrophys. J. Lett. 466, L21 (1996) [arXiv:astro-ph/9605134 [astro-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- A. G. Riess et al. [Supernova Search Team], Astron. J. 114, 722 (1997) [arXiv:astro-ph/9707260 [astro-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- R. J. Foley, A. V. Filippenko, D. C. Leonard, A. G. Riess, P. Nugent and S. Perlmutter, Astrophys. J. Lett. 626, L11-L14 (2005) [arXiv:astro-ph/0504481 [astro-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- S. Blondin and J. L. Tonry, Astrophys. J. 666, 1024-1047 (2007) [arXiv:0709.4488 [astro-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- S. Blondin, T. M. Davis, K. Krisciunas, B. P. Schmidt, J. Sollerman, W. M. Wood-Vasey, A. C. Becker, P. Challis, A. Clocchiatti and G. Damke, et al. Astrophys. J. 682, 724-736 (2008) [arXiv:0804.3595 [astro-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- J. P. Norris, R. J. Nemiroff, J. D. Scargle, C. Kouveliotou, G. J. Fishman, C. A. Meegan, W. S. Paciesas and J. T. Bonnell, Astrophys. J. 424, 540 (1994) [arXiv:astro-ph/9312049 [astro-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- R. A. M. J. Wijers and B. Paczynski, Astrophys. J. Lett. 437, L107 (1994) [arXiv:astro-ph/9406007 [astro-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- D. Band, Astrophys. J. Lett. 432, L23 (1994) [arXiv:astro-ph/9407007 [astro-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- A. Meszaros and P. Meszaros, Astrophys. J. 466, 29 (1996) [arXiv:astro-ph/9512164 [astro-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- T. T. Lee and V. Petrosian, Astrophys. J. 474, 37 (1997) [arXiv:astro-ph/9607127 [astro-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- H. Y. Chang, Astrophys. J. Lett. 557, L85 (2001) [arXiv:astro-ph/0106220 [astro-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- D. F. Crawford, [arXiv:0901.4169 [astro-ph.CO]].
- F. W. Zhang, Y. Z. Fan, L. Shao and D. M. Wei, Astrophys. J. Lett. 778, L11 (2013) [arXiv:1309.5612 [astro-ph.HE]]. [CrossRef]
- A. Singh and S. Desai, JCAP 02, no.02, 010 (2022) [arXiv:2108.00395 [astro-ph.HE]]. [CrossRef]
- M. R. S. Hawkins, Astrophys. J. Lett. 553, L97 (2001) [arXiv:astro-ph/0105073 [astro-ph]]. [CrossRef]
- D. C. Dai, G. D. Starkman, B. Stojkovic, D. Stojkovic and A. Weltman, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 231302 (2012) [arXiv:1204.5191 [astro-ph.CO]]. [CrossRef]
- S. Lee, Phys. Dark Universe 42, 101286 (2023) [arXiv:2212.03728 [astro-ph.CO]]. [CrossRef]
- L. Ryder, Introduction to General Relativity (Cambridge University Press, 2009).
- S. Weinberg, Cosmology (Oxford University Press, 2008).
- S. Lee, Preprints 2024, 2024021598. [CrossRef]
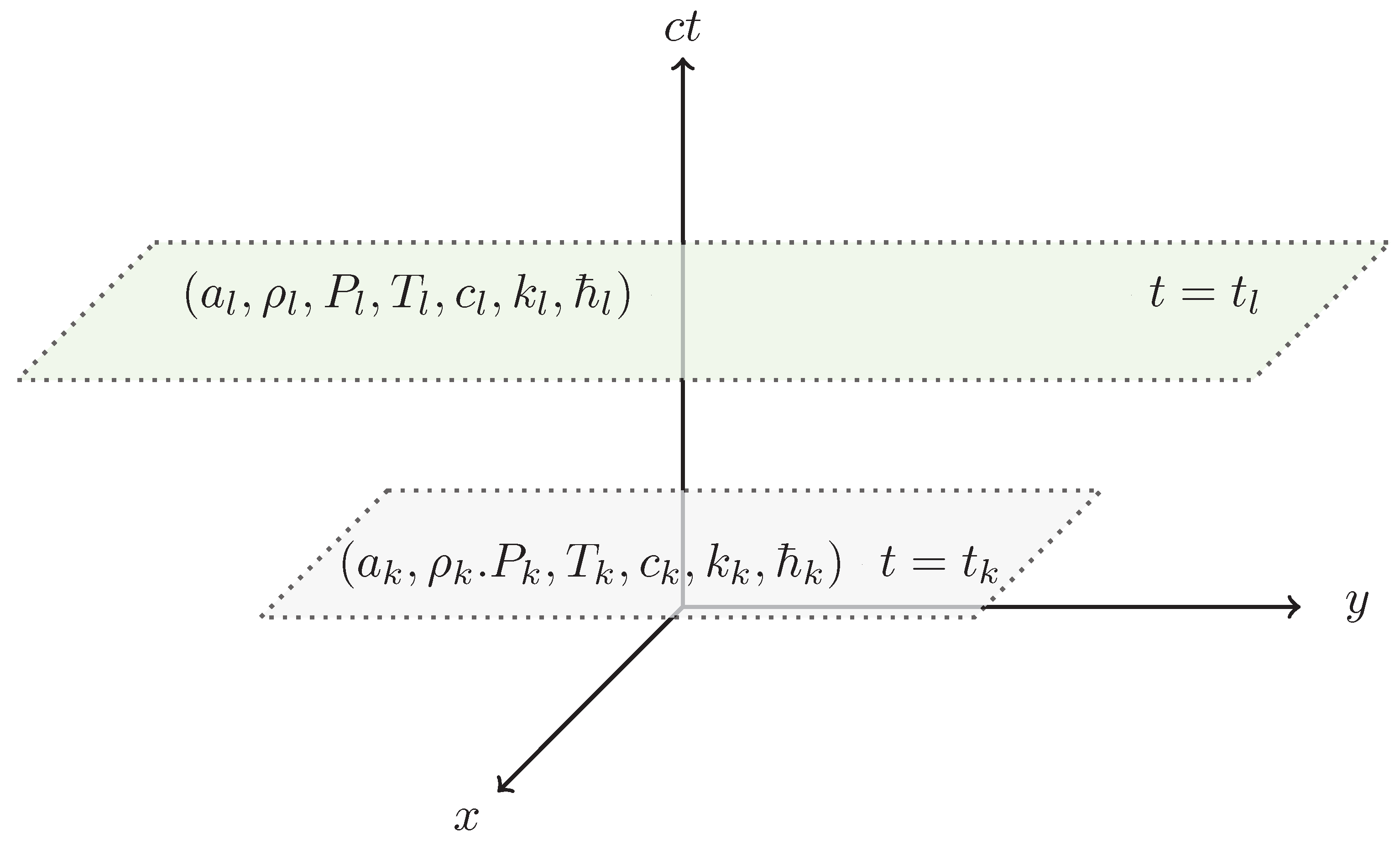
| local physics laws | Special Relativity | Electromagnetism | Thermodynamics |
| quantities | |||
| constants | |||
| energies |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





