Submitted:
27 February 2024
Posted:
27 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
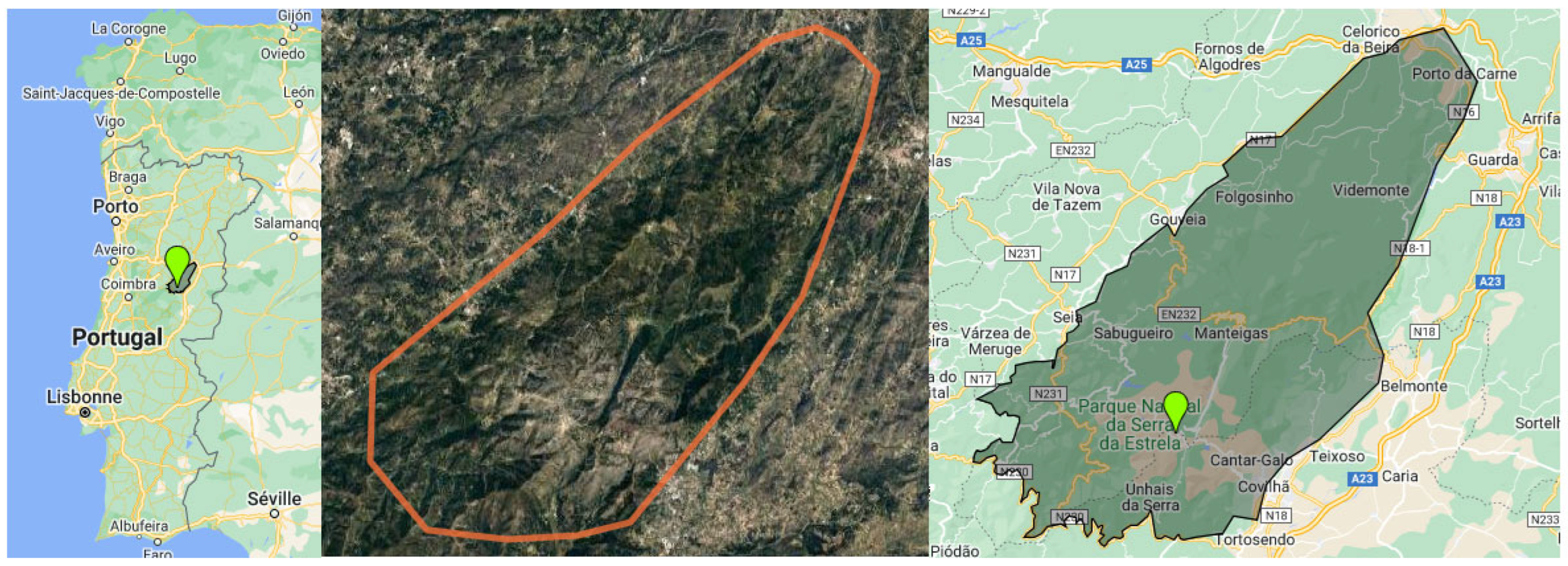
2.1. Geographical and Climate Features of the Serra da Estrela Natural Park
2.2. Ethnobotanical Data Collection and Selection Criteria
3. Results
3.1. Botanical Diversity of NPSE and Ethnopharmacological Uses of Medicinal Plants with Antidiabetic Potential
3.1.1. Asteraceae
3.1.2. Lamiaceae
3.1.3. Fabaceae
3.1.4. Rosaceae
3.1.5. Caryophyllaceae
3.1.6. Polygalaceae
3.1.7. Other Families
3.2. Medicinal Plants with Antidiabetic Potential in NPSE
3.2.1. Asteraceae Family
- Arctium minus (Hill) Bernh.
| Pharmacological Uses | Chemical Constituents | References |
|---|---|---|
| Asteraceae | ||
| Arctium minus (Hill) Bernh | ||
| Antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antinociceptive, acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities, anti-cancer. |
Phenolic acids: Rosmarinic acid, quinic acid, caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, cynarin, hydroxy cinnamoyl quinic acid. Flavonoids: Rutin, isoquercetin, luteolin kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoglucoside, quercimeritrin, astragalin, arabinose, rhamnose, mannose, cellulose, Inulin. Polysaccharides: Pectic substance, rhamnogalacturonan, hemicellulose (arabinan, arabinogalactan, galactan, xylan, xyloglucan, galacturonic acid, glucose, galactose. |
[175,185,187,190–193] |
| Achillea millefolium | ||
| Anxiolytic, antimicrobial, antioxidant, vasoprotective, vasorelaxant, anti-appetite (orexigenic), anti-tumor, antiulcerogenic, hypotensive, analgesic, modulation of mitochondria respiration, anti-inflammatory, anti-neuroinflammatory, anti-proliferative, antiplatelet, skin-rejuvenating, antinociceptive, hepatoprotective, antiplasmodial, anthelmintic, antispasmodic, anti-cancer, antispermatogenic, for haemorrhoids and dysmenorrhea. |
Phenolic acids: Cis and trans-3,5-O-dicaffeoylquinic acids, chlorogenic acid, p-coumaric acid, neochlorogenic acid, ferulic acid, stachydrine. Flavonoids: Resveratrol, morin, myricetin, naringin, naringenin, apigenin, quercetin, luteolin O-acetylhexoside, apigenin O-acetylhexoside, centaureidin, casticin, artemetin, luteolin 7-glucoside, luteolin 4′-O-glucosid, apigenin 7-glucoside, apigenin 4′-O-α-glucopyranoside, 5-Hydroxy-3,6,7,4’-tetramethoxyflavone, kaempferol, isorhamnetin glycosides, rutin, cynaroside, cosmosiin, vicenin-2. Sesquiterpenoids: paulitin, isopaulitin, psilostachyin C, desacetylmatricarin, sintenin, achillicin, 8a-(Angeloyloxy), artabsin 1,4-endoperoxide, 8a-(Tigloyloxy)artabsin 1,4-endoperoxide, 7b-Hydroxy-a-longipin-2-en-1-one, a-Longipin-2-en-1-one (longipinanes), Millefoliumins F and G, leucodin, 8α-angeloxy-leucodin, achillin, 8α-angeloxy-achillin, desacetylmatricarin. Organic acids and phenols: oxalic, quinic, citric acids, fatty acids (with linoleic and palmitic acids), tocopherols (γ-tocopherol), ascorbic acid, carboxylic acid, salicylic acid, thymol, carvacrol, pyrocatechol, adenine, mandelic acid, methyl esters of caprylic-linolenic-undecylenic acid. |
[174,194–221] |
| Anthemis canescens (syn. Matricaria aurea) | ||
| Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-ulcer, analgesic, antibacterial and anti-cancer. |
Phenolic acids: p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, shikimic acid, protocatechuic acid, p-aminobenzoic acid, digalloyl-shikimic acid, epicatechin, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, rosmarinic acid, 7,8-dihydroxycoumarin, chlorogenic acid, 1-O-b-D-glucopyranosyl sinapate, 5-methoxysalicylic acid. Flavonoids: Apigenin, apigenin-7-O-rhamnoglucoside (Rhoifolin), apigenin 8-C-glucoside, apigenin-7-O-glucoside, 4′-Methoxyapigenin (Acacetin), luteolin, luteolin-6-C-glucoside, quercetin, quercetin-3-D-xyloside, quercetin-7-O-rhamnoside, quercetin-3-arabinoside, quercitrin, kaempferol-3-glucuronide, kaempferol-3-O-alpha-L-rhamnoside, kaempferol-3-O-alpha-L-arabinoside, Kaempferide, eriodictyol-7-O-glucoside, baicalin, isovitexin 7-O-glucoside (saponarin), syringetin-3-O-galactoside, rhamnetin, isorhamnetin, isorhamnetin-3-O-rutinoside, isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside, myricitrin, daidzein-8-C-glucoside, cyanidin-3-glucoside, myricetin, diosmetin 7-O-rutinoside, hesperetin-7-O-neohesperidoside, maritimetin-6-O-glucoside, acacetin-7-O-neohesperidoside, acacetin-7-O-rutinoside, naringenin, esculetin, formononetin, resveratrol, eriodictyol. Others: Anthocyanins (delphinidin-3-rutinoside), terpenes alkaloids (gibberellin A4), chalcones (Okanin-4′-O-glucoside), coumarins (Scopoletin, 4-methylumbelliferone). |
[222–227] |
| Arnica montana | ||
| Antiphlogistic, inotropic, antibiotic, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, antiplatelet, uterotonic, anti-rheumatic, anti-osteoarthritic, antimicrobial, improve circulation, increase respiration, ureotonic, antioxidant, hepatoprotective, insecticidal, hypopigmentation, antihair loss, anticough, antihaemorrhagic and analgesic in febrile conditions. |
Phenolic acids: Chlorogenic acid, 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid, 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid Flavonoids: Kaempferol 3-O-glucoside, 6-methoxy-kaempferol 3-O-glucoside, hispidulin, quercetin 3-O-glucoside, quercetin 3-O-glucuronic acid, patuletin 3-O-glucoside, luteolin, apigenin. Sesquiterpene lactones: Helenalin,11a,13-dihydohelenalin. Others: Carotenoids, diterpenes, arnidiol, 2-pyrrolidineacetic acid, pyrrolizidine alkaloids (tussilagine and isotussilagine), polyacetylenes, coumarins (umbelliferone and scopoletin), lignans, dicaffeoyl quinic derivatives (1,3- 3,5 and 4,5 dicaffeoyl quinic acids), umbelliferone, scopoletin, oligosaccharides, sesquiterpene lactones (2,3-dihydroaromaticin, chamissonoid, mexicanin 1). |
[228–230] |
| Bellis perennis | ||
| Wound healing, anxiolytic, anti-tumour, antibacterial, anti-fungal, anti-hyperlipidemic, antioxidant, postpartum anti-hemorrhagic, pancreatic lipase inhibitor, and cytotoxic activities. |
Phenolic acids: Chlorogenic acid, neochlorogenic acid, rosmarinic acid, caffeoylquinic acids. Flavonoids: Isorhamnetin 3-O-β-d-galactopyranoside, isorhamnetin 3-O-β-d-(6 ″-acetyl)-galactopyranoside and kaempferol 3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside. Triterpene saponins: Perennisosides I-VII, bellidioside A, asterbatanoside D, bernardioside A/F/B2, bellissaponin BS6/BA1/BA2, Anthocyanins: Cyanidin 3-O-(4 ″-O-(malonyl)-2 ″O-(β d-glucuronyl)-β-d-glucopyranoside), cyanidin 3-O-(2 ″-O-(β-d-glucuronyl)-β-d-glucopyranoside), cyanidin 3-O-(6 ″-O-(malonyl)-2 ″-O-(β-d-glucuronyl)-β-d-glucopyranoside). |
[231–243] |
| Bidens frondosa | ||
| Antibacterial, antioxidant, antidiarrheal, anti-malarial, anti-inflammatory, allelopathic. |
Phenolic acids and their ethers: Caffeic acid, 4,5-di-O caffeoylquinic acid 1-methyl ether, isoferuloyl ethyl ester, protocatechuic acid. Flavonoids: Okanin-4’-O-(6”-O-acetyl-2”-O-caffeoyl-6”-O-glucopyranoside), okanin-4’-O-(2”-O-caffeoyl-6”-O-p-coumaroyl-β-D-glucopyranoside), 4-O-methylokanin-4’-O-(6”-O-p-coumaroyl-β-D-glucopyranoside), 4-O-methylokanin-4’-O-(6”-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranoside), 4-O-methylokanin-4’-O-(6”-O-acetyl-2”-O-caffeoyl-β-D-glucopyranoside), okanin-4’-O-(6”-O-p-coumaroyl β-D-glucopyranoside), okanin-4’-O-(6”-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranoside), (Z)-6”-O-p-coumaroyl-maritimein, (Z)-6”-O-acetylmaritimein, apigenin, luteolin, luteolin-7-O- β-D-glucopyranoside, luteolin-7-O-(β-dglucopyranosyl)-2-glucopyranoside, kaempferol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, 8,3′,4′-trihydroxyflavone-7-O-(6′′-O-p-coumaroyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside, 6-hydroxyluteolin-7-O-glucoside, 3′′-(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaroyl)-ester of 6-hydroxyluteolin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, 8,3′,4′-trihydroxyflavone-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, 3′-hydroxyscutellarein-7-O-(6′′-Oprotocatechuoyl)-β-glucopyranoside, (−)-4′-methoxy-7-Oβ-dglucopyranosyl-8,3′-dihydroxyflavanone, (−)-4′-methoxy-7-O-(6′′-acetyl)-βdglucopyranosyl-8,3′-dihydroxyflavanone, hesperetin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside. Others: 2′-butoxyethylconiferin, butylconiferin, 2-methoxy-4-(2′-hydroxyethyl)-phenol-1-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, (1′R,2′R)-guaiacyl glycerol 3′-O-β-dglucopyranoside, threo-5-hydroxy3,7-dimethoxyphenylpropane-8,9-diol, 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3-methoxypropane1,2-diol, 3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propane-1,2-diol, guaiacylglycerol, wilfordiol B, caffeoylcalleryanin, 1-O-(E)-caffeoyl-β-dgentiobiose, dihydrophaseic acid, 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene, vanillin, galacturonic acid, galactose, glucose, arabinose, xylose, rhamnose. |
[244–248] |
| Calendula arvensis | ||
| Antibacterial, anti-fungal, antiparasitic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, wound healing, antimutagenic, immunomodulatory, and anti-cancer. |
Phenolic acids: Isomeric form hydroxy ferulic acid hexoside, 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid, 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid, caffeic acid, sinapic acid, sinapic acid hexoside, hexoside derivative, caffeoylshikimic acid, 3,4-O-dicaffeoylquinic acid, 5-O-feruloyl quinic acid, protocatechuic acid pentoside, quinic acid with an aldonic residue. Flavonoids: Quercetin hydrate, quercetin dihexoside, quercetin-3-O-rutinoside, quercetin-3-O-neohesperidoside, quercetin-3-omalonylhexoside, quercetin acetyl hexoside, quercetin hexoside I, quercetin 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, quercetin 3-O-β-D-galactopyranoside, apigenin-8-C-pentose-6-chexose or apigenin-8-chexose-6-C- pentose, apigenin-O-hexosylpentosyl, isorhamnetin-3-O-hexoside. Saponins: 3-O-(β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1⟶3)-β-D-glucopyranosyl) oleanolic acid-28-O- β-D-glucopyranoside, 3β-O-(β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1⟶3)-β-D-glucopyranosyl) oleanolic acid, 3β-O-(β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1⟶3)-β-D-glucopyranosyluronic acid) oleanolic acid-28-O- β-D-glucopyranoside, 3β-O-(β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1⟶3)-β-D-glucopyranosyluronic acid) oleanolic acid, 4-O-(β-D-fucopyranosyl)-4-alloaromadendrole, arvensoside A, arvensoside B, derivatives of arvensoside B, calenduloside D, calenduloside C, 4-O-(β-D-fucopyranosyl)-4-alloaromadendrole, 4-O-(β -D-fucopyranosyl)-4-alloaromadendrol-2″-methylpropanoyl esters, 4-O-(β -D-fucopyranosyl)-4-alloaromadendrol -2″-methyl-2″-butenoyl esters, Sesquiterpeneglycosides: 3α,7β-dihydroxy-5β,6β-epoxyeudesm-4(15)-ene-11-(O-β-D-fucopyranoside-2′,4′ -diangelate-3′-acetate), 7β-Hydroxy-3β-acetoxy-5β,6β-epoxyeudesm-5(15)-ene-11-(O-β-D-ficopyranoside-2′,4′-diangelate-3′-acetate), 3α,7β-Dihydroxy-5β,6β-epoxyeudesm-4(15)-ene-11-(O-β-D-fucopyranoside-2′,4′-diangelate-3′-isobutyrate), 3α,7β-dihydroxy -5β, 6β-epoxyeudesm-4(15)-ene-11-(O-β-D-fucopyranoside-2′, 4′-diangelate-3′-methylbutyrate), and 3α,7β-dihydroxy-15-acetoxyeudesm-4(5)-ene-11-(O-β-D-fucopyranoside-2′,4′-diangelate-3′-acetate). Carboxylic acids/Fatty acids: Stearic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid, palmitic acid, palmitoleic acid, α-linolenic acid, quinic acid, citric acid, and tetracosanoic acid. Polysaccharides: L-threonic acid, D-(−)-tagatofuranose, D-(−)-fructofuranose, D-(−)-fructopyranose, D-(−)-psicopyranose, D-(+)-mannopyranose, D-(+)-galactopyranose, β-D-glucopyranose, D-gluconic acid, galactaric acid, sucrose, cellobiose. Others: Ethyl butyrate, 2-methyl-3-furanthiol, methional, 1-octen-3-one, ethyl hexanoate, 2-6-Dimethyl-3 ethyl pyrazine, (E)-2-nonenal, (E,E)-2,4-octadienal, 5-methyl-2-furanaldehyde, citronellol, phenethylacetate, α-terpineol, lactone-like, and δ-decalactone, Neophytadiene, phytol, α-bisabolol, 8,14-cedranoxide, stigmasterol, stigmast-5-ene, amyrin, lup-20(29)-en-28-al, 3-oxo-ursan-28-oic acid, myo-inositol, 1H-benzocyclohepten-9-ol, 1-hexacosanol, untriacontane, 4-aminobutanoic acid, isomer of platynecine derivative, ligstroside hexoside, calendasaponin A, calenduloside G isomer, β-sitosterol. |
[249] |
| Chamaemelum nobile (syn. Anthemis nobilis L. or Chamomilla nobilis) | ||
| Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antinociceptive, antimutagenic, sedative, anxiolytic, antispasmodic, anxiety, depression, sleep quality and insomnia, postoperative gastrointestinal dysfunction, diarrhoea, colic, nausea, vomiting, acute, diuretic, chronic pain, antibacterial, anti-fungal, insecticidal, hypotensive, antiplatelet aggregation, antioxidant, effect in asthma and polycystic ovary, nervous endocrine, cytotoxic, bronchodilator, antispasmodic, carminative, anti-emetic, antispasmodic, cytostatic, anti-oedema sedative properties |
Phenolic acids: The glucose esters caffeic acid, ferulic acid, anthenobilic acid, trans-caffeic acid-glucose ester, trans- and cis- forms of the caffeic acid, 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid, 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid-hexoside, 3,4-O-dicaffeoylquinic acid, protocatechuic acid, caffeoyl-hexoside-methylglutarate, 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid, p-coumaroyl-hexoside-methylglutarate 1,3,5-O-Tricaffeoylquinic acid, Flavonoids: Apigenin, apigenin 6-C-glucose-8-C-glucose, apigenin O-glucuronide, apigenin O-glucuronylhexoside, luteolin, luteolin O-hexoside, luteolin O-rutinoside, luteolin O-acetylhexoside, luteolin-7-glucoside, luteolin O-pentosylhexoside, luteolin O-glucuronide, luteolin O-rhamnosylhexoside, quercetin, quercetin 3-O-glucuronide, quercetin 7-O-malonylhexoside, quercetin O-acetylhexoside, isorhamnetin O-acetylhexoside, myricetin 3-O-glucoside, rutin, anthemoside (apigenin2,3-dihydorycinnamoyl acid 7-O-β-D-glucose), cosmosioside (apigenin 7-O-β-D-glucose), apiin (apigenin 7-O-β-D-apiosylglucoside), chamaemeloside [apigenin 7-O-β-D-glucose-6˝-(3˝´-hydroxy-3˝´-methyl-glutarate)], luteolin 7-O-β-D-glucose, quercetin 3-O-α-L-rhamnoside, kaempferol, kaempferol O-pentosylhexoside, catechins. Terpenoids and steroids: α-bisabolol, chamazulene, anthesterols, β-amyrin, taraxasterol, pseudotaraxasterol, β-sitosterol. Coumarins: Herniarin, umbelliferone, scopoletin-7-glucoside. Others: Angelic and tiglic acid esters, anthemic acid, choline, phenolic, phytosterols, inositol, oxalic acid, quinic acid, malic acid, citric acid, fumaric acids, octulosonic acid, betahydroperoxyisonobilin, hydroxyisonobiline, germacranolide-type sesquiterpene lactones (nobilin, 3-epinobilin, 1,10-epoxynobilin, 3-dehydronobilin), amyl and isobutyl alcohols, 1β-Hydroperoxyisonobilin, alkyl hydroperoxides, Cis- and trans-spiroether derivatives, cis- and trans-dehydromatricariaester and tiophenesetrs, polyacetylenes. |
[250–252] |
| Cichorium intybus | ||
| The hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, sedative, immunomodulatory effect, cardiovascular, hypolipidemic, gastro-protective, anti-tumour, anti-leukaemic, cytotoxic, antimicrobial, allergenic, antibiotic, anti-cancer, anti hyperuricemia, antiprotozoal, anthelmintic, anti-malarial, sedative. |
Phenolic acids: Chlorogenic acid, chicoric acid, p-coumaric acids, protocatechuic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic, iso vanillic, gallic acid, 4-amino-benzoic, p-OH-benzoic, caffeine, ferulic acid, isoferulic acid, vanillic acid, benzoic acid, ellagic acid, alpha-cumaric, 3,4,5-methoxy-cinnamic, salycilic acid, cinnamic acid, 3-O-p-coumaroyl quinic acid. Flavonoids: Quercetin, quercetin glucuronide, luteolin glucuronide, catechin, catechol, epicatechin, cyanidin-3-O-(6″-malonyl-β-glucopyranoside), delphinidin 3,5-di-O-(6-O-malonyl-β-d-glucoside), delphinidin 3-O-(6-O-malonyl-β-d-glucoside)-5-O-β-d-glucoside, delphinidin 3-O-β-d-glucoside-5-O-(6-O-malonyl-β-d-glucoside), delphinidin 3,5-di-O-β-d-glucoside. Fatty acids and derivatives: Lauric acid methyl ester, myristic acid methyl ester, palmitoleic methyl ester, palmitic acid methyl ester, methyl dihydromalvalate, 9,12- linoleic methyl ester, stearic acid methyl ester, methyl linolelaidate, linolenic acid methyl ester, 11-eicosenoic acid methyl ester, eicosanoic acid methyl ester, n-hexadecanyl hexadecanoate, n-pentadecanyl octadec-9-enoate, n-hexadecanyl octadec-9-enoate, n-hexadecanyl octadecenoate, n-octadecanyl octadecenoate, α-linolenic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid, palmitic acid. Sesquiterpene lactones: Lactucin, 8-deoxylactucin, 11(S),13-dihydro-8-deoxylactucin, lactucopicrin, 11(S),13- dihydrolactucopicrin, jacquinelin, crepidiaside B, lactuside A, 11(S), 13-dihydrolactucin, lactucin, 8-deoxylactucin, 11(S), 13-dihydro-8-deoxylactucin, 11(S),13-dihydrolactucopicrin, lactucopicrin Others: Inulin, coumarin, epigallocatechin gallate. |
[253,254] |
| Dittrichia viscosa subsp. Viscosa (Syn. Inula viscosa) | ||
| Antiphlogistic, antiviral, anti-fungal, antibacterial, antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, allelopathic potential, fungicidal, nematicidal, antiulcerogenic, antihelmintic, anti-cancer, neuroprotective effects |
Phenolic acids and derivatives: Caffeic acid, di-o-caffeoylquinic acid, rosmarinic acid, protocatechuic acid hexoside, caffeoyl hexose, p-coumaroyl hexose, 1-O-caffeoylquinic acid, 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid, 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid, di-O-Caffeoylquinic acid, caffeic acid phenethyl ester, (Epi)-rosmanol methyl ether, rosmanol, epirosmanol, dicaffeoylshikimic acid, N-caffeoyl-tryptophan, dihydroxybenzoic acid. Flavonoids: Dihydroquercetin, 3-O-methylquercetin, quercetin-O-(caffeoyl)-hexoside, quercetin dihexoside, quercetin-3-O-(6″-acetyl) hexoside, quercetin rhamnoside, cirsiliol, 3-O-acetylpadmatin, padmatin, nepetin, spinacetin, diosmetin, rhamnetin, hesperetin, hispidulin, catechin, medioresinol, γ-mangostin, banaxanthone E, epi- granilin, naringenin, isorhamnetin, diosmetin, cirsimaritin derivative, genkwanin, rutin, kaempferol-O-deoxyhexoside, kaempferol-3-O-(6″-acetyl) hexoside, kaempferol-3-O-(caffeoyl)-hexoside, aromadendrin, naringenin-7-O-hexoside, isorhamnetin glycoside, isorhamnetin-O-pentosylhexoside, kaempferol-O-(p-coumaroyl)-hexoside, kaempferol-O-(feruloyl)-hexoside, 3,7-dihydroxycoumarin, nepetin, spinacetin, dihydroxycoumarin, padmatin isomer 1/2, cinchonain. Sesquiterpenes: α- and γ- costic acid isomers, ilicic acid, hydroxyalantolactone, tomentosine/inulviscolide, alantolactone, inulanolide, Others: Galloylquinic acid, (Epi)-gallocatechin-3-gallate, paxanthone, proanthocyanidin dimer, prodelphinidin B3, malic acid I and II, caffeoyl-malic acid, shikimoyl blechnic acid. |
[255–265] |
| Galinsoga parviflora | ||
| Antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-arthritic, antiplatelet, anti-inflammatory, anti-fungal. | Kaempferol, gallic acid, 2,4,5-tricaffeolylglucaric acid, 2,3,4,5-tetracaffeolylglucaric acid, 2,3,4-tricaffeolylaltraric acid, 3,4,5-tricaffeolylaltraric acid, beta-sitosterol-3-O-beta-glucoside, quercetine, beta-sitosterol, 3,5,7,3’,4’pentahydroxyflavanone, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid. | [266] |
| Helichrysum stoechas | ||
| Antibacterial, anti-proliferative, neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant treatment for urolithiasis. | Neo-chlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid and crypto-chlorogenic acid, isomeric dicaffeoyl quinic acids, isomeric naringenin glucosides, quercetin, isoquercitrin, kaempferol, apigenin glucosides, tetrahydroxychalcone-glucoside, Helipyrone A/B/C, Italipyrone, 20-prenylitalipyrone, Bitalin A (R)-form, 6-methyleuparin, helipyrone, 5,7-dihydroxy-3,6,8-trimethoxyflavone, quercetagetin-7-O-glucopyranoside, santinol B. | [267–270] |
| Hypochaeris radicata | ||
| Treatment of jaundice, rheumatism and antibacterial, anti-fungal properties with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory, antihemolytic. | Chicoric acid, hypochoeroside C, hypochoeroside D, and 5-O-caffeoylshikimic acid, 4-(3,4-dihydroxybenzyl)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)tetrahydrofuran-3-carboxy-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, 4-(3,4-dihydroxybenzyl)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)tetrahydrofuran-3-carboxy-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-2′-O-methacrylate, (7S,8R,8′R)-7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3′,4′-dihydroxy-7,8,7′,8′-tetrahydronaphtho [8,8′-c]furan-1(3H)-one, and (7S,8R,8′R)-7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3′,4′-dihydroxy-8'-(hydroxymethyl)-7,8,7′,8′-tetrahydronaphthalen-8-carboxylic acid, confertin, scopoletin. | [271–274] |
| Lactuca serriola | ||
| Hepatoprotective, antioxidant, antivenom, allelopathic, sedative, anticonvulsant, antiepileptic, anti-inflammatory, anti-carcinogenic activities | Chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid, quercetin, lactutin, 8-deoxylactucin and jacquilenin, 11-β-13-dihydrolactucin, deacetoxymatricarin (=leucodin, leucomisin), loliolide, guaiane ester, the melampolide glucoside, luteolin-7-O-β-D glucoside, protocatechuic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, lactuside A, kaempferol, lactucone, lactucic acids, lactucopicrin, sesquiterpene esters, vitamins, oxalic acid, β-carotene, iron, lupeol, lupeol acetate, oleanans, α-amyrin, β-amyrin. | [275–282] |
| Onopordum acanthium | ||
| Antihypertensive, bactericide, cardiotonic, hemostatic agent, used against hypotonicity, anti-inflammatory, anti-malarial, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, cytotoxicity, antipyretic, analgesic, anti-tumor, regeneration, phytotoxic. |
Phenolic acids and derivatives: Isochlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, Flavonoids: Apigenin, luteolin, scutellarein, nepetin, chrysoeriol, hispidulin, pectolinarigenin, scutellarein 4’-methyl ether, quercetin, apigenin-7-O-glucoside, apigenin-7-O-rutinoside, apigenin-7-O-β-D-glucuronide, luteolin-7-O-glucoside, quercetin-3-O-glucoside, isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside, riodictyol; cyanin, aconiside. Others: pinoresinol, syringaresinol, medioresinol, nitidanin diisovalerianate; arctiin, aesculin; aesculetin, 4β,15-dihydro-3-dehydrozaluzanin C, zaluzanin C, 4β,15,11β,13-tetrahydrozaluzanin C, onopordopicrin; arctiopicrin, Elemanolide 11(13)-dehydromelitensin β-hydroxyisobutyrate; acanthiolide, α-amyrin; β-amyrin, lupeol; taraxasterol, steroids, heptadecatetraen-(2, 8, 10, 16)-diin-(4, 6)-al-(1), tridecadien-(1, 11)-tetrain-(3, 5, 7, 9), heptadecatetraen-(1, 7, 9, 15)-diin-(11, 13), heptadecatetraen-(2, 8, 10, 16)-diin-(4, 6)-ol-(1), ), linoleic, oleic, palmitic, stearic, pentadecanoic acids, hentriacontanoic acid, nonacosanoic acid, palmitic acid, arachidic, pentadecanoic acid, margaric acid, myristic acid, behenic acid, palmitoleic acid, oleic acid, gadoleic acid, erucic acid, vaccenic acids, α-tocopherol, α-tocotrienol, β-tocopherol, γ-tocopherol, α-tocopherol, 1-amino-2-propanol, stachydrine, choline, phytin. |
[283–290] |
| Senecio vulgaris | ||
| Antioxidant, cytotoxic, antibacterial and anti-fungal |
Phenolic acids and derivatives: Caffeic acid, protocatechuic acid, 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid (chlorogenic acid), dicaffeoylquinic acid, p-hydroxy benzene-acetic acid, vanillic acid, syringic acid, p-hydroxy benzene-acetic acid derivative, p-hydroxycinnamic acid. Flavonoids: Quercitin-3-glucoside (Isoquercitrin), quercetin 3-O-rhamnoside (quercitrin), kaempferol-3-O-di-deoxyhexoside. Pyrrolizidine alkaloid: Retrorsine N-oxide, spartioidine N-oxide, seneciophylline N-oxide, integerrimine N-oxide, senecionine N-oxide, usaramine, neosenkirkine, riddelline, neoplatyphylline, retrorsine, spartioidine, platyphylline, integerrimine, senecionine. |
[291–294] |
| Solidago virgaurea | ||
| Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, spasmolytic, antihypertensive, diuretic effects and benefits in other urinary tract conditions, antibacterial, anti-fungal, antiparasitic, cytotoxic and anti-tumor, antimutagenic, cardioprotective, antisenescence effects. |
Phenolic acids and derivatives: Caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, 5-O-caffeoylquinic (neo chlorogenic) acid, 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid, 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid, 4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid, 3,4,5-tri-O-caffeoylquinic acid, methyl 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinate, 3-hydroxyphenyl acetic acid, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, 5-p-coumaroylquinic acid, homovanilic acid, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, sinapic acid, rosmarinic acid benzoic acid, 3-hydroxybenzoic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic (protocatechuic) acid, salicylic acid, gentisic acid, vanillic acid, gallic acid, leiocarposide, 2-methoxybenzyl-2,6-dimethoxy benzoate, Flavonoids: Quercetin, quercetin-3-O-glucoside (isoquercitrin), quercetin-3-O-galactoside (hyperoside), quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside (quercitrin), quercetin-3-O-rutinoside (rutin), quercetin-3-O-arabinopyranoside (avicularin), kaempferol-3-O-glucoside (astragalin), kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside (afzelin), kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside (nicotiflorin), kaempferol-3-O-robinobioside (biorobin), myricetin 3-rhamnoside (myricitrin), Isorhamnetin-3-O-rutinoside (narcissin), cyanidin-3-gentiobioside mono-C-glycosylflavones, di-C-glycosyl flavones. Others: Virgaureasaponins 1–6, solidagosaponins X-XXIX, bellisaponin BA2, erythrodiol-3-acetate, α-tocopherol quinone, 2-phyten-1-ol. |
[295] |
| Sonchus asper | ||
| Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, insecticidal, and hepatorenal protective, used for treating bronchitis, gastrointestinal infection and cardiac dysfunction, kidney diseases and cancer. |
Phenolic acids and derivatives: Caffeic acid, 3-coumaric acid, chlorogenic acid, gallic acid, luteolin, luteolin-7-o, protocatechuic acid, rosemarinic acid, quinic acid, vanillic acid. Flavonoids: Apigenin, apigenin-7-o, luteolin, pyrocatechol, quercetin, rutin. Others: 11 beta,13-dihydrourospermal A, 15-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-11 beta,13-dihydrourospermal A, 15-O-beta-D-glucopyranosylurospermal A, 15-O-[6'-(p-hydroxyphenylacetyl)]-beta-D-glucopyranosylurospermal A and 14-O-methylacetal-15-O-[6'-( p-hydroxyphenylacetyl)]-beta-D-glucopyranosylurospermal A, asperal, emodin, methyl-(3,8-di-hydroxy-6-methyl-9-oxo-9H-xanthene)-1-carboxylate, |
[119,296–306] |
| Sonchus oleraceus | ||
| Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumour, antibacterial, anti-fungal, antidepressant, anxiolytic, and antinociceptive effects, used for treating cancer, diarrhoea and enteritis. |
Phenolic acids and derivatives: Chicorin, caffeic acid glycoside, 4-cafffeoylquinic acid, 5-caffeoylquinic acid, cis-3’ caffeoylquinic acid, 5-coumaroylquinic acid, caftaric acid, chicoric acid, 3,4 dicaffeoylquinic acid, 3,5 dicaffeoylquinic acid, dicaffeoylquinic acid (isomer), cis-3,5 dicaffeoylquinic acid (isomer), tri-O-caffeyolyquinic acid, cis-3,4 dicaffeoylquinic acid, 4,5 dicaffeoylquinic acid. Flavonoids: Quercetin-glucoronide-glycosyl, quercetin-hexose-hexoside, quercetin glucoside glucoronide, luteolin-glycosyl-glucuronide, luteolin-diglucoside, isorhamnetin diglucoside, luteolin, luteolin glucuronide, luteolin glycoside, quercetin-rutinoside, isorhamnetin rutinoside, luteolin, quercetin acetylglycoside, apigenin glucuronide, apigenin rutinoside, kaempferol acetylglycoside sesquiterpenes, crepidiaside A. Others: 7S,10S- 3,9-dioxo-di-nor-eudesma-4-en-11-oic acid, 6 R,7S,10S-3,9-dioxo-7-hydroxyldi-nor-eudesma-4-en-11-oic acid. |
[307–312] |
| Tanacetum parthenium | ||
| Antioxidant, anxiolytic, antidepressant, anti-migraine agent, anticoagulant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, antiviral, anti-apoptotic, anti-cancer, antiparasitic, pain reliever. |
Phenolic acids and derivatives: 4-o-caffeoyl-quinic acid, 3,4-dicaffeoyl-quinic acid, 3,5-dicaffeoyl-quinic acid, 4,5-dicaffeoyl-quinic acid, neochlorogenic acid, ellagic acid, chlorogenic acid. Flavonoids: Kaempferol-3-rutinoside, 6-hydroxykaempferol-3,6,4′-trimethylether (santin), 6-hydroxykaempferol-3,6-dimethylether, quercetagenin-3,6-dimethylether (axillarin), quercetagenin-3,6,3′-trimethylether (jaceidin), quercetagenin-3,6,4′-trimethylether (centaureidin), apigenin, luteolin, santin, chrysoeriol, luteolin-7-glucoronides, methylquercetin, trihydroxy-methoxyflavone, costunolide, dihydro-β-cyclopyrethrosin, sudachitin, aceronin, tanacetol a isomer, nevadensin, parthenolide, casticin, nevadensin, tanaphillin, 3-β-hydroxyanhydroverlotorin, seco-tanapartholide A/B, hispidulin. |
[313–323] |
| Tanacetum vulgare | ||
| Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumour, antibacterial, antiparasitic, anthelmintic, repellent, insecticidal, antiviral, and anti-fungal. |
Phenolic acids and derivatives: Caffeoylgluconic acid, 1-caffeoylquinic acid, protocatechuic acid, p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid 1-O-hexoside, protocatechuic acid-O-hexoside isomer, syringic acid 4-O-hexoside, neochlorogenic (3-caffeoylquinic) acid, O-caffeoyl hexose, vanillic acid 4-O-hexoside, vanillic acid, caffeoylgluconic acid isomer, O-caffeoyl hexose isómer, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid-hexoside, 3-p-coumaroylquinic acid, caffeoylgluconic acid isomer, O-caffeoyl hexose isomer, quinic acid, chlorogenic (5-caffeoylquinic) acid, p-coumaric acid, 3-feruloylquinic acid, caffeic acid-O-hexoside, caffeic acid, gentisic acid, 5-p-coumaroylquinic acid, 3-caffeoyl-5-hydroxy-dihydrocaffeoylquinic acid, p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, 5-feruloylquinic acid, 1-caffeoyl-3-hydroxy-dihydrocaffeoylquinic acid, vanillic acid-4-O-(6-O-caffeoyl)-hexoside, 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid, 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid, 3-dehydrocaffeoyl-5-caffeoylquinic acid, 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid, shikimic acid, 4-dehydrocaffeoyl-5-caffeoylquinic acid, salicylic acid, 3-feruloyl-4-caffeoylquinic acid, 3-p-coumaroyl-5-caffeoylquinic acid, caffeic acid-O-(salicyl)-hexoside, 3-caffeoyl-5-p-coumaroylquinic acid, 3-feruloyl-5-caffeoylquinic acid, 4-caffeoyl-5-p-coumaroylquinic acid, 4-caffeoyl-5-feruloylquinic acid, 3,4,5-tricaffeoylquinic acid. Flavonoids: Apigenin, apigenin-6,8-diC-hexoside, apigenin 7-O-glucoside, methoxyeriodictyol-O-hexuronide, apigenin-O-hexuronide, luteolin, luteolin-O-hexuronide, luteolin 7-O-glucoside, 6-hydroxyluteolin-O-hexoside, luteolin 7-O-gentiobioside dihexoside (gentiobioside) 6-glucopyranosyl-glucopyranoside, luteolin-7-O-neohesperidoside, luteolin-O-caffeoylhexoside, luteolin-O-acetylhexosidekaempferol 3-O-glucuronide, rutin, quercetin, quercetin 3-O-acetylhexoside, quercetin 7-O-hexuronide, kaempferol, kaempferol 3-O-glucoside, eriodictyol-O-hexuronide, patuletin-O-hexoside, nepetin-O-hexoside, isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside, naringenin-O-hexuronide, hesperetin 7-O-rutinoside (hesperidin), nepetin-O-hexuronide, hispidulin-O-hexuronide, isorhamnetin-O-hexuronide, chrysoeriol-O-hexuronide, hesperetin-O-hexuronide, jaceosidin -O-hexuronide, patuletin (6-methoxyquercetin), nepetin (6-methoxyluteolin) 6-methoxykaempferol, naringenin, hispidulin (scutellarein-6-methyl ether), chrysoeriol, hesperetin, Isorhamnetin, jaceosidin (6-hydroxyluteolin-6,3′-dimethyl ether), quercetagetin-3,6,3′(4′)-trimethyl ether, cirsimaritin (6-hydroxyapigenin-6,7-dimethyl ether), eupatilin, casticin, acacetin. Sesquiterpene lactones and derivatives: α/β thujone, hydroxyarbusculin, ludovicin С, tanacetin/hydroxyraynosin/armefolin, parthenolide, camphor, caryophyllene oxide, dehydrosantamarin, caryophyllene/bisabolene, linoleamide, palmitamide, oleamide. |
[321,324–333] |
| Lamiaceae | ||
| Calamintha nepeta subsp. nepeta (Syn. Clinopodium nepeta) | ||
| Stimulant, tonic, antiseptic, antispasmodic, antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anti-ulcer, phytotoxic. |
Phenolic acids and derivatives: 3-O-Caffeoylquinic acid, 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid, 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid, rosmarinic acid, quercetin-3-O-rutinoside, gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, chlorogenic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, vanillic acid, syringic acid, vanillin, trans-cinnamic acid, coumarin, quinic acid, 12-O-hexosyljasmonate, caffeic acid hexamer, caffeic acid pentamer, rosmarinic acid, 12-O-(6′-caffeoylhexosyl)jasmonate, acacetin 7-O-[hexosyl(1iv → 2″)]deoxyhexosyl(1‴ → 6″) hexoside. Flavonoids: Myricetin, quercetin, luteolin, hesperidin, kaempferol, kaempferol-di-O-hexoside, apigenin, luteolin-8-C-(3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaroyl) hexosyl hexoside, 6,8-C-dihexosylapigenin, caffeic acid dimer, quercetin-3-O-hexoside, quercetin-3-O-[6″-O-(3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaroyl)]hexoside, kaempferol-3-O-hexoside, salvianolic acid B, acacetin, acacetin 7-O-[6iv-O-acetyl-hexosyl(1iv → 2″)]deoxyhexosyl(1‴ → 6″)hexoside, acacetin 7-O-deoxyhexosyl(1‴ → 6″)hexoside, |
[334–342] |
| Lavandula pedunculata | ||
| Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial. |
Phenolic acids and derivatives: Salvianolic acid B, rosmarinic acid, caffeic acid, caffeic acid hexoside, p-coumaroyl hexoside, rosmarinic acid, rosmarinic acid hexoside, sangerinic acid, lithospermic acid A, chlorogenic acid, 3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone, ferulic acid, syringic acid, vanilic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, protocatechuic acid, gallic acid. Flavonoids: Luteolin-O-hexosyl-O-glucuronide, eriodictyol-O-glucuronide, luteolin-7-O-glucuronide, methylluteolin-O-glucuronide, eriodictyol-O-glucuronide, herniarin, myricetin. |
[343–346] |
| Lavandula stoechas | ||
| Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antispasmodic, sedative, antibacterial, anti-fungal, insecticidal, larvicidal, hepatoprotective, renoprotective, and anti-leishmaniasis. |
Phenolic acids and derivatives: Protocatechuic acid, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, rosmarinic acid, ferulic acid, 7-methoxy coumarin. Flavonoids: Flavone di-O-glycosides, flavone 7-O-monoglycosides, pinobanksin, quercetin, pinocembrin, luteolin, vitexin, acacetin, erythrodiol. Others: Ursolic acid, vergatic acid, oleanolic acid, α-amyrin, α-amyrin acetate, β-sitosterol, lupeol, two longipinane derivatives (longipin-2-ene-7β,9α-diol-1-one and longipin-2-ene-7β,9α-diol-1-one-9-monoacetate), lavanol. |
[347–353] |
| Melissa officinalis | ||
| Anti-proliferative, anti-tumor, antioxidant, antiangiogenic, cardioprotective, anxiolytic antidepressant, antinociceptive, neuroprotective, GABA-T inhibitor, anti-kinetoplastidae, analgesic, hypnotic, anti-Alzheimer, antispasmodic, antiviral, anti-fungal, antibacterial, for premenstrual syndromes. |
Phenolic acids: Caffeic acid, caftaric acid, chlorogenic acid, ferulic acid, gentisic acid, p-Coumaric acid, rosmarinic acid. Flavonoids: Apigenin, cynaroside, daidzein, hyperoside, isoquercetin, kaempherol, luteolin, myricetin, quercetin, quercetrol, rutin. Triterpenes: Betulinic acid, oleanolic acid, ursolic acid, 23-sulfate ester of niga-ichigoside F1, 3β,16β,23-trihydroxy-13,28-epoxyurs-11-ene-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, 3,23-Disulfate ester of 2α,3β,19α,23-tetrahydroxyurs-12-en-28-oicacid, 3,23-Disulfate ester of 2α,3β,19α,23-tetrahydroxyurs-12-en-28-oicacid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, 3,23-Disulfate ester of2α,3β,23,29-tetrahydroxyolean-12-en-28-oicacid, 3,23-disulfate ester of 3β-23,29-trihydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid, 3,23-disulfate ester of 2α,3β-23,29-tetrahydroxyolean-12-ene-28-oicacid, 23-sulfate ester of 2α,3β,19 α,23-tetrahydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid, melissioside A, melissioside B, melissioside C. |
[354–357] |
| Mentha aquatica | ||
| Antioxidant, anxiolytic, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, antimicrobial, anti-cancer. |
Phenolic acids: Rosmarinic acid, caffeic acid. Flavonoids: Luteolin-7-O-rutinoid, Eriodictyol-O-rutinoside, naringenin-7-O- rutinoside, hesperetin-7-O- rutinoside, luteolin glucoside, luteolin-7-O-β-D-diglucuronide, eriocitrin, apigenin-7-O-β-D-diglucuronide, luteolin-7-O-glucuronide, narirutin, apigenin-7-O-rutinoside, apigenin-7-O-glucuronide, hesperidin, catechin. Others: methyl ester palmitic acid, methyl ester linolenic acid, ethyl ester linolenic acid, neophytadiene, phytol, viridiflorol, rotundifolone, 2,3-seco-triterpene, 3-O-benzoyltormentic acid, tormentic acid, 1-O-benzoylhyptad, ienic acid, 3-epiursolic acid, hyptadienic acid, 3-epi-maslinic acid, 3-epi-tormentic acid, ursolic acid, β-sitosterol, oleanolic acid, pomolic acid, micromeric acid, 21α-hydroxyursolic acid, pomolic acid, hyptadienic acid, 1-O-linoleoyl-2-O-enadecanoyl-3-O-palmitoleoyl-sn-glycerol, 1-O-oleoyl-2-O-enadecanoyl-3-O-palmitoleoyl-sn-glycerol, 1, 3-O-dioleoyl-2-O-eicosanoyl-sn-glycerol, 1-O-linoleoyl-2-O-palmitoleoyl-sn-glycerol, corosolic acid, asiatic acid, choline, acetic acid, formic acid, lactic acid, quinic acid, salicylic acid, succinic acid, fructose, glucose, sucrose, alanine, aspartic acid, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, phenylalanine, threonine, valine. |
[358–377] |
| Mentha pulegium | ||
| Insecticidal, nematicidal, allelopathic, antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiviral, antileishmanial, anti-tumour, anti-cancer, anti-hemolytic, antihypertensive, anti-inflammatory, burn wound healing, cardioprotective, stomachic, astringent, emmenagogue, decongestant, antispasmodic, antiseptic, depurative, digestive, anti-rheumatic, anti-arthritic, hepatotoxicity. |
Phenolic acids: Gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, ellagic acid, fumaric acid, protocatechuic acid, p-Hydroxybenzoic acid, syringic acid, cinnamic acid, vanillic acid, ferulic acids, p-coumaric acid, chlorogenic acid, rosmarinic acid. Flavonoids: Epicatechin, catechin, apigenin, salvigenin, salvigenin, luteolin, isorhamnetin, quercetagetin-3,6-dimethylether, kaempferol, kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside, hesperidin, thymonin, jaceosidin, pectolinaringenin, ladanein, sorbifolin, pedalitin, diosmin, luteolin, apigenin, naringenin, chrysin, chrysoeriol, vicenin-2, gallocatechin isomer 1. Others: Alterporriol, atropisomer, altersolanol, stemphypyrone, 6-O-methylalater-nin, macrosporin, salvianolic acid, Lithospermic acid, jaceidinisomer 1, Jaceosidin. |
[377–385] |
| Mentha suaveolens | ||
| Antioxidant, antimicrobial, antimutagenic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, insecticidal, anti-cancer, antithermal skin-aging effect. |
Phenolic acids: Cinnamic acid, chlorogenic acid, rosmarinic acid, caffeic acid, p-methyl coumarate, ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid, gallic acid, hydroxybenzoic acid, hydroxybenzoic acid, 3-dihydroxybenzoic acid, vanillic acid, salicylic acid, salicylic acid 2-O-β-glucoside, trans-cinnamic acid, p-methyl coumarate, p-anisic acid. Flavonoids: Hesperidin, rutin, quercetin, naringenin, luteolin, kaempferol, apigenin. |
[358,382,386–393] |
| Origanum vulgare L. | ||
| Antibacterial, anti-fungal, antiviral, antiparasitic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antitumoral, beneficial activity on skin disorders, effects on melanin production, on human sperm mobility, anti-Alzheimer, energy producer, stomach booster, nervous system reliever, laxative, reducing the general weakness of the body, anti-cancer, relief of migraine pain, for external use by rubbing in place of fractures and numbness of body parts, toothache, disinfection, antidiarrhoea, anticonvulsant, expectorant, nourishing, menstrual regulator, anti-urinary tract infection, treatment of sexual dysfunction, colic, sinusitis, relaxing, cardiorespiratory booster, nervous system booster, treatment of blockages, hepatoprotective. |
Phenolic acids: Rosmarinic acid, chlorogenic acid, cinnamic acid, caffeic acid, syringic acid, benzoic acid, vanillic acid, galo-coumaric acid, gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, sinapic acid, trans-cinnamic acid, 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, phenyllactic acid. Flavonoids: Quercetin, apigenin, kaempferol, naringenin, eriodictyol, salvianolic acid B, llithospermic acid B, amburosides A, luteolin, luteolin 7-O-glucuronide, apigenin 7-O-glucuronide, (−)-epigallocatechin, (+)-catechin, rutin, Others: Thymoquinone, thymol, carvacrol, demethylbenzolignanoid, chicoric acid, calleryanin 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate, calleryanin 3-hydroxy,4-methoxybenzoate, gastrodin 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate. |
[394–402] |
| Prunella vulgaris | ||
| Anti-tumour, anti-inflammation, immunoregulation, antiviral, antioxidant, anti-osteoporosis, anti-depression, hypotensive, hypolipemic, cardioprotective, anti-dementia, anti-amnesia. |
Phenolic acids: p-coumaric acid, caffeic acid, rosmarinic acid. Flavonoids: Kaempferol, luteolin, delphinidin, quercetin, quercetin-3-O-β-D-galactoside, homoorinet, cinaroside, quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucoside, kaempferol-3-O-β-D-glucoside. Steroids and derivatives: Beta-sitosterol, spinasterol, stigmasterol, vulgaxanthin-I, poriferasterol monoglucoside, morin, ducosterol, (22E20S24S)-stigmast-7,22-diene-3-e, Stigmast-7-en-3β-ol. Triterpenes: Oleanolic acid, ursolic acid, vulgarsaponin A/B, methyl oleanolate, methyl ursolate, methyl, maslinate, pravuloside A/B, palmitic acid, ethyl palmitate, tetracosanoic acid, stearic acid, 6,9-octodecadienoic acid, 3,6,7-eicosatrienoic acid, oleic acid, peanut oleic acid, moringoic acid, lauric acid, myristic acid, linolenic acid, palmitic acid, myristic acid, and linoleic acid. Coumarins: Umbelliferon, scopoletin, esculetin. |
[403] |
| Salvia verbenaca | ||
| Antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-cancer, antiparasitic, insecticidal, antihemolytic. |
Phenolic acids: p-Hydroxybenzoic acid, p-coumaric acid, rosmarinic acid, vanillic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, 3-O- and 4-O-caffeoylquinic acids. Flavonoids: Naringenin, cirsiliol, luteolin, apigenin, naringin, hesperidin, genkwanin. Others: Palmitic acid, stearic acid, linolenic acid, arachidic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid, palmitoleic acid, arachidic acid, verbenacines, salvinines, 6,7-dehydroroyleanone, cryptanol, sitosterol, campesterol, 6-hydroxysalvonolone, microstegiol, stigmasterol, carnosic acids, methyl carnosate contents, carnosol. |
[393,404–406] |
| Thymus mastichina | ||
| Antibacterial, anti-fungal, antioxidant, anti-cancer, antiviral, insecticidal, insect repellent, anti-Alzheimer, anti-inflammatory. |
Phenolic acids: Rosmarinic acid, hydroxycinnamoylquinic acid, 3-methoxysalicylic acid, caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, salvianolic acid B/E, salvianolic acid A/K isomer. Flavonoids: Quercetin glucoside, 6-hydroxyluteolin-7-O-glucopyranoside, luteolin glucoside, 6- hydroxyapigenin7-Oglucopyranoside, apigenin-7-Oglucoside, naringenin, luteolin, carnosol, apigenin, kaempferol, chrysoeriol-O-hexuronide, sakuranetin, sterubin. Others: Oleanolic acid, ursolic acid, xanthophyll lutein, β-sitosterol. |
[407] |
- Achillea millefolium L.
| Target | Part used/Extraction | Observations | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asteraceae | |||
| Arctium minus (Hill) Bernh | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | 1mg/ml of MeOH, CH2Cl2, EtOAc, and BuOH extracts of leaves (L), flowers (F) and roots (R). | AGLU-LMeOHext = 3.32 ± 9.80, AMY-LMeOHext = 12.65 ± 6.40. AGLU-LCH2Cl2-ext = 87.12 ± 8.06, AMY-LCH2Cl2-ext = 28.84 ± 5.57. AGLU-LEtOAc-ext = na, AMY-LEtOAc-ext = na. AGLU- LBuOH-ext = 24.49 ± 15.92, AMY-LBuOH-ext = 30.50 ± 8.35. AGLU-LAqua-ext = 15.51 ± 6.96, AMY-LAqua-ext = 5.74 ± 5.95. AGLU-FMeOHext = na, AMY-FMeOHext = na. AGLU-FCH2Cl2-ext = 21.68 ± 3.12, AMY-FCH2Cl2-ext = na. AGLU-FEtOAc-ext = 40.69 ± 6.90, AMY-FEtOAc-ext = na. AGLU- FBuOH-ext = 6.40 ± 4.45, AMY- FBuOH-ext = na. AGLU-FAqua-ext = 13.32 ± 2.22, AMY-FAqua-ext = na. AGLU-RMeOHext = na, AMY-RMeOHext = na. AGLU-RCH2Cl2-ext = 68.01 ± 7.02, AMY-RCH2Cl2-ext = na. AGLU-REtOAc-ext = 36.11 ± 10.68, AMY-REtOAc-ext = na. AGLU- FBuOH-ext = na, AMY- FBuOH-ext = na. AGLU-RAqua-ext = 30.40 ± 8.50, AMY-RAqua-ext = na. |
[175] |
| Achillea millefolium | |||
| A-GLU | Hydromethanolic extract of aerial parts. | AI 55% inhibition at 1.6 mg/mL. | [417] |
| A-GLU | Hydroethanolic extract of aerial parts. | The extract promoted the α-glucosidases inhibition by 55% at 1 mg/ml concerning control. It increased the PPARγ (five times) and GLUT4 (two-fold) relative expression than the control (p < 0.05). Finally, it significantly increased INS secretion and [Ca2+]i compared with the control. | [415] |
| INS secretion and calcium mobilization | |||
| PPARγ and GLUT4 expression analysis. | |||
| Arnica montana | |||
| A-AMY | Methanolic extract fractions (dried cell biomass of seeds germinated). | All fractions inhibited α-amylase activity (almost 12%). | [418] |
| Bellis perennis | |||
| Quantification of GLUT4 translocation. |
|
Both extracts had a clear dose-response relationship, with EXT4404 being slightly more effective than EXT4407. However, EXT4407 had no effect at 0.25 mg/L, while EXT4404 at the same concentration only increased by about 4%. Overall, all the extracts are effective inducers of GLUT4 translocation without INS. | [419] |
| Glucose Transport Assay | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Methanol: water (80:20%, v/v) extract of flowers. | IC50A-AMY: 8.48 ± 0.07 mg/ml of dried flowers; IC50A-GLU: 49.62 ± 0.01 mg/ml of dried flowers. | [420] |
| Bidens frondosa | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Ethanolic extracts (80%) of aerial parts. | IC50A-GLU = 0.41 mg/mL, the extracts inhibited α-glucosidase enzyme strongly (64.29–75.22% at 2 mg/mL); inactive on α-amylase activity. | [421] |
| Cichorium intybus | |||
| A-AMY | Aqueous extracts of aerial parts. | IC50A-AMY= 136.13 ± 8.09 µg/mL, | |
| Insulinotropic investigations (IC1) | Caffeic, ferulic acids and Chicoric acid (CAE, extracted from aqueous extract). | Caffeic acid mainly promotes a decrease in hepatic glycogenolysis. Ferulic acid elicits a clear increase in INS release and a reduction of hepatic glycogenolysis. CAE increases INS release and glucose uptake without affecting hepatic glycogenolysis. None of these compounds implicates hepatic glucose 6-phosphatase in contrast to chlorogenic acid, an inhibitor of glucose 6-phosphatase. | [422] |
| Insulin sensitizing investigations (IC2) | |||
| Hepatocyte culture and glycogenolysis test (IC3) | |||
| Evaluation of glucose 6-phosphatase activity (IC4) | |||
| Glucose uptake assay. | Caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid (CGA), and chicoric acid (CAE). | CRA and CGA increased glucose uptake in L6 muscular cells, an effect only observed in the presence of stimulating concentrations of INS. Both CRA and CGA stimulated INS secretion from the INS-1E cells and rat islets of Langerhans. The effect of CRA is only observed in the presence of subnormal glucose levels. |
[423] |
| β-cell culture and measurement of INS secretion. | |||
| Rat pancreatic islet experiments. | |||
| Study of G6Pase and PEPCK expression (IC5). | Three di-O-caffeoylquinic acids (CQA) were extracted from chicory roots methanolic extract. | CQA suppressed hepatic glucose production in H4IIE rat hepatoma cells by reducing the expression of G6Pase and PEPCK. Activation of PI3K and MAPK pathways as a method of controlling gene expression. Promoted increased mitochondrial respiration and cellular metabolism by inducing oxidative phosphorylation and proton leak. |
[424] |
| Gene expression of PI3K and MAPK pathways | |||
| Cellular bioenergetics (IC6). | |||
| Differentiation induction of embryonal carcinoma stem cells into INS-producing cells (IC7) | Methanolic extracts (100%) of leaves. | The extract efficiently induced the differentiation of P19 EC cells into clusters similar to pancreatic islets with the molecular, cellular and functional characteristics of mature β cells. | [425] |
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Aqueous methanolic extracts (80% methanol, 19% H2O, 1% HCl; v/v/v) of the plant. | IC50A-AMY: 18.3 ± 0.7 mg/mL; IC50A-GLU: 4.25 ± 0.08 mg/mL | [426] |
| Glucose uptake test. |
|
Adding NCRAE increased glucose uptake at 50 mg/mL, which agrees with our previous report. At the same concentration of 50 µg/mL, the SCCAM solution has also increased glucose uptake with a value close to the NCRAE values. | [427] |
| Glucose uptake test and lipid accumulation assays. | Methanolic extract (CME) and CME/DT (detannification). | CME and CME/DT exhibited significant glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes with a dose-dependent response. The glucose uptake profile in the presence of PI3K and IRTK inhibitors (Wortmannin and Genistein) substantiates the mechanism used by both extracts. CME inhibited the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes but failed to show glucose uptake in inhibitor-treated cells. The activity exhibited by CME/DT is exactly opposite to CME. PTP1B inhibition assay, mRNA and protein expression analysis revealed the unique behaviour of CME and CME/DT. | [428] |
| PTP1B Inhibition study. | |||
| Glucose uptake assay. | 12, 8-guaianolide sesquiterpene lactones isolated from butan-1-ol and ethyl acetate fractions of roots extract | The compounds significantly facilitated glucose uptake in the hyperglycemic HepG2 cell model at 50 μM. | [265] |
| Dittrichia viscosa subsp. Viscosa (Syn. Inula viscosa) | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Methanol: water (80:20%, v/v) extract of leaves. | IC50A-AMY: 1.381 ± 0.085 mg/mL; IC50A-GLU: 0.118 ± 0.02 mg/mL. | [264] |
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Methanol (MeOH), ethyl acetate (EtOAc) and chloroform (CHL) extracts of leaves. | IC50A-GLU-EtOAc: 29.9 ± 1.04 µg/mL; PI-A-AMY: 22.152 ± 0.387% IC50A-GLU-MeOH: 22.3 ± 2.82 µg/mL; PI-A-AMY: 27.162 ± 1.623% IC50A-GLU-Chlo: 39.8 ± 0.76 µg/mL; PI-A-AMY: 17.157 ± 0.634% |
[429] |
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Tomentosin is extracted and purified from dichloromethane and ethanolic extract. | IC50A-GLU-26.61 ± 0.236 μM; IC50A-AMY: 26.89 ± 1.54 μM | [430] |
| Glucose uptake assay (IC8). | 7-O-Methylaromadendrin (MAD) extracted from methanolic extract of the aerial part of the plant. | MAD significantly stimulated INS-induced glucose uptake. MAD increased the P2a and PPARg2 gene expression. MAD stimulated the reactivation of INS-mediated phosphorylation of PI3K-(Akt/PKB) and AMPK in high glucose-induced, INS-resistant HepG2 cells. |
[431] |
| Study of aP2 and PPARg2 gene expression. | |||
| Galinsoga parviflora | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Aqueous extracts of leaves. | At 2.5mg/mL IA% (A-GLU): 40%, A-AMY: no inhibition | [432] |
| A-GLU | Two compounds, Galinsosides A (1) and B (2), flavanone glucosides extracted from methanolic extract of whole plant. | IC50A-GLU (1): 286 ± 0.68 μM; IC50A-GLU (2): 46.7 ± 0.32 μM. | [433] |
| Helichrysum stoechas | |||
| A-GLU/DPP-4 | Methanol extracts of aerial parts. | IC50A-GLU: 481.01 μg/mL, IC50DPP-4: 81.71 μg/mL. | [267] |
| Hypochaeris radicata | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Aqueous extracts of leaves. HR1: Extract fresh plant materials; HR2: Extract plant materials after blanching; HR3: Blanching water extract. |
IC50A-GLU-HR1: 79.4 ± 1.7 μg/mL; IC50A-GLU-HR2: 99.1 ± 1.9 μg/mL; IC50A-GLU-HR3: 83.4 ± 1.8 μg/mL IC50A-AMY-HR1: 41.9 ± 1.4 μg/mL; IC50A-AMY-HR2: 84.5 ± 1.8 μg/mL; IC50A-AMY-HR3: 51.9 ± 1.5 μg/mL |
[273] |
| Lactuca serriola | |||
| A-GLU | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (1), protocatechuic acid (2), kaempferol (3), quercetin (4), lactuside A (5), luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucoside (6) are extracted from methanolic extracts of the leaves. | IC50A-GLU-(1): 810.31 ± 1.03 µM; IC50A-GLU-(2): 126.65 ± 1.82 µM; IC50A-GLU-(3): 39.72 ± 0.43 µM; IC50A-GLU-(4): 39.82 ± 1.12 µM; IC50A-GLU-(5): 468.98 ± 0.45 µM; IC50A-GLU-(6): 161.29±0.31 µM. | [276] |
| Senecio vulgaris | |||
| A-AMY | Methanol extract (MeOH = 1 mg/ml), Dichloromethane extract (DCM1 = 100 and DCM2 = 50 μg/ml). | MeOH-IA%: 82.46 ± 0.0041%, DCM1-IA%: 90.95 ± 0.0001%, DCM2- IA%: 59.05 ± 0.0001%. | [292] |
| ALDO | Methanol extracts of aerial parts. | IA%: 42.00% at 1mg/mL. | [434] |
| Solidago virgaurea | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Conc-ASE (Concentrated extract obtained after accelerated solvent extraction) Conc-LE (Concentrated extract obtained after Laser extraction). |
Conc-ASE = IC50A-GLU: 9.3±0.9 µg/mL, IC50A-AMY- 33.9±2.4 µg/mL. Conc-LE = IC50A-GLU : 8.7±0.6 µg/mL, IC50A-AMY- 32.1±1.9 µg/mL. |
[435] |
| Sonchus oleraceus | |||
| Glucose uptake assay (IC13) Analysis of p-AMPK/Akt/GSK3-β expression in cells. |
Hydroethanolic extract (90%) of the leaves (SOL). | The glucose uptake in HepG2 cells treated with 200 μg/mL SOL was significantly increased to 145%, but the uptake was lower than that treated with insulin (320%). After treatment with SOL extracts for 24 h, the p-AMPK, Akt, and GSK3β expression levels significantly increased by approximately 1.7, 1.0 and 0.8 times, respectively, compared with the control. | [436] |
| Tanacetum parthenium | |||
| ra-ALDO/AGEs | Methanolic extract (70%) (ME) Ferulic acid (FA), Apigenin (API), Luteolin-7-O-glucoside (LUG), Luteolin (LUT), Chrysosplenol (CHR), Kaempferol (KAE), Santin (SAN) were extracted and purified from the methanolic extract. |
ME: ra-ALDO-IA% (61.1 ± 0.5 %), IC50-ra-ALDO (8.04 ± 0.61 µg/mL), IC50-AGEs (163.71 ± 6.31 µg/mL). FA: IC50-ra-ALDO (3.20 ±0.12 µg/mL), IC50-AGEs (5.59 ± 0.26 µg/mL). API: IC50-ra-ALDO (1.97 ± 0.10 µg/mL), IC50-AGEs (NA). LUG: IC50-ra-ALDO (1.31 ± 0.09 µg/mL), IC50-AGEs (3.43 ± 0.12 µg/mL). LUT: IC50-ra-ALDO (1.76 ± 0.03 µg/mL), IC50-AGEs (6.73 ± 0.43 µg/mL). CHR: IC50-ra-ALDO (1.92 ± 0.08 µg/mL), IC50-AGEs (NA). KAE: IC50-ra-ALDO (1.11 ± 0.03 µg/mL), IC50-AGEs (NA). SAN: IC50-ra-ALDO (NA), IC50-AGEs (NA). |
[437] |
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Ethanolic extract of aerial parts. Extraction by Accelerated solvent extraction (ASE), Microwave−assisted extraction (MAE), Maceration (MAC), Soxhlet (SOX) and Ultrasound−assisted extraction (UAE). |
ASE: IC50A-GLU (1.63 ± 0.02 mmol acarbose equivalent (ACAE)/g extracts), IC50A-AMY (0.51 ± 0.02 ACAE/g extract). MAE: IC50A-GLU (1.64 ± 0.01 mmol ACAE/g extracts), IC50A-AMY (0.53 ± 0.05 mmol ACAE/g extract). MAC: IC50A-GLU (1.65 ± 0.01 mmol ACAE/g extracts), IC50A-AMY (0.52 ± 0.02 mmol ACAE/g extract). SOX: IC50A-GLU (1.67 ± 0.01 mmol ACAE/g extracts), IC50A-AMY (0.51 ± 0.03 mmol ACAE/g extract). UAE: IC50A-GLU (1.64 ± 0.01 mmol ACAE/g extracts), IC50A-AMY (0.56 ± 0.01 mmol ACAE/g extract). |
[438] |
| Tanacetum vulgare | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Hexan, hydroethanolic and infusion of flowers (HEXF, HETF, INFF), Stems (HEXS, HETS, INFS) and Aerial parts (HEXAP, HETAP, INFAP). | HEXF: IC50A-GLU (10.41 ± 0.06 mmol acarbose equivalent (ACAE)/g extracts), IC50A-AMY (0.53 ± 0.01 mmol ACAE/g extract). HETF: IC50A-GLU (10.77 ± 0.15 mmol ACAE/g extracts), IC50A-AMY (0.33 ± 0.01 mmol ACAE/g extract). INFF: IC50A-GLU (3.57 ± 0.13 mmol ACAE/g extracts), IC50A-AMY (0.07 ± 0.01 mmol ACAE/g extract). HEXS: IC50A-GLU (10.60 ± 0.06 mmol ACAE/g extracts), IC50A-AMY (0.50 ± 0.02 mmol ACAE/g extract). HETS: IC50A-GLU (7.54 ± 0.65 mmol ACAE/g extracts), IC50A-AMY (0.33 ± 0.02 mmol ACAE/g extract). INFS: IC50A-GLU (4.00 ± 0.09 mmol ACAE/g extracts), IC50A-AMY (0.10 ± 0.01 mmol ACAE/g extract). HEXAP: IC50A-GLU (10.56 ± 0.04 mmol ACAE/g extracts), IC50A-AMY (0.48 ± 0.03 mmol ACAE/g extract). HETAP: IC50A-GLU (8.67 ± 1.19 mmol ACAE/g extracts), IC50A-AMY (0.35 ± 0.03 mmol ACAE/g extract). INFAP: IC50A-GLU (4.26 ± 0.12 mmol ACAE/g extracts), IC50A-AMY (0.09 ± 0.01 mmol ACAE/g extract). |
[439] |
| Lamiaceae | |||
| Calamintha nepeta subsp. Nepeta (Syn. Clinopodium nepeta) | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Methanolic extract (80%) of leaves. | At 10 mg/ml IA% (A-GLU): 66.62 ± 1.61%, IA% (A-AMY): 16.45 ± 0.94% | [339] |
| A-AMY | Methyl alcohol: water (7:3) extract fractionated with ethyl acetate (AcOEt), dichloromethane (DCM), and n-butanol (BuOH). | IC50A-AMY of DCM, AcOEt, and BuOH >200 µg/mL | [338] |
| A-AMY | Methanolic extract (ME), essential oil (EO), and aqueous extract (AQ). | IC50A-AMY-ME: 24.46 mg/ml, IC50A-AMY-EO: 31.54 mg/ml, IC50A-AMY-AQ: 115.47 mg/ml | [341] |
| Lavandula pedunculata | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Aqueous extract of flowering tops. | IC50A-AMY: 0.44 ± 0.05 mg/mL, IC50A-GLU-131 ± 20 mg/ml. | [440] |
| Intestinal Glucose Absorption in vitro | The extract inhibited the intestinal glucose absorption (IC50 = 81.28 ± 4.01 µg/mL) in a concentration-dependent manner. | ||
| Lavandula stoechas | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Aqueous extract of aerial parts. | IC50A-AMY: 0.485 ± 0.13 mg/mL, IC50A-GLU: 168 ± 40.10 μg/mL | [441] |
| Intestinal Glucose Absorption assay, In situ. | The extract lowered intestinal glucose absorption in situ at 250 mg/kg. | ||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | EO of aerial parts. | IC50A-AMY: 3.00 ± 0.008 mg/mL, IC50A-GLU: 2.58 ± 0.04 mg/mL | [353] |
| Glucose production assay (IC9) | Ethyl acetate (EE) and n-butanol (BE) fractions are prepared from an aqueous extract of aerial parts. | EE and BE at low doses (25–50 µg/mL) significantly decreased hepatic gluconeogenesis in the H4IIE cell line by suppressing the expression of PEPCK and G6Pase. In C2C12 myotubes, both extracts increased the INS-stimulated glucose uptake more effectively than metformin. They also effectively increased the expression of lipoprotein lipase protein levels in INS-resistant myotubes at low doses. EE increased the protein level of PPARγ and stimulated the activation of AKT in INS-resistant H4IIE and C2C12 cell lines. | [442] |
| Glucose uptake assay (IC10) | |||
| Effects on PEPCK and G6Pase gene expression. | |||
| Effects on AKT activation and GLUT4 expression. | |||
| Transcriptome analyses | |||
| A-GLU | Ursolic acid extracted from Methanol (ME), ethanol (ET), methanol-dichloromethane (1: 1, v/v) (MDI), acetone (AC), ethyl acetate (EA), diethyl ether (DEE), and chloroform extracts (CHL). | IC50A-GLU-ME: 49.86 ± 0.36 mg/mL, IC50A-GLU-ET: 17.81 ± 0.55 mg/mL, IC50A-GLU-MDI: 29.57 ± 0.19 mg/mL, IC50A-GLU-AC: 24.63 ± 0.13 mg/mL, IC50A-GLU-EA: 40.31 ± 0.84 mg/mL, IC50A-GLU-DEE: 23.60 ± 1.04 mg/mL, IC50A-GLU-CHL: 26.21 ± 1.00 mg/mL. | [352] |
| A-GLU | EO of flowering leaves. | IC50A-AMY: 106.73 ± 3.27 µg/mL, IC50A-GLU: 98.54 ± 4.84 µg/mL. | [350] |
| Melissa officinalis | |||
| Anti-glycation assay. | Aqueous extract of leaves (AQ). Rosmarinic acid (RA), melitric acid A (MA), salviaic acid A (SA), caffeic acid (CA). |
IC50-AQ: 0.24 mg/mL, IC50-RA: 0.34 mM, IC50-MA: 0.38 mM, IC50-SA: 0.16 mM, IC50-CA: 0.48 mM. | [[443] |
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Aqueous extract of leaves | IA%: 83.9%, A-AMY: No activity. | [444] |
| A-AMY | Lemon balm-based extract with 50% RA | IA%: 50% | [445] |
| Uptake inhibition of glucose (UIG) and fructose (UIF) (IC12) | Methanolic and aqueous extract of leaves. | UIG%: <25%, UIF: No activity for both extracts. | [446] |
| Glucose consumption (IC8) | EO (A, B and C compagnies) | EO-A: 63.64 ± 11.46%, EO-B: 59.96 ± 3.65%, EO-C: 65.63 ± 9.76%. The Western blot data suggest that the key factors of the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase/acetyl-CoA carboxylase pathway can be mediated by the EOs. |
[447] |
| Gene expressions analysis of p-AMPK, AMPK, p-ACC, ACC, PPAR, CEBPα, and SREBP1 proteins. | |||
| Mentha aquatica | |||
| A-AMY | Hydroethanolic extract (70%) of the leaves. | IC50A-AMY: 229.50 ± 4.1 µg/mL. | [448] |
| A-AMY | Methanolic (ME) and aqueous extracts (AQ) of the leaves. | IA%-ME: 61.7 ± 5.5%, IA%-AQ: 14.0 ± 3.0% | [[449] |
| Uptake inhibition of glucose (UIG) and fructose (UIF) (IC12) | Methanolic and aqueous extract of leaves. | UIG%: <25%, UIF: No activity for both extracts. |
[446] |
| Mentha pulegium | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Methanolic and aqueous extract of leaves. | IC50A-GLU-ME: 20.38 µg/mL, IC50A-GLU-AQ: 21.65 µg/mL, IC50A-AMY-ME: 23.11µg/mL, IC50A-GLU-AQ: 36.47 µg/mL | [378] |
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Ethyl acetate fraction of aerial part. | IC50A-GLU: 61.85±1.69 µg/mL, IC50A-AMY: 16.37 ± 0.11 µg/mL | [450] |
| Mentha suaveolens | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | EO of the aerial part. | IC50A-GLU: 141.16 ± 0.2 µg/mL, IC50A-AMY: 94.30 ± 0.06 µg/mL | [390] |
| Origanum vulgare | |||
| A-AMY | Clonal oregano shoots ethanolic extracts (50%) (O-1, O-9, O-11Y, O-11M, O-12, O-17, OK-17, O-23, O-24, O-26, GO-19-1). | The strongest anti-amylase activity was observed for extract O-24, which had an AI index value of 2.32 ± 0.28 and corresponded to 57% inhibition of enzyme activity. Eight of the 11 clonal oregano extracts tested had AI index values greater than or equal to 1.5. For these experiments, an AI index value of 1.5 corresponded to approximately 33% α-amylase enzyme inhibition. | [451] |
| ALDO | Caffeic acid (CA), rosmarinic acid (RO), lithospermic acid B (LTO), 12-hydroxy jasmonic acid 12-O-β-glucopyranoside (HDG), p-menth-3-ene-1,2-diol 1-O-β-glucopyranoside (MDG) isolated from the polar extracts of aerial parts. | ALDO-CA: 8 ± 4.6 %, ALDO-RO: 95 ± 0.0 %, ALDO-LTO: 96 ± 1.7, ALDO-HDG: 77 ± 1.4 %, ALDO-MDG: 41 ± 0.6 %. EB-CA: −7.68 kcal/mol, EB-RO: 15.71 kcal/mol, EB-LTO: −16.08 kcal/mol, EB-HDG: −14.58 kcal/mol, EB-MDG: −10.57 kcal/mol. |
[452] |
| Docking studies of ALDO inhibitory activity (EB). | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Aqueous and ethanolic (12%) extract of plant clonal lines. | At 1000 µg/mL: A-GLU (93.7%), A-AMY (95%). | [444] |
| Analysis of PPARγ- and δ-mediated transactivation, a test of adipogenic potential, INS-stimulated glucose uptake, Neutral red assay. |
Origanum vulgare ssp. vulgare (1): Hexane (Hex), dichloromethane (DCM), and ethyl acetate (EtOAc) extracts of the aerial part. Origanum vulgare ssp. hirtum (2): dichloromethane (DCM), methanol (MeOH) extracts of the aerial part. |
(1): Hex ext = Activation of the γ, δ PPARs, adipocyte differentiation (NA), INS-stimulated GLU-uptake (+), Viability of endothelial cells (NA), Viability of macrophages (NA), DCM ext = Activation of the γ PPARs, adipocyte differentiation (NA), INS-stimulated GLU-uptake (+), Viability of endothelial cells (-), Viability of macrophages (66.1 ± 5.3%). EtOAc ext = Activation of the γ PPARs, adipocyte differentiation (NA), INS-stimulated GLU-uptake (+), Viability of endothelial cells (NA), Viability of macrophages (2.7 ± 1.4%). (2): DCM ext = Activation of the γ PPARs, adipocyte differentiation (NA), INS-stimulated GLU-uptake (+), Viability of endothelial cells (NA), Viability of macrophages (NA), MeOH ext = Activation of the γ, δ PPARs, adipocyte differentiation (NA), INS-stimulated GLU-uptake (+), Viability of endothelial cells (NA), Viability of macrophages (NA). |
[453] |
| DPP-IV/PTP1B | Methanolic extracts of leaves: Commercial oregano extract (E1) and Greenhouse-grown oregano extract (E2). Chemical fractionation by flash chromatography system (fractions FA to FI). |
DPP-IV-IC50: (E1) = 28.4 ± 6.3 μM GAE, (E2) = 86.2 ± 18.8 μM GAE, FA>500 μM GAE, FB = 206.3 ± 47.2 μM GAE, FC>500 μM GAE, FD = 317.4 ± 60.7 μM GAE, FE = 20.3 ± 3.9 μM GAE, FF = 23.3 ± 1.9 μM GAE, FG = NA, FH = NA, FI = NA. PTP1B-IA: (E1)/(E2) = NA, FA = 7.0 ± 3.5 %, FB = 13.3 ± 4.2 %, FC = 1.3 ± 1.0 %, FD = NA, FE = 32.1 ± 3.3 %, FF = 77.4 ± 18.4 %, FG = NA, FH = NA, FI = NA. |
[454] |
| A-GLU/A-AMY | (1): EO of O. vulgare subsp. Hirtum. (2): EO of O. vulgare subsp. Vulgare. |
IC50A-AMY (1): 0.14 ± 0.008 mmol ACEs/g; IC50A-GLU (1): 0.88 ± 0.03 mmol ACEs/g. IC50A-AMY (2): 0.13 ± 0.004 mmol ACEs/g, IC50A-GLU (2): 6.04 ± 0.91 mmol ACEs/g. |
[396] |
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Methanolic extract (80%) of leaves. | A-GLU-IA = 58.41 ± 1.97 %, A-AMY-IA = 6.79 ± 0.57 %. | [339] |
| A-GLU | Aqueous acetonitrile (50%) of powder leaves. | IC50A-GLU = 0.35 ± 0.03 μg/mL, AGEs-IC50 = 0.55 ± 0.07 mg/mL. Cells treated with extract leaf extract at a 100 μg/mL concentration showed significantly enhanced 2-NBDG uptake compared with INS-treated cells. The extract decreased the promoter activity and the mRNA and protein expression of PEPCK and SREBP-1c. I. The extract inhibited the expression of CPY2E1 and enhanced the expression of GLUT2. |
[399] |
| AGEs assay | |||
| Glucose uptake assay (IC13). | |||
| The mRNA and protein expression of PEPCK, SREBP-1c, GLUT2, CYP2E1 (IC14). | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY/LIPA | Ethanolic extracts (80% v/v). | IC50A-AMY = 44.71 ± 0.86 µg/mL, IC50A-GLU = 7.11 ± 1.37 µg/mL, IC50-LIPA = 922.35 ± 30.99 µg/mL. | [401] |
| Prunella vulgaris | |||
| Study of Glucose Production (IC15). | Methanolic extract of arial part (PVA). Rosmarinic and caffeic acids were extracted from solid residue PVA by organic solvent, representing about 26% and 0.3% w/w of total extract. |
The PVA lowered glucose production from glycogen (glycogenolysis), dihydroxyacetone, and alanine (gluconeogenesis). None of the phenolic acids influenced PEPCK mRNA expression, which INS downregulated. G6Pase mRNA was decreased by INS, increased by PVA, and remained unaffected by other treatments. Both compounds significantly increased GK mRNA expression; PVA did not affect this gene expression. | [455] |
| The mRNA expression analysis of G6Pase, GLUK, CALM, PEPCK and GK (IC16). | |||
| ra-ALDO / hu-ALDO / AGEs assay | Aqueous extract (AQE) partitioned sequentially with n-hexane (HEX), methylene chloride (CH2Cl2), ethyl acetate (EtOAc), n-butanol (BuOH) and water (H2O). Compounds (C1 to C6) isolated from AQE fractionation. |
ra-ALDO: AQE-IA = 36.18 ± 1.13 %, HEX-IA = 33.94 ± 0.49 %, CH2Cl2-IA= 32.49 ± 0.54 %, EtOAc-IA = 87.33 ± 2.39 % (IC50 = 2.99 ± 0.10 𝜇g/mL), BuOH-IA = 59.56 ± 2.34 %, H2O-IA = NA, C1 = NA, C2 = NA, C3-IC50 = 8.35 ± 0.51 𝜇M, C4-IC50 = 2.77 ± 0.48 𝜇M, C5-IC50 = 3.20 ± 0.55 𝜇M, C6 = NA. hu-ALDO: C1 = NA, C2 = NA, C3 = NA, C4-IC50 = 18.62 ± 0.40 𝜇M, C5-IC50 = 12.58 ± 0.32 𝜇M, C6 = NA. AGEs assay: AQE-IA = 29.26 ± 0.94%, HEX-IA = 33.94 ± 0.41%, CH2Cl2-IA = 54.03 ± 1.00 % (IC50 = 186.72 ± 2.05 µg/mL), EtOAc-IA = 68.31 ± 1.06 % (IC50 = 141.34 ± 1.27 µg/mL), BuOH-IA = 40.47 ± 0.68 %, H2O-IA = 30.24 ± 1.01 %, C1-IA = 9.33 ± 0.27%, C2= NA, C3 = NA, C4 = 20.67 ± 0.37 %, C5-IA = 74.81 ± 1.41 % (IC50 = 33.16 ± 0.54 µg/mL), C6-IA = 88.69 ± 0.56 % (IC50 = 304.36 ± 3.41 µg/mL). |
[456] |
| Cas-3 activity and activation of the apoptotic signaling pathway (IC16) analysis (Bax/Bcl-2, Fas/FasL, phospho-JNK, phospho-ERK, phospho-p38, NF-κB binding activity, phosphorylated-IκB, TNF-α, IL-6). |
Aqueous extract (AQE). | AQE administration significantly prevented IL-1β-increased INS-1 cell death and LDH activity and attenuated IL-1β-increased cas-3 activity. | [457] |
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Hydroethanolic extract of inflorescence (PV) contained RA (4.5%), CA (9.8%) and pCA (11.6%). | IC50A-GLU-PV: 90.9 μg/ml, IC50A-AMY-PV: 47.2 μg/ml IC50A-GLU-CA: 4.7 μg/ml, IC50A-AMY-CA: 5.1 μg/ml IC50A-GLU-RA: 11.6 μg/ml, IC50A-AMY-RA: 21.7 μg/ml |
[458] |
| NPMDA | Active coumpouds tested (Kaempferol, luteolin, delphinidin, quercetin, beta-sitosterol, spinasterol, stigmasterol, vulgaxanthin-I, poriferasterol monoglucoside, stigmast-7-enol, morin) | The sterols and flavonoids play an active role by affecting the TNF signalling pathway, AGE-RAGE signalling pathway, MAPK pathway, and PI3K-Akt pathway-related targets such as IL-6 and INS. | [459] |
| A-GLU | Hydroethanolic extract (75%) (HE) partitioned sequentially with Petroleum ether (PE), Ethyl acetate (EtOAc), n-butanol (BuOH), and water (H2O) fractions. Compounds Caffeic acid (C1), Isoquercitrin (C2) and Rosmarinic acid (C3) isolated from AQE fractionation. |
HE-IC50 = 130.46 ± 4.33 µg/mL, PE-IC50 = 194.61 ± 4.69 µg/mL, EtOAc-IC50 = 69.13 ± 2.86 µg/mL, BuOH-IC50 = 124.97 ± 2.56 µg/mL, H2O-IC50 = 191.88 ± 3.34 µg/mL, C1-IC50 = 3.91 ± 0.07 µg/mL, C2-IC50 = 85.52 ± 2.94 µg/mL, C3-IC50 = 0.65 ± 0.04 µg/mL. | [460] |
| Salvia verbenaca | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Methanolic extract (85%) (ME) and decoction (DE) of the aerial part. | IC50A-GLU-ME: 50.5 ± 1.40 µg/ml, IC50A-AMY-ME = 101.30 ± 0.08 µg/ml. IC50A-GLU-DE: 313.7 ± 1.36 µg/ml, IC50A-AMY-DE = NA. |
[405] |
| Thymus mastichina | |||
| A-GLU/A-AMY | Essential oil. | IC50A-GLU = 100 ± 0.0 µg/mL, IC50A-AMY = 4600 ± 0.0 µg/mL. | [461] |
- Anthemis canescens var. aurea
- Bellis perennis L. and Bidens frondose
- Chamaemelum nobile
- Cichorium intybus L.
| Part Used/Extract tested | Model/Parameters studies | Intervention and Duration | Observations | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asteraceae | ||||
| Arctium minus (Hill) Bernh | ||||
| R/DEC | Male diabetic GK (Goto-kakizak) rats. | 125 g/L DR ad libitum / 4 weeks. |
The DEC led to a GK rats’ occasional glycaemia decrease. It did not significantly affect glycemic control; long-lasting treatments induced toxic effects. The DEC decreased several parameters of GK liver mitochondria respiratory activity. | [184] |
| R/L/AQ | ALLO-induced diabetic rats. | RAQ (500 mg/kg) and LAQ (200 mg/kg) OG / 21 days. |
RAQ was reduced by 34.6 ± 5.8%, and LAQ was reduced by 6.2 ± 22.9 %. | [176] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B1) | ||||
| Achillea millefolium | ||||
| NI/HET | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 25 mg/kg/day and 100 mg/kg/day OG / 28 days. |
Compared to Metformin, the HET reduces lipid abnormality, HYG and hepatic enzymes with a dose-dependent effect in diabetic rats. | [408] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B2) | ||||
| NI/AQ/MET | OGTT | 250 and 500 mg·kg−1 BW DR / 18h. |
The AQ/MET at dose levels of 250 and 500 mg/kg BW showed a significant decrease in BG level, TGL, VLDL, cholesterol, SGOT, SGPT, and ALP in diabetic rats. | [410] |
| ALLO-induced diabetic rats. | 250 and 500 mg/kg BW DR / 14 days. |
|||
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B3) | ||||
| AP/HET (70%) | OGTT | 100 mg/kg 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2 and 3 h |
The HET showed significant glucose diminution on oral glucose tolerance tests and in acute experimental T2DM assay. It reduced the BG levels in a dose-dependent manner. | [415] |
| STZ-induced diabetic mice. | 33, 100 and 330 mg/kg 1, 3, 5, and 7 h |
|||
| AP/HET | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 100 mg/ kg/ day i.p. / 14 days |
The HET significantly reduced the expression of both IL-1β and iNOS genes. The serum INS levels in the HET group animals increased while the BG levels decreased significantly. The HET enhanced overexpression of IL-1β and iNOS genes, which may have a protective effect on β-cells. | [416] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B4) and IL-1β/ iNOS gene expression. | ||||
| NI/HET | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 250 mg/kg NI / 21 days |
The results indicated that the HET improves renal function due to antioxidant activity and modulates some biochemical factors in diabetic rats. | [414] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B5) Analysis of oxidative stress-related factors (O1). | ||||
| Anthemis canescens (syn. Matricaria aurea) | ||||
| ET/EA/DCM/HEX | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | ETH1= 100 mg/kg, ETH2=200 mg/kg EA1= 100 mg/kg, EA2=200 mg/kg DCM1= 100 mg/kg, DCM2=200 mg/kg HEX1=100 mg/kg, HEX2=200 mg/kg OG / 4 weeks. |
Treatment with either ETH1/2 extracts or pioglitazone successfully ameliorated INS resistance, hyperlipidemia, and fatty liver without significantly affecting fasting INS levels or pancreatic secretory capacity. It increased liver protection from injury associated with T2DM, as evidenced by a significant decrease in ALT and AST. | [222] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B6). | ||||
| Oxidative stress and antioxidant markers in the liver (O2) | ||||
| Bellis perennis | ||||
| L/F/ EXT4404/EXT4407/HMET |
Avian embryos in the first two-thirds of embryonic development (lasting 21 days) Hens egg test-chorioallantoic membrane (HET-CAM) assay. |
EXT4404 (300 mg/L), EXT4407 (300 mg/L), HMET (300 mg/L). | All three extracts resulted in a comparable decrease in BG levels (~20% after 1 h and 30% after 2 h) and were statistically significant after 2 h incubation. The three extracts significantly reduced BG levels at both time points with comparable efficacy (~12% after 1 and 2 h). |
[419] |
| Bidens frondosa | ||||
| AP/ET (80%) | OGTT | 250 and 500 mg/kg BW OG / 7 days |
ET exhibited weak to moderate hypoglycaemic effects on normoglycemic rats at the tested doses. In OGTT, higher doses of the extract indicated significant inhibitory activities. The ET lowered BG levels in varying ratios. The body weight of the animals was not changed significantly during this experiment. | [421] |
| Healthy and STZ-induced diabetic rats. | ||||
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B1) | ||||
| Chamaemelum nobile (syn. Anthemis nobilis L. or Chamomilla nobilis) | ||||
| AP/AQ | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 20 mg/kg BW OG / 15 days. |
Single oral administration of AQ reduced BG levels in normal and STZ diabetic rats. BG levels were decreased in normal and STZ diabetic rats, respectively, after 15 days of treatment. | [462] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B7) | ||||
| Cichorium intybus | ||||
| R/AQ | ALLO-induced diabetic rat | 2.5, 5, 10, and 15 g DPM/kg OG / 2 weeks |
Treatment with 10 g/kg of the herbal mixture significantly lowered glycaemic values compared to the diabetic controls. The treatment with the highest tested concentration (15 g/kg) completely restored BG level to normoglycemic values in experimental groups. The lipid status of treated animals and serum AST, ALT, ALP, CRE, URE and MDA were completely normalised. The polyherbal mixture completely restored the histopathological changes in the liver, kidneys and hippocampus. | [469] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P1) | ||||
| WP/ET (80%) | STZ-induced diabetic rats (Male Sprague–Dawley rats) | 125 mg of plant extract/kg BW OG / 14 days |
Daily administration of ET (125 mg/kg) for 14 days to diabetic rats attenuated BG by 20%, TG by 91%, and tTC by 16%. | [466] |
| OGTT | ||||
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B8) | ||||
| R / AQ | STZ- niacinamide (NIA/STZ) induced diabetic rats | 125 mg/kg BW i. p. injections / 28 days. |
The extract prevented body-weight loss and decreased BG level. ALT activities and TG, TC and HbA1c levels decreased, and NO concentration increased in the chicory-treated groups. Unlike late-stage diabetes, fasting serum INS concentrations were higher, and the OGTT pattern was approximated to normal in chicory-treated early-stage diabetic rats. | [483] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B9) | ||||
| OGTT | ||||
| AP / CAE | Healthy rats. | 3, 15 or 30 mg/ kg i. p. injections / 4 days. |
The CAE can decrease BG without any effect hepatic effect. Daily i.p. administrations of CAE improve i.p. glucose tolerance in a dose-dependent manner, mainly via an INS sensitising effect. | [422] |
| OGTT | ||||
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B10) | ||||
| S / CQA-ET | Healthy rats. | Diet with CQA-ET FEE / 28 days |
The CQA-ET was found to decrease the atherogenic index to the level observed in the control rats’ group and to increase blood antioxidant status. Both dietary supplements reduced the content of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances in kidney and heart tissue compared with the experimental group. | [484] |
| High-fructose diets | ||||
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P2) | ||||
| Antioxidant status of rats (O3) | ||||
| NCRAE, SCCAM | STZ-induced diabetic rats | 15 mg/kg i. p. injections / 7 days. |
Both NCRAE and SCCAM can improve glucose tolerance in STZ diabetic rats after a subchronic administration of seven days. Alone, NCRAE significantly decreases the basal HYG after six days of treatment. | [427] |
| OGTT | ||||
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B11). | ||||
| Dittrichia viscosa subsp. iscosa (Syn. Inula viscosa) | ||||
| L / AuNPs | High-fat diet (HFD)/STZ-induced diabetes in rats | 2.5 mg/kg i. p. injections / 21 days. |
Treatment with AuNP significantly lowered the BG level, the gene expression, and the activity of hepatic PEPCK in comparison to the untreated diabetic group. The AuNPs synthesised can alleviate HYG in HFD/STZ-induced diabetes in rats by reducing hepatic gluconeogenesis by inhibiting the expression and activity of the hepatic PEPCK gene. | [485] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B12) | ||||
| AP / AQ | Normal and STZ-induced diabetes rats | 20 mg/kg OG / for 2 weeks. |
A significant reduction in BG levels 2 h was observed in normal rats after a single oral administration. Repeated daily oral administration significantly reduced BG levels after 4 days of treatment. In diabetic rats, a significant reduction in BG levels was observed 1 h after a single oral administration. Repeated oral administration reduced BG levels on the 4th day. No change in TC and TG levels was observed after a single and repeated oral administration in both normal and diabetic rats. Plasma INS levels and body weight remained unchanged after 15 days of repeated oral administration in normal and diabetic rats. |
[486] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B13) | ||||
| Galinsoga parviflora | ||||
| WP / HET 80% | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 400 mg/kg BW NI |
The extract reduced the BG level equivalent to GLIB (5 mg/kg BW) in diabetic rats. | [487] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B13) | ||||
| Lactuca serriola | ||||
| L / AQ | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 200 and 500 mg/kg BW OG / NI |
Both doses of extracts restored β -cell function and INS secretion. |
[488] |
| OGTT | ||||
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B14) | ||||
| Onopordum acanthium | ||||
| L / MET | STZ-induced diabetic rats | 200 and 400 mg/kg OG / 8 days |
Administration of extracts significantly increases INS content in β-cells with a marked enhancement of pancreatic islet structure, significantly reducing BG level and BW loss. Extract treatment suppressed the increase of inflammatory cell score in myocardial tissue with an M2–like macrophage elevation. | [489] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B15) | ||||
| Solidago virgaurea | ||||
| AP / HE | ALLO-induced diabetic rat. | 250 mg/kg BW OG 15 days |
Extract significantly reduced BG level, serum AMY activity, TNF-α level, and pancreatic MDA level, as well as increasing the serum INS, liver GLY level, pancreatic SOD, and CAT activities in comparison with their corresponding diabetic rats. | [490] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P3) | ||||
| Sonchus asper | ||||
| NI / ME | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 200 mg/kg 21 days |
The ME improve the activity of the antioxidant enzymes, TBARS contents, and cholesterol profile of the diabetic rats. DTR’s BG and INS levels were significantly lower in treatment than the diabetic rats on day 21. | [491] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P4) | ||||
| Sonchus oleraceus | ||||
| WP / ME | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 75, 150, 300 mg/Kg 14 days |
The Me (150 mg/Kg) treatment exhibited 39.40% glycaemia reduction. The measurement of stress markers in plasma, liver and kidney after ME administration showed a significant reduction in MDA and hydrogen peroxide levels, coupled with a substantial increase in CAT activity. | [492] |
| OGTT | ||||
| Antioxidant status of rats (O4) | ||||
| L / HET (90%) | STZ-induced diabetes in rats | 100, 200, 400 mg/kg/day BW 6 weeks |
HET significantly increased both SOD activity and GSH levels while causing a reduction of MDA levels in the liver. Moreover, HET ameliorates STZ-induced liver function and pathological damage. DTR fed with HET daily for 6 weeks showed significantly decreased levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in the liver. HET decreased MyD88, TGF-β, and TLR4 expression levels in the liver of DTR. | [493] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P5) | ||||
| L / HET (90%) | HFD/STZ-induced diabetes in rats | 100, 200, 400 mg/kg/day BW 6 weeks |
In DTR treated by HET (400 mg/kg/day for 6 weeks), TG, TC, and LDL-c were reduced by 43%, 22%, and 16%, respectively. Meanwhile, it was also found that daily feeding of DTR decreased plasma glucose levels by approximately 23%. DTR with HET at 400 mg/kg/day for 6 weeks show portal tract and mild fibrous expansion without sep inflammation formed of lymphocytes. The administration of HET exhibited a protective effect against the hepatic damage induced by STZ, which was also corroborated by the apparent condition and colour observed in HET-administered rats. | [436] |
| OGTT | ||||
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P6) | ||||
| L / ET (80%) | ALLO-induced diabetic rat. | 100, 200, and 300 mg/kg BW 56 days |
The treatment of SOE 200 and 300 mg/kg in diabetic rats for two months dramatically decreased BG, total lipid, TC, TG, and LDLc, while HDLc levels improved liver and kidney functions. The histological assay revealed that the treatment of SOE 300 mg/kg significantly improved the pancreas tissues. | [494] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P7) | ||||
| Lamiaceae | ||||
| Lavandula pedunculata | ||||
| FTO / AQ | Healthy Rats | 1 g/kg BW NI |
Acute and chronic oral administration of extract reduced the peak of the BG (30 min) and the area under the curve. The effect was at the same amplitude as the positive control Metformin. | [440] |
| Acute OGTT and Chronic | ||||
| OGTT for plant mixtures | ||||
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B13). | ||||
| Lavandula stoechas | ||||
| AP / EO | ALLO-induced diabetic rat. | 50 mg/kg BW i. p. injections / 15 days. |
Subacute EO administration prevented BW gain decline and protected against alloxan-induced increase in hepatic and renal relative weights. EO treatment corrected the BG level significantly, protected against lipoperoxidation and decreased (−SH) group levels, and reversed antioxidant enzyme depletion. Induced by alloxan treatment. Treatment with EO significantly protected against hepatic and renal dysfunctions and the disturbance of lipid metabolic parameters induced by alloxan treatment. |
[495] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B16). | ||||
| AP / EO | ALLO-induced diabetic rat | 50 mg and 160 mg/kg BW i. p. injections / 15 days |
EO treatment protects against decreased BW gain, relative reproductive organ weights, testosterone level, and sperm quality decline. EO treatment protects against oxidative damage to DTR’s male reproductive organ systems. | [496] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P8) | ||||
| R / ET (70%) | ALLO-induced diabetic rat. | 50, 100, and 150 mg/kg BW i. p. injections / NI |
The extract significantly reduced BG levels of DTR in a dose-dependent manner. | [497] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B13). | ||||
| NI / EO | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 0.05 ml DDR / 21 days |
The percentage of healing was highest in the EO group on Days 7, 14, and 21. Microscopic examination of the biopsies supported accelerated wound healing on Days 7 and 14. Reduced mononuclear cell density and increased hair follicle and adipose tissue development were observed in the T2DM-EO group on Day 7. On Day 14, the T2DM-EO group increased collagen levels and hair follicles. | [498] |
| Wound healing test | ||||
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P9) | ||||
| AP / AQ | ALLO-induced diabetic rat | 150 mg/kg OG / NI |
Oral extract administration reduced HYG induced by sucrose and starch in normal and diabetic rats. | [441] |
| OGTT | ||||
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B13). | ||||
| Melissa officinalis | ||||
| EO | db/db mice | 0.0125 mg EO/d FEE / 6 weeks |
Mice administered EO for 6 weeks showed significantly reduced BG (65 %; P < 0·05) and TG concentrations, improved glucose tolerance, as assessed by an OGTT, and significantly higher serum INS levels than the CGr. All the genes were significantly upregulated, whereas G6Pase and PEPCK expression was down-regulated in the livers of the EO group. | [499] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B17). | ||||
| OGTT | ||||
| L / ET | HFD C57BL/6 mice | 200 mg/kg/day FEE / 6 weeks |
The DTR revealed significantly reduced fasting BG concentrations (14% decrease versus vehicle). The extract showed no significant effects on FPIL. It significantly decreased the HFD-induced INS resistance by 35%. It reduced the HFD-provoked rise in fasting plasma concentrations of nonesterified FAs by 59% and plasma TAG gain by 66%. The extract-fed mice showed reduced plasma levels of LDL/VLDL-c (32% decrease) and a slight decrease in TC (8% decrease). The extract treatment led to an increase in the HDL/LDL ratio of 56%. |
[500] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B18). | ||||
| NI / EO | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 0.01, 0.02 and 0.04 mg/day FEE / 4 weeks |
EO at both high doses restored glycemia and reduced the BW of DTR compared to untreated diabetic animals. | [501] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B1). | ||||
| L / HAE | ALLO-induced diabetic rat. | 20, 100 or 500 mg/Kg BW OG / 4 weeks |
There was a significant decrease in blood sugar levels, TC, TG and LDL in DTR with HAE. An increase in HDL levels was observed in HAE-DTR. | [502] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B19). | ||||
| L / HE-EA (ALS-L1023) | HFD C57BL/6 mice | HFD supplemented with 0.4% (w/w) ALS-L1023 (HFD-ALS) FEE / 12 weeks |
Administration of ALS-L1023 to high-fat-diet-induced OMI caused reductions in BW gain, VFM, and VAS without changes in FC profiles. ALS-L1023 improved HYG, HYIN, BG and INIT and normalised INS-positive β-cell area in OMI. ALS-L1023 decreased hepatic LIA and concomitantly increased the expression of PPARα target genes responsible for fatty acid β-oxidation in livers. | [503] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P10) | ||||
| OGTT and IPITT | ||||
| L / HE / EA | Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty (OLETF) rats | HFD with 0.4% or 0.8% (w/w) of extract FEE / 4 weeks |
The EAE administration resulted in a BW reduction without changes in FI. It also markedly inhibited HYG and HYIN, restoring the β-cell mass severely impaired in OLETF rats. There was a decrease in LIA in the liver and skeletal muscle of the ORAT after treatment with EAE. After EAE treatment, the liver and skeletal muscle increases the expression levels of FAs-oxidizing enzymes (AMPKα2, ACOX, MCAD, and VLCAD). The EAE attenuated the pancreatic inflammation, including the infiltration of CD68-positive macrophages and mast cells, and attenuated the expression of inflammatory factors (IL-6 and CD68). | [504] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P111) | ||||
| Mentha aquatica | ||||
| L / AQ | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 50 mg, 100mg and 150mg OG / 90 days. |
FBG and HbA1c levels decreased in DTR. The BW and INS levels of DTR were significantly increased. The levels of TC TG were reduced, and the levels of HDL were significantly increased. The ALB of DTR were significantly increased. However, the levels of UR and CREA were decreased in DTR. TBARS/MDA level formation significantly decreased in DTR. The activities of CAT, SOD, GPx, and GST were increased in DTR. DTR at a dose of 100 mg/kg bw/day showed normal glomeruli, normal intertubular vessels, and tubular epithelial cells, indicating degenerative changes in the kidney. |
[505] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P12) | ||||
| Mentha pulegium | ||||
| AP / AQ | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 20 mg/kg BW OG / 15 days |
The AQE caused a significant reduction in BG levels in DTR. The morphometric analysis and histological sections realised in the pancreas and liver have shown the beneficial effect of AQE in the cellular population. According to OGTT, the AQE has improved glucose tolerance in normal rats. | [506] |
| OGTT | ||||
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P13) | ||||
| AP / AQ | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 20 mg/kg BW OG / 15 days |
The AQE alleviated hyperlipidemia in diabetic rats by lowering significantly the TC levels without affecting the TG levels significantly. It exerted some increasing activity on plasma HDL-c level. | [507] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B20). | ||||
| Mentha suaveolens | ||||
| AP / AQ | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 20 mg/kg BW OG / 15 days |
The AQE decrease the BG, TC and TG levels in both normal and diabetic rats. The AQE treatment was demonstrated to act positively on the liver and pancreas histopathological tissues. | [508] |
| OGTT | ||||
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P14) | ||||
| Origanum vulgare L. | ||||
| L / AQ | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 20 mg/kg OG / 2 weeks |
The AQE produced a significant decrease in BG levels in DTR. The BG levels were normalised from the fourth day after daily repeated oral administration of AQE. No changes in basal plasma INS concentrations were observed after treatment in either normal or DTR. | [509] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B4). | ||||
| L / AQ | STZ-induced diabetic rats | 20 mg/kg OG / 6 weeks |
Administration of AQE significantly decreased BG levels, HbA1c, and AMY in DTR. | [510] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B21). | ||||
| L / ME / AQ | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 5 mg/kg per day i. p. injections / 10 days |
ME reduced diabetes incidence and preserved normal insulin secretion. ME scavenged reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and alleviated the need to upregulate antioxidant enzymes. ME treatment attenuated the pro-inflammatory response mediated by T helper 17 cells. It enhanced anti-inflammatory T helper 2 and T regulatory cells by impacting specific signalling pathways and transcription factors. | [511] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P15) | ||||
| L / EtOAc | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 2 mg/mouse OG / 10 days |
EtOAc treatment significantly preserved pancreatic islets and reduced diabetes incidence in DTR. Besides the down-modulatory effect on macrophages, EtOAc reduced the number of total CD4+ and activated CD4+CD25+ T cells. EtOAc affected the number of T helper 1 (Th1) and T helper 17 (Th17) cells by downregulating their key transcription factors T-bet and RORγT. | [512] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P16) | ||||
| L / AQ | ALLO-induced diabetic rat. | 150 mg/kg, 300 mg/kg BW 300 mg/ kg Equal mixture (150 mg chamomile + 150 mg oregano) OG / 6 weeks |
Treatment with higher or lower doses or a mixture of extracts had significant weight gain, hypoglycemic effect, decreased AMY activity, and increased INS levels. Restoration of the renal profile and lipid profile with an increase in HDL-C and the reversal of Bax and Bcl-2 were well observed, with a 300 mg/kg mixture showing synergistic activity of the extracts compared to individual low doses of 150 mg/kg. | [513] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B22). | ||||
| L / HE | Glucose-induced-diabetic zebrafish | 10 μg/L FEE / 24H |
The BG level, TC and TG were significantly reduced in diabetic zebrafish treated. | [514] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B23). | ||||
| L / INF | ALLO-induced diabetic rat. | 55 mL OG / 40 days |
The INF reduced BG levels after the first day of treatment, compared to the diabetic CGr. The INF appears to stimulate INS secretion. | [515] |
| Measurement of biochemical parameters (B10). | ||||
| Prunella vulgaris | ||||
| WP / AQ | db/db mice HCF/HFD | 100 mg, 200mg/kg/day DR / 8 weeks |
AQE treatment markedly lowered BG and SBP. The CRE clearance was restored by treatment with AQE. The AQE markedly decreased TC, TG, LDL-c, MDA and TGFβ1 and increased HDL-c and NO levels. AQE ameliorated vascular relaxation of aortic rings by acetylcholine or SNP-inducement in a dose-dependent manner. AQE treatment significantly reduced the aortic expressions of ICAM-1, VCAM-1, ET-1, and nitrotyrosine. The expression of eNOS in aortic was increased by AQE treatment. | [516] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P17). | ||||
| Fr / HE / TAP | STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 50 mg/kg, 100mg/kg, 200 mg/kg of TAP OG / 6 weeks |
The BW and the levels of BG, FMN, MDA, NO, and the activity of NOS in serum decreased significantly compared with the STZ group in a dose-dependent manner. The activity of SOD in serum and BW increased significantly compared with the STZ group in a dose-dependent manner. The DTR showed a significant increase in SOD mRNA expression in pancreatic β cells. Histopathological examination also showed the protective effect of TAP on pancreatic β cells. | [517] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P18). | ||||
| HFOR / HE / AQ | Male CD-1 (ICR) mice / FFF | 8.02 g/kg OG / 10 weeks |
HEE could improve glucose intolerance and normalise the lipid profile. HEE provokes an increase in peripheral and hepatic INS sensitivity, a decrease in FAs level, enhanced GLUK activity and GLY content and improved serum antioxidant activity. Hepatic histopathological examination showed that HEE administration markedly decreased fatty deposits in the liver of mice. | [518] |
| OGTT and IPITT | ||||
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P19). | ||||
| IF / PV(HE) / CARF / CA / RA | ALLO-induced diabetic rat model. | 50, 100, 150 mg/kg i.p. injections / 8 weeks |
CARF reduced BG levels and improved in-vivo oxidative stress. CARF reduced HbA1c levels more significantly than PV and equivalent amounts of CA or RA. CARF had significantly increased serum-INS, ameliorated thermal hyperalgesia and tactile allodynia more significantly than the effects of PV and equivalent amounts of CA or RA. The tested compounds showed potential restoration of the lipid peroxide levels. | [458] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P20). | ||||
| WP / AQ | Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) STZ-induced diabetic rats. | 100 mg, 300mg/kg/day DR / 8 weeks |
In DTR, AQE significantly decreased BG and BUN and ameliorated plasma CRE. AQE reduced the PAS positivity staining intensity and basement membrane thickening in the glomeruli of DTR. | [519] |
| Measurement of physiological and biochemical parameters (P21). | ||||
3.2.2. Lamiaceae Family
- Lavandula stoechas
- Melissa officinalis
- Mentha sp.
- Origanum vulgare L.
- Prunella vulgaris
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maleki, V.; Jafari-Vayghan, H.; Saleh-Ghadimi, S.; Adibian, M.; Kheirouri, S.; Alizadeh, M. Effects of Royal Jelly on Metabolic Variables in Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. Complement Ther Med 2019, 43, 20–27. [CrossRef]
- ADA 15. Diabetes Advocacy: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, S152–S153. [CrossRef]
- Bełtowski, J.; Wójcicka, G.; Jamroz-Wiśniewska, A. Hydrogen Sulfide in the Regulation of Insulin Secretion and Insulin Sensitivity: Implications for the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. Biochem Pharmacol 2018, 149, 60–76. [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Gaglia, J.L.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; et al. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Am Diabetes Assoc 2022, 46, S19–S40. [CrossRef]
- Halim, M.; Halim, A. The Effects of Inflammation, Aging and Oxidative Stress on the Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus (Type 2 Diabetes). Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews 2019, 13, 1165–1172. [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, O.M. Molecular Pathways Associated with Oxidative Stress in Diabetes Mellitus. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 2018, 108, 656–662. [CrossRef]
- Asmat, U.; Abad, K.; Ismail, K. Diabetes Mellitus and Oxidative Stress—A Concise Review. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal 2016, 24, 547–553. [CrossRef]
- LeRoith, D. β-Cell Dysfunction and Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: Role of Metabolic and Genetic Abnormalities. American Journal of Medicine 2002, 113, 3–11. [CrossRef]
- Mooradian, A.D. Diabetes-Related Perturbations in the Integrity of Physiologic Barriers. J Diabetes Complications 2023, 37, 108552. [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Yu, M.G.; Li, Q.; Park, K.; King, G.L. Insulin’s Actions on Vascular Tissues: Physiological Effects and Pathophysiological Contributions to Vascular Complications of Diabetes. Mol Metab 2021, 52, 101236. [CrossRef]
- Cooper, S.A.; Whaley-Connell, A.; Habibi, J.; Wei, Y.; Lastra, G.; Manrique, C.; Stas, S.; Sowers, J.R. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Insulin Resistance. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2007, 293. [CrossRef]
- Rawshani, A.; Rawshani, A.; Franzén, S.; Eliasson, B.; Svensson, A.-M.; Miftaraj, M.; McGuire, D.K.; Sattar, N.; Rosengren, A.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S. Mortality and Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2017, 376, 1407–1418. [CrossRef]
- Nabrdalik, K.; Kwiendacz, H.; Moos, J.; Moos, Ł.; Kulpa, J.; Brzoza, Z.; Stompór, T.; Gumprecht, J.; Lip, G.Y.H. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Is Associated With Diabetic Kidney Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: The Silesia Diabetes-Heart Project. Curr Probl Cardiol 2023, 48, 101726. [CrossRef]
- Koulis, C.; Watson, A.M.D.; Gray, S.P.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K.A. Linking RAGE and Nox in Diabetic Micro- and Macrovascular Complications. Diabetes Metab 2015, 41, 272–281. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, W.; Ji, Q.; Ran, X.; Kuang, H.; Yu, X.; Fang, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Xue, Y.; et al. Prevalence of Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study in Mainland China. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2023, 198, 110602. [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimpour, S.; Zakeri, M.; Esmaeili, A. Crosstalk between Obesity, Diabetes, and Alzheimer’s Disease: Introducing Quercetin as an Effective Triple Herbal Medicine. Ageing Res Rev 2020, 62, 101095. [CrossRef]
- The International Diabetes Federation IDF Diabetes Atlas; 2021.
- World Health Organisation Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/diabetes#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 23 July 2023).
- SNS Servico National de Saude-Diabetes. Available online: https://www.sns.gov.pt/noticias/2018/05/14/diabetes/ (accessed on 23 July 2023).
- Soares, A.R.; Coelho, M.; Tracey, M.; Carvalho, D.; Silva-Nunes, J. Epidemiological, Social and Economic Burden of Severe Hypoglycaemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus in Portugal: A Structured Literature Review. Diabetes Therapy 2023, 14, 265. [CrossRef]
- João Filipe, R. Diabetes: Factos e Números 2016, 2017 e 2018. Revista Portuguesa de Diabetes 2020, 15, 19–27.
- Kyrou, I.; Tsigos, C.; Mavrogianni, C.; Cardon, G.; Van Stappen, V.; Latomme, J.; Kivelä, J.; Wikström, K.; Tsochev, K.; Nanasi, A.; et al. Sociodemographic and Lifestyle-Related Risk Factors for Identifying Vulnerable Groups for Type 2 Diabetes: A Narrative Review with Emphasis on Data from Europe. BMC Endocr Disord 2020, 20, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Ojo, O.A.; Ibrahim, H.S.; Rotimi, D.E.; Ogunlakin, A.D.; Ojo, A.B. Diabetes Mellitus: From Molecular Mechanism to Pathophysiology and Pharmacology. Med Nov Technol Devices 2023, 19, 100247. [CrossRef]
- Wołos-Kłosowicz, K.; Bandurska-Stankiewicz, E. Effects of Common Weight Loss Plans on Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Prim Care Diabetes 2022, 16, 252–256. [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; E., M.; Yu, S. A Meta-Analysis of Passive Smoking and Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2015, 107, 9–14. [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.J.; Hu, H.Y.; Lee, Y.L.; Ko, M.C.; Ku, P.W.; Yen, Y.F.; Chu, D. Frequency of Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Clinical Nutrition 2019, 38, 1368–1372. [CrossRef]
- The Lancet Type 2 Diabetes: The Urgent Need to Protect Young People. The Lancet 2018, 392, 2325. [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, M.S.; Cabieses, B.; Repetto, P. Type 2 Diabetes in Young People: Adding Socioeconomic Inequality to the Discussion. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2019, 156, 107795. [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.D.; Zhao, Y.; Patel, R.; Patao, C.; Malik, S.; Bertoni, A.G.; Correa, A.; Folsom, A.R.; Kachroo, S.; Mukherjee, J.; et al. Cardiovascular Risk Factor Targets and Cardiovascular Disease Event Risk in Diabetes: A Pooling Project of the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study, Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis, and Jackson Heart Study. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 668–676. [CrossRef]
- Meeks, K.A.C.; Freitas-Da-Silva, D.; Adeyemo, A.; Beune, E.J.A.J.; Modesti, P.A.; Stronks, K.; Zafarmand, M.H.; Agyemang, C. Disparities in Type 2 Diabetes Prevalence among Ethnic Minority Groups Resident in Europe: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Intern Emerg Med 2016, 11, 327–340. [CrossRef]
- 2020; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Diabetes Statistics Report; Atlanta, 2020.
- Ciarambino, T.; Crispino, P.; Leto, G.; Mastrolorenzo, E.; Para, O.; Giordano, M. Influence of Gender in Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complication. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 8850. [CrossRef]
- Kautzky-Willer, A.; Leutner, M.; Harreiter, J. Sex Differences in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetologia 2023 66:6 2023, 66, 986–1002. [CrossRef]
- Gerdts, E.; medicine, V.R.-Z.-N.; 2019, undefined Sex Differences in Cardiometabolic Disorders. nature.comE Gerdts, V Regitz-ZagrosekNature medicine, 2019•nature.com 2019, 25, 1657–1666. [CrossRef]
- Tramunt, B.; Smati, S.; Grandgeorge, N.; Lenfant, F.; Arnal, J.F.; Montagner, A.; Gourdy, P. Sex Differences in Metabolic Regulation and Diabetes Susceptibility. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 453–461. [CrossRef]
- Geer, E.B.; Shen, W. Gender Differences in Insulin Resistance, Body Composition, and Energy Balance. Gend Med 2009, 6, 60–75. [CrossRef]
- Christen, T.; Trompet, S.; Noordam, R.; van Klinken, J.B.; van Dijk, K.W.; Lamb, H.J.; Cobbaert, C.M.; den Heijer, M.; Jazet, I.M.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Sex Differences in Body Fat Distribution Are Related to Sex Differences in Serum Leptin and Adiponectin. Peptides (N.Y.) 2018, 107, 25–31. [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Senthil Kumar, S.P.D. Sex Differences in Obesity-Related Glucose Intolerance and Insulin Resistance. Glucose Tolerance 2012. [CrossRef]
- Palmisano, B.T.; Zhu, L.; Eckel, R.H.; Stafford, J.M. Sex Differences in Lipid and Lipoprotein Metabolism. Mol Metab 2018, 15, 45–55. [CrossRef]
- Colditz, G.A.; Willett, W.C.; Rotnitzky, A.; Manson, J.E. Weight Gain as a Risk Factor for Clinical Diabetes Mellitus in Women. Ann Intern Med 1995, 122, 481–486. [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Gastaldelli, A.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Scherer, P.E. Why Does Obesity Cause Diabetes? Cell Metab 2022, 34, 11–20. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Xie, J.; medicine, X.Y.-D.; 2013, undefined Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes and Pre-diabetes among Overweight or Obese Children in Tianjin, China. Wiley Online LibraryH Zhu, X Zhang, MZ Li, J Xie, XL YangDiabetic medicine, 2013•Wiley Online Library 2013, 30, 1457–1465. [CrossRef]
- He, Q.X.; Zhao, L.; Tong, J.S.; Liang, X.Y.; Li, R.N.; Zhang, P.; Liang, X.H. The Impact of Obesity Epidemic on Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Prim Care Diabetes 2022, 16, 736–744. [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Faisal, H.; Mamoon, R.; Thomas, B.; Mohammed, A.; Winnie, W.; Kolawole Adeshina, K.; Rajjit, S.; Michael, J.; Shamly, A. Evaluation of Fucoxanthin Content in Popular Weight Loss Supplements: The Case for Stricter Regulation of Dietary Supplements. J Obes Weight Loss Medicat 2019, 5. [CrossRef]
- 2022; North Dakota Century Code 23-01-40 North Dakota 2022 Diabetes Report; 2022.
- Word Health Organization Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 23 July 2023).
- Aras, M.; Tchang, B.G.; Pape, J. Obesity and Diabetes. Nursing Clinics of North America 2021, 56, 527–541. [CrossRef]
- North Dakota Century Code Health and Safety Chapter 23-01, Section 23-01-40, Diabetes Goals and Plans.; 2022.
- The, N.; Richardson, A.; Care, P.G.-L.-D.; 2013, undefined Timing and Duration of Obesity in Relation to Diabetes: Findings from an Ethnically Diverse, Nationally Representative Sample. Am Diabetes AssocNS The, AS Richardson, P Gordon-LarsenDiabetes Care, 2013•Am Diabetes Assoc 2001, 36, 865–872. [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, M.; Bentham, J.; Stevens, G.A.; Zhou, B.; Danaei, G.; Lu, Y.; Bixby, H.; Cowan, M.J.; Riley, L.M.; Hajifathalian, K.; et al. Trends in Adult Body-Mass Index in 200 Countries from 1975 to 2014: A Pooled Analysis of 1698 Population-Based Measurement Studies with 19·2 Million Participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1377–1396. [CrossRef]
- Power, C.; care, C.T.-D.; 2011, undefined Changes in BMI, Duration of Overweight and Obesity, and Glucose Metabolism: 45 Years of Follow-up of a Birth Cohort. Am Diabetes AssocC Power, C ThomasDiabetes care, 2011•Am Diabetes Assoc 2011, 34. [CrossRef]
- Dandona, P.; Aljada, A. A Rational Approach to Pathogenesis and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis. American Journal of Cardiology 2002, 90, 27–33. [CrossRef]
- Incalza, M.A.; D’Oria, R.; Natalicchio, A.; Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. Oxidative Stress and Reactive Oxygen Species in Endothelial Dysfunction Associated with Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases. Vascul Pharmacol 2018, 100, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Hopps, E.; Noto, D.; Caimi, G.; Averna, M.R. A Novel Component of the Metabolic Syndrome: The Oxidative Stress. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2010, 20, 72–77. [CrossRef]
- Salas-Salvadó, J.; Martinez-González, M.Á.; Bulló, M.; Ros, E. The Role of Diet in the Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases 2011, 21. [CrossRef]
- Testa, R.; Bonfigli, A.R.; Prattichizzo, F.; La Sala, L.; De Nigris, V.; Ceriello, A. The “Metabolic Memory” Theory and the Early Treatment of Hyperglycemia in Prevention of Diabetic Complications. Nutrients 2017, 9. [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Ni, H.; Wu, M.; Tang, Z.; Halim, M.; Shi, D. ROS-Mediated Glucose Metabolic Reprogram Induces Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2016, 476, 204–211. [CrossRef]
- Nita, M.; Grzybowski, A. The Role of the Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Stress in the Pathomechanism of the Age-Related Ocular Diseases and Other Pathologies of the Anterior and Posterior Eye Segments in Adults. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Rolo, A.P.; Palmeira, C.M. Diabetes and Mitochondrial Function: Role of Hyperglycemia and Oxidative Stress. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2006, 212, 167–178. [CrossRef]
- Luca, P. Pros and Cons of Selective Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase-2 versus Dual/Cyclooxygenase Inhibition: Is Two Better than One? J Rheumatol 2001, 28, 2375–2382.
- Hakim, J. Reactive Oxygen Species and Inflammation. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil 1993, 187, 286–295. [CrossRef]
- Pickup, J.C. Inflammation and Activated Innate Immunity in the Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 813–823. [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association 5. Prevention or Delay of Type 2 Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, S51–S54. [CrossRef]
- Raptis, S.A.; Dimitriadis, G.D. Oral Hypoglycemic Agents: Insulin Secretagogues, α-Glucosidase Inhibitors and Insulin Sensitizers. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology and Diabetes 2001, 109. [CrossRef]
- Sudhir, R.; Mohan, V. Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Treat Endocrinol 2002, 1, 105–116. [CrossRef]
- Chehade, J.M.; Mooradian, A.D. A Rational Approach to Drug Therapy of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Drugs 2000, 60, 95–113. [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, M.T. Current Therapeutic Options in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Practical Approach. Clin Med Res 2003, 1, 189–200. [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R. Oral and Injectable (Non-Insulin) Pharmacological Agents for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Endotext 2022.
- McFarlane, S.I. Insulin Therapy and Type 2 Diabetes: Management of Weight Gain. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension 2009, 11, 601. [CrossRef]
- Chentli, F.; Azzoug, S.; Mahgoun, S. Diabetes Mellitus in Elderly. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 2015, 19, 744–752. [CrossRef]
- Bastaki, S. Diabetes Mellitus and Its Treatment. International Journal of Diabetes and Metabolism 2005, 13, 111–134. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Tripathi, P.; Pandey, R.; Srivatava, R.; Goswami, S. Alternative Therapies Useful in the Management of Diabetes: A Systematic Review. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 2011, 3, 504–512. [CrossRef]
- Gurib-Fakim, A. Medicinal Plants: Traditions of Yesterday and Drugs of Tomorrow. Mol Aspects Med 2006, 27, 1–93. [CrossRef]
- Kouretas, D.; Skaperda, Z.; Wu, P.; Wang, X. Natural Drugs: A New Direction for the Prevention and Treatment of Diabetes. Molecules 2023, Vol. 28, Page 5525 2023, 28, 5525. [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, B.; Sahoo, N.; Sahoo, S.K. Trends in Diabetes Care with Special Emphasis to Medicinal Plants: Advancement and Treatment. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 2021, 33, 102014. [CrossRef]
- Shabab, S.; Gholamnezhad, Z.; Mahmoudabady, M. Protective Effects of Medicinal Plant against Diabetes Induced Cardiac Disorder: A Review. J Ethnopharmacol 2021, 265, 113328. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Ma, Q.; Ye, L.; Piao, G. The Traditional Medicine and Modern Medicine from Natural Products. Molecules 2016, 21. [CrossRef]
- Swamy, M.K.; Sinniah, U.R. Patchouli (Pogostemon Cablin Benth.): Botany, Agrotechnology and Biotechnological Aspects. Ind Crops Prod 2016, 87, 161–176. [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Swamy, M.; Sinniah, U.; Molecules, M.A.-; 2017, undefined Leptadenia Reticulata (Retz.) Wight & Arn. (Jivanti): Botanical, Agronomical, Phytochemical, Pharmacological, and Biotechnological Aspects. mdpi.comSK Mohanty, MK Swamy, UR Sinniah, M AnuradhaMolecules, 2017•mdpi.com 2017, 22. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Bansal, A.; Singh, V.; Chopra, T.; Poddar, J. Flavonoids, Alkaloids and Terpenoids: A New Hope for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. J Diabetes Metab Disord 2022, 21, 941. [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, H.; Pandey, M.; Hua, C.K.; Mun, C.S.; Jing, J.K.; Kong, L.; Ern, L.Y.; Ashraf, N.A.; Kit, S.W.; Yee, T.S.; et al. An Update on Natural Compounds in the Remedy of Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. J Tradit Complement Med 2018, 8, 361. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gnanaraj, C.; Arulselvan, P.; El-Seedi, H.; Teng, H. A Review on Advanced Microencapsulation Technology to Enhance Bioavailability of Phenolic Compounds: Based on Its Activity in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Trends Food Sci Technol 2019, 85, 149–162. [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghipour, I.; Nasimi Shad, A.; Askari, V.R.; Maharati, A.; Baradaran Rahimi, V. How Caffeic Acid and Its Derivatives Combat Diabetes and Its Complications: A Systematic Review. J Funct Foods 2023, 110, 105862. [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Ata, A.; Kumar, N.V.A.; Sharopov, F.; Ramírez-Alarcón, K.; Ruiz-Ortega, A.; Ayatollahi, S.A.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Kobarfard, F.; Zakaria, Z.A.; et al. Antidiabetic Potential of Medicinal Plants and Their Active Components. Biomolecules 2019, 9. [CrossRef]
- Khan, V.; Najmi, A.K.; Akhtar, M.; Aqil, M.; Mujeeb, M.; Pillai, K.K. A Pharmacological Appraisal of Medicinal Plants with Antidiabetic Potential. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 2012, 4, 27. [CrossRef]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Heinrich, M.; Atanasov, A.G. Ethnopharmacology-A Bibliometric Analysis of a Field of Research Meandering between Medicine and Food Science? Front Pharmacol 2018, 9, 347011. [CrossRef]
- Weckerle, C.S.; de Boer, H.J.; Puri, R.K.; van Andel, T.; Bussmann, R.W.; Leonti, M. Recommended Standards for Conducting and Reporting Ethnopharmacological Field Studies. J Ethnopharmacol 2018, 210, 125–132. [CrossRef]
- Jansen, Jan. Geobotanical Guide of the Serra Da Estrela. 2002, 0–276.
- Vieira, G.; Jansen, J. Environmental Setting of the Serra Da Estrela, Portugal: A Short-Note. In; T. Pinto Correia, R.G.H. Bunce, D.C. Howard, Eds.; UK, 2005 ISBN 9780954713003.
- Pedro Pacheco Marques Serra Da Estrela: Management and Conservation of Priority Habitats; Associação.; Gráfica do Tortosendo, Lda: Rua do Fundo do Povo, 51-53 – 6215-399 Paul - Portugal, 2006.
- Alexandre, S.; Catarina, M.; Claudia, D.; Fatima, S.J.C.L.S.T.B. Plantas Aromáticas e Medicinais Do Parque Natural Da Serra Da Estrela : Guia Etnobotânico. 2011.
- da Cunha, A.P.; José Alves Ribeiro; Odete Rodrigues Roque. Plantas Aromáticas Em Portugal: Caracterização e Utilizações. ; 2007.
- Fernandes, R.B. Fernandes, R.B. (1992). As Explorações Botânicas Do Instituto Botânico Da Universidade de Coimbra No Parque Natural Da Serra Da Estrela Nos Últimos 50 Anos. Anu. Soc. Brot. 1992, 58, 1–12.
- Jansen, J. Stands of Cytisus Oromediterraneus in the Serra Da Estrela, with Some Remarks on the Habitats of the Bluethroat (Luscinia Svecica Cyanecula). 11 Seminário Técnico Conservaçao da Natureza na Serra da Estrela, Parque Natural da Serra da Estrela, Manteigas 1994.
- Boa, V.; Coelho, H. 1 ; Amaro, C.; 1 ; Castanheira, I. 1 ; Delgado, F. 1 ; Jacinto, P. 1 ; Oliveira, M.R.; Caldeira, R.E. 1 Inventariação e Propagação de Thymus Mastichina Na Beira Interior. II Congresso Nacional de Plnatas Aromáticas e Medicinais, Gerês, 28 a 29 de Setembro de 2007 2007, 46–51.
- Gil, C.; Duarte, A.P. Antioxidant Activity of Extracts of Portuguese Shrubs: Pterospartum Tridentatum, Cytisus Scoparius and Erica Spp. Article in Journal of Medicinal Plants Research 2009.
- Carocho, M.; Barros, L.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Calhelha, R.C.; Soković, M.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.; Buelga, C.S.; Morales, P.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Basil as Functional and Preserving Ingredient in “Serra Da Estrela” Cheese. Food Chem 2016, 207, 51–59. [CrossRef]
- Carocho, M.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Antonio, A.L.; Bento, A.; Morales, P.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. The Incorporation of Plant Materials in “Serra Da Estrela” Cheese Improves Antioxidant Activity without Changing the Fatty Acid Profile and Visual Appearance. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology 2015, 117, 1607–1614. [CrossRef]
- Mora, C. A Synthetic Map of the Climatopes of the Serra Da Estrela (Portugal). J Maps 2010, 6, 591–608. [CrossRef]
- Presidência do Conselho de Ministros Resolução Do Conselho de Ministros 76/2000 Proposto Para Integrar o Sítio “Serra Da Estrela” a Rede Natura 2000,; 1976.
- Ministério do Ambiente Decreto Regulamentar 50/97, Reclassifica o Parque Natural Da Serra Da Estrela. Available online: https://dre.tretas.org/dre/88089/decreto-regulamentar-50-97-de-20-de-novembro (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- CISE Centro de Interpretação Da Serra Da Estrela Available online: http://www.cise.pt/pt/index.php/cise/missao (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Presidência do Conselho de Ministros Resolução Do Conselho de Ministros n.o 76/00 Proposto Para Integrar o Sítio “Serra Da Estrela” a Rede Natura 2000,; 2000;
- Jansen, J.; Sequeire, M.P.S.M. The Vegetation of Shallow Waters and Seasonally Inundated Habitats (Littorelletea and Isoeto-Nanojuncetea) in the Higher Parts of the Serra Da Estrela. Mitteilungen des Badischen Landesvereins fur Naturkunde. 1999, 17, 449–462.
- Cesargarcia; Ceciliasérgio; Janjansen, & The Bryophyte Flora of the Natural Park of Serra Da Estrela (Portugal): Conservation and Biogeographical Approaches. 2008, 29, 49–73.
- Daveau, S.; Coelho, C., V.C.; Carvalho, L. Repartition et Rythme Des Precipitations Au Portugal; DAVEAU, D., Ed.; Mem. CEG.; Lisbon, 1977; Vol. 3.
- Google Maps Serra Da Estrela Available online: https://www.google.com/maps/place/Serra+da+Estrela/@40.32303,-7.5960533,15z/data=!3m1!4b1!4m6!3m5!1s0xd3d28a0408be839:0x1d00ebbed2102ce0!8m2!3d40.3230306!4d-7.5960533!16zL20vMDNqdHNw?entry=ttu (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- WCVP The World Checklist of Vascular Plants. Available online: https://powo.science.kew.org/about-wcvp (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Sociedade Portuguesa de Botânica Flora-On. Available online: https://flora-on.pt/ (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- INaturalist INaturalist. Available online: https://www.inaturalist.org/pages/what+is+it (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- IPCC Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/ (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Adler, C.; Huggel, C.; Orlove, B.; Nolin, A. Climate Change in the Mountain Cryosphere: Impacts and Responses. Reg Environ Change 2019, 19, 1225–1228. [CrossRef]
- Abram, N.J.; Henley, B.J.; Gupta, A. Sen; Lippmann, T.J.R.; Clarke, H.; Dowdy, A.J.; Sharples, J.J.; Nolan, R.H.; Zhang, T.; Wooster, M.J.; et al. Connections of Climate Change and Variability to Large and Extreme Forest Fires in Southeast Australia. Commun Earth Environ 2021, 2. [CrossRef]
- Albrich, K.; Rammer, W.; Seidl, R. Climate Change Causes Critical Transitions and Irreversible Alterations of Mountain Forests. Glob Chang Biol 2020, 26, 4013–4027. [CrossRef]
- Körner, C. Mountain Ecosystems in a Changing Environment. Eco Mont 2014, 6, 71–77. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Badola, R.; Chettri, N.; Chaudhary, R.P.; Zomer, R.; Pokhrel, B.; Hussain, S.A.; Pradhan, S.; Pradhan, R. Sustaining Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services in the Hindu Kush Himalaya. The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment: Mountains, Climate Change, Sustainability and People 2019, 127–165. [CrossRef]
- The Royal Botanic Gardens, K. Plants of the World Online Available online: https://powo.science.kew.org/results?q=Prunella%20vulgaris (accessed on 7 December 2023).
- Cabral, C.; Cavaleiro, C.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Cruz, M.T.; Lopes, M.C.; Salgueiro, L. Otanthus Maritimus (L.) Hoffmanns. & Link as a Source of a Bioactive and Fragrant Oil. Ind Crops Prod 2013, 43, 484–489. [CrossRef]
- Kenny, O.; Smyth, T.J.; Walsh, D.; Kelleher, C.T.; Hewage, C.M.; Brunton, N.P. Investigating the Potential of Under-Utilised Plants from the Asteraceae Family as a Source of Natural Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Extracts. Food Chem 2014, 161, 79–86. [CrossRef]
- Simpson, M.G. Diversity and Classification of Flowering Plants: Eudicots. Plant Systematics 2010, 275–448. [CrossRef]
- Broholm, S.K.; Teeri, T.H.; Elomaa, P. Molecular Control of Inflorescence Development in Asteraceae. Adv Bot Res 2014, 72, 297–333. [CrossRef]
- Harris, E.M. Inflorescence and Floral Ontogeny in Asteraceae: A Syn (Doctoral Dissertation, Thesis of Historical and Current Concepts. Botanical Review 1995, 61, 93–278.
- Mohanta, Y.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Nongbet, A.; Chakrabartty, I.; Mahanta, S.; Sarma, B.; Panda, J.; Panda, S.K. Potential Use of the Asteraceae Family as a Cure for Diabetes: A Review of Ethnopharmacology to Modern Day Drug and Nutraceuticals Developments. Front Pharmacol 2023, 14, 1153600. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Barral, M.; Carpena, M.; Gullón, P.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Otero, P.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Traditional Plants from Asteraceae Family as Potential Candidates for Functional Food Industry. Food Funct 2021, 12, 2850–2873. [CrossRef]
- Woldeamanuel, M.M.; Geda, M.K.; Mohapatra, S.; Bastia, T.K.; Rath, P.; Panda, A.K. Ethnobotanical Study of Endemic and Non-Endemic Medicinal Plants Used by Indigenous People in Environs of Gullele Botanical Garden Addis Ababa, Central Ethiopia: A Major Focus on Asteraceae Family. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Michel, J.; Abd Rani, N.Z.; Husain, K. A Review on the Potential Use of Medicinal Plants From Asteraceae and Lamiaceae Plant Family in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11. [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Da Silva, L.C.N.; Sahal, D.; Leonti, M. Editorial: Ethnopharmacological Studies for the Development of Drugs with Special Reference to Asteraceae. Front Pharmacol 2019, 10. [CrossRef]
- Bessada, S.M.F.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Asteraceae Species with Most Prominent Bioactivity and Their Potential Applications: A Review. Ind Crops Prod 2015, 76, 604–615. [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Luyten, W. Antiparasitic Activity in Asteraceae with Special Attention to Ethnobotanical Use by the Tribes of Odisha, India. Parasite 2018, 25. [CrossRef]
- Devkota, H.P.; Aftab, T. Medicinal Plants of the Asteraceae Family: Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activities. Medicinal Plants of the Asteraceae Family: Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activities 2022, 1–230. [CrossRef]
- Mouhid, L.; Gómez De Cedrón, M.; Vargas, T.; García-Carrascosa, E.; Herranz, N.; García-Risco, M.; Reglero, G.; Fornari, T.; De Molina, A.R. Identification of Antitumoral Agents against Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells from Asteraceae and Lamiaceae Plant Extracts. BMC Complement Altern Med 2018, 18. [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, H.; Matos, F.J.A. Plantas Medicinais No Brasil: Nativas e Exoticas; Instituto Plantarum, Ed.; 2002.
- Petlevski, R.; Hadžija, M.; Slijepčevič, M.; Juretič, D. Effect of “antidiabetis” Herbal Preparation on Serum Glucose and Fructosamine in NOD Mice. J Ethnopharmacol 2001, 75, 181–184. [CrossRef]
- Paradise, L. Homeopathic Pharmaceutical Compositions; 1998.
- Chaachouay, N.; Benkhnigue, O.; Fadli, M.; Ibaoui, H. El; Zidane, L. Ethnobotanical and Ethnopharmacological Studies of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Used in the Treatment of Metabolic Diseases in the Moroccan Rif. cell.comN Chaachouay, O Benkhnigue, M Fadli, H El Ibaoui, L ZidaneHeliyon, 2019•cell.com 2017. [CrossRef]
- Wazaify, M.; Afifi, F.; El-Khateeb, M.; Ajlouni, K. Complementary and Alternative Medicine Use among Jordanian Patients with Diabetes. Complement Ther Clin Pract 2011, 17, 71–75.
- Dei Cas, L.; Pugni, F.; Fico, G. Tradition of Use on Medicinal Species in Valfurva (Sondrio, Italy). J Ethnopharmacol 2015, 163, 113–134. [CrossRef]
- Errajraji, A.; Ouhdouch, F.; El-Anssari, N. Usage Des Plantes Médicinales Dans Le Traitement Du Diabète de Type 2 Au Maroc: Use of Medicinal Plants for Type 2 Diabetes Treatment, in Morocco. Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques 2010, 4, 301–304. [CrossRef]
- Trojan-Rodrigues, M.; Alves, T.L.S.; Soares, G.L.G.; Ritter, M.R. Plants Used as Antidiabetics in Popular Medicine in Rio Grande Do Sul, Southern Brazil. J Ethnopharmacol 2012, 139, 155–163. [CrossRef]
- Pullaiah, T. Encyclopedia of World Medicinal Plants; Regency Publication.; 2006.
- Móricz, Á.M.; Ott, P.G.; Häbe, T.T.; Darcsi, A.; Böszörményi, A.; Alberti, Á.; Krüzselyi, D.; Csontos, P.; Béni, S.; Morlock, G.E. Effect-Directed Discovery of Bioactive Compounds Followed by Highly Targeted Characterization, Isolation and Identification, Exemplarily Shown for Solidago Virgaurea. Anal Chem 2016, 88, 8202–8209. [CrossRef]
- Kamau, L.N.; Mbaabu, M.P.; Mbaria, J.M.; Karuri, G.P.; Kiama, S.G. Knowledge and Demand for Medicinal Plants Used in the Treatment and Management of Diabetes in Nyeri County, Kenya. J Ethnopharmacol 2016, 189, 218–229. [CrossRef]
- Cornara, L.; La Rocca, A.; Marsili, S.; Mariotti, M.G. Traditional Uses of Plants in the Eastern Riviera (Liguria, Italy). J Ethnopharmacol 2009, 125, 16–30. [CrossRef]
- Benkhnigue, O.; Akka, B.; Salhi, S.; Fadli, M.; Douira, A.; Zidane, L. Catalogue Des Plantes Médicinales Utilisées Dans Le Traitement Du Diabète Dans La Région d’Al Haouz-Rhamna (Maroc). m.elewa.orgO Benkhnigue, FB Akka, S Salhi, M Fadli, A Douira, L ZidaneJ Anim Plant Sci, 2014•m.elewa.org 2014, 23, 3539–3568.
- Tamokou, J. de D.; Mbaveng, A.T.; Kuete, V. Antimicrobial Activities of African Medicinal Spices and Vegetables. Medicinal Spices and Vegetables from Africa: Therapeutic Potential Against Metabolic, Inflammatory, Infectious and Systemic Diseases 2017, 207–237. [CrossRef]
- Simpson, M.G. Diversity and Classification of Flowering Plants: Eudicots. Plant Systematics 2019, 285–466. [CrossRef]
- Kokkini, S.; Karousou, R.; Hanlidou, E. HERBS | Herbs of the Labiatae. Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition 2003, 3082–3090. [CrossRef]
- Etsassala, N.G.E.R.; Hussein, A.A.; Nchu, F. Potential Application of Some Lamiaceae Species in the Management of Diabetes. Plants 2021, Vol. 10, Page 279 2021, 10, 279. [CrossRef]
- Ghourri, M.; Zidane, L.; Douira, A. Catalogue Des Plantes Médicinales Utilisées Dans Le Traitement de La Lithiase Rénale Dans La Province de Tan-Tan (Maroc Saharien). Int J Biol Chem Sci 2014, 7, 1688. [CrossRef]
- Skalli, S.; Hassikou, R.; Arahou, M. An Ethnobotanical Survey of Medicinal Plants Used for Diabetes Treatment in Rabat, Morocco. Heliyon 2019, 5. [CrossRef]
- Idm’hand, E.; Msanda, F.; Cherifi, K. Ethnopharmacological Review of Medicinal Plants Used to Manage Diabetes in Morocco. Clinical Phytoscience 2020 6:1 2020, 6, 1–32. [CrossRef]
- Arifah, F.H.; Nugroho, A.E.; Rohman, A.; Sujarwo, W. A Review of Medicinal Plants for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: The Case of Indonesia. South African Journal of Botany 2022, 149, 537–558. [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, A.; El-Hilaly, J.; Israili, Z.H.; Lyoussi, B. Ethnopharmacological Survey of Plants Used in the Traditional Treatment of Hypertension and Diabetes in South-Eastern Morocco (Errachidia Province). J Ethnopharmacol 2007, 110, 105–117. [CrossRef]
- Eddouks, M.; Ajebli, M.; Hebi, M. Ethnopharmacological Survey of Medicinal Plants Used in Daraa-Tafilalet Region (Province of Errachidia), Morocco. J Ethnopharmacol 2017, 198, 516–530. [CrossRef]
- Ziyyat, A.; Legssyer, A.; Mekhfi, H.; Dassouli, A.; Serhrouchni, M.; Benjelloun, W. Phytotherapy of Hypertension and Diabetes in Oriental Morocco. J Ethnopharmacol 1997, 58, 45–54. [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Cetto, A.; Heinrich, M. Mexican Plants with Hypoglycaemic Effect Used in the Treatment of Diabetes. J Ethnopharmacol 2005, 99, 325–348. [CrossRef]
- Mahomoodally, M.F.; Mootoosamy, A.; Wambugu, S. Traditional Therapies Used to Manage Diabetes and Related Complications in Mauritius: A Comparative Ethnoreligious Study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Cheung, H.Y.; Zhang, Q.F. Enhanced Analysis of Triterpenes, Flavonoids and Phenolic Compounds in Prunella Vulgaris L. by Capillary Zone Electrophoresis with the Addition of Running Buffer Modifiers. J Chromatogr A 2008, 1213, 231–238. [CrossRef]
- Orch, H.; Douira, A.; Zidane, L. Étude Ethnobotanique Des Plantes Médicinales Utilisées Dans Le Traitement Du Diabète, et Des Maladies Cardiaques Dans La Région d’Izarène (Nord Du Maroc). J Appl Biosci 2015, 86, 7940. [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Liu, H.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y. Study on the Mechanism of Prunella Vulgaris L on Diabetes Mellitus Complicated with Hypertension Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analyses. J Diabetes Res 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Sokovic, M.; Marin, P.D.; Brkic, D.; Griensven, L.J.L.D. van Chemical Composition and Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oils against Human Pathogenic Bacteria. Food 2008, 1, 220–226.
- Nadon, B.; Jackson, S. The Polyploid Origins of Crop Genomes and Their Implications: A Case Study in Legumes. Advances in Agronomy 2020, 159, 275–313. [CrossRef]
- Harris, S. TROPICAL FORESTS | Woody Legumes (Excluding Acacias). Encyclopedia of Forest Sciences 2004, 1793–1797. [CrossRef]
- Tekdal, D. Plant Genes for Abiotic Stress in Legumes. Abiotic Stress and Legumes: Tolerance and Management 2021, 291–301. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Bamboriya, S.D.; Rani, K.; Meena, R.S.; Sheoran, S.; Loyal, A.; Kumawat, A.; Jhariya, M.K. Grain Legumes: A Diversified Diet for Sustainable Livelihood, Food, and Nutritional Security. Advances in Legumes for Sustainable Intensification 2022, 157–178. [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Sandoval, S.N.; Guardado-Felix, D.; Gutiérrez-Uribe, J.A. Legumes in Human Health and Nutrition. Encyclopedia of Human Nutrition: Volume 1-4, Fourth Edition 2023, 1–4, 430–437. [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Singh, J.P.; Kaur, A.; Singh, N. Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Potential of Grain Legume Seeds: A Review. Food Res Int 2017, 101, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Hummer, K.E.; Janick, J. Rosaceae: Taxonomy, Economic Importance, Genomics. Genetics and Genomics of Rosaceae 2009, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- George, J.P.; Konrad, H.; Collin, E.; Thevenet, J.; Ballian, D.; Idzojtic, M.; Kamm, U.; Zhelev, P.; Geburek, T. High Molecular Diversity in the True Service Tree (Sorbus Domestica) despite Rareness: Data from Europe with Special Reference to the Austrian Occurrence. Ann Bot 2015, 115, 1105–1115. [CrossRef]
- Cachi, A.; Wünsch, A.; Vilanova, A.; … M.G.-P.; 2017, undefined S-locus Diversity and Cross-compatibility of Wild Prunus Avium for Timber Breeding. Wiley Online LibraryAM Cachi, A Wünsch, A Vilanova, M Guàrdia, M Ciordia, N AletàPlant Breeding, 2017•Wiley Online Library 2017, 136, 126–131. [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Rawat, D.S. Medicinal Plants of the Family Caryophyllaceae: A Review of Ethno-Medicinal Uses and Pharmacological Properties. Integr Med Res 2015, 4, 123–131. [CrossRef]
- Böttger, S.; Melzig, M.F. Triterpenoid Saponins of the Caryophyllaceae and Illecebraceae Family. Phytochem Lett 2011, 4, 59–68. [CrossRef]
- Forest, F.; Chase, M.W.; Persson, C.; Crane, P.R.; Hawkins, J.A. THE ROLE OF BIOTIC AND ABIOTIC FACTORS IN EVOLUTION OF ANT DISPERSAL IN THE MILKWORT FAMILY (POLYGALACEAE). Evolution (N Y) 2007, 61, 1675–1694. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Bădărau, A.S.; Swamy, M.K.; Shaw, S.; Maggi, F.; da Silva, L.E.; López, V.; Yeung, A.W.K.; Mocan, A.; Atanasov, A.G. Arctium Species Secondary Metabolites Chemodiversity and Bioactivities. Front Plant Sci 2019, 10. [CrossRef]
- İlgün, S.; Karatoprak, G.Ş.; Polat, D.Ç.; Şafak, E.K.; Yıldız, G.; Küpeli Akkol, E.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E. Phytochemical Composition and Biological Activities of Arctium Minus (Hill) Bernh.: A Potential Candidate as Antioxidant, Enzyme Inhibitor, and Cytotoxic Agent. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1852. [CrossRef]
- De Liz Oliveira Cavalli, V.L.; Sordi, C.; Tonini, K.; Grando, A.; Muneron, T.; Guigi, A.; Júnior, W.A.R. Avaliação in Vivo Do Efeito Hipoglicemiante de Extratos Obtidos Da Raiz e Folha de Bardana Arctium Minus (Hill.) Bernh. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2007, 17, 64–70. [CrossRef]
- Tawfick, M.M.; Xie, H.; Zhao, C.; Shao, P.; Farag, M.A. Inulin Fructans in Diet: Role in Gut Homeostasis, Immunity, Health Outcomes and Potential Therapeutics. Int J Biol Macromol 2022, 208, 948–961. [CrossRef]
- Akram, W.; Garud, N.; therapeutics, R.J.-D. discoveries &; 2019, undefined Role of Inulin as Prebiotics on Inflammatory Bowel Disease. jstage.jst.go.jpW Akram, N Garud, R JoshiDrug discoveries & therapeutics, 2019•jstage.jst.go.jp 2019, 13, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Roberfroid, M.B. Prebiotics: Preferential Substrates for Specific Germs? American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2001, 73. [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Fan, C.; Luan, T.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Dai, Y.; Li, P. The Protective Effects of Inulin-Type Fructans Against High-Fat/Sucrose Diet-Induced Gestational Diabetes Mice in Association With Gut Microbiota Regulation. Front Microbiol 2022, 13, 832151. [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Luo, J.; Cai, Y.; Fu, M.; Li, W.; Shi, L.; Liu, J.; Dong, R.; Xu, X.; Tu, L.; et al. Inulin-Type Fructans Change the Gut Microbiota and Prevent the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy. Pharmacol Res 2022, 183, 106367. [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, L.; Xue, J.; Yang, X.; Dong, X.; Sha, L.; Lei, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Z.; et al. Dietary Inulin Alleviates Diverse Stages of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via Anti-Inflammation and Modulating Gut Microbiota in Db/Db Mice. Food Funct 2019, 10, 1915–1927. [CrossRef]
- Fernanda M. Ferreira; Francisco P. Peixoto; Raquel Seiçad; Maria S. Santos Diabetes and Medicinal Plants in Portugal. In Natural Products: Research Reviews Vol. 1 ; V. K. Gupta, Ed.; 2012; pp. 1–41.
- Ferreira, F.M.; Peixoto, F.P.; Nunes, E.; Sena, C.; Seiça, R.; Santos, S.M. Inhibitory Effect of Arctium Minus on Mitochondrial Bioenergetics in Diabetic Goto-Kakizaki Rats. Scientific Research and Essay 2010, 5, 2136–2142.
- Fischer, S.P.M.; Brusco, I.; Camponogara, C.; Piana, M.; Faccin, H.; Gobo, L.A.; de Carvalho, L.M.; Oliveira, S.M. Arctium Minus Crude Extract Presents Antinociceptive Effect in a Mice Acute Gout Attack Model. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26, 505–519. [CrossRef]
- Erdemoglu, N.; Turan, N.N.; Akkol, E.K.; Sener, B.; Abacioglu, N. Estimation of Anti-Inflammatory, Antinociceptive and Antioxidant Activities on Arctium Minus (Hill) Bernh. Ssp. Minus. J Ethnopharmacol 2009, 121, 318–323. [CrossRef]
- Guettaf, S.; Benmerzoug, A.; Chawki, B.; Çakmak, Y.S.; Dahamna, S.; Baghiani, A.; Harzallah, D. Contribution to Pharmacological Valorisation of Algerian Arctium Minus (Hill) Bernh. Subsp. Atlanticum (Pomel) Maire; Antioxidant an d Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activities. Curr Enzym Inhib 2022, 18, 135–144. [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhao, C.; Guven, E.C.; Paoli, P.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Ramkumar, K.M.; Wang, S.; Buleu, F.; Pah, A.; Turi, V.; et al. Dietary Polyphenols as Antidiabetic Agents: Advances and Opportunities. Food Front 2020, 1, 18–44. [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Sarker, M.M.R.; Sultana, T.N.; Chowdhury, M.N.R.; Rashid, M.A.; Chaity, N.I.; Zhao, C.; Xiao, J.; Hafez, E.E.; Khan, S.A.; et al. Antidiabetic Phytochemicals From Medicinal Plants: Prospective Candidates for New Drug Discovery and Development. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Kenny, O.; Smyth, T.J.; Walsh, D.; Kelleher, C.T.; Hewage, C.M.; Brunton, N.P. Investigating the Potential of Under-Utilised Plants from the Asteraceae Family as a Source of Natural Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Extracts. Food Chem 2014, 161, 79–86. [CrossRef]
- Saleh, N.A.M.; Bohm, B.A. Flavonoids of Arctium Minus (Compositae). Experientia 1971, 27, 1494. [CrossRef]
- Erdemoglu, N.; Turan, N.N.; Akkol, E.K.; Sener, B.; Abacioglu, N. Estimation of Anti-Inflammatory, Antinociceptive and Antioxidant Activities on Arctium Minus (Hill) Bernh. Ssp. Minus. J Ethnopharmacol 2009, 121, 318–323. [CrossRef]
- Watkins, F.; Pendry, B.; Sanchez-Medina, A.; Corcoran, O. Antimicrobial Assays of Three Native British Plants Used in Anglo-Saxon Medicine for Wound Healing Formulations in 10th Century England. J Ethnopharmacol 2012, 144, 408–415. [CrossRef]
- Vitalini, S.; Beretta, G.; Iriti, M.; Orsenigo, S.; Basilico, N.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Iorizzi, M.; Fico, G. Phenolic Compounds from Achillea Millefolium L. and Their Bioactivity. Acta Biochim Pol 2011, 58, 203–209. [CrossRef]
- Trumbeckaite, S.; Benetis, R.; Bumblauskiene, L.; Burdulis, D.; Janulis, V.; Toleikis, A.; Viškelis, P.; Jakštas, V. Achillea Millefolium L. s.l. Herb Extract: Antioxidant Activity and Effect on the Rat Heart Mitochondrial Functions. Food Chem 2011, 127, 1540–1548. [CrossRef]
- De Souza, P.; Gasparotto, A.; Crestani, S.; Stefanello, M.É.A.; Marques, M.C.A.; Silva-Santos, J.E. Da; Kassuya, C.A.L. Hypotensive Mechanism of the Extracts and Artemetin Isolated from Achillea Millefolium L. (Asteraceae) in Rats. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 819–825. [CrossRef]
- Potrich, F.B.; Allemand, A.; da Silva, L.M.; dos Santos, A.C.; Baggio, C.H.; Freitas, C.S.; Mendes, D.A.G.B.; Andre, E.; de Paula Werner, M.F.; Marques, M.C.A. Antiulcerogenic Activity of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Achillea Millefolium L.: Involvement of the Antioxidant System. J Ethnopharmacol 2010, 130, 85–92. [CrossRef]
- Gharibi, S.; Tabatabaei, B.E.S.; Saeidi, G.; Goli, S.A.H.; Talebi, M. Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of Three Iranian Endemic Achillea Species. Ind Crops Prod 2013, 50, 154–158. [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.I.; Barros, L.; Dueñas, M.; Pereira, E.; Carvalho, A.M.; Alves, R.C.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Chemical Composition of Wild and Commercial Achillea Millefolium L. and Bioactivity of the Methanolic Extract, Infusion and Decoction. Food Chem 2013, 141, 4152–4160. [CrossRef]
- Dall’Acqua, S.; Bolego, C.; Cignarella, A.; Gaion, R.M.; Innocenti, G. Vasoprotective Activity of Standardized Achillea Millefolium Extract. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1031–1036. [CrossRef]
- Candan, F.; Unlu, M.; Tepe, B.; Daferera, D.; Polissiou, M.; Sökmen, A.; Akpulat, H.A. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of the Essential Oil and Methanol Extracts of Achillea Millefolium Subsp. Millefolium Afan. (Asteraceae). J Ethnopharmacol 2003, 87, 215–220. [CrossRef]
- Baretta, I.P.; Felizardo, R.A.; Bimbato, V.F.; Santos, M.G.J. Dos; Kassuya, C.A.L.; Gasparotto Junior, A.; Da Silva, C.R.; De Oliveira, S.M.; Ferreira, J.; Andreatini, R. Anxiolytic-like Effects of Acute and Chronic Treatment with Achillea Millefolium L. Extract. J Ethnopharmacol 2012, 140, 46–54. [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.I.; Barros, L.; Dueñas, M.; Pereira, E.; Carvalho, A.M.; Alves, R.C.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Chemical Composition of Wild and Commercial Achillea Millefolium L. and Bioactivity of the Methanolic Extract, Infusion and Decoction. Food Chem 2013, 141, 4152–4160. [CrossRef]
- Jonsdottir, G.; Omarsdottir, S.; Vikingsson, A.; Hardardottir, I.; Freysdottir, J. Aqueous Extracts from Menyanthes Trifoliate and Achillea Millefolium Affect Maturation of Human Dendritic Cells and Their Activation of Allogeneic CD4 + T Cells in Vitro. J Ethnopharmacol 2011, 136, 88–93. [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, A.M.; Baggio, C.H.; Freitas, C.S.; Rieck, L.; de Sousa, R.S.; Da Silva-Santos, J.E.; Mesia-Vela, S.; Marques, M.C.A. Safety and Antiulcer Efficacy Studies of Achillea Millefolium L. after Chronic Treatment in Wistar Rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2006, 107, 277–284. [CrossRef]
- Csupor-Löffler, B.; Hajdú, Z.; Zupkó, I.; Réthy, B.; Falkay, G.; Forgo, P.; Hohmann, J. Antiproliferative Effect of Flavonoids and Sesquiterpenoids from Achillea Millefolium s.l. on Cultured Human Tumour Cell Lines. Phytotherapy Research 2009, 23, 672–676. [CrossRef]
- Chanishvili, S.; Badridze, G.; … L.R.-R.J. of; 2007, undefined Effect of Altitude on the Contents of Antioxidants in Leaves of Some Herbaceous Plants. researchgate.netS Chanishvili, G Badridze, L Rapava, N JanukashviliRussian Journal of Ecology, 2007•researchgate.net 2007, 38, 367–373. [CrossRef]
- Si, X.T.; Zhang, M.L.; Shi, Q.W.; Kiyota, H. Chemical Constituents of the Plants in the Genus Achillea. Chem Biodivers 2006, 3, 1163–1180. [CrossRef]
- Jenabi, E.; Fereidoony, B. Effect of Achillea Millefolium on Relief of Primary Dysmenorrhea: A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2015, 28, 402–404. [CrossRef]
- Arias-Durán, L.; Estrada-Soto, S.; Hernández-Morales, M.; Chávez-Silva, F.; Navarrete-Vázquez, G.; León-Rivera, I.; Perea-Arango, I.; Villalobos-Molina, R.; Ibarra-Barajas, M. Tracheal Relaxation through Calcium Channel Blockade of Achillea Millefolium Hexanic Extract and Its Main Bioactive Compounds. J Ethnopharmacol 2020, 253, 112643. [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, N.; Babaei, K.; Farsaraei, S.; Moghaddam, M.; Ghasemi Pirbalouti, A. Changes in Essential Oil Compositions, Total Phenol, Flavonoids and Antioxidant Capacity of Achillea Millefolium at Different Growth Stages. Ind Crops Prod 2020, 152, 112570. [CrossRef]
- Arias-Durán, L.; Estrada-Soto, S.; Hernández-Morales, M.; Millán-Pacheco, C.; Navarrete-Vázquez, G.; Villalobos-Molina, R.; Ibarra-Barajas, M.; Almanza-Pérez, J.C. Antihypertensive and Vasorelaxant Effect of Leucodin and Achillin Isolated from Achillea Millefolium through Calcium Channel Blockade and NO Production: In Vivo, Functional Ex Vivo and in Silico Studies. J Ethnopharmacol 2021, 273, 113948. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, G.; Li, J.; Aisa, H.A. Chlorine-Containing Guaianolide Sesquiterpenoids from Achillea Millefolium L. with Inhibitory Effects against LPS-Induced NO Release in BV-2 Microglial Cells. Phytochemistry 2023, 207, 113567. [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, A.; Seyedsadeghi, M.; Miran, M.; Ahari, S.S.; Layegh, H.; Mostafalou, S. Therapeutic Effect of Achillea Millefolium on the Hemorrhoids; A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J Herb Med 2023, 39, 100657. [CrossRef]
- Mohammadhosseini, M.; Sarker, S.D.; Akbarzadeh, A. Chemical Composition of the Essential Oils and Extracts of Achillea Species and Their Biological Activities: A Review. J Ethnopharmacol 2017, 199, 257–315. [CrossRef]
- Asgary, S.; Naderi, G.; Ghannadi, A.; … M.G.-J. of M.; 2003, undefined Protective Effect of Achillea Millefolium, Crataegus Curvisepala and Matricaria Chamomilla on Oxidative Hemolysis of Human Erythrocytes and-SH Capacity. jmp.ir.
- Nematy, M.; Mazidi, M.; Jafari, A.; … S.B.-A. journal of; 2017, undefined The Effect of Hydro-Alcoholic Extract of Achillea Millefolium on Appetite Hormone in Rats. ncbi.nlm.nih.govM Nematy, M Mazidi, A Jafari, S Baghban, H Rakhshandeh, A Norouzy, H EsmailyAvicenna journal of phytomedicine, 2017•ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- Ali, S.I.; Gopalakrishnan, B.; Venkatesalu, V. Pharmacognosy, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Properties of Achillea Millefolium L.: A Review. Phytotherapy Research 2017, 31, 1140–1161. [CrossRef]
- Düsman, E.; Almeida, I.V. De; Coelho, A.C.; Balbi, T.J.; Düsman Tonin, L.T.; Vicentini, V.E.P. Antimutagenic Effect of Medicinal Plants Achillea Millefolium and Bauhinia Forficata in Vivo. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2013, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial, Antioxidant Activities and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Achillea Millefolium L., Anethum Graveolens L., and Carum Copticum L. Essential Oils. J Herb Med 2015, 5, 217–222. [CrossRef]
- Gharibi, S.; Tabatabaei, B.E.S.; Saeidi, G.; Goli, S.A.H. Effect of Drought Stress on Total Phenolic, Lipid Peroxidation, and Antioxidant Activity of Achillea Species. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2016, 178, 796–809. [CrossRef]
- Ismail, Y.; Fahmy, D.M.; Ghattas, M.H.; Ahmed, M.M.; Zehry, W.; Saleh, S.M.; Abo-elmatty, D.M. Integrating Experimental Model, LC-MS/MS Chemical Analysis, and Systems Biology Approach to Investigate the Possible Antidiabetic Effect and Mechanisms of Matricaria Aurea (Golden Chamomile) in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Yousefbeyk, F.; Hemmati, G.; Gholipour, Z.; Ghasemi, S.; Evazalipour, M.; Schubert, C.; Koohi, D.E.; Böhm, V. Phytochemical Analysis, Antioxidant, Cytotoxic, and Antimicrobial Activities of Golden Chamomile (Matricaria Aurea (Loefl.) Schultz Bip). Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung - Section C Journal of Biosciences 2022, 77, 331–342. [CrossRef]
- Rizwana, H.; Soliman Alwahibi, M.; Soliman, D. Antimicrobial Activity and Chemical Composition of Flowers of Matricaria Aurea a Native Herb of Saudi Arabia Article In. International Journal of Pharmacology 2016. [CrossRef]
- Kheder, F.B.H.; Mahjoub, M.A.; Zaghrouni, F.; Kwaja, S.; Helal, A.N.; Mighri, Z. Chemical Composition Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of the Essential Oils of Matricaria Aurea Loefl. Growing in Tunisia. 10.1080/0972060X.2014.884777 2014, 17, 493-505. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Abdullah, M.M.S.; Mahmood, A.; Al-Mayouf, A.M.; Alkhathlan, H.Z. Evaluation of Matricaria Aurea Extracts as Effective Anti-Corrosive Agent for Mild Steel in 1.0 M HCl and Isolation of Their Active Ingredients. mdpi.comM Khan, MMS Abdullah, A Mahmood, AM Al-Mayouf, HZ AlkhathlanSustainability, 2019•mdpi.com 2019, 11. [CrossRef]
- Bohm, B.A.; Stuessy, T.F. Flavonoids of the Sunflower Family (Asteraceae). Flavonoids of the Sunflower Family (Asteraceae) 2001. [CrossRef]
- Kriplani, P.; Guarve, K.; Baghael, U.S. Arnica Montana L. – a Plant of Healing: Review. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2017, 69, 925–945. [CrossRef]
- Duthen, S.; Gadéa, A.; Trempat, P.; Boujedaini, N.; Fabre, N. Comparison of the Phytochemical Variation of Non-Volatile Metabolites within Mother Tinctures of Arnica Montana Prepared from Fresh and Dried Whole Plant Using UHPLC-HRMS Fingerprinting and Chemometric Analysis. Molecules 2022, 27. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bai, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kan, J.; Jin, C. Isolation, Structural Characterization and Bioactivities of Naturally Occurring Polysaccharide–Polyphenolic Conjugates from Medicinal Plants—A Reivew. Int J Biol Macromol 2018, 107, 2242–2250. [CrossRef]
- Schöpke, T.; Wray, V.; Rzazewska, B.; Hiller, K. Bellissaponins BA1 and BA2, Acylated Saponins from Bellis Perennis. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 627–631. [CrossRef]
- Scognamiglio, M.; Esposito, A.; D’Abrosca, B.; Pacifico, S.; Fiumano, V.; Tsafantakis, N.; Monaco, P.; Fiorentino, A. Isolation, Distribution and Allelopathic Effect of Caffeic Acid Derivatives from Bellis Perennis L. Biochem Syst Ecol 2012, 43, 108–113. [CrossRef]
- Avato, P.; Tava, A. Acetylenes and Terpenoids of Bellis Perennis. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 141–147. [CrossRef]
- Scognamiglio, M.; Esposito, A.; D’Abrosca, B.; Pacifico, S.; Fiumano, V.; Tsafantakis, N.; Monaco, P.; Fiorentino, A. Isolation, Distribution and Allelopathic Effect of Caffeic Acid Derivatives from Bellis Perennis L. Biochem Syst Ecol 2012, 43, 108–113. [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Li, X.; Nishida, E.; Nakamura, S.; Matsuda, H.; Muraoka, O.; Morikawa, T. Medicinal Flowers. XXI. Structures of Perennisaponins A, B, C, D, E, and F, Acylated Oleanane-Type Triterpene Oligoglycosides, from the Flowers of Bellis Perennis. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 2008, 56, 559–568. [CrossRef]
- Toki, K.; Saito, N.; Honda, T. Three Cyanidin 3-Glucuronylglucosides from Red Flowers of Bellis Perennis. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 3769–3771. [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, T.; Li, X.; Nishida, E.; Ito, Y.; Matsuda, H.; Nakamura, S.; Muraoka, O.; Yoshikawa, M. Perennisosides I-VII, Acylated Triterpene Saponins with Antihyperlipidemic Activities from the Flowers of Bellis Perennis. J Nat Prod 2008, 71, 828–835. [CrossRef]
- Gudej, J.; Nazaruk, J. Flavonol Glycosides from the Flowers of Bellis Perennis. Fitoterapia 2001, 72, 839–840. [CrossRef]
- Karakas, F.; Karakas, A.; … H.C.-A.J. of; 2011, undefined Effects of Common Daisy (Bellis Perennis L.) Aqueous Extracts on Anxiety-like Behaviour and Spatial Memory Performance in Wistar Albino Rats. academicjournals.orgFP Karakas, A Karakas, H Coşkun, AU TurkerAfrican Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 2011•academicjournals.org 2011, 5, 1378–1388. [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan Karakaş, F.; Karakaş, A.; Boran, Ç.; Uçar Türker, A.; Nuray Yalçin, F.; Bilensoy, E. The Evaluation of Topical Administration of Bellis Perennis Fraction on Circular Excision Wound Healing in Wistar Albino Rats. Taylor & FrancisFP Karakaş, A Karakaş, Ç Boran, AU Türker, FN Yalçin, E BilensoyPharmaceutical biology, 2012•Taylor & Francis 2012, 50, 1031–1037. [CrossRef]
- Karakas, F.P.; Turker, A.U. An Efficient in Vitro Regeneration System for Bellis Perennis L. and Comparison of Phenolic Contents of Field-Grown and in Vitro-Grown Leaves by LC-MS/MS. Ind Crops Prod 2013, 48, 162–170. [CrossRef]
- Karakas, F.P.; Turker, A.U.; Karakas, A.; Mshvildadze, V.; Pichette, A.; Legault, J. In Vitro Cytotoxic, Antibacterial, Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activities and Phenolic Content in Wild-Grown Flowers of Common Daisy—A Medicinal Plant. J Herb Med 2017, 8, 31–39. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Asada, Y.; Koike, K.; Nikaido, T.; Furuya, T.; Yoshikawa, T. Bellisosides A–F, Six Novel Acylated Triterpenoid Saponins from Bellis Perennis (Compositae). Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 2921–2929. [CrossRef]
- Lapava, N. Bidens Frondosa: Component Composition and Pharmacological Profile. In Proceedings of the International scientific conference of young scientists “current development of health care technology”; Vilar, Moscow, 2021; pp. 475–484.
- Brandão, M.G.L.; Krettli, A.U.; Soares, L.S.R.; Nery, C.G.C.; Marinuzzi, H.C. Antimalarial Activity of Extracts and Fractions from Bidens Pilosa and Other Bidens Species (Asteraceae) Correlated with the Presence of Acetylene and Flavonoid Compounds. J Ethnopharmacol 1997, 57, 131–138. [CrossRef]
- Le, J.; Lu, W.; Xiong, X.; Wu, Z.; Chen, W. Anti-Inflammatory Constituents from Bidens Frondosa. Molecules 2015, Vol. 20, Pages 18496-18510 2015, 20, 18496–18510. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Bajpai, V.K.; Dung, N.T.; Kang, S.C. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of the Essential Oil and Methanol Extracts of Bidens Frondosa Linn. Int J Food Sci Technol 2011, 46, 1238–1244. [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, S.; Panchagnula, G.K.; Subbaraju, G. V. Synthesis and Antioxidative Activity of 3′,4′,6,7-Tetrahydroxyaurone, a Metabolite of Bidens Frondosa. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2004, 68, 2183–2185. [CrossRef]
- Khouchlaa, A.; El Baaboua, A.; El Moudden, H.; Lakhdar, F.; Bakrim, S.; El Menyiy, N.; Belmehdi, O.; Harhar, H.; El Omari, N.; Balahbib, A.; et al. Traditional Uses, Bioactive Compounds, and Pharmacological Investigations of Calendula Arvensis L.: A Comprehensive Review. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci 2023, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, R.; Barros, L.; Dueñas, M.; Calhelha, R.C.; Carvalho, A.M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Queiroz, M.J.R.P.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Nutrients, Phytochemicals and Bioactivity of Wild Roman Chamomile: A Comparison between the Herb and Its Preparations. Food Chem 2013, 136, 718–725. [CrossRef]
- Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC) Assessment Report on Chamaemelum Nobile (L.) All., Flos ; London, 2012.
- Al-Snafi, A.E. Medical Importance of Anthemis Nobilis (Chamaemelum Nobile)-a Review. Some of the Authors of This Publication Are Also Working on These Related Projects: Pharmacology of Medicinal Plants View Project Immunological Effects of Medicinal Plants: A Review (Part 2). View Project; 2016.
- Aisa, H.A.; Xin, X.; Tang, D. Chemical Constituents and Their Pharmacological Activities of Plants from Cichorium Genus. Chin Herb Med 2020, 12, 224–236. [CrossRef]
- Puhlmann, M.L.; de Vos, W.M. Back to the Roots: Revisiting the Use of the Fiber-Rich Cichorium Intybus L. Taproots. Advances in Nutrition 2020, 11, 878–890. [CrossRef]
- Brahmi-Chendouh, N.; Piccolella, S.; Crescente, G.; Pacifico, F.; Boulekbache, L.; Hamri-Zeghichi, S.; Akkal, S.; Madani, K.; Pacifico, S. A Nutraceutical Extract from Inula Viscosa Leaves: UHPLC-HR-MS/MS Based Polyphenol Profile, and Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activities. J Food Drug Anal 2019, 27, 692. [CrossRef]
- Vuko, E.; Dunkić, V.; Maravić, A.; Ruščić, M.; Nazlić, M.; Radan, M.; Ljubenkov, I.; Soldo, B.; Fredotović, Ž. Not Only a Weed Plant—Biological Activities of Essential Oil and Hydrosol of Dittrichia Viscosa (L.) Greuter. Plants 2021, 10. [CrossRef]
- Kheyar-Kraouche, N.; da Silva, A.B.; Serra, A.T.; Bedjou, F.; Bronze, M.R. Characterization by Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry and Antioxidant Activity of an Ethanolic Extract of Inula Viscosa Leaves. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2018, 156, 297–306. [CrossRef]
- Parolin, P.; Ion Scotta, M.; Bresch, C. Biología de Dittrichia Viscosa, Una Planta Ruderal Del Mediterráneo: Revisión. Phyton (Buenos Aires) 2014, 83, 251–262.
- Ozkan, E.; Karakas, F.P.; Yildirim, A.B.; Tas, I.; Eker, I.; Yavuz, M.Z.; Turker, A.U. Promising Medicinal Plant Inula Viscosa L.: Antiproliferative, Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Phenolic Profiles. Progress in Nutrition 2019, 21, 652–661. [CrossRef]
- Rozenblat, S.; Grossman, S.; Bergman, M.; Gottlieb, H.; Cohen, Y.; Dovrat, S. Induction of G2/M Arrest and Apoptosis by Sesquiterpene Lactones in Human Melanoma Cell Lines. Biochem Pharmacol 2008, 75, 369–382. [CrossRef]
- Kheyar-Kraouche, N.; Boucheffa, S.; Bellik, Y.; Farida, K.; Brahmi-Chendouh, N. Exploring the Potential of Inula Viscosa Extracts for Antioxidant, Antiproliferative and Apoptotic Effects on Human Liver Cancer Cells and a Molecular Docking Study. BioTechnologia 2023, 104, 183. [CrossRef]
- Asraoui, F.; Kounnoun, A.; Cacciola, F.; Mansouri, F. El; Kabach, I.; Majdoub, Y.O. El; Alibrando, F.; Arena, K.; Trovato, E.; Mondello, L.; et al. Phytochemical Profile, Antioxidant Capacity, α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Potential of Wild Moroccan Inula Viscosa (L.) Aiton Leaves. Molecules 2021, 26, 3134. [CrossRef]
- Rotundo, G.; Paventi, G.; Barberio, A.; De Cristofaro, A.; Notardonato, I.; Russo, M. V.; Germinara, G.S. Biological Activity of Dittrichia Viscosa (L.) Greuter Extracts against Adult Sitophilus Granarius (L.) (Coleoptera, Curculionidae) and Identification of Active Compounds. Sci Rep 2019, 9. [CrossRef]
- Mrid, R. Ben; Bouchmaa, N.; Kabach, I.; Zouaoui, Z.; Chtibi, H.; El Maadoudi, M.; Kounnoun, A.; Cacciola, F.; El Majdoub, Y.O.; Mondello, L.; et al. Dittrichia Viscosa L. Leaves: A Valuable Source of Bioactive Compounds with Multiple Pharmacological Effects. Molecules 2022, 27. [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-H.; Pan, Y.-A.; Lv, H.; Ding, X.-Q.; Yin, D.-Q.; Gai, Y.-N.; Niu, G.-T.; Ren, B.-R.; Qian, X.-G.; Chen, J.; et al. One New 12, 8-Guaianolide Sesquiterpene Lactone with Antihyperglycemic Activity from the Roots of Cichorium Intybus. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Ripanda, A.; Luanda, A.; Sule, K.S.; Mtabazi, G.S.; Makangara, J.J. Galinsoga Parviflora (Cav.): A Comprehensive Review on Ethnomedicinal, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Studies. Heliyon 2023, 9. [CrossRef]
- Les, F.; Venditti, A.; Cásedas, G.; Frezza, C.; Guiso, M.; Sciubba, F.; Serafini, M.; Bianco, A.; Valero, M.S.; López, V. Everlasting Flower (Helichrysum Stoechas Moench) as a Potential Source of Bioactive Molecules with Antiproliferative, Antioxidant, Antidiabetic and Neuroprotective Properties. Ind Crops Prod 2017, 108, 295–302. [CrossRef]
- Albayrak, S.; Aksoy, A.; Sagdic, O.; Hamzaoglu, E. Compositions, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Helichrysum (Asteraceae) Species Collected from Turkey. Food Chem 2010, 119, 114–122. [CrossRef]
- Onaran, M.; Orhan, N.; Farahvash, A.; Ekin, H.N.I.; Kocabiyik, M.; Gönül, I.I.; Şen, I.; Aslan, M. Successful Treatment of Sodium Oxalate Induced Urolithiasis with Helichrysum Flowers. J Ethnopharmacol 2016, 186, 322–328. [CrossRef]
- Bremner, P.; Rivera, D.; Calzado, M.A.; Obón, C.; Inocencio, C.; Beckwith, C.; Fiebich, B.L.; Muñoz, E.; Heinrich, M. Assessing Medicinal Plants from South-Eastern Spain for Potential Anti-Inflammatory Effects Targeting Nuclear Factor-Kappa B and Other pro-Inflammatory Mediators. J Ethnopharmacol 2009, 124, 295–305. [CrossRef]
- Jamuna, S.; Karthika, K.; Paulsamy, S.; Thenmozhi, K.; Kathiravan, S.; Venkatesh, R. Confertin and Scopoletin from Leaf and Root Extracts of Hypochaeris Radicata Have Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activities. Ind Crops Prod 2015, 70, 221–230. [CrossRef]
- Shulha, O.; Çiçek, S.S.; Wangensteen, H.; Kroes, J.; Mäder, M.; Girreser, U.; Sendker, J.; Jöhrer, K.; Greil, R.; Schühly, W.; et al. Lignans and Sesquiterpene Lactones from Hypochaeris Radicata Subsp. Neapolitana (Asteraceae, Cichorieae). Phytochemistry 2019, 165, 112047. [CrossRef]
- Sicari, V.; Loizzo, M.R.; Silva, A.S.; Romeo, R.; Spampinato, G.; Tundis, R.; Leporini, M.; Musarella, C.M. The Effect of Blanching on Phytochemical Content and Bioactivity of Hypochaeris and Hyoseris Species (Asteraceae), Vegetables Traditionally Used in Southern Italy. Foods 2021, Vol. 10, Page 32 2020, 10, 32. [CrossRef]
- Senguttuvan, J.; Paulsamy, S.; Karthika, K. Phytochemical Analysis and Evaluation of Leaf and Root Parts of the Medicinal Herb, Hypochaeris Radicata L. for in Vitro Antioxidant Activities. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2014, 4, S359. [CrossRef]
- Shoaib Akhtar, M.; Naveed Mushtaq, M.; Ali, I.; Pharm Sci, P.J.; Farooq Awan, A.; Anjum, I.; Fatima, A.; Mannan, A. Anti-Oxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Lactuca Serriola and Its Phytochemical Screening by HPLC and FTIR Analysis. researchgate.netAF Awan, MS Akhtar, I Anjum, MN Mushtaq, A Fatima, A Mannan, I AliPakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2020•researchgate.net 2020, 33, 2823–2830. [CrossRef]
- Fatah, N.H.A.; Amen, Y.; Abdel Bar, F.M.; Halim, A.F.; Saad, H.-E.A. Supporting Information Antioxidants and α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Lactuca Serriola L. Nat. Prod 2020, 14, 410–415.
- Abd-ElGawad, A.M.; Elshamy, A.I.; El-Nasser El Gendy, A.; Al-Rowaily, S.L.; Assaeed, A.M. Preponderance of Oxygenated Sesquiterpenes and Diterpenes in the Volatile Oil Constituents of Lactuca Serriola L. Revealed Antioxidant and Allelopathic Activity. Chem Biodivers 2019, 16, e1900278. [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Nabavi, S.M.; Latifi, A.M.; Mirzaei, M.; Habtemariam, S.; Moghaddam, A.H. Mitigating Role of Quercetin against Sodium Fluoride-Induced Oxidative Stress in the Rat Brain. Pharm Biol 2012, 50, 1380–1383. [CrossRef]
- Elsharkawy, E.; Aljohar, H. Anticancer Screening of Medicinal Plants Growing in the Northern Region of Saudi Arabia. Natl J Physiol Pharm Pharmacol 2016, 6, 241–246. [CrossRef]
- El-Esawi, M.A.; Elkelish, A.; Elansary, H.O.; Ali, H.M.; Elshikh, M.; Witczak, J.; Ahmad, M. Genetic Transformation and Hairy Root Induction Enhance the Antioxidant Potential of Lactuca Serriola L. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A. Traditional Use of Kahu (Lactuca Scariola L.)-a Review. Global Journal of Research on Medicinal Plants & Indigenous Medicine 2013, 2, 465–474.
- Ullah, M.I.; Anwar, R.; Kamran, S.; Gul, B.; Elhady, S.S.; Youssef, F.S. Evaluation of the Anxiolytic and Anti-Epileptogenic Potential of Lactuca Serriola Seed Using Pentylenetetrazol-Induced Kindling in Mice and Metabolic Profiling of Its Bioactive Extract. Antioxidants 2022, Vol. 11, Page 2232 2022, 11, 2232. [CrossRef]
- Ghods, R.; Gharouni, M.; Amanlou, M.; Sharifi, N.; Ghobadi, A.; Amin, G. Effect of Onopordon Acanthium L. as Add on Antihypertensive Therapy in Patients with Primary Hypertension Taking Losartan: A Pilot Study. Adv Pharm Bull 2018, 8, 69. [CrossRef]
- Bande-De León, C.; Buendía-Moreno, L.; Abellán, A.; Manzi, P.; Al Mohandes Dridi, B.; Essaidi, I.; Aquilanti, L.; Tejada, L. Clotting and Proteolytic Activity of Freeze-Dried Crude Extracts Obtained from Wild Thistles Cynara Humilis L. and Onopordum Platylepis Murb. Foods 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Molnár, J.; Szebeni, G.J.; Csupor-Löffler, B.; Hajdú, Z.; Szekeres, T.; Saiko, P.; Ocsovszki, I.; Puskás, L.G.; Hohmann, J.; Zupkó, I. Investigation of the Antiproliferative Properties of Natural Sesquiterpenes from Artemisia Asiatica and Onopordum Acanthium on HL-60 Cells in Vitro. Int J Mol Sci 2016, 17. [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Zhou, S.; Shi, K.; Zhang, C.; Shao, H. Chemical Profile and Phytotoxic Action of Onopordum Acanthium Essential Oil. Sci Rep 2020, 10. [CrossRef]
- Garsiya, E.R.; Konovalov, D.A.; Shamilov, A.A.; Glushko, M.P.; Orynbasarova, K.K. Traditional Medicine Plant, Onopordum Acanthium L. (Asteraceae): Chemical Composition and Pharmacological Research. Plants 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, A.; Saremnia, B. Preparation of Extract-Loaded Nanocapsules from Onopordon Leptolepis DC. Ind Crops Prod 2012, 37, 259–263. [CrossRef]
- Khalilov, L.M.; Khalilova, A.Z.; Shakurova, E.R.; Nuriev, I.F.; Kachala, V. V.; Shashkov, A.S.; Dzhemilev, U.M. PMR and 13C NMR Spectra of Biologically Active Compounds. XII. Taraxasterol and Its Acetate from the Aerial Part of Onopordum Acanthium. Chem Nat Compd 2003, 39, 285–288. [CrossRef]
- Tyumkina, T. V.; Nuriev, I.F.; Khalilov, L.M.; Akhmetova, V.R.; Dzhemilev, U.M. PMR and 13C NMR Spectra of Biologically Active Compounds. XIII. Structure and Stereochemistry of a New Phenylpropanoid Glycoside Isolated from Onopordum Acanthium Seeds. Chem Nat Compd 2009, 45, 61–65. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, L.; Xiong, A.; Li, D.; Wang, Z. Authentication of Senecio Scandens and S. Vulgaris Based on the Comprehensive Secondary Metabolic Patterns Gained by UPLC–DAD/ESI-MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2011, 56, 165–172. [CrossRef]
- Conforti, F.; Loizzo, M.R.; Statti, G.; Houghton, P.; Menichini, F. Biological Properties of Different Extracts of Two Senecio Species. Int J Food Sci Nutr 2006, 57, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Acito, M.; Russo, C.; Fatigoni, C.; Mercanti, F.; Moretti, M.; Villarini, M. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Senecio Vulgaris L. Extracts: An In Vitro Assessment in HepG2 Liver Cells. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, Vol. 19, Page 14824 2022, 19, 14824. [CrossRef]
- Loizzo, M.R.; Statti, G.A.; Tundis, R.; Conforti, F.; Bonesi, M.; Autelitano, G.; Houghton, P.J.; Miljkovic-Brake, A.; Menichini, F. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Senecio Inaequidens DC. and Senecio Vulgaris L. Phytotherapy Research 2004, 18, 777–779. [CrossRef]
- Fursenco, C.; Calalb, T.; Uncu, L.; Dinu, M.; Ancuceanu, R. Solidago Virgaurea L.: A Review of Its Ethnomedicinal Uses, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacological Activities. Biomolecules 2020, Vol. 10, Page 1619 2020, 10, 1619. [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.A.; Khan, M.R.; Sahreen, S. Brain Antioxidant Markers, Cognitive Performance and Acetylcholinesterase Activity of Rats: Efficiency of Sonchus Asper. Behavioral and Brain Functions 2012, 8, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.A.; Khan, M.R.; Sahreen, S. Protective Effect of Sonchus Asper Extracts against Experimentally Induced Lung Injuries in Rats: A Novel Study. Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology 2012, 64, 725–731. [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.A.; Khan, M.R.; Sahreen, S.; Bokhari, J. Prevention of CCl4-Induced Nephrotoxicity with Sonchus Asper in Rat. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2010, 48, 2469–2476. [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.A. Protective Effects of Sonchus Asper (L.) Hill, (Asteraceae) against CCl4-Induced Oxidative Stress in the Thyroid Tissue of Rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 2012, 12, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.R.; Badar, I.; Siddiquah, A. Prevention of Hepatorenal Toxicity with Sonchus Asper in Gentamicin Treated Rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 2011, 11, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.N.; Sati, S.C.; Kumar, P. An Invasive Plant Sonchus Asper (L.) Hill: A Review of Its Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacological Properties. Indian Journal of Natural Products and Resources (IJNPR) [Formerly Natural Product Radiance (NPR)] 2022, 13, 468–473. [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.U.; Khan, F.U.; Hussain, J.; Badshah, S.; Muhammad, N.; Khan, R.A.; Kait, C.F.; Ali, M.A.; Khan, H.; Aslam, M.W.; et al. Asperal: A New Clerodane Diterpene from Sonchus Asper. Asian Journal of Chemistry 2014, 26, 2699–2701. [CrossRef]
- Helal, A.M.; Nakamura, N.; El-Askary, H.; Hattori, M. Sesquiterpene Lactone Glucosides from Sonchus Asper. Phytochemistry 2000, 53, 473–477. [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.Z.; Yu, X.F.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Zou, Z.D. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activity of Six Edible Wild Plants (Sonchus Spp.) in China. Nat Prod Res 2011, 25, 1893–1901. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Yang, P.L. Research Progress of Sonchus Species. Int J Food Prop 2018, 21, 147–157. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, M.L.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.H.; Wang, M.H. Sonchus Asper Extract Inhibits LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress and pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Nutr Res Pract 2015, 9, 579–585. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lin, X.; Xiao, J.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, B.; Teng, H. Sonchus Oleraceus Linn Protects against LPS-Induced Sepsis and Inhibits Inflammatory Responses in RAW264.7 Cells. J Ethnopharmacol 2019, 236, 63–69. [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, B.; Che, Y. Two New Sesquiterpenes from Sonchus Oleraceus and Inhibitory Mechanism on Murine Haemangioendothelioma (EOMA) Cell Lines. Nat Prod Res 2021, 36, 2814–2820. [CrossRef]
- Nobela, O.; Ndhlala, A.R.; Tugizimana, F.; Njobeh, P.; Raphasha, D.G.; Ncube, B.; Madala, N.E. Tapping into the Realm of Underutilised Green Leafy Vegetables: Using LC-IT-Tof-MS Based Methods to Explore Phytochemical Richness of Sonchus Oleraceus (L.) L. South African Journal of Botany 2022, 145, 207–212. [CrossRef]
- Huyan, T.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Shahid, M.R.; Yang, H.; Li, H.Q. Anti-Tumor Effect of Hot Aqueous Extracts from Sonchus Oleraceus (L.) L. and Juniperus Sabina L – Two Traditional Medicinal Plants in China. J Ethnopharmacol 2016, 185, 289–299. [CrossRef]
- El-Desouky, T.A. Evaluation of Effectiveness Aqueous Extract for Some Leaves of Wild Edible Plants in Egypt as Anti-Fungal and Anti-Toxigenic. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06209. [CrossRef]
- Vilela, F.C.; De Mesquita Padilha, M.; Alves-Da-Silva, G.; Soncini, R.; Giusti-Paiva, A. Antidepressant-Like Activity of Sonchus Oleraceus in Mouse Models of Immobility Tests. https://home.liebertpub.com/jmf 2010, 13, 219–222. [CrossRef]
- Végh, K.; Riethmüller, E.; Hosszú, L.; Darcsi, A.; Müller, J.; Alberti, Á.; Tóth, A.; Béni, S.; Könczöl, Á.; Balogh, G.T.; et al. Three Newly Identified Lipophilic Flavonoids in Tanacetum Parthenium Supercritical Fluid Extract Penetrating the Blood-Brain Barrier. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2018, 149, 488–493. [CrossRef]
- Hordiei, K.; Gontova, T.; Trumbeckaite, S.; Yaremenko, M.; Raudone, L. Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Tanacetum Parthenium Cultivated in Different Regions of Ukraine: Insights into the Flavonoids and Hydroxycinnamic Acids Profile. Plants 2023, Vol. 12, Page 2940 2023, 12, 2940. [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, J.; Reyes-Pérez, V.; Hernández-Navarro, M.D.; Dorantes-Barrón, A.M.; Almazán, S.; Estrada-Reyes, R. Anxiolytic- and Antidepressant-like Effects of an Aqueous Extract of Tanacetum Parthenium L. Schultz-Bip (Asteraceae) in Mice. J Ethnopharmacol 2017, 200, 22–30. [CrossRef]
- Benassi-Zanqueta, É.; Marques, C.F.; Valone, L.M.; Pellegrini, B.L.; Bauermeister, A.; Ferreira, I.C.P.; Lopes, N.P.; Nakamura, C.V.; Dias Filho, B.P.; Natali, M.R.M.; et al. Evaluation of Anti-HSV-1 Activity and Toxicity of Hydroethanolic Extract of Tanacetum Parthenium (L.) Sch.Bip. (Asteraceae). Phytomedicine 2019, 55, 249–254. [CrossRef]
- di Giacomo, V.; Ferrante, C.; Ronci, M.; Cataldi, A.; Di Valerio, V.; Rapino, M.; Recinella, L.; Chiavaroli, A.; Leone, S.; Vladimir-Knežević, S.; et al. Multiple Pharmacological and Toxicological Investigations on Tanacetum Parthenium and Salix Alba Extracts: Focus on Potential Application as Anti-Migraine Agents. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2019, 133, 110783. [CrossRef]
- Ataollahi, M.; Akrami, E.; Kalani, M.; Zarei, M.; Chijan, M.R.; Sedigh-Rahimabadi, M.; Alipanah, H. Evaluation of Anticoagulant and Inflammatory Effects of Tanacetum Parthenium (L.) in a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J Herb Med 2022, 36, 100613. [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, F.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Dong, M.; He, G.; Galyean, R.D.; He, L.; Huang, G. Identification of Antioxidant Phenolic Compounds in Feverfew (Tanacetum Parthenium) by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS and NMR. Phytochemical Analysis 2007, 18, 401–410. [CrossRef]
- Rabito, M.F.; Britta, E.A.; Pelegrini, B.L.; Scariot, D.B.; Almeida, M.B.; Nixdorf, S.L.; Nakamura, C.V.; Ferreira, I.C.P. In Vitro and in Vivo Antileishmania Activity of Sesquiterpene Lactone-Rich Dichloromethane Fraction Obtained from Tanacetum Parthenium (L.) Schultz-Bip. Exp Parasitol 2014, 143, 18–23. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cui, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Trends in Parthenolide Research over the Past Two Decades: A Bibliometric Analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17843. [CrossRef]
- LIU, X.; WANG, X. Recent Advances on the Structural Modification of Parthenolide and Its Derivatives as Anticancer Agents. Chin J Nat Med 2022, 20, 814–829. [CrossRef]
- Toraman, E.; Budak, B.; Bayram, C.; Sezen, S.; Mokhtare, B.; Hacımüftüoğlu, A. Role of Parthenolide in Paclitaxel-Induced Oxidative Stress Injury and Impaired Reproductive Function in Rat Testicular Tissue. Chem Biol Interact 2024, 387, 110793. [CrossRef]
- Coté, H.; Boucher, M.-A.; Pichette, A.; Legault, J. Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, Antibiotic, and Cytotoxic Activities of Tanacetum Vulgare L. Essential Oil and Its Constituents. Medicines 2017, Vol. 4, Page 34 2017, 4, 34. [CrossRef]
- Bączek, K.B.; Kosakowska, O.; Przybył, J.L.; Pióro-Jabrucka, E.; Costa, R.; Mondello, L.; Gniewosz, M.; Synowiec, A.; Węglarz, Z. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activity of Essential Oils and Extracts from Costmary (Tanacetum Balsamita L.) and Tansy (Tanacetum Vulgare L.). Ind Crops Prod 2017, 102, 154–163. [CrossRef]
- Schinella, G.R.; Giner, R.M.; Del Carmen Recio, M.; De Buschiazzo, P.M.; Ríos, J.L.; Máñez, S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of South American Tanacetum Vulgare. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2011, 50, 1069–1074. [CrossRef]
- Kavallieratos, N.G.; Skourti, A.; Nika, E.P.; Mártonfi, P.; Spinozzi, E.; Maggi, F. Tanacetum Vulgare Essential Oil as Grain Protectant against Adults and Larvae of Four Major Stored-Product Insect Pests. J Stored Prod Res 2021, 94, 101882. [CrossRef]
- Ak, G.; Gevrenova, R.; Sinan, K.I.; Zengin, G.; Zheleva, D.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Senkardes, I.; Brunetti, L.; Leone, S.; Di Simone, S.C.; et al. Tanacetum Vulgare L. (Tansy) as an Effective Bioresource with Promising Pharmacological Effects from Natural Arsenal. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2021, 153, 112268. [CrossRef]
- Babich, O.; Larina, V.; Krol, O.; Ulrikh, E.; Sukhikh, S.; Gureev, M.A.; Prosekov, A.; Ivanova, S. In Vitro Study of Biological Activity of Tanacetum Vulgare Extracts. Pharmaceutics 2023, Vol. 15, Page 616 2023, 15, 616. [CrossRef]
- Vilhelmova, N.; Simeonova, L.; Nikolova, N.; Pavlova, E.; Gospodinova, Z.; Antov, G.; Galabov, A.; Nikolova, I. Antiviral, Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Effects of Tanacetum Vulgare L. Crude Extract In Vitro. Folia Med (Plovdiv) 2020, 62, 172–179. [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, Á.L.; Habtemariam, S.; Juan-Badaturuge, M.; Jackson, C.; Parra, F. In Vitro Anti HSV-1 and HSV-2 Activity of Tanacetum Vulgare Extracts and Isolated Compounds: An Approach to Their Mechanisms of Action. Phytotherapy Research 2011, 25, 296–301. [CrossRef]
- Lazarevic, J.; Kostic, I.; Milanovic, S.; Šešlija Jovanović, D.; Krnjajic, S.; C¨alic, D.; Stankovic, S.; Kostic, M. Repellent Activity of Tanacetum Parthenium (L.) and Tanacetum Vulgare (L.) Essential Oils against Leptinotarsa Decemlineata (Say). Bull Entomol Res 2021, 111, 190–199. [CrossRef]
- Kļaviņa, A.; Keidāne, D.; Ganola, K.; Lūsis, I.; Šukele, R.; Bandere, D.; Kovalcuka, L. Anthelmintic Activity of Tanacetum Vulgare L. (Leaf and Flower) Extracts against Trichostrongylidae Nematodes in Sheep In Vitro. Animals 2023, Vol. 13, Page 2176 2023, 13, 2176. [CrossRef]
- Arantes, S.M.; Piçarra, A.; Guerreiro, M.; Salvador, C.; Candeias, F.; Caldeira, A.T.; Martins, M.R. Toxicological and Pharmacological Properties of Essential Oils of Calamintha Nepeta, Origanum Virens and Thymus Mastichina of Alentejo (Portugal). Food and Chemical Toxicology 2019, 133, 110747. [CrossRef]
- Marongiu, B.; Piras, A.; Porcedda, S.; Falconieri, D.; Maxia, A.; Goncalves, M.J.; Cavaleiro, C.; Salgueiro, L. Chemical Composition and Biological Assays of Essential Oils of Calamintha Nepeta (L.) Savi Subsp. Nepeta (Lamiaceae). Nat Prod Res 2010, 24, 1734–1742. [CrossRef]
- Božović, M.; Ragno, R.; Tzakou, O. Calamintha Nepeta (L.) Savi and Its Main Essential Oil Constituent Pulegone: Biological Activities and Chemistry. Molecules 2017, Vol. 22, Page 290 2017, 22, 290. [CrossRef]
- Rodenak-Kladniew, B.; Castro, M.A.; Gambaro, R.C.; Girotti, J.; Cisneros, J.S.; Viña, S.; Padula, G.; Crespo, R.; Castro, G.R.; Gehring, S.; et al. Cytotoxic Screening and Enhanced Anticancer Activity of Lippia Alba and Clinopodium Nepeta Essential Oils-Loaded Biocompatible Lipid Nanoparticles against Lung and Colon Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2045. [CrossRef]
- Beddiar, H.; Boudiba, S.; Benahmed, M.; Tamfu, A.N.; Ceylan, Ö.; Hanini, K.; Kucukaydin, S.; Elomari, A.; Bensouici, C.; Laouer, H.; et al. Chemical Composition, Anti-Quorum Sensing, Enzyme Inhibitory, and Antioxidant Properties of Phenolic Extracts of Clinopodium Nepeta L. Kuntze. Plants 2021, 10, 1955. [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, S.; Moreira, E.; Grosso, C.; Andrade, P.B.; Valentão, P.; Romano, A. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant Activity and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities of Extracts from Aromatic Plants Used in Mediterranean Diet. J Food Sci Technol 2017, 54, 219. [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, S.; Galasso, S.; Piccolella, S.; Kretschmer, N.; Pan, S.P.; Marciano, S.; Bauer, R.; Monaco, P. Seasonal Variation in Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Calamintha Nepeta (L.) Savi. Food Research International 2015, 69, 121–132. [CrossRef]
- Benabed, K.H.; Boussoussa, H.; Khacheba, I.; bekhaoua, A.; Douadji, F.Z.; Daïdi, S.; Djaâfour, S.; Yousfi, M. Alpha-Amylase Inhibitory Activity of Extracts from Algerian Calamintha Nepeta (L.). Curr Enzym Inhib 2023, 19, 136–141. [CrossRef]
- Araniti, F.; Lupini, A.; Mercati, F.; Statti, G.A.; Abenavoli, M.R. Calamintha Nepeta L. (Savi) as Source of Phytotoxic Compounds: Bio-Guided Fractionation in Identifying Biological Active Molecules. Acta Physiol Plant 2013, 35, 1979–1988. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Yang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Mao, S.; Shen, C. Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Capacities of 10 Common Edible Flowers from China. J Food Sci 2014, 79, C517–C525. [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.L.; Pereira, E.; Soković, M.; Carvalho, A.M.; Barata, A.M.; Lopes, V.; Rocha, F.; Calhelha, R.C.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Phenolic Composition and Bioactivity of Lavandula Pedunculata (Mill.) Cav. Samples from Different Geographical Origin. Molecules 2018, Vol. 23, Page 1037 2018, 23, 1037. [CrossRef]
- Boutahiri, S.; Eto, B.; Bouhrim, M.; Mechchate, H.; Saleh, A.; Al Kamaly, O.; Drioiche, A.; Remok, F.; Samaillie, J.; Neut, C.; et al. Lavandula Pedunculata (Mill.) Cav. Aqueous Extract Antibacterial Activity Improved by the Addition of Salvia Rosmarinus Spenn., Salvia Lavandulifolia Vahl and Origanum Compactum Benth. Life 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- Dobros, N.; Zawada, K.D.; Paradowska, K. Phytochemical Profiling, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Plants Belonging to the Lavandula Genus. Molecules 2023, 28. [CrossRef]
- Ez zoubi, Y.; Bousta, D.; Farah, A. A Phytopharmacological Review of a Mediterranean Plant: Lavandula Stoechas L. Clinical Phytoscience 2020 6:1 2020, 6, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, A.; Anwar, R.; Gohar, U.F.; Ahmad, M.; Marc, R.A.; Mureşan, C.C.; Irimie, M.; Bobescu, E. Biomolecular Evaluation of Lavandula Stoechas L. For Nootropic Activity. Plants 2021, 10, 1259. [CrossRef]
- Selmi, S.; Jallouli, M.; Gharbi, N.; Marzouki, L. Hepatoprotective and Renoprotective Effects of Lavender (Lavandula Stoechas L.) Essential Oils Against Malathion-Induced Oxidative Stress in Young Male Mice. https://home.liebertpub.com/jmf 2015, 18, 1103–1111. [CrossRef]
- Balahbib, A.; El Omari, N.; Bakrim, S.; Benali, T.; Ullah, R.; Alotaibi, A.; El Mrabti, H.N.; Goh, B.H.; Ardianto, C.; Ming, L.C.; et al. Evaluation of Antioxidant, Antidiabetic, and Dermatoprotective Properties of Lavandula Stoechas Essential Oils and Their Main Chemotypes. Heliyon 2023, 20. [CrossRef]
- Benali, T.; Lemhadri, A.; Harboul, K.; Chtibi, H.; Khabbach, A.; Jadouali, S.M.; Quesada-Romero, L.; Louahlia, S.; Hammani, K.; Ghaleb, A.; et al. Chemical Profiling and Biological Properties of Essential Oils of Lavandula Stoechas L. Collected from Three Moroccan Sites: In Vitro and In Silico Investigations. Plants 2023, Vol. 12, Page 1413 2023, 12, 1413. [CrossRef]
- Aydin, T.; Saglamtas, R.; Gumustas, M.; Genisel, M.; Kazaz, C.; Cakir, A. Lavandula Stoechas L. Subsp. Stoechas, a New Herbal Source for Ursolic Acid: Quantitative Analysis, Purification and Bioactivity Studies. Chem Biodivers 2023, 20, e202300414. [CrossRef]
- El Hachlafi, N.; Benkhaira, N.; Al-Mijalli, S.H.; Mrabti, H.N.; Abdnim, R.; Abdallah, E.M.; Jeddi, M.; Bnouham, M.; Lee, L.H.; Ardianto, C.; et al. Phytochemical Analysis and Evaluation of Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Antidiabetic Activities of Essential Oils from Moroccan Medicinal Plants: Mentha Suaveolens, Lavandula Stoechas, and Ammi Visnaga. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2023, 164, 114937. [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, A.; Sahebkar, A.; Javadi, B. Melissa Officinalis L. – A Review of Its Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology. J Ethnopharmacol 2016, 188, 204–228. [CrossRef]
- Petrisor, G.; Motelica, L.; Craciun, L.N.; Oprea, O.C.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A. Melissa Officinalis: Composition, Pharmacological Effects and Derived Release Systems—A Review. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [CrossRef]
- Alimoradi, Z.; Jafari, E.; Abdi, F.; Griffiths, M.D. Therapeutic Applications of Lemon Balm (Melissa Officinalis) for Obstetrics and Gynecological Health Issues: A Systematic Review. J Herb Med 2023, 42, 100751. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.; Duarte, A.P.; Ferreira, S. Antimicrobial Activity of Melissa Officinalis and Its Potential Use in Food Preservation. Food Biosci 2021, 44, 101437. [CrossRef]
- Zeljković, S.Ć.; Šišková, J.; Komzáková, K.; De Diego, N.; Kaffková, K.; Tarkowski, P. Phenolic Compounds and Biological Activity of Selected Mentha Species. Plants 2021, 10, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Olsen, H.T.; Stafford, G.I.; van Staden, J.; Christensen, S.B.; Jäger, A.K. Isolation of the MAO-Inhibitor Naringenin from Mentha Aquatica L. J Ethnopharmacol 2008, 117, 500–502. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.M.; Pereira, O.R.; Cardoso, S.M.; Oliveira, P.J.; Moreno, A.J.M. Mentha Aquatica L. Extract Effects on Mitochondrial Bioenergetics. 18th European Bioenergetics Conference 2014.
- Hanafy, D.M.; Prenzler, P.D.; Burrows, G.E.; Ryan, D.; Nielsen, S.; El Sawi, S.A.; El Alfy, T.S.; Abdelrahman, E.H.; Obied, H.K. Biophenols of Mints: Antioxidant, Acetylcholinesterase, Butyrylcholinesterase and Histone Deacetylase Inhibition Activities Targeting Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment. J Funct Foods 2017, 33, 345–362. [CrossRef]
- Benabdallah, A.; Boumendjel, M.; Aissi, O.; Rahmoune, C.; Boussaid, M.; Messaoud, C. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant Activity and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory of Wild Mentha Species from Northeastern Algeria. South African Journal of Botany 2018, 116, 131–139. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.R.; Macias, R.I.R.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Cardoso, S.M. Hepatoprotection of Mentha Aquatica L., Lavandula Dentata L. and Leonurus Cardiaca L. Antioxidants 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Jäger, A.K.; Almqvist, J.P.; Vangsøe, S.A.K.; Stafford, G.I.; Adsersen, A.; Van Staden, J. Compounds from Mentha Aquatica with Affinity to the GABA-Benzodiazepine Receptor. South African Journal of Botany 2007, 73, 518–521. [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.T.; Soo, W.N.; Chen, Y.H.; Shyur, L.F. Essential Oil of Mentha Aquatica Var. Kenting Water Mint Suppresses Two-Stage Skin Carcinogenesis Accelerated by BRAF Inhibitor Vemurafenib. Molecules 2019, Vol. 24, Page 2344 2019, 24, 2344. [CrossRef]
- Thi, N.Q.N.; Duc, L.T.; Minh, L. V.; Tien, L.X. Phytochemicals and Antioxidant Activity of Aqueous and Ethanolic Extracts of Mentha Aquatica L. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 2020, 991, 012027. [CrossRef]
- Ferhat, M.; Erol, E.; Beladjila, K.A.; Çetintaş, Y.; Duru, M.E.; Öztürk, M.; Kabouche, A.; Kabouche, Z. Antioxidant, Anticholinesterase and Antibacterial Activities of Stachys Guyoniana and Mentha Aquatica. Pharm Biol 2017, 55, 324–329. [CrossRef]
- Dhifi, W.; Litaiem, M.; Jelali, N.; Hamdi, N.; Mnif, W. Journal of Essential Oil Bearing Plants Identification of A New Chemotye of the Plant Mentha Aquatica Grown in Tunisia: Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Biological Activities of Its Essential Oil. 2013. [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Braga, L.E.; da Silva, G.G.; de Oliveira Sousa, I.M.; de Oliveira, E.C.S.; Jorge, M.P.; Monteiro, K.M.; Sedano, T.C.; Foglio, M.A.; Ruiz, A.L.T.G. Gastrointestinal Effects of Mentha Aquatica L. Essential Oil. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 2127–2137. [CrossRef]
- de Souza, L.B.; Tinti, S.V.; Sousa, I.M. de O.; Montanari, I.; da Costa, J.L.; de Carvalho, J.E.; Foglio, M.A.; Ruiz, A.L.T.G. Mentha Aquatica L. Aerial Parts: In Vitro Anti-Proliferative Evaluation on Human Tumour and Non-Tumour Cell Lines. Nat Prod Res 2022, 36, 3117–3123. [CrossRef]
- Rahimifard, N.; HAJI, M.; Hedayati, M.; BAGHERI, O. Cytotoxic Effects of Essential Oils and Extracts of Some Mentha Species on Vero, Hela and Hep2 Cell Lines. 2010.
- Anderson, W.; Barrows, M.; Lopez, F.; Rogers, S.; Ortiz-Coffie, A.; Norman, D.; Hodges, J.; McDonald, K.; Barnes, D.; McCall, S.; et al. Investigation of the Anxiolytic Effects of Naringenin, a Component of Mentha Aquatica, in the Male Sprague-Dawley Rat. Holist Nurs Pract 2012, 26, 52–57. [CrossRef]
- Safaiee, P.; Taghipour, A.; Vahdatkhoram, F.; Movagharnejad, K. Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Mentha Aquatica: The Effects of Sonication Time, Temperature and Drying Method. Chemical Papers 2019, 73, 3067–3073. [CrossRef]
- Venditti, A.; Frezza, C.; Celona, D.; Sciubba, F.; Foddai, S.; Delfini, M.; Serafini, M.; Bianco, A.; Venditti, A.; Frezza, C.; et al. Phytochemical Comparison with Quantitative Analysis between Two Flower Phenotypes of <em>Mentha Aquatica</Em> L.: Pink-Violet and White. AIMS Molecular Science 2017 3:288 2017, 4, 288–300. [CrossRef]
- Mimica-Dukić, N.; Božin, B.; Soković, M.; Mihajlović, B.; Matavulj, M. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Three Mentha Species Essential Oils. Planta Med 2003, 69, 413–419. [CrossRef]
- Conforti, F.; Ioele, G.; Statti, G.A.; Marrelli, M.; Ragno, G.; Menichini, F. Antiproliferative Activity against Human Tumor Cell Lines and Toxicity Test on Mediterranean Dietary Plants. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2008, 46, 3325–3332. [CrossRef]
- Saqib, S.; Ullah, F.; Naeem, M.; Younas, M.; Ayaz, A.; Ali, S.; Zaman, W. Mentha: Nutritional and Health Attributes to Treat Various Ailments Including Cardiovascular Diseases. Molecules 2022, Vol. 27, Page 6728 2022, 27, 6728. [CrossRef]
- Gülçin, İ.; Gören, A.C.; Taslimi, P.; Alwasel, S.H.; Kılıc, O.; Bursal, E. Anticholinergic, Antidiabetic and Antioxidant Activities of Anatolian Pennyroyal (Mentha Pulegium)-Analysis of Its Polyphenol Contents by LC-MS/MS. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 2020, 23. [CrossRef]
- Bouyahya, A.; Et-Touys, A.; Bakri, Y.; Talbaui, A.; Fellah, H.; Abrini, J.; Dakka, N. Chemical Composition of Mentha Pulegium and Rosmarinus Officinalis Essential Oils and Their Antileishmanial, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities. Microb Pathog 2017, 111, 41–49. [CrossRef]
- Cherrat, L.; Espina, L.; Bakkali, M.; Pagán, R.; Laglaoui, A. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Mentha Pulegium, Lavandula Stoechas and Satureja Calamintha Scheele Essential Oils and an Evaluation of Their Bactericidal Effect in Combined Processes. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies 2014, 22, 221–229. [CrossRef]
- Chraibi, M.; Farah, A.; Lebrazi, S.; El Amine, O.; Iraqui Houssaini, M.; Fikri-Benbrahim, K. Antimycobacterial Natural Products from Moroccan Medicinal Plants: Chemical Composition, Bacteriostatic and Bactericidal Profile of Thymus Satureioides and Mentha Pulegium Essential Oils. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2016, 6, 836–840. [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, A.; Khusro, A.; Ahmadian, E.; Dizaj, S.M.; Dinparast, L.; Bahadori, M.B.; Hasanzadeh, A.; Cucchiarini, M. Phytochemical and Nutra-Pharmaceutical Attributes of Mentha Spp.: A Comprehensive Review. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2021, 14, 103106. [CrossRef]
- Al-Rajhi, A.M.H.; Qanash, H.; Almuhayawi, M.S.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; Bakri, M.M.; Ganash, M.; Salama, H.M.; Selim, S.; Abdelghany, T.M. Molecular Interaction Studies and Phytochemical Characterization of Mentha Pulegium L. Constituents with Multiple Biological Utilities as Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, Anticancer and Anti-Hemolytic Agents. Molecules 2022, 27. [CrossRef]
- Amtaghri, S.; Slaoui, M.; Eddouks, M. Mentha Pulegium: A Plant With Several Medicinal Properties. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2023, 23. [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.Y.; Hameed, I.H.; Ibraheam, I.A. Mentha Pulegium: Medicinal Uses, Anti-Hepatic, Antibacterial, Antioxidant Effect and Analysis of Bioactive Natural Compounds: A Review. Res J Pharm Technol 2017, 10, 3580–3584. [CrossRef]
- Pietrella, D.; Angiolella, L.; Vavala, E.; Rachini, A.; Mondello, F.; Ragno, R.; Bistoni, F.; Vecchiarelli, A. Beneficial Effect of Mentha Suaveolens Essential Oil in the Treatment of Vaginal Candidiasis Assessed by Real-Time Monitoring of Infection. BMC Complement Altern Med 2011, 11, 18. [CrossRef]
- Oumzil, H.; Ghoulami, S.; Rhajaoui, M.; Ilidrissi, A.; Fkih-Tetouani, S.; Faid, M.; Benjouad, A. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Essential Oils of Mentha Suaveolens. Wiley Online LibraryH Oumzil, S Ghoulami, M Rhajaoui, A Ilidrissi, S Fkih-Tetouani, M Faid, A BenjouadPhytotherapy Research: An International Journal Devoted to, 2002•Wiley Online Library 2002, 16, 727–731. [CrossRef]
- Aldogman, B.; Bilel, H.; Moustafa, S.M.N.; Elmassary, K.F.; Ali, H.M.; Alotaibi, F.Q.; Hamza, M.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; El-Ghorab, A.H. Investigation of Chemical Compositions and Biological Activities of Mentha Suaveolens L. from Saudi Arabia. Molecules 2022, 27. [CrossRef]
- Sytar, O.; Hemmerich, I.; Zivcak, M.; Rauh, C.; Brestic, M. Comparative Analysis of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds Composition from 26 Medicinal Plants. Saudi J Biol Sci 2018, 25, 631–641. [CrossRef]
- Al-Mijalli, S.H.; Assaggaf, H.; Qasem, A.; El-Shemi, A.G.; Abdallah, E.M.; Mrabti, H.N.; Bouyahya, A. Antioxidant, Antidiabetic, and Antibacterial Potentials and Chemical Composition of Salvia Officinalis and Mentha Suaveolens Grown Wild in Morocco. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yeom, M.; Shin, S.; Jeon, K.; Park, D.; Jung, E. Protective Effects of Aqueous Extract of Mentha Suaveolens against Oxidative Stress-Induced Damages in Human Keratinocyte HaCaT Cells. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Moreno, L.; Bello, R.; Primo-Yúfera, E.; Esplugues, J. Pharmacological Properties of the Methanol Extract from Mentha Suaveolens Ehrh. Phytotherapy Research 2002, 16, 10–13. [CrossRef]
- El-Akhal, J.; Oliveira, A.P.; Bencheikh, R.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Morato, M. Vasorelaxant Mechanism of Herbal Extracts from Mentha Suaveolens, Conyza Canadensis, Teucrium Polium and Salvia Verbenaca in the Aorta of Wistar Rats. Molecules 2022, Vol. 27, Page 8752 2022, 27, 8752. [CrossRef]
- Oniga, I.; Pus, C.; Silaghi-Dumitrescu, R.; Olah, N.K.; Sevastre, B.; Marica, R.; Marcus, I.; Sevastre-Berghian, A.C.; Benedec, D.; Pop, C.E.; et al. Origanum Vulgare Ssp. Vulgare: Chemical Composition and Biological Studies. Molecules 2018, Vol. 23, Page 2077 2018, 23, 2077. [CrossRef]
- Lombrea, A.; Antal, D.; Ardelean, F.; Avram, S.; Pavel, I.Z.; Vlaia, L.; Mut, A.M.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Dehelean, C.A.; Soica, C.; et al. A Recent Insight Regarding the Phytochemistry and Bioactivity of Origanum Vulgare L. Essential Oil. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, Vol. 21, Page 9653 2020, 21, 9653. [CrossRef]
- Sarikurkcu, C.; Zengin, G.; Oskay, M.; Uysal, S.; Ceylan, R.; Aktumsek, A. Composition, Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Enzyme Inhibition Activities of Two Origanum Vulgare Subspecies (Subsp. Vulgare and Subsp. Hirtum) Essential Oils. Ind Crops Prod 2015, 70, 178–184. [CrossRef]
- Milos, M.; Mastelic, J.; Jerkovic, I. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Effect of Glycosidically Bound Volatile Compounds from Oregano (Origanum Vulgare L. Ssp. Hirtum). Food Chem 2000, 71, 79–83. [CrossRef]
- Jafari Khorsand, G.; Morshedloo, M.R.; Mumivand, H.; Emami Bistgani, Z.; Maggi, F.; Khademi, A. Natural Diversity in Phenolic Components and Antioxidant Properties of Oregano (Origanum Vulgare L.) Accessions, Grown under the Same Conditions. Scientific Reports 2022 12:1 2022, 12, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, P.; Liu, H.; Sun, X.; Liang, J.; Sun, L.; Chen, Y. Hypoglycemic Activity of Origanum Vulgare L. and Its Main Chemical Constituents Identified with HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS. Food Funct 2021, 12, 2580–2590. [CrossRef]
- Vujicic, M.; Nikolic, I.; Kontogianni, V.G.; Saksida, T.; Charisiadis, P.; Orescanin-Dusic, Z.; Blagojevic, D.; Stosic-Grujicic, S.; Tzakos, A.G.; Stojanovic, I. Methanolic Extract of Origanum Vulgare Ameliorates Type 1 Diabetes through Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Apoptotic Activity. British Journal of Nutrition 2015, 113, 770–782. [CrossRef]
- Parra, C.; Muñoz, P.; Bustos, L.; Parra, F.; Simirgiotis, M.J.; Escobar, H. UHPLC-DAD Characterization of Origanum Vulgare L. from Atacama Desert Andean Region and Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Enzyme Inhibition Activities. Molecules 2021, 26. [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Berkay Yılmaz, Y.; Antika, G.; Salehi, B.; Tumer, T.B.; Kulandaisamy Venil, C.; Das, G.; Patra, J.K.; Karazhan, N.; Akram, M.; et al. Phytochemical Constituents, Biological Activities, and Health-Promoting Effects of the Genus Origanum. Phytotherapy Research 2021, 35, 95–121. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-J.; Wang, X.-H.; Dai, Y.-Y.; Ma, M.-H.; Rahman, K.; Nian, H.; Zhang, H. Prunella Vulgaris: A Comprehensive Review of Chemical Constituents, Pharmacological Effects and Clinical Applications. Curr Pharm Des 2019, 25, 359–369. [CrossRef]
- Mrabti, H.N.; El Menyiy, N.; Charfi, S.; Saber, M.; Bakrim, S.; Alyamani, R.A.; Rauf, A.; Ali, A.M.H.; Abdallah, E.M.; El Omari, N.; et al. Phytochemistry and Biological Properties of Salvia Verbenaca L.: A Comprehensive Review. Biomed Res Int 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Mamache, W.; Amira, S.; Ben Souici, C.; Laouer, H.; Benchikh, F. In Vitro Antioxidant, Anticholinesterases, Anti-α-Amylase, and Anti-α-Glucosidase Effects of Algerian Salvia Aegyptiaca and Salvia Verbenaca. J Food Biochem 2020, 44, e13472. [CrossRef]
- Nassar, M.; Zadri, F.; Slimani, S. Assessment of Protective Effects of Methanolic Extract of Salvia Verbenaca Roots Against Oxidative Damage Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide. Turk J Pharm Sci 2021, 18, 360. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Lopes, A.C.; Vaz, F.; Filipe, M.; Alves, G.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Coutinho, P.; Araujo, A.R.T.S. Thymus Mastichina: Composition and Biological Properties with a Focus on Antimicrobial Activity. Pharmaceuticals 2020, Vol. 13, Page 479 2020, 13, 479. [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.; Ashkar, F.; Koohpeyma, F.; Mahmoodi, M.; Gholamalizadeh, M.; Mazloom, Z.; Doaei, S. Hydroalcoholic Extract of Achillea Millefolium Improved Blood Glucose, Liver Enzymes and Lipid Profile Compared to Metformin in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Lipids Health Dis 2020, 19, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Coskun, O.; Kanter, M.; Korkmaz, A.; Oter, S. Quercetin, a Flavonoid Antioxidant, Prevents and Protects Streptozotocin-Induced Oxidative Stress and β-Cell Damage in Rat Pancreas. Pharmacol Res 2005, 51, 117–123. [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, K.G.; Ganai, B.A.; Akbar, S.; Dar, M.Y.; Masood, A. β-Cell Protective Efficacy, Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Effects of Extracts of Achillea Millifolium in Diabetic Rats. Chin J Nat Med 2012, 10, 185–189. [CrossRef]
- Nematy, M.; Mazidi, M.; Jafari, A.; Baghban, S.; Rakhshandeh, H.; Norouzy, A.; Esmaily, H.; Etemad, L.; Patterson, M.; Mohammadpour, A.H. The Effect of Hydro-Alcoholic Extract of Achillea Millefolium on Appetite Hormone in Rats. Avicenna J Phytomed 2017, 7, 10.
- Asakawa, A.; Inui, A.; Kaga, T.; Yuzuriha, H.; Nagata, T.; Ueno, N.; Makino, S.; Fujimiya, M.; Niijima, A.; Fujino, M.A.; et al. Ghrelin Is an Appetite-Stimulatory Signal from Stomach with Structural Resemblance to Motilin. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 337–345. [CrossRef]
- Asgary, S.; Naderi, G.; Ghannadi, A.; Gharipour, M.; Golbon, S. Protective Effect of Achillea Millefolium, Crataegus Curvisepala and Matricaria Chamomilla on Oxidative Hemolysis of Human Erythrocytes and -SH Capacity. Journal of Medicinal Plants 2003, 2, 41–48.
- Karimi, A.; Niazkar, H.R.; Sefidmooye Azar, P.; Tutunchi, H.; Karimi, M.; Asghariazar, V.; Kooshki, F. Protective Effect of Hydro-Alcoholic Extract of Achillea Millefolium on Renal Injury and Biochemical Factors in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Nutr Food Sci 2021, 51, 1068–1083. [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Silva, F.; Cerón-Romero, L.; Arias-Durán, L.; Navarrete-Vázquez, G.; Almanza-Pérez, J.; Román-Ramos, R.; Ramírez-Ávila, G.; Perea-Arango, I.; Villalobos-Molina, R.; Estrada-Soto, S. Antidiabetic Effect of Achillea Millefollium through Multitarget Interactions: α-Glucosidases Inhibition, Insulin Sensitization and Insulin Secretagogue Activities. J Ethnopharmacol 2018, 212, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Zolghadri, Y.; Fazeli, M.; Kooshki, M.; Shomali, T.; Karimaghayee, N.; Dehghani, M. Achillea Millefolium L. Hydro- Alcoholic Extract Protects Pancreatic Cells by Down Regulating IL- 1β and INOS Gene Expression in Diabetic Rats. Int J Mol Cell Med 2014, 3, 255.
- Noda, K.; Kato, E.; Kawabata, J. Intestinal α-Glucosidase Inhibitors in Achillea Millefolium. 10.1177/1934578X1701200828 2017, 12, 1259-1261. [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Trujillo, A.; Cruz-Sosa, F.; Luria-Pérez, R.; Gutiérrez-Rebolledo, G.A.; Román-Guerrero, A.; Burrola-Aguilar, C.; Zepeda-Gómez, C.; Estrada-Zúñiga, M.E. Arnica Montana Cell Culture Establishment, and Assessment of Its Cytotoxic, Antibacterial, α-Amylase Inhibitor, and Antioxidant In Vitro Bioactivities. Plants 2021, 10. [CrossRef]
- Haselgrübler, R.; Stadlbauer, V.; Stübl, F.; Schwarzinger, B.; Rudzionyte, I.; Himmelsbach, M.; Iken, M.; Weghuber, J. Insulin Mimetic Properties of Extracts Prepared from Bellis Perennis. Molecules : A Journal of Synthetic Chemistry and Natural Product Chemistry 2018, 23. [CrossRef]
- Nowicka, P.; Wojdyło, A. Anti-Hyperglycemic and Anticholinergic Effects of Natural Antioxidant Contents in Edible Flowers. Antioxidants 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Icoz, U.G.; Orhan, N.; Altun, L.; Aslan, M. In Vitro and in Vivo Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Activity Studies on Standardized Extracts of Two Bidens Species. J Food Biochem 2017, 41, e12429. [CrossRef]
- Azay-Milhau, J.; Ferrare, K.; Leroy, J.; Aubaterre, J.; Tournier, M.; Lajoix, A.D.; Tousch, D. Antihyperglycemic Effect of a Natural Chicoric Acid Extract of Chicory (Cichorium Intybus L.): A Comparative in Vitro Study with the Effects of Caffeic and Ferulic Acids. J Ethnopharmacol 2013, 150, 755–760. [CrossRef]
- Tousch, D.; Lajoix, A.D.; Hosy, E.; Azay-Milhau, J.; Ferrare, K.; Jahannault, C.; Cros, G.; Petit, P. Chicoric Acid, a New Compound Able to Enhance Insulin Release and Glucose Uptake. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008, 377, 131–135. [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.M.P.; Rathinasabapathy, T.; Esposito, D.; Komarnytsky, S. Structural Constraints and Importance of Caffeic Acid Moiety for Anti-Hyperglycemic Effects of Caffeoylquinic Acids from Chicory. Mol Nutr Food Res 2017, 61, 1601118. [CrossRef]
- Ebrahiminia, M.; Esmaeili, F.; Shabani, L. In Vitro Differentiation Induction of Embryonal Carcinoma Stem Cells into Insulin-Producing Cells by Cichorium Intybus L. Leaf Extract. J Ethnopharmacol 2020, 246, 112214. [CrossRef]
- Dalar, A.; Konczak, I. Cichorium Intybus from Eastern Anatolia: Phenolic Composition, Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities. Ind Crops Prod 2014, 60, 79–85. [CrossRef]
- Ferrare, K.; Bidel, L.P.R.; Awwad, A.; Poucheret, P.; Cazals, G.; Lazennec, F.; Azay-Milhau, J.; Tournier, M.; Lajoix, A.D.; Tousch, D. Increase in Insulin Sensitivity by the Association of Chicoric Acid and Chlorogenic Acid Contained in a Natural Chicoric Acid Extract (NCRAE) of Chicory (Cichorium Intybus L.) for an Antidiabetic Effect. J Ethnopharmacol 2018, 215, 241–248. [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, V.S.; Anand, S.; Sangeetha, K.N.; Sujatha, S.; Arun, B.; Lakshmi, B.S. Tannins Present in Cichorium Intybus Enhance Glucose Uptake and Inhibit Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes through PTP1B Inhibition. Chem Biol Interact 2008, 174, 69–78. [CrossRef]
- Asraoui, F.; Kounnoun, A.; Cacciola, F.; Mansouri, F. El; Kabach, I.; Majdoub, Y.O. El; Alibrando, F.; Arena, K.; Trovato, E.; Mondello, L.; et al. Phytochemical Profile, Antioxidant Capacity, α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Potential of Wild Moroccan Inula Viscosa (L.) Aiton Leaves. Molecules 2021, Vol. 26, Page 3134 2021, 26, 3134. [CrossRef]
- Aydin, T.; Saglamtas, R.; Dogan, B.; Kostekci, E.; Durmus, R.; Cakir, A. A New Specific Method for Isolation of Tomentosin with a High Yield from Inula Viscosa (L.) and Determination of Its Bioactivities. Phytochemical Analysis 2022, 33, 612–618. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Lee, J.-J.; Kim, I.-S.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.-S.; Myung, C.-S. 7-O-Methylaromadendrin Stimulates Glucose Uptake and Improves Insulin Resistance in Vitro. Article Biol. Pharm. Bull 2010, 33, 1494–1499.
- Ranilla, L.G.; Kwon, Y.I.; Apostolidis, E.; Shetty, K. Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant Activity and in Vitro Inhibitory Potential against Key Enzymes Relevant for Hyperglycemia and Hypertension of Commonly Used Medicinal Plants, Herbs and Spices in Latin America. Bioresour Technol 2010, 101, 4676–4689. [CrossRef]
- Ferheen, S.; Ur-Rehman, A.; Afza, N.; Malik, A.; Iqbal, L.; Azam Rasool, M.; Irfan Ali, M.; Bakhsh Tareen, R. Galinsosides A and B, Bioactive Flavanone Glucosides from Galinsoga Parviflora. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2009, 24, 1128–1132. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-M.; Lee, J.-M.; Choi, K.; Ku, J.-J.; Park, K.-W. Inhibition of Aldose Reductase from Rat Lenses by Methanol Extracts from Korean Folk Plants. Natural Product Sciences 2010, 16, 285–290.
- Paun, G.; Neagu, E.; Alecu, A.; Albu, C.; Seciu-Grama, A.-M.; Radu, G.L. Evaluation of the Antioxidant, and Antidiabetic Properties of Flavonoids and Isoflavonoids-Rich Extracts of Medicago Sativa and Solidago Virgaurea. Complementary and Alternative Medicine Preprints 2023. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lin, X.; Fan, X.; Qian, Y.; Lv, Q.; Teng, H. Sonchus Oleraceus Linn Extract Enhanced Glucose Homeostasis through the AMPK/Akt/ GSK-3β Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Liver and HepG2 Cell Culture. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2020, 136, 111072. [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Quispe, Y.N.G.; Wang, Z.; Zuo, G.; Lim, S.S. Aldose Reductase, Protein Glycation Inhibitory and Antioxidant of Peruvian Medicinal Plants: The Case of Tanacetum Parthenium L. and Its Constituents. Molecules 2019, Vol. 24, Page 2010 2019, 24, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Zengin, G.; Cvetanović, A.; Gašić, U.; Stupar, A.; Bulut, G.; Şenkardes, I.; Dogan, A.; Ibrahime Sinan, K.; Uysal, S.; Aumeeruddy-Elalfi, Z.; et al. Modern and Traditional Extraction Techniques Affect Chemical Composition and Bioactivity of Tanacetum Parthenium (L.) Sch.Bip. Ind Crops Prod 2020, 146, 112202. [CrossRef]
- Ak, G.; Gevrenova, R.; Sinan, K.I.; Zengin, G.; Zheleva, D.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Senkardes, I.; Brunetti, L.; Leone, S.; Di Simone, S.C.; et al. Tanacetum Vulgare L. (Tansy) as an Effective Bioresource with Promising Pharmacological Effects from Natural Arsenal. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2021, 153, 112268. [CrossRef]
- Boutahiri, S.; Bouhrim, M.; Abidi, C.; Mechchate, H.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Noman, O.M.; Elombo, F.K.; Gressier, B.; Sahpaz, S.; Bnouham, M.; et al. Antihyperglycemic Effect of Lavandula Pedunculata: In Vivo, In Vitro and Ex Vivo Approaches. Pharmaceutics 2021, Vol. 13, Page 2019 2021, 13, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Elrherabi, A.; Bouhrim, M.; Abdnim, R.; Berraaouan, A.; Ziyyat, A.; Mekhfi, H.; Legssyer, A.; Bnouham, M. Antihyperglycemic Potential of the Lavandula Stoechas Aqueous Extract via Inhibition of Digestive Enzymes and Reduction of Intestinal Glucose Absorption. J Ayurveda Integr Med 2023, 14, 100795. [CrossRef]
- Kulabas, S.S.; Ipek, H.; Tufekci, A.R.; Arslan, S.; Demirtas, I.; Ekren, R.; Sezerman, U.; Tumer, T.B. Ameliorative Potential of Lavandula Stoechas in Metabolic Syndrome via Multitarget Interactions. J Ethnopharmacol 2018, 223, 88–98. [CrossRef]
- Yui, S.; Fujiwara, S.; Harada, K.; Motoike-Hamura, M.; Sakai, M.; Matsubara, S.; Miyazaki, K. Beneficial Effects of Lemon Balm Leaf Extract on In Vitro Glycation of Proteins, Arterial Stiffness, and Skin Elasticity in Healthy Adults. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 2017, 63, 59–68. [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-I.I.; Vattem, D.A.; Shetty, K. Evaluation of Clonal Herbs of Lamiaceae Species for Management of Diabetes and Hypertension. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2006, 15, 107–118.
- Mccue, P.P.; Shetty, K. Inhibitory Effects of Rosmarinic Acid Extracts on Porcine Pancreatic Amylase in Vitro. Asia Pacific J Clin Nutr 2004, 13, 101–106.
- Schreck, K.; Melzig, M.F. Traditionally Used Plants in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: Screening for Uptake Inhibition of Glucose and Fructose in the Caco2-Cell Model. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12. [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.F.; Hsieh, C.T.; Hsieh, T.J.; Chang, F.R.; Wang, C.K. In Vitro Anti-Diabetic Effect and Chemical Component Analysis of 29 Essential Oils Products. J Food Drug Anal 2015, 23, 124. [CrossRef]
- Marrelli, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Nicoletti, M.; Menichini, F.; Conforti, F. In Vitro Investigation of the Potential Health Benefits of Wild Mediterranean Dietary Plants as Anti-Obesity Agents with α-Amylase and Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitory Activities. J Sci Food Agric 2014, 94, 2217–2224. [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, T.; Melzig, M.F. Medicinal Plants Traditionally Used for Treatment of Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus – Screening for Pancreatic Lipase and α-Amylase Inhibition. Phytotherapy Research 2016, 30, 260–266. [CrossRef]
- Abbou, F.; Azzi, R.; Ouffai, K.; El Haci, I.A.; Belyagoubi-Benhammou, N.; Bensouici, C.; Benamar, H. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibitory Properties of Phenolic-Rich Fractions from the Aerial Parts of Mentha Pulegium L. South African Journal of Botany 2022, 146, 196–204. [CrossRef]
- Mccue, P.; Vattem, D.; Shetty, K. Inhibitory Effect of Clonal Oregano Extracts against Porcine Pancreatic Amylase in Vitro. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2004, 13, 401–408.
- Koukoulitsa, C.; Zika, C.; Geromichalos, G.D.; Demopoulos, V.J.; Skaltsa, H. Evaluation of Aldose Reductase Inhibition and Docking Studies of Some Secondary Metabolites, Isolated from Origanum Vulgare L. Ssp. Hirtum. Bioorg Med Chem 2006, 14, 1653–1659. [CrossRef]
- Christensen, K.B.; Minet, A.; Svenstrup, H.; Grevsen, K.; Zhang, H.; Schrader, E.; Rimbach, G.; Wein, S.; Wolffram, S.; Kristiansen, K.; et al. Identification of Plant Extracts with Potential Antidiabetic Properties: Effect on Human Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR), Adipocyte Differentiation and Insulin-Stimulated Glucose Uptake. Phytotherapy Research 2009, 23, 1316–1325. [CrossRef]
- Bower, A.M.; Real Hernandez, L.M.; Berhow, M.A.; De Mejia, E.G. Bioactive Compounds from Culinary Herbs Inhibit a Molecular Target for Type 2 Diabetes Management, Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV. J Agric Food Chem 2014, 62, 6147–6158. [CrossRef]
- Valentová, K.; Nhu, T.T.; Moncion, A.; De Waziers, I.; Ulrichová, J. Induction of Glucokinase MRNA by Dietary Phenolic Compounds in Rat Liver Cells in Vitro. J Agric Food Chem 2007, 55, 7726–7731. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Kim, J.K.; Jang, J.M.; Kwon, S.O.; Cui, C.B.; Lim, S.S. The Inhibitory Effect of Prunella Vulgaris L. on Aldose Reductase and Protein Glycation. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Gao, M.; Ha, T.; Kelley, J.; Young, A.; Breuel, K. Prunella Vulgaris Aqueous Extract Attenuates IL-1β-Induced Apoptosis and NF-ΚB Activation in INS-1 Cells. Exp Ther Med 2012, 3, 919–924. [CrossRef]
- Raafat, K.; Wurglics, M.; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M. Prunella Vulgaris L. Active Components and Their Hypoglycemic and Antinociceptive Effects in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Mice. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2016, 84, 1008–1018. [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Liu, H.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y. Study on the Mechanism of Prunella Vulgaris L on Diabetes Mellitus Complicated with Hypertension Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analyses. J Diabetes Res 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, F.; Cao, Y.; Cai, G.; Wei, Q.; Shi, S.; Guo, Y. Screening of Potent α-Glucosidase Inhibitory and Antioxidant Polyphenols in Prunella Vulgaris L. by Bioreaction–HPLC–Quadrupole-Time-of-Flight-MS/MS and in Silico Analysis. J Sep Sci 2022, 45, 3393–3403. [CrossRef]
- Aazza, S.; El-Guendouz, S.; Graça Miguel, M.; Antunes, M.D.; Faleiro, M.L.; Correia, A.I.; Figueiredo, A.C. Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Hyperglycaemic Activities of Essential Oils from Thymbra Capitata, Thymus Albicans, Thymus Caespititius, Thymus Carnosus, Thymus Lotocephalus and Thymus Mastichina from Portugal. Nat Prod Commun . 2016, 11, 1029–1038.
- Eddouks, M.; Lemhadri, A.; Zeggwagh, N.A.; Michel, J.B. Potent Hypoglycaemic Activity of the Aqueous Extract of Chamaemelum Nobile in Normal and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2005, 67, 189–195. [CrossRef]
- König, G.M.; Wright, A.D.; Keller, W.J.; Judd, R.L.; Bates, S.; Day, C. Hypoglycaemic Activity of an HMG-Containing Flavonoid Glucoside, Chamaemeloside, from Chamaemelum Nobile. Planta Med 1998, 64, 612–614. [CrossRef]
- Witherup, K.M.; McLaughlin, J.L.; Judd, R.L.; Ziegler, M.H.; Medon, P.J.; Keller, W.J. Identification of 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaric Acid (HMG) as a Hypoglycemic Principle of Spanish Moss (Tillandsia Usneoides). J Nat Prod 1995, 58, 1285–1290. [CrossRef]
- Yonei, Y.; Miyazaki, R.; Takahashi, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Nomoto, K.; Yagi, M.; Kawai, H.; Kubo, M.; Matsuura, N. Anti-Glycation Effect of Mixed Herbal Extract in Individuals with Pre-Diabetes Mellitus A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel Group Study. ANTI-AGING MEDICINE 2010, 7, 26–35. [CrossRef]
- Pushparaj, P.N.; Low, H.K.; Manikandan, J.; Tan, B.K.H.; Tan, C.H. Anti-Diabetic Effects of Cichorium Intybus in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2007, 111, 430–434. [CrossRef]
- Ghamarian, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Su, X.; Amiri, A.; Ahadi, A.; Nowrouzi, A. Effect of Chicory Seed Extract on Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) and Metabolic Profile in Early and Late Stage Diabetic Rats. DARU, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2012, 20. [CrossRef]
- Jurgoński, A.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Zduńczyk, Z.; Król, B. Caffeoylquinic Acid-Rich Extract from Chicory Seeds Improves Glycemia, Atherogenic Index, and Antioxidant Status in Rats. Nutrition 2012, 28, 300–306. [CrossRef]
- Petrović, A.; Madić, V.; Stojanović, G.; Zlatanović, I.; Zlatković, B.; Vasiljević, P.; Đorđević, L. Antidiabetic Effects of Polyherbal Mixture Made of Centaurium Erythraea, Cichorium Intybus and Potentilla Erecta. J Ethnopharmacol 2024, 319, 117032. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Lin, L.G.; Ye, W.C. Techniques for Extraction and Isolation of Natural Products: A Comprehensive Review. Chinese Medicine (United Kingdom) 2018, 13. [CrossRef]
- Oršolić, N.; Sirovina, D.; Odeh, D.; Gajski, G.; Balta, V.; Šver, L.; Jembrek, M.J. Efficacy of Caffeic Acid on Diabetes and Its Complications in the Mouse. Molecules 2021, 26. [CrossRef]
- Schaalan, M.; El-Abhar, H.S.; Barakat, M.; El-Denshary, E.S. Westernized-like-Diet-Fed Rats: Effect on Glucose Homeostasis, Lipid Profile, and Adipocyte Hormones and Their Modulation by Rosiglitazone and Glimepiride. J Diabetes Complications 2009, 23, 199–208. [CrossRef]
- Saleh Aldayel, T.; Alshammari, G.M.; Mohammed Omar, U.; Grace, M.H.; Ann Lila, M.; Yahya, M.A. Hypoglycaemic, Insulin Releasing, and Hepatoprotective Effect of the Aqueous Extract of Aloe Perryi Baker Resin (Socotran Aloe) in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Taylor & FrancisTS Aldayel, GM Alshammari, UM Omar, MH Grace, MA Lila, MA YahyaJournal of Taibah University for Science, 2020•Taylor & Francis 2020, 14, 1671–1685. [CrossRef]
- Peungvicha, P.; Temsiririrkkul, R.; Prasain, J.K.; Tezuka, Y.; Kadota, S.; Thirawarapan, S.S.; Watanabe, H. 4-Hydroxybenzoic Acid: A Hypoglycemic Constituent of Aqueous Extract of Pandanus Odorus Root. J Ethnopharmacol 1998, 62, 79–84. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Cheung, F.; Hong, M.; Feng, Y. The Potential and Action Mechanism of Polyphenols in the Treatment of Liver Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, D.; Albert, A.; Paul, E.; Ananthapadmanabhan, K.; Andiappan, R.; Sadasivam, S.G. Rutin Ameliorates Metabolic Acidosis and Fibrosis in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Nephropathy and Cardiomyopathy in Experimental Rats. Mol Cell Biochem 2020, 471, 41–50. [CrossRef]
- Quine, S.; Rep, P.R.-P.; 2005, undefined Effects of (-)-Epicatechin, a Flavonoid on Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidants in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Liver, Kidney and Heart. researchgate.netSD Quine, PS RaghuPharmacol Rep, 2005•researchgate.net 2005.
- Zhang, L.; He, S.; Yang, F.; Yu, H.; Xie, W.; Dai, Q.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, K. Hyperoside Ameliorates Glomerulosclerosis in Diabetic Nephropathy by Downregulating MiR-21. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2016, 94, 1249–1256. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Lou, Y.; Bao, J.; Yu, J. Hyperoside Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy Induced by STZ via Targeting the MiR-499–5p/APC Axis. J Pharmacol Sci 2021, 146, 10–20. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ren, G. Antidiabetic Activity of Isoquercetin in Diabetic KK -A y Mice. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2011, 8. [CrossRef]
- Jayachandran, M.; Zhang, T.; Ganesan, K.; Xu, B.; Chung, S.S.M. Isoquercetin Ameliorates Hyperglycemia and Regulates Key Enzymes of Glucose Metabolism via Insulin Signaling Pathway in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2018, 829, 112–120. [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, T.O.; Ajala-Lawal, R.A.; Adeyiga, A.B. Caffeic Acid Abrogates 1,3-Dichloro-2-Propanol-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Upregulating Nuclear Erythroid-Related Factor 2 and Downregulating Nuclear Factor-Kappa B. Hum Exp Toxicol 2019, 38, 1092–1101. [CrossRef]
- Ghamarian, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Su, X.; Amiri, A.; Ahadi, A.; Nowrouzi, A. Effect of Chicory Seed Extract on Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) and Metabolic Profile in Early and Late Stage Diabetic Rats. DARU, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2012, 20, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Jurgoński, A.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Zduńczyk, Z.; Król, B. Caffeoylquinic Acid-Rich Extract from Chicory Seeds Improves Glycemia, Atherogenic Index, and Antioxidant Status in Rats. Nutrition 2012, 28, 300–306. [CrossRef]
- Ayyoub, S.; Al-Trad, B.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Alshaer, W.; Al Zoubi, M.; Omari, S.; Fayyad, D.; Tambuwala, M.M. Biosynthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Dittrichia Viscosa and in Vivo Assessment of Its Anti-Diabetic Efficacy. Drug Deliv Transl Res 2022, 12, 2993. [CrossRef]
- Zeggwagh, N.A.; Ouahidi, M.L.; Lemhadri, A.; Eddouks, M. Study of Hypoglycaemic and Hypolipidemic Effects of Inula Viscosa L. Aqueous Extract in Normal and Diabetic Rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2006, 108, 223–227. [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, I.; El-Aziz, E.A.; Hafez, S.; El-Shazly, A. Chemical Constituents and Biological Activities of Galinsoga Parviflora Cav. (Asteraceae) from Egypt. Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung - Section C Journal of Biosciences 2013, 68, 285–292. [CrossRef]
- Salih, B.A. Effect of Lactuca Serriola on β-Cell Dysfunction and Glucose Tolerance Induced by High Sucrose Fed in Albino Rats. J Phys Conf Ser 2019, 1294, 062092. [CrossRef]
- Sharef, A.Y.; Hamdi, B.A.; Alrawi, R.A.; Ahmad, H.O. Onopordum Acanthium L. Extract Attenuates Pancreatic β-Cells and Cardiac Inflammation in Streptozocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. PLoS One 2023, 18. [CrossRef]
- Sanad, F.A.A.; Ahmed, S.F.; El-Tantawy, W.H. Antidiabetic and Hypolipidemic Potentials of Solidago Virgaurea Extract in Alloxan-Induced Diabetes Type 1. Arch Physiol Biochem 2022, 128, 716–723. [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.A.; Khan, M.R.; Shah, N.A.; Sahreen, S.; Siddiq, P. Modulation of Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats by n-Hexane Extract of Sonchus Asper. Toxicol Ind Health 2015, 31, 955–959. [CrossRef]
- Teugwa, C.M.; Mejiato, P.C.; Zofou, D.; Tchinda, B.T.; Boyom, F.F. Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Profiles of Two African Medicinal Plants: Picralima Nitida (Apocynaceae) and Sonchus Oleraceus (Asteraceae). BMC Complement Altern Med 2013, 13, 175. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fan, X.; Lin, X.; Qian, L.; Zengin, G.; Delmas, D.; Paoli, P.; Teng, H.; Xiao, J. Phenolic Extract from Sonchus Oleraceus L. Protects Diabetes-Related Liver Injury in Rats through TLR4/NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. eFood 2020, 1, 77–84. [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.S.; Abdel-Alim, M.; Said, H.E.M.; Foda, M.F. Phenolic Profiles, Antihyperglycemic, Anti-Diabetic, and Antioxidant Properties of Egyptian Sonchus Oleraceus Leaves Extract: An In Vivo Study. Molecules 2023, 28. [CrossRef]
- Sebai, H.; Selmi, S.; Rtibi, K.; Souli, A.; Gharbi, N.; Sakly, M. Lavender (Lavandula Stoechas L.) Essential Oils Attenuate Hyperglycemia and Protect against Oxidative Stress in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. Lipids Health Dis 2013, 12, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Sebai, H.; Selmi, S.; Rtibi, K.; Gharbi, N.; Sakly, M. Protective Effect of Lavandula Stoechas and Rosmarinus Officinalis Essential Oils Against Reproductive Damage and Oxidative Stress in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. https://home.liebertpub.com/jmf 2015, 18, 241–249. [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.B.; Akram, M.; Muhammad Asif, H.; Qayyum, I.; Hashmi, A.M.; Munir, N.; Khan, F.S.; Riaz, M.; Ahmad, S. Antihyperglycemic Activity of Hydroalcoholic Extracts of Selective Medicinal Plants Curcuma Longa, Lavandula Stoechas, Aegle Marmelos, and Glycyrrhiza Glabra and Their Polyherbal Preparation in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Mice. Dose-Response 2019, 17. [CrossRef]
- Demir, D.; Toygar, I.; Soylu, E.; Aksu, A.T.; Türeyen, A.; Yıldırım, I.; Çetinkalp, Ş. The Effect of Lavandula Stoechas on Wound Healing in an Experimental Diabetes Model. Cureus 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.J.; Cho, S.Y.; Bhuiyan, M.J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.J. Anti-Diabetic Effects of Lemon Balm (Melissa Officinalis) Essential Oil on Glucose- and Lipid-Regulating Enzymes in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. British Journal of Nutrition 2010, 104, 180–188. [CrossRef]
- Weidner, C.; Wowro, S.J.; Freiwald, A.; Kodelja, V.; Abdel-Aziz, H.; Kelber, O.; Sauer, S. Lemon Balm Extract Causes Potent Antihyperglycemic and Antihyperlipidemic Effects in Insulin-Resistant Obese Mice. Mol Nutr Food Res 2014, 58, 903–907. [CrossRef]
- Hasanein, P.; Riahi, H. Antinociceptive and Antihyperglycemic Effects of Melissa Officinalis Essential Oil in an Experimental Model of Diabetes. Medical Principles and Practice 2015, 24, 47–52. [CrossRef]
- Moshtaghian, J.; Khodsooz, S.; Moshtaghian, J.; Eivani, M. Antihyperglycemic and Antihyperlipidemic Effects of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Melissa Officinalis (Lemon Balm) in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. Physiology and Pharmacology 2016, 20, 24–30.
- Lee, D.; Shin, Y.; Roh, J.S.; Ahn, J.; Jeoong, S.; Shin, S.S.; Yoon, M. Lemon Balm Extract ALS-L1023 Regulates Obesity and Improves Insulin Sensitivity via Activation of Hepatic PPARα in High-Fat Diet-Fed Obese C57BL/6J Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, Vol. 21, Page 4256 2020, 21, 4256. [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Lee, D.; Ahn, J.; Lee, M.; Shin, S.S.; Yoon, M. The Herbal Extract ALS-L1023 from Melissa Officinalis Reduces Weight Gain, Elevated Glucose Levels and β-Cell Loss in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty Rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2021, 264, 113360. [CrossRef]
- Yellanur Konda, P.; Egi, J.Y.; Dasari, S.; Katepogu, R.; Jaiswal, K.K.; Nagarajan, P. Ameliorative Effects of Mentha Aquatica on Diabetic and Nephroprotective Potential Activities in STZ-Induced Renal Injury. Comp Clin Path 2020, 29, 189–199. [CrossRef]
- Farid, O.; Zeggwagh, N.A.; Ouadi, F. EL; Eddouks, M. Mentha Pulegium Aqueous Extract Exhibits Antidiabetic and Hepatoprotective Effects in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2018, 19, 292–301. [CrossRef]
- Farid, O.; Eddouks, M. Evaluation of the Anti-Hypercholesterolemic and Antioxidant Activity of Mentha Pulegium (L.) Aqueous Extract in Normal and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Nat Prod J 2019, 10, 236–243. [CrossRef]
- Ajebli, M.; Eddouks, M. Pharmacological and Phytochemical Study of Mentha Suaveolens Ehrh in Normal and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Nat Prod J 2018, 8, 213–227. [CrossRef]
- Lemhadri, A.; Zeggwagh, N.A.; Maghrani, M.; Jouad, H.; Eddouks, M. Anti-Hyperglycaemic Activity of the Aqueous Extract of Origanum Vulgare Growing Wild in Tafilalet Region. J Ethnopharmacol 2004, 92, 251–256. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Nassier, O.A. The Antihyperglycaemic Effect of the Aqueous Extract of Origanium Vulgare Leaves in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Jordan J Biol Sci 2013, 6, 31–38. [CrossRef]
- Vujicic, M.; Nikolic, I.; Kontogianni, V.G.; Saksida, T.; Charisiadis, P.; Orescanin-Dusic, Z.; Blagojevic, D.; Stosic-Grujicic, S.; Tzakos, A.G.; Stojanovic, I. Methanolic Extract of Origanum Vulgare Ameliorates Type 1 Diabetes through Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Apoptotic Activity. British Journal of Nutrition 2015, 113, 770–782. [CrossRef]
- Vujicic, M.; Nikolic, I.; Kontogianni, V.G.; Saksida, T.; Charisiadis, P.; Vasic, B.; Stosic-Grujicic, S.; Gerothanassis, I.P.; Tzakos, A.G.; Stojanovic, I. Ethyl Acetate Extract of Origanum Vulgare L. Ssp. Hirtum Prevents Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes in C57BL/6 Mice. J Food Sci 2016, 81, H1846–H1853. [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, R.; Ashraf, E.A.; Essam, M.A. Chamomile and Oregano Extracts Synergistically Exhibit Antihyperglycemic, Antihyperlipidemic, and Renal Protective Effects in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2017, 95, 84–92. [CrossRef]
- Martha erez Guti errez, R.P.; Fernando Martínez Jer onimo, F.; Guadalupe Contreras Soto, J.; Mu, A.; Ramírez, niz; Fernanda Estrella Mendoza, M. Optimization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of Polyphenols from the Polyherbal Formulation of Cinnamomum Verum, Origanum Majorana, and Origanum Vulgare and Their Anti-Diabetic Capacity in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Heliyon 2017, e08682. [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.L.A. e.; Lucarini, R.; dos Santos, F.F.; Martins, C.H.G.; Pauletti, P.M.; Januario, A.H.; Santos, M.F.C.; Cunha, W.R. Hypoglycemic Effect of Rosmarinic Acid-Rich Infusion (RosCE) from Origanum Vulgare in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. Nat Prod Res 2022, 36, 4525–4531. [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.M.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Yoon, J.J.; Lee, S.M.; Kang, D.G.; Lee, H.S. Anti-Diabetic Atherosclerosis Effect of Prunella Vulgaris in Db/Db Mice with Type 2 Diabetes. 10.1142/S0192415X12500693 2012, 40, 937-951. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.S.; Lu, J.G.; Gu, Z.L.; Gu, G.X. Effects of Triterpenic Acid from Prunella Vulgaris L. On Glycemia and Pancreas in Rat Model of Streptozotozin Diabetes. Chin Med J (Engl) 2013, 126, 1647–1653. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, O.; Liu, J.; Cai, S.; Wang, R.; Zhou, F.; Ji, B. Anti-Diabetic Effects of the Ethanol Extract of a Functional Formula Diet in Mice Fed with a Fructose/Fat-Rich Combination Diet. J Sci Food Agric 2015, 95, 401–408. [CrossRef]
- Namgung, S.; Yoon, J.J.; Yoon, C.S.; Han, B.H.; Choi, E.S.; Oh, H.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, Y.J.; Kang, D.G.; Lee, H.S. Prunella Vulgaris Attenuates Diabetic Renal Injury by Suppressing Glomerular Fibrosis and Inflammation. 10.1142/S0192415X1750029X 2017, 45, 475-495. [CrossRef]
- Upson, Tim.; Andrews, Susyn.; Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. The Genus Lavandula. 2004, 442.
- Soković, M.; Petar, •; Marin, D.; Brkić, D.; Leo, •; Van Griensven, J.L.D. Chemical Composition and Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oils of Ten Aromatic Plants against Human Pathogenic Bacteria.
- Sahranavard, S.; Ghafari, S.; Mosaddegh, M. Medicinal Plants Used in Iranian Traditional Medicine to Treat Epilepsy. Seizure 2014, 23, 328–332. [CrossRef]
- Cocco, E.; Maccioni, D.; Sanjust, E.; Falconieri, D.; Farris, E.; Maxia, A. Ethnopharmacobotany and Diversity of Mediterranean Endemic Plants in Marmilla Subregion, Sardinia, Italy. Plants 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Nayebi, N.; Esteghamati, A.; Meysamie, A.; Khalili, N.; Kamalinejad, M.; Emtiazy, M.; Hashempur, M.H. The Effects of a Melissa Officinalis L. Based Product on Metabolic Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Double-Blinded Controlled Clinical Trial. J Complement Integr Med 2019, 16. [CrossRef]
- Asadi, A.; Shidfar, F.; Safari, M.; Hosseini, A.F.; Fallah Huseini, H.; Heidari, I.; Rajab, A. Efficacy of Melissa Officinalis L. (Lemon Balm) Extract on Glycemic Control and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Clinical Trial. Phytotherapy Research 2019, 33, 651–659. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M. The Role of PPARα in Lipid Metabolism and Obesity: Focusing on the Effects of Estrogen on PPARα Actions. Pharmacol Res 2009, 60, 151–159. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M. PPAR in Obesity: Sex Difference and Estrogen Involvement. PPAR Res 2010. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Mishra, S.; Malik, A.; Satya, S. Insecticidal Properties of Mentha Species: A Review. Ind Crops Prod 2011, 34, 802–817. [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, A.; Khusro, A.; Ahmadian, E.; Dizaj, S.M.; Dinparast, L.; Bahadori, M.B.; Hasanzadeh, A.; Cucchiarini, M. Phytochemical and Nutra-Pharmaceutical Attributes of Mentha Spp.: A Comprehensive Review. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2021, 14, 103106. [CrossRef]
- Peter, K. Handbook of Herbs and Spices: Volume 3. 2006.
- Rahman, M.M.; Dhar, P.S.; Sumaia; Anika, F.; Ahmed, L.; Islam, M.R.; Sultana, N.A.; Cavalu, S.; Pop, O.; Rauf, A. Exploring the Plant-Derived Bioactive Substances as Antidiabetic Agent: An Extensive Review. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2022, 152, 113217. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.S.P.; Banegas-Luna, A.J.; Peña-García, J.; Pérez-Sánchez, H.; Apostolides, Z. Evaluation of the Anti-Diabetic Activity of Some Common Herbs and Spices: Providing New Insights with Inverse Virtual Screening. Molecules 2019, Vol. 24, Page 4030 2019, 24, 4030. [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.-K.; Yadav, D.; Sharma, N.; Jin, J.-O.; Dipeptidyl, J. Dipeptidyl Peptidase (DPP)-IV Inhibitors with Antioxidant Potential Isolated from Natural Sources: A Novel Approach for the Management of Diabetes. mdpi.comAK Singh, D Yadav, N Sharma, JO JinPharmaceuticals, 2021•mdpi.com 2021, 14. [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.J.; Tzen, J.T.C. The Potential Role of Cyclopeptides from Pseudostellaria Heterophylla, Linum Usitatissimum and Drymaria Diandra, and Peptides Derived from Heterophyllin B as Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitors for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: An In Silico Study. Metabolites 2022, Vol. 12, Page 387 2022, 12, 387. [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.J. Sitagliptin: A Review in Type 2 Diabetes. Drugs 2017, 77, 209–224. [CrossRef]
- Godinho, R.; Mega, C.; Teixeira-De-Lemos, E.; Carvalho, E.; Teixeira, F.; Fernandes, R.; Reis, F. The Place of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes Therapeutics: A “Me Too” or “the Special One” Antidiabetic Class? J Diabetes Res 2015, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Klemann, C.; Wagner, L.; Stephan, M.; von Hörsten, S. Cut to the Chase: A Review of CD26/Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4’s (DPP4) Entanglement in the Immune System. Clin Exp Immunol 2016, 185, 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Olennikov, D.N.; Shamilov, A.A.; Kashchenko, N.I. New Glycoside of Quercetin from the Genus Prunella. Chem Nat Compd 2023, 59, 647–650. [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Xia, B.; Xie, W.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, J.; Li, H.; Liao, D.; Lin, L.; Li, C. Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activities of the Genus Prunella. Food Chem 2016, 204, 483–496. [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y. Prunella Vulgaris L. – A Review of Its Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, Quality Control and Pharmacological Effects. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 23. [CrossRef]
- Commission N. H. List of New Food Materials and Common Foods.; 2016.
- Commission C. P. The 2020 Edition of Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China.; Beijing, China, 2020.
- Li, K.; Hui-Xia, Y. Value of Fructosamine Measurement in Pregnant Women with Abnormal Glucose Tolerance; 2006; Vol. 119.
- Katakami N Mechanism of Development of Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Mellitus. J Atheroscler Thromb 2018, 25, 27–39. [CrossRef]
- La Sala, L.; F Prattichizz; A Ceriello The Link between Diabetes and Atherosclerosis. Eur J Prev Cardiol 2019, 26, 15–24. [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, A.; Grechko, A. V.; Poggio, P.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Alfieri, V.; Orekhov, A.N. The Diabetes Mellitus–Atherosclerosis Connection: The Role of Lipid and Glucose Metabolism and Chronic Inflammation. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [CrossRef]
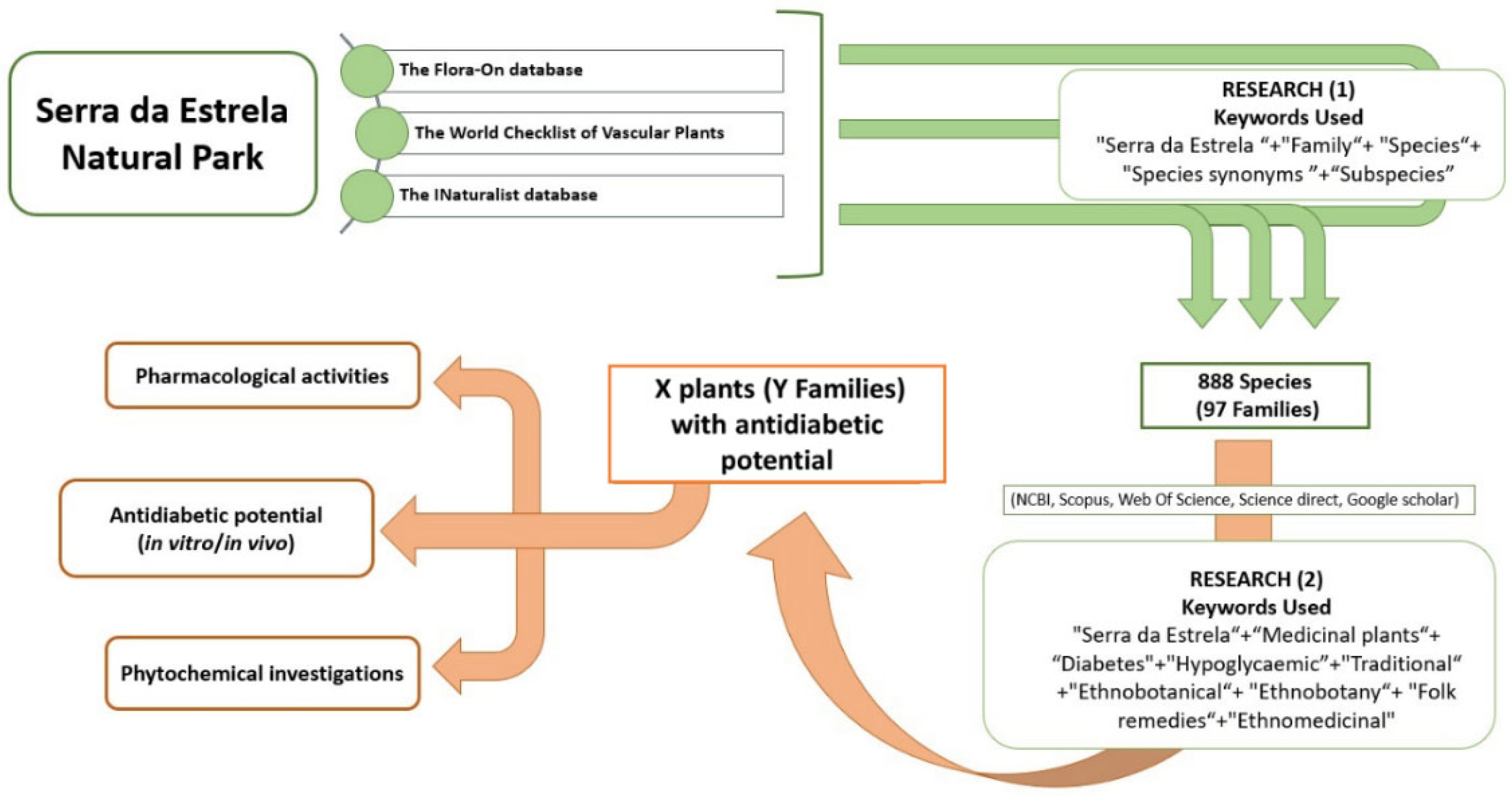
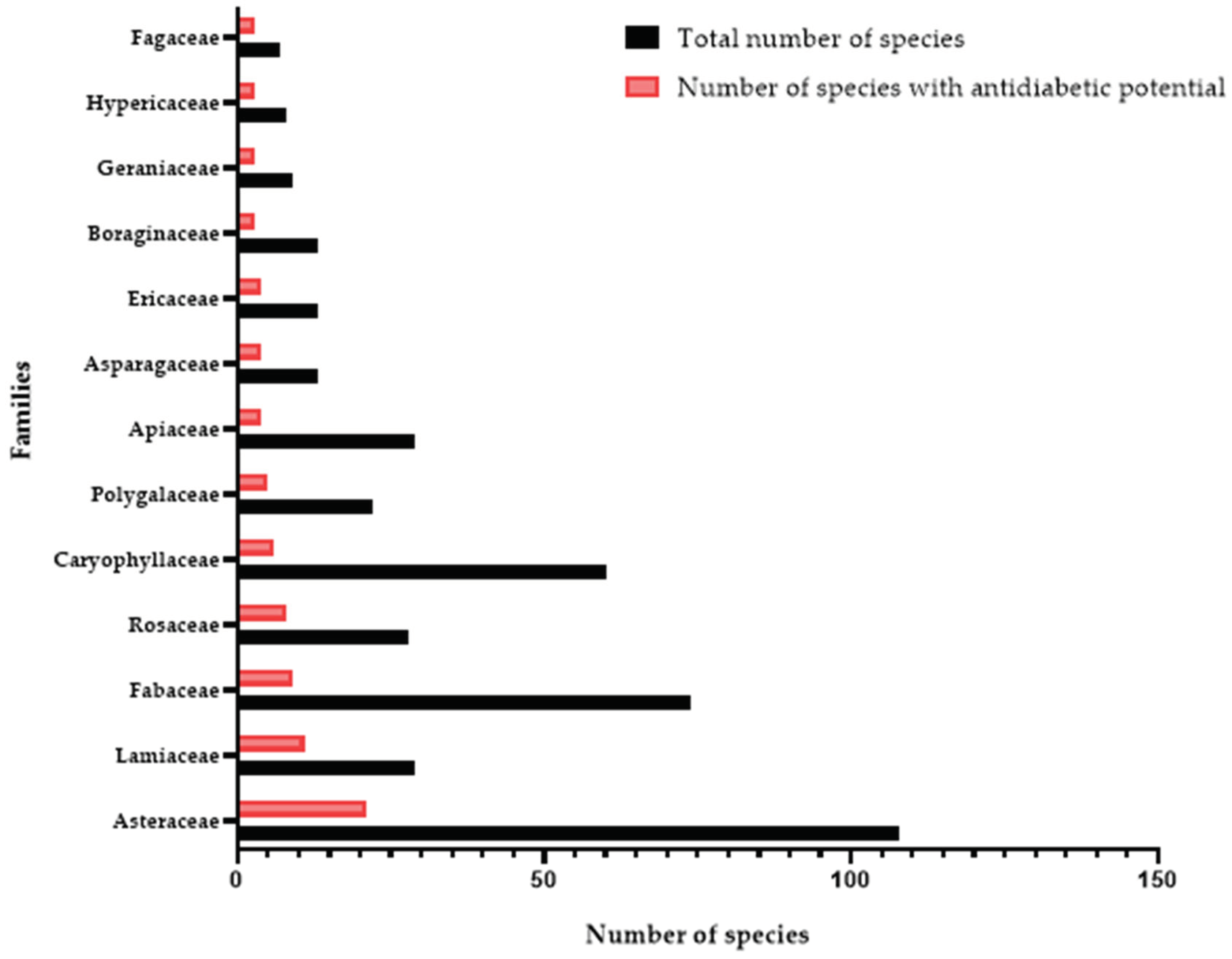
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





