Submitted:
22 February 2024
Posted:
23 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction: a brief overview on cystic fibrosis
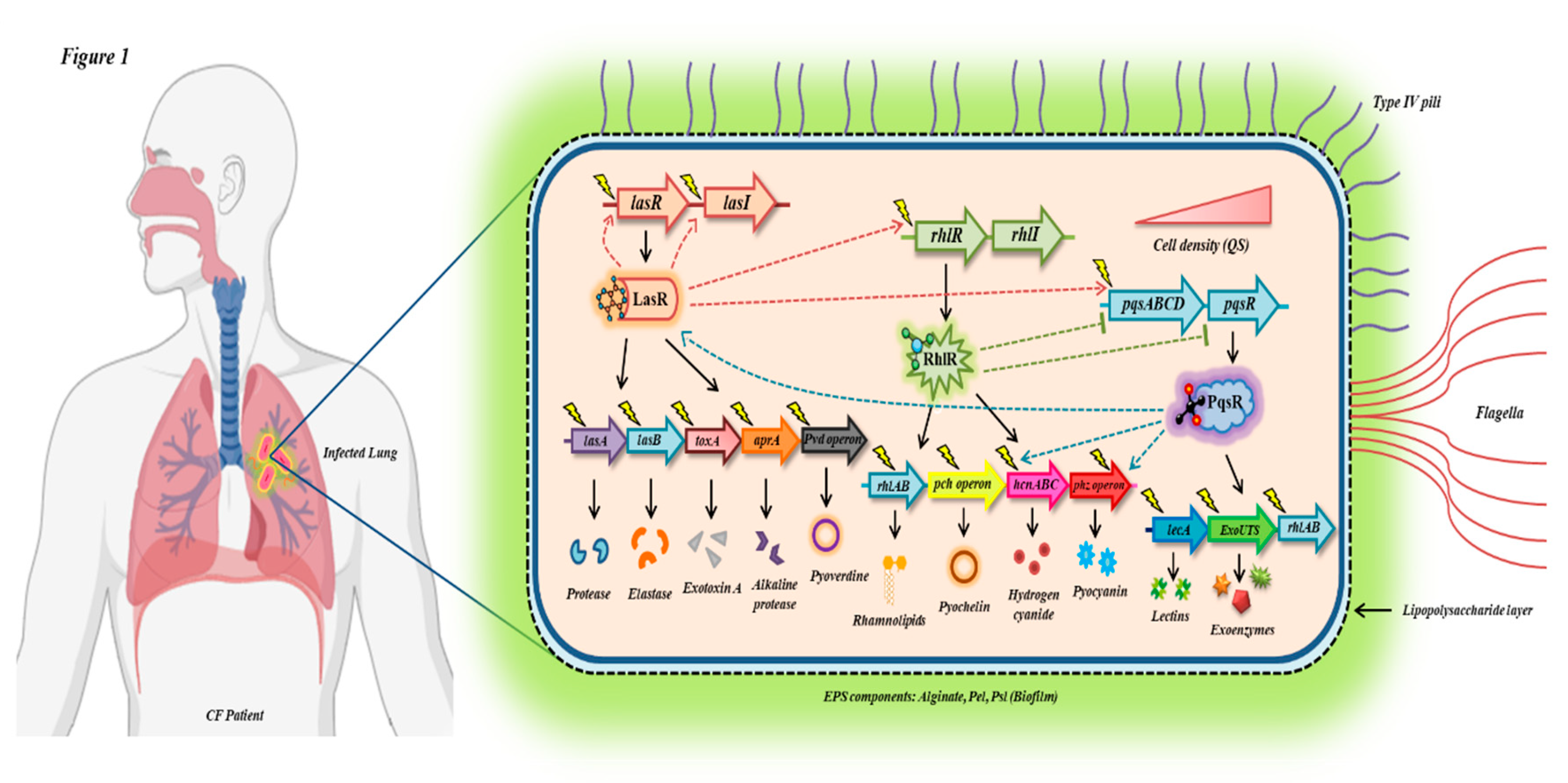
2. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the grim instigator in CF patients
2.1. Reservoir of infection and disease transmission
2.2. Colonization of P. aeruginosa in CF patients
2.3. Persistence of infection and adverse effects
| S. No. | Virulence Factors | Clinical implications | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Flagella/Pili | Binding of pili to asialoGM1 glycolipid residue, present in the respiratory epithelial cells of CF patients facilitates the attachment of P. aeruginosa, thereby leading to its colonization in the lungs | [34] |
| 2 | Exotoxin A (ETA) | ETA harbors ADP-ribosyltransferase (ADPRT) activity which catalyzes the transfer of ADP moiety to elongation factor 2, thereby stalling protein elongation and synthesis, resulting in cell intoxication | [51] |
| 3 | Alginate | P. aeruginosa CF isolates produces mucoid alginate and forms microcolonies in lungs (biofilms). Such alginate biofilms are resistant to antibiotics. Thus, it plays an important role in persistence of P. aeruginosa in the lungs of CF patients | [37] |
| 4 | Pyocyanin | Prevents clearance of P. aeruginosa infection in CF by mitigating ciliary beat frequency in airway epithelium. It inhibits catalase activity inducing oxidative stress on the respiratory epithelium further impairing CFTR function | [52] |
| 5 | LasB elastase (protease) | Important virulence factor for successful establishment of chronic infection. It provokes lung tissue damage and dysregulates host immune responses (down-regulation of CXCR1 on human neutrophils surface), and prevents the mucocilliary clearance of pathogen from the lung airway | [53,54] |
| 6 | Exopolysaccharides (Alginate, Psl, Pel) | Alginate serves as a chelators for hypochlorite and inhibits complement activation, neutrophil migration, chemotaxis, as well as macrophage phagocytosis and killing Psl enhances the attachment of P. aeruginosa to airway cells. Pel acts as a structural anchor in initial stages of biofilm formation and it enhances the resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics |
[28,48] |
| 7 | Alkaline protease | It is responsible for the persistence of pathogen in the lungs by interfering with non-specific defense mechanisms like phagocytosis of the pathogen and specific immune responses such as T cells, natural killer cells and immunoglobulins. It inhibits neutrophil and monocyte function especially chemotaxis, which helps P. aeruginosa to escape the front line defenses of the host | [43] |
| 8 | Lectins | LecA and LecB, extracellular proteins primarily mediate adherence of P. aeruginosa to host cell surface during infection. LecA is involved in host cell invasion and cytotoxicity, while LecB reduces ciliary beating of airway epithelium. The presence of LecB leads to increased retention of cells and EPS in the biofilm. Along with Psl, LecB helps in establishment and stabilization of biofilm | [55] |
| 9 | Rhamnolipids | They play a major role in suppression of polymorphonuclear neutrophilic leucocytes (PMN’s) predominantly present during immune response against CF. Therefore, it eliminates the cellular host immune responses | [56] |
| 10 | Hydrogen cyanide | Acts as a repressor for cytochrome c oxidase in human cell mitochondria and inhibits several metalloenzymes. It is also used as a virulence biomarker (detected in exhaled breath) for patients who have acquired P. aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis infection as it is the only organism frequently found in the CF lung that produces hydrogen cyanide | [57,58] |
| 11 | Siderophores (Pyoverdine and Pyochelin) | Pyoverdine is responsible for chronic P. aeruginosa infection in CF patients. It not only act as an iron chelator but also stimulates septicemia, surface motility and biofilm maturation Pyochelin interacts with pyocyanin forming hydroxyl free radicals. These radicals damage the pulmonary artery endothelial and airway epithelial cells in humans, thereby contributing to pathogenicity in CF lungs |
[28,59,60] |
3. Current line of antimicrobial and alternative therapies: where we stand today
4. Limitations of antimicrobial approach: the fault in our stars
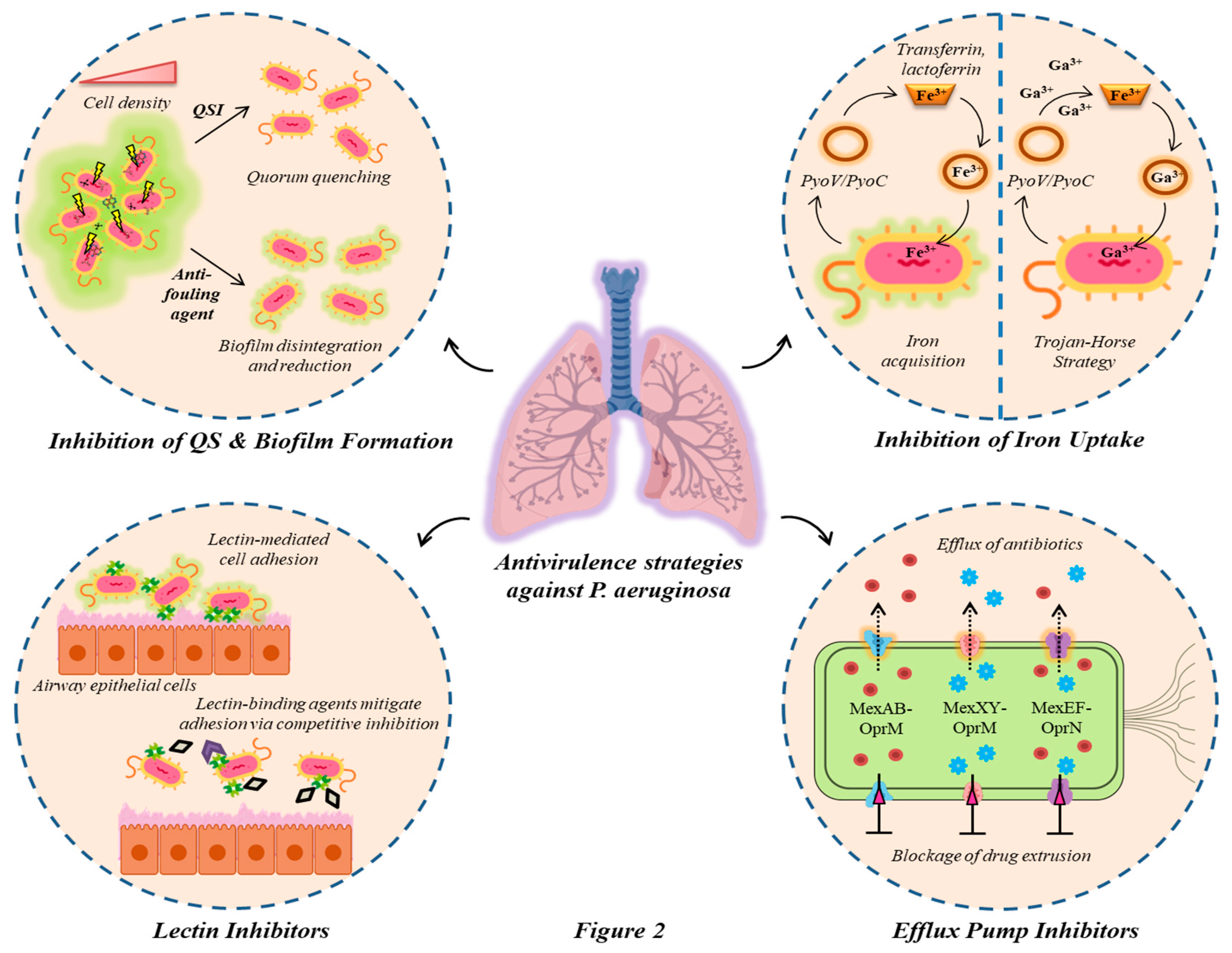
5. Antivirulence strategies to combat P. aeruginosa in CF: the next-generation therapies?
5.1. Targeting QS mechanisms and biofilm inhibition: the communal approach
5.2. Targeting iron acquisition pathways: provoking nutrient deficiency
5.3. Lectin inhibitors: outmaneuvering the battle for cell adhesion
5.4. Efflux pump inhibitors: eroding the pathways for drug extrusion
| Anti-virulence approaches | Therapeutic used | Effect/outcome on disease progression | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quorum sensing and biofilm inhibition | Coumarin | It is described as a potent QSI. Significant reduction in pyocyanin and protease levels as well as biofilm formation were observed in vitro. Decline in intracellular C-di-GMP levels suggested inhibition of biofilm. However, its biofilm-inhibitory effects in wound healing model and Lucilia sericata maggots were reduced. Hence, the therapeutic potential of coumarin in treating wound infections and helping with maggot-based debridement therapy may be limited | [88] |
| Corydothymus capitatus essential oil (CCEO) | CCEO demonstrated a significant decrease in pyocyanin production, ranging from 84% to 100%, across all tested strains. In nearly half of the strains, inhibition and reduction of mature biofilm was reported. It also displayed a substantial impact on the swarming and swimming motility of P. aeruginosa for nearly all strains examined | [28] |
|
| Baicalin | Baicalin exhibited potent anti-QS and anti-biofilm properties. The study showcased its dose-dependent inhibitory effect on virulence phenotypes (LasA protease, LasB elastase, pyocyanin, rhamnolipid, motilities and exotoxin A) which are regulated by QS. Decrease in signaling molecule 3-oxo-C12-HSL and C4-HSL was also observed due to repressed QS regulatory gene expression level. In vivo treatment with baicalin in C. elegans and mouse peritoneal implant infection model resulted in lowered P. aeruginosa pathogenicity | [89] | |
| Dyer Ex Eichler extract (DSE) | Remarkable reduction in P. aeruginosa biofilm formation was observed both in vitro as well as in vivo rat model. Further it subdued surface hydrophobicity and extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) accumulation. qRT-PCR results revealed reduction in four QS genes (lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR) and biofilm related gene ndvB | [91] | |
| M34 and Clofoctol | M34 and its derivatives potentially affects the transcription factor PqsR, impeding the binding between PQS and pqsR, disrupting the production of pqs-dependent signaling molecules, and offering protection against P. aeruginosa infection in mice Clofoctol, FDA-approved compound; acts by inhibiting the pqs system and decreasing the mortality rate of Galleria mellonella larvae infected with P. aeruginosa by targeting PqsR. PqsR inhibition leads to decreased production of 2-alkyl-4-quinolones (AQs) and hence of AQs-dependent virulence factors, with consequent attenuation of P. aeruginosa infectivity |
[28,97] | |
| Furanone C-30 | When used in combination with tobramycin, Furanone C-30 effectively reduced protease production. It was also used in combination with gallium (a siderophore) which resulted in reduction of virulence factor and QS genes. Additionally it disrupted Las pathway (especially LasR) and increased the susceptibility of P.aeruginosa biofilms towards tobramycin | [98] | |
| Niclosamide | Niclosamide acts on the 3OC12-HSL signaling pathway through a mechanism that remains to be fully characterized. It reduces the synthesis of 3OC12-HSL as well as QS-dependent virulence factors (pyocyanin and elastase), resulting in decreased virulence in the Galleria mellonella infection model. The efficacy of niclosamide against CF isolates in inhibiting QS and virulence was highly variable and strain-dependent. It demonstrated low range of effectiveness and its inhibition of las signal production did not correspond to a decrease in the production of virulence factors | [131] |
|
| Luteolin | Biofilm formation, production of virulence factors, and motility (swimming, swarming, twitching) of P. aeruginosa was effectively inhibited by luteolin. It attenuated the accumulation of the QS-signaling molecules N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone (OdDHL) and N-butanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (BHL). In addition, it downregulated the QS genes (lasR, lasI, rhlR, and rhlI) | [132] | |
| Inhibiting iron uptake |
Gallium nitrate (Ga(NO3)3) |
Gallium suppressed the growth and formation of biofilms in P. aeruginosa and eliminated both planktonic and biofilm bacteria in vitro. Its mechanism involves reducing bacterial iron uptake and disrupting iron signaling mediated by the transcriptional regulator pvdS required for pyoverdine synthesis. Furthermore, the study demonstrated the efficacy of Gallium in murine lung infection models | [110] |
| Koelreuteria paniculata leaf extract silver nanoparticles | The research demonstrated that the Ka-AgNPs significantly mitigates QS-regulated virulence factors in PAO1 and effectively suppress the formation of biofilm of PAO1. Further, the expression of QS-regulated virulence genes was reduced as well. These results suggest that the phyto-synthesized AgNPs could be used as promising anti-infective agents for treating drug-resistant P. aeruginosa | [133] |
|
| Lactoferrin | Inhibitory/destructive effects of lactoferrin (2 mg/ml) on biofilm formation as well as pre-formed biofilm were observed. Further, pre-treatment with FeCl2 partially restored biofilm formation, suggesting its role as an iron-chelator that may be implicated to the inhibitory mechanism of lactoferrin | [111] |
|
| N,N’-bis (2-hydroxybenzyl) ethylenediamine-N,N’-diacetic acid (HBED) | HBED showed inhibitory effects on growth and biofilm formation in all clinical strains of P. aeruginosa isolated from CF patients, under aerobic or anaerobic conditions. The addition of HBED significantly decreased the biomass and when combined with colistin, HBED notably augmented the microcolony-killing effects of colistin, leading to nearly complete eradication of the biofilm. Thus, the combination of HBED and colistin demonstrates high efficacy in vitro against biofilms formed by clinical strains of P. aeruginosa | [134] | |
| Lectin inhibitors |
Fucose/galactose inhalation | Lectin specific sugars, fucose and Galactose prevented binding of P. aeruginosa lectins I and II responsible for adherence of bacteria in the airway cells. The competitive inhibition of P. aeruginosa lectins by the sugars may overcome particular mechanisms of bacterial resistance in patients with airway infection. Reductions in tumor necrosis factor alpha and colony growth of P. aeruginosa were also reported | [119] |
| Thio- and Seleno-tetravalent glycoconjugates | Both thio- and seleno-tetravalent glycoconjugates act as ligands for lectin PA-IL (one of the major virulence factor in P. aeruginosa associated with CF) consequently inhibiting binding of LecA. It also demonstrated approximately 64 times higher supression of LecA compared to d-galactose | [121] | |
| Efflux pump inhibitors (EPI) | Phe-Arg-β-naphthylamide (PAβN) | PAβN functions as an anti-QS and anti-biofilm agent against P. aeruginosa CF isolates. It has been shown to permeabilize the bacterial cell membrane in a dose-dependent manner, thereby increasing the efficacy of bulky β-lactam antibiotics (incapable of crossing the membranes). It also repressed the activity of efflux pumps like MexCD-OprJ and MexEF-OprN and negatively impacted bacterial growth and virulence factors in insect model of infection | [124,125] |
| TXA09155 (Conformationally Constrained Indole carboxamide + levofloxacin | TXA09155 served as a potential EPI in P. aeruginosa. When used at concentration of 6.25 µg/mL it increased potency of antibiotics by 8 times. TXA09155 is known to improvise killing dynamics of moxifloxacin and decrease frequency of resistance (FoR) to levofloxacin. Combination of TXA09155 and levofloxacin was used effectively in treatment of burn wound victims, as it significantly reduced emergence of MDR strains of P. aeruginosa against carbapenams | [127] |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflict of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Davis, P.B. Cystic Fibrosis Since 1938. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2006, 173, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, G.; Macek, M.; Mehta, A. Cystic fibrosis across Europe: EuroCareCF analysis of demographic data from 35 countries. Journal of Cystic Fibrosis 2010, 9, S5–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, R.C. An overview of the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis lung disease. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2002, 54, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, V.S.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Tang, X.X.; Reznikov, L.; Abou Alaiwa, M.; Ernst, S.E.; Karp, P.H.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.L.; Heilmann, K.P.; Leidinger, M.R.; et al. Airway acidification initiates host defense abnormalities in cystic fibrosis mice. Science 2016, 351, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döring, G.; Gulbins, E. Cystic fibrosis and innate immunity: how chloride channel mutations provoke lung disease. Cellular Microbiology 2009, 11, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciro, D.O.; Padoan, R.; Blau, H.; Marostica, A.; Fuoti, M.; Volpi, S.; Pilotta, A.; Meyerovitch, J.; Sher, D.; Assael, B.M. Growth retardation and reduced growth hormone secretion in cystic fibrosis. Clinical observations from three CF centers. Journal of Cystic Fibrosis 2013, 12, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisonneuve, P.; Marshall, B.C.; Knapp, E.A.; Lowenfels, A.B. Cancer Risk in Cystic Fibrosis: A 20-Year Nationwide Study From the United States. JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2013, 105, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derichs, N. Targeting a genetic defect: cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator modulators in cystic fibrosis. European Respiratory Review 2013, 22, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veit, G.; Avramescu, R.G.; Chiang, A.N.; Houck, S.A.; Cai, Z.; Peters, K.W.; Hong, J.S.; Pollard, H.B.; Guggino, W.B.; Balch, W.E.; et al. From CFTR biology toward combinatorial pharmacotherapy: expanded classification of cystic fibrosis mutations. Molecular Biology of the Cell 2016, 27, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, A. “Cystic fibrotics could survive cholera, choleraics could survive cystic fibrosis”; hypothesis that explores new horizons in treatment of cystic fibrosis. Medical Hypotheses 2015, 85, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yong, M.I.N.; Li, J.I.A.; Dong, X.; Yu, T.; Fu, X.; Hu, L. High level of CFTR expression is associated with tumor aggression and knockdown of CFTR suppresses proliferation of ovarian cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncology Reports 2015, 33, 2227–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.Z.; Wagener, J.S.; Bost, T.; Martinez, J.; Accurso, F.J.; Riches, D.W.H. Early Pulmonary Inflammation in Infants with Cystic Fibrosis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 1995, 151, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, A.C.; Turvey, S.E.; Alves, M.P.; Regamey, N.; Tummler, B.; Hartl, D. Current concepts: host-pathogen interactions in cystic fibrosis airways disease. European Respiratory Review 2014, 23, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, S.; Hayes, D.; Wozniak, D.J. Cystic Fibrosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the Host-Microbe Interface. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hector, A.; Kirn, T.; Ralhan, A.; Graepler-Mainka, U.; Berenbrinker, S.; Riethmueller, J.; Hogardt, M.; Wagner, M.; Pfleger, A.; Autenrieth, I.; et al. Microbial colonization and lung function in adolescents with cystic fibrosis. Journal of Cystic Fibrosis 2016, 15, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.J.; LiPuma, J.J. The Microbiome in Cystic Fibrosis. Clinics in Chest Medicine 2016, 37, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, A.R.; Smyth, R.L.; Tong, C.Y.; Hart, C.A.; Heaf, D.P. Effect of respiratory virus infections including rhinovirus on clinical status in cystic fibrosis. Archives of Disease in Childhood 1995, 73, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collinson, J.; Nicholson, K.G.; Cancio, E.; Ashman, J.; Ireland, D.C.; Hammersley, V.; Kent, J.; O’Callaghan, C. Effects of upper respiratory tract infections in patients with cystic fibrosis. Thorax 1996, 51, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, A.C.; Waters, V.J. Opportunistic Pathogens in Cystic Fibrosis: Epidemiology and Pathogenesis of Lung Infection. Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society 2022, 11, S3–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, T.J.; Ramsay, K.A.; Vidmar, S.; Carlin, J.B.; Bell, S.C.; Wainwright, C.E.; Grimwood, K.; Francis, P.W.; Dakin, C.; Cheney, J.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa genotypes acquired by children with cystic fibrosis by age 5-years. Journal of Cystic Fibrosis 2015, 14, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, J.; Harjai, K.; Chhibber, S. Revisiting the virulence hallmarks of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a chronicle through the perspective of quorum sensing. Environmental Microbiology 2021, 24, 2630–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losito, A.R.; Raffaelli, F.; Del Giacomo, P.; Tumbarello, M. New Drugs for the Treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections with Limited Treatment Options: A Narrative Review. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbdulWahab, A.; Zahraldin, K.; Sid Ahmed, M.; Jarir, S.; Muneer, M.; Mohamed, S.; Hamid, J.; Hassan, A.I.; Ibrahim, E. The emergence of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients on inhaled antibiotics. Lung India 2017, 34, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, P.M.; Shen, G.; Splaingard, M.; Colby, C.E.; Laxova, A.; Kosorok, M.R.; Rock, M.J.; Mischler, E.H. Acquisition ofPseudomonas aeruginosain Children With Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatrics 1997, 100, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederiksen, B.; Koch, C.; Hiby, N. Changing Epidemiology ofPseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Danish Cystic Fibrosis Patients (1974-1995). Pediatric Pulmonology 1999, 28, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S.C.; Skoric, B.; Ramsay, K.A.; Carzino, R.; Gibson, A.-M.; Hart, E.; Harrison, J.; Bell, S.C.; Kidd, T.J. Geographical Differences in First Acquisition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Cystic Fibrosis. Annals of the American Thoracic Society 2013, 10, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denton, M.; Kerr, K.; Mooney, L.; Keer, V.; Rajgopal, A.; Brownlee, K.; Arundel, P.; Conway, S. Transmission of colistin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa between patients attending a pediatric cystic fibrosis center. Pediatric Pulmonology 2002, 34, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkey, M.; Lepine, F.; Maura, D.; Bandyopadhaya, A.; Lesic, B.; He, J.; Kitao, T.; Righi, V.; Milot, S.; Tzika, A.; Rahme, L. Identification of anti-virulence compounds that disrupt quorum-sensing regulated acute and persistent pathogenicity. PLoS Pathogens, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiehlmann, L.; Cramer, N.; Ulrich, J.; Hedtfeld, S.; Weißbrodt, H.; Tümmler, B. Effective prevention of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cross-infection at a cystic fibrosis centre – Results of a 10-year prospective study. International Journal of Medical Microbiology 2012, 302, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, S. Segregation is good for patients with cystic fibrosis. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine 2008, 101, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, P.J.; Izydorcyzk, C.; Clark, S.; Blanchard, A.; Wang, P.W.; Yau, Y.; Waters, V.; Guttman, D.S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain-sharing in Early Infection Among Children With Cystic Fibrosis. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2021, 73, e2521–e2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pier, G.B.; Grout, M.; Zaidi, T.S.; Olsen, J.C.; Johnson, L.G.; Yankaskas, J.R.; Goldberg, J.B. Role of Mutant CFTR in Hypersusceptibility of Cystic Fibrosis Patients to Lung Infections. Science 1996, 271, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A. Pathogenesis of bacterial bronchitis in cystic fibrosis. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1997, 16, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiman, L.; Prince, A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa pili bind to asialoGM1 which is increased on the surface of cystic fibrosis epithelial cells. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1993, 92, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, T.S.; Prince, A. Cystic fibrosis: a mucosal immunodeficiency syndrome. Nature Medicine 2012, 18, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz-Mejías, M.; Jurado-Martín, I.; McClean, S. Understanding Pseudomonas aeruginosa–Host Interactions: The Ongoing Quest for an Efficacious Vaccine. Cells 2020, 9, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiby, N. Prospects for the Prevention and Control of Pseudomonal Infection in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Paediatric Drugs 2000, 2, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Weert–van Leeuwen, P.B.; Van Meegen, M.A.; Speirs, J.J.; Pals, D.J.; Rooijakkers, S.H.M.; Van der Ent, C.K.; Terheggen-Lagro, S.W.J.; Arets, H.G.M.; Beekman, J.M. Optimal Complement-Mediated Phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Monocytes Is Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator–Dependent. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 2013, 49, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, P.J.; Scordo, J.M.; Arcos, J.; Kirkby, S.E.; Wewers, M.D.; Wozniak, D.J.; Torrelles, J.B. Modifications of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell envelope in the cystic fibrosis airway alters interactions with immune cells. Scientific Reports 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vencken, S.F.; Greene, C.M. Toll-Like Receptors in Cystic Fibrosis: Impact of Dysfunctional microRNA on Innate Immune Responses in the Cystic Fibrosis Lung. Journal of Innate Immunity 2016, 8, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stover, C.K.; Pham, X.Q.; Erwin, A.L.; Mizoguchi, S.D.; Warrener, P.; Hickey, M.J.; Brinkman, F.S.L.; Hufnagle, W.O.; Kowalik, D.J.; Lagrou, M.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature 2000, 406, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, S.S. Lung infection with alginate-producing, mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. APMIS Suppl 1992, 28, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kharazmi, A. Interactions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Proteases with the Cells of the Immune System. Antibiot. Chemother. 1989; 42, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.D.; Pearson, E.; Ristroph, K.D.; Duncan, G.A.; Ensign, L.M.; Suk, J.S.; Hanes, J.; Prud’homme, R.K. Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyocyanin production reduced by quorum-sensing inhibiting nanocarriers. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2018, 544, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, P.L.; Weadge, J.T.; Nivens, D.E.; Franklin, M.J. Biosynthesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Extracellular Polysaccharides, Alginate, Pel, and Psl. Frontiers in Microbiology 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, M.S.; Pang, B.; Mishra, M.; Swords, W.E.; Wozniak, D.J.; Pier, G. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa Exopolysaccharide Psl Facilitates Surface Adherence and NF-κB Activation in A549 Cells. mBio 2010, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, L.; Kolter, R. Genes involved in matrix formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14 biofilms. Molecular Microbiology 2003, 51, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ausubel, F.M.; Colvin, K.M.; Gordon, V.D.; Murakami, K.; Borlee, B.R.; Wozniak, D.J.; Wong, G.C.L.; Parsek, M.R. The Pel Polysaccharide Can Serve a Structural and Protective Role in the Biofilm Matrix of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Pathogens 2011, 7, e1001264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicki, G.S.; Rasouliyan, L.; McMullen, A.H.; Wagener, J.S.; McColley, S.A.; Pasta, D.J.; Quittner, A.L. Longitudinal assessment of health-related quality of life in an observational cohort of patients with cystic fibrosis. Pediatric Pulmonology 2010, 46, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Clemente, M.; de la Rosa, D.; Máiz, L.; Girón, R.; Blanco, M.; Olveira, C.; Canton, R.; Martinez-García, M.A. Impact of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection on Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Airway Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2020, 9, 3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallant, C.V.; Raivio, T.L.; Olson, J.C.; Woods, D.E.; Storey, D.G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis clinical isolates produce exotoxin A with altered ADP-ribosyltransferase activity and cytotoxicity The GenBank accession numbers for the toxA sequences are: strain 4384, AF227419; strain 5154, AF227420; strain 5166, AF227421; strain 5552, AF227422; strain 5585, AF227423; strain 5588, AF227424. Microbiology 2000, 146, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, C.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Thomsen, K.; Kolpen, M.; Rybtke, M.; Lauland, A.S.; Trøstrup, H.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Immune Responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Infections. Frontiers in Immunology 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, A.; Ortombina, A.; Boschi, F.; Cremonini, E.; Boaretti, M.; Sorio, C.; Melotti, P.; Bergamini, G.; Lleo, M. Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa secreted virulence factors reduces lung inflammation in CF mice. Virulence 2018, 9, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llanos, A.; Achard, P.; Bousquet, J.; Lozano, C.; Zalacain, M.; Sable, C.; Revillet, H.; Murris, M.; Mittaine, M.; Lemonnier, M.; et al. Higher levels of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasB elastase expression are associated with early-stage infection in cystic fibrosis patients. Scientific Reports 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos da Silva, D.; Matwichuk, M.L.; Townsend, D.O.; Reichhardt, C.; Lamba, D.; Wozniak, D.J.; Parsek, M.R. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa lectin LecB binds to the exopolysaccharide Psl and stabilizes the biofilm matrix. Nature Communications 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreindler, J.L.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Jakobsen, T.H.; Phipps, R.; Nielsen, A.K.; Rybtke, M.T.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Givskov, M.; Høiby, N.; et al. Quorum Sensing and Virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa during Lung Infection of Cystic Fibrosis Patients. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.E.; Brown, G.C. The inhibition of mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase by the gases carbon monoxide, nitric oxide, hydrogen cyanide and hydrogen sulfide: chemical mechanism and physiological significance. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes 2008, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilchrist, F.J.; Belcher, J.; Jones, A.M.; Smith, D.; Smyth, A.R.; Southern, K.W.; Španěl, P.; Webb, A.K.; Lenney, W. Exhaled breath hydrogen cyanide as a marker of earlyPseudomonas aeruginosainfection in children with cystic fibrosis. ERJ Open Research 2015, 1, 00044–02015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britigan, B.E.; Rasmussen, G.T.; Cox, C.D. Augmentation of oxidant injury to human pulmonary epithelial cells by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa siderophore pyochelin. Infection and Immunity 1997, 65, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banin, E.; Vasil, M.L.; Greenberg, E.P. Iron and Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2005, 102, 11076–11081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, B.M.; Tsifansky, M.D.; Yang, Y.; Yeo, Y. Challenges and advances in the development of inhalable drug formulations for cystic fibrosis lung disease. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery 2011, 8, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, M.; Rayner, O.; Smyth, A.R. Prophylactic anti-staphylococcal antibiotics for cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, M.N.; Loutit, J.; Griffith, D.C. Aerosol antibiotics: considerations in pharmacological and clinical evaluation. Current Opinion in Biotechnology 2008, 19, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, B.C.; McColley, S.A.; Kissner, D.G.; Rolfe, M.W.; Rosen, J.M.; McKevitt, M.; Moorehead, L.; Montgomery, A.B.; Geller, D.E. Fosfomycin/Tobramycin for Inhalation in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis with Pseudomonas Airway Infection. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2012, 185, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Stableforth, D. The Treatment of Respiratory Pseudomonas Infection in Cystic Fibrosis. Drugs 2000, 60, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zobell, J.T.; Young, D.C.; Waters, C.D.; Stockmann, C.; Ampofo, K.; Sherwin, C.M.T.; Spigarelli, M.G. Optimization of anti-pseudomonal antibiotics for cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbations: I. aztreonam and carbapenems. Pediatric Pulmonology 2012, 47, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zobell, J.T.; Waters, C.D.; Young, D.C.; Stockmann, C.; Ampofo, K.; Sherwin, C.M.T.; Spigarelli, M.G. Optimization of anti-pseudomonal antibiotics for cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbations: II. cephalosporins and penicillins. Pediatric Pulmonology 2012, 48, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oermann, C.M.; Retsch-Bogart, G.Z.; Quittner, A.L.; Gibson, R.L.; McCoy, K.S.; Montgomery, A.B.; Cooper, P.J. An 18-month study of the safety and efficacy of repeated courses of inhaled aztreonam lysine in cystic fibrosis. Pediatric Pulmonology 2010, 45, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döring, G.; Meisner, C.; Stern, M. A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled phase III study of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa flagella vaccine in cystic fibrosis patients. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2007, 104, 11020–11025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, R.S.; Fellner, C. CFTR Modulators for the Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis. P T 2014, 39, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wainwright, C.E.; Elborn, J.S.; Ramsey, B.W.; Marigowda, G.; Huang, X.; Cipolli, M.; Colombo, C.; Davies, J.C.; De Boeck, K.; Flume, P.A.; et al. Lumacaftor–Ivacaftor in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Homozygous for Phe508delCFTR. New England Journal of Medicine 2015, 373, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lister, P.D.; Wolter, D.J.; Hanson, N.D. Antibacterial-ResistantPseudomonas aeruginosa: Clinical Impact and Complex Regulation of Chromosomally Encoded Resistance Mechanisms. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 2009, 22, 582–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meletis, G.; Bagkeri, M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Multi-Drug-Resistance Development and Treatment Options. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettman, J.R.; Sztepanacz, J.L.; Kassen, R. The properties of spontaneous mutations in the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Genomics 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradali, M.F.; Ghods, S.; Rehm, B.H.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lifestyle: A Paradigm for Adaptation, Survival, and Persistence. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, E.; Gill, E.E.; Falsafi, R.; Yeung, A.; Liu, S.; Hancock, R.E.W. Broad-Spectrum Adaptive Antibiotic Resistance Associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa Mucin-Dependent Surfing Motility. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, S.R.; Blimkie, T.; Falsafi, R.; Hancock, R.E.W. Multidrug Adaptive Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Swarming Cells. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2020, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prayle, A.; Watson, A.; Fortnum, H.; Smyth, A. Side effects of aminoglycosides on the kidney, ear and balance in cystic fibrosis. Thorax 2010, 65, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patangia, D.V.; Anthony Ryan, C.; Dempsey, E.; Paul Ross, R.; Stanton, C. Impact of antibiotics on the human microbiome and consequences for host health. MicrobiologyOpen 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrows, J.A.; Toon, M.; Bell, S.C. Antibiotic desensitization in adults with cystic fibrosis. Respirology 2003, 8, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, B.S.; Zhang, W.; Harrison, J.J.; Quach, T.P.; Song, J.L.; Penterman, J.; Singh, P.K.; Chopp, D.L.; Packman, A.I.; Parsek, M.R. The extracellular matrix protects Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms by limiting the penetration of tobramycin. Environmental Microbiology 2013, 15, 2865–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.-K.; Nichols, B.L.B.; Edgar, K.J.; Murgia, X.; Loretz, B.; Lehr, C.-M. Challenges and strategies in drug delivery systems for treatment of pulmonary infections. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2019, 144, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, S.W.; Cheung, G.Y.C.; Otto, M. Different drugs for bad bugs: antivirulence strategies in the age of antibiotic resistance. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2017, 16, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenfort, K.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing signal–response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2016, 14, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, M.; Peter Greenberg, E. A network of networks: Quorum-sensing gene regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. International Journal of Medical Microbiology 2006, 296, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeb, S.; Fletcher, M.P.; Chhabra, S.R.; Diggle, S.P.; Williams, P.; Cámara, M. Quinolones: from antibiotics to autoinducers. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 2011, 35, 247–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, M.T.T.; Wibowo, D.; Rehm, B.H.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sass, A.; Van Acker, H.; Wille, J.; Verhasselt, B.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Kaever, V.; Crabbé, A.; Coenye, T. Coumarin Reduces Virulence and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Affecting Quorum Sensing, Type III Secretion and C-di-GMP Levels. Frontiers in Microbiology 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleem, M.N.; Luo, J.; Dong, B.; Wang, K.; Cai, S.; Liu, T.; Cheng, X.; Lei, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Baicalin inhibits biofilm formation, attenuates the quorum sensing-controlled virulence and enhances Pseudomonas aeruginosa clearance in a mouse peritoneal implant infection model. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrenna, G.; Artini, M.; Ragno, R.; Relucenti, M.; Fiscarelli, E.V.; Tuccio Guarna Assanti, V.; Papa, R.; Selan, L. Anti-Virulence Properties of Coridothymus capitatus Essential Oil against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates from Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elekhnawy, E.; Negm, W.A.; El-Aasr, M.; Kamer, A.A.; Alqarni, M.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Obaidullah, A.J.; Fawzy, H.M. Histological assessment, anti-quorum sensing, and anti-biofilm activities of Dioon spinulosum extract: in vitro and in vivo approach. Scientific Reports 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizalapur, S.; Kimyon, Ö.; Biswas, N.N.; Gardner, C.R.; Griffith, R.; Rice, S.A.; Manefield, M.; Willcox, M.; Black, D.S.; Kumar, N. Design, synthesis and evaluation of N-aryl-glyoxamide derivatives as structurally novel bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 2016, 14, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Krishnan, T.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yin, W.F.; Chong, Y.M.; Tan, L.Y.; Chong, T.M.; Chan, K.-G. Non-antibiotic quorum sensing inhibitors acting against N-acyl homoserine lactone synthase as druggable target. Scientific Reports 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Loughlin, C.T.; Miller, L.C.; Siryaporn, A.; Drescher, K.; Semmelhack, M.F.; Bassler, B.L. A quorum-sensing inhibitor blocks Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence and biofilm formation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2013, 110, 17981–17986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Maurer, C.K.; Kirsch, B.; Steinbach, A.; Hartmann, R.W. Overcoming the Unexpected Functional Inversion of a PqsR Antagonist in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An In Vivo Potent Antivirulence Agent Targeting pqs Quorum Sensing. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2013, 53, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteley, M.; Starkey, M.; Lepine, F.; Maura, D.; Bandyopadhaya, A.; Lesic, B.; He, J.; Kitao, T.; Righi, V.; Milot, S.; et al. Identification of Anti-virulence Compounds That Disrupt Quorum-Sensing Regulated Acute and Persistent Pathogenicity. PLoS Pathogens 2014, 10, e1004321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, F.; Baldelli, V.; Halliday, N.; Pantalone, P.; Polticelli, F.; Fiscarelli, E.; Williams, P.; Visca, P.; Leoni, L.; Rampioni, G. Identification of FDA-Approved Drugs as Antivirulence Agents Targeting the pqs Quorum-Sensing System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulenburg, H.; Rezzoagli, C.; Archetti, M.; Mignot, I.; Baumgartner, M.; Kümmerli, R. Combining antibiotics with antivirulence compounds can have synergistic effects and reverse selection for antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLOS Biology 2020, 18, e3000805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.-J.; Choi, H.; Hong, S.; Moon, H.R.; Lee, J.-H.; Oglesby, A.G. Antipathogenic Compounds That Are Effective at Very Low Concentrations and Have Both Antibiofilm and Antivirulence Effects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology Spectrum 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawoud, N.T.A.; El-Fakharany, E.M.; Abdallah, A.E.; El-Gendi, H.; Lotfy, D.R. Synthesis, and docking studies of novel heterocycles incorporating the indazolylthiazole moiety as antimicrobial and anticancer agents. Scientific Reports 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutruzzolà, F.; Frankenberg-Dinkel, N.; O’Toole, G.A. Origin and Impact of Nitric Oxide in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Journal of Bacteriology 2016, 198, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, P.; Guo, T.; Gu, X.; Bai, B.; Zhang, S.; Chang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S. Design, synthesis and evaluation of oxazolopyridinone derivatives as quorum sensing inhibitors. Bioorganic Chemistry 2023, 130, 106266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Cabra, N.; Movellan, J.; Marradi, M.; Gracia, R.; Salvador, C.; Dupin, D.; Loinaz, I.; Torrents, E. Neutralization of ionic interactions by dextran-based single-chain nanoparticles improves tobramycin diffusion into a mature biofilm. npj Biofilms and Microbiomes 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alontaga, A.Y.; Rodriguez, J.C.; Schönbrunn, E.; Becker, A.; Funke, T.; Yukl, E.T.; Hayashi, T.; Stobaugh, J.; Moënne-Loccoz, P.; Rivera, M. Structural Characterization of the Hemophore HasAp from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: NMR Spectroscopy Reveals Protein−Protein Interactions between Holo-HasAp and Hemoglobin. Biochemistry 2008, 48, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelis, P. Iron uptake and metabolism in pseudomonads. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2010, 86, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gifford, A.H.; Moulton, L.A.; Dorman, D.B.; Olbina, G.; Westerman, M.; Parker, H.W.; Stanton, B.A.; O’Toole, G.A. Iron Homeostasis during Cystic Fibrosis Pulmonary Exacerbation. Clinical and Translational Science 2012, 5, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visca, P.; Imperi, F.; Lamont, I.L. Pyoverdine siderophores: from biogenesis to biosignificance. Trends in Microbiology 2007, 15, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelis, P.; Matthijs, S.; Van Oeffelen, L. Iron uptake regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BioMetals 2009, 22, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, R.W.; Cox, C.D.; Vasil, M.L. Coordinate regulation of siderophore and exotoxin A production: molecular cloning and sequencing of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa fur gene. Journal of Bacteriology 1993, 175, 2589–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Thoendel, M.; Olakanmi, O.; Britigan, B.E.; Singh, P.K. The transition metal gallium disrupts Pseudomonas aeruginosa iron metabolism and has antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2007, 117, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.K. Iron sequestration by human lactoferrin stimulates P. aeruginosa surface motility and blocks biofilm formation. BioMetals 2004, 17, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, V. Active transport of iron and siderophore antibiotics. Current Opinion in Microbiology 2002, 5, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negash; Norris; Hodgkinson. Siderophore–Antibiotic Conjugate Design: New Drugs for Bad Bugs? Molecules 2019, 24, 3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau-Marquis, S.; O’Toole, G.A.; Stanton, B.A. Tobramycin and FDA-Approved Iron Chelators Eliminate Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms on Cystic Fibrosis Cells. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 2009, 41, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tielker, D.; Hacker, S.; Loris, R.; Strathmann, M.; Wingender, J.; Wilhelm, S.; Rosenau, F.; Jaeger, K.-E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa lectin LecB is located in the outer membrane and is involved in biofilm formation. Microbiology 2005, 151, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, E.C.; Mitchell, B.S.; Schumacher, D.U.; Grant, G.; Schumacher, U. Pseudomonas aeruginosa II lectin stops human ciliary beating: therapeutic implications of fucose. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 1997, 155, 2102–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadam, R.U.; Bergmann, M.; Hurley, M.; Garg, D.; Cacciarini, M.; Swiderska, M.A.; Nativi, C.; Sattler, M.; Smyth, A.R.; Williams, P.; et al. A Glycopeptide Dendrimer Inhibitor of the Galactose-Specific Lectin LecA and of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2011, 50, 10631–10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, E.M.V.; Crusz, S.A.; Kolomiets, E.; Buts, L.; Kadam, R.U.; Cacciarini, M.; Bartels, K.-M.; Diggle, S.P.; Cámara, M.; Williams, P.; et al. Inhibition and Dispersion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms by Glycopeptide Dendrimers Targeting the Fucose-Specific Lectin LecB. Chemistry & Biology 2008, 15, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauber, H.P.; Schulz, M.; Pforte, A.; Mack, D.; Zabel, P.; Schumacher, U. Inhalation with Fucose and Galactose for Treatment of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in Cystic Fibrosis Patients. International Journal of Medical Sciences 2008, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolomiets, E.; Swiderska, M.A.; Kadam, R.U.; Johansson, E.M.V.; Jaeger, K.E.; Darbre, T.; Reymond, J.L. Glycopeptide Dendrimers with High Affinity for the Fucose-Binding Lectin LecB from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illyés, T.Z.; Malinovská, L.; Rőth, E.; Tóth, B.; Farkas, B.; Korsák, M.; Wimmerová, M.; Kövér, K.E.; Csávás, M. Synthesis of Tetravalent Thio- and Selenogalactoside-Presenting Galactoclusters and Their Interactions with Bacterial Lectin PA-IL from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules 2021, 26, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorusso, A.B.; Carrara, J.A.; Barroso, C.D.N.; Tuon, F.F.; Faoro, H. Role of Efflux Pumps on Antimicrobial Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 15779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, P. Fitness of in vitro selected Pseudomonas aeruginosanalB and nfxB multidrug resistant mutants. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2002, 50, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampioni, G.; Pillai, C.R.; Longo, F.; Bondì, R.; Baldelli, V.; Messina, M.; Imperi, F.; Visca, P.; Leoni, L. Effect of efflux pump inhibition on Pseudomonas aeruginosa transcriptome and virulence. Scientific Reports 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, M.A.; Lamers, R.P.; Cavallari, J.F.; Burrows, L.L. The Efflux Inhibitor Phenylalanine-Arginine Beta-Naphthylamide (PAβN) Permeabilizes the Outer Membrane of Gram-Negative Bacteria. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbian, D.L.; Omri, A. The Impact of an Efflux Pump Inhibitor on the Activity of Free and Liposomal Antibiotics against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Rosado-Lugo, J.D.; Datta, P.; Sun, Y.; Cao, Y.; Banerjee, A.; Yuan, Y.; Parhi, A.K. Evaluation of a Conformationally Constrained Indole Carboxamide as a Potential Efflux Pump Inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.D.; Galazzo, J.L.; Staley, A.L.; Lee, J.C.; Warren, M.S.; Fuernkranz, H.; Chamberland, S.; Lomovskaya, O.; Miller, G.H. Microbial fermentation-derived inhibitors of efflux-pump-mediated drug resistance. Il Farmaco 2001, 56, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.-i.; Nakayama, K.; Ohtsuka, M.; Kuru, N.; Yokomizo, Y.; Sakamoto, A.; Takemura, M.; Hoshino, K.; Kanda, H.; Nitanai, H.; et al. MexAB-OprM specific efflux pump inhibitors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Part 7: Highly soluble and in vivo active quaternary ammonium analogue D13-9001, a potential preclinical candidate. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 2007, 15, 7087–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, R.; Sakurai, K.; Yamasaki, S.; Hayashi, K.; Nagata, C.; Hoshino, K.; Onodera, Y.; Nishino, K.; Yamaguchi, A. Structural basis for the inhibition of bacterial multidrug exporters. Nature 2013, 500, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collalto, D.; Giallonardi, G.; Fortuna, A.; Meneghini, C.; Fiscarelli, E.; Visca, P.; Imperi, F.; Rampioni, G.; Leoni, L. In vitro Activity of Antivirulence Drugs Targeting the las or pqs Quorum Sensing Against Cystic Fibrosis Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates. Frontiers in Microbiology 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.F.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, S.N.; Mei, J.; Zhang, X.C.; Sun, Y.J.; Zhao, B.T. An innovative role for luteolin as a natural quorum sensing inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Life Sciences 2021, 274, 119325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Paliya, B.S.; Singh, B.N. Superior inhibition of virulence and biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 by phyto-synthesized silver nanoparticles through anti-quorum sensing activity. Microbial Pathogenesis 2022, 170, 105678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettrick, K.; Hassan, K.; Lamont, I.; Reid, D. The Iron-chelator, N,N’-bis (2-hydroxybenzyl) Ethylenediamine-N,N’-diacetic acid is an Effective Colistin Adjunct against Clinical Strains of Biofilm-Dwelling Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





