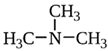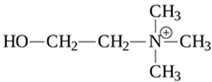1. Introduction
Trace Amines (TAs) are generally synthesized endogenously by decarboxylation of amino acids by the body itself and the constitutive microbiota containing bacterial decarboxylases, as well as entering the body with nutritional products (exo-nutrients) involving bacterial fermentation [1]. The name “trace” reflects the relatively low content level of these substances in mammalian tissues [2]. The first and most studied of the trace amines is beta-phenylethylamine that was discovered in 1876 in the laboratory of Marceli Nencki when studying the breakdown of chicken egg proteins [3]. During this process, beta-phenylethylamine is formed from phenylalanine under the influence of bacterial decarboxylases. This group of biogenic amines also includes p-tyramine, p-octopamine, p-synephrine, tryptamine and other amines.
As of today, there are 6 known human functional receptors (6 genes) associated with trace amines (TAAR) that are included in the group of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) [1]. So far, TAAR1 has been studied the most. It is known that the trace amine-associated receptors (TAARs) are represented in the brain where they participate in regulating the operation of the major monoaminergic neurotransmitter systems, such as dopaminergic and serotoninergic. TAs are also represented in the peripheral organs and tissues, including immune system cells [1,4]. As of today, there are accumulating amount of data allowing a discission about the expression of TAAR family receptors in different populations of immune system cells, however, little is known about the regulatory role of these receptors in inflammation processes. The article overviews the available information on the potential role of trace amines and their receptors in the human and other mammalian immune system cells that express the genes of TAARs.
2. The History of the Discovery of Trace Amine Receptors
The new family of G protein coupled receptors (GPCR), known as trace amine system receptors, was first discovered in 2001 by two independent groups of researchers [5,6]. In 2005, a new standartized nomenclature system (TAAR) was proposed for receptors associated with trace amines [7].
Various types of animals are distinguished by the number of genes coding these receptors. In the zebra fish over 100 TA receptors have been identified. The flying fox has 26 identified functional TAAR genes. The bottle nosed dolphins are the only vertebrates in whom functional TA receptor genes have not been found [8]. Nine TAAR receptors genes have been isolated in humans (TAAR1–9), the functionally active are six: TAAR1, TAAR 2, TAAR 5, TAAR 6, TAAR 8 and TAAR 9 [9]. TAAR3, TAAR 4 and TAAR 7 are pseudogenes and are not functional in humans [10].
The human TAAR genes are located on the 6q23.2 chromosome [5,6]. TAAR1 among the TAAR family of receptors has been studied the most. The receptor is expressed both in the central nervous system, where it regulates dopamine-, serotonin- and glutamatergic neurotransmitter systems, and in the peripheral organs and tissues, including in the immune system cells [1]. TAAR1 is expressed in the central nervous system in the ventral tegmental are (VTA), substantia nigra, dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN), amygdaloid body, renal cortex of the medial temporal lobe, base of the hippocampus (subiculum), prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, hypothalamus, cerebrospinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve, nucleus of the solitary tract and medulla oblongata vomiting center [5,10–14]. In the peripheral organs and tissues there is known TAAR1 expression in the beta-cells of the Langerhans islets, pancreas, mucous membrane of the stomach, intestine, white fatty tissues, spine, as well as on the variety of immune cells. The other functional TAAR isoforms are represented predominantly in the olfactory system where they perform a chemosensory function sensing innate odors, however in the brain and peripheral tissues the expression of these receptors also appears, including in the immune system cells [1].
With the emergence of the “brain-gut-microbiome axis,” we take the opportunity to overview what is known about trace amines in the brain, the defined sources of trace amines in the gut, and emerging understandings on the levels of trace amines in various gastrointestinal disorders. In particular, it was found that TAAR1 may be implicated in inflammatory bowel diseases. Further, TAAR1 may serve as a novel therapeutic drug target to be further investigated for the treatment of the comorbid gut, immunological and neuropsychiatric disorders [15].
3. Ligands of the TAAR Family Receptors
The endogenous ligands activating TAAR1 are beta-phenylethylamine (PEA), p-tyramine (TYR) and tryptamine, when trimethylamine (TMA), tertiary amine, product of microbial degradation of carnitine and choline is the best known agonist of TAAR5 [16]. Dopamine metabolite 3-methoxytyramine (3-MT) and the thyroid hormone metabolite 3-iodotyronamine (T1AM) are also endogenous TAAR1 agonists [1]. 3-IT has been also reported to be a TAAR5 inverse agonist [17]. Several synthetic ligands for TAAR1 and TAAR5 have also been identified [1]. At the same time, dopamine and serotonin (5-HT) show partial agonism towards TAAR1 [1,7]. A number of psychotropic substances, including amphetamine-like compounds display a high affinity for TAAR1 as well [1,18].
Some synthetic compounds are non-selective TAAR1 agonists, for example imidazoline receptor ligands (clonidine, idazoxane, guanabenz) [19], apomorphine [20], ractopamine [21] and others [1].
To date, only one selective TAAR1 antagonist has been described in details. This is N-(3-ethoxyphenyl)-4-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide (EPPTB). This substance is more effective against mouse TAAR1 compared to rat and human receptors. There is assumption that EPPTB may be an inverse agonist [22,23].
There are accumulating data on the capacity of agonists of trace amine receptors to affect the immune system cells functions. For example, it has been reported that 2-phenylethylamine, tyramine and T1AM are capable of acting as chemo-attractants, stimulating migration of neutrophils, intensifying secretion of IL-4 by T-lymphocytes and production of IgE by plasmocytes [24,25]. Other evidence on the potential role of TAARs in immune cell functions are summarized in the
Table 1.
4. Lymphoid Cells
B-Lymphocytes
TAAR1 and TAAR2 are predominantly expressed on B-lymphocytes, while TAAR5, TAAR6, TAAR9 are also present there but to a lesser degree [24]. B-lymphocytes play a key role in inflammation development, in part due to their involvement in IgE synthesis. TAAR1 and its closest relative TAAR2 are also found in blood polymorphonuclear cells (PMN) and T cells. Both receptors are co-expressed in a subpopulation of PMN, where they are involved in the chemosensory migration toward the TAAR1 agonists PEA, tyramine and T1AM. Furthermore, siRNA-guided experiments have shown that TAAR1 and TAAR2 are necessary for trace amine-induced blood leukocyte functions including secretion of IgE [24]. Demonstrated TAAR1 expression in embryonic centers of B-cell maturation indicates further that TAAR1 can play an important role in the immune response mediated by B-cells [26]. Interestingly, polymorphism of the gene coding the TAAR6 receptor is linked to the effective action of inhalation corticosteroids on patients with bronchial asthma [31].
The study on immortalized B-cellular strains of macaque rhesus monkeys revealed a constitutively high level of TAAR1 receptor expression. This is possibly a consequence of the cellular response to the stimulating effect of the herpes virus used to create cellular strains [32,33]. Here, in the mononuclear cells of the peripheral blood (PBMC) an increase was observed in the receptor expression (with initially low level) in response to stimulation by the mitogene phytohemagglutinin (PHA) [32]. During methamphetamine stimulation of immortalized B-cells, PHA-activated lymphocytes in macaque rhesus monkeys, cells of the HEK293 strain, phosphorylation and activation of enzymes c-AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and protein kinase C (PKC) were observed, as well as activity of transcription factors CREB and NFAT, associated with the development of an inflammatory response [32]. The antagonist TAAR1 EPPTB had the opposite effect, inhibiting the CREB and NFAT factors. The TAAR1 expression level in B-cells may vary depending on the maturation stage. This, it is higher in circulating B-lymphocytes of blood plasma than in mature B-cells of the memory [34,35].
The immuno-detected protein TAAR1 was alsofound in normal and malignant human B-lymphocytes. The effects of TAAR1 agonists on Burkitt’s lymphoma cells of the L3055 strain was evaluated. It was found that as a result of the effect of T1AM and o-phenyl-3-iodotyramine (o-PIT) in malignant cells, the process of apoptosis was launched that was validated by appearance the active form of the enzyme caspase-3 participating in this process [28].
T-Lymphocytes
T-cells are a lymphocyte subgroup playing an important role in cellular immunity reactions. The effect of specific factors activates the T-lymphocytes in different ways, stimulating their regulatory and effector functions, which determines the nature of the immune response [36]. Potula et al., 2010 have showed that the effect of methamphetamine, which is a powerful agonist of TAAR1, caused oxidative stress, damage to T-cell mitochondria and change in their production of cytokines [37]. Methamphetamine also intensifies the expression of m-RNA and functional protein TAAR1 on human T-lymphocytes, TAAR1-dependent stimulates differentiation of Th0 into Th2, intensifying IL-4 production and weakening IL-2 production, at the same time promoting the development of inflammatory reactions as a humoral response. HIV1 infection activates TAAR1 in PBMC, the activation is intensified during the preliminary effect of amphetamine. Activation of TAAR1 may be one of the mechanisms for the action of the virus [27]. Participation of the trace amine system could explain the manifestation of immune dysfunction in people taking amphetamine-like narcotics [27,37].
NK Cells
Natural killer cells (NK) are a type of cytotoxic lymphocytes playing an important role in antiviral immunity, recognition of malignant cells and in the mechanisms of auto-tolerance [38]. 86.7 % of NK cells of human leukocytic film demonstrated a detectable level of mRNA TAAR1, 2, 5, 6, 9 that was measured using the RT-PCR technique [24]. Their specific operating mechanisms have not yet been studied.
5. Myeloid Cells
Monocytes and Macrophages
Monocytes are a group of short-lived leukocytes possessing phagocytic activity. Migrating into tissues they are differentiated into macrophages and dendritic cells. Determining the pathogen conservative structures with the help of pattern-recognizing receptors (such as toll-like receptors), they are capable of phagocytizing a foreign agent, then performing an antigen-presenting function to lymphocytes. This results in interaction between the innate and humoral immunity [39,40]. Babusyte et al. 2013 have demonstrated the variance in TAAR expression on human monocytes with 20 % of the cells did not expressing mRNA in any of the receptors. In the remaining cells, expression was observed in all known functional TAAR except TAAR8, the greatest level corresponds to TAAR2.
Furthermore, inn mouse bone marrow macrophages, selective TAAR agonist RO5256390 inhibited tumor necrosis factor (TNF) synthesis following ATP stimulation. However, this TAAR1 agonist did not affect the ADP-induced secretion of TNF and IL-6 in microglial cells in the mouse CNS [41].
The effect of TAAR1 ligands on mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) was also studied. qRT-PCR revealed increased expression of TAAR1 after exposure to tyramine, which is a TAAR1 agonist. Increased transcription of genes for pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL6, TNF-a, IL1b, was also detected. The TAAR1 antagonist EPPTB inhibited tyrosine-dependent activation of TAAR1 and inflammatory cytokine gene expression in BMDMs. Because macrophage activation is important in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis, the authors suggested that TAAR1 may be a potential therapeutic target for this disease [42].
Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes
Polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) are a group of immune cells that include granulocytes: neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. They form the first line of cellular defense because of the capacity to migrate into the inflammation focus using chemotaxis, the chemo-attractants in this case are biologically active substances released by pathogens and tissue macrophages [43]. TAAR1 and TAAR2 are expressed on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes [24,26]. A chemosensory migration by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes having these receptors, according to the trace amine concentration gradient (PEA, tyramine and T1AM) was demonstrated. The number of migrated leukocytes from the upper into the lower system holes was determined using a Neubauer chamber. TAAR1 and TAAR2 possibly not only are expressed, but in this case perform the function jointly, as indicated by the fact that chemotaxic migration does not occur during neutralization of the effect of one of the genes using small interfering RNA [24]. TAAR1 expression was found also on mast cells of mice [44] and rats [45].
Microglia
TAAR1 is expressed in humans in the cerebral dopaminergic regions, including the Ventral tegmental are, substantia nigra, hippocampus, amygdaloid body and other major formations [5,46]. The TAAR1 receptor was found also in human astrocytes where they perform a signal function through cAMP [47]. In microglia cells the TAAR1 agonist T1AM is capable of reducing the inflammatory response stimulated by beta-amyloid, a factor in tumor necrosis (TNF-a) and by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The inflammatory response is on the part of microglia via inhibition of pro-inflammatory factor release (IL-6, TNFα, NF-kB, MCP1 and MIP1), stimulating the release of anti-inflammatory mediators (IL-10) [29]. It is interesting that the effect of ethanol causes an increase in TAAR1 expression in human microglia cell strains HMO6, which may indicate the influence of alcohol consumption on the functioning of the cerebral immune barrier [34,47]. The study by D’Andrea et al. in 2012 reported that TAAR8 transcription in astroglial cells intensifies after the effect of lipopolysaccharide [48].
6. Immunity Pathophysiology
The study in which 246 bronchial asthma patients have participated, genotyping of 15 single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the TAAR6 gene was performed. The functional changes were also determined in the forced expiratory volume (FEV1) for 1 second after treatment with inhalation glucocorticosteroids (fluticasone). It was found that in patient’s homozygote for the minor allele rs7772821T > G after treatment with FEV1 was considerably greater than in patients carrying the genotypes rs7772821 T/G or T/T. These data suggested the TAAR6 role in treating patients with bronchial asthma [31].
TAAR ligands may be generated by the human constitutive microbiota. Data have appeared on the link be trace amine receptors and the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). We know the role of biogenic amines in the capacity of microbiota representatives in attaching to the layer of epithelial cells and penetrating it. Thus, the strain Enterococcus durans IPLA655 may survive in the intestinal environment and synthesize tyramine in the large intestine leading to stronger adhesion to the intestinal epithelium and lower Th1 activation [49]. A higher level of beta-phenylethylamine in the feces could be one of the Crohn’s disease markers [50]. A role of TAAR9 in intestinal function has been demonstrated in TAAR9 knockout rats [51]. First, gene ontology enrichment analysis have revealed that in the intestine, TAAR9 is co-expressed with genes involved in intestinal mucosa homeostasis and function, including cell organization, differentiation, and death as well as with genes implicated in dopamine signaling, which may suggest a role for this receptor in the regulation of peripheral dopaminergic transmission. Furtermore, analysis of microbiome composition in TAAR9-KO rats revealed significant difference in the number of observed taxa between the microbiome of TAAR9-KO and wild-type rats. In TAAR9-KO rats, the gut microbial community was more variable compared to that in the wild-type rats. The research of Taquet et al. 2012 [51] detected elevated activation of TAAR2, TAAR5 and TAAR9 genes in the material obtained from a biopsy of inflamed large intestine wall tissues in patients with Crohn’s disease. The work of Christian et al., 2018 suggested a TAAR-centric hypothesis for IBD, according to which a change in homeostasis of trace amines in large intestine tissue mucous membrane could lead to immune system cell hyperactivity [16].
Table 2.
Immunological role of TAAR family receptors.
Table 2.
Immunological role of TAAR family receptors.
| Immunological role |
Receptor |
Expression |
Biological function |
References |
| Antibacterial immunity |
TAAR1 |
|
The TAAR1 agonist tyramine intensifies adhesion and invasion of E. Durans in the human large intestine epithelium. |
[49] |
| TAAR8 |
Astrocytes |
TAAR8 transcription in astroglial cells intensifies after the effect of lipopolysaccharide. |
[48] |
| TAAR1TAAR2 |
Granulocytes |
The effect of TAAR agonists stimulates chemosensory migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes |
[24] |
| Antiviral immunity |
TAAR1 |
Peripheral mononuclear blood cells (PBMC). |
HIV1 infection activates TAAR1 in PBMC, the activation is intensified during the preliminary effect of amphetamine. |
[27] |
| Bronchial asthma |
TAAR6 |
- |
The presence of single-nucleotide polymorphisms of the TAAR6 gene affects the results of treating bronchial asthma patients. |
[31] |
| Fibromyalgia |
TAAR1 |
- |
TAAR1 gene polymorphism may be interlinked to the risk of developing fibromyalgia. |
[53] |
| Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) |
TAAR2TAAR5TAAR9 |
Large intestine epitheliocytes |
Elevated TAAR expression was found in the large intestine wall cells in patients with Crohn’s disease. |
[51] |
Study of over 350 genes for associations with fibromyalgia in which 496 patients participated with fibromyalgia and 348 people without chronic pains (control) found statistically significant differences for genes GABRB3 (rs4906902; P = 3.65 x 10(-6), TAAR1 (rs8192619; P = 1.11 x 10(-5) and GBP1 (rs7911; P = 1.06 x 10(-4)). The products of these genes may promote the development of this disease and be the potential target for therapy [53].
The involvement of TAAR1 in the pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis (MS) has been also investigated [53]. RT-PCR was used to study the expression of TAAR1 mRNA in CD14+ monocytes obtained from the peripheral blood of patients with multiple sclerosis. The expression level of TAAR1 in PBMCs of MS patients with multiple sclerosis and non-inflammatory neurological diseases (NIND) was also studied. An increase in the variance of the TAAR1 expression level was found in PBMCs of MS and NIND patients compared to the control group. The authors suggested that TAAR1 expression levels may vary depending on disease subtype. There was a significant decrease in the level of TAAR1 mRNA in CD14+ peripheral blood monocytes of MS patients compared to the control group. Based on the inflammatory nature of the disease, the authors suggest the participation of TAAR1 in anti-inflammatory reactions on the part of monocytes. In vitro, in CD14+ monocyte-derived macrophages, expression of the TAAR1 protein was found predominantly in the cell nucleus. After lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation, a shift towards diffuse intracellular localization of the receptor, presumably cytoplasmic, was noted. In postmortem brain sections using immunocytochemistry and fluorescence microscopy, the TAAR1 protein was identified in macrophages/microglia in normal appearing white matter (NAWM) and at the borders of lesions in multiple sclerosis. TAAR1 staining was weaker in the lesion. The authors hypothesized that the TAAR1 protein is activated in macrophages during the active phase of extravasation and invasion into the central nervous system, which is consistent with data on the role of TAAR1 in the chemotaxis of immune cells [54].
7. Conclusions
It is known now that TAARs are widely represented in human immune system cells. These receptors are expressed both in cells of lymphoid, and myeloid shoot of hematopoiesis. The effect of TAAR agonists models the cytokine response of T-lymphocytes, affects differentiation of Th-cells by regulating the type and intensity of the immune response. Joint activation of TAAR1 and TAAR2 stimulates neutrophil migration, which could indicate the agonist role of these receptors in the primary immune response, for example, in response to bacterial infection. TAAR agonists may stimulate IgE synthesis by B-cells, which could indicate the role in developing reactions of hypersensitivity and such diseases as bronchial asthma. Considering the possibility of constitutive microbiota of the human body to produce biogenic amines capable of activating TAAR, it can be hypothesized that these receptors play a significant role in the development of such diseases as IBD, the pathogenesis of which has still not been fully studied. There are also publications indicating the participation of trace amine receptors in the antitumor protection system. The capability of TAAR agonists to induce apoptosis of Burkitt’s lymphoma cells may potentially be the basis for creating new therapy for this disease.
Thus, further research is needed on the regulatory role of the trace amine system in the pathogenesis of the immune response and determination of the biological mechanisms for their action to develop new methods for treating diseases related to immune system dysfunctions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.V.I., V.A.A., R.R.G. and S.A.A.; wrote the first manuscript, V.I.M. and S.A.A.; supervision, R.R.G.; project administration, S.A.A. All the authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge Saint-Petersburg State University for a research project ID: 95444211, St. Petersburg, Russia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data listed in this review article are publicly accessible on PubMed.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gainetdinov, R.R.; Hoener, M.C.; Berry, M.D. Trace Amines and Their Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 549–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M.D.; Gainetdinov, R.R.; Hoener, M.C.; Shahid, M. Pharmacology of Human Trace Amine-Associated Receptors: Therapeutic Opportunities and Challenges. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 180, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandy, D.K. Trace amine-associated receptor 1-Family archetype or iconoclast. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 116, 355–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.A.; Tolbert, M.D.; Singh, S.J.; Bost, K.L. Expression of neuronal trace amine-associated receptor (Taar) mRNAs in leukocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 192, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borowsky, B.; Adham, N.; Jones, K.A.; Raddatz, R.; Artymyshyn, R.; Ogozalek, K.L.; Durkin, M.M.; Lakhlani, P.P.; Bonini, J.A.; Pathirana, S.; Boyle, N.; Pu, X.; Kouranova, E.; Lichtblau, H.; Ochoa, F.Y.; Branchek, T.A.; Gerald, C. Trace amines: identification of a family of mammalian G protein-coupled receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8966–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunzow, J.R.; Sonders, M.S.; Arttamangkul, S.; Harrison, L.M.; Zhang, G.; Quigley, D.I.; Darland, T.; Suchland, K.L.; Pasumamula, S.; Kennedy, J.L.; Olson, S.B.; Magenis, R.E.; Amara, S.G.; Grandy, D.K. Amphetamine, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, lysergic acid diethylamide, and metabolites of the catecholamine neurotransmitters are agonists of a rat trace amine receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 60, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindemann, L.; Ebeling, M.; Kratochwil, N.A.; Bunzow, J.R.; Grandy, D.K.; Hoener, M.C. Trace amine-associated receptors form structurally and functionally distinct subfamilies of novel G protein-coupled receptors. Genomics 2005, 85, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyun, S.I.; Moriyama, H.; Hoffmann, F.G.; Moriyama, E.N. Molecular Evolution and Functional Divergence of Trace Amine-Associated Receptors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloriam, D.E.; Bjarnadóttir, T.K.; Schiöth, H.B.; Fredriksson, R. High species variation within the repertoire of trace amine receptors. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1040, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, L.; Meyer, C.A.; Jeanneau, K.; Bradaia, A.; Ozmen, L.; Bluethmann, H.; Bettler, B.; Wettstein, J.G.; Borroni, E.; Moreau, J.L.; Hoener, M.C. Trace amine-associated receptor 1 modulates dopaminergic activity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 324, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinter, J.; Mühlhaus, J.; Wienchol, C.L.; Yi, C.X.; Nürnberg, D.; Morin, S.; Grüters, A.; Köhrle, J.; Schöneberg, T.; Tschöp, M.; Krude, H.; Kleinau, G.; Biebermann, H. Inverse agonistic action of 3-iodothyronamine at the human trace amine-associated receptor 5. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, S.; Lignani, G.; Caffino, L.; Maggi, S.; Sukhanov, I.; Leo, D.; Mus, L.; Emanuele, M.; Ronzitti, G.; Harmeier, A.; Medrihan, L.; Sotnikova, T.D.; Chieregatti, E.; Hoener, M.C.; Benfenati, F.; Tucci, V.; Fumagalli, F.; Gainetdinov, R.R. TAAR1 Modulates Cortical Glutamate NMDA Receptor Function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 2217–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.F.; Seaman, R.; Siemian, J.N.; Bhimani, R.; Johnson, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Hoener, M.C.; Park, J.; Dietz, D.M.; Li, J.X. Role of trace amine-associated receptor 1 in nicotine's behavioral and neurochemical effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferragud, A.; Howell, A.D.; Moore, C.F.; Ta, T.L.; Hoener, M.C.; Sabino, V.; Cottone, P. The Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1 Agonist RO5256390 Blocks Compulsive, Binge-like Eating in Rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 1458–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugda Gwilt, K.; González, D.; Olliffe, N.; Oller, H.; Hoffing, R.; Puzan, M.; El Aidy, S.; Miller, G. Actions of Trace Amines in the Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis via Trace Amine-Associated Receptor-1 (TAAR1). Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 40, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christian, S.L.; Berry, M.D. Trace Amine-Associated Receptors as Novel Therapeutic Targets for Immunomodulatory Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinter, J.; Mühlhaus, J.; Wienchol, C.L.; Yi, C.X.; Nürnberg, D.; Morin, S.; Grüters, A.; Köhrle, J.; Schöneberg, T.; Tschöp, M.; Krude, H.; Kleinau, G.; Biebermann, H. Inverse agonistic action of 3-iodothyronamine at the human trace amine-associated receptor 5. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmler, L.D.; Buchy, D.; Chaboz, S.; Hoener, M.C.; Liechti, M.E. In Vitro Characterization of Psychoactive Substances at Rat, Mouse, and Human Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 357, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.A.; Zhou, T.; Ahn, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Q. Human and mouse trace amine-associated receptor 1 have distinct pharmacology towards endogenous monoamines and imidazoline receptor ligands. Biochem. J. 2009, 424, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhanov, I.; Espinoza, S.; Yakovlev, D.S.; Hoener, M.C.; Sotnikova, T.D.; Gainetdinov, R.R. TAAR1-dependent effects of apomorphine in mice. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 17, 1683–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Grandy, D.K.; Janowsky, A. Ractopamine, a livestock feed additive, is a full agonist at trace amine-associated receptor 1. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 350, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradaia, A.; Trube, G.; Stalder, H.; Norcross, R.D.; Ozmen, L.; Wettstein, J.G.; Pinard, A.; Buchy, D.; Gassmann, M.; Hoener, M.C.; Bettler, B. The selective antagonist EPPTB reveals TAAR1-mediated regulatory mechanisms in dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20081–20086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalder, H.; Hoener, M.C.; Norcross, R.D. Selective antagonists of mouse trace amine-associated receptor 1 (mTAAR1): discovery of EPPTB (RO5212773). Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babusyte, A.; Kotthoff, M.; Fiedler, J.; Krautwurst, D. Biogenic amines activate blood leukocytes via trace amine-associated receptors TAAR1 and TAAR2. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 93, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, G.; Krautwurst, D. Trace Amine-Associated Receptors in the Cellular Immune System. Trace Amines Neurol. Disord. 2016, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Li, J.T.; Si, T.M.; Su, Y.A. Research progress on the immunomodulatory effects and mechanisms of trace amine-associated receptor 1. Sheng Li Xue Bao 2023, 75, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sriram, U.; Cenna, J.M.; Haldar, B.; Fernandes, N.C.; Razmpour, R.; Fan, S.; Ramirez, S.H.; Potula, R. Methamphetamine induces trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) expression in human T lymphocytes: role in immunomodulation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasik, A.M.; Millan, M.J.; Scanlan, T.; Barnes, N.M.; Gordon, J. Evidence for functional trace amine associated receptor-1 in normal and malignant B cells. Leuk. Res. 2012, 36, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polini, B.; Ricardi, C.; Bertolini, A.; Carnicelli, V.; Rutigliano, G.; Saponaro, F.; Zucchi, R.; Chiellini, G. T1AM/TAAR1 System Reduces Inflammatory Response and β-Amyloid Toxicity in Human Microglial HMC3 Cell Line. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Andrea, G.; Terrazzino, S.; Fortin, D.; Farruggio, A.; Rinaldi, L.; Leon, A. HPLC electrochemical detection of trace amines in human plasma and platelets and expression of mRNA transcripts of trace amine receptors in circulating leukocytes. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 346, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.S.; Heo, J.S.; Shin, S.W.; Bae, D.J.; Song, H.J.; Jun, J.A.; Kim, J.D.; Park, J.S.; Park, B.L.; Shin, H.D.; Park, C.S. Association between TAAR6 polymorphisms and airway responsiveness to inhaled corticosteroids in asthmatic patients. Pharmacogenet Genom. 2015, 25, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panas, M.W.; Xie, Z.; Panas, H.N.; Hoener, M.C.; Vallender, E.J.; Miller, G.M. Trace amine associated receptor 1 signaling in activated lymphocytes. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012, 7, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, M.; Iwakiri, D.; Kanda, T.; Imaizumi, T.; Takada, K. EB virus-encoded RNAs are recognized by RIG-I and activate signaling to induce type I IFN. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4207–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, L.M.; Somaiya, R.D.; Miller, G.M. Review and Meta-Analyses of TAAR1 Expression in the Immune System and Cancers. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckey, C.J.; Bhattacharya, D.; Goldrath, A.W.; Weissman, I.L.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Memory T and memory B cells share a transcriptional program of self-renewal with long-term hematopoietic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3304–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Pathophysiology of allergic inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potula, R.; Hawkins, B.J.; Cenna, J.M.; Fan, S.; Dykstra, H.; Ramirez, S.H.; Morsey, B.; Brodie, M.R.; Persidsky, Y. Methamphetamine causes mitrochondrial oxidative damage in human T lymphocytes leading to functional impairment. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 2867–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terunuma, H.; Deng, X.; Dewan, Z.; Fujimoto, S.; Yamamoto, N. Potential role of NK cells in the induction of immune responses: implications for NK cell-based immunotherapy for cancers and viral infections. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 27, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, T.H. Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 240–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.; Du, Y.; Xing, C.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, R.F. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling and Its Role in Cell-Mediated Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 812774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.A.; Hoener, M.C.; Moore, C.S.; Berry, M.D. TAAR1 Regulates Purinergic-induced TNF Secretion from Peripheral, But Not CNS-resident, Macrophages. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2023, 18, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugda Gwilt, K.; Olliffe, N.; Hoffing, R.A.; Miller, G.M. Trace amine associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) expression and modulation of inflammatory cytokine production in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages: a novel mechanism for inflammation in ulcerative colitis. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2019, 41, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amulic, B.; Cazalet, C.; Hayes, G.L.; Metzler, K.D.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil function: from mechanisms to disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 459–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattin, J.E.; Schroder, K.; Su, A.I.; Walker, J.R.; Zhang, J.; Wiltshire, T.; Saijo, K.; Glass, C.K.; Hume, D.A.; Kellie, S.; Sweet, M.J. Expression analysis of G Protein-Coupled Receptors in mouse macrophages. Immunome Res. 2008, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geoffrey, R.; Jia, S.; Kwitek, A.E.; Woodliff, J.; Ghosh, S.; Lernmark, A.; Wang, X.; Hessner, M.J. Evidence of a functional role for mast cells in the development of type 1 diabetes mellitus in the BioBreeding rat. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 7275–7286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, S.; Lignani, G.; Caffino, L.; Maggi, S.; Sukhanov, I.; Leo, D.; Mus, L.; Emanuele, M.; Ronzitti, G.; Harmeier, A.; Medrihan, L.; Sotnikova, T.D.; Chieregatti, E.; Hoener, M.C.; Benfenati, F.; Tucci, V.; Fumagalli, F.; Gainetdinov, R.R. TAAR1 Modulates Cortical Glutamate NMDA Receptor Function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 2217–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros, I.E.; Ghorpade, A. HIV-1, methamphetamine and astrocyte glutamate regulation: combined excitotoxic implications for neuro-AIDS. Curr. HIV Res. 2012, 10, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Andrea, G.; D'Arrigo, A.; Facchinetti, F.; Del Giudice, E.; Colavito, D.; Bernardini, D.; Leon, A. Octopamine, unlike other trace amines, inhibits responses of astroglia-enriched cultures to lipopolysaccharide via a β-adrenoreceptor-mediated mechanism. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 517, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández de Palencia, P.; Fernández, M.; Mohedano, M.L.; Ladero, V.; Quevedo, C.; Alvarez, M.A.; López, P. Role of tyramine synthesis by food-borne Enterococcus durans in adaptation to the gastrointestinal tract environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, J.; Willing, B.; Lucio, M.; Fekete, A.; Dicksved, J.; Halfvarson, J.; Tysk, C.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. Metabolomics reveals metabolic biomarkers of Crohn's disease. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhukov, I.S.; Vaganova, A.N.; Murtazina, R.Z.; Alferova, L.S.; Ermolenko, E.I.; Gainetdinov, R.R. Gut Microbiota Alterations in Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 9 (TAAR9) Knockout Rats. Biomolecules. 2022, 12, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taquet, N.; Philippe, C.; Reimund, J.-M.; Muller, C. D. Inflammatory bowel disease G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) expression profiling with microfluidic cards. Crohn’s Disease 2012, 59–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.B.; Maixner, D.W.; Fillingim, R.B.; Slade, G.; Gracely, R.H.; Ambrose, K.; Zaykin, D.V.; Hyde, C.; John, S.; Tan, K.; Maixner, W.; Diatchenko, L. Large candidate gene association study reveals genetic risk factors and therapeutic targets for fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, D.A.; Galloway, D.A.; Hoener, M.C.; Berry, M.D.; Moore, C.S. TAAR1 Expression in Human Macrophages and Brain Tissue: A Potential Novel Facet of MS Neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Table 1.
Expression and biological function of TAARs in human immune system cells.
Table 1.
Expression and biological function of TAARs in human immune system cells.
| Receptor |
Expression in human immune cell populations |
Known ligands |
Biological function |
References |
| TAAR1 |
Peripheral mononuclear cells, B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, polymorphonuclear neutrophils, monocyte, NK-cells |
2-Phenylethylamine (PEA)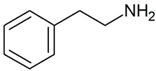
|
Joint effect of phenylethylamine and IL-4 stimulated Ig-E synthesis. Possible joint effect with TAAR2 due to heterodymerization. |
[24] |
| |
Methamphetamine (METH)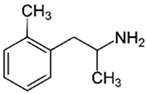
|
Elevated concentration of intracellular calcium, active forms of oxygen. Stimulation of differentiation Th0 into Th2, reduced production of Il-2, intensified production of Il-6. |
[24,26,27] |
| |
|
Phenylethylamine (PEA)

Tyrosine (TYR) 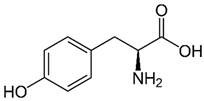
3-iodothyronamine (T1AM)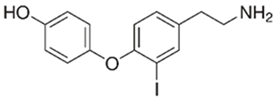
|
Chemosensory migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes towards TAAR agonists. |
[24,28] |
| |
Microglia |
3-iodothyronamine (T1AM)

|
T1AM is capable of reducing b-amyloid stimulated TNF-a and LPS inflammatory response on the part of microglia through inhibition of release of pro-inflammatory factors (IL-6, TNFα, NF-kB, MCP1 and MIP1), stimulating the release of anti-inflammatory mediators (IL-10) |
[29] |
| TAAR2 |
Peripheral mononuclear cells, B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, polymorphonuclear neutrophils, monocyte, NK-cells |
beta-Phenylethylamine (PEA)
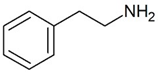
|
–
|
[24] |
| TAAR5 |
B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, polymorphonuclear neutrophils, monocytes, NK-cells |
Trimethylamine (TMA) 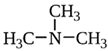
Derivative of choline 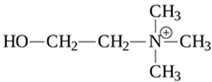
|
– |
[4,24] |
| TAAR6 |
B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, polymorphonuclear neutrophils, monocytes, NK-cells |
Potent ligands have not yet been identified |
– |
[24] |
| TAAR8 |
The research of D’Andrea et al. [30] revealed mRNA expression in leukocytes, however the 2013 research [24] did not confirm these results. |
Potent ligands have not yet been identified |
– |
[24] |
| TAAR9 |
B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, polymorphonuclear neutrophils, monocytes, NK-cells |
Potent ligands have not yet been identified |
- |
[24] |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).