1. Introduction
Tetradenia riparia (Hochst.) Codd is an aromatic plant native to southern Africa, a member of the Lamiaceae [
1]. Commonly known in Brazil as “false myrrh”, is mainly used as an ornamental [
2,
3]. It is considered an important medicinal plant used in to treat a wide range of diseases, such as malaria, angina, yaws, helminths, gastroenteritis, dental abcesses, and other disorders [
4,
5,
6].
Scientific studies on both
T. riparia essential oil (TrEO) in different parts of the world focused mainly on their chemical composition. TrEO is a complex mixture of terpenoids, including monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, and diterpenes (hydrocarbons or oxygenated), in which the last one is the most representative class in the oil [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]. Studies with TrEO showed it to have antimalarial [
12], anti-inflammatory [
13], antifungal [
14], repellent against
Anopheles gambiae [
15], trypanocidal [
16],
anti-tuberculosis [
17], and antimicrobial [
18,
19] activities.
The aims of this study were (i) to determine the chemical composition of essential oil extracted from T. riparia (ii) to test antimicrobial activity against some pathogens strains of TrEO (iii) prepare, characterize and perform necessary hydrophilic-lipophilic balance of Tetradenia riparia essential oil nanoemulsion (NTrEO) (iv) to test insecticidal activity against larvae, pupae, and eggs of Aedes aegypti of TrEO and NTrEO (iv), and Acute toxicity of NTrEO in non-target organisms.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of Isolated Compounds
Hydrodistillation of fresh leaves yielded 0,42% of apale yellow oil, which was analysed by GC/MS. The chemical composition of the oil is recorded in
Table 1. In all, 20 components were detected. We verified that aromadendrene oxide (23.47%), Isogeraniol (8.58%), ledol (7.62%), and Shyobunol (7.58%) were the major constituents in TrEO.
Gazim and collaborators investigated [
2] the seasonality variation in chemical composition, and antimicrobial essential oil activity of collected
T. riparia leaves in southern Brazil and observed a chemovariation that can be environmentally determined by a seasonal influence. In winter, the samples collected showed the highest percentages of calculone (24.70%), abietadiene (13.54%), and viridiflorol (4.20%). In autumn, the major constituents were ledol (8.74%), and cis-muurolol-5-en-4-α-ol (13.78%). Samples collected in spring-summer contained the highest percentages of fenchone (12.67%), 14-hydroxy-9-epi-caryophyllene (24.36%), and α-cadinol (8.33%).
Melo and co-workers have previously investigated the in vitro antimicrobial activity against cariogenic bacteria, and the chemical composition of the essential oil from
Tetradenia riparia identified aromadendrene oxide (14.0%), (E,E)-farnesol (13.6%), dronabinol (12.5%), and fenchone (6.2%) as the major constituents of TrEO [
20]. In another study,
T. riparia leaf oil contained mainly fenchone (18.9%), followed by (
E,E)-farnesol (17.7%), and aromadendrene oxide (17.3%) [
21]. These quantitative and qualitative differences between previous studies and our sample may be attributed to harvesting season, different geographic conditions, and environmental factors.
2.2. Antibacterial Activity
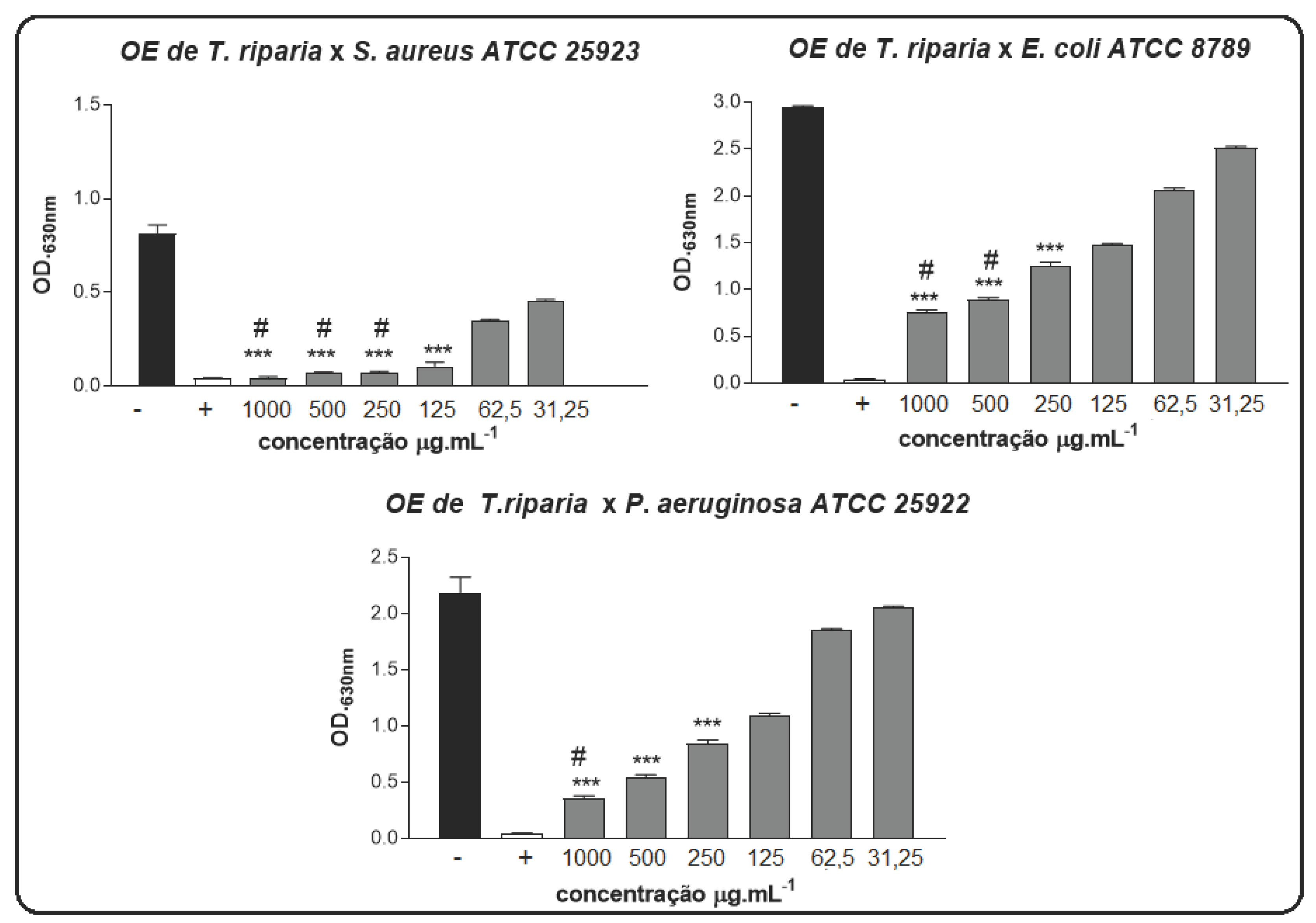
In our study, the antimicrobial activity of EO in forms was determined against two bacterial strains. O dilution method was used to determine the MIC and MBC of the EO samples. The results of antimicrobial activities of EO in free were Gram
+ bacteria
S. aureus are extremely sensitive to TrEO (
Figure 1). MIC 125 μg.mL
-1 and MBC 250 μg.mL
-1, respectively. For Gram negative bacteria
P. aeruginosa against TrEO MIC 250 μg.mL
-1, MBC 1000 μg.mL
-1, against, and bacteria
E. coli, TrEO was noted to have significant inhibitory effects (MIC 250 μg.mL
-1 and MBC 500 μg.mL
-1).
Most studies on antimicrobial properties used the essential oil of
T. riparia [
12,
17,
19,
21]. Gazim et al. [
2], reported the antimicrobial activity against a panel of pathogenic bacteria such as
S. aureus, Bacillus subtilis, and several Gram-negatives viz.
E. coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and
Klebsiella pneumoniae, the results of MIC
S. aureus and
B. subtilis presented the lowest inhibitory values, in concentrations ranging from 7.80 to 31.2 μg.mL
-1. York, Van Vuuren and Wet [
22] used TrEO, in their study considered notorious inhibition values ≤ 2.00 mg.mL
-1, and for
S. aureus, M. smegmatis, M. catarrhalis and
K. pneumoniae they were above this value. Microdilution using CAMBH was also a method to assess the effects of TrROY isolated from TrEO [
17]. The results for this compound were better for gram-positive bacteria, such as
E. faecalis and
S. aureus, both with a MIC of 62.5 μg.mL
-1.
According to these authors, the essential oil is more effective against Gram-positive bacteria compared to the tested Gram-negatives. These authors could not establish the active constituents responsible for the antimicrobial effect, but proposed that the activity is due to monoterpenes, diterpenes, and sesquiterpenes. Their conclusions are similar to the observation of Gazim et al. [
2], and they presume that the antimicrobial activity is due to presence of the monoterpene fenchone, the diterpene calyculone, and several sesquiterpenes, as well as the presence of a new compound: (E,E)-farnesol, as one of the major constituents [
21].
2.3. Development and Analysis of Nanoemulsion
In this study, the characterization of the nanoemulsions considered the droplet size, PdI, and zeta potential. The results revealed that the nanoemulsions presented a bluish reflection, without sedimentation or phase separation. To improve the solubility of essential oils in water, nanoemulsions were developed by the low energy method using phase inversion composition. This nanoencapsulation technique has advantages: it does not heat up, does not contain solvents and is low cost [
23].
The nanoemulsion (NTrEO) prepared from the essential oil of
Tetradenia riparia (TrEO) showed the best hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) was 15.5 (
Supplementary Materials: S1 Table), showing a milky white color with a slightly bluish reflection, without observation of separation of phases or any parameter that indicated instability of the formulation, such as those described by Silva [
24], as shown in
Figure 2. Light scattering in nanoscale colloidal systems causes a characteristic bluish reflection called the tyndall effect and represents a parameter indicative of stability kinetics acquired by nanoemulsions compared to macroemulsions [
25].
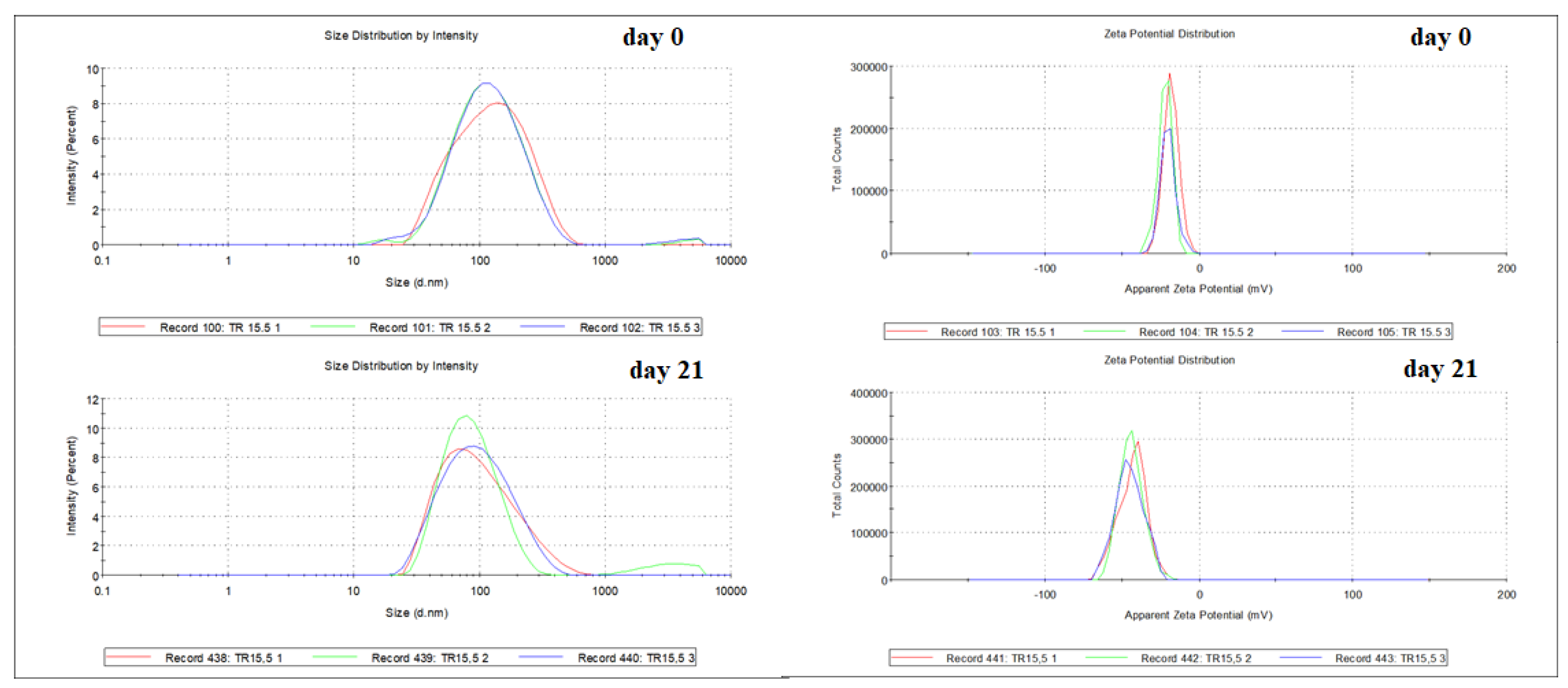
The best results were obtained with the nanoemulsion prepared with polysorbate 80 and polysorbate 20 as a surfactant (HBL 15.5). It had an average particle size of 100.93 ± 0.7 nm, a polydispersity index of 0.26 ± 0.0 (
Figure 3), and a zeta potential of – 20.13 ± 1.6 mV on day 0. The stability of the nanoemulsion (HBL 15.5) was observed over time, being found average particle size of 8.12 ± 0.17 nm, polydispersity index of 0.25 ± 0.0, and zeta potential of -44.17 ± 0.7mV after 21 days (
Table 2). The results showed that the nanoemulsion showed stability with droplet diameters below 170 nm and with a monomodal droplet size distribution [
26].
Considering that the essential oil has hydrophobic properties, that is, it is immiscible in water, its incorporation into the films is facilitated through the formation of an emulsion, which is characterized by having an aqueous phase, an oily phase and a surfactant. As nanoemulsions have the advantage or particle size at nanometer scale, which can increase counter-microorganisms, insects and also improve their physical properties, and characteristics [
27,
28,
29].
2.4. Aedes Aegypti Test
2.4.1. Evaluation of Ovicidal, Larvicidal, and Pupicidal Efficacy of OtEO and NOtEO
The present study reflected spectrum of activity with TrEO and NTrEO against the
Ae. aegypti mosquito larvae, pupae, and eggs. In view of the problems of waste in the environment and the development of insect resistance to synthetic insecticides, the recent trend is to explore natural products derived from plants that could help suppress
Aedes populations. Much research has were conducted with these chemicals that are not toxic to man and domestic animals, and serve as a useful basis for the development of safer and more selective mosquitoes insecticides [
30,
31]. In the last years, several authors have investigated several plant compounds extracted from plants of the Lamiacea family with anti-mosquito potential that included larvicide [
32,
33,
34,
35], ovicides [
36,
37], and pupicidal [
38,
39]. Our studies proved the effective use of
T. riparia essential oil and its nanoformulation for causing negative impacts on different stages of development of
Ae. aegypti. The use of pure oils in water proved that TrEO, in addition to inhibiting the hatching of larvae in ovicidal activity, also causes mortality of
Aedes in their larval and pupal stages, with improved results in the tests with NTrEO, however, it presented high values of LC50 and LC90, being considered low activity against
Ae. aegpyti [
40].
The larvicidal activity was determined by using varying concentrations (100, 200, 300, 400, and 500 µg.mL
-1). The larval mortality percentage was scored after 24 h, and the results are presented in (
Table 3). TrEO the concentration of 400 µg.mL
-1 showed mortality below 50% after 48 h and NtrEO the concentration of 300 µg.mL
-1 showed mortality below 50% after 48 h.
The lethal concentrations LC50 and LC90 values and other related parameters as the fiducial limit were calculated and presented in (
Table 4) In the case of essential oil tested on larvae, LC50 and LC90 were found to be 53.80 µg.mL
-1 and 611.77 µg.mL
-1, respectively. While, for NTrEO, these values came out to be 28.73 µg.mL
-1 and 102.28 µg.mL
-1.
The pupicidal activity of the TrEO was 500 µg.mL
-1, killed 51,2% and NtrEO at concentration of 500 µg.mL
-1, killed 60% after 48 h exposure. The LC50 and LC90 of TrEO were 630.29 µg.mL
-1 and 1445.96 µg.mL
-1, respectively (
Table 5), and LC50 and LC90 of NTrEO were 452.75 µg.mL
-1 and 1496.1 µg.mL
-1, respectively (
Table 6).
NTrEO has strong larvicidal activity when compared TrEO. As a result, TrEO was subjected to GC-MS analysis to identify the chemical components of the oil. The GC-MS profile of the chemicals revealed some essential biologically active metabolites with very strong insecticidal properties α-terpineol reported to have larvicidal or insecticidal activity [
41].
In the present work, the NTrEO exhibited ovicidal activity. The LC50 and LC90 values for the ovicidal activity were 1570.505µg.mL
-1 and 51474.323µg.mL-1, 1297.137µg.mL
-1 and 222932.031µg.mL
-1, for TrEO and NTrEO, respectively (
Table 7).
Tyagi et al. [
40] tested four essential oil samples (clove oil, jasmine oil, deodar and camphor) were tested for larvicidal and pupicidal activity against
Anopheles stephensi and
Aedes aegypti, all EOs showed moderate to high larval and pupal mortality against the both mosquito species except for camphor, which is least-effective among the others. In the same way that Camphor we also found that
T. riparia oil and its nanoemulsion had a moderate larval and pupicidal mortality rate.
Larvicidal studies of TrEO against
Rhipicephalus sanguineus found the lethal concentrations (LCs) to kill
R. sanguineus larvae were (LC50: 2.18 +/- 0.24 and LC99.9: 9.98 +/- 0.10 mg.mL
-1). The mechanism of action of EOs by bioautographic methods indicated an inhibition of 0.70 mg.mL
-1 (EOL) in the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE), which is considered promising as a basis for a new phyto-insecticide [
42].
The toxicity potential of essential oils and their components may exhibit different mean lethal concentrations depending on extrinsic and intrinsic factors of the collected plant, as well as the ecological niche of
Ae. aegypti larvae, which may affect susceptibility [
43]. Also, another factor is the larval stage. Silvério et al. [
44] investigated plant natural products for the control of
Aedes aegypti, and found that the more advanced the larval stage, the greater the detoxification capacity of the tested compound.
In this sense, further studies are needed to evaluate the mechanism of action of EO and the major compounds of T. riparia in the insecticidal action, as well as to correlate the release of the compounds as a function of time.
2.5. Acute Oral Toxicity Study
2.5.1. NOtEO Toxicity to Non-Target Organisms
During the assessment the 14 days of acute toxicity, no mortality was observed in Swiss albino mice (
Mus musculus) treated with NTrEO. Hippocratic screening indicated that animals treated with NTrEO show symptoms of tremors and corneal reflex. The control group (Tween 80) showed no behavioral changes (
Table 8).
The physiological parameters did not indicate significant differences in water consumption and food intake in the NTrEO group compared to the control group. The animals showed weight gain in the NTrEO group and differed from the control group, as shown in
Table 9
Kidneys, hearts, and lungs did not show changes in relative weight. The relative weights of the livers, kidneys, hearts, and lungs of male and female mice treated with NTrEO. The relative weight of the organs of the animals treated with NTrEO (2000 mg.kg
-1) was not changed when compared to the control (
Table 10).
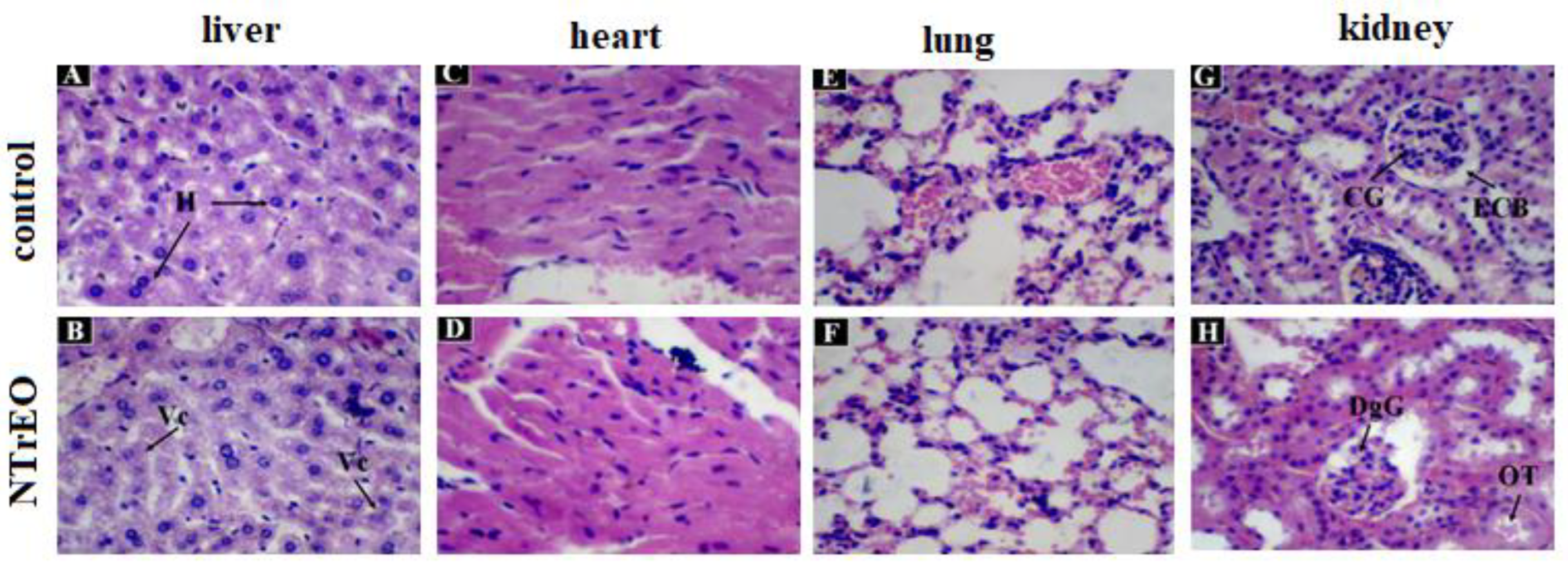
There was no significant difference. The histopathological analysis did not reveal changes in the organs of the control animals, as well as in the heart of the animals treated for both sexes with the dose of 2000 mg.kg
-1 of NTrEO. However, hypertrophied, where cytoplasmic vacuolization (steatosis) in the liver (
Figure 3B), no histopathological change in the heart and lung (
Figure 3D and 3F), and altered kidney with glomerular degeneration (DgG) and tubular obstruction (OT) damage such as dilation of the capillaries of the glomerulus, decreased space in the Bowman capsule, and tubular obstruction (
Figure 3H) in one of the animals treated with NTrEO.
In this study, the histopathological evaluation showed that only the liver and kidneys of the animals treated with NTrEO showed alterations. In the liver, the hepatic lobules, portal spaces and well-delineated hepatic veins were easily visualized and the hepatocytes formed confluent cords to the central-lobular vein. The presence of a slight degree of cytoplasmic vacuolization (steatosis) was observed in the NTrEO group.
In the kidneys, typical renal corpuscles and convoluted proximal and distal tubules (in the cortical), collecting ducts and loop of Henle (in the medulla) were visualized (
Figure 3). The animals treated with the control and NTrEO nanoemulsions showed unaltered pulmonary and cardiac morphology (
Figure 3).
As for the histopathological evaluation of the liver and kidney tissues in this study, it was possible to observe some changes. Several studies report the possibility of the appearance of alterations in these organs of animals treated with different nanoemulsions [
45,
46]. According to Yilmaz and Borchert [
47], formulations developed for controlled release have a high potential to promote side effects of different substances. This action occurs mainly due to the reduced size which, according to Borges et al., [
48], favors rapid absorption and metabolism. These authors also state that nanoemulsions have the potential to cause some toxic effect, as shown in this research.
According to Martins et al., [
41], the liver is the main detoxification organ of mammals, and the kidneys are the excretory organs of great importance, however, they are extremely susceptible to the toxic action of different drugs. In this study, the only histopathological change observed in the liver was hepatic steatosis. This change does not compromise the normal functioning of the organ [
41].
In the kidneys, the changes observed can compromise the normal functioning of the organ, as glomerular degeneration alters normal circulation and prevents the passage of blood for filtration, remaining in the tubules and consequently obstructing them [
41,
49,
50].
According to Souza et al., [
51], liver and kidneys are the most sensitive organs to the possible toxic effects of nanoemulsions. The control group (Tween 80) did not show any changes in any organ.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materia
3.1.1. Collection and Identification of Plant Material
The leaves of Tetradenia riparia were collected in the Fazendinha district (00°02'23"S e 51°06'29"O) in the city of Macapá- Amapá. The species had its identity confirmed and specimens deposited in the Herbarium of Instituto de Pesquisas Científicas e Tecnológicas do Amapá (IEPA) (HAMAB voucher 019182)
3.2. Obtaining the Essential Oil
The leaves of Tetradenia riparia were shade dried at room temperature with ventilation then subjected to hydrodistillation with Clevenger-type apparatus. Dried plant material from (140 g) was added to 1.400 mL of distilled water. The solution was placed in a Clevenger apparatus following the steamdragging distillation methodology for approximately 2h at 100°C. The obtained oil was stored in a freezer at 4 °C until use. The yield of essential oils was calculated based on the dry weight of the leaves of each sample.
3.3. Identification of EO Constituents
The identification of the constituents of the TrEO was performed by gas chromatography coupled to the mass spectrometer (GCMS), using Shimadzu equipment, model GCMS-QP 2010 Plus. 97 DB-5HT column, from J & W Scientific, 30 m long, 0.32 mm diameter, 0.10 μm film thickness, and nitrogen as the carrier gas. The operating conditions of the gas chromatograph were: internal column pressure of 56.7 kPa, split ratio of 1:20, gas flow in the column of 1.0 mL.min-1 (210°C), temperature in the injector of 220°C, temperature in the detector, or the interface (CGMS) of 240 ºC. The initial temperature of the column was 60°C, followed by an increase of 3°C.min
-1 until it reaches 240°C, being kept constant for 30 min. The mass spectrometer was programmed to perform readings in a range from 29 to 400 Da, in 0.5 s intervals, with ionization energy of 70 eV. A standard mixture of n-Alkanes (Sigma-Aldrich C8 - C40) was used to verify the performance of the GC-MS system and calculate the retention index (LRI) of each compound in the sample. The standard (1 μL) of these alkanes was injected into the GC-MS system operating under the conditions described above, and their respective retention times were used as an external reference standard for calculating the LRI, together with the retention times of each compound of interest. The LRI of each component was calculated according to the Equation. 1.
Where LRI is the linear retention index, Tc is the retention time of the compound of interest; Tn + 1 is the retention time of the posterior hydrocarbon; n is the number of carbons from the previous hydrocarbon.
To assist in the identification and characterization of volatile compounds, the calculated linear retention index values will be compared with values found in the literature for columns of the same polarity [
52].
3.4. Antimicrobial Activity
3.4.1. Microorganisms
The evaluation of TrEO antimicrobial activity obtained from T. riparia leaves was tested against test microorganisms provided by Oswaldo Cruz Foundation (FIOCRUZ): two gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli ATCC8789, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC25922) and a gram-positive bacterium (Staphylococcus aureus ATCC25922). The microorganisms were supplied by the bacteria were initially reactivated, from stock cultures, kept in Brain Infusion Heart broth (BHI), for 18 h, at 37 ºC.
3.4.2. Antimicrobial Assay
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the minimum concentration responsible for totally inhibiting bacterial growth. MICs were determined by use of the microdilution method according to the protocol established by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute [
53], with adaptations.
As for the culture medium for antibacterial tests, the (BHI) was prepared according to the measures recommended by the manufacturer to reactivate the bacteria in the stock culture for 18h at 37 ºC. After bacterial growth, an inoculum was prepared in 0.9% saline solution for each colony, adjusted to the McFarland 0.5 scale, subsequently diluted in Brain Infusion Heart broth (BHI), and tested at 1.5 x107UFC.mL-1.
Initially, TrEO was diluted with Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO 2%). Then, the microplate holes were filled with 50 μL of NaCl and 50 μL of the TrEO solution, and serial dilutions were performed in the proportion of 1:2 until the 1:128 dilution. Finally the inoculation was carried out by adding 50 µL of the microbial suspension in all the wells. As a positive control, Amoxycillin (50 μL.mL-1) was used. Control of the culture medium, EO control, and negative control (DMSO 2%) were performed.
The experiments were carried out in triplicates. The microplate was incubated for 24 h at 37 ◦C, after incubation, the growth of the microorganisms was quantified the plates were read in an ELISA reader (DO630 nm). Minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) was considered as the lowest concentration of TrEO in which there was no growth of microorganisms in Petri dishes, that is, there was elimination of microorganisms.
All results were analysed using descriptive statistical techniques such as mean and standard deviation. One-way ANOVA was employed to test the significance and was considered statistically significant, was performed followed by the Bonferroni posttests using GraphPad Prism Software v.7 (San Diego, California, USA). The results were considered significant when p<0.001.
3.5. Preparation of Nanoemulsions
Nanoemulsions were prepared by the low-energy method according to the methodology of [
54,
55,
56], using 99.5% (w/w) water, 0.25% (w/w) EO, and 0.25% (w/w) surfactante, with constant stirring at room temperature. Initially, the oily phase (EO of
T. riparia and the surfactant) was combined and stirred for 30 minutes on a magnetic stirrer.Initially, the TrEO and the surfactant were combined and stirred for 30 minutes on a magnetic stirrer 750 rpm (model AP59-Phoenix, Araraquara, SP, Brazil). Then the deionized water was added dropwise to the oil phase under continuous stirring for another 60 minutes at 750 rpm. The nanoemulsions were stored in glass tubes with a lid and stored at room temperature (25 ± 2 °C). The nanoemulsion had an EO concentration equal to 25.000 µg.mL
-1.
3.5.1. Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance Required (rHBL)
Determination of the required Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance (rHLB) value The rHLB determination of
T. riparia was performed by a blend of sorbitan monooleato and Polysorbate 80 to produce the HLB 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 e 14.5; Polysorbate 80 to produce HLB of 15; and Polysorbate 80 e Polysorbate 20 to produce the HLB 15.5 e 16. The composition and preparation of the emulsions was carried out according to the emulsification method presented above. The rHLB value of the mixture was calculated according to the Eq. 2 [
57], equation 2:
Where rHLB is the required hydrophilic-lipophilic balance, HLBs and HLBp are the hydrophilic-lipophilic equilibrium values of sorbitan and polysorbate, and ms and mp are their respective masses.
3.5.2. Characterization of Nanoemulsions
Nanoemulsions were characterized by particle size, polydispersity index, and zeta potential, using a Zetasizer Nano ZS (Malvern, United Kingdom), equipped with a 10 mW 'red' laser (λ = 632.8 nm), the samples 154 being measured at a dispersion detector angle of 173° for size measurements. Before measurements of particle size, polydispersity index, and zeta potential, nanoemulsions were diluted in deionized water (1:25).
The physical-chemical characterization of the nanoemulsions in each HLB produced was done through the particle size, polydispersity index and potential Zetasizer ZS equipment (Malvern, WORSTS, UK). Each nanoemulsion was diluted in deionized water (1:25 v/v) for analysis The optimized nanoemulsions were monitored on days 0, 7, 14, and 21. The analyzes were performed in triplicate and are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD).
3.6. Aedes Aegypti Test
3.6.1. Larvicidal and Pupicidal Activity
Aedes aegypti L. (Diptera: Culicidae) colonies–Rockefeller strain–were established in the insectarium of the Medical Entomology Laboratory of the Institute of Scientific and Technological Research of the State of Amapá and the tests were carried out in a 12 m2 (3 m x 4 m) room, with controlled climatic conditions: temperature of 25 ± 2 °C, relative humidity of 75 ± 5% and photoperiod of 12 hours [
57,
58,
59].
The methodology used followed the WHO standard protocol [
60] with modification in the test container. After preliminary tests, each group received aliquots of aqueous solutions in the concentrations: 100, 200, 300, 400 and 500 µg.mL-1 pre-solubilized in 5% Tween 80, which were pipetted into a 100 mL beaker containing distilled water. The entire experiment was carried out in quintuplicate with 25 larvae or pupae in each replicate (n = 50). For the negative contro l, 5% Tween 80 and distilled water were used, and as a positive control, sbiotrin was used. The mortality of Pupae or lavae was verified after 24 and 48 of exposure.
3.6.2. Ovicidal Activity
The ovicidal activity was evaluated according to the methodology described by AGUIAR et al. [
61]. Filter papers containing 30 freshly collected Ae. aegypti eggs were exposed for 20 seconds to different concentrations (100- 500 µg.mL
-1) and, later, placed to dry for 10 minutes, then they were introduced into petri dishes (15.0 cm in diameter x 2.0 cm in depth) containing enough distilled water to cover the eggs. This treatment consisted of 3 repetitions.
After 24 hours of exposure of eggs to
T. riparia essential oil and nanoemulsion, hatched larvae were counted daily for 10 days, considering as viable eggs that did not hatch after 10 days. The eggs exposed to water and 1% DMSO were used as the negative control [
62], while a commercial insecticide (0.02% Imiprotin, 0.05% Permetrin, and 0.1% Esbiotrin) was used as the positive control. All assays were performed in triplicates [
59].
3.7. Acute Toxicity of NOtEO in Non-Target Organisms
3.7.1. Experimental Animals
Swiss albino mice (Mus musculus) of both sexes (18-20 g body weight, 4 weeks of age) were obtained from the Multidisciplinary Center for Biological Research for the Area of Science in Laboratory Animals (CEMIB) at the University of Campinas. The animals were acclimated for ten days to ascertain the behavior and eating and physiological habits. They were maintained under standard environmental conditions (12h dark/light cycle; temperature 23±2°C). Industrialized dry food and water (Labina, Purina, Brazil) were made available ad libitum. Every experiment was carried out by the International Animal Care Committee, following the national regulations established for animal experimentation, and was submitted to and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Federal University of Amapá (CEUA - UNIFAP– 002/2019).
3.7.2. Experimental Draw
The acute toxicity study for testing of chemicals was carried out as described above workers [
63]. The investigation of acute toxicity followed, in general, the guidelines of the OECD [
64] for testing the acute toxic dose class (Guideline 423). All animals were deprived of food for 8 hours before the beginning of the experiment. 2000 mg.kg
-1 doses of NTrEO (HBL 15.5) were administered orally by gavage in six animals (n = 6/groups; three males and three females). The second group (negative control) received a mixture of HBL 15,5 surfactant. Each animal was critically observed at 30, 60, 120, 240, and 360 minutes after treatment and every 24 hours for fourteen days [
65]. During this period, Clinical signs and behavioural manifestations there of were recorded everyday by direct observations of some parameters such as feed intake, eye discharge, hind limb jerking, breathing, loss/gain in body weight, o edema, salivation, seizures, startle response and death, and daily water intake (mL) and feed (g) and body weight were evaluated. The animals were sacrificed 14 days after the beginning of the experiment and necropsies were performed on the animals, and various organs of the body: heart, liver, kidney and lung were removed for weighing, macroscopic, and microscopic analysis.
3.7.3. Histopathological Analysis
Histopathological analysis were performed according to the methodology of Souza et al. [
66]. The organs (heart, liver, kidney and lung) were fixed in a 10% formalin buffer solution for 48 hours. Then they were dehydrated in different concentrations of alcohols (70%, 80%, 90%, and 100%) and then diaphanized in xylol and embedded in paraffin (Inlab). The material was stained in Harris hematoxylin (HE-LABORCLIN and yellowish eosin-INLAB). The slides were analyzed in optical microscopes (Olympus-micronal brands BX41) and photographed with an MDCE-5C USB 2.0 (digital) camera.
3.8. Statistical Analysis
The lethal concentration that causes 50% mortality in the population (LC50) was analyzed using the SPSS® program [version 20.0; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA]. Data analysis was performed by analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's test to identify significant differences using the GraphPad Prism program (Version 7.0. For Windows, San Diego, CA, USA).
4. Conclusions
The EO yield of T. riparia was satisfactory when compared to the literature data. It was possible to identify estragole from TrEO. The essential oil has antimicrobial activity against the bacteria tested. Regarding insecticidal activities, it showed potent larvicidal, ovicidal and pupicidal properties of TrEO and NTrEO. These results demonstrate the potential of this species in the development of natural and antimicrobial insecticides. In addition to not being considered toxic to NTrEO, in the Acute Oral Toxicity test. However, more research is needed in this area in order to isolate the effective compounds.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Fig. S1 Chromatogram of the essential oil of T. riparia. Table S2. Physical parameters of T. riparia nano-emulsions in different hydrophilic-lipophilic balance values at 0, 7, 14 and 21 days. Doc. S3 Approved by the Ethics Committee of Federal University of Amapa, Macapa- UNIFAP.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.R., R.M.,R.S. and S.S.; methodology, investigation, E.R.,A.R., D.S., R.T. and A.F.; writing—original draft preparation P.C., A.G. and A.R.; writing—review and editing, R.M.,E.R., R.S., A.R. and S.S.; supervision, S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported by the projects : The Amapá Research Support Foundation (FAPEAP). To the Research Program for SUS - PPSUS - Ministry of Health. The Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) / Ministry of Education (MEC).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Federal University of Amapa, Macapa- UNIFAP(protocol code 02/2019 and date of approval 12 de march de 2019).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
State University of Amapá –UEAP for technical support, to the Pharmaceutical Research laboratory - UNIFAP under the responsibility of Dr. José Carlos Tavares Carvalho. To the Medical Entomology Laboratory - IEPA under the responsibility of Dr. Allan Kardec Ribeiro Galardo. To the Laboratory of Toxicology and Pharmaceutical Chemistry - UNIFAP under the responsibility of Dr. Mayara Amoras Teles Fujishima. The Dean of Research and Graduate Studies - PROPESPG.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Van Puyvelde, L.; Nyirankuliza, S.; Panebianco, R.; Boily, Y.; Geizer, I.; Sebikali, B.; Schamp, N. Active principles of Tetradenia riparia. I. Antimicrobial activity of 8 (14), 15-sandaracopimaradiene-7α, 18-diol. J.ethnopharmacol. 1986, 17, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazim, Z.C.; Rodrigues, F.; Amorin, A.C.L.; de Rezende, C.M.; Soković, M.; Tešević, V.; Cortez, D.A.G. New natural diterpene-type abietane from Tetradenia riparia essential oil with cytotoxic and antioxidant activities. Mol. 2014, 19, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.C.A.; Rosa, M.F.; Fernandez, C.M.; C Bortolucci, W.; Melo, U.Z.; Siqueira, V.L.; Gazim, Z.C. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of the extract and fractions of Tetradenia riparia (Hochst.) Codd (Lamiaceae) leaves from Brazil. Curr. microbiol. 2017, 74, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J.C.; Silva, O.A.; Faria, M.G.; Colauto, N.B.; Gazzin, Z.C.; Colauto, G.A.; Dragunski, D.C. Improved antioxidant activity of a starch and gelatin-based biodegradable coating containing Tetradenia riparia extract. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Gazim; Swain, S.S.; de Araujo Bento, M.C.V.; da Silva Sena, J.; Mukazayire, M.J.; Luyten, W. Ethnomedicinal, phytochemical and pharmacological investigations of Tetradenia riparia (Hochst.) Codd (Lamiaceae). Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njau, E.F.; Ndakidemi, P.A. The genus Tetradenia (Lamiaceae): a review of its ethnomedicinal, botanical, chemical and pharmacological activities. Int. J.Biol. 2017, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurhayat, T.; Betul, D. Chemical Composition of Essential Oil from Tetradenia riparia and its Attractant Activity for Mediterranean Fruit Fly, Ceratitis capitata. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1934578X2095395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarchi, I.G.; Thomazella, M.V.; de Souza Terron, M.; Lopes, L.; Gazim, Z.C.; Cortez, D.A.G.; Lonardoni, M.V.C. Antileishmanial activity of essential oil and 6, 7-dehydroroyleanone isolated from Tetradenia riparia. Exp. Parasitol. 2015, 157, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannweg, K.; Visser, G.; De Jager, K.; Bertling, I. In vitro-induced polyploidy and its effect on horticultural characteristics, essential oil composition and bioactivity of Tetradenia riparia. S. Afr. J.Bot. 2016, 106, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Gonçalves, C.H.; das Almas, L.R.M.; Pinc, M.M.; Antonio, N.C.; Carneiro, V.P.P.; Lourenço, E.L.B.; Alberton, O. Rendimento, caracterização e fitoquímica do óleo essencial de Tetradenia riparia. Braz. J.Dev. 2019, 5, 20207–20217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blythe, E.K.; Tabanca, N.; Demirci, B.; Kendra, P.E. Chemical composition of essential oil from Tetradenia riparia and its attractant activity for Mediterranean fruit fly, Ceratitis capitata. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1934578X20953955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.C.; Simões, R.C.; Tavares, C.P.; Lima, C.A.; Sá, I.S.C.; da Silva, F.M.; Roque, R.A. Toxicity of the essential oil from Tetradenia riparia (Hochstetter.) Codd (Lamiaceae) and its principal constituent against malaria and dengue vectors and non-target animals. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2022, 188, 105265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimira, F. Tetradenia riparia, an ethnobotanical plant with diverse applications, from antimicrobial to anti-proliferative activity against cancerous cell lines: A systematic review. J.Herb. Med. 2022, 32, 100537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanavacca, J.; Iecher Faria, M.G.; Canonico Silva, G.C.; Inumaro, R.S.; Gonçalves, J.E.; Kupski, L.; Gazim, Z.C. Chemical analysis, antifungal and antimycotoxigenic activity of Tetradenia riparia essential oil and crude extract. Food Addit. Contam. 2022, 39, 1296–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omolo, M.O.; Okinyo, D.; Ndiege, I.O.; Lwande, W.; Hassanali, A. Repellency of essential oils of some Kenyan plants against Anopheles gambiae. Phytochem 2004, 65, 2797–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagotti, M.C.; Candido, A.C.; Marçal, M.G.; Vieira, T.M.; Groppo, M.; Silva, M.L.; Magalhães, L.G. Trypanocidal activity of Dysphania ambrosioides, Lippia alba, and Tetradenia riparia essential oils against Trypanosoma cruzi. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2100678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldin, V.P.; de Lima, Scodro; R.B.; Lopes-Ortiz; M.A.; de, Almeida; A.L.; Gazim, Z.C.; Ferarrese, L.; Cardoso, R.F. Anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis activity of essential oil and 6, 7-dehydroroyleanone isolated from leaves of Tetradenia riparia (Hochst.) Codd (Lamiaceae). Phytomedicine 2018, 47, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njau, E.F.; Alcorn, J.M.; Buza, J.; Chirino-Trejo, M.; Ndakidemi, P. Antimicrobial activity of Tetradenia riparia (Hochst.) Lamiaceae, a medicinal plant from Tanzania. European J. Med. Plants, 2014; 4, 1462–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.C.A.; Rosa, M.F.; Fernandez, C.M.; C Bortolucci, W.; Melo, U.Z.; Siqueira, V.L.; Gazim, Z.C. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of the extract and fractions of Tetradenia riparia (Hochst.) Codd (Lamiaceae) leaves from Brazil. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demelo, N.I.; Mantovani, A.L.; de Oliveira, P.F.; Groppo, M.; da Silva Filho, A.A.; Rodrigues, V.; Crotti, A.E. Antischistosomal and cytotoxic effects of the essential oil of Tetradenia riparia (Lamiaceae). Nat.Product Commun. 2015, 10, 1934578X1501000934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, N.I.D.; Carvalho, C.E.D.; Fracarolli, L.; Cunha, W.R.; Veneziani, R.C.S.; Martins, C.H.G.; Crotti, A.E.M. Antimicrobial activity of the essential oil of Tetradenia riparia (Hochst.) Codd.(Lamiaceae) against cariogenic bacteria. Braz. J.Microbiol. 2015, 46, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, T.; Van Vuuren, S.F.; De Wet, H. An antimicrobial evaluation of plants used for the treatment of respiratory infections in rural Maputaland, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 144, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campolo, O.; Giunti, G.; Laigle, M.; Michel, T.; Palmeri, V. Essential oil-based nano-emulsions: Effect of different surfactants, sonication and plant species on physicochemical characteristics. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 157, 112935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musazzi, U.M.; Franzè, S.; Minghetti, P.; Casiraghi, A. Emulsion versus nano-emulsion: how much is the formulative shift critical for a cosmetic product? Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018, 8, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigon, C.; Giuliani, L.M.; Fabiele, M.; Stangarlin, L.; Mattiazzi, J.; Gomes, F.P. Sistemas nanoestruturados contendo óleo de linhaça: desenvolvimento tecnológico e caracterização físico-química de nanoemulsões e nanocápsulas poliméricas. Saúde (Santa Maria) 2017, 43, 153–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Esquena, J.; Rodriguez-Abreu, C.; Solans, C. Key features of nano-emulsion formation by the phase inversion temperature method. J.Dispers. Sci.Technol. 2021, 42, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshbaf-Sadigh, A.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H.; Anarjan, N.; Najian, Y. Preparation of ginger Oil in water nanoemulsion using phase inversion composition technique: Effects of stirring and water addition rates on their physico-chemical properties and stability. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie 2021, 235, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghankar, M.; Maleki-Ravasan, N.; Tahghighi, A.; Karimian, F.; Karami, M. Bioactivities of rose-scented geranium nanoemulsions against the larvae of Anopheles stephensi and their gut bacteria. Plos one 2021, 16, e0246470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, X. Characteristics of two cedarwood essential oil emulsions and their antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Food chem. 2021, 346, 128970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.L.; Brandão, L.B.; da Costa, A.L.P.; Martins, R.L.; Rodrigues, A.B.L.; de Almeida, S.S.M.S. The Potentiality of Plant Species from the Lamiaceae Family for the Development of Herbal Medicine in the Control of Diseases Transmitted by Aedes aegypti. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2022, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumar, K.; Perich, M.J.; Boobar, L.R. Botanical derivatives in mosquito control: a review. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1991, 7, 210–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatropoulos, A.; Kimbaris, A.; Michaelakis, A.; Papachristos, D.P.; Polissiou, M.G.; Emmanouel, N. Chemical composition and assessment of larvicidal and repellent capacity of 14 Lamiaceae essential oils against Aedes albopictus. Parasitol. res. 2018, 117, 1953–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilon, A.C.; Del Grande, M.; Silvério, M.R.; Silva, R.R.; Albernaz, L.C.; Vieira, P.C.; Lopes, N.P. Combination of GC-MS Molecular Networking and Larvicidal Effect against Aedes aegypti for the Discovery of Bioactive Substances in Commercial Essential Oils. Molecules 2022, 27, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, M.; Hashan Arif, E.I.; Muhammad Dimyati, N.I.; Ishak, I.H.; Hamdan, R.H.; Syazwan, S.A.; Peng, T.L. Larvicidal Effect of Vitex ovata Thunb.(Lamiales: Lamiaceae) Leaf Extract towards Aedes (Stegomyia) aegypti (Linnaeus, 1762)(Diptera: Culicidae). Parasitologia 2021, 1, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danga, S.P.Y.; Nukenine, E.N.; Batti, A.C.S.; Younoussa, L.; Keziah, E.A. , Esimone, C.O. Mosquito oviposition-deterrent and ovicidal property of fractions and essential oils from Plectranthus glandulosus and Callistemon rigidus against Aedes aegypti, Anopheles gambiae and Culex quinquefasciatus. Internat. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2018, 12, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Morales, R.M.; Duque, J.E. Dissuasive and biocidal activity of Salvia officinalis (Lamiaceae) with induction of malformations in Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Rev. Colomb.Entomol. 2020, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennyson, S.; Arivoli, S.; Raveen, R.; Selvakumar, S. , Jayakumar, M.; Kumar, L. Bioefficacy of Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don (Apocyanaceae) and Hyptis suaveolens (L.) Poit (Lamiaceae) ethanolic aerial extracts on the larval instars of the Dengue and Chikungunya vector Aedes aegypti Linnaeus 1762 (Diptera: Culicidae). Intern. J. Mosq. Res. 2018, 5, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sivapriyajothi, S.; Kumar, P.M.; Kovendan, K.; Subramaniam, J.; Murugan, K. Larvicidal and pupicidal activity of synthesized silver nanoparticles using Leucas aspera leaf extract against mosquito vectors, Aedes aegypti and Anopheles stephensi. J. Entomol. Acarol. Res 2014, 46, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleel, C.; Tabanca, N.; Buchbauer, G. α-Terpineol, a natural monoterpene: A review of its biological properties. Open Chem. J., 2018, 16, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, V.; Patel, R.; Hazarika, H.; Dey, P.; Goswami, D.; Chattopadhyay, P. Chemical composition and bioefficacy for larvicidal and pupicidal activity of essential oils against two mosquito species. J.Mosq.Res. 2017, 4, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zare Sani, M.; Mogaddam, M.R.A.; Khandaghi, J. Combination of cold induced HLLME with an effervescence-assisted DLLME based on deep eutectic solvent decomposition; application in extraction of some pyrethroid and carbamate pesticides from edible oils. J.Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardeto-Sabec, G.; de Jesus, R.A.; de Oliveira, H.L.M.; de Araujo Almeida Campo, C.F.; Jacomassi, E.; Goncalves, J.E.; Gazim, Z.C. Tetradenia riparia ('Lamiaceae') essential oil: An alternative to 'Rhipicephalus sanguineus'. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2020, 14, 1608–1615. [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, P.; Medeiros, R.S.; Sampaio, P.T.; Vieira, G.; Wiedemann, L.S.; Veiga-Junior, V.F. Influence of abiotic factors on the chemical composition of copaiba oil (Copaifera multijuga Hayne): soil composition, seasonality and diameter at breast height. J.Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvério, M.R.S.; Espindola, L.S.; Lopes, N.P.; Vieira, P.C. Plant natural products for the control of Aedes aegypti: The main vector of important arboviruses. Molecules 2020, 25, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, R.L.; Rodrigues, A.B.L.; de Menezes Rabelo, É.; Santos, L.L.; Brandão, L.B.; Faustino, C.G.; Galardo, A.K.R. Development of larvicide nanoemulsion from the essential oil of Aeollanthus suaveolens Mart. ex Spreng against Aedes aegypti, and its toxicity in non-target organism. Arab. J.Chem. 2021, 14, 103148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato Rodrigues, A.B.; Martins, R.L.; Rabelo, É.D. M.; Tomazi, R.; Santos, L.L.; Brandão, L.B.; de Almeida, S.S.M.D.S. Development of nano-emulsions based on Ayapana triplinervis essential oil for the control of Aedes aegypti larvae. PloS one 2021, 16, e0254225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, E.; Borchert, H.H. Design of a phytosphingosine-containing, positively-charged nanoemulsion as a colloidal carrier system for dermal application of ceramides. Eur. J.Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 60, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, R.S.; Keita, H.; Ortiz, B.L.S.; dos Santos Sampaio, T.I.; Ferreira, I.M.; Lima, E.S.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Anti-inflammatory activity of nanoemulsions of essential oil from Rosmarinus officinalis L.: in vitro and in zebrafish studies. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26, 1057–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badawi, M. S. Histological study of the protective role of ginger on piroxicam-induced liver toxicity in mice. J. Chin. Med.Assoc. 2019, 82, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.B.L.; Martins, R.L.; de Menezes Rabelo, É.; de Matos, J.L.; Santos, L.L.; Brandão, L.B.; de Castrio Cantuaria, P. In silico and in vivo study of adulticidal activity from Ayapana triplinervis essential oils nano-emulsion against Aedes aegypti. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2022, 15, 104033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza Gonçalves, C.H.; das Almas, L.R.M.; Pinc, M.M.; Antonio, N.C.; Carneiro, V.P.P.; Lourenço, E.L.B.; Alberton, O. Rendimento, caracterização e fitoquímica do óleo essencial de Tetradenia riparia. Braz. J. Dev. 2019, 5, 20207–20217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry; Carol Stream: Allured publishing corporation, 2007; Volume 456, pp. 544–545. [Google Scholar]
- Humphries, R.; Bobenchik, A.M.; Hindler, J.A.; Schuetz, A.N. Overview of changes to the clinical and laboratory standards institute performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, M100. J.clin. microbial. 2021, 59, e00213–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostertag, F.; Weiss, J.; McClements, D.J. Low-energy formation of edible nanoemulsions: factors influencing droplet size produced by emulsion phase inversion. J. colloid interface sci. 2012, 388, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.E.; Bezerra, D.C.; Duarte, J.L.; Cruz, R.A.; Souto, R.N.; Ferreira, R.M.; Fernandes, C.P. Essential oil from Pterodon emarginatus as a promising natural raw material for larvicidal nanoemulsions against a tropical disease vector. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2017, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Advances in nanoparticle and microparticle delivery systems for increasing the dispersibility, stability, and bioactivity of phytochemicals. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 38, 107287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botas, G.D.S.; Cruz, R.A.; De Almeida, F.B.; Duarte, J.L.; Araújo, R.S.; Souto, R.N.P.; Fernandes, C.P. Baccharis reticularia DC. and limonene nanoemulsions: promising larvicidal agents for Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) control. Mol. 2017, 22, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, H.; Sofi, G. Mosquito larvicidal efficay of Acorus calamus extracts against Aedes aegypti L. larvae. Asian Pac. J.Trop.l Dis. 2014, 4, S181–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, F.C.; Leite, J.A.; Oliveira, L.H.; Sousa, P.A.; Menezes, M.C.; Moraes, J.P.; Braga, V.A. The larvicidal activity of Agave sisalana against L4 larvae of Aedes aegypti is mediated by internal necrosis and inhibition of nitric oxide production. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Laboratory and Field Testing of Mosquito Larvicides; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Aguiar, D.L. Utilização de óleos essenciais como tecnologia alternativa aos inseticidas sintéticos para o controle do Aedes aegypti. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualberto, S.A.; da Silva Carvalho, K.; Fries, D.D. Avaliação da atividade larvicida de extratos obtidos do caule de Croton linearifolius Mull. Arg.(Euphorbiaceae) sobre larvas de Aedes aegypti (Linnaeus, 1762)(Diptera: Culicidae). Biotemas 2014, 27, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagri, P. , Kumar, V.; Sikka, A.K.; Punia, J.S. Preliminary acute toxicity study on imidacloprid in Swiss albino mice. Vet. world 2013, 6, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, K.P.; Maibach, H.I. OECD guidelines for testing of chemicals. In Dermatotoxicology; CRC Press, 2012; pp. 509–511. [Google Scholar]
- Guideline, P.B.T. OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals. Hershberger 2001, 601, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, G.C.; Duarte, J.L.; Fernandes, C.P.; Moyado, J.A.V.; Navarrete, A.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Obtainment and study of the toxicity of perillyl alcohol nanoemulsion on zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Nanomed Res 2016, 4, 00093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
MIC and MBC of the EO of T. riparia against P. aeruginosa, E. coli, and S. aureus. BHI with 2% DMSO (-), and Amoxiline (+). *** p < 0.001 statistically significant in relation to the negative control, # p < 0.001 statistically significant in relation to the positive control. Statistical analysis was calculated by one-way ANOVA.
Figure 1.
MIC and MBC of the EO of T. riparia against P. aeruginosa, E. coli, and S. aureus. BHI with 2% DMSO (-), and Amoxiline (+). *** p < 0.001 statistically significant in relation to the negative control, # p < 0.001 statistically significant in relation to the positive control. Statistical analysis was calculated by one-way ANOVA.
Figure 2.
Average droplet size of the nanoemulsion prepared with EO of T. riparia in rHLB 15,5 - Day 0: 100.93 ± 0.7 nm and -20.13 ± 1.6 mV; Day 21: 81.12 ± 0.17 nm and -44.17 ± 0.7mV. The different colors represent replicates of the same sample.
Figure 2.
Average droplet size of the nanoemulsion prepared with EO of T. riparia in rHLB 15,5 - Day 0: 100.93 ± 0.7 nm and -20.13 ± 1.6 mV; Day 21: 81.12 ± 0.17 nm and -44.17 ± 0.7mV. The different colors represent replicates of the same sample.
Figure 3.
Histological section of the liver, heart, lungs and kidneys of animals treated orally with Tween 80 (control) and NOETR, at a dose of 2000 mg.kg-1. In A, normal liver of the control group, where hepatocytes are observed (H); In B, hypertrophied, where cytoplasmic vacuolization (steatosis) is observed (Vc); In C and D, heart without histopathological alteration; In E and F, lung no histopathological change; In G, normal kidney of the control group, where the capillaries of the glomerulus (CG) and space of Bowman's capsule (BCS) are observed; In H, altered kidney with glomerular degeneration (DgG) and tubular obstruction (OT).
Figure 3.
Histological section of the liver, heart, lungs and kidneys of animals treated orally with Tween 80 (control) and NOETR, at a dose of 2000 mg.kg-1. In A, normal liver of the control group, where hepatocytes are observed (H); In B, hypertrophied, where cytoplasmic vacuolization (steatosis) is observed (Vc); In C and D, heart without histopathological alteration; In E and F, lung no histopathological change; In G, normal kidney of the control group, where the capillaries of the glomerulus (CG) and space of Bowman's capsule (BCS) are observed; In H, altered kidney with glomerular degeneration (DgG) and tubular obstruction (OT).
Table 1.
Composition of essential oil from Tetradenia riparia.
Table 1.
Composition of essential oil from Tetradenia riparia.
| Peak |
Name |
Rt
|
Area (%) |
LRI |
| 1 |
L-Fenchone |
13.040 |
2.70 |
1121 |
| 2 |
Fenchol |
14.180 |
0.82 |
1138 |
| 3 |
Camphor |
15.477 |
1.05 |
1121 |
| 4 |
(+) -Borneol |
16.505 |
1.10 |
1138 |
| 5 |
γ-Elemene |
24.158 |
1.48 |
1431 |
| 6 |
Isocaryophyllene |
27.640 |
5.12 |
1494 |
| 7 |
Germacrene B |
30.793 |
3.42 |
1603 |
| 8 |
α-Muurolene |
30.957 |
0.95 |
1440 |
| 9 |
Isogeraniol |
31.791 |
8.58 |
1228 |
| 10 |
Δ-Cadinene |
31.966 |
6.64 |
1469 |
| 11 |
6-epi-shyobunol |
32.023 |
4.33 |
1555 |
| 12 |
Germacrene D-4-ol |
33.925 |
5.48 |
1574 |
| 13 |
Viridiflorol |
34.203 |
2.36 |
1530 |
| 14 |
τ-Muurolol |
36.449 |
4.89 |
1580 |
| 15 |
β-Bisabolene |
36.712 |
1.89 |
1500 |
| 16 |
α-Cadinol |
37.025 |
5.07 |
1580 |
| 17 |
Aromadendrene oxide |
37.469 |
23.47 |
1462 |
| 18 |
Shyobunol |
38.256 |
7.58 |
1555 |
| 19 |
Ledol |
48.177 |
7.62 |
1530 |
| 20 |
β-Sitosterol acetate |
53.991 |
5.44 |
2871 |
Table 2.
Average particle size, polydispersity index, and zeta potential during the preparation of the nanoemulsion (HLB = 15,5) of the NTrEO.
Table 2.
Average particle size, polydispersity index, and zeta potential during the preparation of the nanoemulsion (HLB = 15,5) of the NTrEO.
| |
day 0 |
day 07 |
day 14 |
day 21 |
| |
102 |
85.36 |
86.46 |
80.88 |
| Size (nm) |
100.3 |
85.69 |
86.3 |
81.22 |
| |
100.5 |
84.61 |
85.74 |
81.26 |
| Mean ±SD |
100.93 ± 0.7 |
85.22 ± 0.45 |
86.17 ± 0.31 |
81.12 ± 0.17 |
Polydispersity index
(PDI) |
0.261 |
0.257 |
0.27 |
0.247 |
| 0.259 |
0.264 |
0.26 |
0.25 |
| 0.259 |
0.261 |
0.256 |
0.251 |
| Mean ±SD |
0.26 ± 0.0 |
0.26 ± 0.0 |
0.26 ± 0.0 |
0.25 ± 0.0 |
Zeta Potencial
(mV) |
-18.2 |
-34.1 |
-32,7 |
-43.4 |
| -22.1 |
-35.5 |
-31.9 |
-44 |
| -20.1 |
-35 |
-33.6 |
-45.1 |
| Mean ±SD |
-20.13 ± 1.6 |
-34.87 ± 0.57 |
-32.73 ± 0.7 |
-44.17 ± 0.7 |
Table 3.
Percentage of mortality (% ± SD) of the larvae of Ae. aegypti after treatment with different concentrations of T. riparia.
Table 3.
Percentage of mortality (% ± SD) of the larvae of Ae. aegypti after treatment with different concentrations of T. riparia.
| Concentration (µg.mL-1) |
Larvicidal activity (%) |
| Essential oil |
Nanoemulsion |
| 24 h |
48 h |
24 h |
48 h |
| 500 |
46.5 ± 0.58h#
|
52.8 ± 0.44 h#
|
73.6 ± 0.89i#
|
80.8 ± 0.44i#
|
| 400 |
45.6 ± 1.34f#
|
51.2 ± 1.48f#
|
58.4 ± 0.54g#
|
69.6 ± 1.51g#
|
| 300 |
36 ± 0.70e#
|
43.2 ± 0.83e#
|
42.4 ± 0.54e#
|
51.2 ± 1.30e#
|
| 200 |
28.8 ± 1.09c#
|
35.2 ± 0.83c#
|
39.2 ± 0.44d#
|
46.4 ± 1.14d#
|
| 100 |
16 ± 0.70a#
|
23.2 ± 0.83a#
|
31.2 ± 0.83b#
|
37.6 ± 0.54b#
|
| Negative control |
0.0 ± 0.0#
|
0.0 ± 0.0 |
0.0 ± 0.0#
|
0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Positive control |
100 ± 0.0 |
100 ± 0.0 |
100 ± 0.0 |
100 ± 0.0 |
Table 4.
Results of the probit analysis for larvicidal activity against Ae. aegypti larvae.
Table 4.
Results of the probit analysis for larvicidal activity against Ae. aegypti larvae.
| |
Treatment |
LC50 (µg.mL-1) |
LC90 (µg.mL-1) |
x2 (df) |
p - value |
| 24 h |
Essential oil |
538.34 |
4882.4 |
0.988 (3) |
0.005 |
| |
Nanoemulsion |
273.25 |
2108.27 |
0.808 (3) |
0.005 |
| |
Esbiothrin |
0.0034 |
|
|
|
| 48 h |
Essential oil |
411.46 |
4895.47 |
0.993 (3) |
0.005 |
| |
Nanoemulsion |
196.66 |
1311.54 |
0.835 (3) |
0.005 |
| |
Esbiothrin |
0.0034 |
|
|
|
Table 5.
Percentage of mortality (% ± SD) of the pupae of Ae. aegypti after treatment with different concentrations of T. riparia.
Table 5.
Percentage of mortality (% ± SD) of the pupae of Ae. aegypti after treatment with different concentrations of T. riparia.
| Concentration (µg.mL-1) |
Pupicidal activity (%) |
| Essential oil |
Nanoemulsion |
| 24 h |
48 h |
24 h |
48 h |
| 500 |
36.8 ± 0.83h#
|
51.2 ± 0.83f#
|
42. 4 ± 0.54h#
|
60.0 ± 0.70f#
|
| 400 |
21.6 ± 1.95g#
|
39.2 ± 1.64e#
|
23.2 ± 0.83g#
|
36.8 ± 2.16e#
|
| 300 |
14.4 ± 0.54e#
|
21.6 ± 1.14c#
|
20 ± 1.0f#
|
36 ± 1.0d#
|
| 200 |
4 ± 0.70c#
|
8 ± 0.70b#
|
10.4 ± 0.54d#
|
16.8 ± 0.83b#
|
| 100 |
0.0 ± 0.0a#
|
3.2 ± 0.44a#
|
4.0 ± 1.41b#
|
6.4 ± 0.89 a#
|
| Negative control |
0.0 ± 0.0#
|
0.0 ± 0.0#
|
0.0 ± 0.0#
|
0.0 ± 0.0#
|
| Positive control |
100 ± 0.0 |
100 ± 0.0 |
100 ± 0.0 |
100 ± 0.0 |
Table 6.
Results of the probit analysis for pupicidal activity against Ae. aegypti.
Table 6.
Results of the probit analysis for pupicidal activity against Ae. aegypti.
| |
Treatment |
LC50 (µg.mL-1) |
LC90 (µg.mL-1) |
x2 (df) |
p-value |
| 24 h |
Essential oil |
630.29 |
1445.96 |
0.988 (3) |
0.005 |
| |
Nanoemulsion |
713.68 |
2721.87 |
0.951 (3) |
0.005 |
| |
Esbiothrin |
0.0034 |
|
|
|
| 48 h |
Essential oil |
507.70 |
1334.41 |
0.958 (3) |
0.005 |
| |
Nanoemulsion |
452.75 |
1496.1.9 |
0.954 (3) |
0.005 |
| |
Esbiothrin |
0.0034 |
|
|
|
Table 7.
Results of the probit analysis for ovicidal activity against Ae. aegypti.
Table 7.
Results of the probit analysis for ovicidal activity against Ae. aegypti.
| Treatment |
LC50 (µg.mL-1) |
LC90 (µg.mL-1) |
x2 (df) |
p - value |
| 24 h |
|
| Essential oil |
1570.505 |
51474.323 |
0.973 (3) |
0.005 |
| Nanoemulsion |
1297.137 |
222932.031 |
0.919 (3) |
0.005 |
| Esbiothrin |
0.0034 |
|
|
|
Table 8.
Effect of oral administration of NTrEO (2000 mg.kg-1) on behavioral parameters of Swiss albino mice (Mus musculus) during acute dermal toxicity assessment.
Table 8.
Effect of oral administration of NTrEO (2000 mg.kg-1) on behavioral parameters of Swiss albino mice (Mus musculus) during acute dermal toxicity assessment.
| Groups |
genus |
N° of animals |
N° of animals killed |
toxicity symtoms |
| control |
male |
3 |
0 |
none |
| |
female |
3 |
0 |
none |
| NTrEO |
male |
3 |
0 |
corneal reflex |
| |
female |
3 |
0 |
tremors |
Table 9.
Effect of NTrEO at 2000 mg.kg-1 on the weight of different Swiss albino (Mus musculus) organs after 14 days of treatment. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Statistical significance was calculated using One-way Anova followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test (p < 0.05).
Table 9.
Effect of NTrEO at 2000 mg.kg-1 on the weight of different Swiss albino (Mus musculus) organs after 14 days of treatment. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Statistical significance was calculated using One-way Anova followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test (p < 0.05).
parameters |
Control |
NTrEO |
| males |
females |
males |
females |
| water (mL) |
216.66±2.9 |
216.6±0.81 |
214.8±0.8 |
222.77±3.3 |
| ration (g) |
9.5± 2.27 |
11.51±1.9 |
11.54±2.4 |
7.17±1.04 |
| weight (g) |
30.57±0.61 |
30.57±0.99 |
33.86±2.06 |
30.99±3.08 |
Table 10.
Physiological parameters of Swiss albino mice (Mus musculus) treated with NTrEO at 2000 mg. Kg-1. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Statistical significance was calculated using One-way Anova followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test (p < 0.01).
Table 10.
Physiological parameters of Swiss albino mice (Mus musculus) treated with NTrEO at 2000 mg. Kg-1. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Statistical significance was calculated using One-way Anova followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test (p < 0.01).
| animal |
organ |
relative organ weight(%) |
| control |
NTrEO |
| female |
liver |
1.553±0.210 |
1.188±0.375 |
| kidney |
0.474±0.093 |
0.463±0.019 |
| heart |
0.170±0.02 |
0.171±0.027 |
| lungs |
0.240±0.024 |
0.234±0.02 |
| male |
liver |
1.882±0.09 |
2.059±0.29 |
| kidney |
0.578±0.09 |
0.498±0.02 |
| heart |
0.172±0.02 |
0.1873±0.082 |
| lungs |
0.2763±0.06 |
0.207±0.03 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).