1. Introduction
Sleep is a reversible state characterized by an increased perceptual threshold to external stimuli, resulting in a lack of responsiveness to the environment [
1]. It is an indispensable process for the human body, occupying one-third of human life [
2] and playing a crucial role in maintaining physical and mental health. However, sleep disorders are becoming increasingly prevalent in society, affecting 37-58% of adults [
3] and causing significant harm to cognition and physical performance [
4,
5]. Research indicates a close association between sleep and various diseases, including cardiovascular disease [
6], diabetes [
7], mental disorders [
8], and even mortality [
9]. However, the molecular mechanisms regulating sleep remain unclear. Early studies have primarily focused on the role of the central nervous system in the control and potential disruption of sleep [
10]. The involvement of peripheral organs, such as the gut, in sleep regulation, is yet to be fully understood.
The gut microbiome, a highly complex microbial community, may directly or indirectly participate in sleep regulation through the microbiome–gut–brain axis [
11]. Several studies have reported associations between the gut microbiome and sleep. For instance, microbial taxa from the
Christensenellaceae family have been observed to correlate positively with REM sleep and negatively with continuous glucose levels, potentially indicating a relationship between microbiota and metabolic processes during sleep [
12]. In a comparative study, antibiotic-induced microbiota-depleted mice exhibited noticeable differences in sleep/wake architecture compared to control mice [
13]. Gut microbes and their metabolites have been implicated in mediating the ameliorative effects of melatonin on cognitive impairment induced by sleep deprivation [
14]. Conversely, sleep deprivation has been found to significantly reduce the α-diversity in the gut flora, leading to decreased gut microbiome diversity and metabolic dysbiosis [
15].
However, the presence of potential confounding factors such as diet, environment, and age reduces the reliability of these experimental results. Furthermore, due to ethical constraints, many randomized controlled trials are difficult to conduct, limiting the inference of causal relationships between gut microbiota and sleep.
Mendelian randomization is a method for estimating the causal effect of an exposure on an outcome using genetic variants as instrumental variables [
16], addresses some of these challenges. These genetic variants, determined at conception and randomly allocated among individuals, are less susceptible to confounding or reverse causality [
17]. This approach allows for distinguishing between correlation and causation.
In this study, a bidirectional two-sample MR analysis was employed to assess the causal relationship between 412 microbial taxa and pathways and seven sleep-related traits. Notably, the gut microbiome data in this study are derived from the Dutch Microbiome Project (DMP) cohort [
18], which utilizes metagenomic sequencing for microbes, enabling species-level identification. Additionally, this includes the identification of bacterial pathway abundances, facilitating a comprehensive exploration of the relationship between gut microbiota and sleep.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of study design
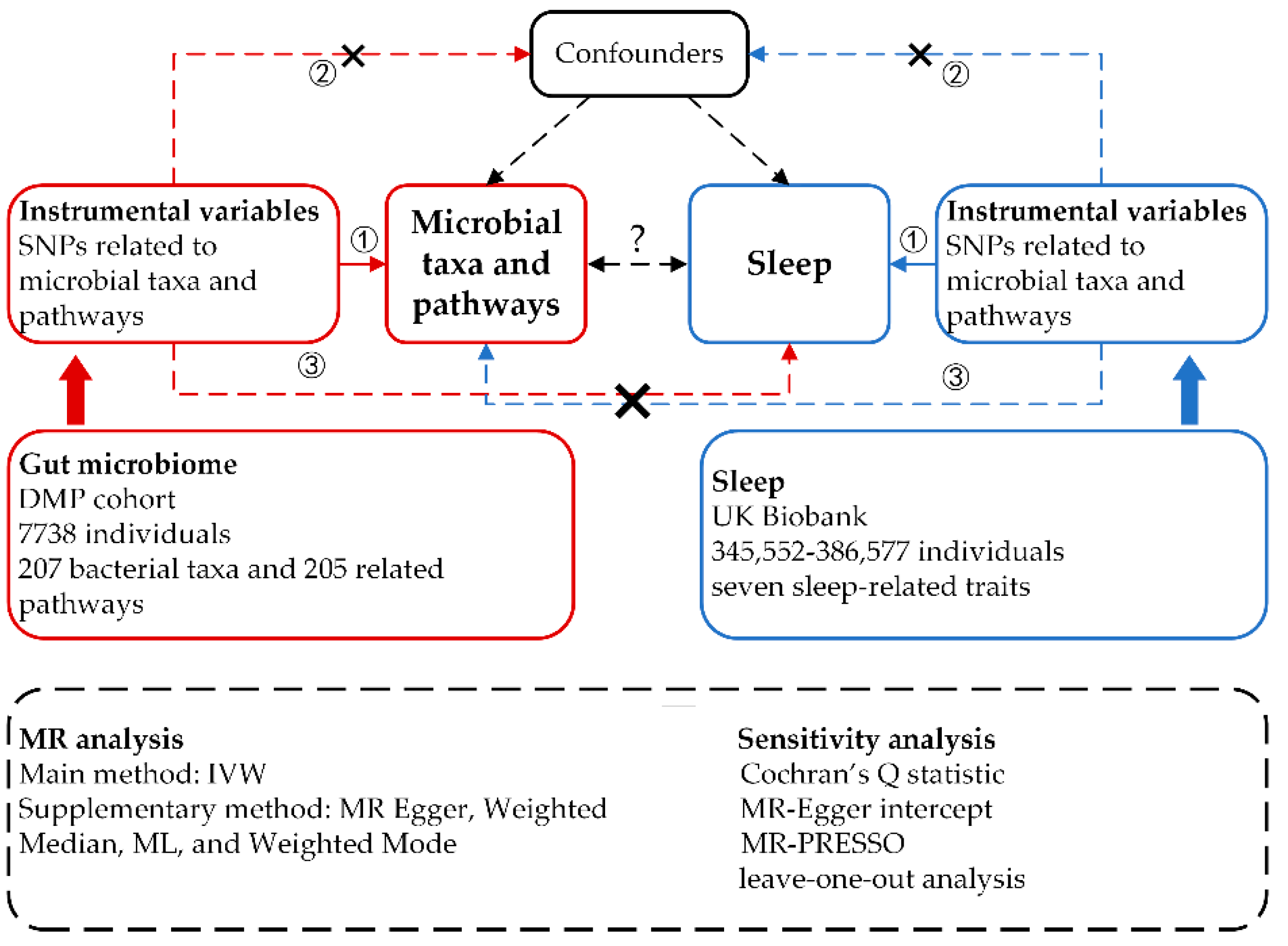
We implemented a bidirectional, two-sample MR design to explore potential causal relationships between 412 microbial taxa and pathways and seven sleep-related traits. For MR-derived causal estimates to be valid, three key assumptions, as outlined in previous studies [
19,
20], must be satisfied: (1) A strong association exists between the genetic variants and the exposure. (2) The genetic variants are independent of any confounding factors that could simultaneously influence the exposure and outcome. (3) The genetic variants affect the outcome risk solely through the exposure, not other pathways. In the forward MR analyses, we considered 207 taxa and 205 pathways as the exposures, with each sleep phenotype serving as the outcome. Conversely, in the reverse MR analyses, each sleep phenotype was treated as the exposure, with the 207 taxa and 205 pathways as the outcomes. To ensure robustness and reliability in our causal inferences, we employed a diverse array of MR methodologies. These included MR Egger, Weighted Median, IVW, Weighted Mode, and Maximum Likelihood (ML) approaches. Additionally, we conducted several sensitivity analyses to further validate our findings, encompassing heterogeneity tests, pleiotropy tests, and leave-one-out analyses.
Figure 1.
Study design of the bidirectional two-sample MR analysis on the associations of gut microbiome and sleep.
Figure 1.
Study design of the bidirectional two-sample MR analysis on the associations of gut microbiome and sleep.
2.2. Data sources
The Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) summary statistics data for the human gut microbiome were sourced from the Dutch Microbiome Project’s GWAS dataset. This extensive project undertook metagenomic sequencing of fecal samples from 7,738 participants in the Netherlands, aiming to elucidate the relationship between human genetic variations and the gut microbiome. This cohort stands out from many existing ones that utilize 16S RNA sequencing by enabling bacterial identification at the species level and identifying the abundance of bacterial pathways. In total, our analysis encompassed 207 taxonomies, including five phyla, ten classes, 13 orders, 26 families, 48 genera, and 105 species, alongside 205 bacterial pathways [
18].
Concerning sleep-associated phenotypes, we utilized GWAS summary data from the study by Jansen et al., which were derived from the UK Biobank. This expansive, population-based cohort includes over 500,000 participants [
21]. The sleep data were obtained from self-reported sleep questionnaires completed during the initial UK Biobank research visit between 2006 and 2010. These questionnaires covered seven sleep-related items: insomnia, morningness, sleep duration, ease of getting up in the morning, daytime napping, daytime sleepiness, and snoring [
22]. The participant counts for these seven phenotypes ranged from 345,552 to 386,577. Further details about these two GWAS summary datasets are available in
Additional file 1: Table S1.
2.3. Instrumental variables selection
In the forward MR analysis, SNPs associated with 207 taxa and 205 pathways representing microbial composition were selected using a locus-wide significance threshold (P < 1.0×10
-5) [
23]. To address the issue of strong linkage disequilibrium, we applied stringent criteria, including an R² cut-off of less than 0.001 and a clumping window of 10,000 kb. This was done to ensure the independence of these SNPs, referencing the 1000 Genomes European data as our standard. SNPs present in the exposure data but absent in the outcome data were excluded [
24]. Additionally, we eliminated SNPs with a minor allele frequency (MAF) below 0.01. To mitigate the risk of weak instrumental bias, SNPs with an F-statistic (calculated as
) lower than 10 were also removed. For palindromic SNPs, forward-strand alleles were inferred using allele frequency data. For the reverse MR analysis, instrumental variables (IVs) for the seven sleep-related traits were selected using a threshold of P < 5.0×10
-8. The screening conditions for this selection were consistent with those employed in the forward MR analysis.
2.4. Mendelian randomization analysis
We employed multiple statistical models to estimate the bidirectional causal relationships between gut microbiota and sleep-related traits. These included MR Egger, Weighted Median, IVW, ML, and Weighted Mode, with IVW serving as the principal method. IVW integrates Wald ratio estimates for each SNP through a meta-analysis approach, providing a comprehensive effect estimate of exposure on outcome. This method is efficient when all genetic variants are valid instrumental variables IVs [
25], but it can be biased in the presence of pleiotropic genetic variables. The ML method, similar to IVW, assumes no heterogeneity and the absence of horizontal pleiotropy in the IVs [
26]. When these conditions are met, ML results are generally consistent with IVW. The Weighted Median approach, which infers causality from the median of weighted empirical density functions derived from individual SNP effect estimates, is robust even if up to half of the genetic variants are invalid [
26]. Weighted Mode groups SNPs based on the similarity of their causal effects and estimates the causal effect using the cluster with the most SNPs [
27]. It offers an unbiased estimate, provided that the SNPs within the largest cluster are valid.
Considering multiple hypothesis testing, we applied a Bonferroni correction for the p-value in the IVW method. Specifically, the threshold for the 207 taxa and 205 pathways was set at 2.4 × 10
-4 (0.05/207, 0.05/205) [
28,
29]. After correction, results with a P-value less than the Bonferroni-corrected thresholds and simultaneously P < 0.05 in the other three methods (Weighted Median, ML, and Weighted Mode) and consistent direction in Egger’s test were considered to have a significant causal relationship. We also reported results as suggestive causal relationships if they had a P < 0.05 but were above the Bonferroni-corrected threshold. Notably, we only considered results based on more than three shared SNPs [
30]. The results were expressed as betas for the risk of sleep-related traits, corresponding to each standard deviation unit increase in the abundance of bacterial taxa and pathways, and vice versa for the betas on bacterial taxa and pathways per one standard deviation unit increase in sleep-related traits.
2.5. Sensitivity analysis
To ascertain the robustness of the identified significant causal relationships, we conducted a series of sensitivity analyses. Cochran’s Q statistic was employed to evaluate heterogeneity among different SNPs [
31]. A p-value greater than 0.05 in this test indicates an absence of significant heterogeneity among the instrumental variables used in our analysis. For assessing potential horizontal pleiotropy, we calculated the intercept of MR-Egger; a P > 0.05 suggests no evident horizontal pleiotropy among the SNPs in our MR analysis [
32]. In addition, we utilized the MR-PRESSO global test to detect horizontal pleiotropy. This test compares the observed distance of all variants to the regression line (residual sum of squares) against the expected distance under the null hypothesis of no horizontal pleiotropy. The MR-PRESSO outlier test was also performed to identify specific horizontal pleiotropic outlier variants [
33]. Furthermore, we conducted a ‘leave-one-out’ analysis, which involves sequentially excluding each SNP to assess its individual influence on the primary causal relationship. All MR analyses and sensitivity tests were performed using the TwoSampleMR (version 0.5.6), MR-PRESSO, and other relevant packages in R (version 4.2.0).
3. Results
3.1. Selection of the instrumental variables
Based on our instrumental variables (IVs) selection criteria, two taxa, species
Bacteroides and species
Lachnospiraceae, were excluded as they lacked SNPs below the threshold of 1.0 × 10
-5. The number of IVs for 205 microbial taxa and 205 pathways ranged from 2 to 19, explaining 0.25–0.78% of the variance in their corresponding taxa and pathways. The lowest F statistic observed among these IVs was 19.51, signifying that all IVs possessed sufficient strength for the MR analysis of the 410 gut microbiotas and associated pathways. In the reverse MR analysis, the number of IVs varied significantly across different sleep-related traits: 46 for sleep duration, 51 for ease of getting up in the morning, and 105 for morningness, accounting for a variance between 0.0077% and 0.05%. These three sleep-related traits are all continuous variables. However, we encountered limitations in identifying adequate IVs for the traits of insomnia, snoring, daytime dozing, and daytime napping. Comprehensive details on the selected IVs are available in the
Additional file 2: Tables S1-S2.
3.2. Suggestive causal relationships between microbial taxa and biological pathways and sleep-related traits
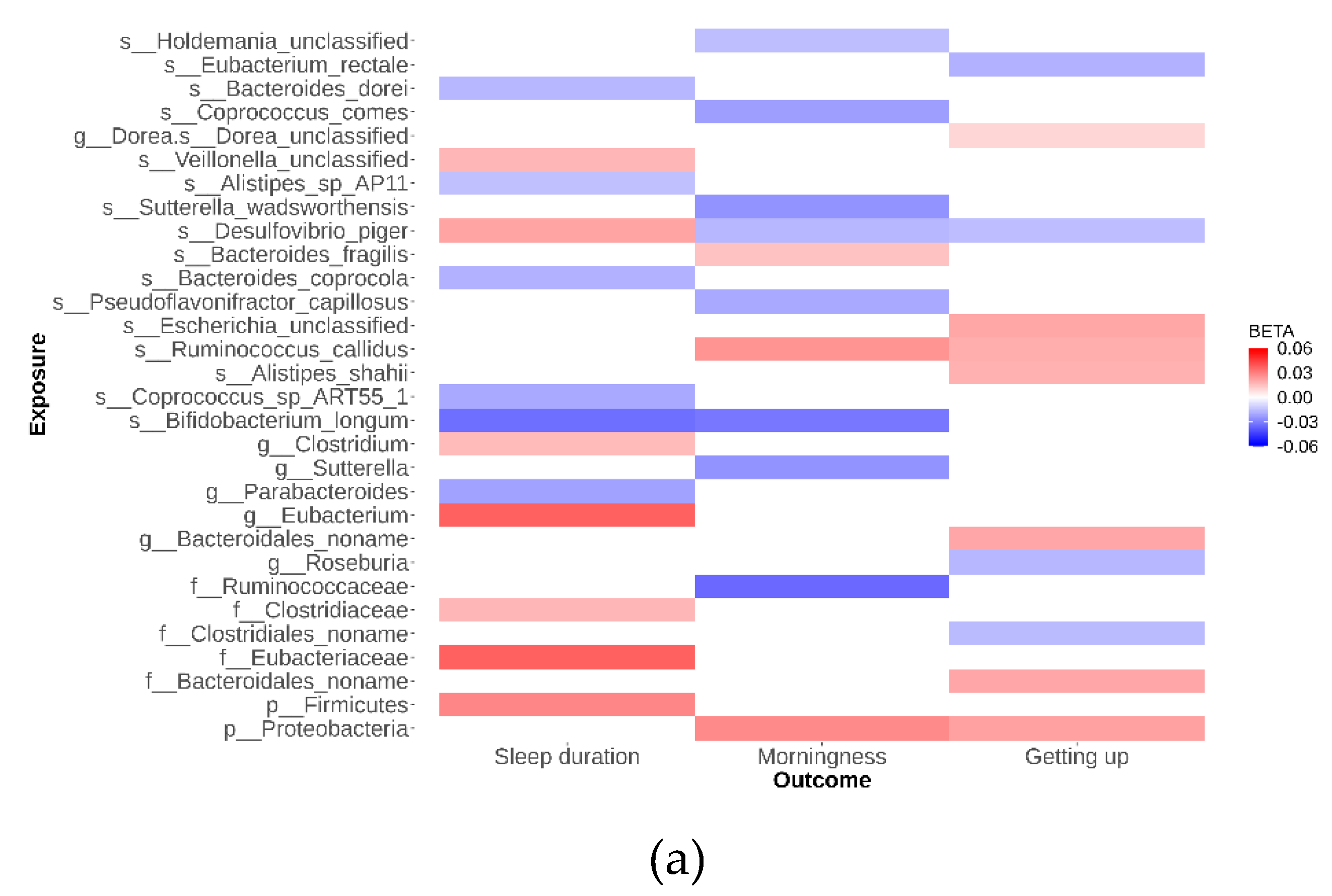
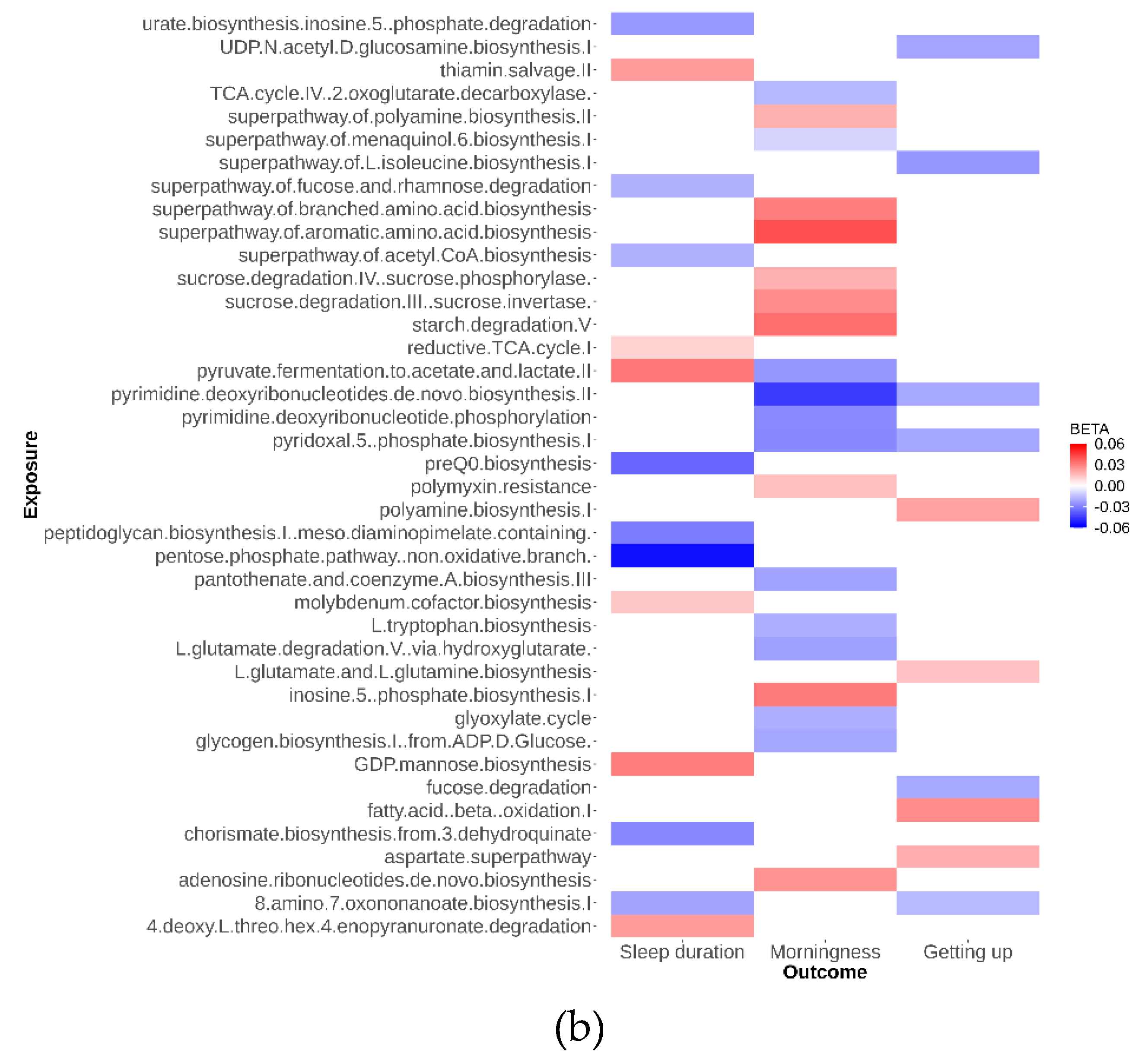
As depicted in
Figure 2, our analysis identified 79 suggestive causal effects of microbial taxa and pathways on sleep-related traits, each conforming at a P
IVW < 0.05. These effects spanned across 70 microbial taxa and pathways and affected three distinct sleep-related traits, with betas ranging from -0.05 to 0.04. Among these 79 suggestive causal relationships, 44 were associated with microbial pathways. Of the 35 taxa identified, 21 were specific at the species level. Conversely, in the analysis of inverse suggestive causal relationships, we observed 45 pairs, with 20 related to pathways (
Additional file 1: Figure S1). Within the remaining 25 pairs, 16 were specific at the species level, with betas ranging from -0.99 to 1.34.
Desulfovibrio emerged as a notable species, exhibiting suggestive causal relationships with all three sleep disorders studied. Specifically, the genetically determined abundance of
Desulfovibrio showed a negative correlation with morningness ((beta -0.02; 95% CI -0.03 to 0.00; P
IVW = 5.0 × 10
-2) and ease of getting up in the morning ((beta -0.02; 95% CI -0.03 to 0.00; P
IVW = 2.3 × 10
-2), while being positively associated with increased sleep duration (beta 0.02; 95% CI 0.003 to 0.04; P
IVW = 2.4 × 10
-2). These findings highlight the potential of metagenomic sequencing data to provide detailed resolution at the species level and emphasize the significant role of pathways in our study. Detailed data supporting these suggestive causal relationships are available in
Additional file 2: Tables S3-S6.
3.3. Causality of genetically determined microbial taxa and pathways on sleep-related traits
Following the application of the Bonferroni correction, two causal relationships were identified that surpassed the threshold (P
IVW < 2.4 × 10
–4). The IVW estimate revealed that a higher abundance of the of the pentose phosphate pathway decreases sleep duration (beta -0.05; 95% CI -0.08 to -0.03; P = 9.00×10
-6) for each SD increase in pathway abundance. Additional methods corroborated this finding: the Weighted Median analysis (beta -0.06; 95% CI -0.09 to -0.03; P = 2.94×10
-4), Weighted Mode analysis (beta -0.06; 95% CI -0.10 to -0.01; P = 4.74×10
-2), and ML analysis (beta -0.05; 95% CI -0.08 to -0.03; P = 3.53×10
-5) indicated consistent results (
Table 1 and
Figure 3). Additionally, the IVW estimate suggested that an increase in fatty acid levels has a positive causal effect on the ease of getting up in the morning (beta 0.03; 95% CI 0.01 to 0.04; P = 8.06×10
-5). This was supported by the Weighted Median analysis (beta 0.03; 95% CI 0.01 to 0.05; P =1.59×10
-3), Weighted Mode analysis (beta 0.04; 95% CI 0.01 to 0.07; P =4.30×10
-3), and ML analysis (beta 0.03; 95% CI 0.01–0.04; P = 1.48×10
-4), all aligning with the IVW findings. In both sets of causal relationships, the direction of effect estimated by MR-Egger was consistent with the results of the other four methods.
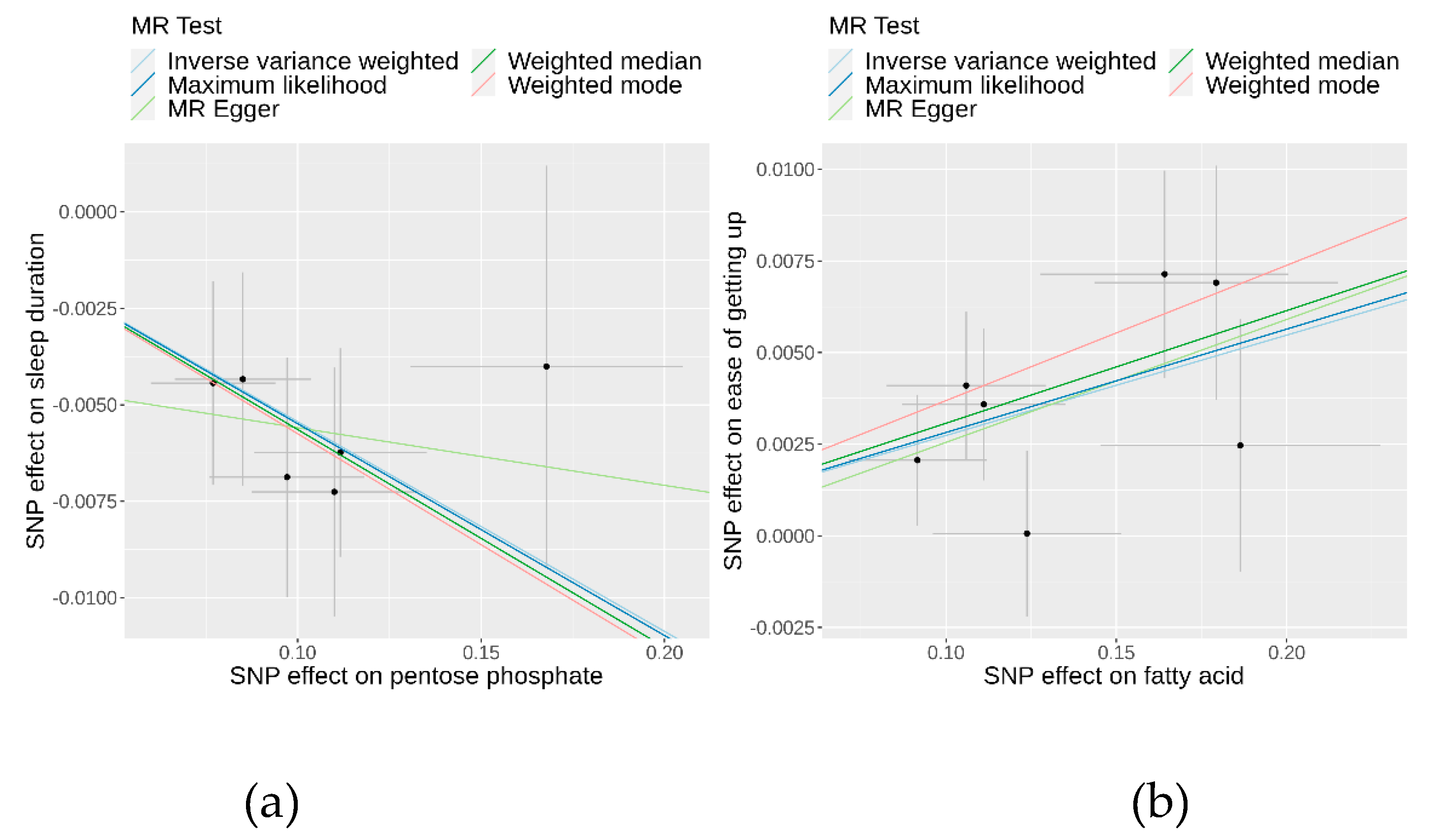
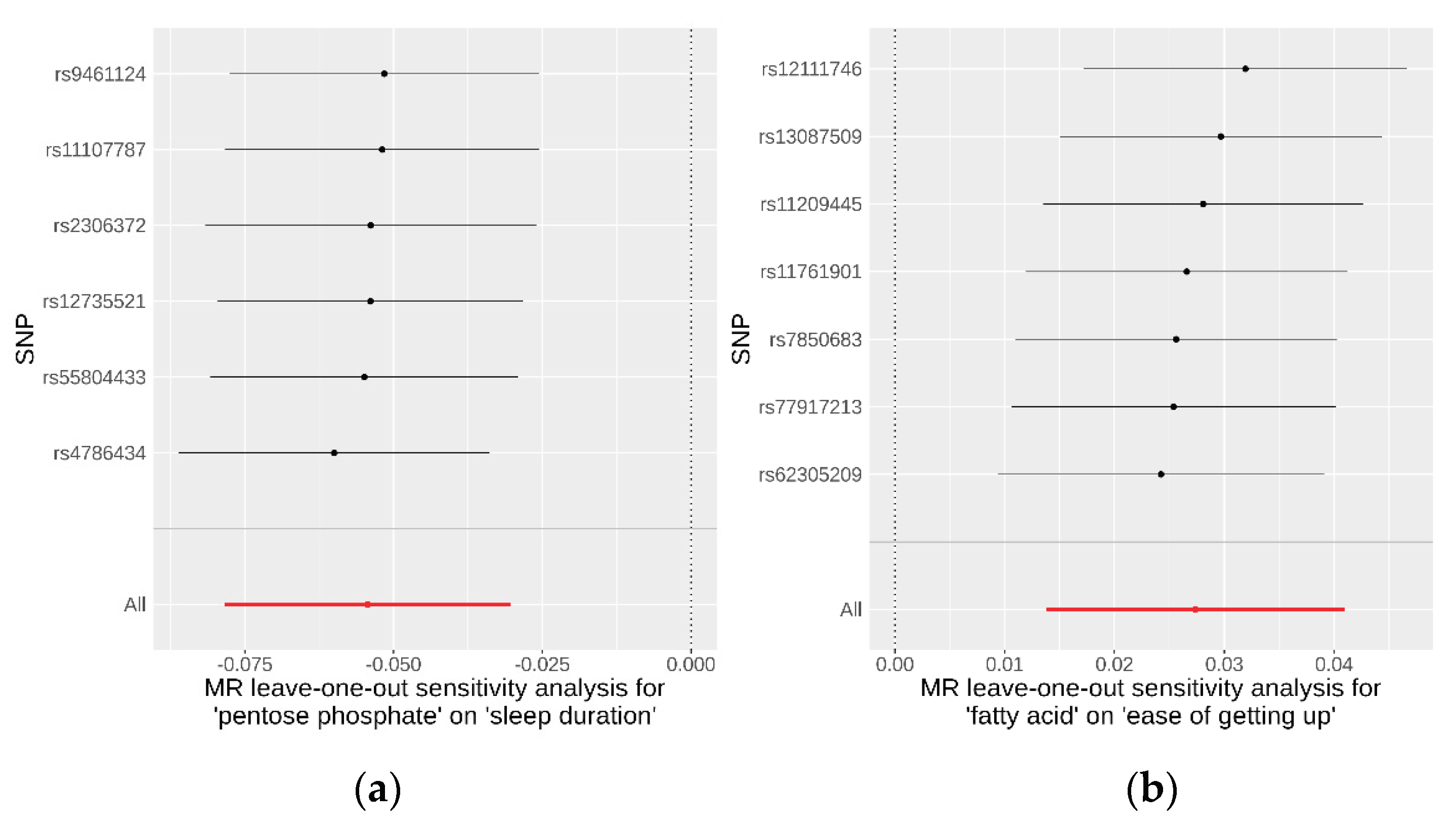
To evaluate the robustness of the causality for the two identified causal relationships, we conducted comprehensive sensitivity and pleiotropy analyses. For the pentose phosphate pathway on sleep duration, the funnel plot (
Additional file 1: Figure S2) displayed a symmetrical distribution of SNPs, indicating no apparent horizontal pleiotropy or heterogeneity in our MR analysis. The Cochran’s Q statistic for the IVW method was 1.41 (P = 0.92), signifying no significant heterogeneity. Additionally, the MR-Egger regression revealed an insignificant intercept (intercept = −0.004, SE = 0.00586, P = 0.52), supporting the absence of horizontal pleiotropy. The MR-PRESSO global test (P = 0.95) and outlier test identified no outlier variants. Furthermore, the leave-one-out analysis confirmed that no individual SNPs significantly influenced the results (
Figure 4). Similarly, SNPs displayed no heterogeneity for the fatty acid pathway on ease of getting up in the morning, with a Cochran’s Q statistic of 4.51 (P = 0.61) in the IVW method. The MR-Egger regression (intercept = −0.0008, SE = 0.0035, P = 0.83), MR-PRESSO global test (P = 0.95), and outlier tests all indicated no evidence of horizontal pleiotropy or outliers. The leave-one-out analysis also demonstrated that the observed result was not driven by any individual SNPs. These sensitivity analyses collectively suggest that the causal effects of both the pentose phosphate and fatty acid pathways on their respective outcomes are robust and reliable. Detailed data on these sensitivity analyses are provided in
Table 2.
4. Discussion
While previous research has explored the causal relationship between the gut microbiome and sleep phenotypes [
24,
34,
35], these studies have predominantly been limited to the genus level, restricting the depth of investigation into specific species of gut microbes and their potential influence on sleep patterns. Our study advances this exploration by utilizing summary statistics of microbial taxa and pathways from the DMP cohort, which can allow identification to the species level and can identify pathways. Through a two-sample MR analysis, we identified 79 suggestive causal effects of microbial taxa and pathways on sleep phenotypes, employing genetic variants as instrumental variables. Notably, eight gut microbiomes were linked to more than one sleep-related trait, indicating a multifaceted relationship. Conversely, our analysis revealed that four sleep-related traits exerted causal effects on 45 microbial taxa and pathways, with three of these taxa and pathways being influenced by more than one type of sleep-related trait. This underscores the complex interplay between sleep and the gut microbiome. Significantly, only two causal relationships surpassed the stringent criteria set by Bonferroni correction. These were the decrease in sleep duration due to the genetically determined relative abundance of the pentose phosphate pathway and the increase in ease of getting up in the morning associated with elevated fatty acid levels. The identification of these pathways highlights their substantial influence on sleep-related traits.
The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) is a crucial glucose-metabolizing pathway with diverse physiological and pathological roles [
36,
37,
38,
39]. It is instrumental in generating biosynthetic precursors such as ribose 5-phosphate and NADPH and in bolstering cellular defense mechanisms against oxidative stress. The pathway's significance extends to various biological processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, anti-infection responses, inflammation, tumorigenesis, and neurodegenerative diseases. Some observational studies have reported the association between PPP and sleep [
40,
41]. For instance, fructus gardeniae, known to alleviate anxiety symptoms caused by sleep deprivation, has been linked to the modulation of intestinal flora. In sleep-deprived mice, PPP was significantly enriched in the group treated with a low dose of gardeniae but not in those receiving a high dose [
42]. This suggests a positive correlation between PPP enrichment and sleep deprivation, aligning with the findings of our study. Notably, research by Rey et al. indicated that inhibiting PPP can alter the circadian rhythm of human cells. This alteration involves circadian transcription factors such as BMAL1/CLOCK and the redox-sensitive transcription factor NRF2 [
37]. We hypothesize that PPP influences sleep duration by affecting the expression of genes related to the circadian rhythm, offering one possible mechanism through which PPP reduces sleep time. Furthermore, the role of adenosine, a compound known to regulate sleep homeostasis [
43], in conjunction with PPP's consumption of adenosine, suggests another potential pathway through which PPP might impact sleep duration.
Numerous studies have established correlations between fatty acids and sleep. For example, significant increases in non-esterified fatty acid (NEFA) levels are observed during restricted sleep periods [
44]. Various fatty acids have been positively correlated with sleep quality [
45], while short-chain fatty acids are known to affect sleep efficiency and latency [
46]. Additionally, research has linked obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) with elevated free fatty acid levels [
47], noting that OSA can increase free fatty acids and other metabolites during sleep, potentially leading to diabetes and cardiovascular diseases [
48]. These findings indicate intricate interactions between fatty acids, sleep quality, and metabolic health. Here, our study identifies a causal relationship between fatty acid pathways and the ease of getting up in the morning, thereby enriching the understanding of the interplay between sleep and fatty acids. Investigative efforts have been made to elucidate underlying mechanisms. For instance, fatty acid β-oxidation has been implicated in regulating θ oscillations during sleep [
49], which is essential for sleep quality and memory consolidation. The association of fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs) with fragmented sleep suggests that different components of fatty acid metabolism may variably affect sleep architecture [
50]. Studies on mice with fatty acid amide hydrolase knockout exhibit enhanced slow-wave sleep [
51], and consumption of short-chain fatty acids has been shown to decrease wakefulness and augment Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep [
52], directly demonstrating the influence of fatty acids on sleep dynamics. We hypothesize that an increased abundance of short-chain fatty acids may reduce NREM sleep, facilitating easier awakening and rising in the morning. This mechanism might involve the regulation of FABP and the synthesis of sleep-promoting compounds like prostaglandin D2 [
53], potentially impacting θ oscillations.
This study boasts several methodological strengths that enhance its validity and reliability. Firstly, the GWAS summary data for seven sleep traits were sourced from a large-scale cohort comprising over 300,000 participants. This substantial sample size allowed the inclusion of a vast array of genetic variants associated with sleep-related traits, thereby boosting the statistical power and minimizing heterogeneity that could arise from analyzing data across different studies. For the gut microbiome, our study utilized the largest available GWAS dataset capable of identifying species and pathways, encompassing 7,738 individuals. In contrast to many cohorts that depend on 16S rRNA measurements, our dataset facilitated an in-depth exploration of causal relationships at both the species level and in terms of bacterial pathway abundances. This approach reinforced the importance of examining species abundance and pathway data in studying the gut microbiome's impact on sleep. Additionally, the diverse sleep phenotypes analyzed in this study allowed for a more nuanced investigation of the associations between the gut microbiome and various aspects of sleep. To mitigate sample overlap bias, the GWAS summary data for exposure and outcome were derived from distinct, non-overlapping cohorts. Given that the datasets primarily consisted of individuals of European descent, population stratification is unlikely to have biased our findings significantly. The application of MR analysis was another critical advantage, providing less biased estimations of causal relationships free from confounding factors. The bidirectional MR approach also enabled the assessment of potential reverse causation. Moreover, the implementation of various MR methods and comprehensive sensitivity analyses further bolstered the reliability and robustness of our results.
While our study presents significant findings, it is essential to consider certain limitations. A major constraint is the reliance on the sample size of the GWAS. Despite using the largest GWAS dataset available that identifies gut microbiota at the species level, the sample size for the gut microbiota remains relatively modest. Therefore, it is necessary to increase the sample size to obtain more reliable IVs to explain the variation of the differences in taxa and pathway abundances. Another limitation arises from the SNP selection criteria. To acquire sufficient SNPs for the gut microbiome, the SNPs included in this study did not meet the conventional GWAS significance threshold (P < 5×10–8). Additionally, the genetic variants used explained only a small fraction of the gut microbiome thus they may not serve as precise proxies. Our understanding of the biological functions of the genetic instruments is still evolving, which introduces a potential risk of violating the independence and exclusion restriction assumptions of MR, particularly concerning pleiotropy. Also, our study's findings are based on data from individuals of European descent and may not be generalizable to non-European populations. Lastly, while this study has identified two pathways with causal effects on sleep-related traits, these findings are primarily based on statistical analyses. Experimental research is required to elucidate the exact roles of these pathways in the pathogenesis of sleep traits and to validate our results further.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our bidirectional two-sample MR study has successfully delineated the potential influence of 79 microbial taxa and pathways on three specific sleep-related traits. Conversely, we identified 45 microbial taxa and pathways that appeared to be impacted by four different sleep phenotypes. Notably, our analysis revealed a robust effect of the pentose phosphate pathway on sleep duration and a significant influence of the fatty acid pathway on the ease of getting up in the morning. These findings shed light on the intricate interplay between microbial pathways and sleep, suggesting the potential of certain microbial factors as risk indicators for developing sleep-related traits. However, while promising, these results necessitate further research for validation and to fully understand the underlying mechanisms of these associations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Additional file 1: Table S1: GWAS summary statistics: source and description; Additional file 1: Figure S1: Suggestive causal relationships of sleep-related traits on microbial taxa and pathways: (a) Sleep-related traits on microbial taxa; (b) Sleep-related traits on pathways; Additional file 1: Figure S2: MR effect size for the causal association of microbial taxa and pathways on sleep-related traits: (a) Pentose phosphate pathway on sleep duration; (b) Fatty acid pathway on ease of getting up in the morning; Additional file 1: Figure S3: Funnel plots for the causal association of microbial taxa and pathways on sleep-related traits: (a) Pentose phosphate pathway on sleep duration; (b) Fatty acid pathway on ease of getting up in the morning; Additional file 2: Table S1: Instrumental variables used in MR analysis of 205 taxa and 205 pathways; Additional file 2: Table S2: Instrumental variables used in MR analysis of 3 sleep-related traits; Additional file 2: Table S3: Full result of MR estimates for the association of microbial taxa and pathways on sleep-related traits; Additional file 2: Table S4: Full result of MR estimates for the association of sleep-related traits on microbial taxa and pathways; Additional file 2: Table S5: 79 suggestive causal relationships of microbial taxa and pathways on sleep-related traits; Additional file 2: Table S6: 45 suggestive causal relationships of sleep-related traits on microbial taxa and pathways.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Z. and G.N.L.; data curation, M.Z., W.S, Z.L., and W.C.; formal analysis, M.Z.; methodology, M.Z. and G.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Z.; writing—review and editing, M.Z. W.S., and G.L.; supervision, G.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 81971292, 82150610506) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (No: 21ZR1428600).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
We obtained our data from a publicly available database that did not involve human participants. Therefore, ethical parameters were not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
We thank UK Biobank, the CNCR Complex Trait Genetics lab and the DMP project for sharing the summary-level data and all efforts from the researchers.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Ferini-Strambi, L.; Galbiati, A.; Combi, R. Sleep disorder-related headaches. Neurological Sciences 2019, 40, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, J. The interplay between sleep and gut microbiota. Brain Research Bulletin 2022, 180, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Bai, J.; Song, J.; Bu, L.; Liang, M.; Suo, H. Targeting microbiota to alleviate the harm caused by sleep deprivation. Microbiological Research 2023, 127467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troynikov, O.; Watson, C.G.; Nawaz, N. Sleep environments and sleep physiology: A review. Journal of thermal biology 2018, 78, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y. Melatonin alleviates acute sleep deprivation-induced memory loss in mice by suppressing hippocampal ferroptosis. Frontiers in pharmacology 2021, 12, 708645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drager, L.F.; McEvoy, R.D.; Barbe, F.; Lorenzi-Filho, G.; Redline, S. Sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease: lessons from recent trials and need for team science. Circulation 2017, 136, 1840–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, A.L.; Hairi, N.N.; Low, W.Y. Psychosocial stress, sleep deprivation, and its impact on type II diabetes mellitus: Policies, guidelines, and initiatives from Malaysia. Faseb Bioadvances 2021, 3, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarokh, L.; Saletin, J.M.; Carskadon, M.A. Sleep in adolescence: Physiology, cognition and mental health. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2016, 70, 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, L.; Guyatt, G.; Tian, J.; Pan, B.; Chang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Ling, J. Insomnia and risk of mortality from all-cause, cardiovascular disease, and cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Sleep medicine reviews 2019, 48, 101215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raven, F.; Van der Zee, E.A.; Meerlo, P.; Havekes, R. The role of sleep in regulating structural plasticity and synaptic strength: implications for memory and cognitive function. Sleep Medicine Reviews 2018, 39, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costea, P.I.; Hildebrand, F.; Arumugam, M.; Bäckhed, F.; Blaser, M.J.; Bushman, F.D.; De Vos, W.M.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Fraser, C.M.; Hattori, M. Enterotypes in the landscape of gut microbial community composition. Nature microbiology 2018, 3, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnoriaga-Rodríguez, M.; Leal, Y.; Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Pérez-Brocal, V.; Moya, A.; Ricart, W.; Fernández-Balsells, M.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Gut microbiota composition and functionality are associated with REM sleep duration and continuous glucose levels. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2023, dgad258. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, Y.; Miyoshi, C.; Obana, N.; Yajima, K.; Hotta-Hirashima, N.; Ikkyu, A.; Kanno, S.; Soga, T.; Fukuda, S.; Yanagisawa, M. Gut microbiota depletion by chronic antibiotic treatment alters the sleep/wake architecture and sleep EEG power spectra in mice. Scientific reports 2020, 10, 19554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites mediate the neuroprotective effect of melatonin in cognitive impairment induced by sleep deprivation. Microbiome 2023, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, W.-H.; Li, S.-X.; He, Z.-M.; Zhu, W.-L.; Ji, Y.-B.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.-M.; Yuan, K.; Bao, Y.-P. Gut microbiota modulates the inflammatory response and cognitive impairment induced by sleep deprivation. Molecular Psychiatry 2021, 26, 6277–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdin, C.A.; Khera, A.V.; Kathiresan, S. Mendelian randomization. Jama 2017, 318, 1925–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genetic epidemiology 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopera-Maya, E.A.; Kurilshikov, A.; van der Graaf, A.; Hu, S.; Andreu-Sanchez, S.; Chen, L.; Vila, A.V.; Gacesa, R.; Sinha, T.; Collij, V. Effect of host genetics on the gut microbiome in 7,738 participants of the Dutch Microbiome Project. Nature genetics 2022, 54, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didelez, V.; Sheehan, N. Mendelian randomization as an instrumental variable approach to causal inference. Statistical methods in medical research 2007, 16, 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angrist, J.; Imbens, G.; Rubin, D.B. Identification of causal effects using instrumental variables. 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, R. What makes UK Biobank special? The Lancet 2012, 379, 1173–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, P.R.; Watanabe, K.; Stringer, S.; Skene, N.; Bryois, J.; Hammerschlag, A.R.; de Leeuw, C.A.; Benjamins, J.S.; Muñoz-Manchado, A.B.; Nagel, M. Genome-wide analysis of insomnia in 1,331,010 individuals identifies new risk loci and functional pathways. Nature genetics 2019, 51, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, S.; van Zuydam, N.R.; Mahajan, A.; Kurilshikov, A.; Vich Vila, A.; Võsa, U.; Mujagic, Z.; Masclee, A.A.; Jonkers, D.M.; Oosting, M. Causal relationships among the gut microbiome, short-chain fatty acids and metabolic diseases. Nature genetics 2019, 51, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, S.; Huang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zheng, X.; Ouyang, D. Associations between gut microbiota and sleep: a two-sample, bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Frontiers in Microbiology 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.; Glymour, M.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Kang, H.; Morrison, J.; Munafò, M.R.; Palmer, T.; Schooling, C.M.; Wallace, C.; Zhao, Q. Mendelian randomization. Nature Reviews Methods Primers 2022, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milligan, B.G. Maximum-likelihood estimation of relatedness. Genetics 2003, 163, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwig, F.P.; Davey Smith, G.; Bowden, J. Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption. International journal of epidemiology 2017, 46, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtin, F.; Schulz, P. Multiple correlations and Bonferroni’s correction. Biological psychiatry 1998, 44, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; He, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qin, C. Causality of genetically determined metabolites on anxiety disorders: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Journal of Translational Medicine 2022, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurilshikov, A.; Medina-Gomez, C.; Bacigalupe, R.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Wang, J.; Demirkan, A.; Le Roy, C.I.; Raygoza Garay, J.A.; Finnicum, C.T.; Liu, X. Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition. Nature genetics 2021, 53, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.F.; Chalumeau, M.; Cohen, R.; Korevaar, D.A.; Khoshnood, B.; Bossuyt, P.M. Cochran's Q test was useful to assess heterogeneity in likelihood ratios in studies of diagnostic accuracy. Journal of clinical epidemiology 2015, 68, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. International journal of epidemiology 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nature genetics 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, M.; Jin, C.; Jiang, X.; Xue, X.; Wu, N.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L. Causal effects of gut microbiota on sleep-related phenotypes: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Clocks & Sleep 2023, 5, 566–580. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.; Jiang, M.; Hu, W.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ji, J.; Wang, S.; Tai, J. Causality Investigation between Gut Microbiota, Derived Metabolites, and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TeSlaa, T.; Ralser, M.; Fan, J.; Rabinowitz, J.D. The pentose phosphate pathway in health and disease. Nature metabolism 2023, 5, 1275–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, G.; Valekunja, U.K.; Feeney, K.A.; Wulund, L.; Milev, N.B.; Stangherlin, A.; Ansel-Bollepalli, L.; Velagapudi, V.; O’Neill, J.S.; Reddy, A.B. The pentose phosphate pathway regulates the circadian clock. Cell metabolism 2016, 24, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stincone, A.; Prigione, A.; Cramer, T.; Wamelink, M.M.; Campbell, K.; Cheung, E.; Olin-Sandoval, V.; Grüning, N.M.; Krüger, A.; Tauqeer Alam, M. The return of metabolism: biochemistry and physiology of the pentose phosphate pathway. Biological Reviews 2015, 90, 927–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalling, N.N.; Nedergaard, M.; DiNuzzo, M. Cerebral metabolic changes during sleep. Current neurology and neuroscience reports 2018, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Li, P.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Wei, S. Integrated metabolomics and proteomics analysis reveals energy metabolism disorders in the livers of sleep-deprived mice. Journal of Proteomics 2021, 245, 104290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, L.N.; Kilkus, J.M.; Booth III, J.N.; Bromley, L.E.; Imperial, J.G.; Penev, P.D. Effects of sleep restriction on the human plasma metabolome. Physiology & behavior 2013, 122, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Guo, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Tao, Y.; Mei, J. Fructus gardeniae ameliorates anxiety-like behaviors induced by sleep deprivation via regulating hippocampal metabolomics and gut microbiota. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2023, 13, 1167312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blutstein, T.; Haydon, P.G. The Importance of astrocyte-derived purines in the modulation of sleep. Glia 2013, 61, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broussard, J.L.; Chapotot, F.; Abraham, V.; Day, A.; Delebecque, F.; Whitmore, H.R.; Tasali, E. Sleep restriction increases free fatty acids in healthy men. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papandreou, C. Independent associations between fatty acids and sleep quality among obese patients with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Journal of Sleep Research 2013, 22, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magzal, F.; Even, C.; Haimov, I.; Agmon, M.; Asraf, K.; Shochat, T.; Tamir, S. Associations between fecal short-chain fatty acids and sleep continuity in older adults with insomnia symptoms. Scientific reports 2021, 11, 4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceló, A.; Piérola, J.; De La Peña, M.; Esquinas, C.; Fuster, A.; Sánchez-De-La-Torre, M.; Carrera, M.; Alonso-Fernandez, A.; Ladaria, A.; Bosch, M. Free fatty acids and the metabolic syndrome in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. European Respiratory Journal 2011, 37, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.; Rathore, A.; Younas, H.; Pham, L.V.; Gu, C.; Beselman, A.; Kim, I.-Y.; Wolfe, R.R.; Perin, J.; Polotsky, V.Y. Obstructive sleep apnea dynamically increases nocturnal plasma free fatty acids, glucose, and cortisol during sleep. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2017, 102, 3172–3181. [Google Scholar]
- Tafti, M.; Petit, B.; Chollet, D.; Neidhart, E.; de Bilbao, F.; Kiss, J.Z.; Wood, P.A.; Franken, P. Deficiency in short-chain fatty acid β-oxidation affects theta oscillations during sleep. Nature genetics 2003, 34, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstner, J.R.; Perron, I.J.; Riedy, S.M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kadotani, H.; Owada, Y.; Van Dongen, H.P.; Galante, R.J.; Dickinson, K.; Yin, J.C. Normal sleep requires the astrocyte brain-type fatty acid binding protein FABP7. Science advances 2017, 3, e1602663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huitron-Resendiz, S.; Sanchez-Alavez, M.; Wills, D.N.; Cravatt, B.F.; Henriksen, S.J. Characterization of the sleep-wake patterns in mice lacking fatty acid amide hydrolase. Sleep 2004, 27, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartorius, T.; Ketterer, C.; Kullmann, S.; Balzer, M.; Rotermund, C.; Binder, S.; Hallschmid, M.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Somoza, V. Monounsaturated fatty acids prevent the aversive effects of obesity on locomotion, brain activity, and sleep behavior. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urade, Y.; Hayaishi, O. Prostaglandins and sleep–wake regulation. Sleep Disorders 2008, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).