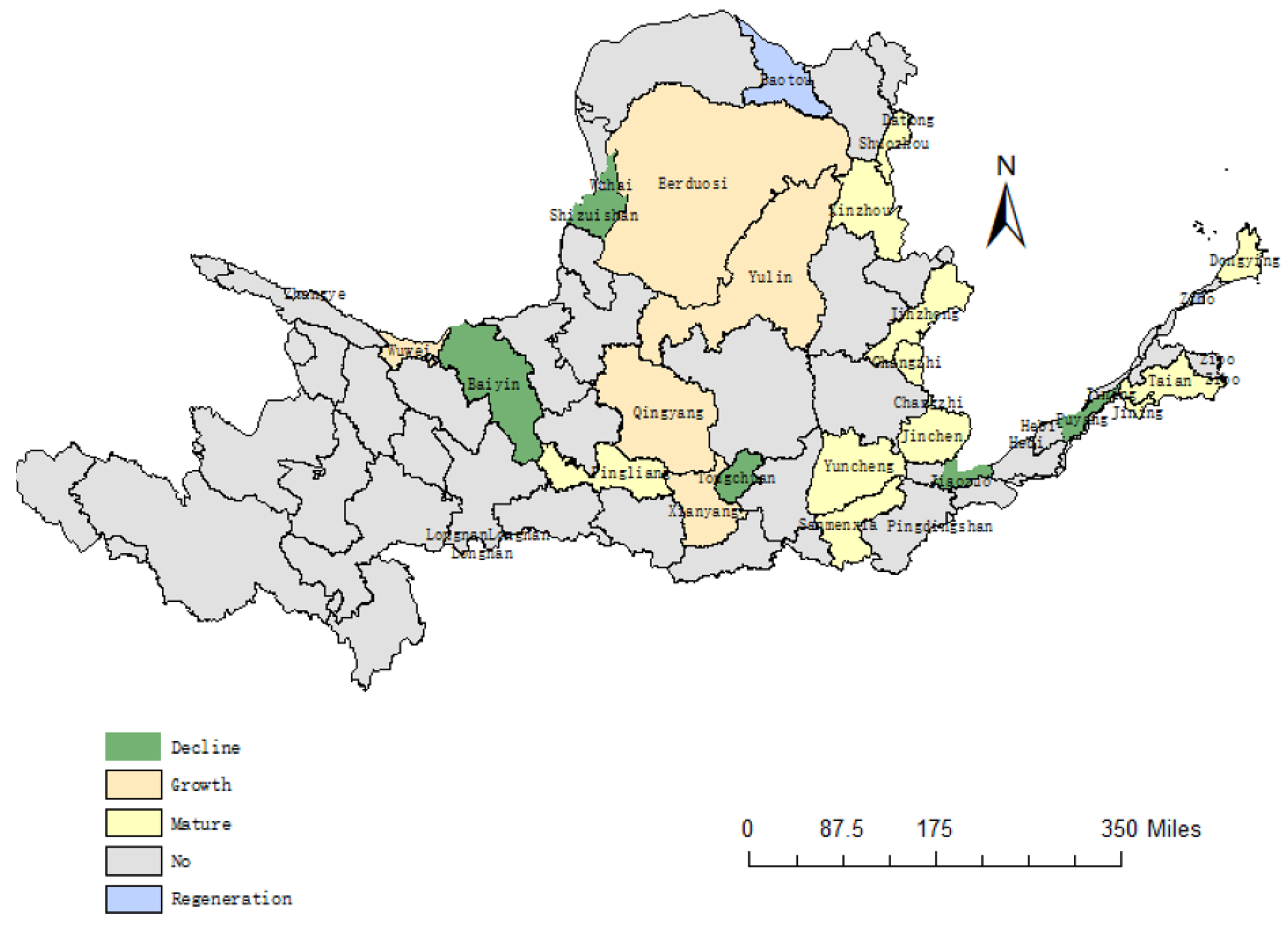
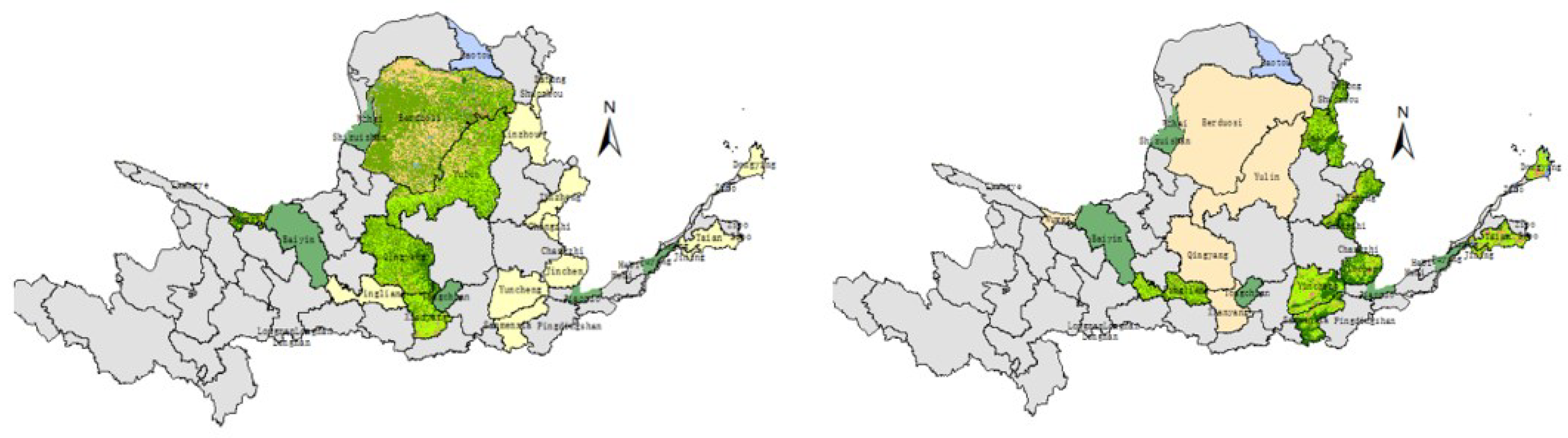
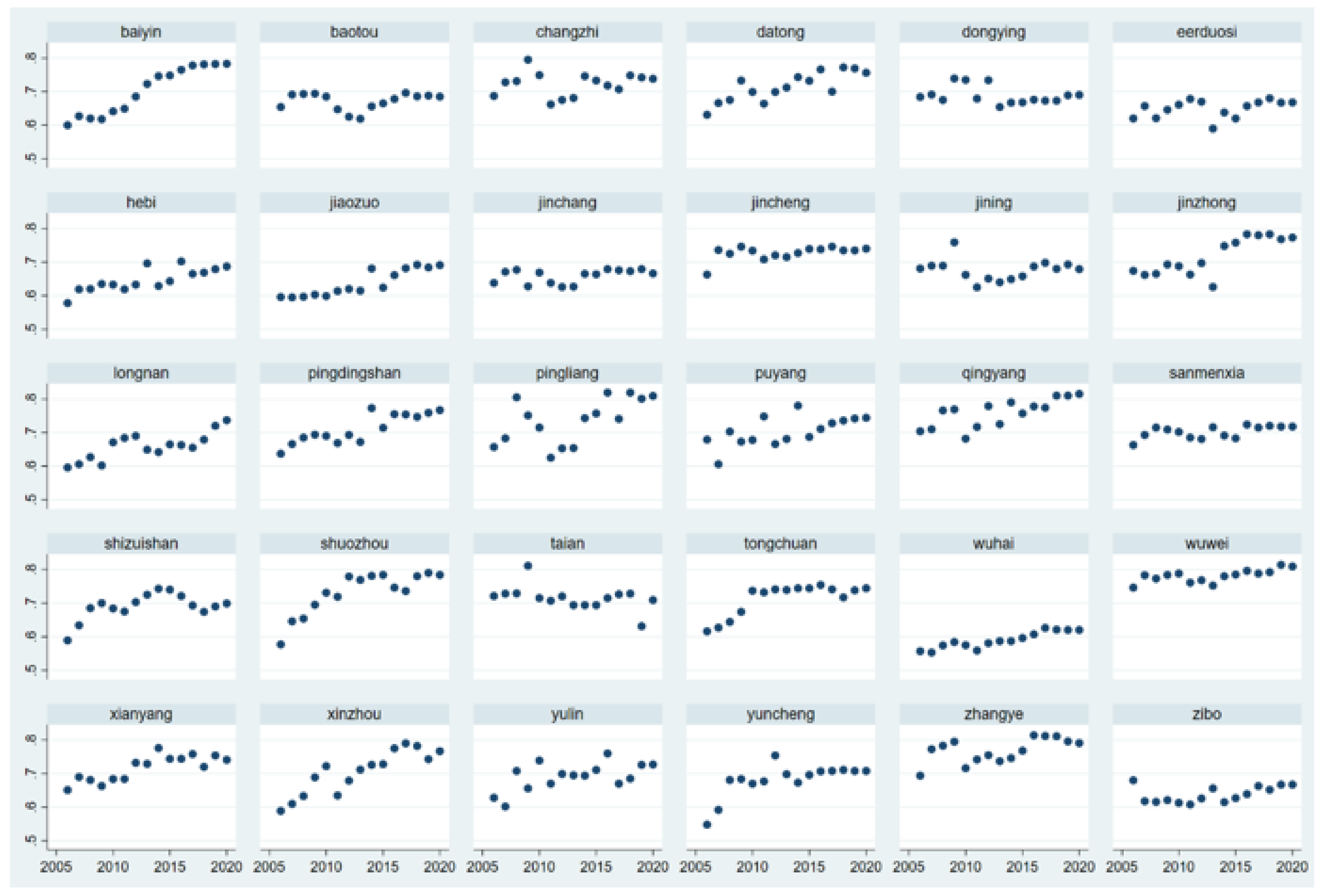
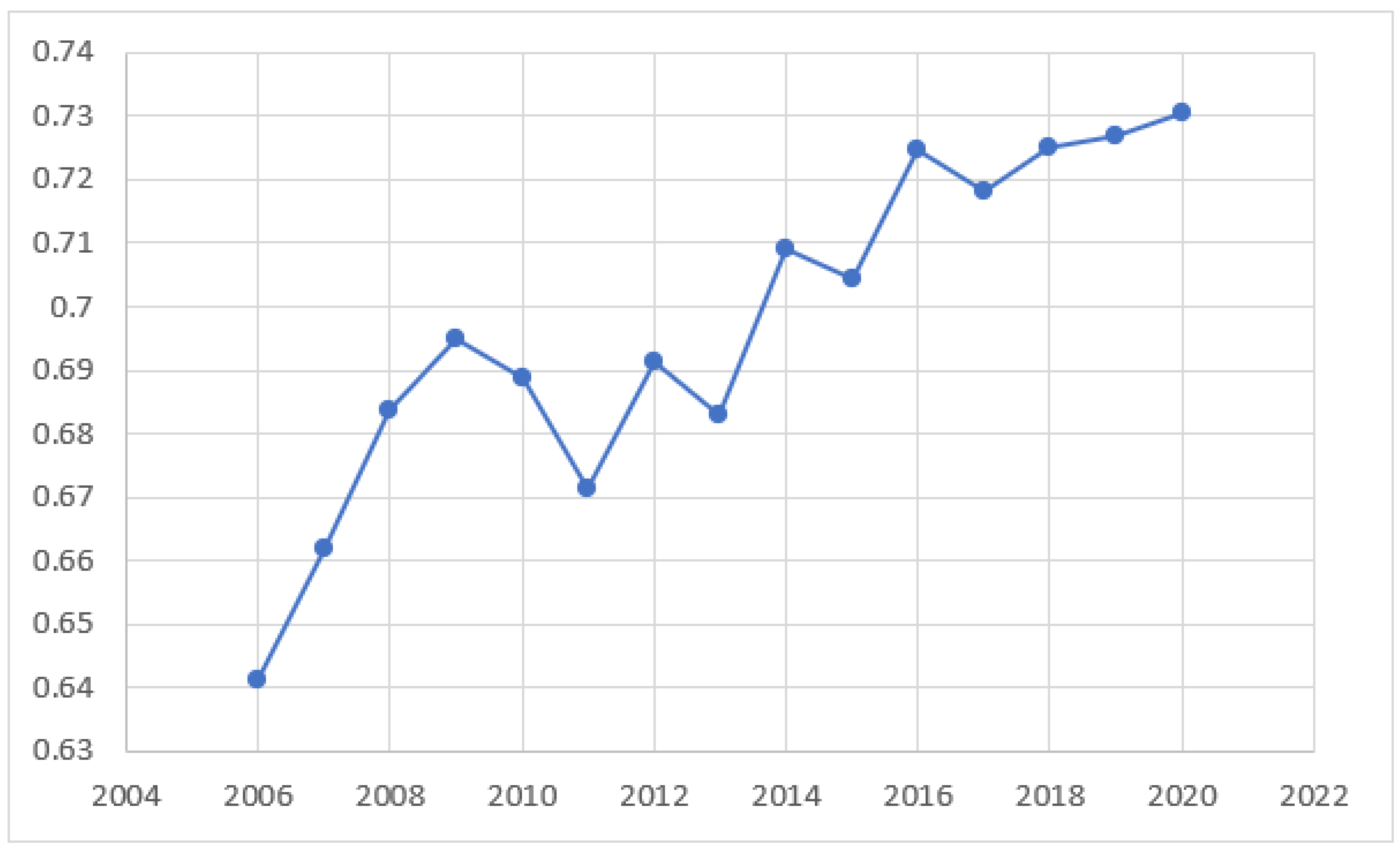
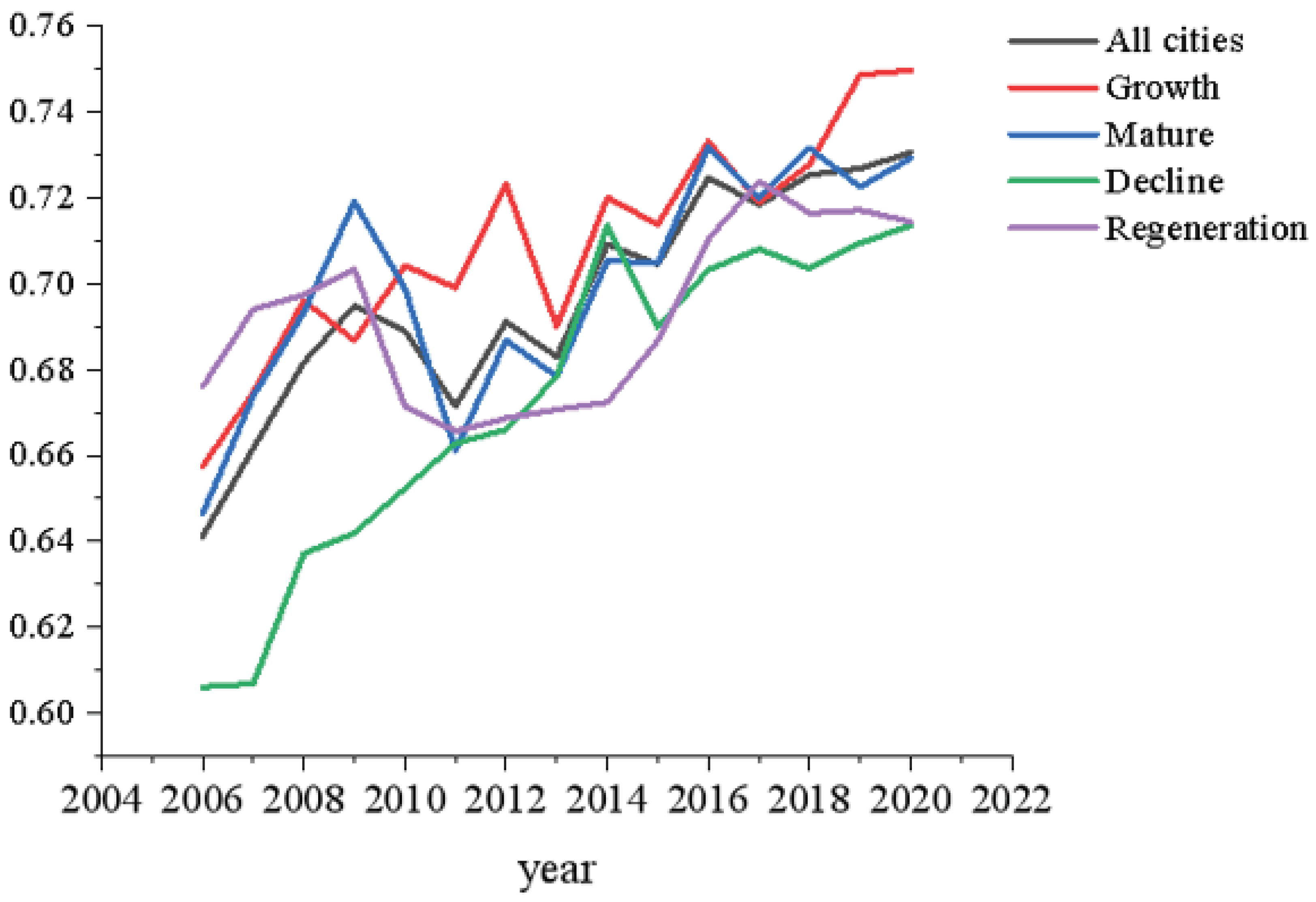
Resource exploitation is a double-edged sword for urban development. On the one hand, resource exploitation provides a material guarantee for industrialization, but on the other hand, it affects the ecological environment, increases the high level of pollutant emissions and aggravates the difficulty of ecological management. As China enters a new stage of high-quality development, the sustainable development of resource-based cities is imminent. In 2013, the State formulated the National Plan for the Sustainable Development of Resource-Based Cities (2013–2020) (hereinafter referred to as the Plan) and put forward the scientific classification of resource-based cities into four categories: growth, maturity, decline and regeneration, and established orderly development, optimized industrial structure and people's livelihood as the principles of sustainable development of resource-based cities. Under the above background, this paper takes the resource-based cities in the Yellow River Basin as the research object, guided by the theory of green economy and sustainable development, analyses the change characteristics and influencing factors of the ecological safety level of resource-based cities in the basin, considers the externality of ecological protection, and analyses the differences in the ecological safety level between upstream and downstream and different types of resource-based cities. With the comprehensive and systematic promotion of ecological protection in the Yellow River Basin, whether there is a narrowing and convergence of ecological safety differences is of great significance to the realization of ecological safety in the Yellow River Basin.
The scientificity and rationality of ecological safety evaluation index system determines the credibility and effectiveness of quantitative evaluation, which is widely used in ecology, soil, environment, economy and other fields, provinces, cities, villages, mining areas and other scales. Kesler, a foreign scholar, earlier established the evaluation framework of regional ecological safety of coal mining earlier, mainly considering the impact of coal mining on the regional ecological environment. Costanza and others further refined the evaluation index system of the ecological safety of mining areas. Aigbedion and others constructed the index system including land structure stability, biodiversity, air pollution, water pollution and other factors in the study of regional ecological safety of mineral resources in Nigeria. Maxim and others [
6] increased vegetation, air and water pollution and surface collapse. Domestic scholars construct the ecological safety index system of coal resource-based cities, focusing on urban land structure, urban ecological function, urban interference and other aspects to complement the ecological evaluation index system of coal resource-based cities. Yu Jian et al. [
18] added regional development index to study the ecological safety of coal resource-based cities in Anhui, Cao Gang et al. [
19] added indicators such as construction land pressure, land use structure and land production pressure to study the ecological safety evaluation of Linxiang City, and Cui Xinyue et al. [
20] added regional policy response indicators such as scientific research, education and energy conservation to study the ecological safety level of Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. They found that the ecological safety of resource-based cities in Anhui Province was slightly worse. Liu Surong and Yang Huimiao [
11], relied on big data technology to survey ecological environment assessment index system of resource-based cities by using the PSR analysis framework in CNKI from 2006 to 2016, and summarized 39 ecological environment assessment index systems of resource-based cities with four layers, three dimensions and 11 elements. Lu Guozhi et al. [
12] used PSR model to analyze the ecological safety of Shizuishan, a coal resource-based city, and added indicators such as coal resource exploitation and mining industry investment ratio, and obtained the overall change of ecological safety through obstacle measurement model and grey prediction. Over-exploitation and limited environmental treatment are the main obstacle factors of ecological safety. To study the causal relationship between natural climate, water resources, land use and other ecological factors and human health and living environment. Zhao Xiang and He Guizhen[
13] used CiteSpace software to summarize the research on DPSIR analysis framework at home and abroad from 1998 to 2019. The DPSIR method has matured in small-scale land and water resources research, and needs to be improved in large-scale research such as agriculture, marine area and city. Ness et al. [
14] used the DPSIR model to construct the evaluation index of ecological sustainable development of resource-based cities, and analyzed the spatial changes of urban ecology before and after environmental constraints. In the research of Shi Xixi and Yang Li [
17], the indicators of resources and science and technology system were added, and the coordination of sustainable development in the Yellow River Basin from 2008 to 2018 was evaluated. It was considered that attaching importance to ecological protection would not reduce the speed of economic development, while unreasonable economic development mode was the root of conflict, and resource productivity was the key factor to solve the conflict. The nexus of ecology-economy-social development could be explored from the perspectives of ecological pollution control, sustainable development and technological progress. Du Yong [
18] selected 26 indicators from four aspects: resource safety, economic development, people's livelihood and well-being, and environmental protection to evaluate the ecological civilization of resource-based cities in China. Chen Dan and Wang Ran [
19] constructed an index evaluation system of three dimensions: environmental carrying capacity, intensive use of resources and environmental quality, and compared the development level of ecological civilization of mining cities in the Middle East and the West. According to the regional characteristics of coal mines, Liu Jin et al. [
20] constructed 28 ecological safety evaluation index systems in four dimensions: resources, environment, society and economy.
After selecting indices, determining weights and comprehensively calculating the ecological safety index, the most critical step is the method of determining weights, including entropy weight method, principal component method, analytical hierarchy process, OWA method, CRITIC method and other weight confirmation methods. Entropy weight method and principal component analytical hierarchy process are common evaluation methods. Ordered weighted average operator (OWA) operator is usually used in combination with geographic information system (GIS) in ecological safty evaluation. Zhang Hong et al. [
21] constructed the ecological safety evaluation system of Dali City from three levels: nature, ecology and landscape, and carried out the multi-criteria decision evaluation of ordered weighted average operator (OWA), multi-criteria decision evaluation, and obtained the ecological safety evaluation results of Dali City under different decision risk coefficients. Bao Yanli and Zhang Hong [
22] combined the PSR model with the EES model, and introduced the CRITIC method into the traditional grey target model to calculate the comprehensive ecological safety level of Yunnan Province in 2017. Li Bingyi and Shi Xueyi [
23] used the ecological footprint comprehensive account model to evaluate the ecological safety of Jincheng, a coal resource-based city, and made suggestions for improvement suggestions from the aspects of industrial structure, land use efficiency and population size. Wu Ge et al. [
24] analyzed the changes of ecological footprint, ecological footprint diversity index, ecological carrying capacity and ecological surplus/deficit in Yan'an, and concluded that although the resource use efficiency is improving, the resource consumption rate is higher than the resource regeneration speed. Xin Boxiong et al. [
25] They calculated the ecological efficiency differences of 28 cities based on three-stage DEA and bootstrap DEA models, and pointed out that the main influencing factors of regional ecological efficiency are regional scale, regional carrying capacity, and regional environmental quality and so on. Yu Jian et al. [
18] used entropy weight fuzzy matter element model to evaluate the ecological safety of Anhui resource-based cities, and compared with the multi-index comprehensive evaluation method, it was concluded that Ma'anshan's ecological safety was poor, while Chizhou and Anqing had a tendency to deteriorate, which was consistent with the analysis results obtained by the multi-index comprehensive method.