Submitted:
29 February 2024
Posted:
01 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Cases of Frequency Dependent Mass
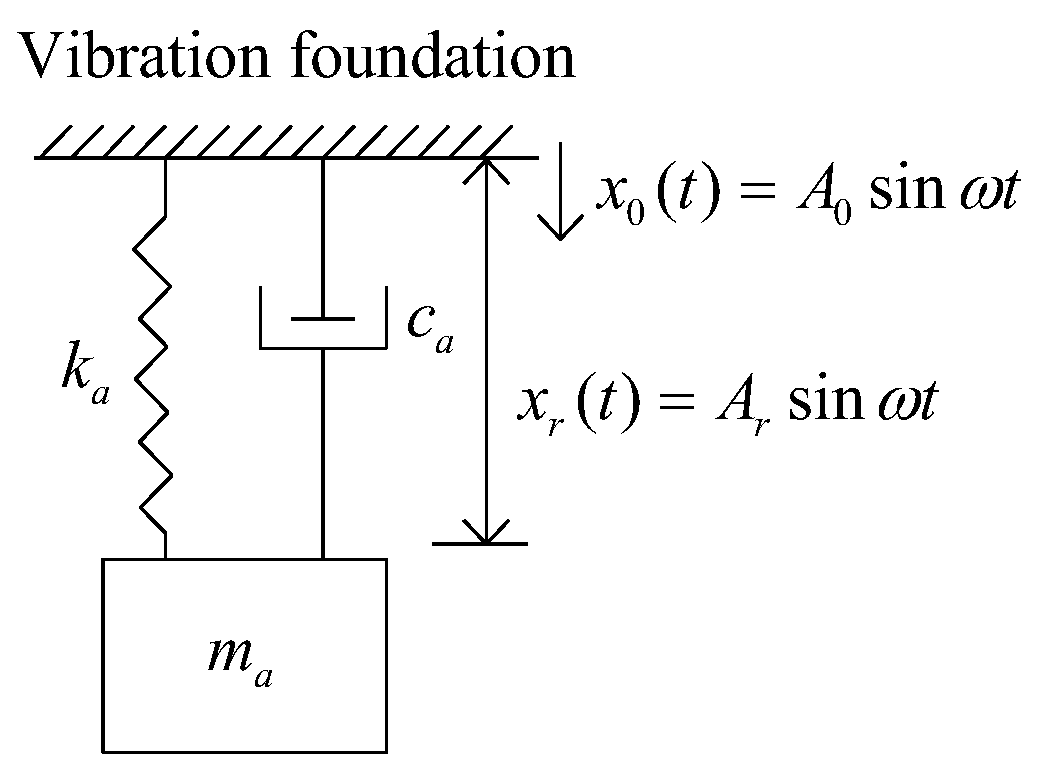
2.1. Frequency Dependent Mass in Auxiliary Mass Damper System
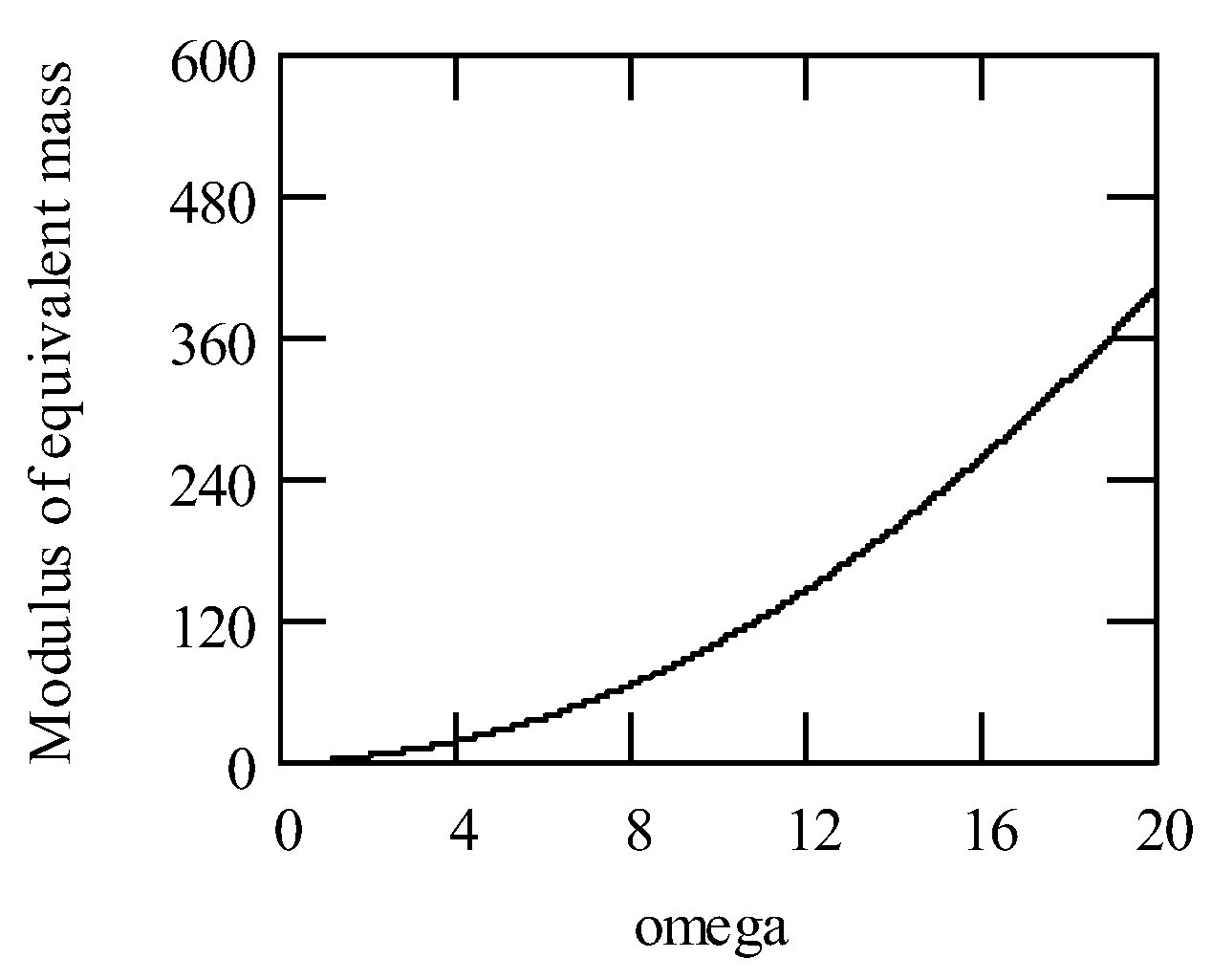
2.2. Added Mass
- qn (n = 1, …, 6): generalized coordinates.
- fn: generalized forces.
- mjn: dry mass of the ship in direction j.
- cjn: dry damping of the ship in direction j.
- kjn: dry stiffness of the ship in direction j.
- madd, jn: added mass of the ship in direction j.
- hjn(t): impulse response function in direction j to an impulse in velocity in direction n.
3. Cases of Frequency Dependent Damping
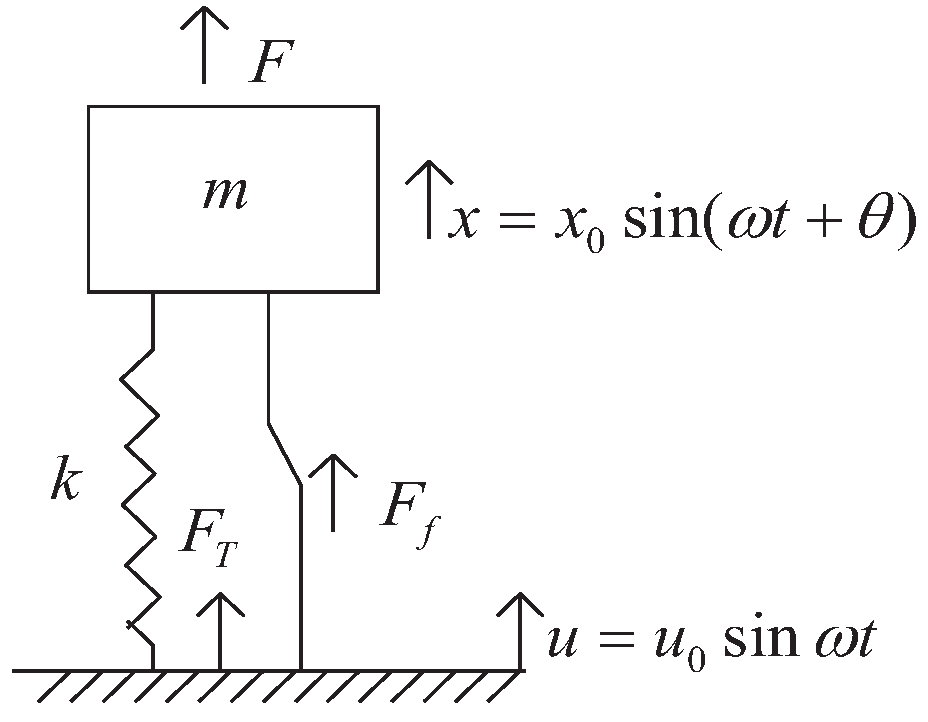
3.1. Rigidly Connected Coulomb Damper
3.2. Rayleigh Damping
3.3. Remarks
4. Cases of Frequency Dependent Stiffness
4.1. Frequency Dependent Stiffness in a Shaft Driven by a Periodic Force
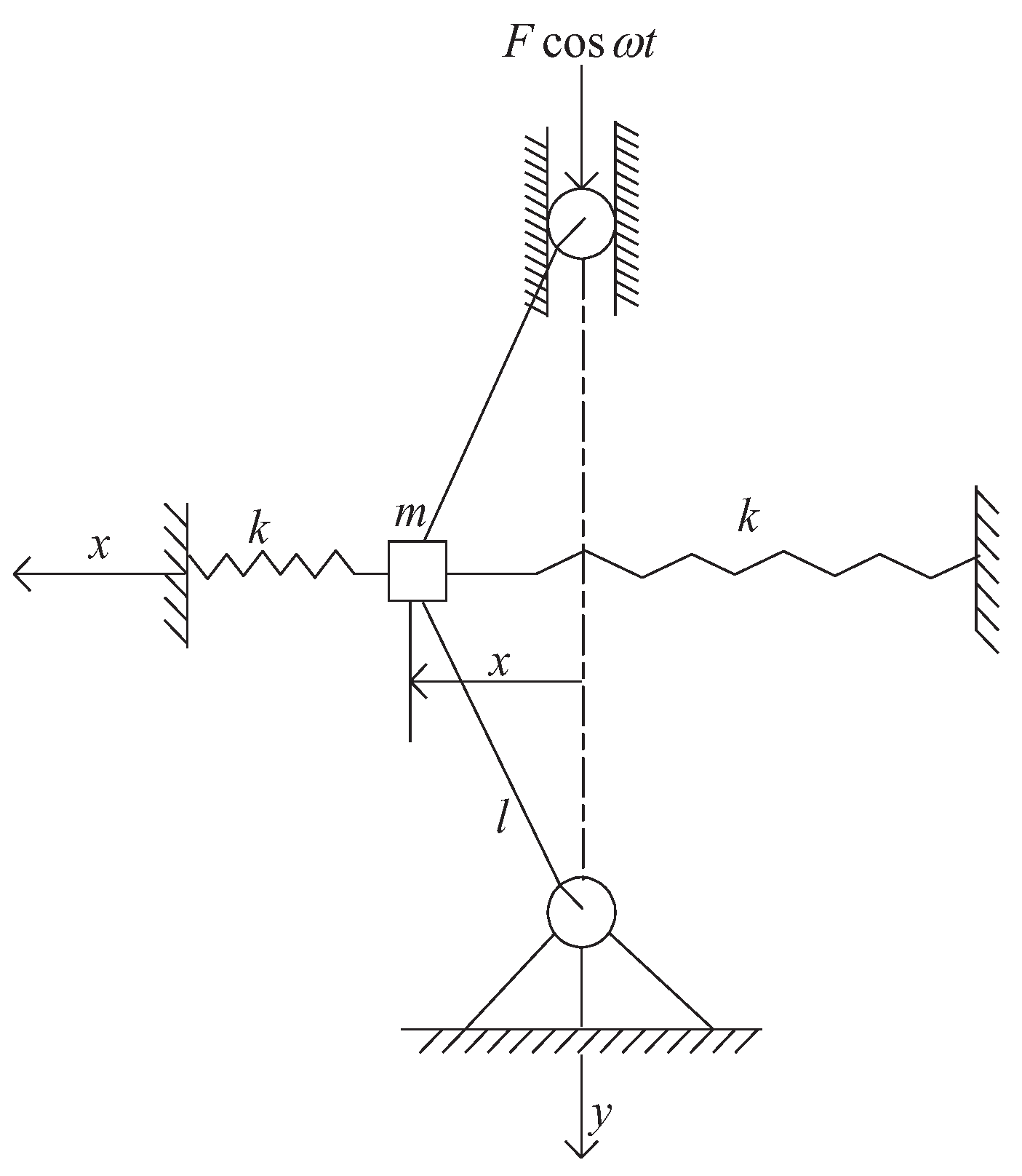
4.2. Frequency Dependent Stiffness in Simple Pendulum
5. General Vibration System with Frequency Dependent Elements
5.1. Motion Equation of General Vibration System
5.2. Vibration Parameters of General Vibration System
5.3. Free Response of General Vibration System with Frequency Dependent Elements
5.4. Impulse Response of General Vibration System with Frequency Dependent Elements
5.5. Step Response of General Vibration System with Frequency Dependent Elements
6. Frequency Transfer Function of General Vibration System with Frequency Dependent Elements
7. Logarithmic Decrement and Q Factor of General Vibration System with Frequency Dependent Elements
8. Li's Vibration System with Frequency Dependent Elements
8.1. Motion Equation of Li's Vibration System
8.2. Vibration Parameters of Li's Vibration System
8.3. Free Response of Li's Vibration System
8.4. Impulse Response of Li's Vibration System
8.5. Step Response of Li's Vibration System
8.6. Frequency Transfer Function of Li's Vibration System
8.7. Logarithmic Decrement and Q Factor of Li's Vibration System
8.8. Equivalent Fractional System of Li's Vibration System
9. Seven Classes of Li's Vibration Systems with Frequency Dependent Elements and Their Fractional Equivalences
9.1. Li's Vibration System of Class I and its Fractional Equivalence
9.2. Li's Vibration System of Class II and its Fractional Equivalence
9.3. Li's Vibration System of Class III and its Fractional Equivalence
9.4. Li's Vibration System of Class IV and its Fractional Equivalence
9.5. Li's Vibration System of Class V and its Fractional Equivalence
9.6. Li's Vibration System of Class VI and its Fractional Equivalence
9.7. Li's Vibration System of Class VII and its Fractional Equivalence
10. Vibration Parameters of Seven Classes of Fractional Vibrators
11. Responses of Seven Classes of Fractional Vibrators
12. Frequency Transfer Funcitons of Seven Classes of Fractional Vibrators
| Fractional vibrators | Frequency transfer functions |
|---|---|
| Class I | |
| Class II | |
| Class III | |
| Class IV | |
| Class V | |
| Class VI | |
| Class VII |
13. Application: Multi-Fractional Damped Euler-Bernoulli Beam
13.1. Multi-Fractional Damped Euler-Bernoulli Beam
13.2. Closed Form Forced Response
14. Nonlinearity of Fractional Vibraitons
15. Conclusions
References
- Harris, C.M. Shock and Vibration Handbook, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Korotkin, A.I. Added Masses of Ship Structures, Fluid Mechanics and Its Applications; Springer: The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 88. [Google Scholar]
- Palley, O.M.; Bahizov, B.; Voroneysk, E.Я. Handbook of Ship Structural Mechanics; Xu, B.H. , Xu, X., Xu, M.Q., Translators; National Defense Industry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kristiansen, E.; Egeland, O. Frequency-dependent added mass in models for controller design for wave motion damping. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2003, 36, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.-S.; Wu, Y.-S.; Liu, Y.-M.; Lin, C.-G. A three-dimensional hydroelasticity theory for ship structures in acoustic field of shallow sea. J. Hydrodyn. 2013, 25, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-S.; Hsieh, M. An experimental method for determining the frequency-dependent added mass and added mass moment of inertia for a floating body in heave and pitch motions. Ocean Eng. 2001, 28, 417–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhai, P. A magnetic field- and frequency-dependent dynamic shear modulus model for isotropic silicone rubber-based magnetorheological elastomers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 204, 108637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaberzadeh, M.; Li, B.; Tan, K.T. Wave propagation in an elastic metamaterial with anisotropic effective mass density. Wave Motion 2019, 89, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wu, M.-Z.; Hamdaoui, M. Mixed integer multi-objective optimization of composite structures with frequency-dependent interleaved viscoelastic damping layers. Comput. Struct. 2016, 172, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemmaghami, A.R.; Kwon, O.-S. Nonlinear modeling of MDOF structures equipped with viscoelastic dampers with strain, temperature and frequency-dependent properties. Eng. Struct. 2018, 168, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdaoui, M.; Robin, G.; Jrad, M.; Daya, E.M. Optimal design of frequency dependent three-layered rectangular composite beams for low mass and high damping. Compos. Struct. 2015, 120, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. Three classes of fractional oscillators. Symmetry 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. Fractional Vibrations with Applications to Euler-Bernoulli Beams; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M. Theory of vibrators with variable-order fractional forces, 7 July 2021. https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.02340.
- Banerjee, J.R. Frequency dependent mass and stiffness matrices of bar and beam elements and their equivalency with the dynamic stiffness matrix. Comput. Struct. 2021, 254, 106616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.E.; Macdonald, J.H.G.; Alexander, N.A. A nonlinear frequency-dependent spring-mass model for estimating loading caused by rhythmic human jumping. Eng. Struct. 2021, 240, 112229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, N.A.; de Oliveira, R. From frequency-dependent mass and stiffness matrices to the dynamic response of elastic systems. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2001, 38, 1813–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, D.; Shen, M.; Sheng, X.; Li, J.; Guo, S. Temperature- and frequency-dependent vibroacoustic response of aluminium extrusions damped with viscoelastic materials. Compos. Struct. 2021, 272, 114148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Y. Time-domain calculation method of improved hysteretic damped system based on frequency-dependent loss factor. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 488, 115658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Hartog, J.P. Mechanical Vibrations, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, L.S. Steady forced vibrations as influenced by damping. Trans. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. 1930, 52, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strutt, J.W.; Rayleigh, J.W.S. The Theory of Sound; Macmillan & Co., Ltd.: London, 1877; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.D.; Xia, L.J. Ship Hull Vibration; The Press of Shanghai Jiaotong University: Shanghai, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Trombetti, T.; Silvestri, S. On the modal damping ratios of shear-type structures equipped with Rayleigh damping systems. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 292, 21–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetti, T.; Silvestri, S. Novel schemes for inserting seismic dampers in shear-type systems based upon the mass proportional component of the Rayleigh damping matrix. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 302, 486–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, D.R.A.; Khan, N.U.; Ramamurti, V. On the role of Rayleigh damping. J. Sound Vib. 1995, 185, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-G.; Wiebe, R. Experimental and numerical investigation of nonlinear dynamics and snap-through boundaries of post-buckled laminated composite plates. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 439, 362–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-H.; Huang, J.-Y.; Lin, C.-M.; Chen, C.-T.; Wen, K.-L. Near-surface frequency-dependent nonlinear damping ratio observation of ground motions using SMART1. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 147, 106798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stollwitzer, A.; Fink, J.; Malik, T. Experimental analysis of damping mechanisms in ballasted track on single-track railway bridges. Eng. Struct. 2020, 220, 110982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jith, J.; Sarkar, S. A model order reduction technique for systems with nonlinear frequency dependent damping. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 77 Pt 2, 1662–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, A.; Jia, Y. Frequency-dependent orthotropic damping properties of Nomex honeycomb composites. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 160, 107372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarraga, O.; Sarría, I.; García-Barruetabeña, J.; Cortés, F. Dynamic analysis of plates with thick unconstrained layer damping. Eng. Struct. 2019, 201, 109809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zheng, H.; Jonckheere, S.; Desmet, W. Explicit and efficient topology optimization of frequency-dependent damping patches using moving morphable components and reduced-order models. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2019, 355, 591–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zheng, H.; Jonckheere, S.; de Walle, A.; Pluymers, B.; Desmet, W. Adaptive model reduction technique for large-scale dynamical systems with frequency-dependent damping. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 332, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ren, J.; Zhe, Z.; Xue, M.; Tong, Y.; Zou, J.; Zheng, Q.; Tang, H. ; A pressure, amplitude and frequency dependent hybrid damping mechanical model of flexible joint. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 471, 115173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouleau, L.; Deü, J.-F.; Legay, A. A comparison of model reduction techniques based on modal projection for structures with frequency-dependent damping. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 90, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdaoui, M.; Ledi, K.S.; Robin, G.; Daya, E.M. Identification of frequency-dependent viscoelastic damped structures using an adjoint method. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 453, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, S.Y.; Zhang, M.; Gou, P. Frequency-dependent aerodynamic damping and its effects on dynamic responses of floating offshore wind turbines. Ocean Eng. 2023, 278, 114444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.-J.; Lin, J.-H.; Chen, H.-R.; Williams, F.W. Random vibration of composite structures with an attached frequency-dependent damping layer. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2008, 39, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adessina, A.; Hamdaoui, M.; Xu, C.; Daya, E.M. Damping properties of bi-dimensional sandwich structures with multi-layered frequency-dependent visco-elastic cores. Compos. Struct. 2016, 154, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.-W.; Roesset, J.M.; Wen, C.-H. A time-domain viscous damping model based on frequency-dependent damping ratios. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2000, 19, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.R.; Farag, N.H.; Pan, J. Evaluation of frequency dependent rubber mount stiffness and damping by impact test. Appl. Acoust. 2005, 66, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Qin, Z.; Chu, F. Parametric study of damping characteristics of rotating laminated composite cylindrical shells using Haar wavelets. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 161, 107500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catania, G.; Sorrentino, S. Dynamical analysis of fluid lines coupled to mechanical systems taking into account fluid frequency-dependent damping and non-conventional constitutive models: Part 1 – Modeling fluid lines. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 50–51, 260–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catania, G.; Sorrentino, S. Dynamical analysis of fluid lines coupled to mechanical systems taking into account fluid frequency-dependent damping and non-conventional constitutive models: Part 2 – Coupling with mechanical systems. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 50–51, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Turner, K. Frequency dependent fluid damping of micro/nano flexural resonators: Experiment, model and analysis. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 2007, 134, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; Kobayashi, S.; Miura, K. Equivalent linear method considering frequency dependent characteristics of stiffness and damping. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2002, 22, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assimaki, D.; Kausel, E. An equivalent linear algorithm with frequency- and pressure-dependent moduli and damping for the seismic analysis of deep sites. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2002, 22, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Dai, Q.; Qin, Z.; Chu, F. Damping characteristics of carbon nanotube reinforced epoxy nanocomposite beams. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 166, 108127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.K.; Viswanath, N.S. Frequency dependent stiffness and damping coefficients of orifice compensated multi-recess hydrostatic journal bearings. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1987, 27, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdaniel, J.G.; Dupont, P.; Salvino, L. A wave approach to estimating frequency-dependent damping under transient loading. J. Sound Vib. 2000, 231, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ding, X.; Li, H. Topology optimization of composite material with high broadband damping. Comput. Struct. 2020, 239, 106331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Yu, R.-P.; Ren, J.-W.; Zhang, Q.-C.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Ni, C.-Y.; Han, B.; Lu, T.J. Enhanced vibration and damping characteristics of novel corrugated sandwich panels with polyurea-metal laminate face sheets. Compos. Struct. 2020, 251, 112591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundén, R.; Dahlberg, T. Frequency-dependent damping in structural vibration analysis by use of complex series expansion of transfer functions and numerical Fourier transformation. J. Sound Vib. 1982, 80, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, A.; Telenko, M.; Chen, L.; Wu, S.F. Determining structural damping and vibroacoustic characteristics of a non-symmetrical vibrating plate in free boundary conditions using the modified Helmholtz equation least squares method. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 495, 115903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro, M. Critical damping in nonviscously damped linear systems. Appl. Math. Model. 2019, 65, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandall, S.H. The role of damping in vibration theory. J. Sound Vib. 1970, 11, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Yin, H.; Li, X.B.; Lv, J.C.; Liang, G.Q.; Wei, Y.T. A new dynamic stiffness model with hysteresis of air springs based on thermodynamics. J. Sound Vib. 2022, 521, 116693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, P.; Kari, L. ; The frequency, amplitude and magnetic field dependent torsional stiffness of a magneto-sensitive rubber bushing. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2012, 60, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Feng, Q.; Wang, A.; Sheng, X.; Cheng, G. Testing research on frequency-dependent characteristics of dynamic stiffness and damping for high-speed railway fastener. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 129, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wu, H.; Jin, H.; Cai, C.S. Noise contribution analysis of a U-shaped girder bridge with consideration of frequency dependent stiffness of rail fasteners. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 205, 109280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Adhikari, S.; Liu, X. Stochastic dynamic stiffness for damped taut membranes. Comput. Struct. 2021, 248, 106483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Thompson, D.; Jeong, H.; Toward, M.; Herron, D.; Vincent, N. Measurements of the high frequency dynamic stiffness of railway ballast and subgrade. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 468, 115081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, J.R.; Ananthapuvirajah, A.; Papkov, S.O. Dynamic stiffness matrix of a conical bar using the Rayleigh-Love theory with applications. Eur. J. Mech. - A/Solids 2021, 86, 104144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, J.R.; Ananthapuvirajah, A.; Liu, X.; Sun, C. Coupled axial-bending dynamic stiffness matrix and its applications for a Timoshenko beam with mass and elastic axes eccentricity. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 159, 107197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Metrikine, A.V.; Steenbergen, M.J.M.M. The equivalent dynamic stiffness of a visco-elastic half-space in interaction with a periodically supported beam under a moving load. Eur. J. Mech. - A/Solids 2020, 84, 104065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, D.; Chang, S.; Kim, S. Effect of additional anti-vibration sleeper track considering sleeper spacing and track support stiffness on reducing low-frequency vibrations. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezghani, F.; del Rincón, A.F.; Souf, M.A.B.; Fernandez, P.G.; Chaari, F.; Rueda, F.V.; Haddar, M. Alternating Frequency Time Domains identification technique: Parameters determination for nonlinear system from measured transmissibility data. Eur. J. Mech. - A/Solids 2020, 80, 103886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Thompson, D.; Squicciarini, G.; Rissmann, M.; Bouvet, P.; Xie, G.; Martínez-Casas, J.; Carballeira, J.; Arteaga, I.L.; Garralaga, M.A.; Chover, J.A. Measurements and modelling of dynamic stiffness of a railway vehicle primary suspension element and its use in a structure-borne noise transmission model. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 182, 108232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zeng, X.; Han, K. Dynamical measurements on viscoelastic behaviors of spiders in electro-dynamic loudspeakers. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 104, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ege, K.; Roozen, N.B.; Leclère, Q.; Rinaldi, R.G. Assessment of the apparent bending stiffness and damping of multilayer plates; modelling and experiment. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 426, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, T.; Adhikari, S.; Alu, A. Probing the frequency-dependent elastic moduli of lattice materials. Acta Mater. 2019, 165, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz-AjaIsidro, J.A.; Carrascal, A.; Diego, S. Influence of the operational conditions on static and dynamic stiffness of rail pads. Mech. Mater. 2020, 148, 103505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozyigit, B. Seismic response of pile supported frames using the combination of dynamic stiffness approach and Galerkin’s method. Eng. Struct. 2021, 244, 112822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, R.; Boominathan, A.; Banerjee, S. Stiffness and load sharing characteristics of piled raft foundations subjected to dynamic loads. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 133, 106117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failla, G.; Santoro, R.; Burlon, A.; Russillo, A.F. An exact approach to the dynamics of locally-resonant beams. Mech. Res. Commun. 2020, 103, 103460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.-L.; Fei, Z.-N.; Zhou, B.-Y.; Gong, H.-B.; Song, P.-J. Two-step dynamics of a semiactive hydraulic engine mount with four-chamber and three-fluid-channel. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 480, 115403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozen, N.B.; Labelle, L.; Leclère, Q.; Ege, K.; Alvarado, S. Non-contact experimental assessment of apparent dynamic stiffness of constrained-layer damping sandwich plates in a broad frequency range using a Nd:YAG pump laser and a laser Doppler vibrometer. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 395, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, Y.; Ilanko, S.; Rayleigh-Ritz method, O.T. Gorman's superposition method and the exact dynamic stiffness method for vibration and stability analysis of continuous systems. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 161, 107470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Ringo, M. Engineering Vibrations; Xia, S.R. , Translator; Shanghai Science and Technology Publishing House: Shanghai, China, 1981. [Google Scholar]

| Fractional vibrations | Equivalent mass | Equivalent damping |
|---|---|---|
| Class I | ||
| Class II | ||
| Class III | ||
| Class IV | ||
| Class V | meq5 = m | |
| Class VI | ||
| Class VII |
| Fractional vibrations | Equivalent stiffness | Equivalent damping ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Class I | keq1 = k | |
| Class II | keq2 = k | |
| Class III | keq3 = k | |
| Class IV | ||
| Class V | keq5 = keq4 | |
| Class VI | keq6 = keq4 | |
| Class VII | keq7 = keq4 |
| Fractional vibrations | Equivalent damping free natural angular frequency | Equivalent damped natural angular frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Class I | ||
| Class II | ||
| Class III | ||
| Class IV | ||
| Class V | ||
| Class VI | ||
| Class VII |
| Fractional vibrators | Logarithmic decrement | Q factor |
|---|---|---|
| Class I | ||
| Class II | ||
| Class III | ||
| Class IV | ||
| Class V | ||
| Class VI | ||
| Class VII |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





